Deck 14: Time Response of Reactive Circuits
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/65
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 14: Time Response of Reactive Circuits
1
Only the number of turns in the primary and secondary of a transformer determines the actual secondary Voltage.
False
2
The impedance matching characteristic for a transformer is needed for a situation Where maximum power transfer to the load is desired.
True
3
A typical transformer fault Would be an open Winding.
True
4
An ideal 10:1 transformer With 20 VA of power has less than 2 VA on the output.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
The phrase ʺMaximum power is delivered to the loadW hen the load resistance equals the source resistanceʺ is a definition of ________.
A)Lenzʹs Law
B)the maximum power transfer theorem
C)Kirchhoffʹs Law
D)Ohmʹs Law
A)Lenzʹs Law
B)the maximum power transfer theorem
C)Kirchhoffʹs Law
D)Ohmʹs Law

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
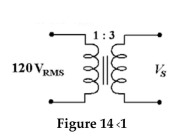
What is the secondary voltage in Figure 14-1 if the turns ratio is 7:1?
A) 840 VRMS
B) 8.59 VRMS
C) 17.1 VRMS
D) 420 VRMS

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
Eddy current loss in a transformer is ________.
A)due to current flowing in the core
B)caused by rapid reversal of the magnetic field
C)another name for flux leakage loss
D)caused by the resistance of the Wire
A)due to current flowing in the core
B)caused by rapid reversal of the magnetic field
C)another name for flux leakage loss
D)caused by the resistance of the Wire

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
An ideal transformer has no power loss.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
A core material is not always necessary for proper operation of a transformer.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
A step-down transformer could have a primary-secondary turns ratio of 4:1.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
The hysteresis loss in a transformer is ________.
A)caused by the resistance of the Wire
B)caused by rapid reversal of the magnetic field
C)another name for flux leakage loss
D)caused by current flowing in the core
A)caused by the resistance of the Wire
B)caused by rapid reversal of the magnetic field
C)another name for flux leakage loss
D)caused by current flowing in the core

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
If a dc voltage is input to a transformerʹs primary, then an ac voltage is induced in its secondary.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
The primary to secondary resistance should be relatively low.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14

What is the secondary voltage in Figure 14-1 if the turns ratio is 1: 3 ?
A) 40 VRMS
B) 240 VRMS
C) 360 VRMS
D) 80 VRMS

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
A transformer can be used as an impedance matching device.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
Autotransformers cannot be used for isolation purposes since there is only one Winding.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
Transformer cores are made from laminated iron to reduce losses.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
A transformer With a turns ratio of 1:7 is a step down transformer.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
The efficiency of all transformers is very low.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
A transformer With a turns ratio of 1:1 is often used to isolate a load from a source.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21

What is the primary current in Figure 14-1 if IS = 40 mA and the turns ratio equals 4:1 ?
A)160 mA
B)4 mA
C)40 mA
D)10 mA

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22

What is the secondary current in Figure 14-1 with a 50
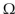 load resistor and 4: 1 turns ratio?
load resistor and 4: 1 turns ratio?A) 600 mA
B) 1.66 A
C) 9.6 A
D) 4.8 A

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23

What is the reflected resistance seen by the primary in Figure 14-1 if the turns ratio is 4: 1 and IS is 40 mA ?
A) 16
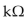
B) 4
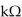
C) 8
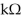
D) 12
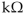

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24

What is the secondary voltage in Figure 14-1 if the turns ratio is 4.5:1?
A)26.7V
B)4.72V
C)540V
D)5.92V

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
When a 1 load resistor is connected across the secondary winding of a transformer with a turns ratio of 1: 2 , the source "sees" a reflected load of______________
A) 1
B) 2
C) 4
D) 250
A) 1
B) 2
C) 4
D) 250

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26

In Figure 14-1, if the secondary current is 50 mA, the primary current is ________.
A)300 mA
B)150 mA
C)48.7 mA
D)50 mA

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27

In Figure 14-1, the primary to secondary turns ratio is 1:3 and the secondary current equals 120 mA.What is the primary current?
A)180 mA
B)40 mA
C)360 mA
D)cannot compute because theVoltage is not given

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28

What is the secondary voltage in Figure 14-1 if the turns ratio is 9:1?
A)26.6V
B)106V
C)13.3V
D)53.2V

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29

In Figure 14-1, the primary to secondary turns ratio is changed to 2.5:1 and the secondary current equals 100 mA . What is the reflected resistance seen by the primary?
A) 3
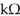
B) 5
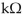
C) 1.2
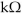
D) 2.5

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
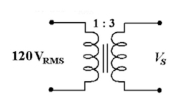
-In Figure 14-1, if the primary to secondary turns ratio is 7.5:1, the output voltage equals________
A) 32 VRMS
B) 16 VRMS
C) 900 VRMS
D) 9 VRMS

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31

What is the secondary current in Figure 14-1 with a 100
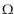 load resistor and 3:1 turns ratio?
load resistor and 3:1 turns ratio?A) 33 mARMS
B) 400 mARMS
C) 40 mARMS
D) 330 mARMS

