Deck 10: Launching the New Ship of State
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/87
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 10: Launching the New Ship of State
1
Alexander Hamilton believed that a national debt
A) would do great harm to the nation's economy.
B) would cause inflation in the long run.
C) could persuade individuals and nations not to lend money to the United States.
D) was beneficial because people to whom the government owed money would work hard to make the nation a success.
E) could only be justified for national defense purposes.
A) would do great harm to the nation's economy.
B) would cause inflation in the long run.
C) could persuade individuals and nations not to lend money to the United States.
D) was beneficial because people to whom the government owed money would work hard to make the nation a success.
E) could only be justified for national defense purposes.
was beneficial because people to whom the government owed money would work hard to make the nation a success.
2
Hamilton believed that, together, his funding and assumption programs would
A) gain the financial and political support of the wealthy class for the federal government.
B) restore the principles of state sovereignty.
C) eventually pay off the national debt.
D) guarantee the fairest treatment of the original holders of government bonds.
E) encourage westward expansion.
A) gain the financial and political support of the wealthy class for the federal government.
B) restore the principles of state sovereignty.
C) eventually pay off the national debt.
D) guarantee the fairest treatment of the original holders of government bonds.
E) encourage westward expansion.
gain the financial and political support of the wealthy class for the federal government.
3
All of the following is an accurate description of the young American nation except
A) its population was still about 90 percent rural.
B) the first official census of 1790 recorded almost 4 million people.
C) all but 5 percent of the people lived east of the Appalachian Mountains.
D) a majority of the population was branching out west of the Appalachian Mountains.
E) foreign visitors looked down at the roughness and crudity of the pioneering life.
A) its population was still about 90 percent rural.
B) the first official census of 1790 recorded almost 4 million people.
C) all but 5 percent of the people lived east of the Appalachian Mountains.
D) a majority of the population was branching out west of the Appalachian Mountains.
E) foreign visitors looked down at the roughness and crudity of the pioneering life.
a majority of the population was branching out west of the Appalachian Mountains.
4
One of the major criticisms of the Constitution by the antifederalists as drafted in Philadelphia was that it
A) was too long and detailed.
B) did not provide for an adequate separation of powers.
C) failed to guarantee property rights.
D) gave too much power to the Supreme Court and federal judges.
E) did not provide guarantees for individual rights.
A) was too long and detailed.
B) did not provide for an adequate separation of powers.
C) failed to guarantee property rights.
D) gave too much power to the Supreme Court and federal judges.
E) did not provide guarantees for individual rights.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 87 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
All of the following are guarantees provided by the Bill of Rights except
A) the right to vote.
B) the right to petition the government.
C) freedom of religion.
D) freedom of the press.
E) right to a trial by a jury.
A) the right to vote.
B) the right to petition the government.
C) freedom of religion.
D) freedom of the press.
E) right to a trial by a jury.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 87 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
One of the first jobs facing the new government formed under the Constitution was to
A) establish a powerful army.
B) reestablish diplomatic ties with Britain.
C) draw up and pass a bill of rights.
D) end the military alliance with France.
E) admit new states to the Union.
A) establish a powerful army.
B) reestablish diplomatic ties with Britain.
C) draw up and pass a bill of rights.
D) end the military alliance with France.
E) admit new states to the Union.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 87 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
As secretary of the treasury, Alexander Hamilton's first objective was to
A) reduce the federal debt.
B) bring more industry to the United States.
C) see that more agricultural products were exported.
D) bolster the national credit.
E) put the country on the gold standard.
A) reduce the federal debt.
B) bring more industry to the United States.
C) see that more agricultural products were exported.
D) bolster the national credit.
E) put the country on the gold standard.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 87 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
The new Constitution did not provide for the creation of a(n)
A) Electoral College.
B) vice president.
C) Supreme Court.
D) cabinet.
E) federal court system.
A) Electoral College.
B) vice president.
C) Supreme Court.
D) cabinet.
E) federal court system.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 87 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
Match the individual with his office in the new government. 
A) A-1, B-3, C-2, D-4
B) A-3, B-1, C-4, D-2
C) A-2, B-4, C-3, D-1
D) A-4, B-2, C-l, D-3
E) A-1, B-4, C-3, D-2

A) A-1, B-3, C-2, D-4
B) A-3, B-1, C-4, D-2
C) A-2, B-4, C-3, D-1
D) A-4, B-2, C-l, D-3
E) A-1, B-4, C-3, D-2

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 87 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
When the new government was launched in 1789,
A) the nation's population was doubling about every twenty-five years.
