Deck 10: Reaction Rates and Chemical Equilibrium
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/52
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 10: Reaction Rates and Chemical Equilibrium
1
For the following reaction, the equilibrium concentration of 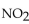 is 0.38 M and equilibrium concentration of
is 0.38 M and equilibrium concentration of 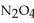 is 1.0 M. What is the value of the equilibrium constant?
is 1.0 M. What is the value of the equilibrium constant?
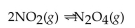
A) 1.0
B) 0.14
C) 2.6
D) 0.38
E) 6.9
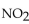 is 0.38 M and equilibrium concentration of
is 0.38 M and equilibrium concentration of 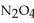 is 1.0 M. What is the value of the equilibrium constant?
is 1.0 M. What is the value of the equilibrium constant?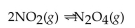
A) 1.0
B) 0.14
C) 2.6
D) 0.38
E) 6.9
6.9
2
A catalyst is
A)a reactant in a chemical reaction.
B)a substance that increases the energy of the products.
C)a product in a chemical reaction.
D)a substance that speeds up a reaction without being consumed in the reaction.
E)a substance that decreases the energy of the products.
A)a reactant in a chemical reaction.
B)a substance that increases the energy of the products.
C)a product in a chemical reaction.
D)a substance that speeds up a reaction without being consumed in the reaction.
E)a substance that decreases the energy of the products.
a substance that speeds up a reaction without being consumed in the reaction.
3
A chemical reaction has reached equilibrium when
A)all reactants have been converted to products.
B)all products have been removed from the reaction mixture.
C)the catalyst has been used up.
D)the rate of the forward reaction equals the rate of the reverse reaction.
E)the concentrations of reactants and products are equal.
A)all reactants have been converted to products.
B)all products have been removed from the reaction mixture.
C)the catalyst has been used up.
D)the rate of the forward reaction equals the rate of the reverse reaction.
E)the concentrations of reactants and products are equal.
the rate of the forward reaction equals the rate of the reverse reaction.
4
The rate of any chemical reaction can be determined by observing
A)the amount of product formed in a unit of time.
B)the number of chemical bonds broken and formed.
C)the ratio of product concentration to reactant concentration.
D)the theoretical yield of the reaction.
E)the percent composition of the final product.
A)the amount of product formed in a unit of time.
B)the number of chemical bonds broken and formed.
C)the ratio of product concentration to reactant concentration.
D)the theoretical yield of the reaction.
E)the percent composition of the final product.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 52 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
The reaction for the decomposition of 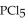 to chlorine and
to chlorine and 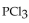 is shown below.
is shown below.
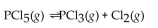
If the equilibrium concentrations are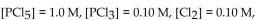
what is the value of the equilibrium constant?
A)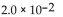
B)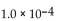
C)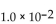
D)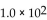
E)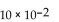
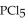 to chlorine and
to chlorine and 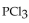 is shown below.
is shown below.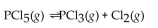
If the equilibrium concentrations are
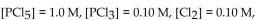
what is the value of the equilibrium constant?
A)
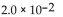
B)
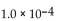
C)
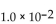
D)
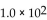
E)
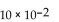

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 52 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
In any chemical reaction, the rate of the reaction can be increased by
A)decreasing the temperature.
B)increasing the concentrations of the reactants.
C)adding water to the reaction.
D)adding product molecules to the reaction mixture.
E)changing the size of the container.
A)decreasing the temperature.
B)increasing the concentrations of the reactants.
C)adding water to the reaction.
D)adding product molecules to the reaction mixture.
E)changing the size of the container.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 52 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
The equilibrium constant for the production of carbon dioxide from carbon monoxide and oxygen is 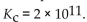
This means that the reaction mixture at equilibrium is likely to consist of
A) mostly starting materials.
B) twice as much product as starting material.
C) an equal mixture of products and reactants.
D) mostly products.
E) twice as much starting material as product.
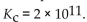
This means that the reaction mixture at equilibrium is likely to consist of
A) mostly starting materials.
B) twice as much product as starting material.
C) an equal mixture of products and reactants.
D) mostly products.
E) twice as much starting material as product.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 52 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
Which of the following equilibrium constants indicates the reaction that gives the smallest amount of product?
A)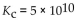
B)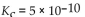
C)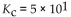
D)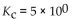
E)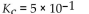
A)
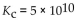
B)
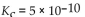
C)
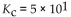
D)
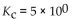
E)
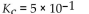

