Deck 20: Enzymes and Vitamins
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/68
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 20: Enzymes and Vitamins
1
When a substrate binds to an enzyme for reaction, it binds to the
A)primary site.
B)allosteric site.
C)end pocket.
D)primary pocket.
E)active site.
A)primary site.
B)allosteric site.
C)end pocket.
D)primary pocket.
E)active site.
active site.
2
The general function of an enzyme in the body is to
A)eliminate waste products from the blood.
B)catalyze chemical reactions.
C)maintain a neutral pH.
D)act as a reactant in carbohydrate storage.
E)maintain homeostasis.
A)eliminate waste products from the blood.
B)catalyze chemical reactions.
C)maintain a neutral pH.
D)act as a reactant in carbohydrate storage.
E)maintain homeostasis.
catalyze chemical reactions.
3
Most enzymes are
A)not proteins.
B)much larger than the substrate.
C)substrate proteins.
D)fluid-mosaic proteins.
E)induced proteins.
A)not proteins.
B)much larger than the substrate.
C)substrate proteins.
D)fluid-mosaic proteins.
E)induced proteins.
much larger than the substrate.
4
Urease catalyzes only the hydrolysis of urea, and no other substrates. This limited activity is called
A)noncompetitive specificity.
B)absolute specificity.
C)extreme specificity.
D)hyperspecificity.
E)rigid specificity.
A)noncompetitive specificity.
B)absolute specificity.
C)extreme specificity.
D)hyperspecificity.
E)rigid specificity.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 68 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
To what main class of enzymes does the enzyme that catalyzes the following reaction belong? 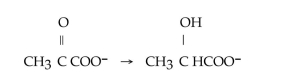
A)isomerase
B)hydrolase
C)oxidoreductase
D)transferase
E)lyase
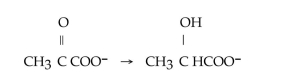
A)isomerase
B)hydrolase
C)oxidoreductase
D)transferase
E)lyase

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 68 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
In the lock-and-key model of enzyme action, the enzyme active site is thought of as
A)an area of the enzyme that can adjust to fit the substrate shape.
B)a lock that bars a noncompetitive inhibitor from reacting.
C)a hydrophilic area on the enzyme surface.
D)a rigid, nonflexible shape that fits the substrate exactly.
E)a key-like shape that fits into a pocket of the substrate surface.
A)an area of the enzyme that can adjust to fit the substrate shape.
B)a lock that bars a noncompetitive inhibitor from reacting.
C)a hydrophilic area on the enzyme surface.
D)a rigid, nonflexible shape that fits the substrate exactly.
E)a key-like shape that fits into a pocket of the substrate surface.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 68 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
To what main class of enzymes does the enzyme that catalyzes the following reaction belong? 
A)transferase
B)isomerase
C)oxidoreductase
D)hydrolase
E)lyase
A)transferase
B)isomerase
C)oxidoreductase
D)hydrolase
E)lyase