B) most people lived in the fast-growing cities.
C) most people lived west of the Allegheny Mountains.
D) New York was the largest city in the nation.
E) a majority of the population lived in New England.
A) the nation's population was doubling about every twenty-five years.
B) most people lived in the fast-growing cities.
C) most people lived west of the Allegheny Mountains.
D) New York was the largest city in the nation.
E) a majority of the population lived in New England.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 87 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
Alexander Hamilton's financial program for the economic development of the United States favored
A) agricultural interests.
B) New England.
C) the wealthy.
D) the poor.
E) the middle class.
A) agricultural interests.
B) New England.
C) the wealthy.
D) the poor.
E) the middle class.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 87 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
Alexander Hamilton's proposed bank of the United States was
A) rejected by the House of Representatives.
B) supported by Thomas Jefferson.
C) enthusiastically supported by George Washington.
D) based on the "necessary and proper," or "elastic," clause in the Constitution.
E) to be owned and operated by the Treasury Department.
A) rejected by the House of Representatives.
B) supported by Thomas Jefferson.
C) enthusiastically supported by George Washington.
D) based on the "necessary and proper," or "elastic," clause in the Constitution.
E) to be owned and operated by the Treasury Department.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 87 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
Hamilton expected that the revenue to pay the interest on the national debt would come from
A) sales taxes and licensing fees.
B) customs duties (tariffs) and excise taxes.
C) income and property taxes.
D) western land sales and foreign loans.
E) capital gains taxes on corporations.
A) sales taxes and licensing fees.
B) customs duties (tariffs) and excise taxes.
C) income and property taxes.
D) western land sales and foreign loans.
E) capital gains taxes on corporations.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 87 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
Alexander Hamilton's financial plan for strengthening the economy and bolstering national credit proposed all of the following except
A) funding the national debt.
B) assuming state debts.
C) subsidies for manufacturers.
D) establishing a national bank.
E) excise taxes.
A) funding the national debt.
B) assuming state debts.
C) subsidies for manufacturers.
D) establishing a national bank.
E) excise taxes.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 87 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
Regarding central authority, early Americans saw it as all of the following except
A) a necessary evil.
B) something to be distrusted.
C) something to be watched.
D) something to be curbed.
E) something to be ultimately eliminated.
A) a necessary evil.
B) something to be distrusted.
C) something to be watched.
D) something to be curbed.
E) something to be ultimately eliminated.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 87 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
The Bill of Rights was intended to protect ____ against the potential tyranny of ____.
A) the prerogatives of Congress, the president
B) the army and the navy, Congress
C) the South, the northern majority
D) individual liberties, a strong central government
E) civilian authorities, the military
A) the prerogatives of Congress, the president
B) the army and the navy, Congress
C) the South, the northern majority
D) individual liberties, a strong central government
E) civilian authorities, the military

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 87 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
Which amendment guards against the danger that enumerating rights might lead to the conclusion that they were the only ones protected?
A) First
B) Second
C) Ninth
D) Tenth
E) none of these
A) First
B) Second
C) Ninth
D) Tenth
E) none of these

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 87 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
The aspect of Hamilton's financial program that received the least support in Congress, because of its heavy agricultural and commercial interests, was
A) funding at par.
B) assumption.
C) the National Bank.
D) a protective tariff.
E) excise taxes.
A) funding at par.
B) assumption.
C) the National Bank.
D) a protective tariff.
E) excise taxes.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 87 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
All of the following were part of Alexander Hamilton's economic program except
A) a national bank.
B) funding the entire national debt at "par."
C) assumption of state debts by the federal government.
D) tariffs.
E) a monetary system based on silver.
A) a national bank.
B) funding the entire national debt at "par."
C) assumption of state debts by the federal government.
D) tariffs.
E) a monetary system based on silver.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 87 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
The ____ Amendment might rightly be called the "states' rights" amendment.
A) First
B) Sixth
C) Eighth
D) Ninth
E) Tenth
A) First
B) Sixth
C) Eighth
D) Ninth
E) Tenth

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 87 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
Arrange the following events in chronological order: (A) XYZ affair, (B) Neutrality Proclamation, (C) Jay's Treaty, (D) the Convention of 1800 with France.