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 52 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
When a reaction is at equilibrium,
A)the products and reactants have the same energy content.
B)no more reactants are converted to products.
C)all reaction stops.
D)the forward and reverse reactions occur at the same rate.
E)the reaction is no longer reversible.
A)the products and reactants have the same energy content.
B)no more reactants are converted to products.
C)all reaction stops.
D)the forward and reverse reactions occur at the same rate.
E)the reaction is no longer reversible.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 52 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
In the following gas phase reaction, Kc is much less than 1. At equilibrium, which of the following statements is true? 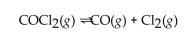
A)The concentration of products is much greater than the concentration of reactants.
B)A catalyst will increase the concentration of products formed.
C)The concentration of reactant is much greater than the concentration of products.
D)The concentrations of products and reactants are approximately equal.
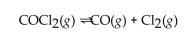
A)The concentration of products is much greater than the concentration of reactants.
B)A catalyst will increase the concentration of products formed.
C)The concentration of reactant is much greater than the concentration of products.
D)The concentrations of products and reactants are approximately equal.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 52 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
Refrigerating perishable foods affects biochemical reactions by
A)improving the appearance of the foods.
B)catalyzing the removal of harmful chemicals from the foods.
C)increasing concentrations of antioxidants.
D)decreasing the rate of reactions affecting spoilage.
E)removing bacteria.
A)improving the appearance of the foods.
B)catalyzing the removal of harmful chemicals from the foods.
C)increasing concentrations of antioxidants.
D)decreasing the rate of reactions affecting spoilage.
E)removing bacteria.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 52 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
The activation energy of a chemical reaction is the energy that
A)is the difference in the energies of the starting materials and products.
B)is needed to initiate the reaction.
C)must be released from the mixture.
D)must be removed from the mixture.
E)activates the catalyst.
A)is the difference in the energies of the starting materials and products.
B)is needed to initiate the reaction.
C)must be released from the mixture.
D)must be removed from the mixture.
E)activates the catalyst.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 52 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
The value of the equilibrium constant for the combination of nitrogen and oxygen to make NO is 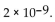
What does this tell you about the concentrations of materials in the equilibrium mixture?
A)The concentration of reactants exceeds the concentration of products.
B)The reactants are solids.
C)The concentration of products exceeds the concentration of reactants.
D)The concentrations of reactants and products are equal.
E)The products are solids.
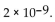
What does this tell you about the concentrations of materials in the equilibrium mixture?
A)The concentration of reactants exceeds the concentration of products.
B)The reactants are solids.
C)The concentration of products exceeds the concentration of reactants.
D)The concentrations of reactants and products are equal.
E)The products are solids.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 52 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
What is the correct form of the equilibrium expression for the reaction of hydrogen and oxygen to form water? The equation is: 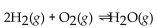
A)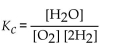
B)
C)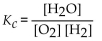
D)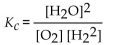
E)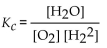
A)
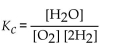
B)

C)
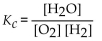
D)
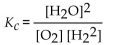
E)
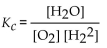

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 52 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
A reaction that can proceed in either the forward or the reverse direction as written is called a ________ reaction.
A)reversible
B)miniscule
C)microscopic
D)favored
E)solid phase
A)reversible
B)miniscule
C)microscopic
D)favored
E)solid phase