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 68 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
The hydrolysis of ester bonds in triglycerides is catalyzed by a(n)
A)lipase.
B)transferase.
C)isomerase.
D)lyase.
E)oxidoreductase.
A)lipase.
B)transferase.
C)isomerase.
D)lyase.
E)oxidoreductase.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 68 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
Substrates are usually bond to the active site of an enzyme by
A)pH changes.
B)ester bonds.
C)the side chains of amino acids in the enzyme protein.
D)competitive inhibition.
E)peptide bonds.
A)pH changes.
B)ester bonds.
C)the side chains of amino acids in the enzyme protein.
D)competitive inhibition.
E)peptide bonds.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 68 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
The active site of an enzyme
A)is where the substrate is held as the reaction takes place.
B)increases the energy of reaction.
C)is remote from the site of substrate attachment.
D)is converted to a product.
E)includes the entire enzyme.
A)is where the substrate is held as the reaction takes place.
B)increases the energy of reaction.
C)is remote from the site of substrate attachment.
D)is converted to a product.
E)includes the entire enzyme.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 68 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
In the induced-fit model of enzyme action, the enzyme active site
A)stays the same shape while causing a change in the shape of the substrate.
B)uses a cofactor to change the shape of a substrate.
C)adjusts shape to adapt to the shape of the substrate.
D)stays the same shape during substrate binding.
E)uses an inhibitor to adjust its shape for the substrate.
A)stays the same shape while causing a change in the shape of the substrate.
B)uses a cofactor to change the shape of a substrate.
C)adjusts shape to adapt to the shape of the substrate.
D)stays the same shape during substrate binding.
E)uses an inhibitor to adjust its shape for the substrate.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 68 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
The presence of enzymes to catalyze bioreactions in our bodies allows
A)bioreactions to occur under extreme conditions of temperature and pH.
B)the rate of a desired chemical reaction to slow down.
C)bioreactions to take place under mild conditions.
D)the activation energy of a reaction to be raised.
E)us to eat non-nutritious substances without consequence.
A)bioreactions to occur under extreme conditions of temperature and pH.
B)the rate of a desired chemical reaction to slow down.
C)bioreactions to take place under mild conditions.
D)the activation energy of a reaction to be raised.
E)us to eat non-nutritious substances without consequence.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 68 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
Compared to an uncatalyzed reaction, an enzyme-catalyzed reaction
A)occurs at a faster rate.
B)uses less substrate.
C)requires more energy.
D)requires a higher temperature.
E)produces different products.
A)occurs at a faster rate.
B)uses less substrate.
C)requires more energy.
D)requires a higher temperature.
E)produces different products.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 68 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
The function of the enzyme-substrate complex is to provide an alternative reaction pathway that
A)changes the concentration of the substrate.
B)lowers the energy of the products.
C)changes the possible product formed.
D)decreases the activation energy for the reaction.
E)lowers the energy of the substrate.
A)changes the concentration of the substrate.
B)lowers the energy of the products.
C)changes the possible product formed.
D)decreases the activation energy for the reaction.
E)lowers the energy of the substrate.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 68 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
The formation of an enzyme-substrate complex is the ________ step in enzyme action.
A)first
B)second
C)third
D)fourth
E)last
A)first
B)second
C)third
D)fourth
E)last

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 68 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
In any reaction catalyzed by an enzyme, the reacting molecule is called the
A)substrate.
B)coenzyme.
C)isozyme.
D)allostere.
E)cofactor.
A)substrate.
B)coenzyme.
C)isozyme.
D)allostere.
E)cofactor.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 68 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
Hexokinase catalyzes only the addition of phosphate to any hexose sugar. This type of activity is called
A)general specificity.
B)noncompetitive specificity.
C)group specificity.
D)collateral specificity.
E)regional specificity.
A)general specificity.
B)noncompetitive specificity.
C)group specificity.
D)collateral specificity.
E)regional specificity.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 68 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
Which of the following is NOT a step in the enzyme-catalyzed conversion of a substrate to product?
A)A new substrate molecule binds to the enzyme for a new cycle.
B)The product is released from the active site.
C)The substrate binds in the active site to form the E-S complex.
D)The enzyme assists in the conversion of the substrate to product.
E)The substrate binds to the enzyme away from the active site.
A)A new substrate molecule binds to the enzyme for a new cycle.
B)The product is released from the active site.
C)The substrate binds in the active site to form the E-S complex.
D)The enzyme assists in the conversion of the substrate to product.
E)The substrate binds to the enzyme away from the active site.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 68 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
To what main class of enzymes does the enzyme that catalyzes the conversion of lactose to galactose and glucose belong?
A)isomerase
B)transferase
C)lyase
D)hydrolase
E)oxidoreductase
A)isomerase
B)transferase
C)lyase
D)hydrolase
E)oxidoreductase