A) C, B, A, D
B) B, A, C, D
C) B, C, A, D
D) C, B, D, A
E) A, B, D, C
A) C, B, A, D
B) B, A, C, D
C) B, C, A, D
D) C, B, D, A
E) A, B, D, C

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 87 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
Britain made neutrality very difficult for the United States during the French and British conflicts of the 1790s by
A) preventing American trade with the European continent.
B) seizing American merchant ships and sailors in the West Indies.
C) declaring that they would never abandon their forts on the American frontier.
D) engaging in a naval arms race on the Great Lakes.
E) sponsoring pro-British agents within the United States.
A) preventing American trade with the European continent.
B) seizing American merchant ships and sailors in the West Indies.
C) declaring that they would never abandon their forts on the American frontier.
D) engaging in a naval arms race on the Great Lakes.
E) sponsoring pro-British agents within the United States.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 87 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
Washington's Neutrality Proclamation of 1793
A) was based on calculations of American self-interest.
B) fulfilled America's obligations under the Franco-American Treaty.
C) was opposed by both Alexander Hamilton and Thomas Jefferson.
D) was based on American ideals of liberty and equality.
E) showed the impossibility of American isolationism.
A) was based on calculations of American self-interest.
B) fulfilled America's obligations under the Franco-American Treaty.
C) was opposed by both Alexander Hamilton and Thomas Jefferson.
D) was based on American ideals of liberty and equality.
E) showed the impossibility of American isolationism.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 87 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
Washington's Neutrality Proclamation eventually came to be seen as the foundation of
A) American foreign policy in Latin America.
B) the American policy of support for liberty and democracy around the world.
C) the "realist" tradition of American foreign policy.
D) the isolationist tradition of American foreign policy.
E) the American support for international organizations as solutions to war.
A) American foreign policy in Latin America.
B) the American policy of support for liberty and democracy around the world.
C) the "realist" tradition of American foreign policy.
D) the isolationist tradition of American foreign policy.
E) the American support for international organizations as solutions to war.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 87 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
Hamilton's major programs seriously infringed on
A) checks and balances.
B) national security.
C) states' rights.
D) free enterprise.
E) executive privilege.
A) checks and balances.
B) national security.
C) states' rights.
D) free enterprise.
E) executive privilege.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 87 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
The event of the 1790s that caused the deepest divisions in American political and social life was
A) the Whiskey Rebellion.
B) the French Revolution.
C) Hamilton's economic and financial policies.
D) the warfare with Little Turtle's Miami Confederacy.
E) the development of a political party system.
A) the Whiskey Rebellion.
B) the French Revolution.
C) Hamilton's economic and financial policies.
D) the warfare with Little Turtle's Miami Confederacy.
E) the development of a political party system.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 87 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
The early Federalist support for the French Revolution turned into angry hostility when
A) the French abandoned their commitment to the Franco-American alliance.
B) the French revolutionaries denounced the American Revolution.
C) the Revolution turned more radical and began its Reign of Terror.
D) the French agent Citizen Genêt arrived in America to stir up trouble.
E) Americans in Paris were harassed and imprisoned.
A) the French abandoned their commitment to the Franco-American alliance.
B) the French revolutionaries denounced the American Revolution.
C) the Revolution turned more radical and began its Reign of Terror.
D) the French agent Citizen Genêt arrived in America to stir up trouble.
E) Americans in Paris were harassed and imprisoned.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 87 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
Jefferson's arguments against the constitutionality of a Bank of the United States were based on the "strict construction" principles especially embodied in
A) the Articles of Confederation.
B) the "necessary and proper" clause of the Constitution.
C) the Virginia and Kentucky Resolutions.
D) the Tenth Amendment in the Bill of Rights.
E) the restrictions on Congress's powers in Article II, Section 9 of the Constitution.
A) the Articles of Confederation.
B) the "necessary and proper" clause of the Constitution.
C) the Virginia and Kentucky Resolutions.
D) the Tenth Amendment in the Bill of Rights.
E) the restrictions on Congress's powers in Article II, Section 9 of the Constitution.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 87 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
The Neutrality Proclamation in 1793
A) declared that America would honor the principles found in the Franco-American Alliance of 1778.
B) required the United States to send troops to France if it was attacked by Britain.