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 52 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
The equation for the formation of ammonia from nitrogen and hydrogen is shown below. What is the form of the equilibrium expression?
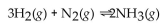
A)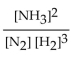
B)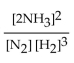
C)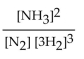
D)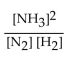
E)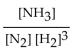
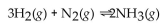
A)
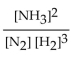
B)
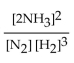
C)
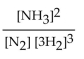
D)
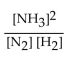
E)
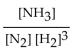

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 52 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
In a catalyzed chemical reaction, one function of a catalyst is to
A)increase the number of successful reactant collisions.
B)increase the temperature at which the reaction is carried out.
C)decrease the concentration of reactants.
D)change the equilibrium concentrations of the products and reactants.
E)increase the energy given off during the reaction.
A)increase the number of successful reactant collisions.
B)increase the temperature at which the reaction is carried out.
C)decrease the concentration of reactants.
D)change the equilibrium concentrations of the products and reactants.
E)increase the energy given off during the reaction.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 52 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
What is the correct form of the equilibrium expression?
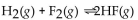
A)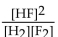
B)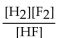
C)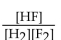
D)
E)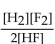
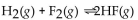
A)
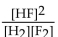
B)
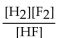
C)
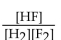
D)

E)
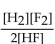

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 52 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
The equilibrium constant for the reaction for the decomposition of 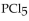 to chlorine and
to chlorine and 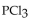 at a certain temperature is 0.042 .
at a certain temperature is 0.042 .
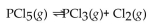
If the equilibrium concentrations are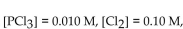 what is the value of
what is the value of 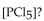
A) 0.0010 M
B) 0.042 M
C) 0.0020 M
D) 0.010 M
E) 0.024 M
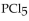 to chlorine and
to chlorine and 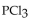 at a certain temperature is 0.042 .
at a certain temperature is 0.042 .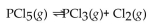
If the equilibrium concentrations are
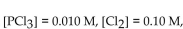 what is the value of
what is the value of 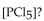
A) 0.0010 M
B) 0.042 M
C) 0.0020 M
D) 0.010 M
E) 0.024 M

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 52 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
For the following reaction, the equilibrium concentrations are: 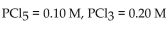 and
and 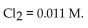 What is the value of the equilibrium constant?
What is the value of the equilibrium constant?
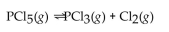
A) 45
B) 0.045
C) 22
D) 0.022
E) 0.10
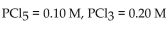 and
and 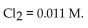 What is the value of the equilibrium constant?
What is the value of the equilibrium constant?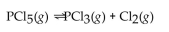
A) 45
B) 0.045
C) 22
D) 0.022
E) 0.10

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 52 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
The reaction of hemoglobin with oxygen can be written as follows.  If the amount of oxygen available to the blood decreases significantly, what happens to the individual involved?
If the amount of oxygen available to the blood decreases significantly, what happens to the individual involved?
A)Anemia results.
B)Oxygen poisoning results.
C)Acclimatization results.
D)Hypoxia results.
E)Nitrogen narcosis results.
 If the amount of oxygen available to the blood decreases significantly, what happens to the individual involved?
If the amount of oxygen available to the blood decreases significantly, what happens to the individual involved?A)Anemia results.
B)Oxygen poisoning results.
C)Acclimatization results.
D)Hypoxia results.
E)Nitrogen narcosis results.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 52 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
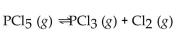 For the reaction at equilibrium, if the volume of the container is increased, the amount of PCl5 present will
For the reaction at equilibrium, if the volume of the container is increased, the amount of PCl5 present willA)stay the same.
B)decrease.
C)triple.
D)double.
E)increase.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 52 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23

