Deck 11: The Aggregate Expenditures Model
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/126
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 11: The Aggregate Expenditures Model
1
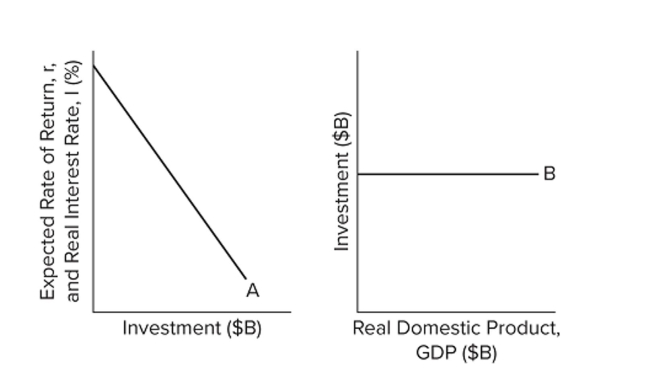 Refer to the diagrams. Other things equal, an interest rate reduction coupled with a rightward shift in curve A will
Refer to the diagrams. Other things equal, an interest rate reduction coupled with a rightward shift in curve A willA) shift curve B upward.
B) shift curve B downward.
C) have no effect on curve B.
D) reduce GDP.
shift curve B upward.
2
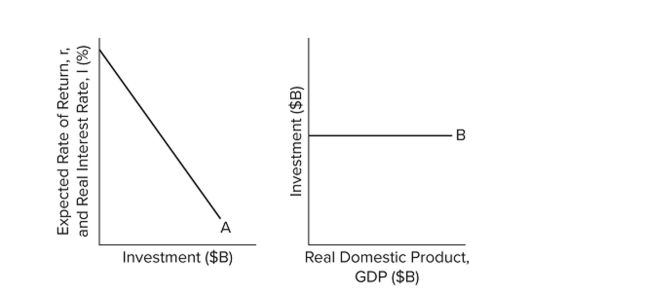 Refer to the diagrams. Other things equal, curve B will shift upward when
Refer to the diagrams. Other things equal, curve B will shift upward whenA) the level of GDP increases.
B) the interest rate increases.
C) curve A shifts to the left.
D) curve A shifts to the right.
curve A shifts to the right.
3
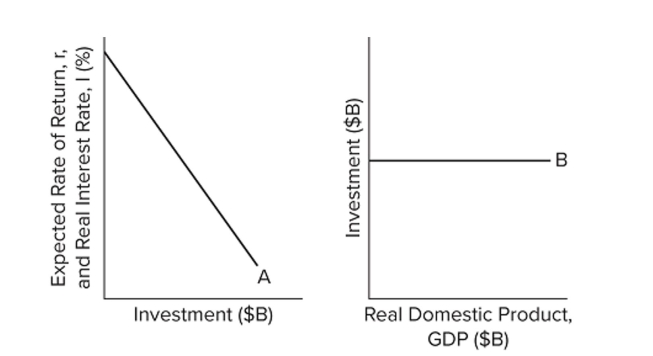 Refer to the diagrams. Other things equal, an interest rate increase will
Refer to the diagrams. Other things equal, an interest rate increase willA) shift curve A to the right and shift curve B upward.
B) shift curve A to the left and shift curve B downward.
C) leave curve A in place but shift curve B downward.
D) leave curve A in place but shift curve B upward.
leave curve A in place but shift curve B downward.
4
The table gives data for a private closed economy. If gross investment is $12 billion, the equilibrium level of GDP will be
A) $380.
B) $370.
C) $360.
D) $350.
A) $380.
B) $370.
C) $360.
D) $350.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 126 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
In the United States from 1929 to 1933, real GDP _____________ and the unemployment rate ________________.
A) declined by 27 percent; rose to 25 percent.
B) increased by 21 percent; fell to 2 percent.
C) declined by 21 percent; rose to 27 percent.
D) declined by 40 percent; rose to 50 percent.
A) declined by 27 percent; rose to 25 percent.
B) increased by 21 percent; fell to 2 percent.
C) declined by 21 percent; rose to 27 percent.
D) declined by 40 percent; rose to 50 percent.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 126 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
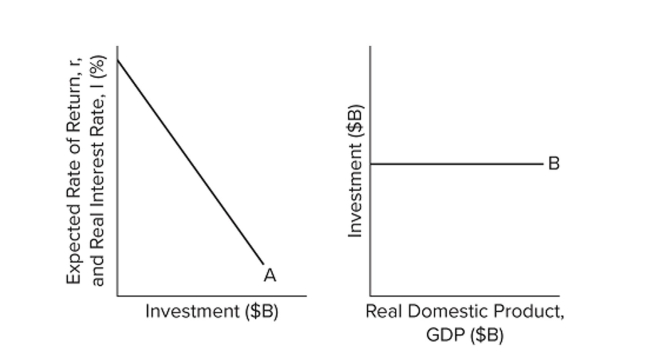 Refer to the diagrams. Other things equal, an interest rate decrease will
Refer to the diagrams. Other things equal, an interest rate decrease willA) shift curve A to the right and shift curve B upward.
B) shift curve A to the left and shift curve B downward.
C) leave curve A in place but shift curve B downward.
D) leave curve A in place but shift curve B upward.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 126 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
In the aggregate expenditures model, it is assumed that investment
A) automatically changes in response to changes in real GDP.
B) changes by less in percentage terms than changes in real GDP.
C) does not respond to changes in interest rates.
D) does not change when real GDP changes.
A) automatically changes in response to changes in real GDP.
B) changes by less in percentage terms than changes in real GDP.
C) does not respond to changes in interest rates.
D) does not change when real GDP changes.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 126 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
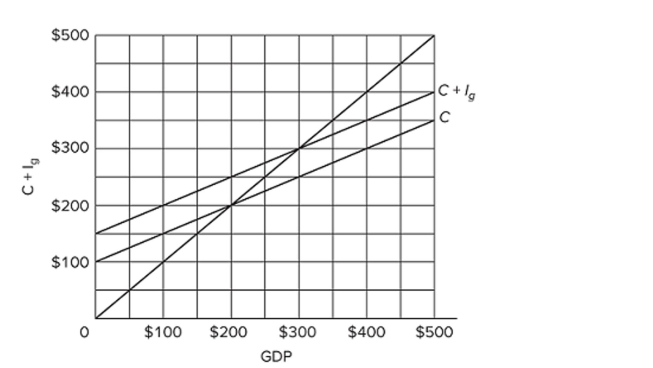 Refer to the diagram for a private closed economy. Unplanned changes in inventories will be zero
Refer to the diagram for a private closed economy. Unplanned changes in inventories will be zeroA) only at the $300 level of GDP.