C) officially proclaimed America's neutrality in Old World quarrels.
D) declared that America would send troops to France if it was attacked by Spain.
E) led the United States to war with Britain in 1812.
A) declared that America would honor the principles found in the Franco-American Alliance of 1778.
B) required the United States to send troops to France if it was attacked by Britain.
C) officially proclaimed America's neutrality in Old World quarrels.
D) declared that America would send troops to France if it was attacked by Spain.
E) led the United States to war with Britain in 1812.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 87 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
In Jay's Treaty, the British
A) pledged to stop seizing American ships.
B) released Americans from their pre-Revolutionary War debt obligations to British merchants.
C) promised to evacuate the chain of forts in the Old Northwest.
D) refused to pay damages for seizures of American ships.
E) promised to stop supplying weapons to the Indians.
A) pledged to stop seizing American ships.
B) released Americans from their pre-Revolutionary War debt obligations to British merchants.
C) promised to evacuate the chain of forts in the Old Northwest.
D) refused to pay damages for seizures of American ships.
E) promised to stop supplying weapons to the Indians.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 87 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
The opposition of Thomas Jefferson and James Madison to the financial plan of Alexander Hamilton resulted in
A) the formation of permanent political parties.
B) Hamilton's dismissal from the cabinet by George Washington.
C) Jefferson's decision to run against George Washington.
D) a sharp conflict between the president and Congress.
E) the revival of antifederalist sentiment.
A) the formation of permanent political parties.
B) Hamilton's dismissal from the cabinet by George Washington.
C) Jefferson's decision to run against George Washington.
D) a sharp conflict between the president and Congress.
E) the revival of antifederalist sentiment.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 87 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
The political party of the "outs" that provided the "loyal opposition" to the party in power throughout the 1790s was
A) the Antifederalists.
B) the Federalists.
C) the Democratic-Republicans.
D) the Whigs.
E) the Tories.
A) the Antifederalists.
B) the Federalists.
C) the Democratic-Republicans.
D) the Whigs.
E) the Tories.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 87 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
The Pennsylvania Whiskey Rebellion of 1794 was a revolt against
A) the federal excise tax on whiskey.
B) Pennsylvania's prohibition laws.
C) the economic competition from Kentucky Bourbon whiskey.
D) the new Bureau of Alcohol, Tobacco, and Firearms.
E) the licensing of whiskey manufacture and sales.
A) the federal excise tax on whiskey.
B) Pennsylvania's prohibition laws.
C) the economic competition from Kentucky Bourbon whiskey.
D) the new Bureau of Alcohol, Tobacco, and Firearms.
E) the licensing of whiskey manufacture and sales.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 87 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
Alexander Hamilton's Bank of the United States was modeled on
A) the Bank of England.
B) the Swiss National Bank.
C) the Rothschild financial houses in Paris.
D) the Chase Manhattan Bank.
E) the state banks of New York and Massachusetts.
A) the Bank of England.
B) the Swiss National Bank.
C) the Rothschild financial houses in Paris.
D) the Chase Manhattan Bank.
E) the state banks of New York and Massachusetts.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 87 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
Match each political leader with his positions on public policy in the 1790s. 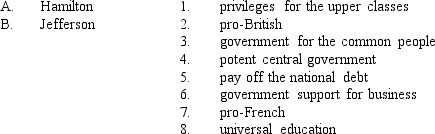
A) A-1, 2, 4, 6-B-3, 5, 7, 8
B) A-1, 5, 6, 7-B-2, 3, 4, 8
C) A-2, 3, 5, 8-B-1, 4, 6, 7
D) A-3, 6, 7, 8-B-1, 2, 4, 5
E) A-5, 2, 6, 3-B-1, 4, 7, 8

A) A-1, 2, 4, 6-B-3, 5, 7, 8
B) A-1, 5, 6, 7-B-2, 3, 4, 8
C) A-2, 3, 5, 8-B-1, 4, 6, 7
D) A-3, 6, 7, 8-B-1, 2, 4, 5
E) A-5, 2, 6, 3-B-1, 4, 7, 8

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 87 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
The United States acquired free navigation of the Mississippi River and the large disputed territory north of Florida in
A) the Treaty of Greenville with the Miami Confederacy.
B) Jay's Treaty with Britain.
C) the Convention of 1800 with France.
D) Pinckney's Treaty with Spain.
