Deck 2: Atoms and Molecules: the Chemical Basis of Life
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/85
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 2: Atoms and Molecules: the Chemical Basis of Life
1
The difference between a stable isotope and a radioisotope is that:
A) the stable isotope emits radiation.
B) the radioisotope emits radiation.
C) the stable isotope emits light.
D) the stable isotope absorbs radiation.
E) the radioisotope has an unequal number of protons and electrons.
A) the stable isotope emits radiation.
B) the radioisotope emits radiation.
C) the stable isotope emits light.
D) the stable isotope absorbs radiation.
E) the radioisotope has an unequal number of protons and electrons.
B
2
Any chemical interaction between atoms:
A) involves neutrons.
B) may potentially involve any electron.
C) involves protons.
D) involves only valence electrons.
E) involves only the nuclear subatomic particles.
A) involves neutrons.
B) may potentially involve any electron.
C) involves protons.
D) involves only valence electrons.
E) involves only the nuclear subatomic particles.
D
3
Which of the following statements is FALSE?
A) The 1st principal energy level contains 1 orbital.
B) The 2nd principal energy level contains 4 orbitals.
C) The 1st principal energy level contains a maximum of 2 electrons.
D) The 2nd energy level contains a maximum of 10 electrons.
E) The 2nd energy level contains 1 spherical orbital and 3 dumbbell-shaped orbitals..
A) The 1st principal energy level contains 1 orbital.
B) The 2nd principal energy level contains 4 orbitals.
C) The 1st principal energy level contains a maximum of 2 electrons.
D) The 2nd energy level contains a maximum of 10 electrons.
E) The 2nd energy level contains 1 spherical orbital and 3 dumbbell-shaped orbitals..
D
4
The chemical behavior of an atom is determined by most directly by the:
A) atomic number.
B) atomic weight.
C) number of energy levels.
D) number of valence electrons.
E) number of neutrons.
A) atomic number.
B) atomic weight.
C) number of energy levels.
D) number of valence electrons.
E) number of neutrons.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 85 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
The representation H-O-H is known as:
A) a structural formula.
B) a simplest formula.
C) a molecular formula.
D) a Lewis structure.
E) an orbital diagram.
A) a structural formula.
B) a simplest formula.
C) a molecular formula.
D) a Lewis structure.
E) an orbital diagram.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 85 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
Figure 2-1
Use the figure below to answer the corresponding question(s).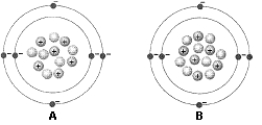
Isotopes differ from each other with respect to the number of:
A) protons only.
B) electrons only.
C) neutrons only.
D) both protons and electrons.
E) both neutrons and protons.
Use the figure below to answer the corresponding question(s).

Isotopes differ from each other with respect to the number of:
A) protons only.
B) electrons only.
C) neutrons only.
D) both protons and electrons.
E) both neutrons and protons.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 85 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
An element is defined as a substance that:
A) is composed of more than one kind of atom.
B) is held together by covalent bonds.
C) cannot be broken into simpler substances by chemical reactions.
D) cannot burn.
E) is soluble in both acid and base.
A) is composed of more than one kind of atom.
B) is held together by covalent bonds.
C) cannot be broken into simpler substances by chemical reactions.
D) cannot burn.
E) is soluble in both acid and base.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 85 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
How many molecules are present in one mole of C6H12O6?
A) 1.7 *10-10 molecules
B) 1.3 F* 1010 molecules
C) 24 molecules
D) 1.7 * 1022 molecules
E) 6.02 * 1023 molecules
A) 1.7 *10-10 molecules
B) 1.3 F* 1010 molecules
C) 24 molecules
D) 1.7 * 1022 molecules
E) 6.02 * 1023 molecules

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 85 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
The particular type of element is determined by the number of:
A) electrons
B) protons
C) neutrons
D) valence electrons
E) energy levels
A) electrons
B) protons
C) neutrons
D) valence electrons
E) energy levels

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 85 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
Figure 2-1
Use the figure below to answer the corresponding question(s).
The difference between the two atoms in Figure 2-1 is:
A) pH.
B) the number of electrons.
C) the number of protons.
D) the number of neutrons.
E) electrical charge.
Use the figure below to answer the corresponding question(s).