B) only at the $200 level of GDP.
C) at all levels of GDP.
D) only at the $400 level of GDP.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 126 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
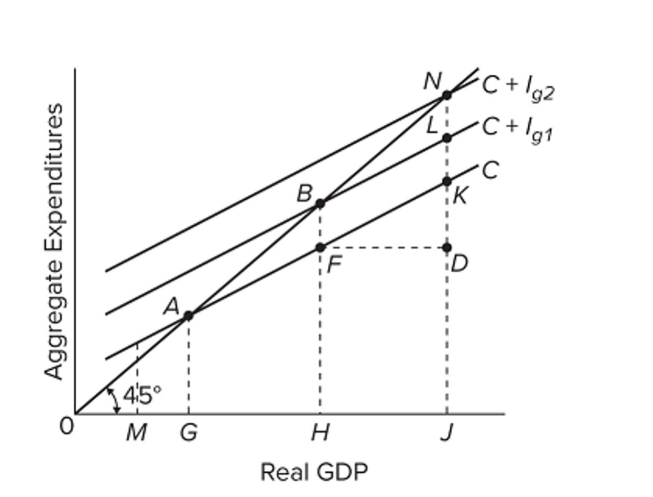 Refer to the diagram, which applies to a private closed economy. If aggregate expenditures are C + Ig2, the amount of saving at income level J is
Refer to the diagram, which applies to a private closed economy. If aggregate expenditures are C + Ig2, the amount of saving at income level J isA) LK.
B) KN.
C) KD.
D) JD.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 126 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
The aggregate expenditures model is built upon which of the following assumptions?
A) Prices are fixed.
B) The economy is at full employment.
C) Prices are fully flexible.
D) Government spending policy has no ability to affect the level of output.
A) Prices are fixed.
B) The economy is at full employment.
C) Prices are fully flexible.
D) Government spending policy has no ability to affect the level of output.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 126 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
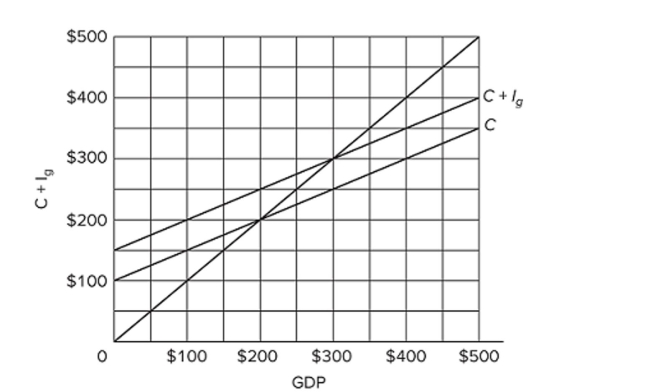 Refer to the diagram for a private closed economy. The equilibrium level of GDP is
Refer to the diagram for a private closed economy. The equilibrium level of GDP isA) $400.
B) $300.
C) $200.
D) $100.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 126 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
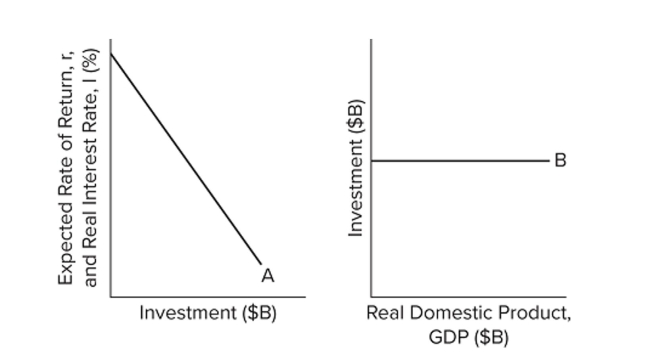 Refer to the diagrams. The location of curve B depends on the
Refer to the diagrams. The location of curve B depends on theA) level of real GDP.
B) location of curve A only.
C) interest rate only.
D) interest rate together with the location of curve A.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 126 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
The level of aggregate expenditures in the private closed economy is determined by the
A) expenditures of consumers and businesses.
B) intersection of the saving schedule and the 45-degree line.
C) equality of the MPC and MPS.
D) intersection of the saving and consumption schedules.
A) expenditures of consumers and businesses.
B) intersection of the saving schedule and the 45-degree line.
C) equality of the MPC and MPS.
D) intersection of the saving and consumption schedules.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 126 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
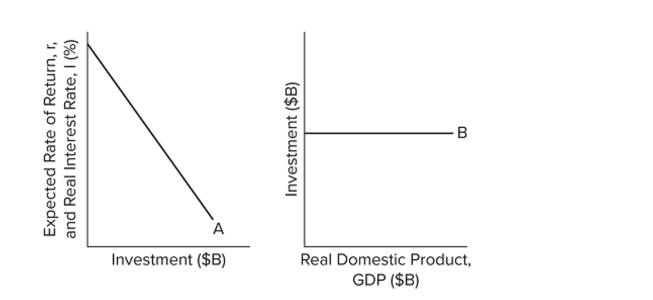 Refer to the diagrams. Curve A
Refer to the diagrams. Curve AA) is an investment schedule, and curve B is a consumption of fixed capital schedule.
B) is an investment demand curve, and curve B is an investment schedule.
C) and curve B are totally unrelated.
D) shifts to the left when curve B shifts upward.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 126 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
A private closed economy includes
A) households, businesses, and government, but not international trade.
B) households, businesses, and international trade, but not government.
C) households and businesses, but not government or international trade.
D) households only.
A) households, businesses, and government, but not international trade.
B) households, businesses, and international trade, but not government.
C) households and businesses, but not government or international trade.
D) households only.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 126 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
John Maynard Keynes created the aggregate expenditures model based primarily on what historical event?
A) bank panic of 1907
B) Great Depression
C) spectacular economic growth during World War II
D) economic expansion of the 1920s
A) bank panic of 1907
B) Great Depression
C) spectacular economic growth during World War II
D) economic expansion of the 1920s

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 126 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
All else equal, a large decline in the real interest rate will shift the
A) investment demand curve leftward.
