Deck 40: Physical Principles of Gas Exchange; Diffusion of Oxygen and Carbon Dioxide Through the Respiratory Membrane
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/14
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 40: Physical Principles of Gas Exchange; Diffusion of Oxygen and Carbon Dioxide Through the Respiratory Membrane
1
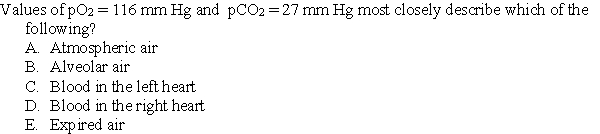
E
2
Following Questions :Consider a patient with an anatomical dead space of 100 mL, a normal respiratory rate of 12 breaths/min, and a normal tidal volume of 600 mL under resting conditions. Match each of the conditions in questions 7-9 with the correct set of changes. Answers may be used more than once. 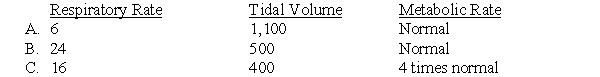
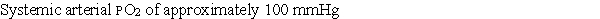
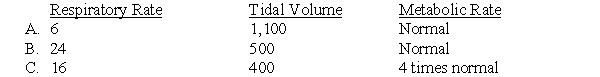
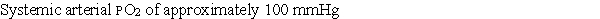
A
3
Following Questions :Consider a patient with an anatomical dead space of 100 mL, a normal respiratory rate of 12 breaths/min, and a normal tidal volume of 600 mL under resting conditions. Match each of the conditions in questions 7-9 with the correct set of changes. Answers may be used more than once. 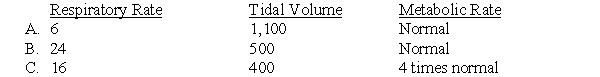

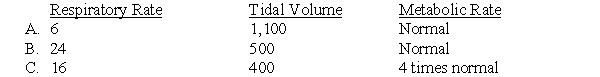

B
4
Following Questions :Consider a patient with an anatomical dead space of 100 mL, a normal respiratory rate of 12 breaths/min, and a normal tidal volume of 600 mL under resting conditions. Match each of the conditions in questions 7-9 with the correct set of changes. Answers may be used more than once. 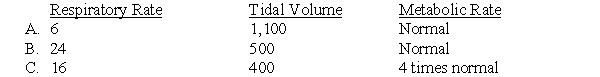

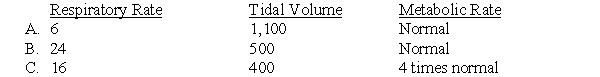


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 14 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
A human experiment is being performed where forearm blood flow is being measured under a variety of conditions. The forearm is warmed, resulting in an increase in blood flow. Which of the following occurs? 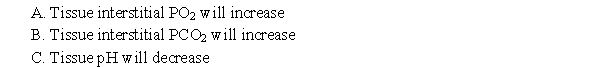
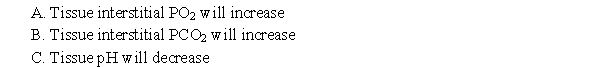

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 14 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
Following Questions :Consider a patient with an anatomical dead space of 100 mL, a normal respiratory rate of 12 breaths/min, and a normal tidal volume of 600 mL under resting conditions. Match each of the conditions in questions 7-9 with the correct set of changes. Answers may be used more than once. 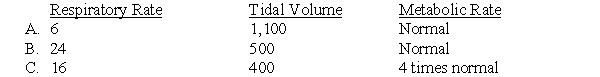
Blood gas measurements in a patient on room air indicates that his systemic arterial oxygen content is normal (19.5 ml O₂/100 ml blood), but his systemic venous oxygen content is low (6 ml O₂/100 ml blood). This is characteristic of which of the following?
A)V/Q less than normal
B)An increase in physiological dead space
C)Pulmonary edema
D)Low hemoglobin concentration
E)Low cardiac output
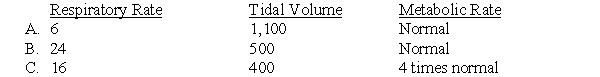
Blood gas measurements in a patient on room air indicates that his systemic arterial oxygen content is normal (19.5 ml O₂/100 ml blood), but his systemic venous oxygen content is low (6 ml O₂/100 ml blood). This is characteristic of which of the following?
A)V/Q less than normal
B)An increase in physiological dead space
C)Pulmonary edema
D)Low hemoglobin concentration
E)Low cardiac output