The difference between the two atoms in Figure 2-1 is:
A) pH.
B) the number of electrons.
C) the number of protons.
D) the number of neutrons.
E) electrical charge.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 85 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
If atom X contains 14 protons, 13 electrons, and 12 neutrons, and atom Y contains 14 protons, 14 electrons, and 12 neutrons, then you conclude that:
A) Y is an ion but X is not.
B) X and Y are both ions.
C) X and Y both have filled valence shells.
D) X and Y are isotopes of the same element.
E) X and Y are atoms of the same element.
A) Y is an ion but X is not.
B) X and Y are both ions.
C) X and Y both have filled valence shells.
D) X and Y are isotopes of the same element.
E) X and Y are atoms of the same element.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 85 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
In a chemical reaction, the product is:
A) generally written on the right side of the equation.
B) always in equilibrium with the reactants.
C) the substance that is generated by the reaction.
D) joined by an ionic bond only.
E) generally written on the right side and is the substance generated by the reaction.
A) generally written on the right side of the equation.
B) always in equilibrium with the reactants.
C) the substance that is generated by the reaction.
D) joined by an ionic bond only.
E) generally written on the right side and is the substance generated by the reaction.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 85 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
An atom has six protons and eight neutrons.Its atomic mass is __________ atomic mass units.
A) two
B) four
C) six
D) eight
E) fourteen
A) two
B) four
C) six
D) eight
E) fourteen

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 85 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
Which of the following choices correctly identifies a reactant in the following chemical equation? CO2 + H2O H2CO3
A) carbonic acid
B) oxygen
C) water
D) sugar
E) carbon monoxide
A) carbonic acid
B) oxygen
C) water
D) sugar
E) carbon monoxide

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 85 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
An organic compound differs from an inorganic compound in that an organic compound:
A) contains carbon.
B) contains two or more atoms.
C) lacks valence electrons.
D) lacks isotopes.
E) is basic rather than acidic.
A) contains carbon.
B) contains two or more atoms.
C) lacks valence electrons.
D) lacks isotopes.
E) is basic rather than acidic.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 85 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
Figure 2-1
Use the figure below to answer the corresponding question(s).
Figure 2-1 represents:
A) two isotopes of the same element.
B) two different elements.
C) two different ions.
D) an acid and a base.
E) a cation and an anion.
Use the figure below to answer the corresponding question(s).

Figure 2-1 represents:
A) two isotopes of the same element.
B) two different elements.
C) two different ions.
D) an acid and a base.
E) a cation and an anion.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 85 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
Which of the following elements is NOT responsible for a significant portion of the mass of living organisms?
A) O
B) S
C) N
D) H
E) C
A) O
B) S
C) N
D) H
E) C

