Deck 4: Trade and Resources: the Heckscher-Ohlin Model
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/133
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 4: Trade and Resources: the Heckscher-Ohlin Model
1
The HeckscherOhlin model of international trade uses
_____ and ______ to explain trade patterns.
A)comparative; absolute advantage
B)factor abundance; factor intensity
C)factor availability; factor usability
D)tariffs; quotas
_____ and ______ to explain trade patterns.
A)comparative; absolute advantage
B)factor abundance; factor intensity
C)factor availability; factor usability
D)tariffs; quotas
B
2
A situation in which one nation produces good A using labor
More intensively (relative to capital) than good B and a
Second nation, producing good A, uses capital more
Intensively (relative to labor) than good B is called:
A)a reversal of factor intensities.
B)a paradox of factor intensities
C)backward technology.
D)micro intensity.
More intensively (relative to capital) than good B and a
Second nation, producing good A, uses capital more
Intensively (relative to labor) than good B is called:
A)a reversal of factor intensities.
B)a paradox of factor intensities
C)backward technology.
D)micro intensity.
A
3
The HeckscherOhlin model assumes that there are two
Countries, each of which produces two goods (say
Manufactures and agriculture) using labor and capital.
Which of the following is an additional assumption of the
HeckscherOhlin model?
A)The ratio of the quantity of labor to the quantity of capital is different for each nation, resulting in different
"endowments" of capital and labor.
B)One nation has larger quantities of both capital and labor than the other country.
C)Capital is a specific resource in producing manufactured goods, and labor is a specific resource in producing
Agricultural goods in each country.
D)Labor and capital can move between countries.
Countries, each of which produces two goods (say
Manufactures and agriculture) using labor and capital.
Which of the following is an additional assumption of the
HeckscherOhlin model?
A)The ratio of the quantity of labor to the quantity of capital is different for each nation, resulting in different
"endowments" of capital and labor.
B)One nation has larger quantities of both capital and labor than the other country.
C)Capital is a specific resource in producing manufactured goods, and labor is a specific resource in producing
Agricultural goods in each country.
D)Labor and capital can move between countries.
A
4
According to the application in the text, why can Nike shoes
Be produced at low cost in foreign countries?
A)Foreign countries have superior technology.
B)Foreign countries are strategic allies for the home country.
C)Labor costs in foreign countries are lower than in the United States.
D)Nike has no competition in the foreign country.
Be produced at low cost in foreign countries?
A)Foreign countries have superior technology.
B)Foreign countries are strategic allies for the home country.
C)Labor costs in foreign countries are lower than in the United States.
D)Nike has no competition in the foreign country.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 133 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
The HeckscherOhlin model assumes that production
Techniques within a nation use the factors of production:
A)at different intensities depending on changing technology and which nation you are discussing.
B)at different intensities for each industry, so that one is more or less intensive in that factor than the other.
C)at the same intensity for each industry-for example, the ratio of capital to labor is the same for every industry in
The nation.
D)in no definite pattern.
Techniques within a nation use the factors of production:
A)at different intensities depending on changing technology and which nation you are discussing.
B)at different intensities for each industry, so that one is more or less intensive in that factor than the other.
C)at the same intensity for each industry-for example, the ratio of capital to labor is the same for every industry in
The nation.
D)in no definite pattern.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 133 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
United States' agricultural production is ________ in
Comparison with Chinese agricultural production.
A)capital intensive
B)labor intensive
C)less subsidized
D)more restrictive
Comparison with Chinese agricultural production.
A)capital intensive
B)labor intensive
C)less subsidized
D)more restrictive

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 133 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
The HeckscherOhlin theorem explains patterns of trade
Between countries using:
A)economies of scale.
B)monopoly power in the industry.
C)abundance or scarcity of resources.
D)tariffs and quota.
Between countries using:
A)economies of scale.
B)monopoly power in the industry.
C)abundance or scarcity of resources.
D)tariffs and quota.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 133 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
Which of the following statements is TRUE?
A)The HeckscherOhlin model offers a reasonable explanation of the pattern of trade and the gains from
Trade.
B)The HeckscherOhlin trade model does not offer an explanation of the pattern of trade.
C)The HeckscherOhlin trade model does not offer an explanation of the gains from trade.
D)The Riparian trade model (with labor as the only input) offers a better explanation of the pattern of trade and the
Gains from trade than the HeckscherOhlin model.
A)The HeckscherOhlin model offers a reasonable explanation of the pattern of trade and the gains from
Trade.
B)The HeckscherOhlin trade model does not offer an explanation of the pattern of trade.
C)The HeckscherOhlin trade model does not offer an explanation of the gains from trade.
D)The Riparian trade model (with labor as the only input) offers a better explanation of the pattern of trade and the
Gains from trade than the HeckscherOhlin model.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 133 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
The HeckscherOhlin model assumes that technology in
Each industry:
A)Is the same in each nation-each firm has access to the most profitable technology.
B)has increasing returns so that one nation will be able to gain a comparative advantage by developing new
Technology.
C)is very different across the world-some nations have access to technology, whereas others do not.
D)is hard to access because R&D is very expensive especially for lowincome nations.
Each industry:
A)Is the same in each nation-each firm has access to the most profitable technology.
B)has increasing returns so that one nation will be able to gain a comparative advantage by developing new
Technology.
C)is very different across the world-some nations have access to technology, whereas others do not.
D)is hard to access because R&D is very expensive especially for lowincome nations.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 133 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
The HeckscherOhlin Model assumes that:
A)factor endowments are the same.
B)consumer tastes are different across countries.
C)the technologies used to produce the two goods are different across the countries.
D)consumer tastes and technologies are the same across countries.
A)factor endowments are the same.
B)consumer tastes are different across countries.
C)the technologies used to produce the two goods are different across the countries.
D)consumer tastes and technologies are the same across countries.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 133 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
The HeckscherOhlin model assumes that the factors of
Production are mobile ______, but immobile _____.
A)in the short run; in the long run
B)in the long run; in the short run
C)domestically; internationally
D)internationally; domestically
Production are mobile ______, but immobile _____.
A)in the short run; in the long run
B)in the long run; in the short run
C)domestically; internationally
D)internationally; domestically

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 133 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
The implication of resources being mobile domestically is
That:
A)there is often unemployment.
B)capital and land are often not suited for use in other industries.
C)labor and capital are paid the same wage and rental price in all domestic industries.
D)they lose the chance to become guest workers in other nations.
That:
A)there is often unemployment.
B)capital and land are often not suited for use in other industries.
C)labor and capital are paid the same wage and rental price in all domestic industries.
D)they lose the chance to become guest workers in other nations.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 133 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
The HeckscherOhlin model simplifies the analysis by
Assuming:
A)there is unemployment of workers in the home country.
B)there are a variety of levels of workers and types of capital.
C)land is an important factor of production.
D)there are only two nations, with two goods and two factors of production.
Assuming:
A)there is unemployment of workers in the home country.
B)there are a variety of levels of workers and types of capital.
C)land is an important factor of production.
D)there are only two nations, with two goods and two factors of production.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 133 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
In the text, which of the following statements is NOT an
Assumption of the HeckscherOhlin model?
A)There are two countries, each of which produces two goods using labor and capital.
B)Labor and capital can move freely between the production of two goods.
C)There is free trade between the countries.
D)Labor and capital can move freely between the two countries.
Assumption of the HeckscherOhlin model?
A)There are two countries, each of which produces two goods using labor and capital.
B)Labor and capital can move freely between the production of two goods.
C)There is free trade between the countries.
D)Labor and capital can move freely between the two countries.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 133 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
A longrun model of trade basic to the determination of how
Mobile factors of production affect national welfare and the
Returns to the factors is known as:
A)the specificfactors model.
B)the Riparian model.
C)the Chicago model of trade.
D)the HeckscherOhlin model.
Mobile factors of production affect national welfare and the
Returns to the factors is known as:
A)the specificfactors model.
B)the Riparian model.
C)the Chicago model of trade.
D)the HeckscherOhlin model.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 133 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
If agriculture is a capitalintensive industry in the United
States and a laborintensive industry in India, then:
A)India should export agricultural goods to the United States.
B)neither country will have an advantage in agricultural production.
C)there is factorintensity reversal in agricultural production between the two countries.
D)it is difficult to determine which country is labor abundant.
States and a laborintensive industry in India, then:
A)India should export agricultural goods to the United States.
B)neither country will have an advantage in agricultural production.
C)there is factorintensity reversal in agricultural production between the two countries.
D)it is difficult to determine which country is labor abundant.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 133 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
In a capitalintensive industry, the labor/capital ratio will:
A)rise as the wage/rental ratio falls.
B)fall as the wage/rental ratio falls.
C)rise as the country's capital stock rises.
D)fall as the country's capital stock falls.
A)rise as the wage/rental ratio falls.
B)fall as the wage/rental ratio falls.
C)rise as the country's capital stock rises.
D)fall as the country's capital stock falls.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 133 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
The HeckscherOhlin model assumes that factors of
Production can move freely _______, but cannot move
_______.
A)domestically; internationally
B)after they are fully trained; before the training period is over
C)internationally; domestically
D)within unskilled occupations; into highskill jobs
Production can move freely _______, but cannot move
_______.
A)domestically; internationally
B)after they are fully trained; before the training period is over
C)internationally; domestically
D)within unskilled occupations; into highskill jobs

