Deck 19: Current Issues in Macro Theory and Policy
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/279
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 19: Current Issues in Macro Theory and Policy
1
Economist Milton Friedman is most closely associated with
A) Keynesian economics.
B) the rational expectations theory.
C) supply-side economics.
D) monetarism.
A) Keynesian economics.
B) the rational expectations theory.
C) supply-side economics.
D) monetarism.
monetarism.
2
The equation underlying the mainstream view of macroeconomics is
A)
B)
C)
D)
A)
B)
C)
D)
3
The equation of exchange indicates that
A) MV = PQ.
B) other things equal, an increase in the demand for money will increase
C) the velocity and the supply of money vary directly with one another.
D) MP = VQ.
A) MV = PQ.
B) other things equal, an increase in the demand for money will increase
C) the velocity and the supply of money vary directly with one another.
D) MP = VQ.
MV = PQ.
4
If a certain household earns and spends $24,000 per year and, on the average, holds a money balance of $6,000, then the velocity of money for this household is
A) 6.
B)
C) 4.
D)
A) 6.
B)
C) 4.
D)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 279 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
In the equation of exchange, the level of aggregate expenditures is indicated by
A) MV.
B)
C) PM.
D)
A) MV.
B)
C) PM.
D)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 279 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
According to the equation of exchange, changes in the money supply can affect
A) only the velocity of money.
B) both the price level and real output.
C) only real output and employment.
D) only the price level.
A) only the velocity of money.
B) both the price level and real output.
C) only real output and employment.
D) only the price level.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 279 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
The basic equation of monetarism is
A)
B)
C)
D)
A)
B)
C)
D)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 279 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
According to monetarists,
A) changes in the money supply are the primary cause of changes in the price level.
B) an expansionary fiscal policy will lower interest rates and overstimulate the economy.
C) changes in the velocity of money are more important than changes in the money supply in causing the level of economic activity to change.
D) the supply of money changes in response to changes in the levels of real output and prices.
A) changes in the money supply are the primary cause of changes in the price level.
B) an expansionary fiscal policy will lower interest rates and overstimulate the economy.
C) changes in the velocity of money are more important than changes in the money supply in causing the level of economic activity to change.
D) the supply of money changes in response to changes in the levels of real output and prices.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 279 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
According to mainstream macroeconomists, U.S. macro instability has resulted from
A) investment "booms" and "busts" and, occasionally, adverse aggregate supply shocks.
B) adherence by the Fed to a monetary rule.
C) government's attempts to balance its budget.
D) wide fluctuations in net exports.
A) investment "booms" and "busts" and, occasionally, adverse aggregate supply shocks.
B) adherence by the Fed to a monetary rule.
C) government's attempts to balance its budget.
D) wide fluctuations in net exports.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 279 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
Which of the following is a component of the equation of exchange?
A) consumption
B) the interest rate
C) investment
D) the velocity of money
A) consumption
B) the interest rate
C) investment
D) the velocity of money

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 279 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
The mainstream view of macro instability is that
A) changes in the money supply directly cause changes in aggregate demand and thus cause changes in real GDP.
B) changes in investment shift the aggregate demand curve and thus cause changes in real GDP.
C) bursts of innovation put the economy on an unsustainable growth path, eventually producing recession.
D) changes in technology and resource availability are the two main sources of fluctuations of real GDP.
A) changes in the money supply directly cause changes in aggregate demand and thus cause changes in real GDP.
B) changes in investment shift the aggregate demand curve and thus cause changes in real GDP.
C) bursts of innovation put the economy on an unsustainable growth path, eventually producing recession.
D) changes in technology and resource availability are the two main sources of fluctuations of real GDP.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 279 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
If M is $400, P is $4, and Q is 300, then V must be
A) 1.33.
B) 3.
C) 5.33.
D) 100.
A) 1.33.
B) 3.
C) 5.33.
D) 100.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 279 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
Monetarists believe that
A) prices and wages are inflexible or sticky.
B) both product and resource markets are monopolistic.
C) velocity is relatively stable.
D) the economy is more stable when active fiscal and monetary policy are used.
A) prices and wages are inflexible or sticky.
B) both product and resource markets are monopolistic.
C) velocity is relatively stable.
D) the economy is more stable when active fiscal and monetary policy are used.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 279 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
In the equation of exchange, V indicates the
A) value or purchasing power of the dollar.
B) number of times per year the average dollar is spent.
C) quantity of real output.
D) reciprocal of the price level.
A) value or purchasing power of the dollar.
B) number of times per year the average dollar is spent.
C) quantity of real output.