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 85 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
Chlorine has seven electrons in its valence shell.The number of electrons it must gain to complete its valence shell is:
A) one.
B) two.
C) three.
D) seven.
E) eight.
A) one.
B) two.
C) three.
D) seven.
E) eight.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 85 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
When a chemical reaction is at equilibrium:
A) the forward reaction is going faster.
B) the reverse reaction is going faster.
C) the forward and reverse reactions are proceeding at equal rates.
D) the forward reaction stops.
E) the reverse reaction stops.
A) the forward reaction is going faster.
B) the reverse reaction is going faster.
C) the forward and reverse reactions are proceeding at equal rates.
D) the forward reaction stops.
E) the reverse reaction stops.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 85 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
Radioisotopes are used in all of the following scientific applications except:
A) dating fossils.
B) determining the sequence of genetic information in DNA.
C) localization of a drug, such as marijuana.
D) the treatment of cancer.
E) measuring the pH of the blood.
A) dating fossils.
B) determining the sequence of genetic information in DNA.
C) localization of a drug, such as marijuana.
D) the treatment of cancer.
E) measuring the pH of the blood.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 85 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
The difference between an electrically neutral atom and an ion is that:
A) an ion has an unequal number of protons and electrons, while an atom has an equal number.
B) an ion has an equal number of protons and electrons, while an atom has an unequal number.
C) an atom has an unequal number of neutrons and protons, while an ion has an equal number.
D) an atom has its electrons in orbitals, while an ion has its electrons in its nucleus.
E) an atom must have an equal number of neutrons and electrons, while an ion does not.
A) an ion has an unequal number of protons and electrons, while an atom has an equal number.
B) an ion has an equal number of protons and electrons, while an atom has an unequal number.
C) an atom has an unequal number of neutrons and protons, while an ion has an equal number.
D) an atom has its electrons in orbitals, while an ion has its electrons in its nucleus.
E) an atom must have an equal number of neutrons and electrons, while an ion does not.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 85 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
In the formation of common table salt, sodium and chlorine interact because:
A) sodium and chlorine share a pair of electrons.
B) sodium and chlorine share two pairs of electrons.
C) chlorine donates seven electrons to sodium.
D) there is no electron exchange.
E) sodium donates one electron to chlorine.
A) sodium and chlorine share a pair of electrons.
B) sodium and chlorine share two pairs of electrons.
C) chlorine donates seven electrons to sodium.
D) there is no electron exchange.
E) sodium donates one electron to chlorine.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 85 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
The cohesiveness between water molecules is due largely to:
A) hydrogen bonds.
B) polar covalent bonds.
C) nonpolar covalent bonds.
D) ionic bonds.
E) hydrophobic interactions.
A) hydrogen bonds.
B) polar covalent bonds.
C) nonpolar covalent bonds.
D) ionic bonds.
E) hydrophobic interactions.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 85 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
Which of the following statements concerning van der Waal interactions is FALSE:
A) They are attractive forces.
B) They are very strong.
C) They involve transient regions of positive and negative charges.
D) They form between nonpolar molecules.
E) They operate over very short distances.
A) They are attractive forces.
B) They are very strong.
C) They involve transient regions of positive and negative charges.
D) They form between nonpolar molecules.
E) They operate over very short distances.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 85 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
Which component becomes oxidized in the following chemical reaction? 4 Fe + 3 O2 2 Fe2O3
A) water
B) iron
C) oxygen
D) rust
E) hydrogen
A) water
B) iron
C) oxygen
D) rust
E) hydrogen

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 85 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
Which component is the oxidizing agent in the following chemical reaction? 4 Fe + 3 O2 2 Fe2O3
A) water
B) iron
C) oxygen
D) rust
E) hydrogen
A) water
B) iron
C) oxygen
D) rust
E) hydrogen

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 85 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
Figure 2-2
Use the figure below to answer the corresponding question(s).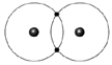
Figure 2-2 represents:
A) elemental helium.
B) molecular hydrogen.
C) molecular helium.
D) a water molecule.
E) molecular oxygen.
Use the figure below to answer the corresponding question(s).

