Deck 24: Industry Comes of Age
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/72
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 24: Industry Comes of Age
1
A "wedding of the rails" (connection of the Union Pacific and Central Pacific Railroads) was finally consummated in 1869 near
A) Omaha, Nebraska
B) Sacramento, California
C) Topeka, Kansas
D) Ogden, Utah
E) Philadelphia, Pennsylvania
A) Omaha, Nebraska
B) Sacramento, California
C) Topeka, Kansas
D) Ogden, Utah
E) Philadelphia, Pennsylvania
Ogden, Utah
2
One of the most significant aspects of the Interstate Commerce Act was that it
A) prevented the railroads from merging and monopolizing traffic.
B) represented the first large-scale attempt by the federal government to regulate business.
C) enabled farmers to determine rail shipping rates.
D) empowered state legislatures to control corrupt railroad practices.
E) invoked the Constitution's interstate commerce clause.
A) prevented the railroads from merging and monopolizing traffic.
B) represented the first large-scale attempt by the federal government to regulate business.
C) enabled farmers to determine rail shipping rates.
D) empowered state legislatures to control corrupt railroad practices.
E) invoked the Constitution's interstate commerce clause.
represented the first large-scale attempt by the federal government to regulate business.
3
The greatest single factor helping to spur the amazing industrialization of the post-Civil War years was
A) agriculture.
B) mining.
C) the steel industry.
D) electric power.
E) the railroad network.
A) agriculture.
B) mining.
C) the steel industry.
D) electric power.
E) the railroad network.
the railroad network.
4
The only transcontinental railroad built without government aid was the
A) New York Central.
B) Northern Pacific.
C) Union Pacific.
D) Atchison, Topeka, and Santa Fe.
E) Great Northern.
A) New York Central.
B) Northern Pacific.
C) Union Pacific.
D) Atchison, Topeka, and Santa Fe.
E) Great Northern.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 72 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
During the Gilded Age, most of the railroad barons
A) rejected government assistance.
B) built their railroads with government assistance.
C) relied exclusively on Chinese labor.
D) refused to get involved in politics.
E) focused on the public benefits of railroad service.
A) rejected government assistance.
B) built their railroads with government assistance.
C) relied exclusively on Chinese labor.
D) refused to get involved in politics.
E) focused on the public benefits of railroad service.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 72 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
One of the key business goals of most post-Civil War business leaders was
A) to stimulate innovation through increased competition.
B) to develop a centrally planned American economy.
C) to fund research on new technologies.
D) to create a large consumer middle class.
E) to eliminate as much competition as possible.
A) to stimulate innovation through increased competition.
B) to develop a centrally planned American economy.
C) to fund research on new technologies.
D) to create a large consumer middle class.
E) to eliminate as much competition as possible.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 72 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
One by-product of the development of the railroads was
A) a scattering of the U.S.population.
B) fewer big cities.
C) the movement of people to cities.
D) a reduction in immigration to the United States.
E) a loss of population in the West.
A) a scattering of the U.S.population.
B) fewer big cities.
C) the movement of people to cities.
D) a reduction in immigration to the United States.
E) a loss of population in the West.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 72 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
Railroad companies justified their heavy subsidies from the federal government on the grounds that
A) railroads were essential to the national defense.
B) returns on railroad bonds would help finance the federal government.
C) railroad building was too costly and risky without government help.
D) railroad subsidies were needed to get pioneers to settle the West.
E) the federal government had already financed the Pony Express.
A) railroads were essential to the national defense.
B) returns on railroad bonds would help finance the federal government.
C) railroad building was too costly and risky without government help.
D) railroad subsidies were needed to get pioneers to settle the West.
E) the federal government had already financed the Pony Express.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 72 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
Carnegie's steel industry was based on mining iron ore in ____ and shipping it to be made into steel in ____.
A) Illinois; Chicago
B) Minnesota; Pittsburgh
C) Canada; Detroit
D) West Virginia; Atlanta
E) Pennsylvania; Philadelphia
A) Illinois; Chicago
B) Minnesota; Pittsburgh
C) Canada; Detroit
D) West Virginia; Atlanta
E) Pennsylvania; Philadelphia