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 133 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
Which of the following statements is CORRECT?
A)The HO model assumes that all resources can freely move between industries.
B)The specificfactors model assumes that all resources can freely move between industries.
C)Both the HO and the specificfactor models assume that all resources can freely move between industries.
D)Neither the HO nor the specificfactor model assumes that all resources can freely move between industries.
A)The HO model assumes that all resources can freely move between industries.
B)The specificfactors model assumes that all resources can freely move between industries.
C)Both the HO and the specificfactor models assume that all resources can freely move between industries.
D)Neither the HO nor the specificfactor model assumes that all resources can freely move between industries.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 133 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
Suppose that country 1 is capital abundant relative to
Country 2.Both produce two goods (X and Y).Factor
Intensity reversal occurs whenever:
A)X is capital intensive in country 1 and labor intensive in country 2.
B)X is capital intensive in both countries.
C)Y is capital intensive in both countries.
D)X is capital intensive in country 1, and Y is labor intensive in country 2.
Country 2.Both produce two goods (X and Y).Factor
Intensity reversal occurs whenever:
A)X is capital intensive in country 1 and labor intensive in country 2.
B)X is capital intensive in both countries.
C)Y is capital intensive in both countries.
D)X is capital intensive in country 1, and Y is labor intensive in country 2.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 133 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
Suppose that the United States and China each produce
Steel and cloth.In the HeckscherOhlin model, if the United
States enjoys a comparative advantage in steel production,
Then:
A)China must have an absolute advantage in cloth production.
B)the United States will also have a comparative advantage in cloth production.
C)China must have a comparative advantage in cloth production.
D)the United States must have an absolute advantage in steel production.
Steel and cloth.In the HeckscherOhlin model, if the United
States enjoys a comparative advantage in steel production,
Then:
A)China must have an absolute advantage in cloth production.
B)the United States will also have a comparative advantage in cloth production.
C)China must have a comparative advantage in cloth production.
D)the United States must have an absolute advantage in steel production.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 133 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
According to the text, identical technologies are a more
Reasonable assumption for:
A)the shoe industry.
B)the call center industry.
C)neither the shoe nor call center industry.
D)both the shoe and call center industries.
Reasonable assumption for:
A)the shoe industry.
B)the call center industry.
C)neither the shoe nor call center industry.
D)both the shoe and call center industries.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 133 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
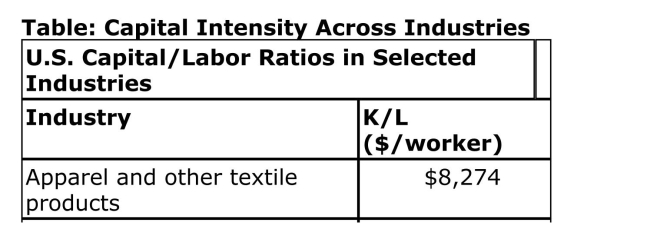
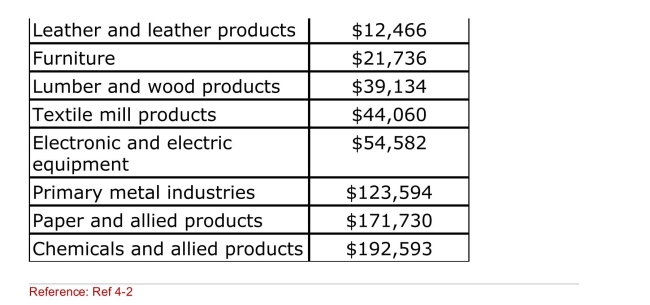
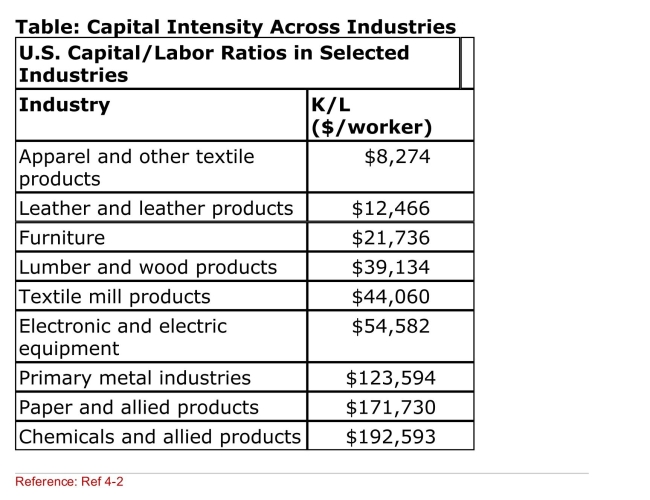
(Table: Capital Intensity Across Industries) According to the
Table, which industry is the MOST labor intensive?
A)Apparel and other textile products
B)Lumber and wood products
C)Primary metal industries
D)Chemicals and allied products