Figure 2-2 represents:
A) elemental helium.
B) molecular hydrogen.
C) molecular helium.
D) a water molecule.
E) molecular oxygen.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 85 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
Table salt dissolves easily in water because:
A) water can form covalent linkages with salt molecules.
B) water can remove electrons from the chloride ion, which causes the latter to dissociate from the sodium and dissolve.
C) water can add electrons to the sodium ion.
D) water is polar and salt is nonpolar.Nonpolar compounds are more soluble in polar solvents because they are able to form strong covalent bonds that result in a breaking up of the molecule being dissolved.
E) the partial positive charge of the hydrogens in the water molecule can associate with the negative charge of the chloride ion, and the partial negative charge of the oxygen of the water molecule can associate with the positive charge of the sodium atom.
A) water can form covalent linkages with salt molecules.
B) water can remove electrons from the chloride ion, which causes the latter to dissociate from the sodium and dissolve.
C) water can add electrons to the sodium ion.
D) water is polar and salt is nonpolar.Nonpolar compounds are more soluble in polar solvents because they are able to form strong covalent bonds that result in a breaking up of the molecule being dissolved.
E) the partial positive charge of the hydrogens in the water molecule can associate with the negative charge of the chloride ion, and the partial negative charge of the oxygen of the water molecule can associate with the positive charge of the sodium atom.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 85 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
The process whereby water molecules surround ions during the process of dissolving is called:
A) reduction.
B) hydration.
C) buffering.
D) oxidation.
E) vaporization.
A) reduction.
B) hydration.
C) buffering.
D) oxidation.
E) vaporization.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 85 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
The covalent bond between a hydrogen atom and the oxygen atom in water is formed when:
A) hydrogen gains an electron from oxygen.
B) hydrogen and oxygen share an electron pair.
C) hydrogen and oxygen both lose electrons from their outer shells.
D) hydrogen and oxygen both gain electrons in their outer shells.
E) hydrogen gains an electron from oxygen.
A) hydrogen gains an electron from oxygen.
B) hydrogen and oxygen share an electron pair.
C) hydrogen and oxygen both lose electrons from their outer shells.
D) hydrogen and oxygen both gain electrons in their outer shells.
E) hydrogen gains an electron from oxygen.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 85 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
A covalent bond:
A) forms only between identical atoms.
B) involves a sharing of only one pair of electrons.
C) is always polar.
D) may be polar or nonpolar depending on the atoms involved.
E) always forms between identical molecules.
A) forms only between identical atoms.
B) involves a sharing of only one pair of electrons.
C) is always polar.
D) may be polar or nonpolar depending on the atoms involved.
E) always forms between identical molecules.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 85 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
Figure 2-2
Use the figure below to answer the corresponding question(s).
The type of bond illustrated in Figure 2-2 is:
A) an ionic bond.
B) a polar bond.
C) a single covalent bond.
D) a hydrogen bond.
E) a double covalent bond.
Use the figure below to answer the corresponding question(s).

The type of bond illustrated in Figure 2-2 is:
A) an ionic bond.
B) a polar bond.
C) a single covalent bond.
D) a hydrogen bond.
E) a double covalent bond.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 85 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
A stalk of celery is placed in a solution of blue colored dye.After one hour, the leaves have blue fluid in their veins.Which property of water is being demonstrated?
A) adhesion and cohesion
B) evaporation and cooling
C) lower density as a solid than as a liquid
D) high specific heat
E) surface tension
A) adhesion and cohesion
B) evaporation and cooling
C) lower density as a solid than as a liquid
D) high specific heat
E) surface tension

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 85 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
Which of the following statements is not correct?
A) Water heats up and cools down very quickly.
B) The amount of heat required to raise the temperature of 1 g of water 1 C is one calorie.
C) Due to hydrogen bonds, water has a high surface tension.
D) Large bodies of water have relatively constant temperatures.
E) When one gram of water evaporates, it removes heat.
A) Water heats up and cools down very quickly.
B) The amount of heat required to raise the temperature of 1 g of water 1 C is one calorie.
C) Due to hydrogen bonds, water has a high surface tension.
D) Large bodies of water have relatively constant temperatures.
E) When one gram of water evaporates, it removes heat.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 85 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
Which covalent bond involves only 2 electrons:
A) single
B) double
C) triple
D) single and double.
E) single and triple.
A) single
B) double
C) triple
D) single and double.
E) single and triple.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 85 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
In a water molecule, because oxygen is more electronegative than hydrogen, the shared electrons are more commonly found around the __________ nucleus than the __________ nucleus.
A) oxygen; hydrogen
B) hydrogen; oxygen
C) hydrogen; other hydrogen
D) oxygen; nitrogen
E) nitrogen; oxygen
A) oxygen; hydrogen
B) hydrogen; oxygen
C) hydrogen; other hydrogen
D) oxygen; nitrogen
E) nitrogen; oxygen