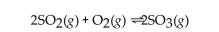
A)The rate of formation of products is increased.
B)The equilibrium shifts to produce more products.
C)The position of the equilibrium remains unchanged.
D)The catalyst for the reaction is used up.
E)The equilibrium shifts to produce more reactants.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 52 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
In the reaction of carbon dioxide with water to give carbonic acid, the only gaseous component is the carbon dioxide. What will happen to the equilibrium concentration of carbonic acid if the concentration of carbon
Dioxide is increased in the container?
A)The concentration of carbonic acid will increase.
B)There will be twice as much carbonic acid as carbon dioxide.
C)The carbonic acid concentration will decrease.
D)There will be more water available for the reaction.
E)The carbonic acid concentration will stay the same.
Dioxide is increased in the container?
A)The concentration of carbonic acid will increase.
B)There will be twice as much carbonic acid as carbon dioxide.
C)The carbonic acid concentration will decrease.
D)There will be more water available for the reaction.
E)The carbonic acid concentration will stay the same.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 52 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
In an exothermic reaction, heat can be considered a
A)catalyst.
B)product.
C)rate.
D)reactant.
E)determinant.
A)catalyst.
B)product.
C)rate.
D)reactant.
E)determinant.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 52 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
For the following reaction, the equilibrium constant 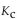 is 2.0 at a certain temperature. Bromine can be liquefied easily and removed from the reaction vessel as it is formed. If this is done, how will it affect the equilibrium reac
is 2.0 at a certain temperature. Bromine can be liquefied easily and removed from the reaction vessel as it is formed. If this is done, how will it affect the equilibrium reac
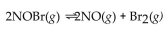
A) The equilibrium constant will change.
B) Less NO will be produced.
C) There will be a larger proportion NOBr in the vessel when equilibrium is reached.
D) The pressure in the vessel will increase.
E) More products will be produced as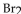 is removed.
is removed.
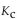 is 2.0 at a certain temperature. Bromine can be liquefied easily and removed from the reaction vessel as it is formed. If this is done, how will it affect the equilibrium reac
is 2.0 at a certain temperature. Bromine can be liquefied easily and removed from the reaction vessel as it is formed. If this is done, how will it affect the equilibrium reac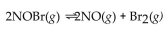
A) The equilibrium constant will change.
B) Less NO will be produced.
C) There will be a larger proportion NOBr in the vessel when equilibrium is reached.
D) The pressure in the vessel will increase.
E) More products will be produced as
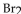 is removed.
is removed.
Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 52 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
For the following reaction, the equilibrium constant 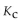 is 2.0 . If the concentration of both products is 0.10 M at equilibrium, what is the concentration of NOBr?
is 2.0 . If the concentration of both products is 0.10 M at equilibrium, what is the concentration of NOBr?
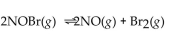
A)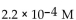
B) 2.2 M
C)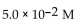
D)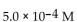
E)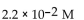
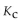 is 2.0 . If the concentration of both products is 0.10 M at equilibrium, what is the concentration of NOBr?
is 2.0 . If the concentration of both products is 0.10 M at equilibrium, what is the concentration of NOBr?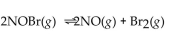
A)
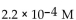
B) 2.2 M
C)
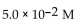
D)
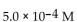
E)
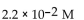