D) reciprocal of the price level.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 279 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
The velocity of money is equal to
A)
B)
C)
D) none of these.
A)
B)
C)
D) none of these.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 279 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
At the equilibrium level of GDP,
A) MV = nominal GDP.
B) MV = real GDP.
C) M = nominal GDP.
D)
A) MV = nominal GDP.
B) MV = real GDP.
C) M = nominal GDP.
D)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 279 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
The mainstream view is that macro instability is caused by
A) erratic growth of the nation's money supply.
B) government interference in the economy.
C) significant changes in investment spending.
D) consumption "booms" and "busts".
A) erratic growth of the nation's money supply.
B) government interference in the economy.
C) significant changes in investment spending.
D) consumption "booms" and "busts".

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 279 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
The velocity of money measures the
A) proportion of the money supply held as an asset.
B) ratio of the transactions demand to the asset demand for money.
C) average annual rate of increase in the money supply.
D) number of times per year the average dollar is spent on final goods and services.
A) proportion of the money supply held as an asset.
B) ratio of the transactions demand to the asset demand for money.
C) average annual rate of increase in the money supply.
D) number of times per year the average dollar is spent on final goods and services.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 279 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
The velocity of money is equal to
A)
B)
C)
D)
A)
B)
C)
D)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 279 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
The velocity of money is the
A) relationship between the money supply and the price level.
B) number of times per year the average dollar is spent on final goods and services.
C) relationship between asset and transactions demands for money.
D) price level divided by aggregate supply.
A) relationship between the money supply and the price level.
B) number of times per year the average dollar is spent on final goods and services.
C) relationship between asset and transactions demands for money.
D) price level divided by aggregate supply.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 279 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
As monetarists view the equation of exchange,
A) V changes erratically and unpredictably.
B) V is quite stable.
C) V usually changes in the same direction of any given change in M.
D) V usually changes in the opposite direction of any given change in M.
A) V changes erratically and unpredictably.
B) V is quite stable.
C) V usually changes in the same direction of any given change in M.
D) V usually changes in the opposite direction of any given change in M.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 279 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
Most monetarists would say that
A) the MV = PQ equation provides a better understanding of the macroeconomy than does the
= GDP equation.
B) most changes in the price level are explainable by changes in the level of real output.
C) the velocity of money is quite unstable.
D) all of these are true.
A) the MV = PQ equation provides a better understanding of the macroeconomy than does the
= GDP equation.
B) most changes in the price level are explainable by changes in the level of real output.
C) the velocity of money is quite unstable.
D) all of these are true.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 279 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
To determine the velocity of money, you would need to know
A) nominal GDP and real GDP.
B) the money supply and the price level.
C) nominal GDP and the money supply.
D) nominal GDP and the interest rate.
A) nominal GDP and real GDP.
B) the money supply and the price level.
C) nominal GDP and the money supply.
D) nominal GDP and the interest rate.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 279 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
Monetarists say that the relationship between the amount of money that households and businesses want to hold and the level of national output and income
A) has decreased historically because of increased accessibility to credit.
B) rises during recession and falls during periods of full employment.
C) falls during recession and rises during periods of full employment.
D) is relatively stable.
A) has decreased historically because of increased accessibility to credit.
B) rises during recession and falls during periods of full employment.
C) falls during recession and rises during periods of full employment.
D) is relatively stable.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 279 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
Monetarists say
A) that, because P is stable, a change in M will change Q proportionately in the opposite direction.
B) a change in the money supply will change aggregate demand and therefore nominal GDP.
C) a change in the money supply will change velocity, which in turn will change nominal GDP.
D) a change in the money supply will change the interest rate, which will change investment spending and nominal GDP.
A) that, because P is stable, a change in M will change Q proportionately in the opposite direction.
B) a change in the money supply will change aggregate demand and therefore nominal GDP.
C) a change in the money supply will change velocity, which in turn will change nominal GDP.
D) a change in the money supply will change the interest rate, which will change investment spending and nominal GDP.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 279 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
If the money supply is constant when both nominal and real GDP are rising, we can conclude that
A) tax rates have been increased.
B) the velocity of money must be increasing.
C) interest rates are falling.
D) the unemployment rate is rising.
A) tax rates have been increased.
B) the velocity of money must be increasing.
C) interest rates are falling.
D) the unemployment rate is rising.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 279 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
The view that inappropriate monetary policy was the main reason for the depth of the Great Depression in the United States is most closely associated with
A) monetarism.
B) the mainstream view.
C) the rational expectations theory.
D) the real-business-cycle theory.
A) monetarism.