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 72 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
Match each railroad entrepreneur with the best description: 
A) A-4, B-2, C-1, D-3
B) A-3, B-4, C-2, D-1
C) A-2, B-1, C-3, D-4
D) A-4, B-3, C-1, D-2
E) A-1, B-3, C-4, D-2

A) A-4, B-2, C-1, D-3
B) A-3, B-4, C-2, D-1
C) A-2, B-1, C-3, D-4
D) A-4, B-3, C-1, D-2
E) A-1, B-3, C-4, D-2

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 72 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
Which of the following was not among the factors that hastened the heavy industrialization of the United States in the three decades following the Civil War?
A) the national reconciliation and harmony between North and South
B) cheap unskilled labor caused by massive immigration
C) the accumulation of large pools of liquid capital for investment
D) the tapping of rich natural resources of coal, oil, and iron
E) technological inventiveness and innovation
A) the national reconciliation and harmony between North and South
B) cheap unskilled labor caused by massive immigration
C) the accumulation of large pools of liquid capital for investment
D) the tapping of rich natural resources of coal, oil, and iron
E) technological inventiveness and innovation

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 72 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
Early railroad owners formed "pools" in order to
A) pool their capital to construct more rail lines.
B) water their stock.
C) divide business in a particular area and share profits.
D) choose the best workers.
E) avoid wasteful competition.
A) pool their capital to construct more rail lines.
B) water their stock.
C) divide business in a particular area and share profits.
D) choose the best workers.
E) avoid wasteful competition.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 72 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
Match each entrepreneur below with the form of business combination with which he is historically identified. 
A) A-2, B-3, C-1
B) A-1, B-2, C-3
C) A-3, B-2, C-1
D) A-1, B-3, C-2
E) A-2, B-1, C-3

A) A-2, B-3, C-1
B) A-1, B-2, C-3
C) A-3, B-2, C-1
D) A-1, B-3, C-2
E) A-2, B-1, C-3

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 72 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
The first efforts to regulate the monopolizing practices of railroad corporations came from
A) Congress.
B) the Supreme Court.
C) private lawsuits.
D) a federal regulatory commission.
E) state legislatures.
A) Congress.
B) the Supreme Court.
C) private lawsuits.
D) a federal regulatory commission.
E) state legislatures.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 72 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
The federal government helped to finance transcontinental railroad construction in the late nineteenth century by providing railroad corporations with
A) cash grants from new taxes.
B) loans and land grants.
C) loans from higher tariffs.
D) reduced prices for iron and steel.
E) subsidized Chinese immigrant labor.
A) cash grants from new taxes.
B) loans and land grants.
C) loans from higher tariffs.
D) reduced prices for iron and steel.
E) subsidized Chinese immigrant labor.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 72 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
Match each entrepreneur below with the field of enterprise with which he is historically identified. 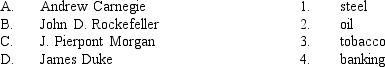
A) A-1, B-3, C-2, D-4
B) A-2, B-4, C-3, D-1
C) A-3, B-1, C-4, D-2
D) A-1, B-2, C-4, D-3
E) A-4, B-2, C-1, D-3
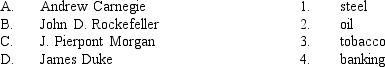
A) A-1, B-3, C-2, D-4
B) A-2, B-4, C-3, D-1
C) A-3, B-1, C-4, D-2
D) A-1, B-2, C-4, D-3
E) A-4, B-2, C-1, D-3