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 133 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
Suppose that Home is a capitalabundant country.When
Home trades with Foreign, a laborabundant country, the
HO model predicts that the price of:
A)the laborintensive good will rise in Home.
B)the laborintensive good will rise in Foreign.
C)the capitalintensive good will rise in Foreign.
D)the capitalintensive good will fall in Home.
Home trades with Foreign, a laborabundant country, the
HO model predicts that the price of:
A)the laborintensive good will rise in Home.
B)the laborintensive good will rise in Foreign.
C)the capitalintensive good will rise in Foreign.
D)the capitalintensive good will fall in Home.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 133 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
Why is the PPF bowed out in the HeckscherOhlin model?
A)Capital is specific to the production of one good.
B)Labor is specific to the production of the other good.
C)There are increasing opportunity costs of producing each good.
D)Labor is not perfectly mobile between the production of the two goods.
A)Capital is specific to the production of one good.
B)Labor is specific to the production of the other good.
C)There are increasing opportunity costs of producing each good.
D)Labor is not perfectly mobile between the production of the two goods.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 133 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
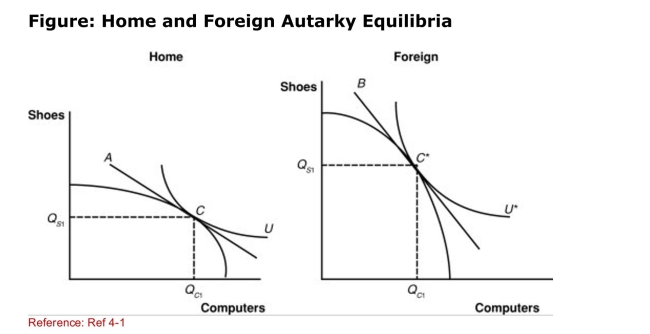 (Figure: Home and Foreign Autarky Equilibria) If shoes are a
(Figure: Home and Foreign Autarky Equilibria) If shoes are aLaborintensive industry, which nation has more labor
Resources relative to its capital resources?
A)Home
B)Foreign
C)neither Home nor Foreign
D)There is not enough information to answer this question.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 133 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
The international equilibrium price (or world price) and
Quantity for a traded item is determined by:
A)the WTO.
B)the U.S.Department of Commerce.
C)the intersection of the export supply schedule and the import demand schedule.
D)trade negotiations conducted by representatives in the two nations.
Quantity for a traded item is determined by:
A)the WTO.
B)the U.S.Department of Commerce.
C)the intersection of the export supply schedule and the import demand schedule.
D)trade negotiations conducted by representatives in the two nations.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 133 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
Consider two products, automobiles and shoes.If shoes are
Labor intensive and automobiles are capital intensive, what
Can we expect in freetrade conditions?
A)The relative price of automobiles in the autoexporting country will decrease.
B)The relative price of shoes in the shoeexporting country will increase.
C)The capitalabundant country will produce more shoes.
D)The laborabundant country will produce more automobiles.
Labor intensive and automobiles are capital intensive, what
Can we expect in freetrade conditions?
A)The relative price of automobiles in the autoexporting country will decrease.
B)The relative price of shoes in the shoeexporting country will increase.
C)The capitalabundant country will produce more shoes.
D)The laborabundant country will produce more automobiles.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 133 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
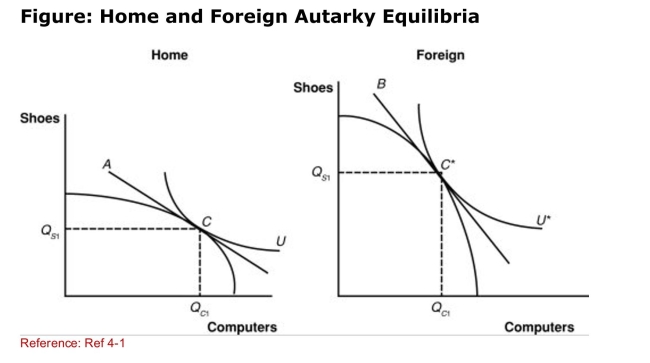 (Figure: Home and Foreign Autarky Equilibria) Which line in
(Figure: Home and Foreign Autarky Equilibria) Which line inThe graph represents the Home relative price of computers in
Terms of shoes?
A)A
B)B
C)C
D)U

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 133 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
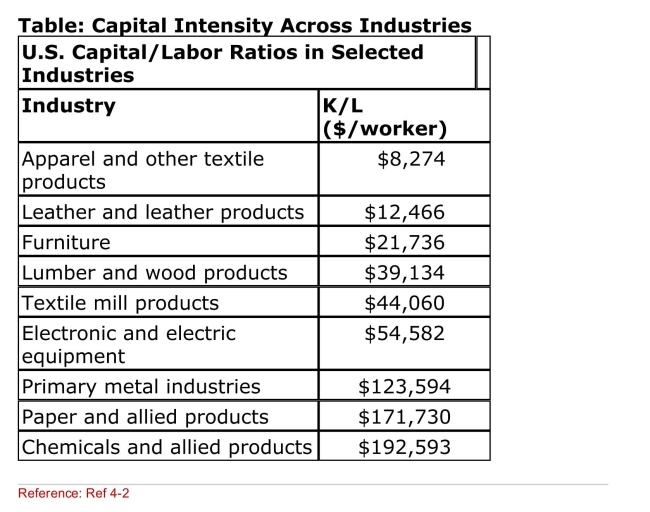 (Table: Capital Intensity Across Industries) Suppose that
(Table: Capital Intensity Across Industries) Suppose thatThe United States is labor abundant relative to Canada.
According to the table, which of the following U.S.
Industry(ies) is (are) MOST likely to export products to
Canada?
A)Furniture
B)Electronic and electrical equipment
C)Primary metal industries
D)Paper and allied products

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 133 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
LCD TVs are capital intensive, and tennis rackets are labor
Intensive.Suppose Canada has $100 billion of capital and 2
Million workers and Mexico has $10 billion of capital and 20
Million workers.According to the HO model:
A)Canada will specialize in and export LCD TVs.
B)Mexico will specialize in and export LCD TVs.
C)Canada will specialize in and export tennis rackets.
D)Mexico will import tennis rackets.
Intensive.Suppose Canada has $100 billion of capital and 2
Million workers and Mexico has $10 billion of capital and 20
Million workers.According to the HO model:
A)Canada will specialize in and export LCD TVs.
B)Mexico will specialize in and export LCD TVs.
C)Canada will specialize in and export tennis rackets.
D)Mexico will import tennis rackets.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 133 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
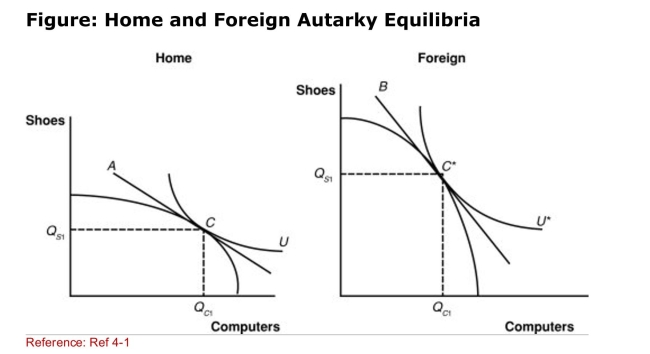 (Figure: Home and Foreign Autarky Equilibria) Which line in
(Figure: Home and Foreign Autarky Equilibria) Which line inThe graph represents Foreign's relative price of computers in
Terms of shoes?
A)A*
B)B*
C)C*
D)U*

