Deck 5: National Income Accounting
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/104
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 5: National Income Accounting
1
NARRBEGIN: Table 5.1
The table given below reports the value of sales at each stage of production of an economics book.
Table 5.1
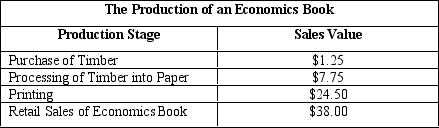
Refer to Table 5.1. Compute the market price of an economics book.
A) $13.50
B) $7.75
C) $24.50
D) $38
E) $71.50
The table given below reports the value of sales at each stage of production of an economics book.
Table 5.1

Refer to Table 5.1. Compute the market price of an economics book.
A) $13.50
B) $7.75
C) $24.50
D) $38
E) $71.50
D
2
Which of the following would be included in the calculation of the GDP for the year 2010?
A) Purchase of a 2004 model Volkswagen sedan in 2010
B) Swapping of baseball cards among two college students
C) Car repairs done by a person on his/her own
D) Fresh lemonade sold at a local diner
E) A lamp sold at a garage sale
A) Purchase of a 2004 model Volkswagen sedan in 2010
B) Swapping of baseball cards among two college students
C) Car repairs done by a person on his/her own
D) Fresh lemonade sold at a local diner
E) A lamp sold at a garage sale
D
3
Which of the following accounts for the largest percentage of output in the United States?
A) The government
B) Business firms
C) Households
D) Banks
E) The rest of the world
A) The government
B) Business firms
C) Households
D) Banks
E) The rest of the world
B
4
The national income accounting system provides a measure of:
A) only the total amount of profits made by the business firms.
B) the total value of all inputs used in production.
C) government budget surplus and deficit.
D) the net exports of a nation.
E) the output of an entire economy.
A) only the total amount of profits made by the business firms.
B) the total value of all inputs used in production.
C) government budget surplus and deficit.
D) the net exports of a nation.
E) the output of an entire economy.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 104 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
Which of the following will be categorized as an intermediate good in national income accounting?
A) The value of oregano used as a seasoning for pizzas
B) The crops consumed by a farmer's family members
C) The present value of a car produced a couple of years before
D) A clunker sold during the current year
E) The value of an antique piece of jewelry handed down over generations in a family
A) The value of oregano used as a seasoning for pizzas
B) The crops consumed by a farmer's family members
C) The present value of a car produced a couple of years before
D) A clunker sold during the current year
E) The value of an antique piece of jewelry handed down over generations in a family

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 104 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
Which of the following would not be included in the calculation of GDP?
A) Vegetables grown and consumed by a nonfarm family
B) The purchase of a new Porsche
C) The sale of meat at the local grocery store
D) The government purchase of an F-14 fighter plane
E) The payment made to an accountant for the preparation of tax forms
A) Vegetables grown and consumed by a nonfarm family
B) The purchase of a new Porsche
C) The sale of meat at the local grocery store
D) The government purchase of an F-14 fighter plane
E) The payment made to an accountant for the preparation of tax forms

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 104 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
NARRBEGIN: Table 5.2
The figure given below shows the various stages of production of a Corvette, a sports car produced by General Motors Company (GMC):
Table 5.2
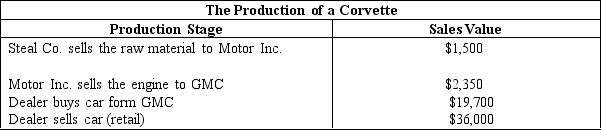
According to Table 5.2, the value added by the dealer is:
A) $2,350.
B) $16,300.
C) $19,700.
D) $36,000.
E) $59,550.
The figure given below shows the various stages of production of a Corvette, a sports car produced by General Motors Company (GMC):
Table 5.2

According to Table 5.2, the value added by the dealer is:
A) $2,350.
B) $16,300.
C) $19,700.
D) $36,000.
E) $59,550.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 104 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
NARRBEGIN: Table 5.1
The table given below reports the value of sales at each stage of production of an economics book.
Table 5.1

Refer to Table 5.1. What is the contribution to GDP from the production of an economics book?
A) $13.50
B) $7.75
C) $24.50
D) $38
E) $71.50
The table given below reports the value of sales at each stage of production of an economics book.
Table 5.1

Refer to Table 5.1. What is the contribution to GDP from the production of an economics book?
A) $13.50
B) $7.75
C) $24.50
D) $38
E) $71.50