B) investment demand curve rightward.
C) investment schedule upward.
D) investment schedule downward.
A) investment demand curve leftward.
B) investment demand curve rightward.
C) investment schedule upward.
D) investment schedule downward.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 126 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
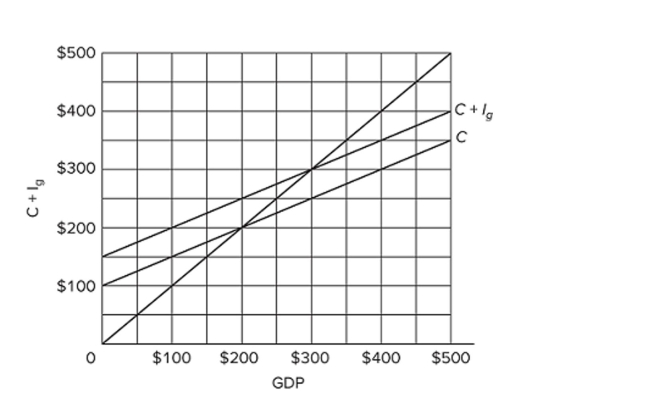 Refer to the diagram for a private closed economy. The $400 level of GDP is
Refer to the diagram for a private closed economy. The $400 level of GDP isA) that output at which saving is zero.
B) too high because consumption exceeds investment.
C) unsustainable because aggregate expenditures exceed GDP.
D) unsustainable because aggregate expenditures are less than GDP.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 126 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
The table gives data for a private closed economy. The MPS is
A) 7/10.
B) 3/10.
C) 2/5.
D) 3/5.
A) 7/10.
B) 3/10.
C) 2/5.
D) 3/5.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 126 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
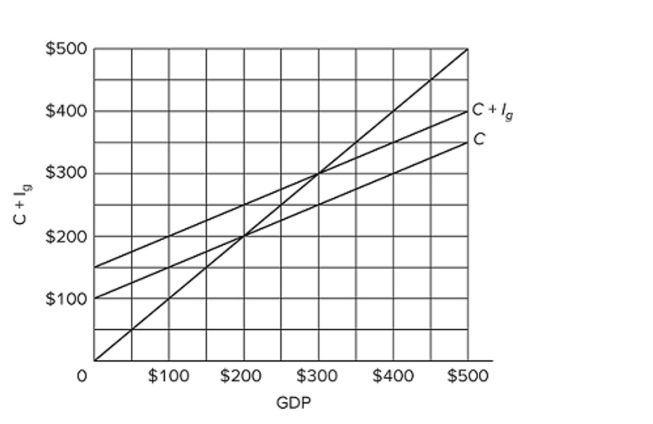 Refer to the diagram for a private closed economy. At the equilibrium level of GDP, investment and saving are both
Refer to the diagram for a private closed economy. At the equilibrium level of GDP, investment and saving are bothA) $50.
B) $100.
C) $20.
D) $40.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 126 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
(Advanced analysis) The given equations describe consumption and investment (in billions of dollars) for a private closed economy.
C = 60 + 0.6Y
I = I0 = 30
In equilibrium, the level of consumption spending will be
A) 170.
B) 270.
C) 160.
D) 195.
C = 60 + 0.6Y
I = I0 = 30
In equilibrium, the level of consumption spending will be
A) 170.
B) 270.
C) 160.
D) 195.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 126 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
A private closed economy will expand when
A) actual GDP is less than potential GDP.
B) unplanned decreases in inventories occur.
C) aggregate expenditures are less than GDP.
D) unplanned increases in inventories occur.
A) actual GDP is less than potential GDP.
B) unplanned decreases in inventories occur.
C) aggregate expenditures are less than GDP.
D) unplanned increases in inventories occur.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 126 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
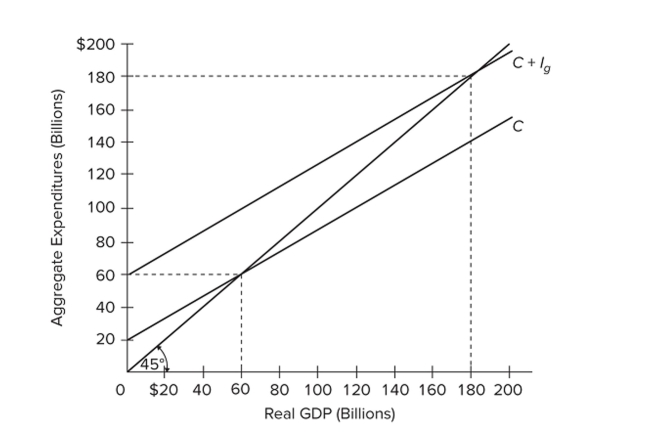 Refer to the diagram for a private closed economy. Aggregate saving in this economy will be zero when
Refer to the diagram for a private closed economy. Aggregate saving in this economy will be zero whenA) C + Ig cuts the 45-degree line.
B) GDP is $180 billion.
C) GDP is $60 billion.
D) GDP is also zero.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 126 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
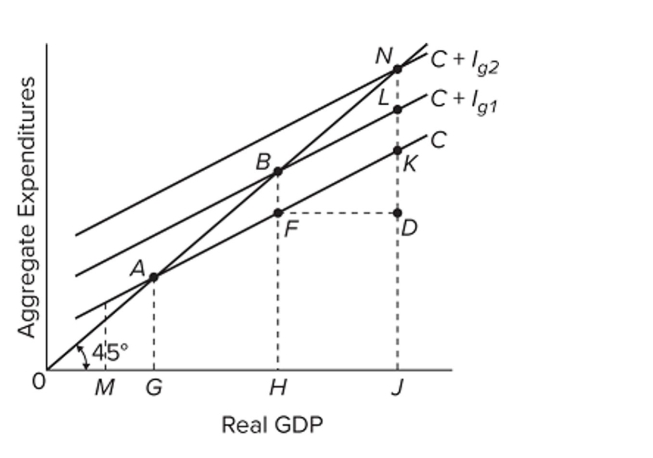 Refer to the diagram, which applies to a private closed economy. If gross investment is Ig1, the equilibrium GDP and the level of consumption will be
Refer to the diagram, which applies to a private closed economy. If gross investment is Ig1, the equilibrium GDP and the level of consumption will beA) H and HB, respectively.
B) J and JI, respectively.
C) J and JK, respectively.
