Deck 11: Neutron Stars and Black Holes
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/70
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 11: Neutron Stars and Black Holes
1
Pulsars cannot be spinning white dwarfs because
A) white dwarfs are not that common.
B) white dwarfs are not dense enough.
C) white dwarfs do not have magnetic fields.
D) a white dwarf spinning that fast would fly apart.
E) all of the above.
A) white dwarfs are not that common.
B) white dwarfs are not dense enough.
C) white dwarfs do not have magnetic fields.
D) a white dwarf spinning that fast would fly apart.
E) all of the above.
a white dwarf spinning that fast would fly apart.
2
The ____ of a black hole is the radius from a black hole at which the escape velocity is approximately equal to the speed of light.
A) Roche limit
B) Lagrangian point
C) Chandraskhar limit
D) Hubble radius
E) event horizon
A) Roche limit
B) Lagrangian point
C) Chandraskhar limit
D) Hubble radius
E) event horizon
event horizon
3
Cygnus X-1 and LMC X-3 are black holes if the masses of the unseen companions are
A) less than 5 solar masses.
B) more than 5 solar masses.
C) between 0.4 and 1.4 solar masses.
D) less than 0.4 solar masses.
E) not larger than the masses of the stars that we can see.
A) less than 5 solar masses.
B) more than 5 solar masses.
C) between 0.4 and 1.4 solar masses.
D) less than 0.4 solar masses.
E) not larger than the masses of the stars that we can see.
more than 5 solar masses.
4
____ occurs when light travels out of a gravitational field, loses energy, and its wavelength grows longer.
A) A gravitational blue shift
B) The solar wind
C) A gravitational redshift
D) A X-ray burst
E) A pulsar wind
A) A gravitational blue shift
B) The solar wind
C) A gravitational redshift
D) A X-ray burst
E) A pulsar wind

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
In A.D. 1054, Chinese astronomers observed the appearance of a new star, whose location is now occupied by
A) a pulsar.
B) a neutron star.
C) a supernova remnant.
D) all of the above.
A) a pulsar.
B) a neutron star.
C) a supernova remnant.
D) all of the above.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
The mass of a neutron star is
A) several time that of the sun.
B) about the same as that of the sun.
C) about the same as Earth.
D) smaller than any of these.
A) several time that of the sun.
B) about the same as that of the sun.
C) about the same as Earth.
D) smaller than any of these.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
The size of a neutron star is
A) about the same as that of our Solar System.
B) about the same as that of the sun.
C) about the same as Earth.
D) smaller than any of these.
A) about the same as that of our Solar System.
B) about the same as that of the sun.
C) about the same as Earth.
D) smaller than any of these.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
____ are neutron stars that have magnetic fields 100 times stronger than the average neutron star.
A) Hypernovae
B) Collapsars
C) Pulsars
D) Kerr singularities
E) Magnetars
A) Hypernovae
B) Collapsars
C) Pulsars
D) Kerr singularities
E) Magnetars

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
The density of a neutron star is
A) about the same as that of a white dwarf.
B) about the same as that of the sun.
C) about the same as an atomic nucleus.
D) zero.
A) about the same as that of a white dwarf.
B) about the same as that of the sun.
C) about the same as an atomic nucleus.
D) zero.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
Hypernovae are
A) supernovae that occur when two red dwarfs collide.
B) supernovae that occur when 10-solar-mass stars explode.
C) supernovae that occur when stars more massive than 25 solar masses explode.
D) one theory to explain the production of gamma-ray bursters.
E) both c and d above.
A) supernovae that occur when two red dwarfs collide.
B) supernovae that occur when 10-solar-mass stars explode.
C) supernovae that occur when stars more massive than 25 solar masses explode.
D) one theory to explain the production of gamma-ray bursters.
E) both c and d above.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
Which of the following objects is considered to possibly contain a black hole?
A) the central star of the Crab nebula
B) the Orion nebula.
C) LMC X-3
D) Algol
E) PSR 1257+12
A) the central star of the Crab nebula
B) the Orion nebula.
C) LMC X-3
D) Algol
E) PSR 1257+12