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 68 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
How many steps are there in the reaction of an enzyme (E)with a substrate (S)to form and release the product (P)?
A)one
B)two
C)three
D)four
E)five
A)one
B)two
C)three
D)four
E)five

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 68 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
An irreversible inhibitor is one that
A)binds to the enzyme with hydrophobic interactions.
B)binds covalently to the enzyme active site.
C)reacts covalently with a cofactor.
D)reacts covalently with the substrate.
E)forms hydrogen bonds with the substrate.
A)binds to the enzyme with hydrophobic interactions.
B)binds covalently to the enzyme active site.
C)reacts covalently with a cofactor.
D)reacts covalently with the substrate.
E)forms hydrogen bonds with the substrate.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 68 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
An increase in concentration of the enzyme LDH1 in the blood can be used to detect
A)anemia.
B)bulimia.
C)heart attack.
D)uremia.
E)kidney damage.
A)anemia.
B)bulimia.
C)heart attack.
D)uremia.
E)kidney damage.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 68 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
Which of the following is NOT true for a competitive inhibitor?
A)It occupies the active site.
B)It binds to the enzyme at a site remote from the active site.
C)It has a structure similar to the substrate.
D)It cannot be converted to products.
A)It occupies the active site.
B)It binds to the enzyme at a site remote from the active site.
C)It has a structure similar to the substrate.
D)It cannot be converted to products.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 68 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
Pepsinogen is an example of a(n)
A)allosteric enzyme.
B)isoenzyme.
C)coenzyme.
D)cofactor.
E)zymogen.
A)allosteric enzyme.
B)isoenzyme.
C)coenzyme.
D)cofactor.
E)zymogen.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 68 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
The optimum temperature for sucrase activity is 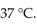 The hydrolysis of sucrose is slowest at which temperature in the choices below?
The hydrolysis of sucrose is slowest at which temperature in the choices below?
A)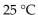
B)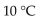
C)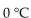
D)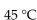
E)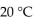
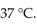 The hydrolysis of sucrose is slowest at which temperature in the choices below?
The hydrolysis of sucrose is slowest at which temperature in the choices below?A)
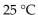
B)
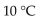
C)
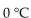
D)
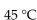
E)
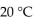

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 68 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
Urea is converted to ammonia and carbon dioxide by the action of urease. What will be the effect on the rate if the temperature of the reaction is lowered from 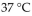 (the optimum temperature) to
(the optimum temperature) to 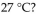
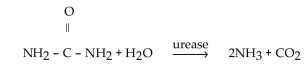
A)There will be no effect.
B)The rate will double.
C)The rate will triple.
D)The rate will slow down.
E)The rate will slow down, then speed up again.
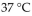 (the optimum temperature) to
(the optimum temperature) to 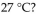
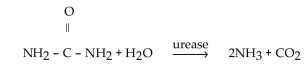
A)There will be no effect.
B)The rate will double.
C)The rate will triple.
D)The rate will slow down.
E)The rate will slow down, then speed up again.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 68 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
When an end product from an enzyme-mediated sequence is also an inhibitor for an earlier step in the reaction sequence, the process is referred to as
A)feedback control.
B)concentration control.
C)negative catalysis.
D)irreversible inhibition.
E)competitive inhibition.
A)feedback control.
B)concentration control.
C)negative catalysis.
D)irreversible inhibition.
E)competitive inhibition.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 68 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
Consider an enzymatic reaction in which the initial concentration of substrate is low. If the amount of enzyme is held constant, but the amount of substrate is increased, the rate of an enzyme catalyzed reaction will
A)stay the same.
B)decrease at first, then increase in a linear fashion.
C)increase in an exponential fashion.
D)be inhibited by the higher concentrations of substrate.
E)increase at first in a linear fashion, then remain at a constant high rate.
A)stay the same.
B)decrease at first, then increase in a linear fashion.
C)increase in an exponential fashion.
D)be inhibited by the higher concentrations of substrate.
E)increase at first in a linear fashion, then remain at a constant high rate.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 68 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
"Physiological conditions" for reactions within the body are approximately
A)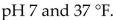
B)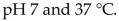
C) pH 7 and 273 K.
D)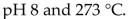
E)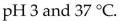
A)
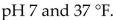
B)
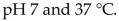
C) pH 7 and 273 K.
D)
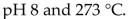
E)
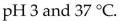

