Deck 30: Inflation: Its Causes and Costs
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/74
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 30: Inflation: Its Causes and Costs
1
Two countries, Alpha and Beta, are otherwise identical except that each dollar in Alpha is used more frequently than each dollar in Beta.For this to be true, it must be the case that, holding other factors equal, __________ in Alpha than in Beta.
A)real GDP is greater
B)the money stock is smaller
C)the price level is greater
D)velocity is less
A)real GDP is greater
B)the money stock is smaller
C)the price level is greater
D)velocity is less
B
2
Menu costs are costs of inflation limited to restaurants and fast-food establishments and are localised to countries.
False
3
An extraordinarily high rate of inflation is called:
A)disinflation
B)hyperinflation
C)hyperdisinflation
D)adverse inflation
A)disinflation
B)hyperinflation
C)hyperdisinflation
D)adverse inflation
B
4
The volume of computer chips produced is a nominal variable, and the revenue from the sale of computer chips is a real variable.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 74 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
Suppose inflation is currently running at 15% and, as a result, sales catalogues have to be reprinted every month.This is an example of shoeleather costs.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 74 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
The equation of exchange describes how money supply times velocity equals real GDP.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 74 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
According to the quantity equation, if velocity and real GDP are constant and the Reserve Bank increases the money supply by five per cent, then the price level
A)decreases by 10 per cent
B)decreases by five per cent
C)is also constant
D)increases by five percent
A)decreases by 10 per cent
B)decreases by five per cent
C)is also constant
D)increases by five percent

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 74 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
The irrelevance of monetary changes for nominal variables is called monetary neutrality.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 74 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
The growth of EFTPOS and internet banking has reduced shoeleather costs as people do not need to go into the bank anymore.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 74 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
Why has Germany had much lower inflation than the US has over the past 50 years?
A)German economists are more skilled than US economists
B)The German economy does not rely on imported oil as much as the US economy does
C)The German economy is still benefiting from its post-World War I period of hyperdeflation
D)German policymakers have been extraordinarily averse to inflation
A)German economists are more skilled than US economists
B)The German economy does not rely on imported oil as much as the US economy does
C)The German economy is still benefiting from its post-World War I period of hyperdeflation
D)German policymakers have been extraordinarily averse to inflation

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 74 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
A period of generally falling prices is called:
A)disinflation
B)depression
C)deflation
D)recession
A)disinflation
B)depression
C)deflation
D)recession

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 74 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
The inflation tax is exactly like other taxes levied when the government prints money.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 74 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
Unexpected inflation has no wealth redistribution effect on the population.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 74 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
If P represents the price of goods and services measured in money, then 1/P is the value of money measured in terms of goods and services.Hence when the overall price level rises, the value of money falls.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 74 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
Because of inflation-induced changes in taxes on capital gains and interest income, higher inflation tends to discourage people from saving and lowers the rate of economic growth.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 74 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
The quantity equation shows that if velocity and output are constant, a given percentage in the money supply will lead to the proportionally different percentage increase in the price level.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 74 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
The phenomenon known as the Fisher effect occurs when inflation causes people to pay an increasing percentage of their income in taxes, even when their real incomes have not changed.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 74 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
Inflation is the increase in the overall level of prices.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 74 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
Deflation is defined as:
A)a period of declining output of goods and services
B)a period of time in which most prices fall
C)a period of time in which the value of money falls
D)a period of business pessimism
A)a period of declining output of goods and services
B)a period of time in which most prices fall
C)a period of time in which the value of money falls
D)a period of business pessimism

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 74 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
Inflation can be measured by the:
A)absolute change in the CPI
B)percentage change in the CPI
C)absolute change in the GDP deflator
D)percentage change in the price of oil
A)absolute change in the CPI
B)percentage change in the CPI
C)absolute change in the GDP deflator
D)percentage change in the price of oil

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 74 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
The supply of money is determined by:
A)the value of money
B)the price level
C)the Reserve Bank
D)the demand for money
A)the value of money
B)the price level
C)the Reserve Bank
D)the demand for money

