Deck 17: The Organic Chemistry of Metabolic Pathways
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/40
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 17: The Organic Chemistry of Metabolic Pathways
1
Consider the deamination of serine to answer the following questions.
a)Draw the structure of the -keto acid produced by the deamination of serine.
b)What is the fate of the amino group in serine when this conversion occurs in a mammalian system?
a)Draw the structure of the -keto acid produced by the deamination of serine.
b)What is the fate of the amino group in serine when this conversion occurs in a mammalian system?
a)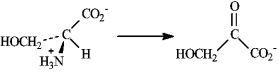
b)The amino group is removed in the deamination as ammonia. The ammonia is in turn converted into urea and excreted during the urea cycle.

b)The amino group is removed in the deamination as ammonia. The ammonia is in turn converted into urea and excreted during the urea cycle.
2
The reaction of fructose 1,6-bisphosphate to give glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate and dihydroxyacetone phosphate is an example of
A) a reverse aldol condensation
B) hydrolysis
C) oxidation
D) dehydration
A) a reverse aldol condensation
B) hydrolysis
C) oxidation
D) dehydration
a reverse aldol condensation
3
A coenzyme frequently encountered in transamination reactions is
A) tetrahydrofolate
B) pyridoxal phosphate
C) thiamine pyrophosphate
D) biotin
A) tetrahydrofolate
B) pyridoxal phosphate
C) thiamine pyrophosphate
D) biotin
pyridoxal phosphate
4
Which group of small molecules best fit the boxes associated with the reaction shown? 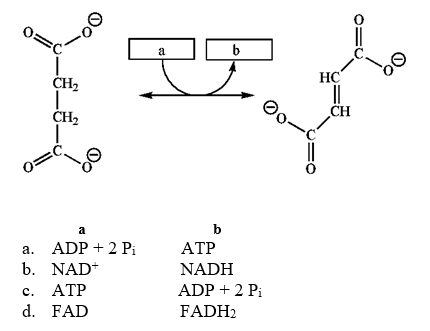


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 40 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
Consider the structure of amylopectin below to answer the following questions. 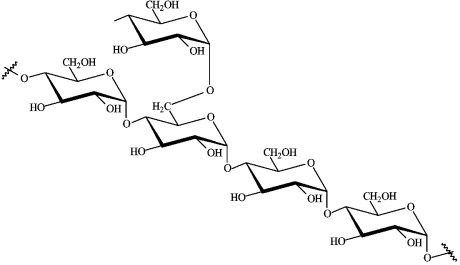 a)Circle the glycosidic links that are hydrolyzed in the small intestine.
a)Circle the glycosidic links that are hydrolyzed in the small intestine.
b)What is the final product of complete hydrolysis of amylpectin?
 a)Circle the glycosidic links that are hydrolyzed in the small intestine.
a)Circle the glycosidic links that are hydrolyzed in the small intestine.b)What is the final product of complete hydrolysis of amylpectin?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 40 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
Instructions: Consider the reaction below to answer the following question(s). 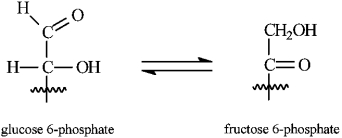
Refer to instructions. Write the mechanism for this isomerization.

Refer to instructions. Write the mechanism for this isomerization.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 40 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
Many biological reactions are endergonic. Explain how it is possible that these reactions occur spontaneously.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 40 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
During the complete catabolism of a molecule of glucose, the ultimate fate of the carbon atoms are
A) pyruvate
B) AcetylCoA
C) carbon dioxide
D) fructose-6-phosphate
E) a, b or c
A) pyruvate
B) AcetylCoA
C) carbon dioxide
D) fructose-6-phosphate
E) a, b or c