B) the mainstream view.
C) the rational expectations theory.
D) the real-business-cycle theory.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 279 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
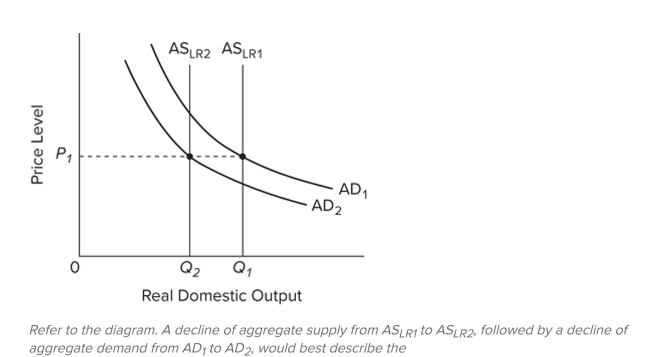
A) direct relationship between aggregate supply and aggregate demand.
B) real-business-cycle view of recession.
C) monetarist view of recession.
D) mainstream, Keynesian-based view of recession.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 279 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
If the nominal GDP is $477 billion and the velocity of money is 4.5, then the money supply is
A) $122 billion.
B) $98 billion.
C) $106 billion.
D) $477 billion.
A) $122 billion.
B) $98 billion.
C) $106 billion.
D) $477 billion.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 279 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
According to monetarists, a change in the money supply changes
A) the velocity of money, which in turn changes the nominal GDP.
B) investment spending, which in turn changes the nominal GDP.
C) the interest rate, which in turn changes the nominal GDP.
D) aggregate demand, which in turn changes the nominal GDP.
A) the velocity of money, which in turn changes the nominal GDP.
B) investment spending, which in turn changes the nominal GDP.
C) the interest rate, which in turn changes the nominal GDP.
D) aggregate demand, which in turn changes the nominal GDP.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 279 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
The real-business-cycle theory holds that business fluctuations are caused by
A) factors affecting aggregate demand.
B) incorrectly anticipated government stabilization policies.
C) significant changes in technology and resource availability.
D) "stop-and-go" monetary policies.
A) factors affecting aggregate demand.
B) incorrectly anticipated government stabilization policies.
C) significant changes in technology and resource availability.
D) "stop-and-go" monetary policies.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 279 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
According to real-business-cycle theory,
A) monetary factors affecting aggregate demand cause macroeconomic instability.
B) recessions result from declines in long-run aggregate supply, rather than decreases in aggregate demand.
C) when real wages fall during recessions, "real" unemployment rates rise.
D) the net long-run costs of business fluctuations are severe.
A) monetary factors affecting aggregate demand cause macroeconomic instability.
B) recessions result from declines in long-run aggregate supply, rather than decreases in aggregate demand.
C) when real wages fall during recessions, "real" unemployment rates rise.
D) the net long-run costs of business fluctuations are severe.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 279 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
In a full-employment economy, a rise in M will cause inflation unless
A) V rises in proportion to the increase in M.
B) the quantity of goods produced declines proportionately.
C) tax reductions accompany the increase in the money supply.
D) the velocity of money diminishes.
A) V rises in proportion to the increase in M.
B) the quantity of goods produced declines proportionately.
C) tax reductions accompany the increase in the money supply.
D) the velocity of money diminishes.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 279 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
According to monetarists, the Great Depression in the United States largely resulted from
A) contractionary fiscal policy.
B) excessive imports relative to exports.
C) significant changes in technology and resource availability.
D) inappropriate monetary policy.
A) contractionary fiscal policy.
B) excessive imports relative to exports.
C) significant changes in technology and resource availability.
D) inappropriate monetary policy.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 279 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
If the amount of money in circulation is $180 billion and the value of the economy's total output is $540 billion, then the
A) circulation period of money must be one-fourth of a year.
B) velocity of money is 4.
C) average price per final good sold is $3.
D) velocity of money is 3.
A) circulation period of money must be one-fourth of a year.
B) velocity of money is 4.
C) average price per final good sold is $3.
D) velocity of money is 3.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 279 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
Assume monetary equilibrium exists-that is, the desired and the actual supply of money are equal -when nominal GDP equals $480 billion and the money supply is $160 billion. According to a strict
Monetarist view, an increase in the money supply of $10 billion will increase the nominal GDP by
A) $30 billion.
B) $25 billion.
C) $20 billion.
D) $10 billion.
Monetarist view, an increase in the money supply of $10 billion will increase the nominal GDP by
A) $30 billion.
B) $25 billion.
C) $20 billion.