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 133 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
There are many reallife examples of factorintensity
Differences across the same industries in different nations.
How does the HeckscherOhlin model handle this?
A)The HO model makes no assumptions about different factor intensities.
B)The HO model assumes that all firms require equal amounts of capital and labor just to be on the safe side.
C)The HO model ignores the possibility of different factor intensities and instead assumes that each industry has the
Same factor intensity in every nation.This assumption
Enables the model to predict trade based on other factors.
D)Actually, the factorintensity reversal issue does not change the predictive value of the model.
Differences across the same industries in different nations.
How does the HeckscherOhlin model handle this?
A)The HO model makes no assumptions about different factor intensities.
B)The HO model assumes that all firms require equal amounts of capital and labor just to be on the safe side.
C)The HO model ignores the possibility of different factor intensities and instead assumes that each industry has the
Same factor intensity in every nation.This assumption
Enables the model to predict trade based on other factors.
D)Actually, the factorintensity reversal issue does not change the predictive value of the model.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 133 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
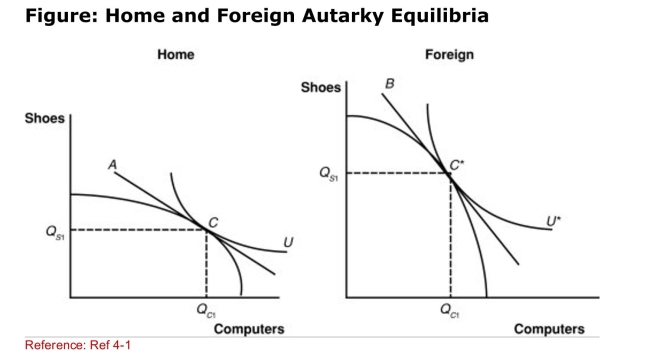 (Figure: Home and Foreign Autarky Equilibria) According to
(Figure: Home and Foreign Autarky Equilibria) According toThe shapes of the two PPFs, which nation has a comparative
Advantage in the production of computers?
A)Home
B)Foreign
C)neither Home nor Foreign
D)There is not enough information to answer this question.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 133 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
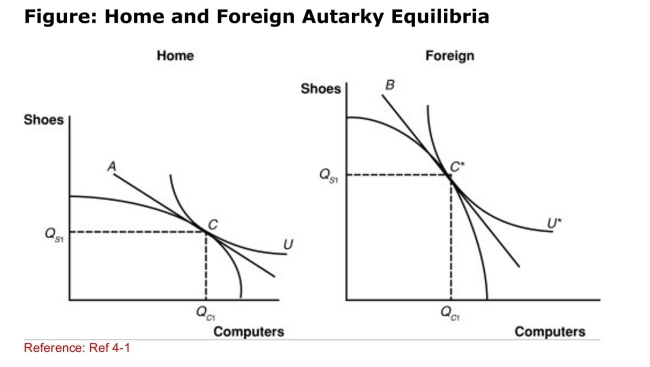 (Figure: Home and Foreign Autarky Equilibria) According to
(Figure: Home and Foreign Autarky Equilibria) According toThe graph, which nation has a higher notrade equilibrium
Relative price for computers (in terms of shoes)?
A)Home
B)Foreign
C)neither Home nor Foreign
D)There is not enough information to answer this question.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 133 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
Wages generally:
A)are higher in laborabundant countries than in capital abundant countries.
B)are lower in laborabundant countries than in capital abundant countries.
C)are the same in both laborabundant and capital abundant countries.
D)have no relationship to labor abundance.
A)are higher in laborabundant countries than in capital abundant countries.
B)are lower in laborabundant countries than in capital abundant countries.
C)are the same in both laborabundant and capital abundant countries.
D)have no relationship to labor abundance.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 133 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
The PPF of a country will be skewed toward the good that:
A)uses its scarce factor intensively.
B)uses its abundant factor intensively.
C)uses its intensive factor abundantly.
D)does not use its intensive factor abundantly.
A)uses its scarce factor intensively.
B)uses its abundant factor intensively.
C)uses its intensive factor abundantly.
D)does not use its intensive factor abundantly.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 133 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
Most trading nations do not completely specialize.
Incomplete specialization is mainly due to:
A)decreasing opportunity costs.
B)increasing opportunity costs.
C)constant opportunity costs.
D)perfectly substitutable resources.
Incomplete specialization is mainly due to:
A)decreasing opportunity costs.
B)increasing opportunity costs.
C)constant opportunity costs.
D)perfectly substitutable resources.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 133 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
 If there are only two nations, one nation's exports are the
If there are only two nations, one nation's exports are theOther's imports; which of the following is identical for both
Nations?
A)only the equilibrium relative price of the first nation's exports
B)only the opportunity cost of the first nation's exports
C)neither the equilibrium relative price nor the opportunity cost of the first nation's exports
D)both the equilibrium relative price and the opportunity cost of the first nation's exports

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 133 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
Malaysia is relatively abundant in labor, whereas Canada is
Relatively abundant in capital.In both countries, shirt
Production is relatively more labor intensive than computer
Production.According to the HeckscherOhlin model,
Malaysia will have a(n) ________ advantage in the
Production of __________.
A)absolute; shirts and computers
B)absolute; computers
C)comparative; shirts
D)comparative; computers
Relatively abundant in capital.In both countries, shirt
Production is relatively more labor intensive than computer
Production.According to the HeckscherOhlin model,
Malaysia will have a(n) ________ advantage in the
Production of __________.
A)absolute; shirts and computers
B)absolute; computers
C)comparative; shirts
D)comparative; computers

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 133 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
Suppose Portugal has 700 workers and 26,000 units of
Capital, and France has 18,000 workers and 700 units of
Capital.Technology is identical in both countries.Assume
That wine is the capitalintensive good and cloth is the
Laborintensive good.Which of the following statements is
CORRECT if the nations start trading with each other?
A)Wages will increase in Portugal.
B)Rental rates in France will increase.
C)Wages in France will decrease.
D)Rental rates in Portugal will increase.
Capital, and France has 18,000 workers and 700 units of
Capital.Technology is identical in both countries.Assume
That wine is the capitalintensive good and cloth is the
Laborintensive good.Which of the following statements is
CORRECT if the nations start trading with each other?
A)Wages will increase in Portugal.
B)Rental rates in France will increase.
C)Wages in France will decrease.
D)Rental rates in Portugal will increase.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 133 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
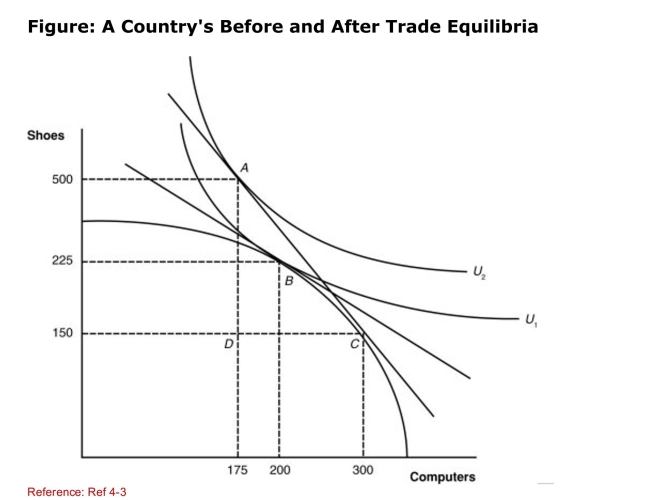 (Figure: A Country's Before and After Trade Equilibria) What
(Figure: A Country's Before and After Trade Equilibria) WhatIs the equilibrium posttrade point of production of this
Nation?
A)A
B)B
C)C
D)D

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 133 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
Figure: A Country's Before and After Trade Equilibria 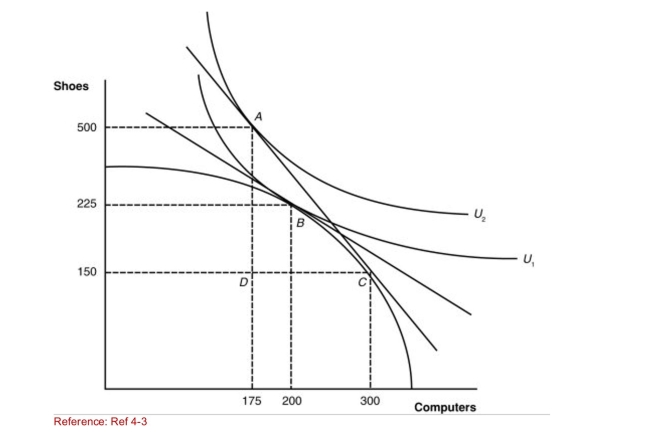 (Figure: A Country's Before and After Trade Equilibria) At
(Figure: A Country's Before and After Trade Equilibria) At
What point will this nation be in a notrade equilibrium?
A)A
B)B
C)C
D)D
 (Figure: A Country's Before and After Trade Equilibria) At
(Figure: A Country's Before and After Trade Equilibria) AtWhat point will this nation be in a notrade equilibrium?
A)A
B)B
C)C
D)D

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 133 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
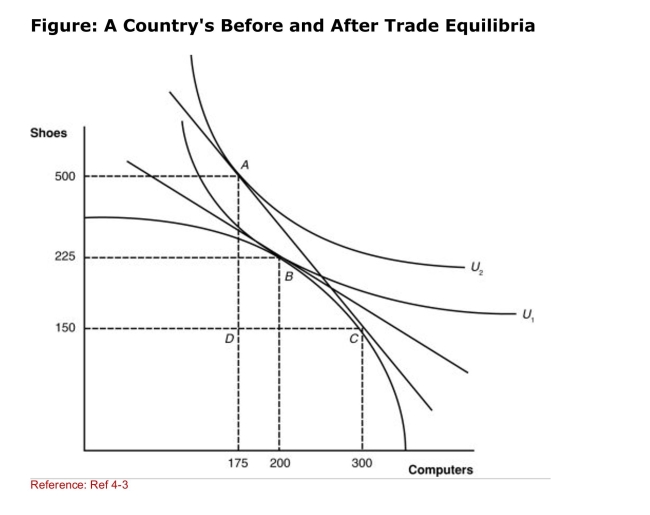 (Figure: A Country's Before and After Trade Equilibria) How
(Figure: A Country's Before and After Trade Equilibria) HowMany shoes will this nation import?
A)0
B)125
C)350
D)500