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
Neutron stars are expected to spin rapidly because
A) they conserved angular momentum when they collapsed.
B) they have high orbital velocities.
C) they have high densities.
D) they have high temperatures.
E) the energy from the supernova explosion that formed them made them spin faster.
A) they conserved angular momentum when they collapsed.
B) they have high orbital velocities.
C) they have high densities.
D) they have high temperatures.
E) the energy from the supernova explosion that formed them made them spin faster.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
The density of a ____ is greater than the density of a ____.
A) white dwarf; neutron star
B) neutron star; black hole
C) pulsar; neutron star
D) pulsar; white dwarf
E) white dwarf; black hole
A) white dwarf; neutron star
B) neutron star; black hole
C) pulsar; neutron star
D) pulsar; white dwarf
E) white dwarf; black hole

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
A ____ has a radius of about 10 km and is supported by the pressure associated with degenerate neutrons.
A) black hole
B) neutron star
C) white dwarf
D) supernova remnant
E) red dwarf
A) black hole
B) neutron star
C) white dwarf
D) supernova remnant
E) red dwarf

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
The peculiar system SS 433 
A) I
B) III
C) II & III
D) I, II, & III
E) I, II, III, & IV

A) I
B) III
C) II & III
D) I, II, & III
E) I, II, III, & IV

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
An isolated black hole in empty intergalactic space would be difficult to detect because
A) there would be no stars behind it whose light would be affected by gravitational lensing.
B) it could not emit light from inside its event horizon.
C) no companion stars would be affected by its gravitational field.
D) no matter would be falling into it to create an X-ray-emitting accretion disk.
E) all of the above.
A) there would be no stars behind it whose light would be affected by gravitational lensing.
B) it could not emit light from inside its event horizon.
C) no companion stars would be affected by its gravitational field.
D) no matter would be falling into it to create an X-ray-emitting accretion disk.
E) all of the above.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
The event horizon
A) is believed to be a singularity.
B) is a crystalline layer.
C) has a radius equal to the Schwarzschild radius.
D) marks the inner boundary of a planetary nebula.
E) is located at the point where synchrotron radiation is created around a pulsar.
A) is believed to be a singularity.
B) is a crystalline layer.
C) has a radius equal to the Schwarzschild radius.
D) marks the inner boundary of a planetary nebula.
E) is located at the point where synchrotron radiation is created around a pulsar.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
Similar to our sun, pulsars' rotations are believed to slow down because
A) they are losing angular momentum into space via outward streaming particles.
B) they are dragging companions stars around in their magnetic field.
C) they are getting tired.
D) of conservation of angular momentum.
E) their mass is increasing.
A) they are losing angular momentum into space via outward streaming particles.
B) they are dragging companions stars around in their magnetic field.
C) they are getting tired.
D) of conservation of angular momentum.
E) their mass is increasing.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
The slowing of clocks in strongly curved space time is known as
A) gravitational radiation.
B) time dilation.
C) gravitational curvature.
D) gravitational redshift.
E) hyperspace drag.
A) gravitational radiation.
B) time dilation.
C) gravitational curvature.
D) gravitational redshift.
E) hyperspace drag.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
Observations from the Compton Gamma Ray Observatory showed that gamma-ray bursters were located throughout the sky. This told us that
A) the bursts were not produced among stars in the disk of our galaxy.
B) the bursts were not produced among stars in the nuclear bulge of our galaxy.
C) the bursts are not associated with planets in our solar system.
D) the bursts were not produced in our sun.
E) all of the above.
A) the bursts were not produced among stars in the disk of our galaxy.
B) the bursts were not produced among stars in the nuclear bulge of our galaxy.
C) the bursts are not associated with planets in our solar system.
D) the bursts were not produced in our sun.
E) all of the above.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
Fraud in science is rare because it is difficult to commit. Why is it difficult to commit fraud in science?
A) Science requires that experimental and theoretical findings be reproducible.
B) All scientists are bound by a code of ethics preventing them from publishing fraudulent work.
C) Scientific results are reviewed by other scientists before they are published.
D) Scientific journals only allow certain highly trusted individuals to publish their work.
E) a and c above.
A) Science requires that experimental and theoretical findings be reproducible.
B) All scientists are bound by a code of ethics preventing them from publishing fraudulent work.
C) Scientific results are reviewed by other scientists before they are published.
D) Scientific journals only allow certain highly trusted individuals to publish their work.
E) a and c above.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
If the inner accretion disk around a black hole has a temperature of 106 K, at what wavelength will it radiate the most energy? Hint: wavelength in nm =3,000,000/T in K
A) 106 nm
B) 3 nm
C) 3*106 nm
D) 1 nm
E) 3*1011 nm
A) 106 nm
B) 3 nm
C) 3*106 nm
D) 1 nm
E) 3*1011 nm