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 104 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
National income accounting can best be characterized as:
A) a set of rules used to summarize economic activity over a given period of time.
B) a method for comparing different political systems.
C) a microeconomic model of the economy used by the Federal Reserve bank.
D) a statistical measure of the income received by consumers as opposed to businesses.
E) a standardized economic report authored by politicians.
A) a set of rules used to summarize economic activity over a given period of time.
B) a method for comparing different political systems.
C) a microeconomic model of the economy used by the Federal Reserve bank.
D) a statistical measure of the income received by consumers as opposed to businesses.
E) a standardized economic report authored by politicians.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 104 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
The term value added is used to describe:
A) the increase in the value of a product that occurs at each stage of production.
B) the amount subtracted from the value of goods because of inflation.
C) the total value of all intermediate goods used in the production of the final good.
D) the amount paid in the final sale of a product or service.
E) the amount subtracted from the value of resources because of depreciation.
A) the increase in the value of a product that occurs at each stage of production.
B) the amount subtracted from the value of goods because of inflation.
C) the total value of all intermediate goods used in the production of the final good.
D) the amount paid in the final sale of a product or service.
E) the amount subtracted from the value of resources because of depreciation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 104 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
Identify the correct statement.
A) National income accounting measures only the flow of output between the different sectors of the economy.
B) National income accounting summarizes the level of production in an economy over a decade.
C) National income accounting explains diagrammatically the flows of goods and services and of money expenditures (income).
D) National income accounting summarizes and categorizes the productive activity in an economy over a year.
E) National income accounting measures the total money supply in the economy.
A) National income accounting measures only the flow of output between the different sectors of the economy.
B) National income accounting summarizes the level of production in an economy over a decade.
C) National income accounting explains diagrammatically the flows of goods and services and of money expenditures (income).
D) National income accounting summarizes and categorizes the productive activity in an economy over a year.
E) National income accounting measures the total money supply in the economy.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 104 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
To avoid double counting in calculating GDP,
A) net exports should be excluded.
B) the value of intermediate goods and services should be excluded.
C) the capital consumption allowance should be excluded.
D) business investment should be excluded.
E) government purchases should be excluded.
A) net exports should be excluded.
B) the value of intermediate goods and services should be excluded.
C) the capital consumption allowance should be excluded.
D) business investment should be excluded.
E) government purchases should be excluded.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 104 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
Productive activity in the underground economy:
A) results in an overstatement of actual income and production in the national accounting system.
B) consists of unrecorded cash transactions.
C) is estimated and included in the national income accounting system.
D) poses no problem for the measurement of gross domestic product.
E) does not affect GDP but is included in the value-added computations.
A) results in an overstatement of actual income and production in the national accounting system.
B) consists of unrecorded cash transactions.
C) is estimated and included in the national income accounting system.
D) poses no problem for the measurement of gross domestic product.
E) does not affect GDP but is included in the value-added computations.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 104 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
When estimating GDP, changes in the level of inventory are calculated because:
A) it indicates the level of employment in the economy.
B) it provides information about a firm's expectations.
C) it is a good indicator of the competitiveness of the economy.
D) it shows the level of business spending by firms.
E) it determines the value of goods produced in a year but not sold in that year.
A) it indicates the level of employment in the economy.
B) it provides information about a firm's expectations.
C) it is a good indicator of the competitiveness of the economy.
D) it shows the level of business spending by firms.
E) it determines the value of goods produced in a year but not sold in that year.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 104 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
A soft-drink bottling company supplies six-packs of orange flavored soda to retailers for a price of $2 each. If the components in each six-pack costs the bottling company $1.50, the value added to each six-pack by the bottling company is:
A) $2.00.
B) $1.50.
C) $1.25.
D) $1.00.
E) $0.50.
A) $2.00.
B) $1.50.
C) $1.25.
D) $1.00.
E) $0.50.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 104 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
Which of the following must be included in the calculation of GDP?
A) The sale of a used car to an auto dealer
B) Bartering lawn care services for car washes
C) A father staying at home to attend to his child
D) The sale of an illegal cable box
E) Payment made for a SAT preparation class
A) The sale of a used car to an auto dealer
B) Bartering lawn care services for car washes
C) A father staying at home to attend to his child
D) The sale of an illegal cable box
E) Payment made for a SAT preparation class

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 104 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
NARRBEGIN: Table 5.2
The figure given below shows the various stages of production of a Corvette, a sports car produced by General Motors Company (GMC):
Table 5.2