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 133 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
Figure: A Country's Before and After Trade Equilibria 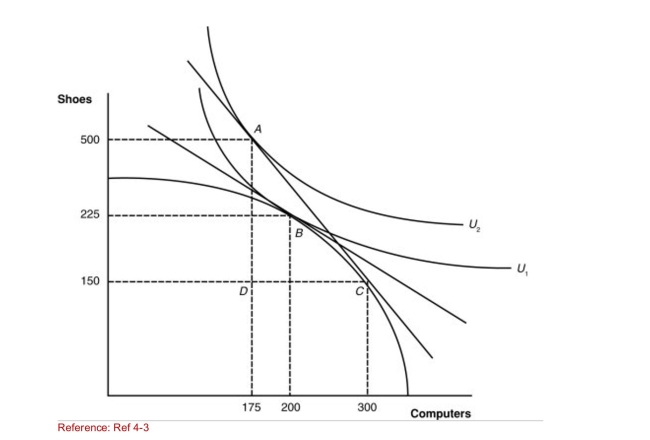 (Figure: A Country's Before and After Trade Equilibria) How
(Figure: A Country's Before and After Trade Equilibria) How
Many shoes will this nation export?
A)0
B)125
C)350
D)500
 (Figure: A Country's Before and After Trade Equilibria) How
(Figure: A Country's Before and After Trade Equilibria) HowMany shoes will this nation export?
A)0
B)125
C)350
D)500

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 133 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
Figure: A Country's Before and After Trade Equilibria 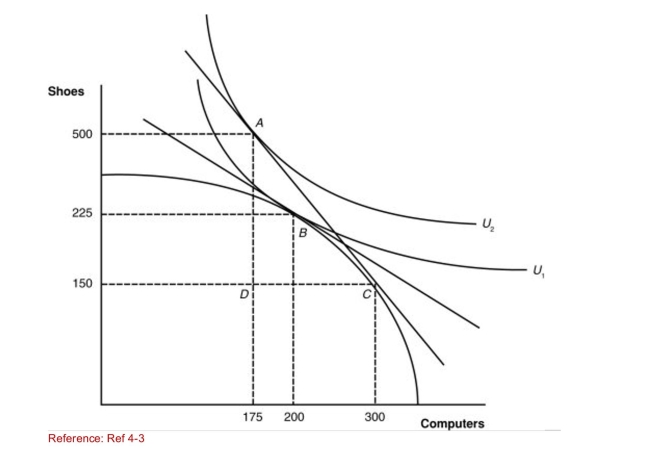 (Figure: A Country's Before and After Trade Equilibria) What
(Figure: A Country's Before and After Trade Equilibria) What
Happened to the relative price of shoes in this nation after
Trade?
A)Shoes became relatively more expensive in terms of computers.
B)Shoes became relatively cheaper in terms of computers.
C)Shoes were not as desirable after trade.
D)The price of shoes did not change-only the quantity.
 (Figure: A Country's Before and After Trade Equilibria) What
(Figure: A Country's Before and After Trade Equilibria) WhatHappened to the relative price of shoes in this nation after
Trade?
A)Shoes became relatively more expensive in terms of computers.
B)Shoes became relatively cheaper in terms of computers.
C)Shoes were not as desirable after trade.
D)The price of shoes did not change-only the quantity.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 133 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
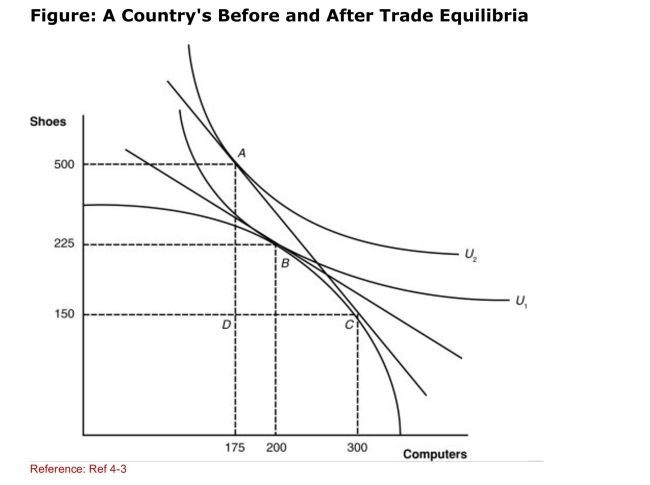 (Figure: A Country's Before and After Trade Equilibria) The
(Figure: A Country's Before and After Trade Equilibria) TheTrade triangle shows the exports that were exchanged for
Imports.What are the three points of the trade triangle?
A)A, B, C
B)A, B, D
C)A, D, C
D)B, C, D

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 133 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
Figure: A Country's Before and After Trade Equilibria 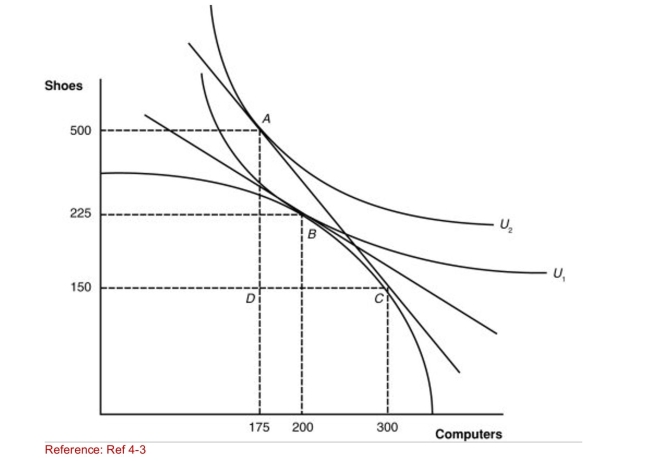 (Figure: A Country's Before and After Trade Equilibria) What
(Figure: A Country's Before and After Trade Equilibria) What
Are the posttrade quantities of shoes and computers
Produced by this nation?
A)300 shoes; 300 computers
B)225 shoes; 175 computers
C)225 shoes; 200 computers
D)150 shoes; 300 computers
 (Figure: A Country's Before and After Trade Equilibria) What
(Figure: A Country's Before and After Trade Equilibria) WhatAre the posttrade quantities of shoes and computers
Produced by this nation?
A)300 shoes; 300 computers
B)225 shoes; 175 computers
C)225 shoes; 200 computers
D)150 shoes; 300 computers

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 133 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
For which of the following does the HeckscherOhlin model
Offer an explanation?
I)gains from trade
II)the pattern of trade.
III)the effects of international trade on the returns to
Mobile resources.
A)I
B)I and II
C)I and III
D)I, II, and III
Offer an explanation?
I)gains from trade
II)the pattern of trade.
III)the effects of international trade on the returns to
Mobile resources.
A)I
B)I and II
C)I and III
D)I, II, and III