D) H and HF, respectively.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 126 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
If an unintended increase in business inventories occurs,
A) we can expect aggregate production to be unaffected.
B) we can expect businesses to increase the level of production.
C) we can expect businesses to lower the level of production.
D) aggregate expenditures must exceed the domestic output.
A) we can expect aggregate production to be unaffected.
B) we can expect businesses to increase the level of production.
C) we can expect businesses to lower the level of production.
D) aggregate expenditures must exceed the domestic output.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 126 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
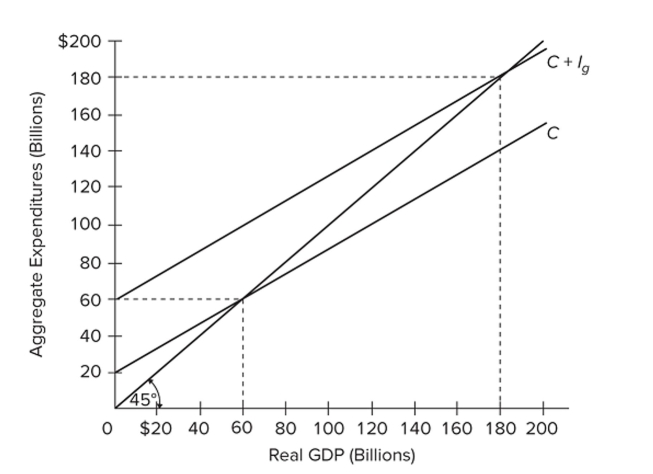 Refer to the diagram for a private closed economy. In this economy, aggregate expenditures
Refer to the diagram for a private closed economy. In this economy, aggregate expendituresA) do not change as GDP increases.
B) increase by $2 for every $5 increase in GDP.
C) increase by $2 for every $4 increase in GDP.
D) increase by $2 for every $3 increase in GDP.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 126 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
If aggregate expenditures exceed GDP in a private closed economy,
A) leakages will exceed injections.
B) planned investment will exceed saving.
C) unplanned investment in inventories will occur.
D) saving will exceed planned investment.
A) leakages will exceed injections.
B) planned investment will exceed saving.
C) unplanned investment in inventories will occur.
D) saving will exceed planned investment.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 126 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
In a private closed economy, when aggregate expenditures exceed GDP,
A) GDP will decline.
B) business inventories will rise.
C) saving will decline.
D) business inventories will fall.
A) GDP will decline.
B) business inventories will rise.
C) saving will decline.
D) business inventories will fall.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 126 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
For a private closed economy, an unintended decline in inventories suggests that
A) aggregate expenditures are less than the business sector expected them to be.
B) aggregate expenditures exceed production.
C) actual investment exceeds saving.
D) planned investment is greater than consumption.
A) aggregate expenditures are less than the business sector expected them to be.
B) aggregate expenditures exceed production.
C) actual investment exceeds saving.
D) planned investment is greater than consumption.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 126 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
The equilibrium level of GDP is associated with
A) an excess of planned investment over saving.
B) no unintended changes in inventories.
C) an unintended decrease in business inventories.
D) an unintended increase in business inventories.
A) an excess of planned investment over saving.
B) no unintended changes in inventories.
C) an unintended decrease in business inventories.
D) an unintended increase in business inventories.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 126 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
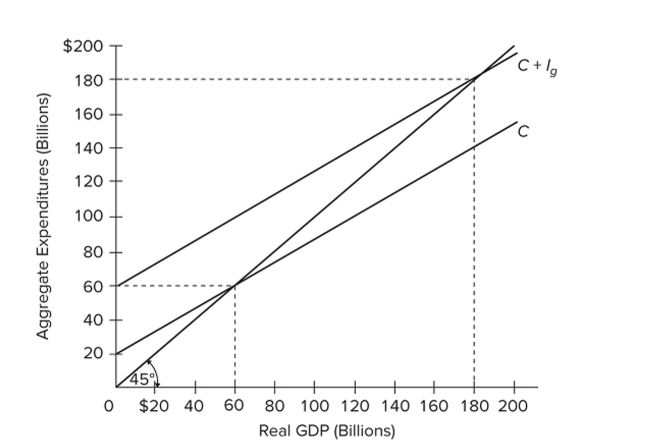 Refer to the diagram for a private closed economy. In this economy, investment
Refer to the diagram for a private closed economy. In this economy, investmentA) decreases as GDP increases.
B) increases as GDP increases.
C) is $40 billion at all levels of GDP.
D) is $60 billion at all levels of GDP.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 126 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
In a private closed economy, when aggregate expenditures equal GDP,
A) consumption equals investment.
B) consumption equals aggregate expenditures.
C) planned investment equals saving.
D) disposable income equals consumption minus saving.
A) consumption equals investment.
B) consumption equals aggregate expenditures.
C) planned investment equals saving.
D) disposable income equals consumption minus saving.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 126 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
(Advanced analysis) The table gives data for a private closed economy. The letters Y, C, S, and I are used to represent real GDP, consumption, saving, and investment, respectively. The equation
Representing the consumption schedule for the economy is
A) C = Y ? 0.6S.
B) Y = C + S.
C) C = 60 + 0.4Y.
D) C = 60 + 0.6Y.
Representing the consumption schedule for the economy is
A) C = Y ? 0.6S.
B) Y = C + S.
C) C = 60 + 0.4Y.
D) C = 60 + 0.6Y.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 126 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
Assume that in a private closed economy, consumption is $240 billion and investment is $50 billion, both at the $280 billion level of domestic output. Thus,
A) saving is $10 billion.
B) unplanned decreases in inventories of $10 billion will occur.
C) the MPC is 0.80.
D) unplanned increases in inventories of $10 billion will occur.
A) saving is $10 billion.
B) unplanned decreases in inventories of $10 billion will occur.
C) the MPC is 0.80.
D) unplanned increases in inventories of $10 billion will occur.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 126 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
(Advanced analysis) The given equations describe consumption and investment (in billions of dollars) for a private closed economy.
C = 60 + 0.6Y
I = I0 = 30
In equilibrium, the level of saving will be
A) 30.
B) 26.
C) 25.
D) 60.
C = 60 + 0.6Y
I = I0 = 30
In equilibrium, the level of saving will be
A) 30.
B) 26.
C) 25.
D) 60.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 126 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
If an unintended increase in business inventories occurs at some level of GDP, then GDP
A) entails a rate of aggregate expenditures in excess of the rate of aggregate production.