E) the XYZ affair with France.
A) the Treaty of Greenville with the Miami Confederacy.
B) Jay's Treaty with Britain.
C) the Convention of 1800 with France.
D) Pinckney's Treaty with Spain.
E) the XYZ affair with France.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 87 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
During its first quarter-century as a nation, the major foreign policy problem facing the United States was
A) the rivalry and warfare between France and Britain.
B) the French and Spanish control of Louisiana and New Orleans.
C) the continued threat from the British in Canada.
D) the attacks on American shipping by the North African Barbary states.
E) the threat of international revolution spreading from France.
A) the rivalry and warfare between France and Britain.
B) the French and Spanish control of Louisiana and New Orleans.
C) the continued threat from the British in Canada.
D) the attacks on American shipping by the North African Barbary states.
E) the threat of international revolution spreading from France.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 87 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
When the French Revolution developed into a war with Britain, George Washington and the American government
A) supported Britain.
B) assisted France militarily.
C) tried to capture French possessions in North America and the West Indies.
D) remained neutral.
E) tried to broker a peace settlement between the two nations.
A) supported Britain.
B) assisted France militarily.
C) tried to capture French possessions in North America and the West Indies.
D) remained neutral.
E) tried to broker a peace settlement between the two nations.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 87 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
The Founders had not envisioned the existence of permanent political parties because they
A) opposed anyone who disagreed with them.
B) disliked politics.
C) were seen as corrupt and narrow-minded.
D) saw them as a sign of disloyalty and lack of national unity.
E) had caused the fall of republican Rome.
A) opposed anyone who disagreed with them.
B) disliked politics.
C) were seen as corrupt and narrow-minded.
D) saw them as a sign of disloyalty and lack of national unity.
E) had caused the fall of republican Rome.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 87 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
The Miami Confederacy led by Chief Little Turtle
A) defeated General Anthony Wayne in the Battle of Fallen Timbers.
B) consisted entirely of members of the Miami tribe.
C) refused to sign the humiliating Treaty of Greenville.
D) were quickly overwhelmed by U.S.military forces.
E) at first handed the U.S.forces one of its worst military defeats.
A) defeated General Anthony Wayne in the Battle of Fallen Timbers.
B) consisted entirely of members of the Miami tribe.
C) refused to sign the humiliating Treaty of Greenville.
D) were quickly overwhelmed by U.S.military forces.
E) at first handed the U.S.forces one of its worst military defeats.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 87 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
Hamiltonian Federalists particularly feared
A) the fickleness of the common people.
B) the power of unelected federal judges.
C) the expansion of the "slave power."
D) Thomas Jefferson's dictatorial tendencies.
E) high taxes.
A) the fickleness of the common people.
B) the power of unelected federal judges.
C) the expansion of the "slave power."
D) Thomas Jefferson's dictatorial tendencies.
E) high taxes.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 87 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
The Sedition Act
A) threatened freedom of speech and the press.
B) established a federal bureau of investigation.
C) lengthened naturalization requirements for new citizens.
D) was never enforced.
E) was held unconstitutional by the Supreme Court.
A) threatened freedom of speech and the press.
B) established a federal bureau of investigation.
C) lengthened naturalization requirements for new citizens.
D) was never enforced.
E) was held unconstitutional by the Supreme Court.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 87 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
The Federalists chose not to nominate their most talented candidate, Alexander Hamilton, for president in 1796 because
A) Hamilton was engaged in a violent feud with Aaron Burr.
B) George Washington refused to endorse Hamilton as his successor.
C) Hamilton's pro-wealthy financial policies had made him politically unpopular.
D) they believed that John Adams's charisma was a better match against Thomas Jefferson.
E) they feared that Hamilton might lead the nation to war against France.
A) Hamilton was engaged in a violent feud with Aaron Burr.
B) George Washington refused to endorse Hamilton as his successor.
C) Hamilton's pro-wealthy financial policies had made him politically unpopular.
D) they believed that John Adams's charisma was a better match against Thomas Jefferson.
E) they feared that Hamilton might lead the nation to war against France.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 87 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
The French revealed their growing hostility to the United States by
A) sending Citizen Genêt to promote a new American Revolution.
B) seizing hundreds of American merchant ships.
C) sending troops to fortify French Louisiana.
D) unilaterally repudiating the Franco-American alliance.