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 40 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
Which enzyme catalyzes the reaction shown? 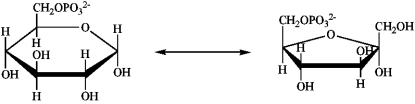
A) an epimerase
B) an isomerase
C) a mutase
D) a dehydrogenase

A) an epimerase
B) an isomerase
C) a mutase
D) a dehydrogenase

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 40 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
The key functional group in the PLP-dependent transamination of an -amino acid is an activated
A) amine
B) imine
C) amide
D) enamine
A) amine
B) imine
C) amide
D) enamine

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 40 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
The formation of amino acids from proteins
A) occurs during anabolism.
B) is endergonic.
C) occurs during digestion.
D) is a cellular process.
E) all of these
A) occurs during anabolism.
B) is endergonic.
C) occurs during digestion.
D) is a cellular process.
E) all of these

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 40 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
Instructions: Consider the reaction below to answer the following question(s). 
Refer to instructions. This reaction proceeds through a common enol structure. Draw the structure of the glucose/fructose enol.

Refer to instructions. This reaction proceeds through a common enol structure. Draw the structure of the glucose/fructose enol.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 40 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
Which group of small molecules best fit the boxes associated with the reaction shown? 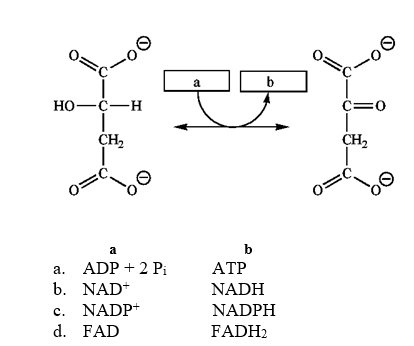


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 40 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
What reaction does glutamate dehydrogenase (GDH) catalyze?
A) The oxidative deamination of glutamate to yield -ketoglutarate.
B) Phosphorylation of carbamate to yield carbamoyl phosphate.
C) The amidation of the carboxyl group of glutamate to form glutamine.
D) The deadenylation of glutamine synthetase (GS).
E) The adenylation of glutamine synthetase.
A) The oxidative deamination of glutamate to yield -ketoglutarate.
B) Phosphorylation of carbamate to yield carbamoyl phosphate.
C) The amidation of the carboxyl group of glutamate to form glutamine.
D) The deadenylation of glutamine synthetase (GS).
E) The adenylation of glutamine synthetase.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 40 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
What product would be obtained from enzymatic transamination of 3-hydroxy-2-ketopropanoic acid? 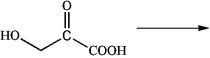


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 40 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
Consider the following reaction. 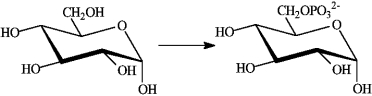 Which of the following describes this reaction?
Which of the following describes this reaction?
A) is so strongly exergonic that it does not require a catalyst
B) is an exergonic reaction not coupled to any other reaction
C) is an endergonic reaction that takes place because it is coupled to the exergonic hydrolysis of ATP
D) is an exergonic reaction that is coupled to the endergonic hydrolysis of ATP
 Which of the following describes this reaction?
Which of the following describes this reaction?A) is so strongly exergonic that it does not require a catalyst
B) is an exergonic reaction not coupled to any other reaction
C) is an endergonic reaction that takes place because it is coupled to the exergonic hydrolysis of ATP
D) is an exergonic reaction that is coupled to the endergonic hydrolysis of ATP

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 40 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
When acetyl-CoA reacts with oxaloacetate to form citrate
A) a new carbon-carbon bond is formed
B) an oxidative decarboxylation reaction takes place
C) a dehydration reaction takes place
D) a rearrangement takes place
A) a new carbon-carbon bond is formed
B) an oxidative decarboxylation reaction takes place
C) a dehydration reaction takes place
D) a rearrangement takes place