According to Table 5.2, the contribution to GDP from the production of this car is
A) $2,350.
B) $16,300.
C) $19,700.
D) $36,000.
E) $59,550.
The figure given below shows the various stages of production of a Corvette, a sports car produced by General Motors Company (GMC):
Table 5.2

According to Table 5.2, the contribution to GDP from the production of this car is
A) $2,350.
B) $16,300.
C) $19,700.
D) $36,000.
E) $59,550.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 104 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
If the value of intermediate goods and services are included in GDP, then:
A) GDP would be understated.
B) GDP would act as a true indicator of economic welfare.
C) there would be double-counting.
D) there would be undercounting.
E) GDP would be able to give a clearer picture of the economy.
A) GDP would be understated.
B) GDP would act as a true indicator of economic welfare.
C) there would be double-counting.
D) there would be undercounting.
E) GDP would be able to give a clearer picture of the economy.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 104 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
Identify the impact of an increase in the inventory stock during a year.
A) Consumption spending will decrease thereby reducing the GDP.
B) The GDP of the country should decrease by the amount of the increase in inventory.
C) The capital investment in the country will increase.
D) Neither the capital investment nor the GDP will change.
E) The GDP of the country should increase by the amount of the increase in inventory.
A) Consumption spending will decrease thereby reducing the GDP.
B) The GDP of the country should decrease by the amount of the increase in inventory.
C) The capital investment in the country will increase.
D) Neither the capital investment nor the GDP will change.
E) The GDP of the country should increase by the amount of the increase in inventory.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 104 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
NARRBEGIN: Table 5.1
The table given below reports the value of sales at each stage of production of an economics book.
Table 5.1

Refer to Table 5.1. What is the value-added by processing timber into paper?
A) $6.50
B) $38
C) $7.75
D) $1.25
E) $24.50
The table given below reports the value of sales at each stage of production of an economics book.
Table 5.1

Refer to Table 5.1. What is the value-added by processing timber into paper?
A) $6.50
B) $38
C) $7.75
D) $1.25
E) $24.50

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 104 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
Which of the following is true of indirect business taxes?
A) They are included in corporate profits.
B) They are not included in the GDP.
C) They reduce the value of total economic output.
D) They are collected by business firms that act as agents for the government.
E) They are the same as personal income taxes.
A) They are included in corporate profits.
B) They are not included in the GDP.
C) They reduce the value of total economic output.
D) They are collected by business firms that act as agents for the government.
E) They are the same as personal income taxes.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 104 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
Which of the following components of GDP accounts for the bulk of national expenditures in the United States?
A) Government purchases
B) Imports
C) Consumption
D) Investment
E) Exports
A) Government purchases
B) Imports
C) Consumption
D) Investment
E) Exports

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 104 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
The difference between gross and net investment is referred to as:
A) a personal tax.
B) the income earned but not received.
C) a capital consumption allowance.
D) an indirect business tax.
E) a statistical discrepancy.
A) a personal tax.
B) the income earned but not received.
C) a capital consumption allowance.
D) an indirect business tax.
E) a statistical discrepancy.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 104 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
If 'C' denotes consumption expenditure, 'I' denotes investment expenditure, 'G' denotes government expenditure and 'X' denotes net exports, then C + I + G + X equals:
A) net national product.
B) disposable personal income.
C) national income.
D) personal income.
E) gross domestic product.
A) net national product.
B) disposable personal income.
C) national income.
D) personal income.
E) gross domestic product.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 104 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
Bill Gates' recent purchase of a new Rolls-Royce automobile produced in Great Britain will:
A) increase the gross domestic product of the United States.
B) have no effect on either country's GDP.
C) decrease Great Britain's GDP.
D) increase the net exports component of U.S. gross domestic product.
E) have to be subtracted from the U.S. GDP.
A) increase the gross domestic product of the United States.
B) have no effect on either country's GDP.
C) decrease Great Britain's GDP.
D) increase the net exports component of U.S. gross domestic product.
E) have to be subtracted from the U.S. GDP.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 104 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
Consider a hypothetical economy, whose GDP was $10,000, consumption equaled $9,800, investment equaled $125, goods exported equaled $255, and goods imported equaled $500, in 2010. Calculate the government spending in this economy during the year.
A) $120
B) $380
C) $245
D) $200
E) $320
A) $120
B) $380
C) $245
D) $200
E) $320