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 72 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
The United States changed to standard time zones when
A) Congress passed a law establishing this system.
B) the railroads needed to develop coordinated schedules across the continent.
C) factories demanded standard time schedules.
D) long-distance telephones required standard time coordination.
E) farmers needed to know train schedules to deliver crops to market.
A) Congress passed a law establishing this system.
B) the railroads needed to develop coordinated schedules across the continent.
C) factories demanded standard time schedules.
D) long-distance telephones required standard time coordination.
E) farmers needed to know train schedules to deliver crops to market.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 72 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
The first federal regulatory agency designed to protect the public interest from business combinations was the
A) Federal Trade Commission.
B) Interstate Commerce Commission.
C) Consumer Affairs division of the Justice Department.
D) Federal Anti-Trust Commission.
E) Federal Communications Commission.
A) Federal Trade Commission.
B) Interstate Commerce Commission.
C) Consumer Affairs division of the Justice Department.
D) Federal Anti-Trust Commission.
E) Federal Communications Commission.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 72 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
Agreements between railroad corporations to divide the business in a given area and share the profits were called
A) pools.
B) trusts.
C) rebates.
D) interlocking directorates.
E) holding companies.
A) pools.
B) trusts.
C) rebates.
D) interlocking directorates.
E) holding companies.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 72 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
J.P.Morgan monitored his competition by placing officers of his bank on the boards of companies that he wanted to control.This method was known as a(n)
A) interlocking directorate.
B) trust.
C) vertical integration.
D) pool.
E) holding company.
A) interlocking directorate.
B) trust.
C) vertical integration.
D) pool.
E) holding company.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 72 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
To help corporations, the courts ingeniously interpreted the Fourteenth Amendment, which was designed to protect the rights of ex-slaves, so as to
A) help freedmen to work in factories.
B) incorporate big businesses.
C) allow big businessmen to avoid paying taxes.
D) protect corporations from state regulation.
E) protect the rights of middle-class corporate workers.
A) help freedmen to work in factories.
B) incorporate big businesses.
C) allow big businessmen to avoid paying taxes.
D) protect corporations from state regulation.
E) protect the rights of middle-class corporate workers.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 72 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
The new industrial age greatly accentuated
A) job security.
B) workmen's compensation and unemployment insurance.
C) class division.
D) regional tensions.
E) conflicts between farmers and urban workers.
A) job security.
B) workmen's compensation and unemployment insurance.
C) class division.
D) regional tensions.
E) conflicts between farmers and urban workers.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 72 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
The Sherman Anti-Trust Act, contrary to its original intent, was at first used to curb the power of
A) manufacturing corporations.
B) labor unions.
C) state legislatures.
D) railroad corporations.
E) banking syndicates.
A) manufacturing corporations.
B) labor unions.
C) state legislatures.
D) railroad corporations.
E) banking syndicates.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 72 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
John D.Rockefeller used all of the following tactics to achieve success in the oil industry except
A) employing company spies.
B) extorting secret rebates from railroads.
C) providing inferior oil products to sell them more cheaply.
D) gaining a near-monopoly on oil refineries.
E) mercilessly squeezing out his competitors.
A) employing company spies.
B) extorting secret rebates from railroads.
C) providing inferior oil products to sell them more cheaply.
D) gaining a near-monopoly on oil refineries.
E) mercilessly squeezing out his competitors.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 72 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
The oil industry became a huge business
A) with the building of electric generator plants.
B) when it was taken over by the government.
C) with the invention of the internal combustion engine.
D) when diesel engines were perfected.
E) when oil was discovered in Texas.
A) with the building of electric generator plants.
B) when it was taken over by the government.
C) with the invention of the internal combustion engine.
D) when diesel engines were perfected.
E) when oil was discovered in Texas.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 72 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
Which one of the following is least like the other four?
A) strike
B) lockout
C) yellow dog contract
D) blacklist
E) company town
A) strike
B) lockout
C) yellow dog contract
D) blacklist
E) company town