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 133 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
Figure: A Country's Before and After Trade Equilibria 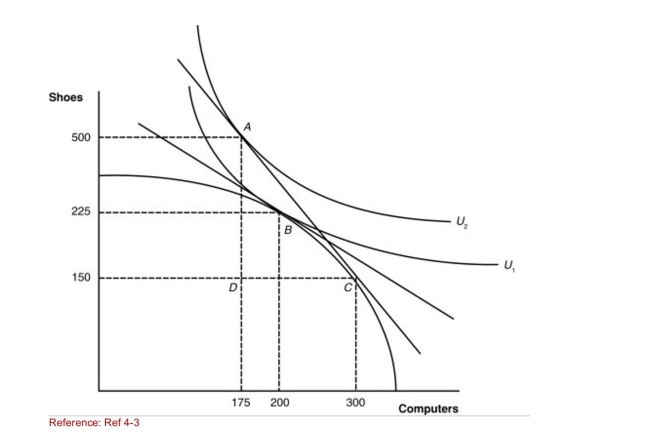 (Figure: A Country's Before and After Trade Equilibria) How
(Figure: A Country's Before and After Trade Equilibria) How
Many computers will this nation import?
A)0
B)125
C)350
D)500
 (Figure: A Country's Before and After Trade Equilibria) How
(Figure: A Country's Before and After Trade Equilibria) HowMany computers will this nation import?
A)0
B)125
C)350
D)500

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 133 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
Suppose Portugal has 700 workers and 26,000 units of
Capital, and France has 18,000 workers and 700 units of
Capital.Technology is identical in both countries.Assume
That wine is the capitalintensive good and cloth is the
Laborintensive good.Which of the following statements is
CORRECT?
A)Portugal will export wine and import cloth.
B)France will export wine and import cloth.
C)There is no basis for trade between France and Portugal.
D)Portugal will export cloth and import wine.
Capital, and France has 18,000 workers and 700 units of
Capital.Technology is identical in both countries.Assume
That wine is the capitalintensive good and cloth is the
Laborintensive good.Which of the following statements is
CORRECT?
A)Portugal will export wine and import cloth.
B)France will export wine and import cloth.
C)There is no basis for trade between France and Portugal.
D)Portugal will export cloth and import wine.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 133 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
Figure: A Country's Before and After Trade Equilibria 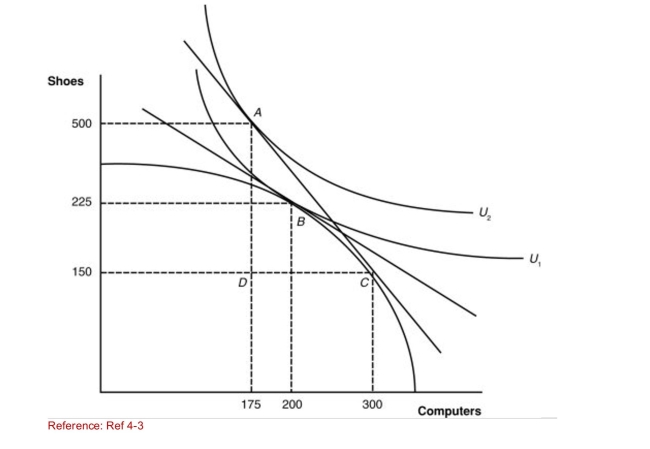 (Figure: A Country's Before and After Trade Equilibria) What
(Figure: A Country's Before and After Trade Equilibria) What
Are the pretrade quantities of shoes and computers
Produced by this nation?
A)300 shoes; 300 computers
B)225 shoes; 175 computers
C)225 shoes; 200 computers
D)150 shoes; 300 computers
 (Figure: A Country's Before and After Trade Equilibria) What
(Figure: A Country's Before and After Trade Equilibria) WhatAre the pretrade quantities of shoes and computers
Produced by this nation?
A)300 shoes; 300 computers
B)225 shoes; 175 computers
C)225 shoes; 200 computers
D)150 shoes; 300 computers

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 133 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
Consider two products, automobiles and shoes.If shoes are
Labor intensive and automobiles are capital intensive, what
Will happen under the HO model?
A)The laborabundant country will export automobiles.
B)The capitalabundant country will export shoes.
C)The laborabundant country will import shoes.
D)The capitalabundant country will import shoes.
Labor intensive and automobiles are capital intensive, what
Will happen under the HO model?
A)The laborabundant country will export automobiles.
B)The capitalabundant country will export shoes.
C)The laborabundant country will import shoes.
D)The capitalabundant country will import shoes.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 133 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
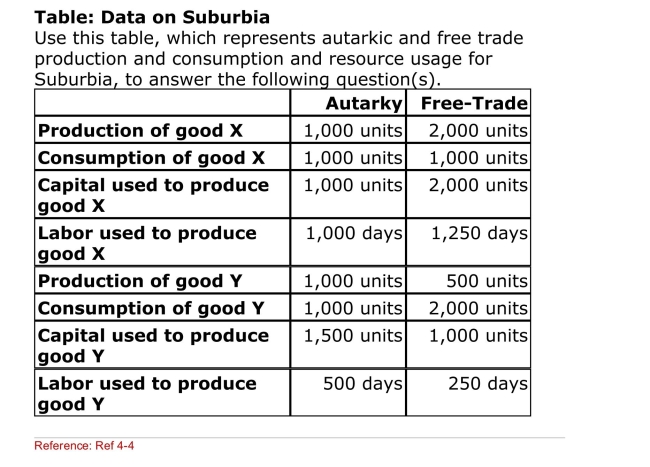 (Table: Data on Suburbia) What is the ratio of total capital
(Table: Data on Suburbia) What is the ratio of total capitalTo total labor in Suburbia?
A)1 unit/day
B)1.5 units/day
C)1.67 units/day
D)3 units/day

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 133 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
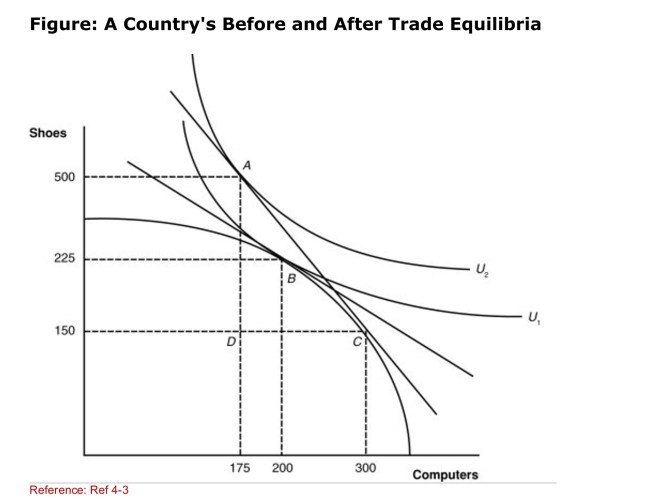 (Figure: A Country's Before and After Trade Equilibria)
(Figure: A Country's Before and After Trade Equilibria)Suppose that the new international relative price of
Computers increases from the pretrade price.If we then
Subtract the number of computers purchased domestically
At the new international price from the number of
Computers produced, we will get one point on
____________ for computers.
A)the import demand schedule
B)the export supply schedule
C)the production possibilities frontier
D)the indifference curve

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 133 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
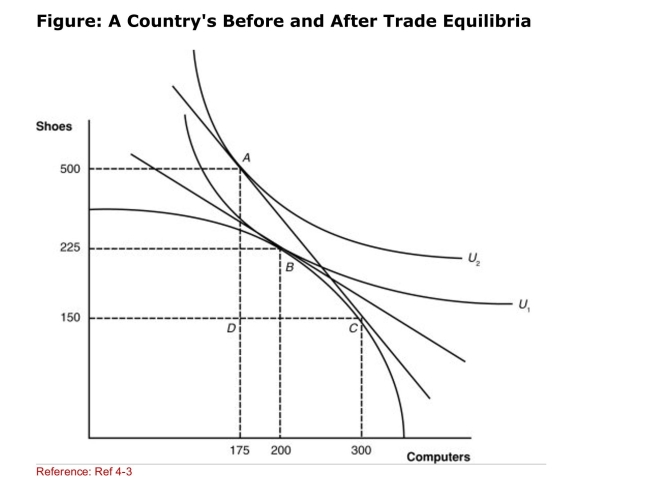 (Figure: A Country's Before and After Trade Equilibria) How
(Figure: A Country's Before and After Trade Equilibria) HowMany computers will this nation export?
A)0
B)125
C)350
D)500

