Deck 56: Cortical and Brain Stem Control of Motor Function
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/12
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 56: Cortical and Brain Stem Control of Motor Function
1
Which of the following structures in the vestibular apparatus is responsible for the detection of angular acceleration?
A)Statoconia
B)Macula
C)Semicircular canals
D)Saccule
A)Statoconia
B)Macula
C)Semicircular canals
D)Saccule
C
2
Fine motor movement of the index finger can be elicited by stimulation of which of the following brain areas?
A)Primary motor cortex
B)Lateral cerebellar hemisphere
C)Premotor cortex
D)Supplemental motor area
A)Primary motor cortex
B)Lateral cerebellar hemisphere
C)Premotor cortex
D)Supplemental motor area
A
3
Decerebrate rigidity caused by simultaneous contraction of both the agonist and antagonist muscles in a limb can be alleviated by which of the following maneuvers?
A)Turning the head sharply toward the limb
B)Bending the head forward
C)Stimulating the pontine reticular formation by lightly stroking the palms of the hand
D)Cutting the dorsal roots associated with the affected limb
A)Turning the head sharply toward the limb
B)Bending the head forward
C)Stimulating the pontine reticular formation by lightly stroking the palms of the hand
D)Cutting the dorsal roots associated with the affected limb
D
4
The rubrospinal tract originates from which area of the brain?
A)Magnocellular area of the red nucleus
B)Superior olivary nucleus
C)Pontine reticular formation
D)Nucleus raphe magnus
A)Magnocellular area of the red nucleus
B)Superior olivary nucleus
C)Pontine reticular formation
D)Nucleus raphe magnus

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 12 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
The maintenance of static equilibrium with the head in a near vertical position is achieved by which of the following?
A)Cristae ampullaris
B)Cupula
C)Maculae
D)Organ of Corti
A)Cristae ampullaris
B)Cupula
C)Maculae
D)Organ of Corti

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 12 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
Which of the following brain regions contributes fibers to the corticospinal tract?
A)Somatic sensory cortex
B)Supplemental motor area
C)Primary motor cortex
D)All of the above
A)Somatic sensory cortex
B)Supplemental motor area
C)Primary motor cortex
D)All of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 12 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
The stretch reflex is used clinically to assess which of the following?
A)Integrity of the corticospinal tract
B)Function of the vestibulo-ocular reflex
C)Level of activity of the gamma motor system
D)Function of the vestibular system
A)Integrity of the corticospinal tract
B)Function of the vestibulo-ocular reflex
C)Level of activity of the gamma motor system
D)Function of the vestibular system

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 12 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
Linear acceleration is most likely to be transduced in which of the following structures?
A)Cristae ampullaris
B)Cupula
C)Maculae
D)Organ of Corti
A)Cristae ampullaris
B)Cupula
C)Maculae
D)Organ of Corti

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 12 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
Which of the following is paired correctly?
A)Gamma motor neuron and extrafusal muscle fiber
B)Alpha motor neuron and intrafusal muscle fiber
C)Betz cells and corticospinal tract
D)Utricle and angular acceleration detection
A)Gamma motor neuron and extrafusal muscle fiber
B)Alpha motor neuron and intrafusal muscle fiber
C)Betz cells and corticospinal tract
D)Utricle and angular acceleration detection

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 12 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
In the right horizontal semicircular canal, rapid rotation of the head in the clockwise direction will cause the endolymph to move in which relative direction?
A)Clockwise
B)Counterclockwise
C)Upward
D)Downward
A)Clockwise
B)Counterclockwise
C)Upward
D)Downward

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 12 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
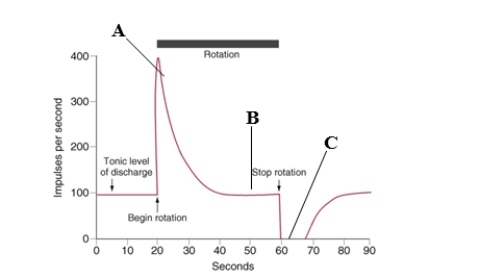
The figure above represents the response of a hair cell in the crista ampullaris of the semicircular canal to stimulation by rotation in a human subject. With the subject's eyes closed, the subjective sensation of rotation will be absent at which point(s)?
A)A
B)B
C)C
D)A and C

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 12 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
The phenomenon of decerebrate rigidity can be explained, at least in part, by which of the following?
A)Stimulation of gamma motor neurons
B)Loss of cerebellar inputs to the red nucleus
C)Overactivity of medullary reticular nuclei involved in motor control
A)Stimulation of gamma motor neurons
B)Loss of cerebellar inputs to the red nucleus
C)Overactivity of medullary reticular nuclei involved in motor control

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 12 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