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 72 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
Most women workers of the late 1800s worked for
A) independence.
B) glamour.
C) economic necessity.
D) enough money to obtain an education.
E) personal spending money.
A) independence.
B) glamour.
C) economic necessity.
D) enough money to obtain an education.
E) personal spending money.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 72 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
America's first billion-dollar corporation was
A) General Electric (GE).
B) Standard Oil.
C) American Telephone and Telegraph (AT&T).
D) The Union Pacific Railroad.
E) United States Steel.
A) General Electric (GE).
B) Standard Oil.
C) American Telephone and Telegraph (AT&T).
D) The Union Pacific Railroad.
E) United States Steel.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 72 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
The South's major attraction for potential investors was
A) readily available raw materials.
B) a warm climate.
C) good transportation.
D) cheap labor.
E) ethnic diversity.
A) readily available raw materials.
B) a warm climate.
C) good transportation.
D) cheap labor.
E) ethnic diversity.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 72 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
One of the greatest changes that industrialization brought about in the lives of workers was
A) their movement to the suburbs.
B) the need for them to adjust their lives to the time clock.
C) the opportunity to live out the ideals of Thomas Jefferson.
D) the narrowing of class divisions.
E) the encounter with other races.
A) their movement to the suburbs.
B) the need for them to adjust their lives to the time clock.
C) the opportunity to live out the ideals of Thomas Jefferson.
D) the narrowing of class divisions.
E) the encounter with other races.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 72 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
The first major product of the oil industry was
A) kerosene.
B) gasoline.
C) lighter fluid.
D) natural gas.
E) heating oil.
A) kerosene.
B) gasoline.
C) lighter fluid.
D) natural gas.
E) heating oil.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 72 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
The gospel of wealth, which associated godliness with wealth,
A) relied on the sayings of Jesus.
B) inspired the wealthy to try to help the poor.
C) was most identified with the Catholic church.
D) was opposed by most clergymen.
E) discouraged efforts to help the poor.
A) relied on the sayings of Jesus.
B) inspired the wealthy to try to help the poor.
C) was most identified with the Catholic church.
D) was opposed by most clergymen.
E) discouraged efforts to help the poor.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 72 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
In the late nineteenth century, tax benefits and cheap, nonunion labor attracted ____ manufacturing to the "new South."
A) textile
B) steel
C) machine tool
D) electrical appliance
E) farm equipment
A) textile
B) steel
C) machine tool
D) electrical appliance
E) farm equipment

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 72 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
The Reverend ____ of Philadelphia became rich by delivering his lecture "Acres of Diamonds" thousands of times.
A) Herbert Spencer
B) William Graham Sumner
C) Charles Darwin
D) Russell Conwell
E) Edward Bellamy
A) Herbert Spencer
B) William Graham Sumner
C) Charles Darwin
D) Russell Conwell
E) Edward Bellamy

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 72 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
The ____ Amendment was especially helpful to giant corporations when defending themselves against regulation by state governments.
A) Fifth
B) Fourteenth
C) Fifteenth
D) Sixteenth
E) Seventeenth
A) Fifth
B) Fourteenth
C) Fifteenth
D) Sixteenth
E) Seventeenth

