Deck 16: The Microcirculation and Lymphatic System: Capillary Fluid Exchange, Interstitial Fluid, and Lymph Flow
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/15
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 16: The Microcirculation and Lymphatic System: Capillary Fluid Exchange, Interstitial Fluid, and Lymph Flow
1
An decrease in which of the following tends to increase lymph flow?
A)Interstitial hydrostatic pressure
B)Plasma colloid osmotic pressure
C)Capillary hydrostatic pressure
D)Interstitial colloid osmotic pressure
E)Capillary hydraulic permeability
A)Interstitial hydrostatic pressure
B)Plasma colloid osmotic pressure
C)Capillary hydrostatic pressure
D)Interstitial colloid osmotic pressure
E)Capillary hydraulic permeability
B
2
A decrease in arteriole diameter would most likely result in which set of changes in a microcirculatory bed? 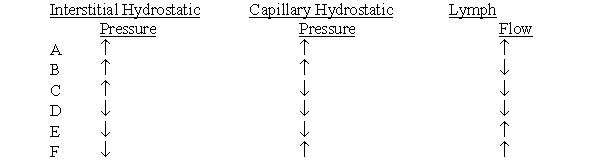

D
3
A 65-year-old man has a 20-year history of alcoholism and liver disease. He visits his physician complaining of swelling of his extremities. A decrease in which of the following is one of the most likely cause of the ascites?
A)Capillary hydrostatic pressure
B)Arteriole conductance
C)Interstitial hydrostatic pressure
D)Plasma colloid osmotic pressure
E)Interstitial colloid osmotic pressure
A)Capillary hydrostatic pressure
B)Arteriole conductance
C)Interstitial hydrostatic pressure
D)Plasma colloid osmotic pressure
E)Interstitial colloid osmotic pressure
D
4
Which one of the following substances in plasma does not contribute to plasma colloid osmotic pressure?
A)Globulins
B)Fibrinogen
C)Albumin
D)NaCl
A)Globulins
B)Fibrinogen
C)Albumin
D)NaCl

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 15 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
A decrease in which of the following tends to decrease filtration rate across a capillary wall?
A)Plasma colloid osmotic pressure
B)Hydraulic conductivity of the wall
C)Plasma albumin concentration
D)Interstitial hydrostatic pressure
E)Arteriole resistance
A)Plasma colloid osmotic pressure
B)Hydraulic conductivity of the wall
C)Plasma albumin concentration
D)Interstitial hydrostatic pressure
E)Arteriole resistance

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 15 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
Listed below are the hydrostatic and oncotic pressures across a muscle capillary wall.
Venous hydrostatic pressure
Arterial pressure
Capillary hydrostatic pressure
Plasma colloid osmotic pressure
Interstitial colloid osmotic pressure
Interstitial hydrostatic pressure
What is the net filtration pressure (in ) for fluid movement across the capillary wall?
A. 0
B. 5
C. 10
D. 15
E. 25
Venous hydrostatic pressure
Arterial pressure
Capillary hydrostatic pressure
Plasma colloid osmotic pressure
Interstitial colloid osmotic pressure
Interstitial hydrostatic pressure
What is the net filtration pressure (in ) for fluid movement across the capillary wall?
A. 0
B. 5
C. 10
D. 15
E. 25

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 15 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
Use the data below to calculate the rate of net fluid movement (in ) across the capillary wall.
Plasma colloid osmotic pressure
Cap illary hydrostatic pressure
Venous hydrostatic pressure
Arterial pressure
Interstitial hydrostatic pressure
Interstitial colloid osmotic pressure
Filtration coefficient
A. 100 (filtration)
B. 200 (reabsorption)
C. 200 (filtration)
D. 300 (filtration)
E. 300 (reabsorption)
Plasma colloid osmotic pressure
Cap illary hydrostatic pressure
Venous hydrostatic pressure
Arterial pressure
Interstitial hydrostatic pressure
Interstitial colloid osmotic pressure
Filtration coefficient
A. 100 (filtration)
B. 200 (reabsorption)
C. 200 (filtration)
D. 300 (filtration)
E. 300 (reabsorption)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 15 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
Which of the following set of changes would be expected to increase the net movement of sodium across a muscle capillary wall?
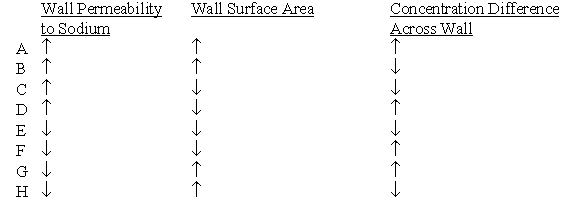