E) expelling Thomas Jefferson as ambassador to France.
A) sending Citizen Genêt to promote a new American Revolution.
B) seizing hundreds of American merchant ships.
C) sending troops to fortify French Louisiana.
D) unilaterally repudiating the Franco-American alliance.
E) expelling Thomas Jefferson as ambassador to France.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 87 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
The main purpose of the Alien and Sedition Acts was to
A) capture French and British spies.
B) protect national security.
C) silence and punish critics of the Federalists.
D) prevent the United States from being overrun by immigrants.
E) promote the re-election of President Adams.
A) capture French and British spies.
B) protect national security.
C) silence and punish critics of the Federalists.
D) prevent the United States from being overrun by immigrants.
E) promote the re-election of President Adams.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 87 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
Federalist advocated rule by
A) the majority.
B) the wealthy and well educated.
C) farmers.
D) industrial workers.
E) a hereditary aristocracy.
A) the majority.
B) the wealthy and well educated.
C) farmers.
D) industrial workers.
E) a hereditary aristocracy.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 87 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
The Virginia and Kentucky resolutions were written in response to
A) the XYZ affair.
B) Thomas Jefferson's presidential candidacy in 1800.
C) the Alien and Sedition Acts.
D) the U.S.army's suppression of the Whiskey Rebellion.
E) the Federalist papers.
A) the XYZ affair.
B) Thomas Jefferson's presidential candidacy in 1800.
C) the Alien and Sedition Acts.
D) the U.S.army's suppression of the Whiskey Rebellion.
E) the Federalist papers.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 87 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
French relations with the United States turned sour in the late 1790s because
A) Jay's Treaty seemed to signal an American alliance with Britain.
B) Congress expelled French agents from American soil.
C) of the XYZ affair.
D) the French revolutionary government now saw the Americans as conservatives.
E) their friend Thomas Jefferson lost the presidency
A) Jay's Treaty seemed to signal an American alliance with Britain.
B) Congress expelled French agents from American soil.
C) of the XYZ affair.
D) the French revolutionary government now saw the Americans as conservatives.
E) their friend Thomas Jefferson lost the presidency

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 87 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
President Adams sought a peaceful solution to the undeclared war with France in order to
A) ensure his chances of reelection in 1800.
B) politically outflank the Hamiltonian wing of the Federalist party.
C) preserve the Franco-American alliance of 1778.
D) prevent the outbreak of a dangerous full-scale war.
E) appease pro-British forces in the United States.
A) ensure his chances of reelection in 1800.
B) politically outflank the Hamiltonian wing of the Federalist party.
C) preserve the Franco-American alliance of 1778.
D) prevent the outbreak of a dangerous full-scale war.
E) appease pro-British forces in the United States.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 87 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
According to the Federalists, the duty of judging the unconstitutionality of legislation passed by Congress lay with
A) state legislatures.
B) the president.
C) state supreme courts.
D) the Supreme Court.
E) the people.
A) state legislatures.
B) the president.
C) state supreme courts.
D) the Supreme Court.
E) the people.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 87 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
One of George Washington's major contributions as president was
A) keeping the nation out of overseas entanglements and foreign wars.
B) establishing the bipartisan tradition in foreign affairs.
C) his advice against forming permanent alliances with foreign nations.
D) ending British interference with American commerce and Indian affairs.
E) maintaining unity with his cabinet.
A) keeping the nation out of overseas entanglements and foreign wars.
B) establishing the bipartisan tradition in foreign affairs.
C) his advice against forming permanent alliances with foreign nations.
D) ending British interference with American commerce and Indian affairs.
E) maintaining unity with his cabinet.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 87 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
The Federalist-dominated Congress's Alien Act was aimed at ____ whereas the Sedition Act was primarily aimed at ____.
A) French agents, newspapers
B) recent immigrants, newspapers
C) recent immigrants, merchants
D) potential spies, rebellious slaves
E) Indians, Congress
A) French agents, newspapers
B) recent immigrants, newspapers
C) recent immigrants, merchants
D) potential spies, rebellious slaves
E) Indians, Congress

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 87 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
According to the "compact theory" advocated by Jefferson and Madison,
A) the federal government was the creation of the thirteen sovereign states.
B) the Constitution was solely the creation of the people.
C) Congress and the president had entered a compact not to expand federal power.
D) treaties signed with foreign powers could not overrule U.S.law.