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 104 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
Consider GDP calculated according to the expenditures approach. Which of the following components of GDP would need to decrease for GDP to increase?
A) Imports
B) Consumption
C) Exports
D) Investment
E) Government spending
A) Imports
B) Consumption
C) Exports
D) Investment
E) Government spending

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 104 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
NARRBEGIN: Table 5.3
The table given below reports the sales value at each stage of production of the soft drink Pepsi.
Table 5.3
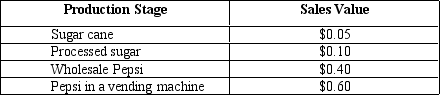
Refer to Table 5.3. Compute GDP according to the income approach if Pepsi is assumed to be the only good produced in the economy.
A) $1.05
B) $0.05
C) $0.20
D) $0.60
E) $0.40
The table given below reports the sales value at each stage of production of the soft drink Pepsi.
Table 5.3

Refer to Table 5.3. Compute GDP according to the income approach if Pepsi is assumed to be the only good produced in the economy.
A) $1.05
B) $0.05
C) $0.20
D) $0.60
E) $0.40

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 104 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
Which of the following is subtracted from GNP when calculating net national product?
A) Interest
B) Capital consumption allowance
C) Rent
D) Indirect business taxes
E) Consumption
A) Interest
B) Capital consumption allowance
C) Rent
D) Indirect business taxes
E) Consumption

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 104 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
Which of the following is included in GDP computation according to the income method?
A) Consumption
B) Profits
C) Investment
D) Government spending
E) Imports
A) Consumption
B) Profits
C) Investment
D) Government spending
E) Imports

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 104 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
The stock of unused goods held by a firm is called:
A) depreciation.
B) indirect taxes.
C) value added.
D) excess capacity.
E) inventory.
A) depreciation.
B) indirect taxes.
C) value added.
D) excess capacity.
E) inventory.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 104 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
A reduction in the value of capital goods over time due to their use in production is called:
A) amortization.
B) erosion.
C) consumption.
D) investment.
E) depreciation.
A) amortization.
B) erosion.
C) consumption.
D) investment.
E) depreciation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 104 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
Which of the following can be a valid reason for Canada's GDP exceeding its GNP in 2001?
A) Net factor income from abroad in Canada was negative.
B) Canada's GNP measurements were flawed.
C) Canada's indirect business taxes were exceptionally high.
D) The World Bank underestimated Canada's net exports.
E) Canada's residents received more foreign aid than they could spend.
A) Net factor income from abroad in Canada was negative.
B) Canada's GNP measurements were flawed.
C) Canada's indirect business taxes were exceptionally high.
D) The World Bank underestimated Canada's net exports.
E) Canada's residents received more foreign aid than they could spend.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 104 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
NARRBEGIN: Table 5.3
The table given below reports the sales value at each stage of production of the soft drink Pepsi.
Table 5.3

Refer to Table 5.3. The value added by the wholesaler is equal to:
A) $0.05.
B) $0.40.
C) $0.20.
D) $1.15.
E) $0.06.
The table given below reports the sales value at each stage of production of the soft drink Pepsi.
Table 5.3

Refer to Table 5.3. The value added by the wholesaler is equal to:
A) $0.05.
B) $0.40.
C) $0.20.
D) $1.15.
E) $0.06.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 104 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
The total expenditure on goods and services in a country must be the same as the total income earned from selling goods and services because:
A) the government annual budget has to balance.
B) net exports in an economy is usually zero.
C) one sector's expenditures are another sector's income.
D) total investment in an economy always equals total saving.
E) the sum of consumption spending and saving is zero.
A) the government annual budget has to balance.
B) net exports in an economy is usually zero.
C) one sector's expenditures are another sector's income.
D) total investment in an economy always equals total saving.
E) the sum of consumption spending and saving is zero.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 104 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
The purchase of a new machine to replace the one that is worn out is:
A) not included in GDP.
B) included in gross investment.
C) considered a personal consumption expenditure.
D) not included in GNP.
E) an increase in inventories.
A) not included in GDP.
B) included in gross investment.
C) considered a personal consumption expenditure.
D) not included in GNP.
E) an increase in inventories.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 104 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
GDP according to the income method is the sum of:
A) wages, rent, interest, and profits.
B) consumption, gross investment, depreciation, and net exports.
C) depreciation, net factor income from abroad, and indirect business taxes.
D) gross investment, wages, profits, rent, and indirect business taxes.
E) consumption, profits, interest, rent, and net exports.
A) wages, rent, interest, and profits.
B) consumption, gross investment, depreciation, and net exports.
C) depreciation, net factor income from abroad, and indirect business taxes.
D) gross investment, wages, profits, rent, and indirect business taxes.
E) consumption, profits, interest, rent, and net exports.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 104 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
The term capital consumption allowance is defined as:
A) the amount of net interest in the economy each year.
B) the estimated value of depreciation and obsolescence in investment goods.
C) the difference between exports and imports.
D) the disposition of disposable personal income.
E) the difference between earnings not received and receipts not earned.
A) the amount of net interest in the economy each year.
B) the estimated value of depreciation and obsolescence in investment goods.
C) the difference between exports and imports.
D) the disposition of disposable personal income.
E) the difference between earnings not received and receipts not earned.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 104 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
What is the approximate percent of GDP produced by private firms in the United States?
A) 4 percent
B) 11 percent
C) 25 percent
D) 57 percent
E) 75 percent
A) 4 percent
B) 11 percent
C) 25 percent
D) 57 percent
E) 75 percent