D) $10 billion.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 279 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
The equation of exchange suggests that, if the supply and velocity of money remain unchanged, an increase in the physical volume of goods and services produced will cause
A) the unemployment rate to rise.
B) the Federal Reserve Banks to sell securities in the open market.
C) a decline in the price level.
D) an automatic budget deficit.
A) the unemployment rate to rise.
B) the Federal Reserve Banks to sell securities in the open market.
C) a decline in the price level.
D) an automatic budget deficit.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 279 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
Monetarists believe the private economy is inherently
A) unstable and the government should take corrective policy actions
B) unstable and the public sector should be large.
C) stable but that the public sector should be large.
D) stable and that the government shouldn't interfere.
A) unstable and the government should take corrective policy actions
B) unstable and the public sector should be large.
C) stable but that the public sector should be large.
D) stable and that the government shouldn't interfere.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 279 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
In the equation of exchange, the nominal GDP is designated by
A) PQ/M.
B) MV/P.
C) PQ.
D) MV.
A) PQ/M.
B) MV/P.
C) PQ.
D) MV.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 279 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
In the real-business-cycle theory,
A) declines in real output cause declines in the money supply and thus aggregate demand.
B) decreases in long-run aggregate supply are fully anticipated and therefore do not reduce real output.
C) technology is constant.
D) economic instability results from inappropriate monetary policy.
A) declines in real output cause declines in the money supply and thus aggregate demand.
B) decreases in long-run aggregate supply are fully anticipated and therefore do not reduce real output.
C) technology is constant.
D) economic instability results from inappropriate monetary policy.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 279 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
Which of the following is not an aggregate-demand-side explanation of business cycles?
A) the real-business-cycle theory
B) the idea of coordination failures
C) mainstream macroeconomics
D) monetarism
A) the real-business-cycle theory
B) the idea of coordination failures
C) mainstream macroeconomics
D) monetarism

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 279 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
New classical economists say that an unanticipated increase in aggregate demand first
A) increases the price level and real output, and then reduces short-run aggregate supply such that the economy returns to the full-employment level of output.
B) increases the price level and real output, and then increases long-run aggregate supply.
C) increases long-run aggregate supply, and then increases the price level and real output.
D) reduces short-run aggregate supply, and then reduces long-run aggregate supply.
A) increases the price level and real output, and then reduces short-run aggregate supply such that the economy returns to the full-employment level of output.
B) increases the price level and real output, and then increases long-run aggregate supply.
C) increases long-run aggregate supply, and then increases the price level and real output.
D) reduces short-run aggregate supply, and then reduces long-run aggregate supply.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 279 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
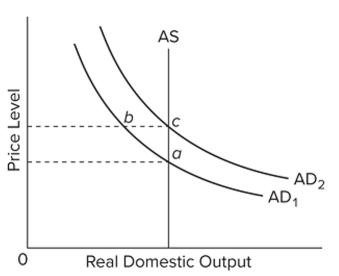
Refer to the diagram. Rational expectations theory says that a fully anticipated shift in aggregate demand from AD1 to AD2 will
A) move the economy from a to b to c.
B) move the economy directly from a to c.
C) move the economy from a to a new equilibrium at b.
D) shift the AS curve to the right.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 279 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
A coordination failure
A) is a real-business-cycle event.
B) is a self-fulfilling prophesy.
C) results from the spending-income multiplier.
D) is a direct outcome of inappropriate fiscal policy.
A) is a real-business-cycle event.
B) is a self-fulfilling prophesy.
C) results from the spending-income multiplier.
D) is a direct outcome of inappropriate fiscal policy.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 279 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
When most consumers and firms reduce spending only because they expect other consumers and firms to reduce spending, and a recession results,
A) a self-correction has occurred.
B) an adverse aggregate supply shock has occurred.
C) a coordination failure has occurred.
D) a real-business downturn has occurred.
A) a self-correction has occurred.
B) an adverse aggregate supply shock has occurred.
C) a coordination failure has occurred.
D) a real-business downturn has occurred.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 279 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
According to new classical economists, the
A) short-run demand for labor curve is vertical.
B) short-run aggregate demand curve is vertical.
C) long-run aggregate supply curve is horizontal.
D) long-run aggregate supply curve is vertical.
A) short-run demand for labor curve is vertical.
B) short-run aggregate demand curve is vertical.
C) long-run aggregate supply curve is horizontal.
D) long-run aggregate supply curve is vertical.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 279 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
New classical economists say that an unanticipated decrease in aggregate demand first
A) decreases the price level and real output, and then decreases long-run aggregate supply.