B) may be either above or below the equilibrium output.
C) is too low for equilibrium.
D) is too high for equilibrium.
A) entails a rate of aggregate expenditures in excess of the rate of aggregate production.
B) may be either above or below the equilibrium output.
C) is too low for equilibrium.
D) is too high for equilibrium.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 126 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
If at some level of GDP the economy is experiencing an unintended decrease in inventories,
A) the aggregate level of saving will decline.
B) the price level will fall.
C) the business sector will lay off workers.
D) domestic output will increase.
A) the aggregate level of saving will decline.
B) the price level will fall.
C) the business sector will lay off workers.
D) domestic output will increase.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 126 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
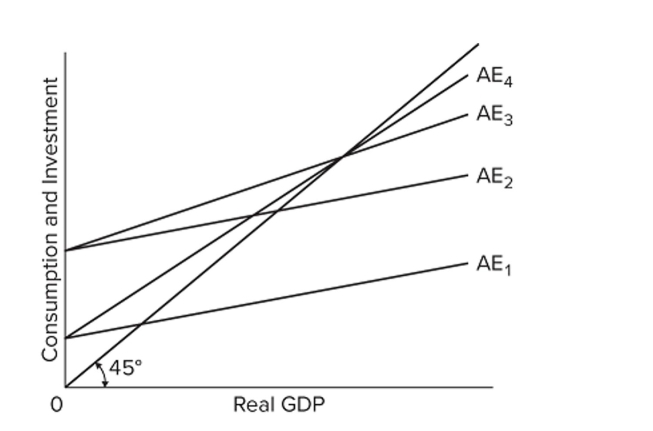 Which two aggregate expenditure schedules AE in the diagram for a private closed economy have the same MPC, assuming investment is the same at each level of income?
Which two aggregate expenditure schedules AE in the diagram for a private closed economy have the same MPC, assuming investment is the same at each level of income?A) AE1 and AE2
B) AE2 and AE3
C) AE1 and AE4
D) AE3 and AE4

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 126 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
(Advanced analysis) The given equations describe consumption and investment (in billions of dollars) for a private closed economy.
C = 60 + 0.6Y
I = I0 = 30
In this economy, the equilibrium level of income (Y) is
A) 360.
B) 225.
C) 200.
D) 135.
C = 60 + 0.6Y
I = I0 = 30
In this economy, the equilibrium level of income (Y) is
A) 360.
B) 225.
C) 200.
D) 135.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 126 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
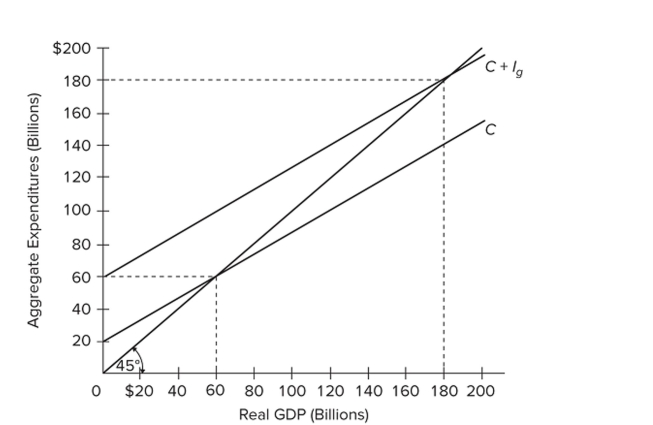 Refer to the diagram for a private closed economy. The equilibrium GDP is
Refer to the diagram for a private closed economy. The equilibrium GDP isA) $60 billion.
B) $180 billion.
C) between $60 and $180 billion.
D) $60 billion at all levels of GDP.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 126 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
(Advanced analysis) The table gives data for a private closed economy. The letters Y, C, S, and I are used to represent real GDP, consumption, saving, and investment, respectively. Equilibrium Y (= GDP)
Is
A) $100.
B) $200.
C) $300.
D) $400.
Is
A) $100.
B) $200.
C) $300.
D) $400.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 126 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
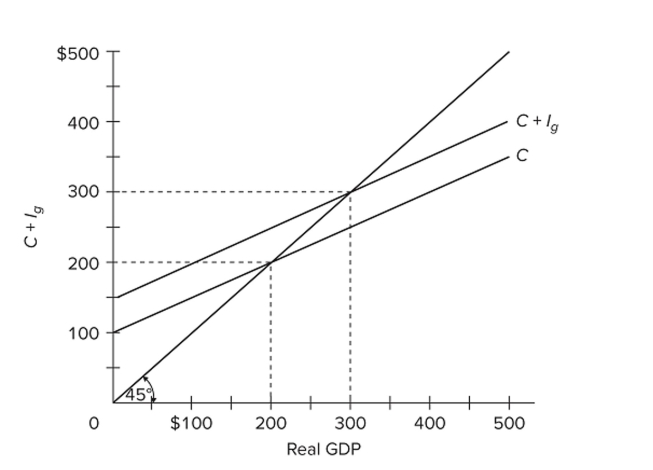 Refer to the diagram for a private closed economy. At the $200 level of GDP,
Refer to the diagram for a private closed economy. At the $200 level of GDP,A) consumption is $200 and planned investment is $50, so aggregate expenditures are $250.
B) consumption is $200 and planned investment is $100, so aggregate expenditures are $300.
C) consumption is $250 and actual investment is $50, so aggregate expenditures are $300.
D) aggregate expenditures fall short of GDP, with the result that GDP will decline.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 126 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
SA=−20 + 0.4Y
Ig = 25 − 3i
(Advanced analysis) The equations refer to a private closed economy, where S is saving, Ig is gross
Investment, i is the real interest rate, and Y is GDP. If the real interest rate is 5 (percent), investment will
Be
A) $10 and the equilibrium GDP will be $75.
B) $15 and the equilibrium GDP will be $100.
C) $10 and the equilibrium GDP will be $120.
D) $15 and the equilibrium GDP will be $180.
Ig = 25 − 3i
(Advanced analysis) The equations refer to a private closed economy, where S is saving, Ig is gross
Investment, i is the real interest rate, and Y is GDP. If the real interest rate is 5 (percent), investment will
Be
A) $10 and the equilibrium GDP will be $75.
B) $15 and the equilibrium GDP will be $100.
C) $10 and the equilibrium GDP will be $120.