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 52 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
When you open a bottle of a soft drink and leave it open, the drink eventually goes flat. This happens because the equilibrium between carbonic acid and carbon dioxide shifts to produce
A)more water.
B)more carbonic acid.
C)more oxygen.
D)more carbon dioxide.
E)more hydrogen ions.
A)more water.
B)more carbonic acid.
C)more oxygen.
D)more carbon dioxide.
E)more hydrogen ions.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 52 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
In the reaction of nitrogen gas with oxygen gas to produce nitrogen oxide, what is the effect of adding more oxygen gas to the initial reaction mixture? The reaction is shown below. 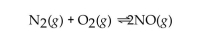
A) The equilibrium is not affected.
B) The equilibrium shifts to produce more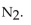
C) The temperature of the reaction mixture is raised.
D) The equilibrium shifts to produce more NO.
E) Extra catalyst is required to reach equilibrium.
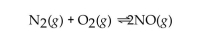
A) The equilibrium is not affected.
B) The equilibrium shifts to produce more
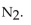
C) The temperature of the reaction mixture is raised.
D) The equilibrium shifts to produce more NO.
E) Extra catalyst is required to reach equilibrium.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 52 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
Carbon monoxide binds to hemoglobin 140 times more strongly than oxygen does. What does this tell you about the equilibrium constants for the two reactions of hemoglobin with carbon monoxide and oxygen?
A)Oxygen and carbon monoxide react with hemoglobin in different fashions.
B)The equilibrium constant for the binding of CO is greater.
C)The equilibrium constant for the binding of oxygen is greater.
D)The concentration of carbon monoxide at equilibrium is twice that of oxygen.
E)Oxygen and carbon monoxide have the same formula mass.
A)Oxygen and carbon monoxide react with hemoglobin in different fashions.
B)The equilibrium constant for the binding of CO is greater.
C)The equilibrium constant for the binding of oxygen is greater.
D)The concentration of carbon monoxide at equilibrium is twice that of oxygen.
E)Oxygen and carbon monoxide have the same formula mass.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 52 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
Treatment of carbon monoxide poisoning can be accomplished by the use of pure oxygen for breathing. This is an example of the use of ________ in a clinical setting.
A)Le Châtelier's principle
B)the ideal gas law
C)a precipitation reaction
D)Henry's law
E)conservation of mass
A)Le Châtelier's principle
B)the ideal gas law
C)a precipitation reaction
D)Henry's law
E)conservation of mass

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 52 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
In the following gas phase reaction, what is the effect of adding more 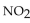 to the starting reaction mixture?
to the starting reaction mixture?
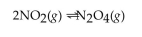
A) It would slow the reaction down.
B) It would decrease the final quantity of products.
C) It would make the reaction more exothermic.
D) It would increase the final quantity of products.
E) It would make the reaction more endothermic.
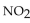 to the starting reaction mixture?
to the starting reaction mixture?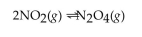
A) It would slow the reaction down.
B) It would decrease the final quantity of products.
C) It would make the reaction more exothermic.
D) It would increase the final quantity of products.
E) It would make the reaction more endothermic.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 52 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
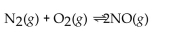 For the reaction at equilibrium, if the volume of the container is decreased, the amount of NO present will
For the reaction at equilibrium, if the volume of the container is decreased, the amount of NO present willA)stay the same.
B)decrease.
C)double.
D)increase.
E)triple.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 52 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
The physiological equilibrium system that keeps the temperature of the body constant is called
A)catalysis.
B)homeostasis.
C)metabolism.
D)stimulation.
E)regulation.
A)catalysis.
B)homeostasis.
C)metabolism.
D)stimulation.
E)regulation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 52 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
For the following equilibrium reaction, which cause and effect are correctly matched? 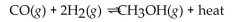
A) remove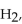 shift left
shift left
B) remove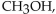 shift left
shift left
C) remove heat, no change
D) add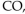 shift left
shift left
E) add heat, shift right
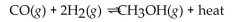
A) remove
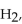 shift left
shift leftB) remove
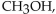 shift left
shift leftC) remove heat, no change
D) add
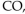 shift left
shift leftE) add heat, shift right

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 52 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
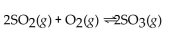 For the reaction at equilibrium, if
For the reaction at equilibrium, if 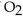 is added, the amount of
is added, the amount of 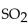 present will
present willA) decrease.
B) increase.
C) stay the same.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 52 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
For the following reaction, the equilibrium constant 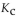 is 0.60 at a certain temperature. If the concentration of NO(g) and NOBr(g) are both 0.50 M ,at equilibrium, what is the concentration of
is 0.60 at a certain temperature. If the concentration of NO(g) and NOBr(g) are both 0.50 M ,at equilibrium, what is the concentration of 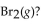
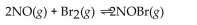
A)0.60 M
B)1.7 M
C)2.8 M
D)1.0 M
E)0.36 M
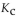 is 0.60 at a certain temperature. If the concentration of NO(g) and NOBr(g) are both 0.50 M ,at equilibrium, what is the concentration of
is 0.60 at a certain temperature. If the concentration of NO(g) and NOBr(g) are both 0.50 M ,at equilibrium, what is the concentration of 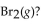
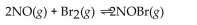
A)0.60 M
B)1.7 M
C)2.8 M
D)1.0 M
E)0.36 M

