Deck 25: Bacteria and Archaea
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/55
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 25: Bacteria and Archaea
1
The volume of a typical bacterium is about __________ the volume of a typical eukaryotic cell.
A) equal to
B) a half
C) a tenth
D) a hundredth
E) a thousandth
A) equal to
B) a half
C) a tenth
D) a hundredth
E) a thousandth
E
2
The most common mode of reproduction in bacteria is:
A) binary fission.
B) transformation.
C) transduction.
D) conjugation.
E) mitosis.
A) binary fission.
B) transformation.
C) transduction.
D) conjugation.
E) mitosis.
A
3
Figure 25-1
Use the figure to answer the corresponding question(s).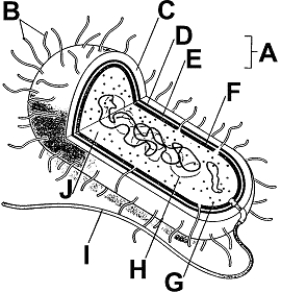
Gram-positive bacteria would stain __________ in a gram stain because of a thick layer of __________ in their cell walls.
A) green; peptidoglycan
B) purple; peptidoglycan
C) green; cellulose
D) purple; polysaccharides
E) red; polysaccharides
Use the figure to answer the corresponding question(s).

Gram-positive bacteria would stain __________ in a gram stain because of a thick layer of __________ in their cell walls.
A) green; peptidoglycan
B) purple; peptidoglycan
C) green; cellulose
D) purple; polysaccharides
E) red; polysaccharides
B
4
Prokaryotes have their genetic information stored in:
A) several small, circular pieces of DNA.
B) a single, small, circular piece of DNA.
C) a large, linear piece of DNA.
D) several small, linear pieces of DNA.
E) a large, circular piece of DNA.
A) several small, circular pieces of DNA.
B) a single, small, circular piece of DNA.
C) a large, linear piece of DNA.
D) several small, linear pieces of DNA.
E) a large, circular piece of DNA.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 55 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
Figure 25-1
Use the figure to answer the corresponding question(s).
What is the function of the structure labeled A in Figure 25-1?
A) to adhere to surfaces or other bacteria
B) to prevent phagocytosis
C) support and protection in hypotonic conditions
D) transmission of DNA between bacteria
E) locomotion
Use the figure to answer the corresponding question(s).

What is the function of the structure labeled A in Figure 25-1?
A) to adhere to surfaces or other bacteria
B) to prevent phagocytosis
C) support and protection in hypotonic conditions
D) transmission of DNA between bacteria
E) locomotion

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 55 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
Figure 25-1
Use the figure to answer the corresponding question(s).
Most bacterial cells keep from bursting in a hypotonic environment by:
A) an efficient water pump.
B) a tough cell membrane.
C) pumping large quantities of salts into the cell.
D) a rigid cell wall.
E) a stiff capsule.
Use the figure to answer the corresponding question(s).