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 68 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
"Physiological pH," the pH for optimum activity for most enzymes, is a pH equal to
A)5.4.
B)8.6.
C)7.4.
D)3.0.
E)9.0.
A)5.4.
B)8.6.
C)7.4.
D)3.0.
E)9.0.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 68 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
The creatine kinase 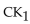 can be used in the diagnosis of
can be used in the diagnosis of
A) hepatitis.
B) cancer.
C) prostatitis.
D) heart attack.
E) rickets.
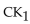 can be used in the diagnosis of
can be used in the diagnosis ofA) hepatitis.
B) cancer.
C) prostatitis.
D) heart attack.
E) rickets.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 68 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
A competitive inhibitor is one that
A)binds to the enzyme at a site far from the active site.
B)forms a complex with the substrate.
C)destroys the substrate.
D)binds to the active site in place of the substrate.
E)binds to the allosteric site on an enzyme.
A)binds to the enzyme at a site far from the active site.
B)forms a complex with the substrate.
C)destroys the substrate.
D)binds to the active site in place of the substrate.
E)binds to the allosteric site on an enzyme.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 68 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
Most enzymes are deactivated permanently above a temperature of about
A)25 °C.
B)40 °C.
C)45 °F.
D)37 °F.
E)50 °C.
A)25 °C.
B)40 °C.
C)45 °F.
D)37 °F.
E)50 °C.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 68 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
Some insecticides kill insects by inhibiting the enzyme
A)penicillinase.
B)lipase.
C)acetylcholinesterase.
D)creatine kinase.
E)alcohol dehydrogenase.
A)penicillinase.
B)lipase.
C)acetylcholinesterase.
D)creatine kinase.
E)alcohol dehydrogenase.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 68 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
A compound that binds to the enzyme at a site other than the active site, and changes its shape so that a substrate cannot enter the active site, is called a(n)
A)proenzyme.
B)irreversible inhibitor.
C)competitive inhibitor.
D)noncompetitive inhibitor.
E)cofactor.
A)proenzyme.
B)irreversible inhibitor.
C)competitive inhibitor.
D)noncompetitive inhibitor.
E)cofactor.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 68 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
Penicillin functions as an antibiotic by
A)acting as an acetylcholinesterase inhibitor.
B)poisoning bacteria with toxins.
C)inhibiting the enzymes for cell wall formation in bacteria.
D)bonding to metal ions in bacterial electron transport systems.
E)raising the temperature of a bacterium.
A)acting as an acetylcholinesterase inhibitor.
B)poisoning bacteria with toxins.
C)inhibiting the enzymes for cell wall formation in bacteria.
D)bonding to metal ions in bacterial electron transport systems.
E)raising the temperature of a bacterium.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 68 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
A noncompetitive inhibitor has a structure that
A)resembles the active site of the enzyme.
B)does not resemble the substrate structure.
C)does not interfere with the enzyme-substrate complex formation.
D)causes a change in the shape of the substrate.
E)can bind to the active site of the enzyme.
A)resembles the active site of the enzyme.
B)does not resemble the substrate structure.
C)does not interfere with the enzyme-substrate complex formation.
D)causes a change in the shape of the substrate.
E)can bind to the active site of the enzyme.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 68 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
Penicillin-resistant bacteria can survive treatment with penicillin because they produce the enzyme
A)penicillinase.
B)penicillin kinase.
C)phosphate lyase.
D)sucrase.
E)bacteriase.
A)penicillinase.
B)penicillin kinase.
C)phosphate lyase.
D)sucrase.
E)bacteriase.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 68 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
In an enzyme-substrate reaction, when excess substrate is present, increasing the concentration of the enzyme will
A)inhibit the formation of products.
B)increase the decomposition rate of the enzyme-substrate complex.
C)increase the amount of reaction occurring.
D)decrease the turnover rate for the substrate.
E)increase the number of substrate molecules available.
A)inhibit the formation of products.
B)increase the decomposition rate of the enzyme-substrate complex.
C)increase the amount of reaction occurring.
D)decrease the turnover rate for the substrate.
E)increase the number of substrate molecules available.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 68 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
Allosteric enzymes can control the output of product by
A)binding an irreversible inhibitor at the active site.
B)binding a positive or negative regulator at a noncompetitive site.
C)reversible inhibition using the product as the inhibitor.
D)changing the pH in the active site.
E)binding the substrate at a site away from the active site.
A)binding an irreversible inhibitor at the active site.
B)binding a positive or negative regulator at a noncompetitive site.
C)reversible inhibition using the product as the inhibitor.
D)changing the pH in the active site.
E)binding the substrate at a site away from the active site.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 68 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
When a cofactor is a small organic molecule, it is known as a(n)
A)isoenzyme.
B)regulator.
C)vitamin.
D)zymogen.
E)coenzyme.
A)isoenzyme.
B)regulator.
C)vitamin.
D)zymogen.
E)coenzyme.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 68 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
Indicate whether each of the following is fat soluble or water soluble.
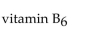
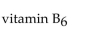