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 52 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
Iron metal reacts with oxygen gas to produce iron(III) oxide. What will be the effect of increasing concentration of oxygen gas in a closed reaction vessel?
A) There is no effect; a catalyst is needed.
B) The rate of production of iron oxide will slow down.
C) More iron oxide will be produced.
D) The reaction mixture will catch fire.
E) Less reaction will take place.
A) There is no effect; a catalyst is needed.
B) The rate of production of iron oxide will slow down.
C) More iron oxide will be produced.
D) The reaction mixture will catch fire.
E) Less reaction will take place.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 52 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
For the following reaction, the equilibrium constant 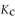 is 0.021 . If the concentration of
is 0.021 . If the concentration of 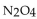 is 0.012 M at equilibrium, what is the concentration of
is 0.012 M at equilibrium, what is the concentration of 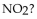
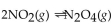
A) 1.3 M
B) 1.8 M
C) 0.012 M
D) 0.57 M
E) 0.76 M
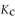 is 0.021 . If the concentration of
is 0.021 . If the concentration of 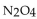 is 0.012 M at equilibrium, what is the concentration of
is 0.012 M at equilibrium, what is the concentration of 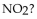
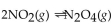
A) 1.3 M
B) 1.8 M
C) 0.012 M
D) 0.57 M
E) 0.76 M

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 52 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
For the following reaction, the equilibrium constant ![<strong>For the following reaction, the equilibrium constant is 2.0 at a certain temperature. The reaction is endothermi What do you expect to happen to the concentration of NO if the temperature is doubled? </strong> A) There will be no change in [NO]. B) The change in concentration of [NO] will depend on the size of the vessel. C) The concentration of [NO] will decrease. D) A catalyst will be needed to make a change in concentration. E) The concentration of [NO] will increase.](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB34225555/11ec7ddd_6598_31c8_8044_ddbac0d245be_TB34225555_11.jpg) is 2.0 at a certain temperature. The reaction is endothermi What do you expect to happen to the concentration of NO if the temperature is doubled?
is 2.0 at a certain temperature. The reaction is endothermi What do you expect to happen to the concentration of NO if the temperature is doubled?
![<strong>For the following reaction, the equilibrium constant is 2.0 at a certain temperature. The reaction is endothermi What do you expect to happen to the concentration of NO if the temperature is doubled? </strong> A) There will be no change in [NO]. B) The change in concentration of [NO] will depend on the size of the vessel. C) The concentration of [NO] will decrease. D) A catalyst will be needed to make a change in concentration. E) The concentration of [NO] will increase.](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB34225555/11ec7ddd_7780_6479_8044_eb00f1d5d353_TB34225555_11.jpg)
A) There will be no change in [NO].
B) The change in concentration of [NO] will depend on the size of the vessel.
C) The concentration of [NO] will decrease.
D) A catalyst will be needed to make a change in concentration.
E) The concentration of [NO] will increase.
![<strong>For the following reaction, the equilibrium constant is 2.0 at a certain temperature. The reaction is endothermi What do you expect to happen to the concentration of NO if the temperature is doubled? </strong> A) There will be no change in [NO]. B) The change in concentration of [NO] will depend on the size of the vessel. C) The concentration of [NO] will decrease. D) A catalyst will be needed to make a change in concentration. E) The concentration of [NO] will increase.](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB34225555/11ec7ddd_6598_31c8_8044_ddbac0d245be_TB34225555_11.jpg) is 2.0 at a certain temperature. The reaction is endothermi What do you expect to happen to the concentration of NO if the temperature is doubled?
is 2.0 at a certain temperature. The reaction is endothermi What do you expect to happen to the concentration of NO if the temperature is doubled?![<strong>For the following reaction, the equilibrium constant is 2.0 at a certain temperature. The reaction is endothermi What do you expect to happen to the concentration of NO if the temperature is doubled? </strong> A) There will be no change in [NO]. B) The change in concentration of [NO] will depend on the size of the vessel. C) The concentration of [NO] will decrease. D) A catalyst will be needed to make a change in concentration. E) The concentration of [NO] will increase.](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB34225555/11ec7ddd_7780_6479_8044_eb00f1d5d353_TB34225555_11.jpg)
A) There will be no change in [NO].
B) The change in concentration of [NO] will depend on the size of the vessel.
C) The concentration of [NO] will decrease.
D) A catalyst will be needed to make a change in concentration.
E) The concentration of [NO] will increase.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 52 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
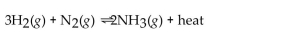 For the reaction at equilibrium, if the concentration of
For the reaction at equilibrium, if the concentration of 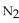 is increased, will the equilibrium shift in the direction i reactants, products, or stay the same?
is increased, will the equilibrium shift in the direction i reactants, products, or stay the same?A) reactants
B) products
C) stay the same