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 15 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
Use the data below to calculate the filtration coefficient for the capillary bed (in mL/min/mmHg). Plasma colloid osmotic pressure
Capillary hydrostatic pressure
Interstitial hydrostatic pressure
Interstitial colloid osmotic pressure
Filtration rate
Venous hydrostatic pressure
A. 10
B. 15
C. 20
D. 25
E. 30
Capillary hydrostatic pressure
Interstitial hydrostatic pressure
Interstitial colloid osmotic pressure
Filtration rate
Venous hydrostatic pressure
A. 10
B. 15
C. 20
D. 25
E. 30

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 15 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
A healthy 20 -year-old medical student has an exercise stress test. Which set of changes would be expected to occur in the student's skeletal muscles during exercise?
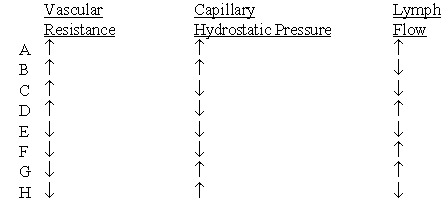


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 15 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
Which of the following is true regarding plasma colloid osmotic pressure?
A)It is less than interstitial colloid osmotic pressure
B)It decreases by 50% in the muscle capillaries as blood flows from the arteriole end to the venous end
C)It is primarily caused by the presence of substances in the plasma such as sodium and potassium
D)It increases in response to an increase in plasma albumin concentration
A)It is less than interstitial colloid osmotic pressure
B)It decreases by 50% in the muscle capillaries as blood flows from the arteriole end to the venous end
C)It is primarily caused by the presence of substances in the plasma such as sodium and potassium
D)It increases in response to an increase in plasma albumin concentration

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 15 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
An increase in which of the following would tend to decrease lymph flow?
A)Hydraulic conductivity of the capillary wall
B)Plasma colloid osmotic pressure
C)Capillary hydrostatic pressure
D)Precapillary arteriole diameter
E)Interstitial colloid osmotic pressure
A)Hydraulic conductivity of the capillary wall
B)Plasma colloid osmotic pressure
C)Capillary hydrostatic pressure
D)Precapillary arteriole diameter
E)Interstitial colloid osmotic pressure

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 15 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
A decrease in which of the following tends to increase filtration rate across a capillary wall?
A)Arterial pressure
B)Hydraulic conductivity of the wall
C)Interstitial albumin concentration
D)Capillary hydrostatic pressure
E)Arteriole resistance
A)Arterial pressure
B)Hydraulic conductivity of the wall
C)Interstitial albumin concentration
D)Capillary hydrostatic pressure
E)Arteriole resistance

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 15 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
A decrease in which of the following tends to increase capillary hydrostatic pressure?
A)Arteriole diameter
B)Arteriole resistance
C)Interstitial albumin concentration
D)Capillary filtration coefficient
E)Plasma colloid osmotic pressure
A)Arteriole diameter
B)Arteriole resistance
C)Interstitial albumin concentration
D)Capillary filtration coefficient
E)Plasma colloid osmotic pressure

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 15 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
A decrease in which of the following would be expected in the skeletal microcirculation in a patient with nephrosis?
A)Capillary filtration rate
B)Plasma colloid osmotic pressure
C)Lymph flow
D)Capillary hydraulic permeability
E)Arteriole resistance
A)Capillary filtration rate
B)Plasma colloid osmotic pressure
C)Lymph flow
D)Capillary hydraulic permeability
E)Arteriole resistance

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 15 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