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 72 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
The federal courts in the late nineteenth century frequently suppressed labor unions by
A) forcing workers to sign "yellow dog" contracts.
B) issuing injunctions against strikes.
C) declaring government regulations unconstitutional.
D) preventing workers from forming unions.
E) convicting labor leaders of corrupt practices.
A) forcing workers to sign "yellow dog" contracts.
B) issuing injunctions against strikes.
C) declaring government regulations unconstitutional.
D) preventing workers from forming unions.
E) convicting labor leaders of corrupt practices.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 72 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
The group most dramatically affected by the new industrial age of the late nineteenth century was
A) Native Americans.
B) African Americans.
C) women.
D) southerners.
E) small town residents.
A) Native Americans.
B) African Americans.
C) women.
D) southerners.
E) small town residents.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 72 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
Many Southerners saw employment in the textile mills as
A) attractive places to work.
B) unacceptable.
C) a poor alternative to farming.
D) institutions that broke up families.
E) a salvation, as the only work available to them.
A) attractive places to work.
B) unacceptable.
C) a poor alternative to farming.
D) institutions that broke up families.
E) a salvation, as the only work available to them.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 72 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
During the age of industrialization, the South
A) took full advantage of the new economic trends.
B) attracted a substantial number of immigrants.
C) turned away from agriculture.
D) held to its "Old South" ideology.
E) remained overwhelmingly rural and agricultural.
A) took full advantage of the new economic trends.
B) attracted a substantial number of immigrants.
C) turned away from agriculture.
D) held to its "Old South" ideology.
E) remained overwhelmingly rural and agricultural.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 72 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
The image of the Gibson Girl represented
A) a revival of the revolutionary ideal of "republican motherhood."
B) a portrayal of the modern corporate business woman.
C) the portrayal of women as sex objects in advertising.
D) an independent and athletic "new woman."
E) a sentimental image of a woman as mother.
A) a revival of the revolutionary ideal of "republican motherhood."
B) a portrayal of the modern corporate business woman.
C) the portrayal of women as sex objects in advertising.
D) an independent and athletic "new woman."
E) a sentimental image of a woman as mother.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 72 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
The only national labor union to survive the post-Civil War period was the
A) National Labor Union.
B) Knights of Labor.
C) American Federation of Labor.
D) Knights of Columbus.
E) Congress of Industrial Organizations.
A) National Labor Union.
B) Knights of Labor.
C) American Federation of Labor.
D) Knights of Columbus.
E) Congress of Industrial Organizations.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 72 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
One group barred from membership in the Knights of Labor was
A) African Americans.
B) lawyers.
C) women.
D) Irish.
E) social reformers.
A) African Americans.
B) lawyers.
C) women.
D) Irish.
E) social reformers.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 72 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
The National Labor Union's greatest success before it collapsed in the depression of the 1870s was
A) an eight-hour day for all workers.
B) government arbitration for industrial disputes.
C) equal pay for women.
D) an eight-hour day for government workers.
E) establishing producers' cooperatives and safety regulations.
A) an eight-hour day for all workers.
B) government arbitration for industrial disputes.
C) equal pay for women.
D) an eight-hour day for government workers.
E) establishing producers' cooperatives and safety regulations.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 72 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
Although public attitudes toward unions had softened by 1900,
A) workers almost never won a strike.
B) Congress refused to recognize Labor Day as a federal holiday.
C) most employers continued to fight organized labor.
D) Congress declared the AFL illegal.
E) workers began to turn toward the Socialist party.
A) workers almost never won a strike.
B) Congress refused to recognize Labor Day as a federal holiday.
C) most employers continued to fight organized labor.
D) Congress declared the AFL illegal.
E) workers began to turn toward the Socialist party.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 72 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
One of the discoveries labor historians have made regarding American workers' social mobility is that
A) skilled laborers rose rapidly while unskilled laborers almost never did.
B) the greatest opportunities for workers were on the American frontier.
C) ingenuity and inventiveness were more important than wage rates.
D) different ethnic groups defined success in different ways.
E) European immigrant workers were content with lower status.
A) skilled laborers rose rapidly while unskilled laborers almost never did.
B) the greatest opportunities for workers were on the American frontier.
C) ingenuity and inventiveness were more important than wage rates.
D) different ethnic groups defined success in different ways.
E) European immigrant workers were content with lower status.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 72 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
Changes in the national economy in late-nineteenth-century America resulted in
A) a lower standard of living for most wage laborers.
B) a decline in agriculture relative to manufacturing.
C) the industrialization of the South.
D) sharper class distinctions.
E) a movement of women into the work force.
A) a lower standard of living for most wage laborers.
B) a decline in agriculture relative to manufacturing.
C) the industrialization of the South.
D) sharper class distinctions.
E) a movement of women into the work force.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 72 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
The people who have found fault with the "captains of industry" generally argued that these businessmen
A) did not really achieve the economic progress they claimed.
B) brutalized workers and stripped them of their spiritual quality of life.
C) undermined the religious and moral foundations of America.
D) were narrow-minded and uneducated.
E) failed to understand government's necessary role in social reform.
A) did not really achieve the economic progress they claimed.
B) brutalized workers and stripped them of their spiritual quality of life.
C) undermined the religious and moral foundations of America.
D) were narrow-minded and uneducated.
E) failed to understand government's necessary role in social reform.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 72 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
The Knights of Labor was weakened by
A) its nostalgic dream that all workers could eventually become capitalists.
B) stiff competition from the National Labor Union.
C) its association in the public mind with the Haymarket riot.
D) its inclusion of both skilled and unskilled workers.
E) its hostility to the Catholic church.
A) its nostalgic dream that all workers could eventually become capitalists.
B) stiff competition from the National Labor Union.
C) its association in the public mind with the Haymarket riot.
D) its inclusion of both skilled and unskilled workers.
E) its hostility to the Catholic church.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 72 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
The Knights of Labor campaigned, above all, for
A) a minimum wage.
B) workers' safety standards.
C) paid vacation.
D) the eight hour day.
E) a socialist revolution.
A) a minimum wage.
B) workers' safety standards.
C) paid vacation.
D) the eight hour day.
E) a socialist revolution.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 72 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
Corrupt practices common in the late-nineteenth-century railroad industry included
A) "stock watering."
B) bribing judges and legislatures.
C) "pools."
D) secret rebates and kickbacks.
E) distributing free passes to journalists and politicians.
A) "stock watering."
B) bribing judges and legislatures.
C) "pools."
D) secret rebates and kickbacks.
E) distributing free passes to journalists and politicians.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 72 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
The event that precipitated the collapse of the Knights of Labor was
A) Terence Powderly's seizure of power in the union.
B) the assassination of President McKinley.
C) the Pullman Strike.
D) the national railroad strikes of 1877.
E) the Haymarket Square bombing.
A) Terence Powderly's seizure of power in the union.
B) the assassination of President McKinley.
C) the Pullman Strike.
D) the national railroad strikes of 1877.
E) the Haymarket Square bombing.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 72 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
Railroading in the late nineteenth century significantly contributed to
A) the growth of agriculture.
B) urbanization.
C) feminism.
D) ecological damage.
E) industrialization.
A) the growth of agriculture.
B) urbanization.
C) feminism.
D) ecological damage.
E) industrialization.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 72 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
Match each labor organization below with the correct description. 
A) A-3, B-1, C-2
B) A-3, B-2, C-1
C) A-1, B-2, C-3
D) A-1, B-3, C-2
E) A-2, B-1, C-3