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 74 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
An increase in the money supply:
A)increases the ability of the economy to produce goods and services, increases the demand for goods and services, and increases the price level
B)leaves unchanged the ability of the economy to produce goods and services, increases the demand for goods and services and increases the price level
C)leaves unchanged the ability of the economy to produce goods and services, increases the demand for goods and services and decreases the price level
D)leaves unchanged the ability of the economy to produce goods and services, decreases the demand for goods and services, and decreases the price level
A)increases the ability of the economy to produce goods and services, increases the demand for goods and services, and increases the price level
B)leaves unchanged the ability of the economy to produce goods and services, increases the demand for goods and services and increases the price level
C)leaves unchanged the ability of the economy to produce goods and services, increases the demand for goods and services and decreases the price level
D)leaves unchanged the ability of the economy to produce goods and services, decreases the demand for goods and services, and decreases the price level

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 74 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
The most important variable affecting the demand for money in the long run is the:
A)nominal interest rate
B)real interest rate
C)price level
D)velocity of money
A)nominal interest rate
B)real interest rate
C)price level
D)velocity of money

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 74 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
NARRBEGIN: 11-1
Graph 11-1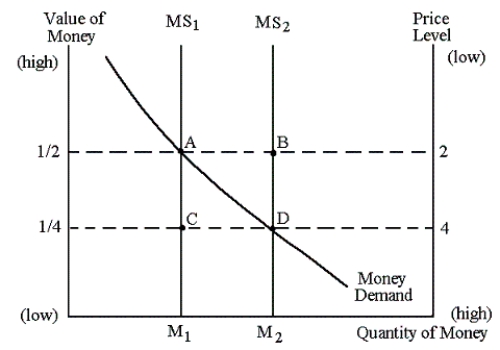
At point B in Graph11-1:
A)the value of money is less than its equilibrium level
B)money supply is greater than money demand
C)the price level is higher than its equilibrium level
D)money demand is greater than money supply
Graph 11-1

At point B in Graph11-1:
A)the value of money is less than its equilibrium level
B)money supply is greater than money demand
C)the price level is higher than its equilibrium level
D)money demand is greater than money supply

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 74 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
The principle of monetary neutrality implies that an increase in the money supply will:
A)decrease the price level
B)lower nominal interest rates
C)lower the unemployment rate
D)not affect real interest rates
A)decrease the price level
B)lower nominal interest rates
C)lower the unemployment rate
D)not affect real interest rates

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 74 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
According to the classical dichotomy, which of the following is determined by monetary factors?
A)The real wage
B)The nominal wage
C)The real interest rate
D)Real GDP
A)The real wage
B)The nominal wage
C)The real interest rate
D)Real GDP

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 74 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
The relative price of oil is a(n):
A)actual variable
B)monetary variable
C)nominal variable
D)real variable
A)actual variable
B)monetary variable
C)nominal variable
D)real variable

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 74 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
Real GDP measures:
A)the dollar value of the economy's output of goods and services
B)the total quantity of goods and services produced
C)the total income received from producing goods and services in current dollars
D)all of the above
A)the dollar value of the economy's output of goods and services
B)the total quantity of goods and services produced
C)the total income received from producing goods and services in current dollars
D)all of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 74 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
In the long run, countries with higher rates of money growth usually have:
A)higher rates of inflation
B)lower rates of inflation
C)faster growth rates of real output
D)smaller budget deficits
A)higher rates of inflation
B)lower rates of inflation
C)faster growth rates of real output
D)smaller budget deficits

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 74 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
When money is neutral, an increase in the rate of inflation from 2 per cent to 5 per cent will _____.
A)increase the nominal interest rate by 3percentage points
B)increase the real interest rate by 3 percentage points
C)decrease the nominal interest rate by 3 percentage points
D)increase the nominal interest rate by less than 3 percentage points
A)increase the nominal interest rate by 3percentage points
B)increase the real interest rate by 3 percentage points
C)decrease the nominal interest rate by 3 percentage points
D)increase the nominal interest rate by less than 3 percentage points

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 74 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
In the long run, the _____ adjusts to equilibrate the quantity of money supplied with the quantity demanded.
A)real interest rates
B)money supply
C)price level
D)nominal interest rates
A)real interest rates
B)money supply
C)price level
D)nominal interest rates

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 74 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
The demand for money is:
A)positively related to the interest rate
B)positively related to the price level
C)positively related to the money supply
D)negatively related to the money supply
A)positively related to the interest rate
B)positively related to the price level
C)positively related to the money supply
D)negatively related to the money supply