D) $15 and the equilibrium GDP will be $180.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 126 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
When investment remains the same at each level of GDP in a private closed economy, the slope of the aggregate expenditures schedule
A) exceeds the MPC.
B) is less than the MPC.
C) equals the MPS.
D) equals the MPC.
A) exceeds the MPC.
B) is less than the MPC.
C) equals the MPS.
D) equals the MPC.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 126 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
At equilibrium real GDP in a private closed economy,
A) the MPC must equal the APC.
B) the slope of the aggregate expenditures schedule equals the MPS.
C) aggregate expenditures and real GDP are equal.
D) planned saving and consumption are equal.
A) the MPC must equal the APC.
B) the slope of the aggregate expenditures schedule equals the MPS.
C) aggregate expenditures and real GDP are equal.
D) planned saving and consumption are equal.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 126 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
SA=−20 + 0.4Y
Ig = 25 − 3i
(Advanced analysis) The equations refer to a private closed economy, where S is saving, Ig is gross
Investment, i is the real interest rate, and Y is GDP. In equilibrium, the level of saving will be
A) $10.
B) $15.
C) $20.
D) $30.
Ig = 25 − 3i
(Advanced analysis) The equations refer to a private closed economy, where S is saving, Ig is gross
Investment, i is the real interest rate, and Y is GDP. In equilibrium, the level of saving will be
A) $10.
B) $15.
C) $20.
D) $30.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 126 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
Ig = 80
SA=−80 + 0.4Y
(Advanced analysis) The equations refer to a private closed economy, where Ig is gross investment, S
Is saving, and Y is gross domestic product (GDP). The equilibrium GDP will be
A) $160.
B) $400.
C) $360.
D) $480.
SA=−80 + 0.4Y
(Advanced analysis) The equations refer to a private closed economy, where Ig is gross investment, S
Is saving, and Y is gross domestic product (GDP). The equilibrium GDP will be
A) $160.
B) $400.
C) $360.
D) $480.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 126 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
(Advanced analysis) If S = −60 + 0.25Y and Ig = 60, where S is saving, Ig is gross investment, and Y is gross domestic product (GDP), then the equilibrium level of GDP is
A) $200.
B) $320.
C) $360.
D) $480.
A) $200.
B) $320.
C) $360.
D) $480.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 126 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
Ig = 80 S = −80 + 0.4Y
(Advanced analysis) The equations refer to a private closed economy, where Ig is gross investment, S
Is saving, and Y is gross domestic product (GDP). In equilibrium, saving will be
A) $40.
B) $120.
C) $60.
D) $80.
(Advanced analysis) The equations refer to a private closed economy, where Ig is gross investment, S
Is saving, and Y is gross domestic product (GDP). In equilibrium, saving will be
A) $40.
B) $120.
C) $60.
D) $80.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 126 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
Ig = 80
SA=−80 + 0.4Y
(Advanced analysis) The equations refer to a private closed economy, where Ig is gross investment, S
Is saving, and Y is gross domestic product (GDP). In equilibrium, consumption will be
A) $400.
B) $280.
C) $320.
D) $360.
SA=−80 + 0.4Y
(Advanced analysis) The equations refer to a private closed economy, where Ig is gross investment, S
Is saving, and Y is gross domestic product (GDP). In equilibrium, consumption will be
A) $400.
B) $280.
C) $320.
D) $360.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 126 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
C = 40 + 0.8Y Ig = 60 − 2i
I = 10
(Advanced analysis) The equations are for a private closed economy, where C is consumption, Y is the
Gross domestic product, Ig is gross investment, and i is the interest rate. The equilibrium level of GDP
In this economy is
A) $240.
B) $300.
C) $360.
D) $400.
I = 10
(Advanced analysis) The equations are for a private closed economy, where C is consumption, Y is the
Gross domestic product, Ig is gross investment, and i is the interest rate. The equilibrium level of GDP
In this economy is
A) $240.
B) $300.
C) $360.
D) $400.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 126 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
(Advanced analysis) The table gives data for a private closed economy. The letters Y, C, S, and I are used to represent real GDP, consumption, saving, and investment, respectively. The equation
Representing the investment schedule for the economy is
A) I = 0.3Y.
B) I = 80 ? 0.3Y.
C) I = 30 + 0.1Y.
D) I = I0 = 30.
Representing the investment schedule for the economy is
A) I = 0.3Y.
B) I = 80 ? 0.3Y.
C) I = 30 + 0.1Y.
D) I = I0 = 30.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 126 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
If unintended increases in business inventories occur, we can expect
A) a decline in GDP and rising unemployment.
B) inflation.
C) an increase in consumption.
D) an offsetting increase in planned investment.
A) a decline in GDP and rising unemployment.
B) inflation.
C) an increase in consumption.
D) an offsetting increase in planned investment.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 126 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
SA=−20 + 0.4Y
Ig = 25 − 3i
(Advanced analysis) The equations refer to a private closed economy, where S is saving, Ig is gross
Investment, i is the real interest rate, and Y is GDP. In equilibrium, the level of consumption will be
A) $80.
B) $95.
C) $65.
D) $70.
Ig = 25 − 3i
(Advanced analysis) The equations refer to a private closed economy, where S is saving, Ig is gross
Investment, i is the real interest rate, and Y is GDP. In equilibrium, the level of consumption will be
A) $80.
B) $95.
C) $65.
D) $70.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 126 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
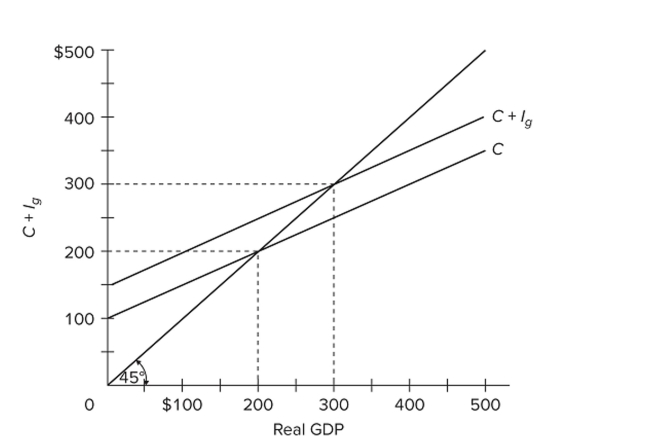 Refer to the diagram for a private closed economy. The MPC and MPS are
Refer to the diagram for a private closed economy. The MPC and MPS areA) 0.6 and 0.4, respectively.