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 68 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
An enzyme that removes H from a substrate is classified as a(n)________.
A)lyase
B)isomerase
C)hydrolase
D)transferase
E)oxidoreductase
A)lyase
B)isomerase
C)hydrolase
D)transferase
E)oxidoreductase

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 68 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
The names of many enzymes can be recognized by the suffix ________.
A)-ite
B)-ine
C)-ose
D)-ate
E)-ase
A)-ite
B)-ine
C)-ose
D)-ate
E)-ase

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 68 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
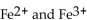 ions are used in the functioning of
ions are used in the functioning ofA) urease.
B) pepsin.
C) creatine kinase.
D) alcohol dehydrogenase.
E) the cytochrome oxidase system.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 68 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
The full name of the enzyme LDH is ________.
A)lactate dehydrogenase
B)liver decompensation hexase
C)liver dihydrogen kinase
D)lipase dehydrogenase
E)lactate dehydrase
A)lactate dehydrogenase
B)liver decompensation hexase
C)liver dihydrogen kinase
D)lipase dehydrogenase
E)lactate dehydrase

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 68 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
A diet very low in vitamin C can lead over time to the condition ________.
A)scurvy
B)carpal tunnel syndrome
C)cancer
D)anorexia nervosa
E)rickets
A)scurvy
B)carpal tunnel syndrome
C)cancer
D)anorexia nervosa
E)rickets

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 68 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
The optimum pH for the activity of trypsin is about ________.
A)4.0
B)6.5
C)7.4
D)8.0
E)2.0
A)4.0
B)6.5
C)7.4
D)8.0
E)2.0

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 68 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
One deficiency disease that can be traced to insufficient intake of vitamin D is ________.
A)pernicious anemia
B)rickets
C)beriberi
D)scurvy
E)pellagra
A)pernicious anemia
B)rickets
C)beriberi
D)scurvy
E)pellagra