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 52 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
The rule or principle that describes the effect of changing reaction conditions on an equilibrium is known as
________ principle.
________ principle.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 52 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
Write the equilibrium expression for the reaction of nitrogen and hydrogen to give ammonia,
NH3.
NH3.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 52 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
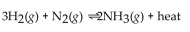
For the reaction at equilibrium, if the temperature is lowered, will the equilibrium shift in the direction of reactar products, or stay the same?
A) reactants
B) products
C) stay the same

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 52 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
What is the correct form of the equilibrium expression? 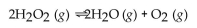
A)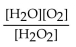
B)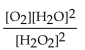
C)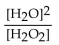
D)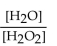
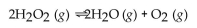
A)
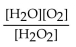
B)
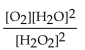
C)
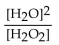
D)
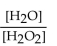

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 52 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
For the following reaction, the equilibrium constant 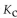 is 2.0 at a certain temperature. Write the equilibrium expression of the equilibrium constant,
is 2.0 at a certain temperature. Write the equilibrium expression of the equilibrium constant, 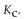
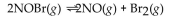
A)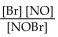
B)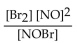
C)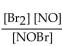
D)
E)
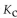 is 2.0 at a certain temperature. Write the equilibrium expression of the equilibrium constant,
is 2.0 at a certain temperature. Write the equilibrium expression of the equilibrium constant, 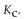
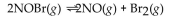
A)
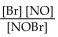
B)
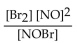
C)
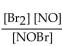
D)

E)


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 52 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
An equilibrium constant with a value greater than 1 means the reaction favors the ________.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 52 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
The equilibrium between hemoglobin and oxyhemoglobin in the blood can be represented by the following reaction.
Write the form of the equilibrium expression.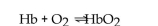
Write the form of the equilibrium expression.
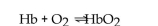

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 52 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
The ________ is the energy difference between reactants and products in a chemical reaction.
A)product energy
B)heat of reaction
C)activation energy
D)overall energy
E)transition energy
A)product energy
B)heat of reaction
C)activation energy
D)overall energy
E)transition energy

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 52 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
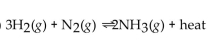 For the reaction at equilibrium, if the volume is increased, will the equilibrium shift in the direction of reactants, products, or stay the same?
For the reaction at equilibrium, if the volume is increased, will the equilibrium shift in the direction of reactants, products, or stay the same?A)reactants
B)products
C)stay the same

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 52 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
A mixture at equilibrium that contains less product than reactant has a 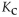 that is _____ than 1 .
that is _____ than 1 .
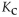 that is _____ than 1 .
that is _____ than 1 .
Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 52 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
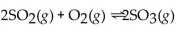
For the reaction at equilibrium, if
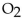 is removed, the amount of
is removed, the amount of 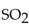 present will
present willA) increase
B) decrease
C) stay the same

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 52 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