E) Hamilton's use of the "necessary and proper clause" violated the Constitutional compact.
A) the federal government was the creation of the thirteen sovereign states.
B) the Constitution was solely the creation of the people.
C) Congress and the president had entered a compact not to expand federal power.
D) treaties signed with foreign powers could not overrule U.S.law.
E) Hamilton's use of the "necessary and proper clause" violated the Constitutional compact.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 87 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
In the 1796 presidential campaign, Jeffersonians especially attacked the Federalists for
A) creating the Bank of the United States.
B) crushing the Whiskey Rebellion and negotiating Jay's Treaty.
C) opening the possibility of restricting the spread of slavery.
D) their inability to negotiate a peace with Britain.
E) violating civil liberties.
A) creating the Bank of the United States.
B) crushing the Whiskey Rebellion and negotiating Jay's Treaty.
C) opening the possibility of restricting the spread of slavery.
D) their inability to negotiate a peace with Britain.
E) violating civil liberties.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 87 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
John Jay's 1794 treaty with Britain
A) increased George Washington's already huge popularity.
B) virtually guaranteed an American war with France.
C) alienated America from Spain.
D) created deeper splits between Federalists and Democratic-Republicans.
E) led to the election of Thomas Jefferson.
A) increased George Washington's already huge popularity.
B) virtually guaranteed an American war with France.
C) alienated America from Spain.
D) created deeper splits between Federalists and Democratic-Republicans.
E) led to the election of Thomas Jefferson.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 87 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
The Jeffersonians were especially outraged by Jay's Treaty because
A) the use of Chief Justice John Jay as a diplomat seemed to violate the separation of powers.
B) the British refused to promise to evacuate forts on U.S.soil.
C) the agreement would harm the South by suppressing the international slave trade.
D) it exposed George Washington as a self-serving Federalist partisan.
E) it seemed like an abject surrender of American interests to Britain in exchange for empty promises.
A) the use of Chief Justice John Jay as a diplomat seemed to violate the separation of powers.
B) the British refused to promise to evacuate forts on U.S.soil.
C) the agreement would harm the South by suppressing the international slave trade.
D) it exposed George Washington as a self-serving Federalist partisan.
E) it seemed like an abject surrender of American interests to Britain in exchange for empty promises.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 87 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
The immediate cause of the undeclared war between the United States and France was
A) the XYZ affair.
B) the Genêt mission.
C) Napoleon's seizure of dictatorial power.
D) John Adams's election.
E) Jay's Treaty.
A) the XYZ affair.
B) the Genêt mission.
C) Napoleon's seizure of dictatorial power.
D) John Adams's election.
E) Jay's Treaty.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 87 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
Federalists strongly supported
A) law and order.
B) states' rights.
C) strict construction.
D) popular democracy.
E) freedom of speech and the press.
A) law and order.
B) states' rights.
C) strict construction.
D) popular democracy.
E) freedom of speech and the press.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 87 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
The United States finally negotiated a peace settlement with France in 1800 mainly because Napoleon
A) took enough bribe money to make an agreement possible.
B) wanted to end the American squabble and expand his empire.
C) realized that the French could not win a military victory over the American forces.
D) was hoping to make a future deal over Louisiana.
E) realized that Jefferson would soon be coming to power in the United States.
A) took enough bribe money to make an agreement possible.
B) wanted to end the American squabble and expand his empire.
C) realized that the French could not win a military victory over the American forces.
D) was hoping to make a future deal over Louisiana.
E) realized that Jefferson would soon be coming to power in the United States.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 87 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
Washington's Farewell Address in 1796
A) endorsed the democratic development of two contending political parties in America.
B) warned against the dangers of permanent foreign alliances.
C) was delivered to a joint session of Congress by Washington himself.
D) proposed a two-term limitation on the presidency.
E) warned the European powers against intervention or colonization in the Americas.
A) endorsed the democratic development of two contending political parties in America.
B) warned against the dangers of permanent foreign alliances.
C) was delivered to a joint session of Congress by Washington himself.
D) proposed a two-term limitation on the presidency.
E) warned the European powers against intervention or colonization in the Americas.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 87 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
Thomas Jefferson argued that a landless class of voters could be avoided in part by
A) a redistribution of land.
B) a reduced property tax.
C) abolishing the property qualification to vote.
D) continuing slavery.