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 74 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
The notion that nominal variables are heavily influenced by the quantity of money, and that money is largely irrelevant to understanding the determinants of real variables, is called:
A)monetarism
B)the quantity theory
C)the Fisher effect
D)the classical dichotomy
A)monetarism
B)the quantity theory
C)the Fisher effect
D)the classical dichotomy

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 74 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
NARRBEGIN: 11-1
Graph 11-1
When the money supply curve in Graph11-1 shifts from MS2 to MS1:
A)the equilibrium value of money increases
B)the equilibrium price level increases
C)the supply of money has increased
D)the demand for goods and services will increase
Graph 11-1

When the money supply curve in Graph11-1 shifts from MS2 to MS1:
A)the equilibrium value of money increases
B)the equilibrium price level increases
C)the supply of money has increased
D)the demand for goods and services will increase

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 74 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
If the price level is below the equilibrium level, then:
A)money demand will be greater than money supply
B)money supply will be equal to money demand
C)the price level will rise
D)the price level will fall
A)money demand will be greater than money supply
B)money supply will be equal to money demand
C)the price level will rise
D)the price level will fall

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 74 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
NARRBEGIN: 11-1
Graph 11-1
When the money supply curve in Graph11-1 shifts from MS2 to MS1:
A)the equilibrium price level increases
B)this may be due to the RBA selling government securities
C)this is due to the RBA buying government securities
D)the demand for goods and services increasing
Graph 11-1

When the money supply curve in Graph11-1 shifts from MS2 to MS1:
A)the equilibrium price level increases
B)this may be due to the RBA selling government securities
C)this is due to the RBA buying government securities
D)the demand for goods and services increasing

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 74 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
If the money supply is increased, the:
A)interest rate will increase, which will increase the quantity of money demanded to restore equilibrium
B)interest rate will increase, which will decrease the quantity of money demanded to restore equilibrium
C)price level will decrease, which will decrease the quantity of money demanded to restore equilibrium
D)price level will increase which will increase the quantity of money demanded to restore equilibrium
A)interest rate will increase, which will increase the quantity of money demanded to restore equilibrium
B)interest rate will increase, which will decrease the quantity of money demanded to restore equilibrium
C)price level will decrease, which will decrease the quantity of money demanded to restore equilibrium
D)price level will increase which will increase the quantity of money demanded to restore equilibrium

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 74 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
Which of the following statements is correct?
A)economic variables measured in physical units are nominal variables, and economic variables measured in monetary units are real variables
B)economic variables measured in physical units are real variables, and economic variables measured in monetary units are nominal variables
C)economic variables measured in physical units are actual variables, and economic variables measured in monetary units are nominal variables
D)economic variables measured in physical units are real variables, and economic variables measured in monetary units are actual variables
A)economic variables measured in physical units are nominal variables, and economic variables measured in monetary units are real variables
B)economic variables measured in physical units are real variables, and economic variables measured in monetary units are nominal variables
C)economic variables measured in physical units are actual variables, and economic variables measured in monetary units are nominal variables
D)economic variables measured in physical units are real variables, and economic variables measured in monetary units are actual variables

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 74 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
Nominal GDP measures:
A)the dollar value of the economy's output of goods and services
B)the total quantity of goods and services produced
C)the total income received from producing goods and services in constant dollars
D)all of the above
A)the dollar value of the economy's output of goods and services
B)the total quantity of goods and services produced
C)the total income received from producing goods and services in constant dollars
D)all of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 74 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
According to the quantity equation, if velocity and output are constant, then an increase in the money supply leads to _____ in inflation.
A)a less than proportional increase
B)a less than proportional decrease
C)the same percentage increase
D)a greater than proportional increase
A)a less than proportional increase
B)a less than proportional decrease
C)the same percentage increase
D)a greater than proportional increase

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 74 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
Which of the following variables is not a real variable?
A)The amount of corn
B)The nominal interest rate adjusted for inflation
C)The dollar wage
D)The price of bananas relative to the price of oranges
A)The amount of corn
B)The nominal interest rate adjusted for inflation
C)The dollar wage
D)The price of bananas relative to the price of oranges