B) decreases long-run aggregate supply, and then decreases the price level and real output.
C) reduces short-run aggregate supply, and then reduces long-run aggregate supply.
D) decreases the price level and real output, and then increases short-run aggregate supply such that the economy returns to the full-employment level of output.
A) decreases the price level and real output, and then decreases long-run aggregate supply.
B) decreases long-run aggregate supply, and then decreases the price level and real output.
C) reduces short-run aggregate supply, and then reduces long-run aggregate supply.
D) decreases the price level and real output, and then increases short-run aggregate supply such that the economy returns to the full-employment level of output.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 279 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
New classical economists
A) stress the importance of federal budget deficits in stimulating aggregate demand.
B) hold that, left alone, the economy gravitates to its full-employment level of output.
C) emphasize tax cuts as means of increasing aggregate supply.
D) advocate active use of monetary policy to stabilize the economy.
A) stress the importance of federal budget deficits in stimulating aggregate demand.
B) hold that, left alone, the economy gravitates to its full-employment level of output.
C) emphasize tax cuts as means of increasing aggregate supply.
D) advocate active use of monetary policy to stabilize the economy.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 279 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
Rational expectations theory is based on the assumption that
A) wages and prices are flexible upward but inflexible downward.
B) both product and resource markets are very competitive.
C) product markets are competitive, but resource markets are monopolistic.
D) both product and resource markets are monopolistic.
A) wages and prices are flexible upward but inflexible downward.
B) both product and resource markets are very competitive.
C) product markets are competitive, but resource markets are monopolistic.
D) both product and resource markets are monopolistic.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 279 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
Rational expectations theory assumes that
A) people behave rationally and that all product and resource prices are flexible both upward and downward.
B) firms pay above-market wages to elicit work effort.
C) markets fail to coordinate the actions of households and businesses.
D) markets are dominated by monopolistic firms.
A) people behave rationally and that all product and resource prices are flexible both upward and downward.
B) firms pay above-market wages to elicit work effort.
C) markets fail to coordinate the actions of households and businesses.
D) markets are dominated by monopolistic firms.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 279 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
Rational expectations theory implies that the
A) aggregate demand curve is vertical.
B) long-run aggregate supply curve is vertical.
C) long-run aggregate supply curve is horizontal.
D) long-run aggregate supply curve is quite flat.
A) aggregate demand curve is vertical.
B) long-run aggregate supply curve is vertical.
C) long-run aggregate supply curve is horizontal.
D) long-run aggregate supply curve is quite flat.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 279 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
New classical economists say that a fully anticipated decrease in aggregate demand
A) shifts the long-run aggregate supply curve to the right.
B) shifts the long-run aggregate supply curve to the left.
C) moves the economy down along its vertical long-run aggregate supply curve.
D) eventually results in a self-correcting increase in aggregate demand.
A) shifts the long-run aggregate supply curve to the right.
B) shifts the long-run aggregate supply curve to the left.
C) moves the economy down along its vertical long-run aggregate supply curve.
D) eventually results in a self-correcting increase in aggregate demand.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 279 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
Assume that many households and businesses reduce their spending only because they expect other households and consumers to reduce their spending. Also suppose that all households and
Consumers would be better off if they did not reduce their spending. This situation best describes
The
A) real-business-cycle theory.
B) rational expectations theory.
C) concept of coordination failures.
D) adaptive expectations theory.
Consumers would be better off if they did not reduce their spending. This situation best describes
The
A) real-business-cycle theory.
B) rational expectations theory.
C) concept of coordination failures.
D) adaptive expectations theory.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 279 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
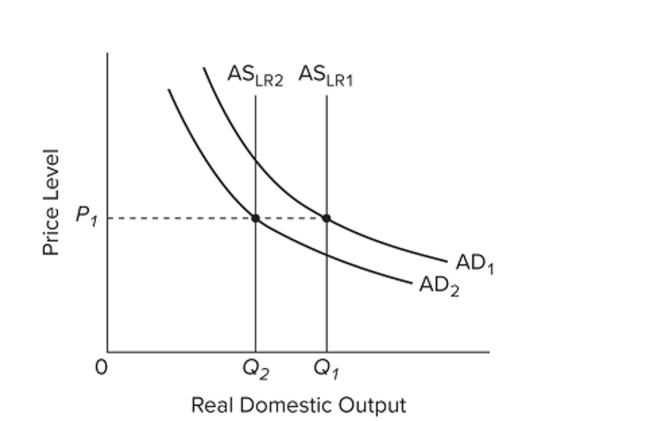 Refer to the diagram. The real-business-cycle view of recession would best be described by
Refer to the diagram. The real-business-cycle view of recession would best be described byA) a decrease of aggregate demand from to , followed by a decrease in aggregate supply from to .