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 104 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
NARRBEGIN: Table 5.3
The table given below reports the sales value at each stage of production of the soft drink Pepsi.
Table 5.3

Refer to Table 5.3. If this Pepsi were the only good produced in the economy, what would GDP by the expenditures approach be equal to?
A) $0.05
B) $0.20
C) $0.40
D) $1.15
E) $0.60
The table given below reports the sales value at each stage of production of the soft drink Pepsi.
Table 5.3

Refer to Table 5.3. If this Pepsi were the only good produced in the economy, what would GDP by the expenditures approach be equal to?
A) $0.05
B) $0.20
C) $0.40
D) $1.15
E) $0.60

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 104 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
National income is the sum of:
A) personal income and personal tax payments.
B) proprietors' income, rental income, compensation of employees, corporate profits, and interest receipts net of indirect business taxes and the capital consumption allowance.
C) wages, transfer payments, interest paid to businesses, and tax revenue.
D) NNP and the capital consumption allowance.
E) consumption, investment, government spending, and net exports.
A) personal income and personal tax payments.
B) proprietors' income, rental income, compensation of employees, corporate profits, and interest receipts net of indirect business taxes and the capital consumption allowance.
C) wages, transfer payments, interest paid to businesses, and tax revenue.
D) NNP and the capital consumption allowance.
E) consumption, investment, government spending, and net exports.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 104 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
NARRBEGIN: Table 5.4
The table given below reports the value of different economic variables of a country during a year.
Table 5.4
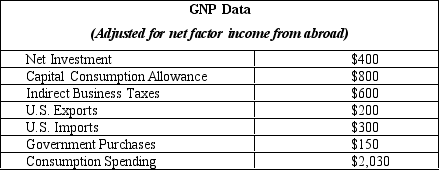
Refer to Table 5.4. What will be the value of gross investment?
A) $400
B) $1,200
C) $1,000
D) $1,800
E) Indeterminate
The table given below reports the value of different economic variables of a country during a year.
Table 5.4

Refer to Table 5.4. What will be the value of gross investment?
A) $400
B) $1,200
C) $1,000
D) $1,800
E) Indeterminate

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 104 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
NARRBEGIN: Scenario 5.1
Scenario 5.1
Suppose that personal income is $250 billion. Furthermore, assume that retained corporate earnings are $2 billion, social security taxes are $15 billion, social security benefit checks equal $16 billion, the capital consumption allowance is $32 billion, and corporate taxes amount to $40 billion.
Refer to Scenario 5.1. What will be the value of net national product in this country?
A) $209 billion
B) $219 billion
C) $283 billion
D) $291 billion
E) $323 billion
Scenario 5.1
Suppose that personal income is $250 billion. Furthermore, assume that retained corporate earnings are $2 billion, social security taxes are $15 billion, social security benefit checks equal $16 billion, the capital consumption allowance is $32 billion, and corporate taxes amount to $40 billion.
Refer to Scenario 5.1. What will be the value of net national product in this country?
A) $209 billion
B) $219 billion
C) $283 billion
D) $291 billion
E) $323 billion