B) 0.7 and 0.3, respectively.
C) both 0.5.
D) both 0.7.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 126 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
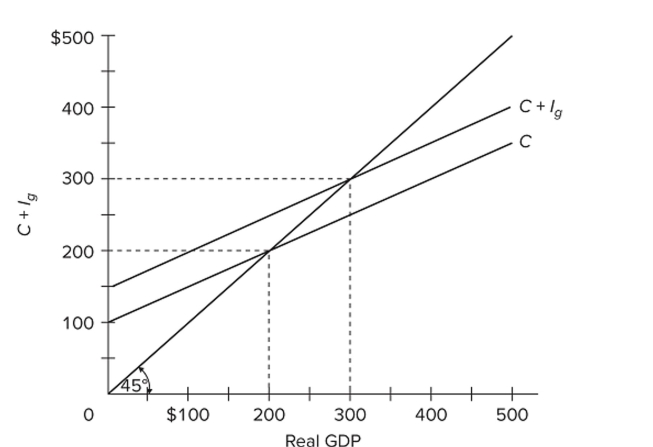 Refer to the diagram for a private closed economy. At the $300 level of GDP,
Refer to the diagram for a private closed economy. At the $300 level of GDP,A) aggregate expenditures and GDP are equal.
B) consumption is $200 and planned investment is $50.
C) saving exceeds planned investment.
D) consumption plus saving is $400.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 126 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
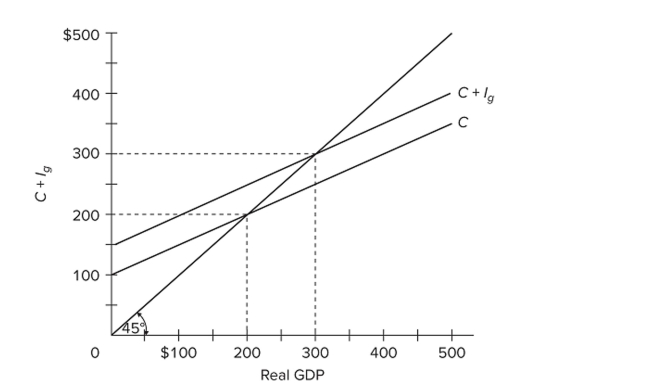 Refer to the diagram for a private closed economy. Gross investment
Refer to the diagram for a private closed economy. Gross investmentA) is positively related to the level of GDP.
B) is negatively related to the level of GDP.
C) is independent of the level of GDP.
D) must be subtracted from consumption to determine aggregate expenditures.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 126 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
C = 40 + 0.8Y Ig = 60 − 2i
I = 10
(Advanced analysis) The equations are for a private closed economy, where C is consumption, Y is the
Gross domestic product, Ig is gross investment, and i is the interest rate. Given that the interest rate is
10 (percent), the amount that businesses will want to invest will be
A) $58.
B) $60.
C) $40.
D) $20.
I = 10
(Advanced analysis) The equations are for a private closed economy, where C is consumption, Y is the
Gross domestic product, Ig is gross investment, and i is the interest rate. Given that the interest rate is
10 (percent), the amount that businesses will want to invest will be
A) $58.
B) $60.
C) $40.
D) $20.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 126 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
In a private closed economy, _____ investment is equal to saving at all levels of GDP and equilibrium occurs only at that level of GDP where _____ investment is equal to saving.
A) planned; actual
B) actual; planned
C) gross; net
D) net; gross
A) planned; actual
B) actual; planned
C) gross; net
D) net; gross

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 126 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
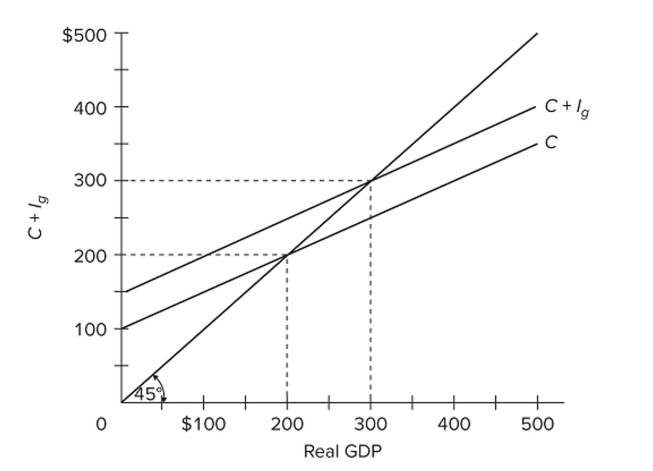 Refer to the diagram for a private closed economy. At the $400 level of GDP,
Refer to the diagram for a private closed economy. At the $400 level of GDP,A) aggregate expenditures exceed GDP, with the result that GDP will rise.
B) consumption is $350 and planned investment is zero, so aggregate expenditures are $350.
C) consumption is $300 and planned investment is $50, so aggregate expenditures are $350.
D) consumption is $300 and actual investment is $100, so aggregate expenditures are $400.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 126 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
Actual investment equals saving
A) at all levels of GDP.
B) at all below-equilibrium levels of GDP.
C) at all above-equilibrium levels of GDP.
D) only at the equilibrium GDP.
A) at all levels of GDP.
B) at all below-equilibrium levels of GDP.
C) at all above-equilibrium levels of GDP.
D) only at the equilibrium GDP.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 126 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
Refer to the tables of information for a private closed economy. The multiplier for this economy is
A) 2.
B) 2.5.
C) 3.
D) 4.
A) 2.
B) 2.5.
C) 3.
D) 4.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 126 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
Refer to the tables of information for a private closed economy. The data suggest that
A) the interest rate and the equilibrium GDP are directly related.
B) the interest rate and the equilibrium GDP are inversely related.
C) the interest rate and the equilibrium GDP are unrelated.
D) as the interest rate falls, investment also falls.
A) the interest rate and the equilibrium GDP are directly related.
B) the interest rate and the equilibrium GDP are inversely related.
C) the interest rate and the equilibrium GDP are unrelated.
D) as the interest rate falls, investment also falls.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 126 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
Refer to the tables of information for a private closed economy. If the real interest rate is 9 percent, the equilibrium GDP will be
A) $600.
B) $500.
C) $400.
D) $300.
A) $600.
B) $500.