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 40 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
Which group of small molecules best fit the boxes associated with the reaction shown? 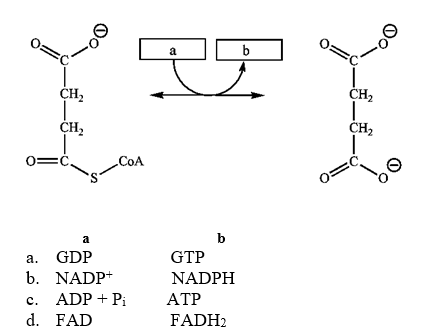


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 40 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
Which group of small molecules best fit the boxes associated with the reaction shown? 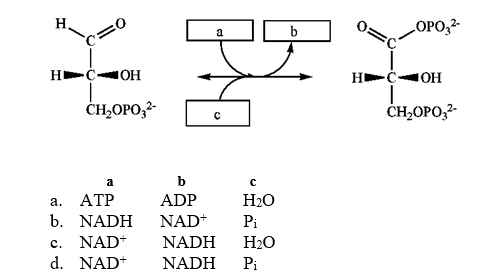


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 40 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
What amino acid is the following -keto acid derived from? 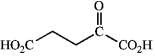


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 40 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
The source of oxygen for -oxidation is:
A) CO2
B) O2
C) Peroxide
D) Water
E) None of these is the source of oxygen for -oxidation.
A) CO2
B) O2
C) Peroxide
D) Water
E) None of these is the source of oxygen for -oxidation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 40 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
Instructions: Match a term or structure from the list below to each of the following definitions or names.
The product of the citric acid cycle, which is a reactant in the first step.
A)electron-transport chain
B)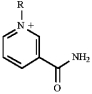
C)citric acid cycle
D)Embden-Meyerhoff
E)glycolysis
F)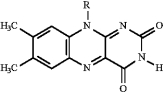
G)Hans Krebs
H)catabolism
I)ATP
J)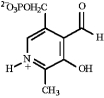
K)anabolism
L)acetyl CoA
M)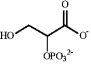
N)metabolism
O)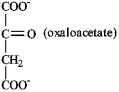
The product of the citric acid cycle, which is a reactant in the first step.
A)electron-transport chain
B)

C)citric acid cycle
D)Embden-Meyerhoff
E)glycolysis
F)

G)Hans Krebs
H)catabolism
I)ATP
J)

K)anabolism
L)acetyl CoA
M)

N)metabolism
O)
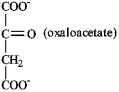

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 40 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
Instructions: Match a term or structure from the list below to each of the following definitions or names.
The "energy currency" of the cell.
A)electron-transport chain
B)
C)citric acid cycle
D)Embden-Meyerhoff
E)glycolysis
F)
G)Hans Krebs
H)catabolism
I)ATP
J)
K)anabolism
L)acetyl CoA
M)
N)metabolism
O)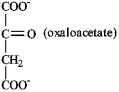
The "energy currency" of the cell.
A)electron-transport chain
B)

C)citric acid cycle
D)Embden-Meyerhoff
E)glycolysis
F)

G)Hans Krebs
H)catabolism
I)ATP
J)

K)anabolism
L)acetyl CoA
M)

N)metabolism
O)
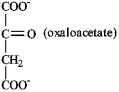

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 40 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
Instructions: Match a term or structure from the list below to each of the following definitions or names.
Pathways that break down larger biomolecules into smaller ones.
A)electron-transport chain
B)
C)citric acid cycle
D)Embden-Meyerhoff
E)glycolysis
F)
G)Hans Krebs
H)catabolism
I)ATP
J)
K)anabolism
L)acetyl CoA
M)
N)metabolism
O)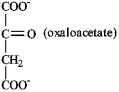
Pathways that break down larger biomolecules into smaller ones.
A)electron-transport chain
B)

C)citric acid cycle
D)Embden-Meyerhoff
E)glycolysis
F)