A) A-3, B-1, C-2
B) A-3, B-2, C-1
C) A-1, B-2, C-3
D) A-1, B-3, C-2
E) A-2, B-1, C-3

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 72 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
The Knights of Labor believed that conflict between capital and labor would disappear when
A) the government owned the means of production.
B) a labor-oriented political party gained power in Washington.
C) business recognized unions and established fair wage rates.
D) corporations established profit-sharing systems with workers.
E) labor would own and operate cooperative businesses and industries.
A) the government owned the means of production.
B) a labor-oriented political party gained power in Washington.
C) business recognized unions and established fair wage rates.
D) corporations established profit-sharing systems with workers.
E) labor would own and operate cooperative businesses and industries.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 72 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
The factors promoting the growth of manufacturing in post-Civil War America included
A) plentiful cheap labor.
B) available investment capital.
C) abundant natural resources.
D) effective government planning.
E) massive immigration.
A) plentiful cheap labor.
B) available investment capital.
C) abundant natural resources.
D) effective government planning.
E) massive immigration.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 72 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
The first transcontinental railroad was completed by the construction efforts of the ____ and ____ railroads.
A) Union Pacific
B) Northern Pacific
C) Central Pacific
D) Southern Pacific
E) Atchison, Topeka, and Santa Fe
A) Union Pacific
B) Northern Pacific
C) Central Pacific
D) Southern Pacific
E) Atchison, Topeka, and Santa Fe