C) $400.
D) $300.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 126 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
Refer to the tables of information for a private closed economy. The multiplier in this economy is
A) 4.
B) 5.
C) 2.5.
D) 3.5.
A) 4.
B) 5.
C) 2.5.
D) 3.5.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 126 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
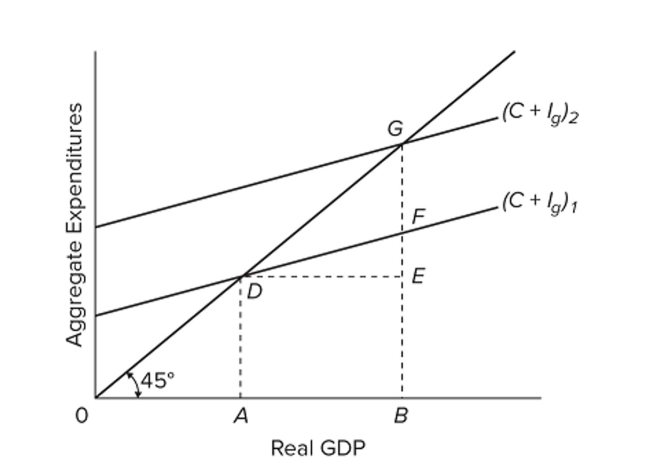 Refer to the diagram for a private closed economy. The marginal propensity to consume is
Refer to the diagram for a private closed economy. The marginal propensity to consume isA) GF/GB.
B) DA/GB.
C) FE/DE.
D) FB/0B.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 126 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
Refer to the tables of information for a private closed economy. In this economy, a 3 percentage point decrease in the interest rate will
A) increase equilibrium GDP by $200.
B) increase equilibrium GDP by $50.
C) increase equilibrium GDP by $100.
D) decrease equilibrium GDP by $50.
A) increase equilibrium GDP by $200.
B) increase equilibrium GDP by $50.
C) increase equilibrium GDP by $100.
D) decrease equilibrium GDP by $50.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 126 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
Refer to the tables of information for a private closed economy. If the real interest rate is 20 percent, the equilibrium GDP will be
A) $100.
B) $200.
C) $300.
D) $400.
A) $100.
B) $200.
C) $300.
D) $400.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 126 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
Which of the following statements is correct for a private closed economy?
A) Saving equals planned investment only at the equilibrium level of GDP.
B) All levels of GDP where planned investment exceeds saving will be too high for equilibrium.
C) Planned and actual investment are identical at all possible levels of GDP.
D) Saving equals actual investment only at the equilibrium level of GDP.
A) Saving equals planned investment only at the equilibrium level of GDP.
B) All levels of GDP where planned investment exceeds saving will be too high for equilibrium.
C) Planned and actual investment are identical at all possible levels of GDP.
D) Saving equals actual investment only at the equilibrium level of GDP.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 126 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
Suppose that the level of GDP increased by $100 billion in a private closed economy where the marginal propensity to consume is 0.5. Aggregate expenditures must have increased by
A) $100 billion.
B) $50 billion.
C) $500 billion.
D) $5 billion.
A) $100 billion.
B) $50 billion.
C) $500 billion.
D) $5 billion.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 126 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
Refer to the tables of information for a private closed economy. If the real interest rate is 10 percent, the equilibrium GDP will be
A) $100.
B) $200.
C) $300.
D) $400.
A) $100.
B) $200.
C) $300.
D) $400.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 126 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72
What will be the effect of an excess of planned investment over saving in a private closed economy with unemployed resources?
A) a decline in the rate of interest
B) an unintended accumulation of inventories by businesses
C) a rise in the real GDP
D) The federal budget will automatically move toward a deficit.
A) a decline in the rate of interest
B) an unintended accumulation of inventories by businesses
C) a rise in the real GDP
D) The federal budget will automatically move toward a deficit.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 126 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73
Saving is always equal to
A) planned investment less unintended increases in inventories.
B) actual investment.
C) planned investment.
D) unintended changes in inventories.
A) planned investment less unintended increases in inventories.
B) actual investment.
C) planned investment.
D) unintended changes in inventories.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 126 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
74
Investment and saving are, respectively,
A) income and wealth.
B) stocks and flows.
C) injections and leakages.
D) leakages and injections.
A) income and wealth.
B) stocks and flows.
C) injections and leakages.
D) leakages and injections.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 126 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
75
Planned investment plus unintended increases in inventories equals
A) actual investment.
B) consumption.
C) consumption minus saving.
D) unintended saving.
A) actual investment.
B) consumption.
C) consumption minus saving.
D) unintended saving.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 126 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
76
(Advanced analysis) Assume the saving schedule for a private closed economy is S = −20 + 0.2Y, where S is saving and Y is gross domestic product. The multiplier for this economy is
A) 3.
B) 4.
C) 5.
D) 10.
A) 3.
B) 4.
C) 5.
D) 10.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 126 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
77
(Advanced analysis) In a private closed economy, (a) the marginal propensity to save is 0.25, (b) consumption equals income at $120 billion, and (c) the level of investment is $40 billion. What is the
Equilibrium level of income?
A) $280 billion
B) $320 billion
C) $262 billion
D) $198 billion
Equilibrium level of income?
A) $280 billion
B) $320 billion
C) $262 billion
D) $198 billion

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 126 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
78
(Advanced analysis) Assume the consumption schedule for a private closed economy is C = 40 + 0.75Y, where C is consumption and Y is gross domestic product. The multiplier for this economy is
A) 3.
B) 4.
C) 5.
D) 10.
A) 3.
B) 4.
C) 5.
D) 10.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 126 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
79
At the $180 billion equilibrium level of income, saving is $38 billion in a private closed economy. Planned investment must be
A) $138 billion.
B) $126 billion.
C) $38 billion.
D) $180 billion.
A) $138 billion.
B) $126 billion.
C) $38 billion.
D) $180 billion.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 126 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
80
Unintended changes in inventories
A) cause the economy to move away from the equilibrium GDP.
B) are treated as components of consumption.
C) bring actual investment and saving into equality only at the equilibrium level of GDP.
D) bring actual investment and saving into equality at all levels of GDP.
A) cause the economy to move away from the equilibrium GDP.
B) are treated as components of consumption.
C) bring actual investment and saving into equality only at the equilibrium level of GDP.
D) bring actual investment and saving into equality at all levels of GDP.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 126 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