E) restricting the amount of property owned by each citizen.
A) a redistribution of land.
B) a reduced property tax.
C) abolishing the property qualification to vote.
D) continuing slavery.
E) restricting the amount of property owned by each citizen.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 87 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
How would Hamilton and Jefferson each assess the condition and power of the federal government today? How would they assess the condition of civil liberties and "states' rights"?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 87 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
Why did the French Revolution create such fierce passions and deep divisions among Americans? How did attitudes toward the French Revolution, and France, line up with domestic political divisions between Hamiltonian Federalists and Jeffersonian Republicans?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 87 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
Thomas Jefferson appealed to all of the following groups except
A) small shopkeepers.
B) small farmers.
C) the middle class.
D) merchants and manufacturers.
E) artisans.
A) small shopkeepers.
B) small farmers.
C) the middle class.
D) merchants and manufacturers.
E) artisans.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 87 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
Compare and contrast the Federalists and Republicans, especially their views on democracy, government power, the economy, and foreign affairs.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 87 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
Jeffersonians believed in all of the following except
A) opposition to a national debt.
B) agriculture as the ideal occupation.
C) every adult white male's right to vote.
D) freedom of speech and the press.
E) universal public education.
A) opposition to a national debt.
B) agriculture as the ideal occupation.
C) every adult white male's right to vote.
D) freedom of speech and the press.
E) universal public education.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 87 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
Did Hamilton's dramatic expansion of federal powers confirm the fears of the Antifederalists about the new government? Was Hamilton right that only an economically powerful federal government could survive?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 87 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
Wars with both Britain and France nearly broke out in the 1790s, but neither did.Was this the result of wise statesmanship or the stalemate in Europe? What might have been the consequence of a war with one or the other great power?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 87 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
To the Jeffersonian Republicans, the ideal citizen of a republic was a(n)
A) seaboard merchant.
B) urban worker.
C) indentured servant.
D) independent farmer.
E) industrialist.
A) seaboard merchant.
B) urban worker.
C) indentured servant.
D) independent farmer.
E) industrialist.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 87 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
Why was a relatively minor revolt like the Whiskey Rebellion so important for the new federal government?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 87 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
Compare and contrast the underlying principles and implications of the "loose" and "strict" construction of the Constitution.How did each theory regard the actual text of the Constitution itself?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 87 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72
According to the text's authors, "critics claimed [Hamilton] loved his adopted country more than he loved his countrymen." How could Hamilton reconcile his strong patriotism and commitment to create a powerful America with his deep suspicion of ordinary American people?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 87 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73
The text's authors claim that "it was fortunate for the Republic that the Federalists had the helm [control of the government] for a time." Do you agree? Why or why not?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 87 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
74
Thomas Jefferson favored a political system in which
A) the central government possessed the bulk of the power.
B) cities were the primary focus of political activity.
C) a large standing army ensured peace.
D) the states retained the majority of political power.
E) manufacturing interests dominated.
A) the central government possessed the bulk of the power.
B) cities were the primary focus of political activity.
C) a large standing army ensured peace.
D) the states retained the majority of political power.
E) manufacturing interests dominated.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 87 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
75
Summarize the central argument of the Kentucky and Virginia resolutions.Explain why they are key documents in American history.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 87 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
76
What were the essential goals of Hamilton's economic and financial policies? Why did they stir so much opposition?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 87 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
77
President Franklin Roosevelt once said that he believed in using "Hamiltonian means" to achieve "Jeffersonian ends." What might he have meant? How would Hamilton and Jefferson each respond to this unusual approach?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 87 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
78
Very early in its national history, the United States established a tradition of isolationism in its foreign policy.How did the Neutrality Proclamation and Washington's Farewell Address contribute to this tradition?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 87 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
79
Hamiltonian Federalists advocated
A) government regulation of business and agriculture.
B) a strong central government and federal aid to business.
C) low taxes and low tariffs.
D) a system of free public schools and universities.
E) neutrality in American foreign relations.
A) government regulation of business and agriculture.
B) a strong central government and federal aid to business.
C) low taxes and low tariffs.
D) a system of free public schools and universities.
E) neutrality in American foreign relations.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 87 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
80
Was the Jeffersonian Republican party essentially a negative response to Hamilton's policies, or was it a more positive assertion of ideals of democracy, liberty, and limited government?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 87 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