Most bacterial cells keep from bursting in a hypotonic environment by:
A) an efficient water pump.
B) a tough cell membrane.
C) pumping large quantities of salts into the cell.
D) a rigid cell wall.
E) a stiff capsule.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 55 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
Penicillin works most effectively against gram-positive bacteria because:
A) penicillin affects cell membranes.
B) they have a thick peptidoglycan cell wall, and penicillin affects the synthesis of peptidoglycans.
C) they have special protein channels that allow penicillin to enter the cell and halt the cell cycle.
D) they are smaller than gram-negative bacteria and, thus, easily take up penicillin by diffusion.
E) they contain prophages that negatively interact with penicillin.
A) penicillin affects cell membranes.
B) they have a thick peptidoglycan cell wall, and penicillin affects the synthesis of peptidoglycans.
C) they have special protein channels that allow penicillin to enter the cell and halt the cell cycle.
D) they are smaller than gram-negative bacteria and, thus, easily take up penicillin by diffusion.
E) they contain prophages that negatively interact with penicillin.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 55 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
Rod-shaped bacteria are called:
A) streptococci.
B) bacilli.
C) diplococci.
D) vibrio.
E) spirochete.
A) streptococci.
B) bacilli.
C) diplococci.
D) vibrio.
E) spirochete.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 55 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
Even though bacteria lack membrane-bound organelles, such as chloroplasts and mitochondria, they can still perform the functions of these organelles by localizing certain metabolic enzymes on:
A) the nuclear membranes.
B) the endoplasmic reticulum.
C) the plasma membrane.
D) ribosomes.
E) the cell wall.
A) the nuclear membranes.
B) the endoplasmic reticulum.
C) the plasma membrane.
D) ribosomes.
E) the cell wall.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 55 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
Some bacteria avoid being phagocytized by a host's immune system by means of:
A) efficient use of their flagella.
B) ameboid motion.
C) their capsule.
D) changing their cell wall structure.
E) eliminating the use of a membrane.
A) efficient use of their flagella.
B) ameboid motion.
C) their capsule.
D) changing their cell wall structure.
E) eliminating the use of a membrane.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 55 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
Bacteria:
A) are incapable of locomotion.
B) move by means of pili
C) move by means of cilia.
D) move by means of a rotating flagella.
E) move by means of a whiplike flagella.
A) are incapable of locomotion.
B) move by means of pili
C) move by means of cilia.
D) move by means of a rotating flagella.
E) move by means of a whiplike flagella.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 55 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
Plasmids of bacteria often have genes involved in:
A) reproduction.
B) motility.
C) viral resistance.
D) antibiotic resistance.
E) photosynthesis.
A) reproduction.
B) motility.
C) viral resistance.
D) antibiotic resistance.
E) photosynthesis.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 55 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
Figure 25-1
Use the figure to answer the corresponding question(s).
The structure in Figure 25-1 labeled C is:
A) a ribosome.
B) the plasma membrane.
C) the capsule.
D) the cell wall.
E) the flagellum.
Use the figure to answer the corresponding question(s).

The structure in Figure 25-1 labeled C is:
A) a ribosome.
B) the plasma membrane.
C) the capsule.
D) the cell wall.
E) the flagellum.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 55 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
A chain of round bacteria would be called:
A) spirilla.
B) diplococci.
C) bacilli.
D) streptococci.
E) streptobacilli.
A) spirilla.
B) diplococci.
C) bacilli.
D) streptococci.
E) streptobacilli.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 55 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
Pili are involved in adhesion of bacterial cells to a substrate or host, or in transmission of __________ between bacteria.
A) ribosomes
B) cytoplasm
C) vectors
D) RNA
E) DNA
A) ribosomes
B) cytoplasm
C) vectors
D) RNA
E) DNA

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 55 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
The walls of bacteria contain peptidoglycan, which is:
A) lipids crosslinked with sugars.
B) sugars crosslinked with proteins.
C) a protein.
D) a lipid.
E) a polysaccharide.
A) lipids crosslinked with sugars.
B) sugars crosslinked with proteins.
C) a protein.
D) a lipid.
E) a polysaccharide.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 55 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
Small circles of DNA called __________ exist in addition to the bacterial chromosome.
A) capsids
B) plasmids
C) chromatids
D) pili
E) centromeres
A) capsids
B) plasmids
C) chromatids
D) pili
E) centromeres

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 55 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
Which of the following statements about bacteria is false?
A) A small percentage of bacteria are pathogenic.
B) Some bacteria can photosynthesize.
C) Bacteria are important decomposers.
D) Bacteria are not cellular and are sometimes not classified as life forms.
E) Bacteria convert atmospheric nitrogen into ammonia and then nitrates that can be used by plants.
A) A small percentage of bacteria are pathogenic.
B) Some bacteria can photosynthesize.
C) Bacteria are important decomposers.
D) Bacteria are not cellular and are sometimes not classified as life forms.
E) Bacteria convert atmospheric nitrogen into ammonia and then nitrates that can be used by plants.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 55 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
Small hairlike structures on the surface of bacteria are called:
A) capsids.
B) pili.
C) chromatids.
D) plasmids.
E) virons.
A) capsids.
B) pili.
C) chromatids.
D) plasmids.
E) virons.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 55 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
__________ is a form of genetic exchange in bacteria that involves contact between two cells.
A) Transformation
B) Transduction
C) Conjugation
D) Binary fission
E) Budding
A) Transformation
B) Transduction
C) Conjugation
D) Binary fission
E) Budding