B) an increase in aggregate demand from to , which in turn causes a decrease in aggregate supply from to .
C) a decrease in aggregate supply from to , followed by a decrease in aggregate demand from to .
D) a decrease in aggregate supply from to , followed by an increase in aggregate demand from to .

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 279 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
A) new classical economics.
B) mainstream economics.
C) the real-business-cycle theory.
D) a coordination failure.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 279 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
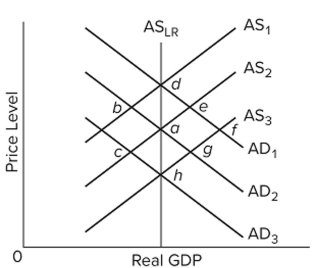
Refer to the figure and assume the economy initially is in equilibrium at point a. In the new classical theory, an unanticipated increase in aggregate demand from AD2 to AD1 would move the economy
A) directly from a to d.
B) from a to b to d.
C) from a to e to d.
D) directly from a to f.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 279 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
The real-business-cycle theory
A) is a monetarist view of the business cycle.
B) is the mainstream view of the business cycle.
C) assumes that the supply of money is constant.
D) says that macro instability results from shifts in the long-run aggregate supply curve.
A) is a monetarist view of the business cycle.
B) is the mainstream view of the business cycle.
C) assumes that the supply of money is constant.
D) says that macro instability results from shifts in the long-run aggregate supply curve.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 279 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
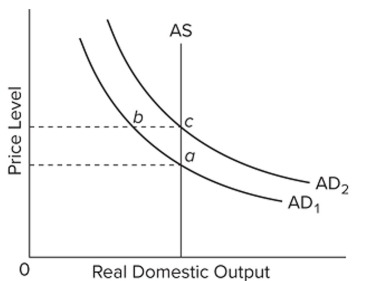
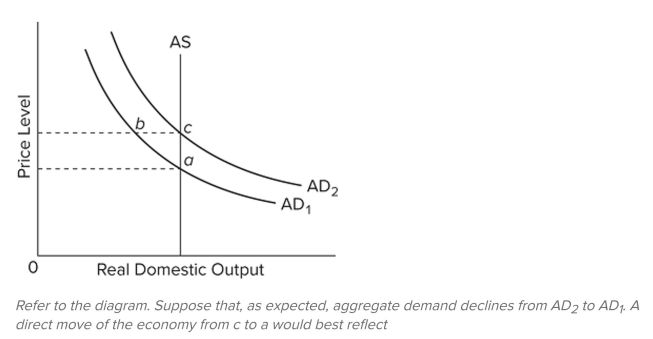
Refer to the diagram. Rational expectations theory says that a fully anticipated decrease in aggregate demand from AD2 to AD1 will
A) move the economy from a to b to c.
B) shift the AS curve to the left.
C) move the economy from c to a new equilibrium at b.
D) move the economy directly from c to a.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 279 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
The idea that an economy can get stuck in either an unemployment equilibrium or an inflation equilibrium is most closely associated with
A) new classical economics.
B) the real-business-cycle theory.
C) monetarism.
D) the idea of coordination failures.
A) new classical economics.
B) the real-business-cycle theory.
C) monetarism.
D) the idea of coordination failures.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 279 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
New classical economists say that a fully anticipated increase in aggregate demand
A) shifts the long-run aggregate supply curve to the right.
B) shifts the long-run aggregate supply curve to the left.
C) moves the economy up along its vertical long-run aggregate supply curve.
D) eventually results in a self-correcting decrease in aggregate demand.
A) shifts the long-run aggregate supply curve to the right.
B) shifts the long-run aggregate supply curve to the left.
C) moves the economy up along its vertical long-run aggregate supply curve.
D) eventually results in a self-correcting decrease in aggregate demand.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 279 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
An efficiency wage is
A) a below-market wage.
B) an above-market wage.
C) a "wage" that contains a profit-sharing component.
D) a wage that is free to rise or fall from day to day, depending on labor supply and demand.
A) a below-market wage.
B) an above-market wage.
C) a "wage" that contains a profit-sharing component.
D) a wage that is free to rise or fall from day to day, depending on labor supply and demand.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 279 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
A higher wage could result in a lower labor cost per unit of output than a lower wage if the higher wage
A) is accompanied by an offsetting decline in fringe benefits.
B) increases supervision costs.
C) reduces job turnover.