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 85 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
Which of the following atoms would most likely be involved in an ionic bond?
A) hydrogen
B) oxygen
C) sodium
D) hydrogen and oxygen.
E) hydrogen and sodium.
A) hydrogen
B) oxygen
C) sodium
D) hydrogen and oxygen.
E) hydrogen and sodium.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 85 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
Covalently bonded atoms with similar electronic negativities are:
A) ionic.
B) polar.
C) nonpolar.
D) partially positive.
E) partially negative.
A) ionic.
B) polar.
C) nonpolar.
D) partially positive.
E) partially negative.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 85 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
An atom becomes a cation if:
A) it gains one or more electron.
B) it loses one or more electron.
C) it shares electrons.
D) one or more of its electrons changes energy levels.
E) it emits radiation.
A) it gains one or more electron.
B) it loses one or more electron.
C) it shares electrons.
D) one or more of its electrons changes energy levels.
E) it emits radiation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 85 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
Which characteristic of water molecules directly contributes to the remarkable "water walking" success of the aquatic insects pictured in the accompanying figure? 
A) hydrogen bonds
B) capillary action
C) nonpolar covalent bonds
D) ionic bonds
E) adhesive forces

A) hydrogen bonds
B) capillary action
C) nonpolar covalent bonds
D) ionic bonds
E) adhesive forces

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 85 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
Which characteristic of water makes the existence of pH possible?
A) ionization
B) polarity
C) adhesion
D) cohesion
E) hydrophobicity
A) ionization
B) polarity
C) adhesion
D) cohesion
E) hydrophobicity

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 85 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
At what temperature is water most dense?
A) 0 degrees Celsius
B) 1 degree Celsius
C) 4 degrees Celsius
D) 10 degrees Celsius
E) 100 degrees Celsius
A) 0 degrees Celsius
B) 1 degree Celsius
C) 4 degrees Celsius
D) 10 degrees Celsius
E) 100 degrees Celsius

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 85 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
Explain how the number of valence electrons is related to the chemical properties of an atom.Use two specific examples in your explanation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 85 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
This characteristic of a molecule determines the ability of hydrogen bonds to form between it and hydrogen:
A) A nonpolar atom.
B) An atom with a partial positive charge.
C) An atom with a partial negative charge.
D) A hydrophobic molecule.
E) An atom with a filled valence shell.
A) A nonpolar atom.
B) An atom with a partial positive charge.
C) An atom with a partial negative charge.
D) A hydrophobic molecule.
E) An atom with a filled valence shell.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 85 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
Compare and contrast the formation, properties, and characteristics of covalent and ionic bonds.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 85 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
In a mixture, which would be present in the least amount?
A) solvent
B) solute
C) water
D) both solvent and solute
E) both solvent and water
A) solvent
B) solute
C) water
D) both solvent and solute
E) both solvent and water

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 85 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
Evaporative cooling is a process whereby __________ moving __________ molecules vaporize, thus __________ large amounts of heat.
A) slow; water; adding
B) fast; water; removing
C) slow; oxygen; adding
D) fast; oxygen; removing
E) fast; carbon dioxide; removing
A) slow; water; adding
B) fast; water; removing
C) slow; oxygen; adding
D) fast; oxygen; removing
E) fast; carbon dioxide; removing

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 85 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
Diagram and carefully label two water molecules using a ball-and-stick model.Then use this diagram to demonstrate how hydrogen bonds form between them.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 85 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
Identify the chemical(s) that act(s) as a buffer in human blood:
A) bicarbonate
B) hydrogen ions
C) carbon dioxide
D) water
E) hydroxide ions
A) bicarbonate
B) hydrogen ions
C) carbon dioxide
D) water
E) hydroxide ions