G)Hans Krebs
H)catabolism
I)ATP
J)

K)anabolism
L)acetyl CoA
M)

N)metabolism
O)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 40 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
Instructions: Match a term or structure from the list below to each of the following definitions or names.
Reactions that put smaller molecules together to synthesize larger biomolecules.
A)electron-transport chain
B)
C)citric acid cycle
D)Embden-Meyerhoff
E)glycolysis
F)
G)Hans Krebs
H)catabolism
I)ATP
J)
K)anabolism
L)acetyl CoA
M)
N)metabolism
O)
Reactions that put smaller molecules together to synthesize larger biomolecules.
A)electron-transport chain
B)

C)citric acid cycle
D)Embden-Meyerhoff
E)glycolysis
F)

G)Hans Krebs
H)catabolism
I)ATP
J)

K)anabolism
L)acetyl CoA
M)

N)metabolism
O)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 40 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
All of the following are byproducts of -oxidation, except:
A) Acetyl CoA
B) ADP
C) NADH
D) FADH2
E) All of these are byproducts of -oxidation.
A) Acetyl CoA
B) ADP
C) NADH
D) FADH2
E) All of these are byproducts of -oxidation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 40 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
Instructions: Match a term or structure from the list below to each of the following definitions or names.
Acetyl groups are oxidized to yield carbon dioxide and water.
A)electron-transport chain
B)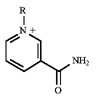
C)citric acid cycle
D)Embden-Meyerhoff
E)glycolysis
F)
G)Hans Krebs
H)catabolism
I)ATP
J)
K)anabolism
L)acetyl CoA
M)
N)metabolism
O)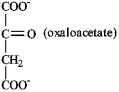
Acetyl groups are oxidized to yield carbon dioxide and water.
A)electron-transport chain
B)

C)citric acid cycle
D)Embden-Meyerhoff
E)glycolysis
F)

G)Hans Krebs
H)catabolism
I)ATP
J)

K)anabolism
L)acetyl CoA
M)

N)metabolism
O)
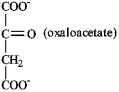

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 40 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
What is the structure of the -keto acid formed by transamination of the amino acid isoleucine? 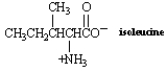
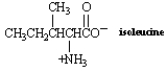

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 40 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
Draw the structure of the ultimate organic glycolysis product of -glucose. 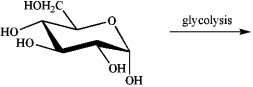


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 40 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
Instructions: Consider the reaction below to answer the following questions:
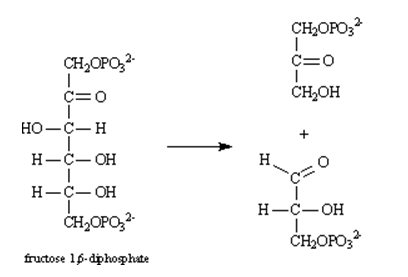
Refer to instructions. Draw arrows on the structure below showing electron flow in this reaction.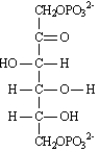

Refer to instructions. Draw arrows on the structure below showing electron flow in this reaction.


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 40 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
How many molecules of acetyl CoA are produced in the catabolism of stearic acid?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 40 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
Draw and name the major product of the reaction of -glucose with ATP.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 40 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
Instructions: Consider the reaction below to answer the following questions:

Refer to instructions. This reaction is an example of:
A) an aldol reaction
B) a Claisen reaction
C) a reverse Claisen reaction
D) a reto aldol reaction

Refer to instructions. This reaction is an example of:
A) an aldol reaction
B) a Claisen reaction
C) a reverse Claisen reaction
D) a reto aldol reaction