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 72 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
By 1900, organized labor in America
A) had temporarily ceased to exist.
B) enrolled nearly half of the industrial labor force.
C) was accepted by the majority of employers as a permanent part of the new industrial economy.
D) had begun to develop a more positive image with the public.
E) relied heavily on the National Labor Relations Board.
A) had temporarily ceased to exist.
B) enrolled nearly half of the industrial labor force.
C) was accepted by the majority of employers as a permanent part of the new industrial economy.
D) had begun to develop a more positive image with the public.
E) relied heavily on the National Labor Relations Board.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 72 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
Thomas Edison was instrumental in the invention of the
A) electric light.
B) telephone.
C) mimeograph machine.
D) motion picture.
E) radio.
A) electric light.
B) telephone.
C) mimeograph machine.
D) motion picture.
E) radio.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 72 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
Some historians more favorable to American industrial capitalism have emphasized that
A) most employers tried to treat their workers well.
B) few Europeans brought their political philosophies to the United States.
C) the businessmen donated a great deal to charities and education.
D) almost any American worker could rise from rags to riches.
E) large numbers of American workers made small improvements in their economic condition.
A) most employers tried to treat their workers well.
B) few Europeans brought their political philosophies to the United States.
C) the businessmen donated a great deal to charities and education.
D) almost any American worker could rise from rags to riches.
E) large numbers of American workers made small improvements in their economic condition.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 72 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
Over the last century, historians' criticisms of the industrial capitalism of the Gilded Age have included
A) the romantic idea that industrialization diminished workers' spiritual quality of life.
B) the assertion that workers were brutalized by the industrial system.
C) the argument that American living standards were not raised by industrialization.
D) the claim that American industrialization sharpened class divisions.
E) the assertion that most great American fortunes came from inherited wealth.
A) the romantic idea that industrialization diminished workers' spiritual quality of life.
B) the assertion that workers were brutalized by the industrial system.
C) the argument that American living standards were not raised by industrialization.
D) the claim that American industrialization sharpened class divisions.
E) the assertion that most great American fortunes came from inherited wealth.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 72 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
What were the three most significant consequences of the industrialization of the American economy after the Civil War? Explain your choices.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 72 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
Industrialization and the accompanying technological advances are usually seen as the central developments of American "progress." In what ways were they genuinely liberating developments for American society and for individual Americans, and in what ways did these developments come at a high cost for workers and for society?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 72 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
Was the "gospel of wealth" a genuine faith of America's industrial capitalists, or largely a hypocritical justification for exploitation? Why did so many ordinary Americans share this view of wealth and poverty?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 72 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
To what extent was the South such an exception to the general industrial development of the late nineteenth century?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 72 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
Compare and contrast the National Labor Union, Knights of Labor, and American Federation of Labor in regard to their origins, goals, and leadership.Account for the failure of the first two and for the success of the AFL.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 72 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
Compare and contrast the provisions of the Interstate Commerce Act and the Sherman Anti-Trust Act.Explain the motives behind their enactment and evaluate the success of each.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 72 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
To what extent did the railroad have an impact on late-nineteenth-century American economic, social, and political life? Is it fair to say that industrialization was largely due to the railroads?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 72 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
In what ways does the development of the railroad industry in the late nineteenth century illustrate the limitations of the myth of individual free enterprise in American history? What did government hope to attain by its subsidies of railroad construction? What, in fact, did it attain? Was the arrangement a good one for society as a whole?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 72 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
Late-nineteenth-century America saw a growing class division in American society.Yet Americans were very reluctant to develop a true class consciousness as either upper-class capitalists or proletarian workers.Why? How did this relative absence of class consciousness affect the economic and social developments of the time (including women's roles and labor unions)?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 72 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
Assess the validity of the following statement, "labor unions found it difficult to organize industrial workers in the late nineteenth century."

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 72 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
Business leaders of the late nineteenth century have been characterized both as greedy and unscrupulous "robber barons" and as great "captains of industry" whose entrepreneurial skill and tactics produced economic growth.Which view do you find more persuasive? Why?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 72 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72
Assess the validity of the following statement, "the Constitution and the courts were on the side of the corporations in the late nineteenth century." Cite passages from the Constitution and court decisions to illustrate your assessment.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 72 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