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32

In Figure 14-1, if the primary to secondary turns ratio is changed to 4:1 and a 1 kΩ load resistor is in the secondary, the secondary current equals ________.
A)30 mA
B)240 mA
C)120 mA
D)480 mA

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33

-In Figure 14-1, if the secondary current is 50 mA , the reflected resistance seen by the primary equals_____
A) 7.2
B) 14.4
C) 800
D) 2.4

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34

-In Figure 14-1, if the primary to secondary turns ratio is 9:1 and a 1 load resistor is placed in the secondary, the reflected resistance seen by the primary equals_______
A) 111
B) 162
C) 81
D) 1

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35

-What is the reflected resistance seen by the primary in Figure 14-1 if the turns ratio is 3: 1 and IS is 240 mA ?
A) 9000
B) 1500
C) 167
D) 500

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36

What is the primary current in Figure 14-1 if the turns ratio equals 1: 3 and Is equals 240 mA ?
A) 1.2 A
B) 720 mA
C) 120 mA
D) 60 mA

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37

In Figure 14-1, if there are five times more turns in the primary than in the secondary, then What is the secondary voltage?
A)120V
B)12V
C)24V
D)600V

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
When a 1 load resistor is connected across the secondary winding of a transformer with a turns ratio of 2: 1 , the source "sees" a reflected load of________
A) 4
B) 500
C) 2
D) 1
A) 4
B) 500
C) 2
D) 1

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
If 10W of power are applied to the primary of an ideal transformer With a turns ratio of 1:5, the power delivered to the secondary load is ________.
A)0.5W
B)0W
C)10W
D)50W
A)0.5W
B)0W
C)10W
D)50W

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40

-In Figure 14-1, if a load resistor of 75 is placed in the secondary circuit,What is the secondary current?
A)533 mA
B)16 A
C)4.8 A
D)5.33 A

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
The reflected load in a transformer is defined as the actual load as it appears to the source and results from:
A)theVoltage ratio.
B)the power ratio.
C)the current ratio.
D)the turns ratio.
A)theVoltage ratio.
B)the power ratio.
C)the current ratio.
D)the turns ratio.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42

A)150
B)12.2
C)3.06
D)The primary should have less turns than the secondary.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
WhichW indingW ill have the lowest measured resistance in a transformerW ith four secondary Windings?
A)the 5 VSecondary
B)the 12 VSecondary
C)the 6.3 VSecondary
D)the 550 VSecondary
A)the 5 VSecondary
B)the 12 VSecondary
C)the 6.3 VSecondary
D)the 550 VSecondary

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
A step-up transformerW ill increase ________ and decrease ________.
A)power, current
B)current, impedance
C)voltage, impedance
D)voltage, power
A)power, current
B)current, impedance
C)voltage, impedance
D)voltage, power

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
What is the likeliestW ay to fix a center-tapped transformerW hich outputs unequal voltages on each half of the secondary?
A)Replace the transformer.
B)Remove some turns from the half with the higherVoltage winding.
C)Add some turns to the half wiIth the lowerVoltage winding.
D)Do not concern yourself; the customer will probably not notice the problem.
A)Replace the transformer.
B)Remove some turns from the half with the higherVoltage winding.
C)Add some turns to the half wiIth the lowerVoltage winding.
D)Do not concern yourself; the customer will probably not notice the problem.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
A matching transformer's primary needs______ more turns than its secondary to match a 600 audio signal distribution line to an 8 speaker.
A) 0.013
B) 8.66
C) 75
D) 0.115
A) 0.013
B) 8.66
C) 75
D) 0.115

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
The small dot placed on schematics of transformers indicates:
A)the phase of theVoltages.
B)the polarity of theVoltages.
C)the direction of the winding.
D)all of these.
A)the phase of theVoltages.
B)the polarity of theVoltages.
C)the direction of the winding.
D)all of these.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
The turns ratio required to match a 50 source to a 200 load is_____
A) 4: 1
B) 1: 2
C) 1: 4
D) 2: 1
A) 4: 1
B) 1: 2
C) 1: 4
D) 2: 1

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
If a 12 V battery is connected across the primary of a transformerW ith a turns ratio of 1:4, then the secondary voltage is ________.
A)3V
B)0V
C)12V
D)48V
A)3V
B)0V
C)12V
D)48V

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
A step-up transformerW ill increase ________ and decrease ________.
A)impedance, current
B)current,Voltage
C)voltage, impedance
D)current, impedance
A)impedance, current
B)current,Voltage
C)voltage, impedance
D)current, impedance

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
For a transformer to operate properly, it must:
A)be supplied with the proper AC signal.
B)work within itsVoltage, current and power ratings.
C)be connected to a load.
D)all of these.
A)be supplied with the proper AC signal.
B)work within itsVoltage, current and power ratings.
C)be connected to a load.
D)all of these.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
What is the problem if a power transformer is delivering a low output voltage even though the primary voltage is correct?
A)a partially shorted secondary
B)a shorted primary
C)an open primary
D)an open secondary
A)a partially shorted secondary
B)a shorted primary
C)an open primary
D)an open secondary