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 55 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
Identify and briefly discuss two ecological roles filled by bacteria.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 55 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
Compare and contrast the metabolic diversity of bacteria in one of the two groups below.
A.
Obligate anaerobes, facultative anaerobes, and aerobes
B.
Autotrophic and heterotrophic bacteria
A.
Obligate anaerobes, facultative anaerobes, and aerobes
B.
Autotrophic and heterotrophic bacteria

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 55 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
__________ are dormant structures formed by bacteria in response to adverse environmental conditions.
A) Capsids
B) Endospores
C) Exotoxins
D) Endotoxins
E) Heterocysts
A) Capsids
B) Endospores
C) Exotoxins
D) Endotoxins
E) Heterocysts

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 55 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
The dense cytoplasm of the prokaryote contains ribosomes and storage granules.
____________________
____________________

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 55 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
A(n) __________ bacterium would not be able to survive in the presence of oxygen.
A) facultative aerobic
B) facultative anaerobic
C) facultative autotrophic
D) obligate aerobic
E) obligate anaerobic
A) facultative aerobic
B) facultative anaerobic
C) facultative autotrophic
D) obligate aerobic
E) obligate anaerobic

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 55 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
The Archaea differ from the Bacteria and eukaryotes by having different __________ in their cell membranes, but the Archaea are similar to eukaryotes in their __________ process.
A) sugars; replication
B) sugars; transcription
C) lipids; replication
D) lipids; translation
E) proteins; transcription
A) sugars; replication
B) sugars; transcription
C) lipids; replication
D) lipids; translation
E) proteins; transcription

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 55 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
Woese and his co-workers demonstrated that the Archaea were different from the Bacteria because of differences noted in their:
A) mechanism of cellular respiration.
B) preferred habitats.
C) signature sequences of SSU rRNA.
D) ability to utilize oxygen..
E) resistance to antibiotics.
A) mechanism of cellular respiration.
B) preferred habitats.
C) signature sequences of SSU rRNA.
D) ability to utilize oxygen..
E) resistance to antibiotics.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 55 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
The most significant difference between the Archaea and the Bacteria is:
A) lack of a nuclear envelope in the Archaea.
B) the absence of the 70S ribosomes in the Bacteria.
C) the presence of a single filament flagellum in the Bacteria.
D) the absence of peptidoglycans in the cell walls of the Archaea.
E) the presence of fatty acids in the plasma membranes of the Archaea.
A) lack of a nuclear envelope in the Archaea.
B) the absence of the 70S ribosomes in the Bacteria.
C) the presence of a single filament flagellum in the Bacteria.
D) the absence of peptidoglycans in the cell walls of the Archaea.
E) the presence of fatty acids in the plasma membranes of the Archaea.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 55 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
Bacterial __________ cause systemic symptoms such as fever, whereas bacterial __________ cause more specific maladies.
A) phages; prophages
B) prophages; phages
C) endotoxins; exotoxins
D) exotoxins; endotoxins
E) exotoxins; phages
A) phages; prophages
B) prophages; phages
C) endotoxins; exotoxins
D) exotoxins; endotoxins
E) exotoxins; phages

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 55 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
A bacterium that uses the oxidation of inorganic compounds to provide energy for manufacturing nutritious organic compounds is a:
A) photoautotroph.
B) parasite.
C) saprotroph.
D) chemoautotroph.
E) pathogen.
A) photoautotroph.
B) parasite.
C) saprotroph.
D) chemoautotroph.
E) pathogen.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 55 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
Most bacteria are:
A) photoheterotrophs.
B) chemoheterotrophs.
C) autotrophs.
D) heterotrophs.
E) chemoautotrophs.
A) photoheterotrophs.
B) chemoheterotrophs.
C) autotrophs.
D) heterotrophs.
E) chemoautotrophs.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 55 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
__________ are Archaea that are typically found in abnormally hot environments.
A) Extreme halophiles
B) Extreme thermophiles
C) Pyrrhanogens
D) Methanogens
E) Psychrophiles
A) Extreme halophiles
B) Extreme thermophiles
C) Pyrrhanogens
D) Methanogens
E) Psychrophiles