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
A black hole can be thought of as
A) a very massive object of finite size.
B) a shell of material expanding from a white dwarf.
C) a massive body of infinitely small size.
D) a burnt out white dwarf.
A) a very massive object of finite size.
B) a shell of material expanding from a white dwarf.
C) a massive body of infinitely small size.
D) a burnt out white dwarf.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
The escape velocity of an object depends on 
A) I, II, III, & IV
B) I & II
C) I & III
D) I, II, & IV
E) I, III, & IV

A) I, II, III, & IV
B) I & II
C) I & III
D) I, II, & IV
E) I, III, & IV

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
Which of the following can you never know about a black hole?
A) mass
B) rotation
C) electrical charge
D) the elements of the material that has fallen in
A) mass
B) rotation
C) electrical charge
D) the elements of the material that has fallen in

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
For a point mass equal to that of the sun, how far does the Schwarzschild radius extend from its center?
A) A few kilometers away
B) A few solar radii away
C) A few astronomical units (AU) away
D) A few parsecs away
A) A few kilometers away
B) A few solar radii away
C) A few astronomical units (AU) away
D) A few parsecs away

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
Millisecond pulsars that are very old are
A) believed to be the result of mass transfer from a companion that increased the spin of the pulsar.
B) all single objects.
C) not spinning as rapidly as they seem because they have four hot spots that produce the flashes.
D) X-ray binaries.
E) gamma-ray bursters.
A) believed to be the result of mass transfer from a companion that increased the spin of the pulsar.
B) all single objects.
C) not spinning as rapidly as they seem because they have four hot spots that produce the flashes.
D) X-ray binaries.
E) gamma-ray bursters.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
The Schwarzschild radius of a 1- 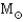 black hole is approximately
black hole is approximately
A) 3 km.
B) 1,500,000 km, the size of the sun.
C) 150,000,000 km or 1 AU.
D) 3*13 km or 1 pc.
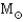 black hole is approximately
black hole is approximatelyA) 3 km.
B) 1,500,000 km, the size of the sun.
C) 150,000,000 km or 1 AU.
D) 3*13 km or 1 pc.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
A pulsar requires that a neutron star 
A) I & III
B) I & IV
C) II, III, & IV
D) I, III, & IV
E) I, II, III, & IV