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 133 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
Figure: A Country's Before and After Trade Equilibria 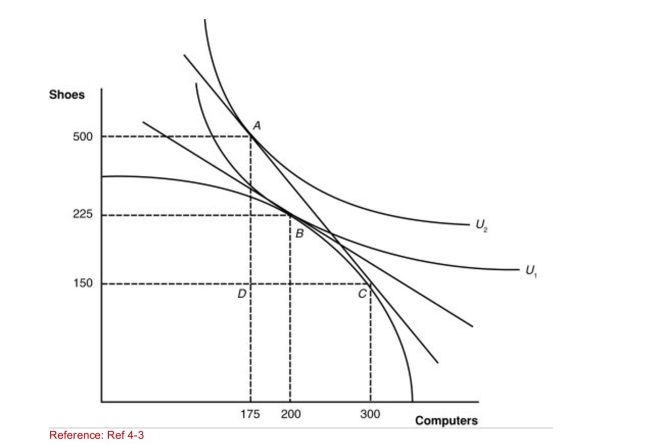 (Figure: A Country's Before and After Trade Equilibria)
(Figure: A Country's Before and After Trade Equilibria)
Suppose that the new international relative price of
Computers increases from the pretrade price.If we then
Subtract the number of shoes produced domestically at the
New international price from the number of shoes consumed
At this price, we will get one point on ____________ for
Shoes.
A)the import demand schedule
B)the export supply schedule
C)the production possibilities frontier
D)the indifference curve
 (Figure: A Country's Before and After Trade Equilibria)
(Figure: A Country's Before and After Trade Equilibria)Suppose that the new international relative price of
Computers increases from the pretrade price.If we then
Subtract the number of shoes produced domestically at the
New international price from the number of shoes consumed
At this price, we will get one point on ____________ for
Shoes.
A)the import demand schedule
B)the export supply schedule
C)the production possibilities frontier
D)the indifference curve

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 133 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
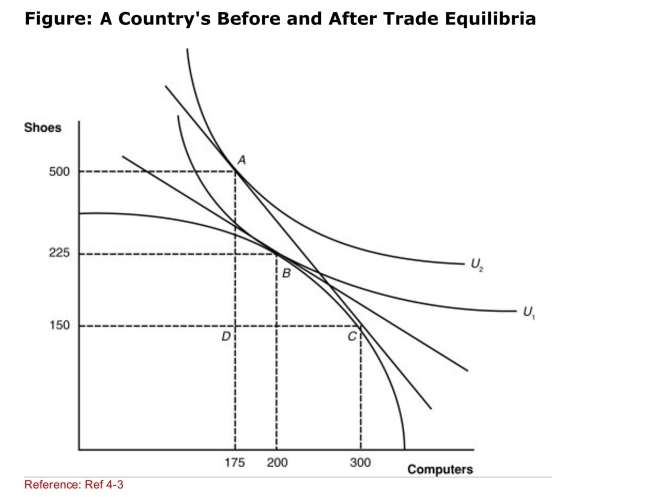 (Figure: A Country's Before and After Trade Equilibria) If
(Figure: A Country's Before and After Trade Equilibria) IfThe new international relative price of computers increases
From its pretrade position, how will the slope of the price
Line change in the graph?
A)The slope will increase.
B)The slope will decrease.
C)The slope will not change but the price line will shift to the right.
D)The slope will not change but the price line will shift to the left.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 133 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
The conclusion that a laborabundant country exports the
Good using labor intensively in production and a capital
Abundant country exports the good using capital intensively
In production is known as:
A)factorintensity reversal.
B)the HeckscherOhlin theorem.
C)Riparian comparative advantage.
D)the StolperSamuelson theorem.
Good using labor intensively in production and a capital
Abundant country exports the good using capital intensively
In production is known as:
A)factorintensity reversal.
B)the HeckscherOhlin theorem.
C)Riparian comparative advantage.
D)the StolperSamuelson theorem.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 133 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
Table: Data on Suburbia
Use this table, which represents autarkic and free trade
Production and consumption and resource usage for
Suburbia, to answer the following question(s).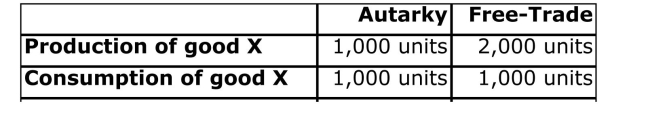
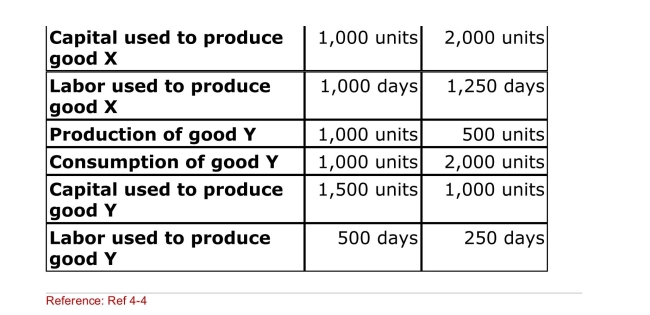
(Table: Data on Suburbia) Which of the following statement
Is CORRECT?
A)Surburbia is a laborintensive country.
B)Suburbia is a laborabundant country.
C)Suburbia is a capitalintensive country.
D)Suburbia is a capitalabundant country.
Use this table, which represents autarkic and free trade
Production and consumption and resource usage for
Suburbia, to answer the following question(s).


(Table: Data on Suburbia) Which of the following statement
Is CORRECT?
A)Surburbia is a laborintensive country.
B)Suburbia is a laborabundant country.
C)Suburbia is a capitalintensive country.
D)Suburbia is a capitalabundant country.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 133 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
In his test of the HO model for the United States, Leontief
Found that :
A)the United States was importing laborintensive commodities.
B)the U.S.capital/labor ratio for imported goods was larger than that for the exported goods.
C)the U.S.capital/labor ratio for imported goods was smaller than that for the exported goods.
D)there was a trade imbalance in the United States.
Found that :
A)the United States was importing laborintensive commodities.
B)the U.S.capital/labor ratio for imported goods was larger than that for the exported goods.
C)the U.S.capital/labor ratio for imported goods was smaller than that for the exported goods.
D)there was a trade imbalance in the United States.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 133 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
Which of the following is NOT an explanation of Leontief's
Paradox?
A)Leontief did not distinguish between highskilled and lowskilled labor.
B)The United States was not engaged in completely free trade in 1947 as the HO assumes.
C)The data from 1947 might be unusual because the war had recently ended.
D)United States' trading partners gave preferential treatment to US exports.
Paradox?
A)Leontief did not distinguish between highskilled and lowskilled labor.
B)The United States was not engaged in completely free trade in 1947 as the HO assumes.
C)The data from 1947 might be unusual because the war had recently ended.
D)United States' trading partners gave preferential treatment to US exports.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 133 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
Leontief discovered a "paradox" in his test of the HOmodel
For the United States.He expected the United States to
Export _____intensive goods and import _____ intensive
Goods; but his study indicated the reverse was TRUE.
A)land; technology
B)labor; land
C)capital; labor
D)labor; capital
For the United States.He expected the United States to
Export _____intensive goods and import _____ intensive
Goods; but his study indicated the reverse was TRUE.
A)land; technology
B)labor; land
C)capital; labor
D)labor; capital