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 104 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
NARRBEGIN: Table 5.5
The table given below reports the value of the different economic variables of a nation during a year.
Table 5.5
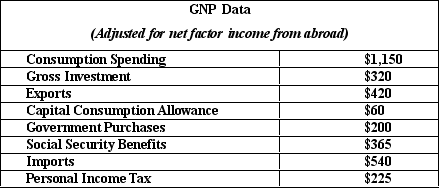
Refer to Table 5.5. For the economy described in the table above, disposable personal income is:
A) $1,440.
B) $1,630.
C) $1,550.
D) $1,610.
E) $1,870.
The table given below reports the value of the different economic variables of a nation during a year.
Table 5.5

Refer to Table 5.5. For the economy described in the table above, disposable personal income is:
A) $1,440.
B) $1,630.
C) $1,550.
D) $1,610.
E) $1,870.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 104 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
NARRBEGIN: Scenario 5.1
Scenario 5.1
Suppose that personal income is $250 billion. Furthermore, assume that retained corporate earnings are $2 billion, social security taxes are $15 billion, social security benefit checks equal $16 billion, the capital consumption allowance is $32 billion, and corporate taxes amount to $40 billion.
Refer to Scenario 5.1. Gross national product of this nation will be:
A) $177 billion.
B) $259 billion.
C) $291 billion.
D) $343 billion.
E) $323 billion.
Scenario 5.1
Suppose that personal income is $250 billion. Furthermore, assume that retained corporate earnings are $2 billion, social security taxes are $15 billion, social security benefit checks equal $16 billion, the capital consumption allowance is $32 billion, and corporate taxes amount to $40 billion.
Refer to Scenario 5.1. Gross national product of this nation will be:
A) $177 billion.
B) $259 billion.
C) $291 billion.
D) $343 billion.
E) $323 billion.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 104 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
Which of the following is true of nominal GDP?
A) It acts as an indicator of the general price level in the economy.
B) It measures the real level of output in the economy.
C) It measures national output based on the current year's prices.
D) It tends to rise by a smaller amount than real GDP when the general price level increases.
E) It measures changes in the output of intermediate goods and services.
A) It acts as an indicator of the general price level in the economy.
B) It measures the real level of output in the economy.
C) It measures national output based on the current year's prices.
D) It tends to rise by a smaller amount than real GDP when the general price level increases.
E) It measures changes in the output of intermediate goods and services.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 104 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
NARRBEGIN: Table 5.5
The table given below reports the value of the different economic variables of a nation during a year.
Table 5.5

Refer to Table 5.5. For the economy described in the table above, personal income is:
A) $1,235.
B) $1,375.
C) $1,325.
D) $1,600.
E) $1,855.
The table given below reports the value of the different economic variables of a nation during a year.
Table 5.5

Refer to Table 5.5. For the economy described in the table above, personal income is:
A) $1,235.
B) $1,375.
C) $1,325.
D) $1,600.
E) $1,855.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 104 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
The difference between GNP and NNP is equal to:
A) the statistical discrepancy in calculation.
B) the capital consumption allowance.
C) the difference between government spending and transfer payments.
D) the value of net exports.
E) the change in inventory.
A) the statistical discrepancy in calculation.
B) the capital consumption allowance.
C) the difference between government spending and transfer payments.
D) the value of net exports.
E) the change in inventory.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 104 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
NARRBEGIN: Scenario 5.1
Scenario 5.1
Suppose that personal income is $250 billion. Furthermore, assume that retained corporate earnings are $2 billion, social security taxes are $15 billion, social security benefit checks equal $16 billion, the capital consumption allowance is $32 billion, and corporate taxes amount to $40 billion.
Refer to Scenario 5.1. The national income of this nation will be:
A) $236 billion
B) $249 billion
C) $251 billion
D) $279 billion
E) $290 billion
Scenario 5.1
Suppose that personal income is $250 billion. Furthermore, assume that retained corporate earnings are $2 billion, social security taxes are $15 billion, social security benefit checks equal $16 billion, the capital consumption allowance is $32 billion, and corporate taxes amount to $40 billion.
Refer to Scenario 5.1. The national income of this nation will be:
A) $236 billion
B) $249 billion
C) $251 billion
D) $279 billion
E) $290 billion

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 104 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
Personal income is equal to:
A) national income plus business profits.
B) disposable personal income minus personal taxes.
C) national income minus transfer payments.
D) national income plus welfare benefits minus corporate retained earnings.
E) disposable personal income plus transfer payments.
A) national income plus business profits.
B) disposable personal income minus personal taxes.
C) national income minus transfer payments.
D) national income plus welfare benefits minus corporate retained earnings.
E) disposable personal income plus transfer payments.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 104 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
NARRBEGIN: Table 5.4
The table given below reports the value of different economic variables of a country during a year.
Table 5.4