A) I & III
B) I & IV
C) II, III, & IV
D) I, III, & IV
E) I, II, III, & IV

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
The object left behind after the 1054 AD supernova explosion has been observed at the center of the Crab nebula. The object is a
A) white dwarf.
B) neutron star.
C) red giant.
D) protostar.
A) white dwarf.
B) neutron star.
C) red giant.
D) protostar.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
The Schwarzschild radius of a 2- 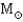 black hole is approximately
black hole is approximately
A) 6 km.
B) 4 km.
C) 2 km.
D) 12 km.
E) 36 km.
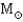 black hole is approximately
black hole is approximatelyA) 6 km.
B) 4 km.
C) 2 km.
D) 12 km.
E) 36 km.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
The escape velocity at the event horizon around a black hole is
A) smaller than the speed of light.
B) equal to the speed of light.
C) much larger than the speed of light.
D) irrelevant since nothing (including light) can escape from a black hole.
A) smaller than the speed of light.
B) equal to the speed of light.
C) much larger than the speed of light.
D) irrelevant since nothing (including light) can escape from a black hole.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
None of the pulsars emit pulses of visible light because
A) pulsars are too hot to emit visible light.
B) pulsars contain black holes that won't let visible light escape.
C) the gravitational field of a pulsar is so great that the visible light emitted is redshifted.
D) pulsars are too far away for the visible light to be bright enough to be detected at Earth.
E) A few pulsars do emit visible light pulses.
A) pulsars are too hot to emit visible light.
B) pulsars contain black holes that won't let visible light escape.
C) the gravitational field of a pulsar is so great that the visible light emitted is redshifted.
D) pulsars are too far away for the visible light to be bright enough to be detected at Earth.
E) A few pulsars do emit visible light pulses.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
The first pulsar was discovered by ____ in November of 1967.
A) Jocelyn Bell
B) Isaac Newton
C) Albert Einstein
D) Walter Baade
E) Edwin Hubble
A) Jocelyn Bell
B) Isaac Newton
C) Albert Einstein
D) Walter Baade
E) Edwin Hubble

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
Why don't all supernova remnants contain pulsars?
A) All supernova remnants do contain pulsars.
B) Some supernova explosions form white dwarfs instead of the neutron stars necessary for pulsars.
C) Pulsars slow down and quit producing the pulses before the supernova remnant dissipates.
D) The pulsar may be tipped so that the beams do not sweep past Earth.
E) b and c above.
A) All supernova remnants do contain pulsars.
B) Some supernova explosions form white dwarfs instead of the neutron stars necessary for pulsars.
C) Pulsars slow down and quit producing the pulses before the supernova remnant dissipates.
D) The pulsar may be tipped so that the beams do not sweep past Earth.
E) b and c above.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
At extremely high densities and temperatures, electrons can be forced to fuse with protons. This reaction produces
A) hydrogen.
B) helium and energy.
C) degenerate electrons.
D) neutrons and neutrinos.
E) large amounts of radio radiation.
A) hydrogen.
B) helium and energy.
C) degenerate electrons.
D) neutrons and neutrinos.
E) large amounts of radio radiation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
The singularity of a black hole
A) is found outside the event horizon.
B) is located within the event horizon.
C) can only be located if the black hole is in a binary system.
D) doesn't exist since all black holes have a finite size.
A) is found outside the event horizon.
B) is located within the event horizon.
C) can only be located if the black hole is in a binary system.
D) doesn't exist since all black holes have a finite size.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
The material that accretes onto a neutron star or black hole is expected to emit X-rays because
A) the material will produce synchrotron radiation.
B) hydrogen nuclei begin to fuse and emit high-energy photons.
C) the material will become hot enough that it will radiate most strongly at X-ray wavelengths.
D) as the material slows down it converts thermal energy to gravitational potential energy.
E) none of the above.
A) the material will produce synchrotron radiation.
B) hydrogen nuclei begin to fuse and emit high-energy photons.
C) the material will become hot enough that it will radiate most strongly at X-ray wavelengths.
D) as the material slows down it converts thermal energy to gravitational potential energy.
E) none of the above.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
The search for black holes involves searching for
A) single stars that emit large amounts of X-rays.
B) X-ray binaries where the compact companion has a mass in excess of 3.
C) large spherical regions from which no light is detected.
D) pulsars with periods less than one millisecond.
E) pulsars that are orbited by planets.
A) single stars that emit large amounts of X-rays.
B) X-ray binaries where the compact companion has a mass in excess of 3.
C) large spherical regions from which no light is detected.
D) pulsars with periods less than one millisecond.
E) pulsars that are orbited by planets.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
An isolated black hole in space would be difficult to detect because
A) there would be no light source nearby.
B) it would not be rotating rapidly.
C) it would be stationary.
D) very little matter would be falling into it.
E) there would be very few stars behind it whose light the black hole could block out.
A) there would be no light source nearby.
B) it would not be rotating rapidly.
C) it would be stationary.
D) very little matter would be falling into it.
E) there would be very few stars behind it whose light the black hole could block out.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
Neutron stars have densities roughly the same as that of the atomic nucleus.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
Which of the kinds of stars below would you expect to find in a 11-billion-year-old globular cluster of stars?
A) cool, low luminosity main sequence stars
B) white dwarfs
C) neutron stars
D) red giants
E) all of the above
A) cool, low luminosity main sequence stars
B) white dwarfs
C) neutron stars
D) red giants
E) all of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
The figure shows an image of an isolated black hole. A black hole emits 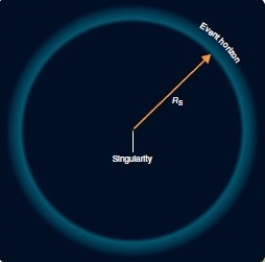
A) light with wavelengths in the black color region.
B) no light from inside the event horizon.
C) light which is blueshifted to shorter wavelengths as it escapes.
D) light which is redshifted to shorter wavelengths as it escapes.