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 133 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
Economist Wassily Leontief tested the HeckscherOhlin
Model to determine whether it correctly predicted the
Capital and labor content of imports and exports of:
A)Russia.
B)China.
C)the United States.
D)Belgium.
Model to determine whether it correctly predicted the
Capital and labor content of imports and exports of:
A)Russia.
B)China.
C)the United States.
D)Belgium.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 133 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
Leontief suggested that his results were not a paradox once
We account for differences in:
A)resource endowments.
B)capital stocks.
C)labor forces.
D)resource productivities.
We account for differences in:
A)resource endowments.
B)capital stocks.
C)labor forces.
D)resource productivities.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 133 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
Leontief found that:
A)U.S.trade increased after World War II.
B)U.S.exports were capital intensive compared with its importcompeting production.
C)U.S.exports were labor intensive compared with its importcompeting production.
D)U.S.exports were neither capital nor labor intensive.
A)U.S.trade increased after World War II.
B)U.S.exports were capital intensive compared with its importcompeting production.
C)U.S.exports were labor intensive compared with its importcompeting production.
D)U.S.exports were neither capital nor labor intensive.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 133 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
Which of the following offers an explanation for the Leontief
Paradox?
I)Leon tief's assumption that U.S.and foreign
Technologies are the same is incorrect.
II)Leontief did not incorporate land a nd other resources.
III)Leontief did not distinguish between skilled and.
Unskilled labor.
A)I, II, and III
B)I and II
C)I and III
D)I
Paradox?
I)Leon tief's assumption that U.S.and foreign
Technologies are the same is incorrect.
II)Leontief did not incorporate land a nd other resources.
III)Leontief did not distinguish between skilled and.
Unskilled labor.
A)I, II, and III
B)I and II
C)I and III
D)I

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 133 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
The Leontief paradox found that:
A)exports should always be capital intensive.
B)imports should always be labor intensive.
C)U.S.exports were labor intensive.
D)U.S.exports were capital intensive.
A)exports should always be capital intensive.
B)imports should always be labor intensive.
C)U.S.exports were labor intensive.
D)U.S.exports were capital intensive.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 133 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
Table: Data on Suburbia
Use this table, which represents autarkic and free trade
Production and consumption and resource usage for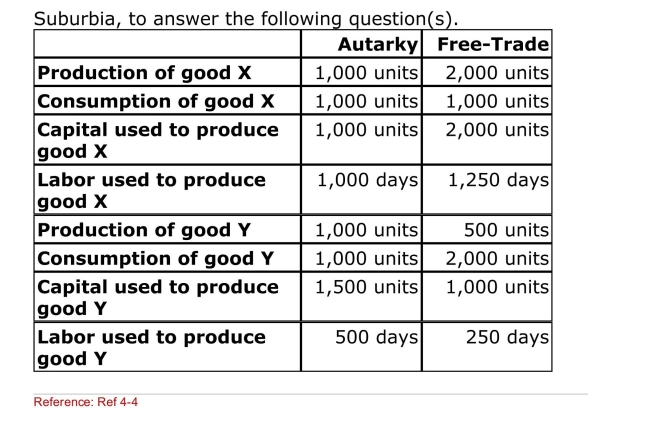
(Table: Data on Suburbia) How many units of which product
Will Suburbia import?
A)2,000 units of X
B)1,000 units of X
C)2,000 units of Y
D)1,500 units of Y
Use this table, which represents autarkic and free trade
Production and consumption and resource usage for

(Table: Data on Suburbia) How many units of which product
Will Suburbia import?
A)2,000 units of X
B)1,000 units of X
C)2,000 units of Y
D)1,500 units of Y

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 133 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
 (Table: Factor Use in Trade) In the hypothetical economy
(Table: Factor Use in Trade) In the hypothetical economyProvided in the table, what is the capitaltolabor ratio for
Exports?
A)$1,849
B)$35,500
C)$18,490
D)$1,920

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 133 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
Leontief's study of U.S.postWorld War II trade concluded
That the:
A)United States did not gain from trade.
B)United States exported laborintensive goods
C)HO model did not explain trade between Europe and the United States.
D)United States exported capitalintensive goods.
That the:
A)United States did not gain from trade.
B)United States exported laborintensive goods
C)HO model did not explain trade between Europe and the United States.
D)United States exported capitalintensive goods.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 133 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72
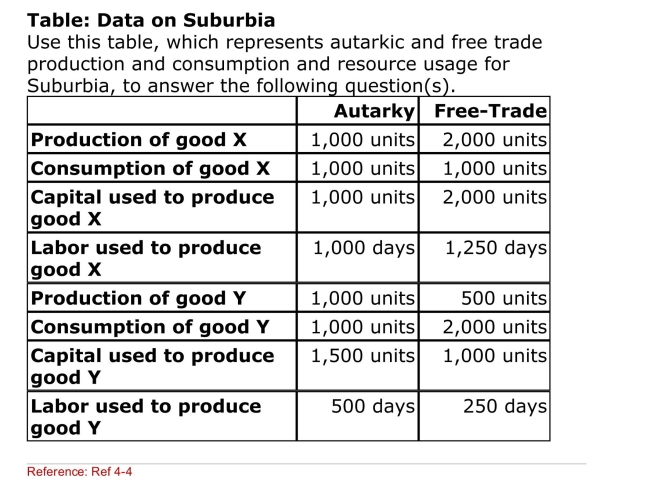 (Table: Data on Suburbia) Which of the following
(Table: Data on Suburbia) Which of the followingStatements is TRUE regarding the change in the marginal
Product of labor as Suburbia moved from autarky to a free
Trade situation?
A)The MPL in good X production rose.
B)The MPL in good Y production fell.
C)The MPL in good X and good Y production both rose
D)The MPL in good X and good Y production both fell.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 133 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73
Which of the following countries had the MOST illiterate
Labor in 2010?
A)the United States
B)China
C)Japan
D)India
Labor in 2010?
A)the United States
B)China
C)Japan
D)India

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 133 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
74
Compared with the rest of the world in 2010, the United
States was MOST abundant in:
A)capital.
B)skilled labor.
C)lessskilled labor.
D)arable land.
States was MOST abundant in:
A)capital.
B)skilled labor.
C)lessskilled labor.
D)arable land.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 133 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
75
Which of the following countries has the MOST physical
Capital?
A)the United States
B)China
C)Japan
D)India
Capital?
A)the United States
B)China
C)Japan
D)India

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 133 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
76
What was "paradoxical" about Leontief's test of the HO
Model on U.S.trade?
A)Leontief concluded that U.S.imports were more labor intensive than U.S.exports.
B)Leontief concluded that U.S.imports were more capital intensive than U.S.exports.
C)Leontief concluded that U.S.imports were primarily agricultural products.
D)Leontief concluded that U.S.exports were not internationally competitive.
Model on U.S.trade?
A)Leontief concluded that U.S.imports were more labor intensive than U.S.exports.
B)Leontief concluded that U.S.imports were more capital intensive than U.S.exports.
C)Leontief concluded that U.S.imports were primarily agricultural products.
D)Leontief concluded that U.S.exports were not internationally competitive.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 133 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
77
Which of the following statements is NOT an explanation of
Leontief's paradox?
A)Leontief ignored the fact that the United States imports a variety of products rather than just one.
B)He ignored the fact that U.S.labor is highly skilled.
C)He ignored the importance of land as a factor in many U.S.exports.
D)Trade patterns in 1947 might have been affected by the fact that World War II had ended only two years earlier.
Leontief's paradox?
A)Leontief ignored the fact that the United States imports a variety of products rather than just one.
B)He ignored the fact that U.S.labor is highly skilled.
C)He ignored the importance of land as a factor in many U.S.exports.
D)Trade patterns in 1947 might have been affected by the fact that World War II had ended only two years earlier.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 133 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
78
Which of the following countries had the MOST R&D
Scientists in 2010?
A)the United States
B)China
C)Japan
D)India
Scientists in 2010?
A)the United States
B)China
C)Japan
D)India

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 133 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
79
 (Table: Factor Use in Trade) In the hypothetical economy
(Table: Factor Use in Trade) In the hypothetical economyProvided in the table, what is the capitaltolabor ratio for
Imports?
A)$31,250
B)$21,500
C)$1,600
D)$3,125

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 133 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
80
The Leontief paradox questioned the validity of:
A)the comparative advantage model.
B)the HeckscherOhlin model.
C)the Riparian model.
D)the specificfactors model.
A)the comparative advantage model.
B)the HeckscherOhlin model.
C)the Riparian model.
D)the specificfactors model.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 133 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