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 14 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 14 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
Following Questions :Consider a patient with an anatomical dead space of 100 mL, a normal respiratory rate of 12 breaths/min, and a normal tidal volume of 600 mL under resting conditions. Match each of the conditions in questions 7-9 with the correct set of changes. Answers may be used more than once. 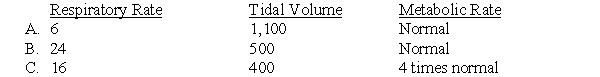
For a patient at sea level (barometric pressure = 760 mm Hg) and breathing 40%, oxygen calculate alveolar pO₂ is which of the following?
A)149
B)159
C)235
D)285
E)304
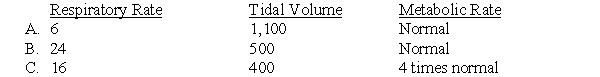
For a patient at sea level (barometric pressure = 760 mm Hg) and breathing 40%, oxygen calculate alveolar pO₂ is which of the following?
A)149
B)159
C)235
D)285
E)304

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 14 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
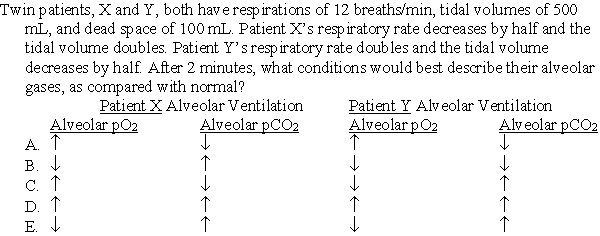

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 14 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
A child has been eating M&Ms (plain) and inhaled one down his airway, blocking his left bronchiole. Which of the following will describe the changes that occur? 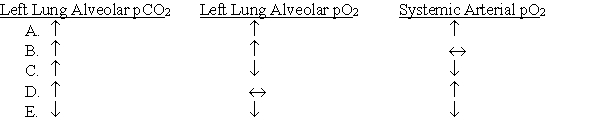


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 14 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
If alveolar surface area is decreased 50% and pulmonary edema leads to a doubling of diffusion distance, how does diffusion of oxygen compare with normal?
A)25% increase
B)50% increase
C)25% decrease
D)50% decrease
E)75% decrease
A)25% increase
B)50% increase
C)25% decrease
D)50% decrease
E)75% decrease

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 14 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 14 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
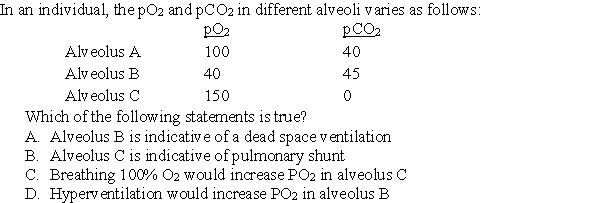

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 14 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
Following Questions :Consider a patient with an anatomical dead space of 100 mL, a normal respiratory rate of 12 breaths/min, and a normal tidal volume of 600 mL under resting conditions. Match each of the conditions in questions 7-9 with the correct set of changes. Answers may be used more than once. 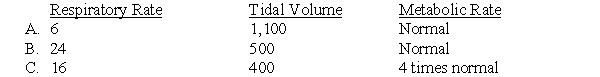
A patient has a normal oxygen partial pressure and content in pulmonary venous blood but his systemic arterial blood shows a significantly lower than normal oxygen partial pressure and content. This is diagnostic of which of the following?
A)Diffusion limitation
B)Right-to-left shunt
C)Pulmonary ventilation/perfusion nonuniformity
D)Stagnant hypoxia (low cardiac output)
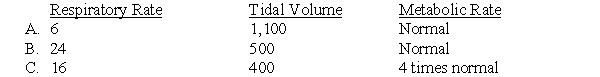
A patient has a normal oxygen partial pressure and content in pulmonary venous blood but his systemic arterial blood shows a significantly lower than normal oxygen partial pressure and content. This is diagnostic of which of the following?
A)Diffusion limitation
B)Right-to-left shunt
C)Pulmonary ventilation/perfusion nonuniformity
D)Stagnant hypoxia (low cardiac output)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 14 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