D) increases worker absenteeism.
A) is accompanied by an offsetting decline in fringe benefits.
B) increases supervision costs.
C) reduces job turnover.
D) increases worker absenteeism.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 279 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
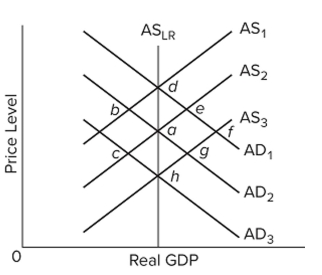
Refer to the figure and assume the economy initially is in equilibrium at point a. In the new classical theory, a fully anticipated decrease in aggregate demand from AD2 to AD3 would move the economy
A) directly from a to h.
B) from a to g to h.
C) directly from a to d.
D) from a to c to h.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 279 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
An efficiency wage is
A) a wage payment necessary to compensate workers for risk of injury on the job.
B) a "wage" that contains a profit-sharing component as well as traditional hourly pay.
C) an above-market wage that minimizes a firm's labor cost per unit of output.
D) a wage that automatically rises with the national index of labor productivity.
A) a wage payment necessary to compensate workers for risk of injury on the job.
B) a "wage" that contains a profit-sharing component as well as traditional hourly pay.
C) an above-market wage that minimizes a firm's labor cost per unit of output.
D) a wage that automatically rises with the national index of labor productivity.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 279 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
Mainstream economists question the new classical assumption that
A) excessive growth of the money supply is a cause of inflation.
B) the price level is determined by aggregate demand and aggregate supply.
C) demand creates its own supply.
D) wages and prices are equally flexible upward and downward.
A) excessive growth of the money supply is a cause of inflation.
B) the price level is determined by aggregate demand and aggregate supply.
C) demand creates its own supply.
D) wages and prices are equally flexible upward and downward.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 279 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
Which of the following pairs helps explain why self-correction from a decline in aggregate demand in the economy may be slow rather than rapid?
A) theory of compensation wage differentials; theory of derived demand for labor
B) efficiency wage theory; minimum wage laws
C) insider-outsider theory; principle-agent problem
D) externalities; efficiency wage theory
A) theory of compensation wage differentials; theory of derived demand for labor
B) efficiency wage theory; minimum wage laws
C) insider-outsider theory; principle-agent problem
D) externalities; efficiency wage theory

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 279 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
Suppose aggregate demand in the economy sharply declines. Mainstream economists say that the price level (at least for a time) will _______ and real output will _________.
A) decrease; remain constant
B) increase; remain constant
C) remain constant; decrease
D) remain constant; increase
A) decrease; remain constant
B) increase; remain constant
C) remain constant; decrease
D) remain constant; increase

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 279 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
Refer to the table. At the $8 wage, labor cost per unit of output is
A) $1.25.
B) $1.50.
C) $2.00.
D) $1.67.
A) $1.25.
B) $1.50.
C) $2.00.
D) $1.67.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 279 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
If firms are paying efficiency wages, they
A) may be reluctant to increase nominal wages when aggregate demand increases.
B) are highly vulnerable to import competition.
C) may be targeted for takeover by firms paying market wages.
D) may be reluctant to cut wages when aggregate demand declines.
A) may be reluctant to increase nominal wages when aggregate demand increases.
B) are highly vulnerable to import competition.
C) may be targeted for takeover by firms paying market wages.
D) may be reluctant to cut wages when aggregate demand declines.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 279 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
The traditional monetary rule is the idea that
A) the annual rate of increase in the money supply should be equal to the potential annual growth rate of real GDP.
B) the annual rate of increase in the money supply should be equal to the long-term increase in the price level.
C) an expansionary fiscal policy should always be accompanied by an easy monetary policy.
D) monetary policy only affects the economy 6 to 9 months after the money supply is changed.
A) the annual rate of increase in the money supply should be equal to the potential annual growth rate of real GDP.
B) the annual rate of increase in the money supply should be equal to the long-term increase in the price level.
C) an expansionary fiscal policy should always be accompanied by an easy monetary policy.
D) monetary policy only affects the economy 6 to 9 months after the money supply is changed.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 279 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
If prices and wages are inflexible downward, a decrease in aggregate demand will
A) reduce the price level but not real output.
B) increase short-run aggregate supply.
C) decrease short-run aggregate supply.
D) reduce real output but not the price level.
A) reduce the price level but not real output.
B) increase short-run aggregate supply.
C) decrease short-run aggregate supply.
D) reduce real output but not the price level.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 279 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72
Suppose that, as expected, aggregate demand in the economy sharply declines. New classical economists say that the price level will _____________ and real output will ____________.