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 55 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
The first bacterium that was clearly identified as the cause of an infectious disease was:
A) Legionella pneumophila, which causes Legionnaires' disease.
B) Chlamydia sp., which causes pelvic inflammatory disease in women.
C) Clostridium botulinum, which causes botulism.
D) Vibrio cholerae, which causes cholera.
E) Bacillus anthracis, which causes anthrax.
A) Legionella pneumophila, which causes Legionnaires' disease.
B) Chlamydia sp., which causes pelvic inflammatory disease in women.
C) Clostridium botulinum, which causes botulism.
D) Vibrio cholerae, which causes cholera.
E) Bacillus anthracis, which causes anthrax.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 55 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
The energy parasite Chlamydia is known to:
A) eradicate males from a population.
B) convert males into females.
C) cause infected females to lay eggs that develop without fertilization.
D) reduce the number of males in a population.
E) lack peptidoglycan in cell wall.
A) eradicate males from a population.
B) convert males into females.
C) cause infected females to lay eggs that develop without fertilization.
D) reduce the number of males in a population.
E) lack peptidoglycan in cell wall.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 55 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
Koch's postulates include all the following except:
A) when a sample of a pure culture is injected into a healthy host, it causes the same disease.
B) a sample of the microorganism from a diseased host can be grown in pure culture.
C) the microorganism can be recovered from an experimentally infected host.
D) the microorganism must be visible in the electron microscope.
E) the pathogen must be present in every individual with the disease.
A) when a sample of a pure culture is injected into a healthy host, it causes the same disease.
B) a sample of the microorganism from a diseased host can be grown in pure culture.
C) the microorganism can be recovered from an experimentally infected host.
D) the microorganism must be visible in the electron microscope.
E) the pathogen must be present in every individual with the disease.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 55 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
The most familiar prokaryotes belong to the:
A) Fungi.
B) Archaea.
C) Protista.
D) Bacteria.
E) Viroids.
A) Fungi.
B) Archaea.
C) Protista.
D) Bacteria.
E) Viroids.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 55 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
One unique characteristic associated with some of the extreme halophilic Archaea is that:
A) they are found at deep-sea vents on the sea floor.
B) they are a source of most known antibiotics.
C) they have photosynthetic ability involving a purple bacteriorhodopsin pigment.
D) they fix atmospheric nitrogen that is then used by plants.
E) most form symbiotic associations.
A) they are found at deep-sea vents on the sea floor.
B) they are a source of most known antibiotics.
C) they have photosynthetic ability involving a purple bacteriorhodopsin pigment.
D) they fix atmospheric nitrogen that is then used by plants.
E) most form symbiotic associations.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 55 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
The symbiotic bacteria found in the root nodules of legumes do all of the following EXCEPT:
A) supply the plant with the nitrogen it needs in the form of nitrates.
B) are motile bacteria.
C) are Rhizobial bacteria.
D) are soil-dwelling bacteria.
E) digest wood.
A) supply the plant with the nitrogen it needs in the form of nitrates.
B) are motile bacteria.
C) are Rhizobial bacteria.
D) are soil-dwelling bacteria.
E) digest wood.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 55 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
Which of the following statements concerning biofilms is FALSE?
A) They are formed by bacteria living in a watery environment.
B) They enable bacteria to attach to solid surfaces.
C) They are usually less than 2 m thick.
D) An example is dental plaque.
E) They may develop on surgical implants.
A) They are formed by bacteria living in a watery environment.
B) They enable bacteria to attach to solid surfaces.
C) They are usually less than 2 m thick.
D) An example is dental plaque.
E) They may develop on surgical implants.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 55 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
Which of the following statements concerning an F factor is FALSE?
A) It is found in recipient cells, not donor cells.
B) It is a DNA sequence.
C) It is found in F+ cells.
D) The F stands for fertility.
E) It is involved with forming sex pili.
A) It is found in recipient cells, not donor cells.
B) It is a DNA sequence.
C) It is found in F+ cells.
D) The F stands for fertility.
E) It is involved with forming sex pili.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 55 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
Gram-negative cell walls have an outer membrane that contains lipids and peptidoglycans.
____________________
____________________