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 85 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
What is the OH -- concentration of a solution having a pH of 2?
A) 1 *10-12
B) 1 *10-10
C) 1 *10-7
D) 1* 10-2
E) 1 *10-1
A) 1 *10-12
B) 1 *10-10
C) 1 *10-7
D) 1* 10-2
E) 1 *10-1

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 85 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
When a small amount of hydrochloric acid (HCl) is added to a solution of Na2HPO4, the pH of the solution does not change markedly.The pH also does not change drastically when a small amount of sodium hydroxide (NaOH) is added to this same solution.Based on these observations, the compound Na2HPO4 is:
A) able to donate hydrogen atoms to HCl.
B) able to remove hydrogen ions from the OH - of NaOH.
C) acting as a buffer.
D) an enzyme facilitating the reaction between HCl and NaOH.
E) acting as a solvent.
A) able to donate hydrogen atoms to HCl.
B) able to remove hydrogen ions from the OH - of NaOH.
C) acting as a buffer.
D) an enzyme facilitating the reaction between HCl and NaOH.
E) acting as a solvent.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 85 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
List the four elements that account for over 90% of the mass of living organisms and identify an important biological function of each element.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 85 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
Which of the following would most likely form electrolytes in water?
A) glucose
B) ethanol
C) an organic compound
D) an inorganic compound
E) a nonionic compound
A) glucose
B) ethanol
C) an organic compound
D) an inorganic compound
E) a nonionic compound

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 85 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
A salt is a compound in which the hydrogen ion of __________ is replaced by some other cation.
A) a base
B) an acid
C) an anion
D) a hydroxide ion
E) water
A) a base
B) an acid
C) an anion
D) a hydroxide ion
E) water

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 85 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
Identify the hydrogen ion concentration that represents the lowest pH from the following list:
A) 1 *10 - 3
B) 1 * 10- 4
C) 1 * 10 - 7
D) 1 *10-11
E) 1 *10-14
A) 1 *10 - 3
B) 1 * 10- 4
C) 1 * 10 - 7
D) 1 *10-11
E) 1 *10-14

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 85 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
Which of the following has a pH closest to that of human blood?
A) beer
B) coffee
C) rain water
D) sea water
E) oven cleaner
A) beer
B) coffee
C) rain water
D) sea water
E) oven cleaner

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 85 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
A solution having a pH of 6 would:
A) have equal concentrations of hydrogen ions and hydroxide ions.
B) have a higher concentrations of hydroxide ions than hydrogen ions.
C) be slightly acidic.
D) be slightly basic.
E) be neutral.
A) have equal concentrations of hydrogen ions and hydroxide ions.
B) have a higher concentrations of hydroxide ions than hydrogen ions.
C) be slightly acidic.
D) be slightly basic.
E) be neutral.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 85 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
It takes 1 calorie of heat to raise the temperature of 1 gram of water 1 degree Celsius at sea level.This is referred to as the __________ of water.
A) heat of fusion
B) heat of vaporization
C) specific heat
D) heat of transformation
E) heat of homeostasis
A) heat of fusion
B) heat of vaporization
C) specific heat
D) heat of transformation
E) heat of homeostasis

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 85 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
Which property of water enables living things to survive in ponds covered with ice?
A) high heat of vaporization
B) high specific heat
C) degree of surface tension
D) cohesion
E) greatest density at 4oC
A) high heat of vaporization
B) high specific heat
C) degree of surface tension
D) cohesion
E) greatest density at 4oC

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 85 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
A pH of 4 is __________ times more __________ than a pH of 7.
A) 3; basic
B) 3; acidic
C) 1000; neutral
D) 1000; basic
E) 1000; acidic
A) 3; basic
B) 3; acidic
C) 1000; neutral
D) 1000; basic
E) 1000; acidic

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 85 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
MATCHING
Match the type of bond or interaction with its description.
a.hydrogen bond
c.ionic bond
b.van de Waals interaction
d.covalent bond
Strong attractive force resulting from the transfer of electrons between atoms
Match the type of bond or interaction with its description.
a.hydrogen bond
c.ionic bond
b.van de Waals interaction
d.covalent bond
Strong attractive force resulting from the transfer of electrons between atoms