A) fall; remain constant
B) fall; fall
C) remain constant; fall
D) remain constant; rise
A) fall; remain constant
B) fall; fall
C) remain constant; fall
D) remain constant; rise

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 279 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73
A higher wage could result in a lower labor cost per unit of output than a lower wage if the higher wage
A) brings forth greater work effort.
B) increases supervision costs.
C) increases job turnover.
D) increases worker absenteeism.
A) brings forth greater work effort.
B) increases supervision costs.
C) increases job turnover.
D) increases worker absenteeism.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 279 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
74
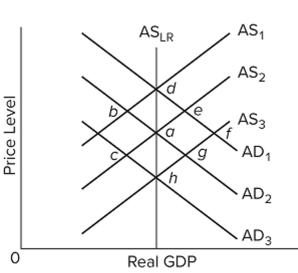
Refer to the figure and assume the economy initially is in equilibrium at point a. In the new classical theory, an unanticipated decrease in aggregate demand from AD2 to AD3 would move the economy
A) directly from a to h.
B) from a to g to h.
C) directly from a to d.
D) from a to c to h.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 279 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
75
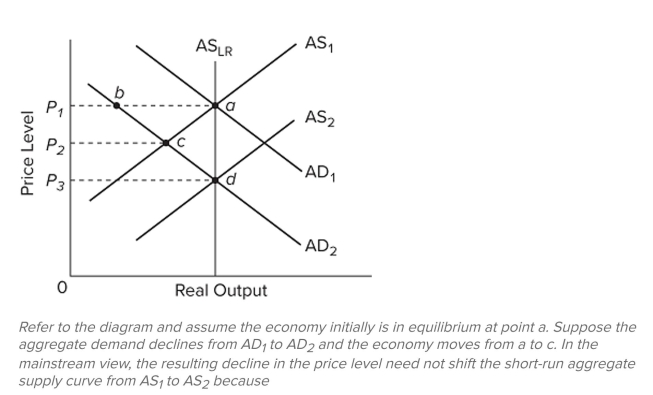
A) supply creates its own demand.
B) nominal wages are (at least for a time) inflexible downward.
C) firms misperceive the price-level decline as being permanent.
D) deflation reduces the purchasing power of the dollar.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 279 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
76
In new classical economics, a "price-level surprise"
A) has no effect on the economy.
B) causes a temporary change in real output.
C) causes a permanent change in real output.
D) can never occur since people correctly anticipate the future.
A) has no effect on the economy.
B) causes a temporary change in real output.
C) causes a permanent change in real output.
D) can never occur since people correctly anticipate the future.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 279 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
77
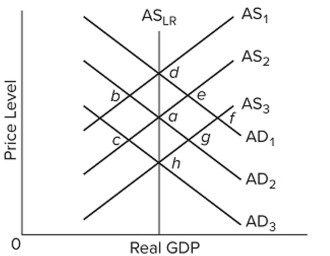
Refer to the figure and assume the economy initially is in equilibrium at point a. In the new classical theory, a fully anticipated increase in aggregate demand from AD2 to AD1 would move the economy
A) directly from a to d.
B) from a to b to d.
C) from a to e to d.
D) directly from a to f.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 279 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
78
In new classical economics, the change in output caused by a "price-level surprise"
A) is shown as a shift of the long-run aggregate supply curve.
B) does not alter the rate of unemployment, even in the short run.
C) is soon reversed through a shift of the short-run aggregate supply curve.
D) permanently changes the rate of unemployment.
A) is shown as a shift of the long-run aggregate supply curve.
B) does not alter the rate of unemployment, even in the short run.
C) is soon reversed through a shift of the short-run aggregate supply curve.
D) permanently changes the rate of unemployment.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 279 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
79
Refer to the table. The e?ciency wage is
A) $10.
B) $9.
C) $8
D) $6.
A) $10.
B) $9.
C) $8
D) $6.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 279 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
80
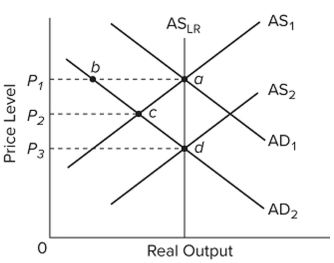
Refer to the diagram and assume the economy initially is in equilibrium at point a. In the mainstream view, a decline in aggregate demand from AD1 to AD2 would likely move the economy
A) directly from a to d.
B) directly from a to b.
C) from a to c, then quickly from c to d.
D) from a to c, then eventually from c to b.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 279 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