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 68 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
A noncompetitive inhibitor
A)binds at the active site of the enzyme.
B)alters the three-dimensional structure of the enzyme.
C)has its effect reversed by adding more substrate.
D)has a structure similar to the substrate.
E)increases the rate of the enzyme-catalyzed reaction.
A)binds at the active site of the enzyme.
B)alters the three-dimensional structure of the enzyme.
C)has its effect reversed by adding more substrate.
D)has a structure similar to the substrate.
E)increases the rate of the enzyme-catalyzed reaction.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 68 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
The water-soluble B and C vitamins supply
A)essential fatty acids.
B)essential amino acids.
C)coenzymes required by some enzymes.
D)competitive inhibitors needed to regulate enzyme activity.
E)substrates necessary for most of the reactions in the body.
A)essential fatty acids.
B)essential amino acids.
C)coenzymes required by some enzymes.
D)competitive inhibitors needed to regulate enzyme activity.
E)substrates necessary for most of the reactions in the body.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 68 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
Vitamin D is an example of a(n)
A)must be obtained from the diet daily.
B)fat soluble vitamin.
C)water-soluble vitamin.
D)essential mineral.
E)essential amino acid.
A)must be obtained from the diet daily.
B)fat soluble vitamin.
C)water-soluble vitamin.
D)essential mineral.
E)essential amino acid.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 68 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
An enzyme that converts a cis double bond to a trans double bond is classified as a(n)________.
A)lyase
B)transferase
C)hydrolase
D)isomerase
E)oxidoreductase
A)lyase
B)transferase
C)hydrolase
D)isomerase
E)oxidoreductase

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 68 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
Another name for a zymogen is a(n)________.
A)prosthetic group
B)proenzyme
C)isozyme
D)cofactor
E)coenzyme
A)prosthetic group
B)proenzyme
C)isozyme
D)cofactor
E)coenzyme

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 68 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
Indicate whether each of the following is fat soluble or water soluble.
vitamin A
vitamin A

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 68 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
A biological catalyst is called a(n)________.
A)cofactor
B)enzyme
C)lipid
D)substrate
E)coenzyme
A)cofactor
B)enzyme
C)lipid
D)substrate
E)coenzyme

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 68 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
Coenzymes such as water-soluble vitamins are needed in only small amounts because
A)they can be stored in the liver for future use.
B)only small amounts of enzymes are present in each cell.
C)they can be eliminated in the urine.
D)each vitamin molecule can be reused many times as a cofactor.
E)only small amounts of substrates are available at any one time.
A)they can be stored in the liver for future use.
B)only small amounts of enzymes are present in each cell.
C)they can be eliminated in the urine.
D)each vitamin molecule can be reused many times as a cofactor.
E)only small amounts of substrates are available at any one time.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 68 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
The optimum pH for the activity of pepsin is about ________.
A)6.5
B)7.4
C)7.6
D)4.0
E)2.0
A)6.5
B)7.4
C)7.6
D)4.0
E)2.0

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 68 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
Enzymes that catalyze the same reactions but have slightly different structures are called ________.
A)noncompetitive
B)competitive
C)cofactors
D)isoenzymes
E)coenzymes
A)noncompetitive
B)competitive
C)cofactors
D)isoenzymes
E)coenzymes

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 68 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
The B vitamins are examples of
A)water-soluble vitamins.
B)essential minerals.
C)vitamins that are stored in the liver.
D)essential amino acids.
E)fat soluble vitamins.
A)water-soluble vitamins.
B)essential minerals.
C)vitamins that are stored in the liver.
D)essential amino acids.
E)fat soluble vitamins.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 68 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
Indicate whether each of the following is fat soluble or water soluble.
pantothenic acid
pantothenic acid

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 68 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
Indicate whether each of the following is fat soluble or water soluble.
ascorbic acid
ascorbic acid

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 68 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
Indicate whether each of the following is fat soluble or water soluble.
folic acid
folic acid

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 68 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
Indicate whether each of the following is fat soluble or water soluble.
vitamin D
vitamin D

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 68 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
Indicate whether each of the following is fat soluble or water soluble.
riboflavin
riboflavin

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 68 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
Indicate whether each of the following is fat soluble or water soluble.
vitamin K
vitamin K

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 68 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
Indicate whether each of the following is fat soluble or water soluble.
niacin
niacin

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 68 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
Indicate whether each of the following is fat soluble or water soluble.
vitamin E
vitamin E

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 68 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