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 74 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
According to the quantity equation, if velocity and real GDP are constant and the Reserve Bank increases the money supply by five per cent then the price level:
A)decreases by 10 per cent
B)decreases by five percent
C)is also constant
D)increases by five per cent
A)decreases by 10 per cent
B)decreases by five percent
C)is also constant
D)increases by five per cent

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 74 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
Which of the following statements is not correct when more money is created?
A)The price level must rise
B)The quantity of output must rise
C)The velocity of money must fall
D)None of the above
A)The price level must rise
B)The quantity of output must rise
C)The velocity of money must fall
D)None of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 74 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
Expected inflation redistributes wealth from _____.
A)creditors to debtors
B)owners of real property to owners of financial assets
C)debtors to creditors
D)the government to fixed income recipients
A)creditors to debtors
B)owners of real property to owners of financial assets
C)debtors to creditors
D)the government to fixed income recipients

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 74 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
According to the Fisher effect, an increase in the rate of inflation from three per cent to four per cent will _____.
A)increase the nominal interest rate by seven percentage points
B)increase the real interest rate by three percentage points
C)decrease the nominal interest rate by three percentage points
D)increase the nominal interest rate by one percentage point
A)increase the nominal interest rate by seven percentage points
B)increase the real interest rate by three percentage points
C)decrease the nominal interest rate by three percentage points
D)increase the nominal interest rate by one percentage point

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 74 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
The classical dichotomy is:
A)the separation of money and goods markets
B)the theoretical separation of nominal and real variables
C)the separation of the monetary system and production system
D)the separation of goods and services produced today and goods and services produced tomorrow
A)the separation of money and goods markets
B)the theoretical separation of nominal and real variables
C)the separation of the monetary system and production system
D)the separation of goods and services produced today and goods and services produced tomorrow

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 74 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
Money neutrality is the proposition that:
A)changes in the money supply do not affect real variables
B)changes in the money demand do not affect real variables
C)changes in the money supply do not affect prices
D)changes in the money demand do not affect prices
A)changes in the money supply do not affect real variables
B)changes in the money demand do not affect real variables
C)changes in the money supply do not affect prices
D)changes in the money demand do not affect prices

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 74 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
According to the quantity equation, if velocity is constant at two and real GDP is constant at 10 000, then, if the money supply is increased from 6250 to 6500, the price level:
A)increases to 1.25
B)increases to 1.3
C)increases to 1.5
D)is constant at 1.25
A)increases to 1.25
B)increases to 1.3
C)increases to 1.5
D)is constant at 1.25

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 74 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
According to the Fisher effect, if the real interest rate is three per cent and the inflation rate is seven per cent, then the nominal interest rate equals:
A)three per cent
B)four per cent
C)seven per cent
D)10 per cent
A)three per cent
B)four per cent
C)seven per cent
D)10 per cent

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 74 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
The demand for money depends on:
A)the interest rate
B)the average level of prices in the economy
C)income
D)all of the above
A)the interest rate
B)the average level of prices in the economy
C)income
D)all of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 74 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
The inflation tax:
A)is collected by the government every time people use money for transaction
B)transfers wealth from government to households
C)is paid by everyone who holds money
D)all of the above
A)is collected by the government every time people use money for transaction
B)transfers wealth from government to households
C)is paid by everyone who holds money
D)all of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 74 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
Consider a simple economy that produces only chocolates.The economy produces 100 bars of chocolates in a year, and a chocolate bar costs $5.If the quantity of money supplied in the economy is $25, then the velocity of money is:
A)2.5
B)10
C)20
D)1000
A)2.5
B)10
C)20
D)1000

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 74 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
If the bank posts a nominal interest rate of seven per cent per year and the inflation rate is four per cent per year, then the real interest rate is:
A)minus three per cent
B)three per cent
C)four per cent
D)11 per cent
A)minus three per cent
B)three per cent
C)four per cent
D)11 per cent

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 74 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
The Fisher effect is:
A)the one-for-one adjustment of the nominal GDP to the inflation rate
B)the one-for-one adjustment of the nominal interest rate to the nominal GDP
C)the one-for-one adjustment of the nominal interest rate to the inflation rate
D)the one-for-one adjustment of the nominal GDP to the rate of money growth
A)the one-for-one adjustment of the nominal GDP to the inflation rate
B)the one-for-one adjustment of the nominal interest rate to the nominal GDP
C)the one-for-one adjustment of the nominal interest rate to the inflation rate
D)the one-for-one adjustment of the nominal GDP to the rate of money growth