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 40 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
Instructions: Match a term or structure from the list below to each of the following definitions or names.
Discoverer of the glycolysis pathway.
A)electron-transport chain
B)
C)citric acid cycle
D)Embden-Meyerhoff
E)glycolysis
F)
G)Hans Krebs
H)catabolism
I)ATP
J)
K)anabolism
L)acetyl CoA
M)
N)metabolism
O)
Discoverer of the glycolysis pathway.
A)electron-transport chain
B)

C)citric acid cycle
D)Embden-Meyerhoff
E)glycolysis
F)

G)Hans Krebs
H)catabolism
I)ATP
J)

K)anabolism
L)acetyl CoA
M)

N)metabolism
O)
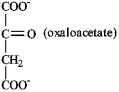

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 40 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
Instructions: Match a term or structure from the list below to each of the following definitions or names.
Pyridoxal phosphate, the cofactor in transaminations.
A)electron-transport chain
B)
C)citric acid cycle
D)Embden-Meyerhoff
E)glycolysis
F)
G)Hans Krebs
H)catabolism
I)ATP
J)
K)anabolism
L)acetyl CoA
M)
N)metabolism
O)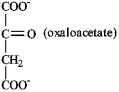
Pyridoxal phosphate, the cofactor in transaminations.
A)electron-transport chain
B)

C)citric acid cycle
D)Embden-Meyerhoff
E)glycolysis
F)

G)Hans Krebs
H)catabolism
I)ATP
J)

K)anabolism
L)acetyl CoA
M)

N)metabolism
O)
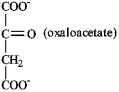

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 40 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
How many passages through the -oxidation pathway are required to completely degrade the following fatty acid?
CH3(CH2)12CO2H
CH3(CH2)12CO2H

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 40 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
Instructions: Match a term or structure from the list below to each of the following definitions or names.
-Coenzyme NAD+ required in the -oxidation of fatty acids, glycolysis, and the citric acid cycle.
A)electron-transport chain
B)
C)citric acid cycle
D)Embden-Meyerhoff
E)glycolysis
F)
G)Hans Krebs
H)catabolism
I)ATP
J)
K)anabolism
L)acetyl CoA
M)
N)metabolism
O)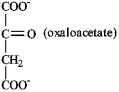
-Coenzyme NAD+ required in the -oxidation of fatty acids, glycolysis, and the citric acid cycle.
A)electron-transport chain
B)

C)citric acid cycle
D)Embden-Meyerhoff
E)glycolysis
F)

G)Hans Krebs
H)catabolism
I)ATP
J)

K)anabolism
L)acetyl CoA
M)

N)metabolism
O)
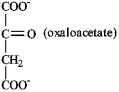

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 40 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
All of the following describe -oxidation, except:
A) Two-carbon units are eliminated during each cycle.
B) The process employs NAD+ as an oxidant.
C) The process is the primary route to fatty acid degradation.
D) The 2-carbon groups are eliminated from the methyl end of the fatty acid.
E) Fatty acids are attached to coenzyme A during the process.
A) Two-carbon units are eliminated during each cycle.
B) The process employs NAD+ as an oxidant.
C) The process is the primary route to fatty acid degradation.
D) The 2-carbon groups are eliminated from the methyl end of the fatty acid.
E) Fatty acids are attached to coenzyme A during the process.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 40 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
Draw the product of the following reaction, which is involved in the catabolism of triacylglycerols. 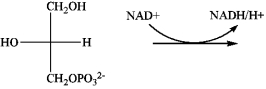


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 40 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
Instructions: Consider the reaction below to answer the following question(s). 
Refer to instructions. The isomerization of glucose 6-phosphate to fructose 6-phosphate is an example of:
A) an elimination reaction
B) an oxidation reaction
C) keto-enol tautomerism
D) a conjugate addition reaction

Refer to instructions. The isomerization of glucose 6-phosphate to fructose 6-phosphate is an example of:
A) an elimination reaction
B) an oxidation reaction
C) keto-enol tautomerism
D) a conjugate addition reaction

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 40 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