Refer to Table 5.4. Calculate the NNP for this country.
A) $2,680
B) $2,480
C) $3,280
D) $3,880
E) $4,480
The table given below reports the value of different economic variables of a country during a year.
Table 5.4

Refer to Table 5.4. Calculate the NNP for this country.
A) $2,680
B) $2,480
C) $3,280
D) $3,880
E) $4,480

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 104 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
Personal income is equal to:
A) NI minus personal income tax.
B) NI minus net factor income from abroad.
C) NI plus income currently earned but not received - income currently received but not earned.
D) NI minus indirect business taxes.
E) NI plus income currently received but not earned - income currently earned but not received.
A) NI minus personal income tax.
B) NI minus net factor income from abroad.
C) NI plus income currently earned but not received - income currently received but not earned.
D) NI minus indirect business taxes.
E) NI plus income currently received but not earned - income currently earned but not received.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 104 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
NARRBEGIN: Table 5.4
The table given below reports the value of different economic variables of a country during a year.
Table 5.4

Refer to Table 5.4. Calculate the national income of this country.
A) $1,880
B) $2,480
C) $3,280
D) $3,880
E) $4,280
The table given below reports the value of different economic variables of a country during a year.
Table 5.4

Refer to Table 5.4. Calculate the national income of this country.
A) $1,880
B) $2,480
C) $3,280
D) $3,880
E) $4,280

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 104 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
Which of the following is not included in national income?
A) Corporate profits
B) Interest earnings
C) Capital consumption allowance
D) Rental income
E) Stockbroker commissions
A) Corporate profits
B) Interest earnings
C) Capital consumption allowance
D) Rental income
E) Stockbroker commissions

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 104 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
If net investment spending in a nation is zero, we can conclude that:
A) gross investment exceeds the capital consumption allowance.
B) the capital consumption allowance exceeds gross investment.
C) imports equal exports.
D) gross investment equals the capital consumption allowance.
E) no investment goods were produced in the economy.
A) gross investment exceeds the capital consumption allowance.
B) the capital consumption allowance exceeds gross investment.
C) imports equal exports.
D) gross investment equals the capital consumption allowance.
E) no investment goods were produced in the economy.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 104 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
Which of the following would not be included as part of personal income?
A) Welfare benefits
B) Food stamps distributed by the government
C) Social security benefits
D) Indirect business taxes
E) Corporate dividend payments to stockholders
A) Welfare benefits
B) Food stamps distributed by the government
C) Social security benefits
D) Indirect business taxes
E) Corporate dividend payments to stockholders

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 104 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
If nominal GDP of a country increased and real GDP remained unchanged in a particular year, which of the following is most likely to have taken place?
A) Output increased and the price level increased.
B) Output increased and the price level decreased.
C) Output remained contant and the price level increased.
D) Output decreased and the price level decreased.
E) Output increased and the price level remained constant.
A) Output increased and the price level increased.
B) Output increased and the price level decreased.
C) Output remained contant and the price level increased.
D) Output decreased and the price level decreased.
E) Output increased and the price level remained constant.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 104 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
Which of the following is true of real GDP?
A) It measures a nation's output in terms of current year prices.
B) It measures a nation's output in constant year prices.
C) It measures the degree of change in the general price level in an economy.
D) It measures the change in the value of an economy's output.
E) It measures the value of both intermediate and final goods and services produced in an economy.
A) It measures a nation's output in terms of current year prices.
B) It measures a nation's output in constant year prices.
C) It measures the degree of change in the general price level in an economy.
D) It measures the change in the value of an economy's output.
E) It measures the value of both intermediate and final goods and services produced in an economy.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 104 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
Which of the following represents the amount of income that is actually available to people for consumption and saving?
A) Net national product
B) National income
C) Disposable personal income
D) Gross national product
E) Personal income
A) Net national product
B) National income
C) Disposable personal income
D) Gross national product
E) Personal income

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 104 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
NARRBEGIN: Table 5.4
The table given below reports the value of different economic variables of a country during a year.
Table 5.4

Refer to Table 5.4. Compute the GNP of the country.
A) $2,680
B) $2,480
C) $3,280
D) $3,880
E) $4,480
The table given below reports the value of different economic variables of a country during a year.
Table 5.4