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 74 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
Suppose inflation is currently running at 15% and, as a result, sales catalogues have to be reprinted every month.This is an example of:
A)noise in the price system
B)menu costs due to inflation
C)an unexpected redistribution in wealth
D)shoe-leather costs of inflation
A)noise in the price system
B)menu costs due to inflation
C)an unexpected redistribution in wealth
D)shoe-leather costs of inflation

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 74 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
If the price level is above the equilibrium level, then:
A)money demand will be greater than money supply
B)money demand will be smaller than money supply
C)money supply will be equal to money demand
D)the price level will rise
A)money demand will be greater than money supply
B)money demand will be smaller than money supply
C)money supply will be equal to money demand
D)the price level will rise

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 74 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
Paying for a government program by printing money:
A)reduces the opportunity cost of the program
B)is exactly like imposing an income tax to pay for the program
C)imposes an inflation tax to pay for the program
D)all of the above
A)reduces the opportunity cost of the program
B)is exactly like imposing an income tax to pay for the program
C)imposes an inflation tax to pay for the program
D)all of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 74 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
If between when you purchase an asset and sell it, the general price level and the price of the asset both double, then you have realised a:
A)capital gain
B)real gain
C)capital loss
D)real loss
A)capital gain
B)real gain
C)capital loss
D)real loss

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 74 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
According to the quantity equation, if velocity is constant at 2.5 and real GDP is constant at 8000, then, if the money supply is increased from 4800 to 5280, the price level:
A)increases to 1.1
B)increases to 1.5
C)increases to 1.65
D)is constant at 1.5
A)increases to 1.1
B)increases to 1.5
C)increases to 1.65
D)is constant at 1.5

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 74 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
The quantity equation states that:
A)money times velocity equals nominal GDP
B)money times velocity equals real GDP
C)money times prices equals nominal GDP
D)money times prices equals real GDP
A)money times velocity equals nominal GDP
B)money times velocity equals real GDP
C)money times prices equals nominal GDP
D)money times prices equals real GDP

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 74 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
Define the quantity equation and illustrate how it affects the price level in the economy.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 74 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
Define money demand.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 74 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
Is David Hume's description of the classical dichotomy and monetary neutrality a good description of the actual economy? Explain.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 74 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
According to the equation of exchange, what is the relationship between money growth and inflation along a long-term growth path?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 74 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
Unexpected inflation redistributes wealth among debtors and creditors.Who benefits - creditors or debtors? Explain.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 74 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
Explain inflation tax.How does government collect the inflation tax and who pays this tax?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 74 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
How do the relative-price distortions caused by inflation create a misallocation of resources?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 74 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
Given that petrol is key to the transport sector and all other sectors in Australia, why does the constant changing of price petrol not create menu costs?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 74 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
Calculate the velocity of money for each of the following situations:
a.The money supply is 1000, the price level is 20 and output is 200
b.The money supply is 50, the price level is 100 and output is 20
c.The money supply is 25, the price level is 25 and output is 200
d.The money supply is 800, the price level is 2 and output is 300
a.The money supply is 1000, the price level is 20 and output is 200
b.The money supply is 50, the price level is 100 and output is 20
c.The money supply is 25, the price level is 25 and output is 200
d.The money supply is 800, the price level is 2 and output is 300

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 74 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
What are the costs of inflation?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 74 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
What is the classical dichotomy, and to whom do we attribute it?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 74 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72
By reducing the cash rate in the US to almost zero per cent, what would critics of the Federal Reserve Bank (the Fed - The US central bank) believe about the Fed's ability to stimulate the economy?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 74 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73
Is there a relationship between money growth and hyperinflation?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 74 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
74
Unexpected inflation redistributes wealth from _____.
A)creditors to debtors
B)owners of real property to owners of financial assets
C)debtors to creditors
D)the government to fixed income recipients
A)creditors to debtors
B)owners of real property to owners of financial assets
C)debtors to creditors
D)the government to fixed income recipients

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 74 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