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 85 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
Match the term with its description:
a.adhesion
c.surface tension
b.cohesion
d.capillary action
Responsible for the ability of water molecules to move in the microscopic spaces between soil particles
a.adhesion
c.surface tension
b.cohesion
d.capillary action
Responsible for the ability of water molecules to move in the microscopic spaces between soil particles

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 85 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
The tetrahedron shape of a methane molecule is the result of orbital hybridization.
__________________
__________________

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 85 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
MATCHING
Match the type of bond or interaction with its description.
a.hydrogen bond
c.ionic bond
b.van de Waals interaction
d.covalent bond
In a structural formula this is represented by a straight line
Match the type of bond or interaction with its description.
a.hydrogen bond
c.ionic bond
b.van de Waals interaction
d.covalent bond
In a structural formula this is represented by a straight line

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 85 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
A solution having a pH of 8 is slightly acidic.
__________________
__________________

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 85 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
Specific heat refers to the amount of energy required to change 1 gram of a substance from the liquid phase to the vapor phase.
__________________
__________________

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 85 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
Water is most dense at 4 C.
__________________
__________________

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 85 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
MATCHING
Match the type of bond or interaction with its description.
a.hydrogen bond
c.ionic bond
b.van de Waals interaction
d.covalent bond
Very weak attractive force joining nonpolar molecules
Match the type of bond or interaction with its description.
a.hydrogen bond
c.ionic bond
b.van de Waals interaction
d.covalent bond
Very weak attractive force joining nonpolar molecules

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 85 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
An example of an anion is K+.
__________________
__________________

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 85 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
MATCHING
Match the type of bond or interaction with its description.
a.hydrogen bond
c.ionic bond
b.van de Waals interaction
d.covalent bond
Holds adjacent water molecules together
Match the type of bond or interaction with its description.
a.hydrogen bond
c.ionic bond
b.van de Waals interaction
d.covalent bond
Holds adjacent water molecules together

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 85 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
Match the term with its description:
a.adhesion
c.surface tension
b.cohesion
d.capillary action
Directly responsible for the ability of certain insects to walk on water
a.adhesion
c.surface tension
b.cohesion
d.capillary action
Directly responsible for the ability of certain insects to walk on water

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 85 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72
An inorganic compound is one that contains carbon.
__________________
__________________

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 85 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73
MATCHING
Match the type of bond or interaction with its description.
a.hydrogen bond
c.ionic bond
b.van de Waals interaction
d.covalent bond
Strong attractive force resulting from the sharing of electrons between atoms
Match the type of bond or interaction with its description.
a.hydrogen bond
c.ionic bond
b.van de Waals interaction
d.covalent bond
Strong attractive force resulting from the sharing of electrons between atoms

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 85 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
74
An atom having a filled valence shell is stable and unreactive.
__________________
__________________

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 85 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
75
The atomic mass determines the type of element.
__________________
__________________

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 85 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
76
MATCHING
Match the type of bond or interaction with its description.
a.hydrogen bond
c.ionic bond
b.van de Waals interaction
d.covalent bond
Weak attractive force joining a hydrogen atom with an electronegative atom such as oxygen
Match the type of bond or interaction with its description.
a.hydrogen bond
c.ionic bond
b.van de Waals interaction
d.covalent bond
Weak attractive force joining a hydrogen atom with an electronegative atom such as oxygen

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 85 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
77
A substance that is resistant to changes in pH is called a buffer.
__________________
__________________

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 85 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
78
Oxidation occurs when an atom gains one or more electrons.
__________________
__________________

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 85 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
79
When atoms react to form an ionic bond, electrons are shared between those atoms.
__________________
__________________

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 85 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
80
Match the term with its description:
a.adhesion
c.surface tension
b.cohesion
d.capillary action
Sticking together of like molecules
a.adhesion
c.surface tension
b.cohesion
d.capillary action
Sticking together of like molecules

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 85 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