A) light with wavelengths in the black color region.
B) no light from inside the event horizon.
C) light which is blueshifted to shorter wavelengths as it escapes.
D) light which is redshifted to shorter wavelengths as it escapes.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
The ____________________ of a black hole in a binary system can emit X-rays and allow us to detect the presence of the black hole.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
A scientific theory can be proven true if the correct experiments are performed.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
Theory predicts that neutron stars may not exceed 3 solar masses.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
When a star of mass comparable to the sun dies it become a black hole.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
We expect neutron stars to spin rapidly because they conserve angular momentum.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
LMC X-3 is a binary system that is believed to contain a black hole.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
The ____________________ of a black hole is the radius from the black hole at which the escape velocity is equal to the speed of light.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
If the accretion disk around a black hole emits X-rays outside the event horizon, the X-rays can escape.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
A(n) ____________________ is a rapidly spinning neutron star that accelerates charged particles near the poles of its magnetic field.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
The ____________________ theory describes pulsars as rotating neutron stars with strong magnetic fields that confine high-speed charged particles in two beams emanating from the magnetic poles of the neutron star.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
Neutron stars were first discovered in the 1930's.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
Many pulsars have periods that are gradually increasing as the spinning neutron stars lose energy.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
Pulsars could not be pulsating stars because the pulses are too short.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
The event horizon marks the boundary within which the density is roughly the same as that of the atomic nucleus.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
To tell the difference between a neutron star and a black hole in an X-ray binary, we must find the temperature of the object.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
A(n) ____________________ periodically emits large amounts of X-ray radiation as material accretes around a neutron star or black hole.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
Unseen objects in our galaxy have been found by the bending effect they have on more distant stars' light passing near them. These small objects that don't emit light are calculated to have masses of about 10* the mass of the sun. Which is the best choice for these objects?
A) black hole
B) neutron star
C) white dwarf
D) main-sequence stars
A) black hole
B) neutron star
C) white dwarf
D) main-sequence stars

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
Why might we suspect that a black hole in a binary system could emit X-rays?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
If neutron stars contain no nuclear fuel, why are they hot?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
What evidence do we have that pulsars are neutron stars?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
What observational evidence do we have that black holes exist?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
How are neutron stars and white dwarfs similar?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
Why do we not expect to find a 5-solar-mass neutron star?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
Why does our theory predict that neutron stars will spin rapidly?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
If the sun and stars are supported by gas pressure, what supports a neutron star?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
How can an old pulsar have a very short pulsar period, say less than 0.03 seconds?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
Why does our theory predict that neutron stars will have strong magnetic fields?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