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 55 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
Transformation, conjugation, and transduction are forms of vertical gene transfer for prokaryotes.
____________________
____________________

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 55 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
Prokaryotes have a nucleus which contains DNA.
____________________
____________________

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 55 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
MATCHING
Match the group of bacteria with the description
a.resemble fungi
d.lack cell walls
b.waxy cell wall
e.contain chlorophyll
c.lack proteoglycan in cell walls
Describe endotoxins and exotoxins.What effects do they each have on infected persons?
Match the group of bacteria with the description
a.resemble fungi
d.lack cell walls
b.waxy cell wall
e.contain chlorophyll
c.lack proteoglycan in cell walls
Describe endotoxins and exotoxins.What effects do they each have on infected persons?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 55 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
After an endospore forms, the cell membrane of the original cell lyses, releasing the endospore.
____________________
____________________

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 55 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
In transduction, two prokaryotic cells of different mating types come together and genetic material is transferred from one cell to another.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 55 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
MATCHING
Match the group of bacteria with the description
a.resemble fungi
d.lack cell walls
b.waxy cell wall
e.contain chlorophyll
c.lack proteoglycan in cell walls
Actinomycetes
Match the group of bacteria with the description
a.resemble fungi
d.lack cell walls
b.waxy cell wall
e.contain chlorophyll
c.lack proteoglycan in cell walls
Actinomycetes

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 55 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
MATCHING
Match the group of bacteria with the description
a.resemble fungi
d.lack cell walls
b.waxy cell wall
e.contain chlorophyll
c.lack proteoglycan in cell walls
Mycobacteria
Match the group of bacteria with the description
a.resemble fungi
d.lack cell walls
b.waxy cell wall
e.contain chlorophyll
c.lack proteoglycan in cell walls
Mycobacteria

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 55 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
Bacteriad chemoautotrophs use organic chemicals as an energy source.
____________
____________

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 55 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
MATCHING
Match the group of bacteria with the description
a.resemble fungi
d.lack cell walls
b.waxy cell wall
e.contain chlorophyll
c.lack proteoglycan in cell walls
Cyanobacteria
Match the group of bacteria with the description
a.resemble fungi
d.lack cell walls
b.waxy cell wall
e.contain chlorophyll
c.lack proteoglycan in cell walls
Cyanobacteria

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 55 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
MATCHING
Match the group of bacteria with the description
a.resemble fungi
d.lack cell walls
b.waxy cell wall
e.contain chlorophyll
c.lack proteoglycan in cell walls
Chlamydia
Match the group of bacteria with the description
a.resemble fungi
d.lack cell walls
b.waxy cell wall
e.contain chlorophyll
c.lack proteoglycan in cell walls
Chlamydia

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 55 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
MATCHING
Match the group of bacteria with the description
a.resemble fungi
d.lack cell walls
b.waxy cell wall
e.contain chlorophyll
c.lack proteoglycan in cell walls
Mycoplasma
Match the group of bacteria with the description
a.resemble fungi
d.lack cell walls
b.waxy cell wall
e.contain chlorophyll
c.lack proteoglycan in cell walls
Mycoplasma

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 55 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
MATCHING
Match the group of bacteria with the description
a.resemble fungi
d.lack cell walls
b.waxy cell wall
e.contain chlorophyll
c.lack proteoglycan in cell walls
Discuss the distinction between gram-negative and gram-positive bacteria.In the laboratory, how is this determined? What are differences between these two groups of bacteria?
Match the group of bacteria with the description
a.resemble fungi
d.lack cell walls
b.waxy cell wall
e.contain chlorophyll
c.lack proteoglycan in cell walls
Discuss the distinction between gram-negative and gram-positive bacteria.In the laboratory, how is this determined? What are differences between these two groups of bacteria?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 55 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
Prokaryotes reproduce asexually by the processes of binary fission, budding, and transformation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 55 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
Bacterial plasmids often have genes that code for genetic exchange or antibiotic resistance.
____________________
____________________

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 55 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