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
The turns ratio of a transformer (n)is defined as:
A)the number of turns in the secondary divided by the number of turns in the primary.
B)the number of turns in the primary divided by the number of turns in the secondary.
C)the number of turns in the primary multiplied by the number of turns in the secondary.
D)the number of turns in the secondary multiplied by the number of turns in the primary.
A)the number of turns in the secondary divided by the number of turns in the primary.
B)the number of turns in the primary divided by the number of turns in the secondary.
C)the number of turns in the primary multiplied by the number of turns in the secondary.
D)the number of turns in the secondary multiplied by the number of turns in the primary.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
The relationship for the voltage ratio in a transformer is:
A) the same as the turns ratio
B) opposite to the turns ratio
C) more than the turns ratio
D) less than the turns ratio
A) the same as the turns ratio
B) opposite to the turns ratio
C) more than the turns ratio
D) less than the turns ratio

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
The relationship for the current ration 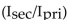 in a transformer is:
in a transformer is:
A) less than the turns ratio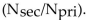
B) the inverse of the turns ratio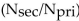
C) more than the turns ratio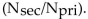
D) the same as the turns ratio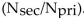
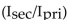 in a transformer is:
in a transformer is:A) less than the turns ratio
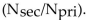
B) the inverse of the turns ratio
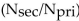
C) more than the turns ratio
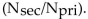
D) the same as the turns ratio
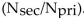

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
The relationship for the impedance matching ratio 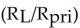 in a transformer is:
in a transformer is:
A) equal to the turns ratio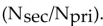
B) opposite to the turns ratio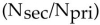 squared.
squared.
C) equal to the turns ratio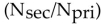 squared.
squared.
D) opposite to the turns ratio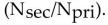
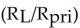 in a transformer is:
in a transformer is:A) equal to the turns ratio
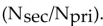
B) opposite to the turns ratio
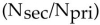 squared.
squared.C) equal to the turns ratio
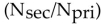 squared.
squared.D) opposite to the turns ratio
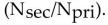

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
When the turns ratio of a transformer is 1:10 and the primary AC voltage in 6 V, then the secondary voltage is ________.
A)6V
B)36V
C)60V
D)0.6V
A)6V
B)36V
C)60V
D)0.6V

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
Transformers ________.
A)match the impedance of a source to the impedance of a load
B)convert a higherVoltage into a lowerVoltage
C)convert a lower current into a higher current
D)all of these
A)match the impedance of a source to the impedance of a load
B)convert a higherVoltage into a lowerVoltage
C)convert a lower current into a higher current
D)all of these

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
To couple two circuits togetherW ith no change in either voltage or current, use ________.
A)a step-down transformer
B)a step-up transformer
C)a power transformer
D)an isolation transformer
A)a step-down transformer
B)a step-up transformer
C)a power transformer
D)an isolation transformer

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
Although the input voltage to the transformerʹs primary is correct, the transformer is outputting zero volts. A probable trouble is ________.
A)an open primary
B)a partially shorted primary
C)a shorted primary
D)a partially shorted secondary
A)an open primary
B)a partially shorted primary
C)a shorted primary
D)a partially shorted secondary

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
The measured voltage on the secondary of a given transformer is 0 V.W hich of the following could have caused this?
A)open secondary
B)open primary
C)shorted load
D)any of the above
A)open secondary
B)open primary
C)shorted load
D)any of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
36 V of dc is applied to aW indings ratio of 1:2.W hat is the secondary voltage?
A)something slightly less than 72V ince transformers do have some loss
B)144V
C)72V
D)none of the above
A)something slightly less than 72V ince transformers do have some loss
B)144V
C)72V
D)none of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
How can theW indings ratio be safely determined for an unmarked transformer?
A)StandardizedW
Ire color codes indicate Windings ratio.
B)The turns ratio is the same as the ratio of primary resistance to secondary resistance ratio.
C)Apply known lowVoltage ac to the primary and measure the secondary output. The ratio of
TheVoltages is the same as the Windings ratio.
D)either A or C
A)StandardizedW
Ire color codes indicate Windings ratio.
B)The turns ratio is the same as the ratio of primary resistance to secondary resistance ratio.
C)Apply known lowVoltage ac to the primary and measure the secondary output. The ratio of
TheVoltages is the same as the Windings ratio.
D)either A or C

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
An autotransformer differs from most transformers in that:
A)it does not isolate the primaryVoltage from the secondary Voltage.
B)primary and secondary Windings are the same.
C)source current flows through both the Windings.
D)all of these.
A)it does not isolate the primaryVoltage from the secondary Voltage.
B)primary and secondary Windings are the same.
C)source current flows through both the Windings.
D)all of these.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
A center tap transformer has a connection at the midpoint of the secondaryW inding resulting in:
A)two 180 degree out of phase secondaryVoltages.
B)secondaryVoltages half that of a non-center tapped transformerW
Ith the same turns ratio.
C)two equal magnitude secondaryVoltages.
D)all of these.
A)two 180 degree out of phase secondaryVoltages.
B)secondaryVoltages half that of a non-center tapped transformerW
Ith the same turns ratio.
C)two equal magnitude secondaryVoltages.
D)all of these.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