Refer to Table 5.4. Compute the GNP of the country.
A) $2,680
B) $2,480
C) $3,280
D) $3,880
E) $4,480

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 104 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
The circular flow diagram shows the flow of money and goods and services between households, firms, government, and foreign countries.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 104 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
If both real GDP and nominal GDP of a country increased at the same rate in a particular year, which of the following is most likely to have taken place?
A) Output increased and the price level increased
B) Output increased and the price level decreased
C) Output decreased and the price level increased
D) Output decreased and the price level decreased
E) Output increased and the price level remained constant
A) Output increased and the price level increased
B) Output increased and the price level decreased
C) Output decreased and the price level increased
D) Output decreased and the price level decreased
E) Output increased and the price level remained constant

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 104 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
Suppose the price index is 100 in the base year and the price of a pound of oranges in that year is $1.96. Now, if the price index changes to 105 in the following year, how much would a pound of oranges cost?
A) $2.45
B) $0.25
C) $1.96
D) $2.06
E) $1.50
A) $2.45
B) $0.25
C) $1.96
D) $2.06
E) $1.50

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 104 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
NARRBEGIN: Table 5.7
The table given below reports the price of soda over four consecutive years.
Table 5.7
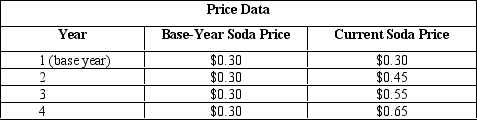
Refer to Table 5.7. Compute the price index for the third year.
A) 150
B) 183
C) 100
D) 118
E) 130
The table given below reports the price of soda over four consecutive years.
Table 5.7

Refer to Table 5.7. Compute the price index for the third year.
A) 150
B) 183
C) 100
D) 118
E) 130

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 104 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
NARRBEGIN: Table 5.6
The table given below lists the price per unit and output of computers and calculators (the only two goods produced by a nation) for the years 1995 and 2003.
Table 5.6
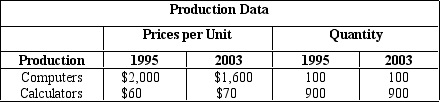
Refer to Table 5.6. What is the constant-dollar real GDP growth from 1995 to 2003 using 1995 as the base year?
A) 50 percent
B) zero percent
C) -75 percent
D) 100 percent
E) 14 percent
The table given below lists the price per unit and output of computers and calculators (the only two goods produced by a nation) for the years 1995 and 2003.
Table 5.6

Refer to Table 5.6. What is the constant-dollar real GDP growth from 1995 to 2003 using 1995 as the base year?
A) 50 percent
B) zero percent
C) -75 percent
D) 100 percent
E) 14 percent

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 104 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
National income accounting fills in the dollar values in the circular flow.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 104 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
Consider a small country producing only two commodities (coffee beans and corn). Following are the price and output of these two commodities in the year 2008:  Assuming that the output of these two commodities remains constant, while the price of each rises by 10 percent in 2009, compute the value of real GDP in 2009.
Assuming that the output of these two commodities remains constant, while the price of each rises by 10 percent in 2009, compute the value of real GDP in 2009.
A) $12,000
B) $10,560
C) $9,600
D) $8,400
E) $6,560
 Assuming that the output of these two commodities remains constant, while the price of each rises by 10 percent in 2009, compute the value of real GDP in 2009.
Assuming that the output of these two commodities remains constant, while the price of each rises by 10 percent in 2009, compute the value of real GDP in 2009.A) $12,000
B) $10,560
C) $9,600
D) $8,400
E) $6,560

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 104 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
NARRBEGIN: Table 5.6
The table given below lists the price per unit and output of computers and calculators (the only two goods produced by a nation) for the years 1995 and 2003.
Table 5.6

Refer to Table 5.6. What is the constant-dollar real GDP growth from 1995 to 2003 using 2003 as the base year?
A) 50 percent
B) zero percent
C) -75 percent
D) 100 percent
E) 14 percent
The table given below lists the price per unit and output of computers and calculators (the only two goods produced by a nation) for the years 1995 and 2003.
Table 5.6

Refer to Table 5.6. What is the constant-dollar real GDP growth from 1995 to 2003 using 2003 as the base year?
A) 50 percent
B) zero percent
C) -75 percent
D) 100 percent
E) 14 percent

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 104 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
NARRBEGIN: Table 5.6
The table given below lists the price per unit and output of computers and calculators (the only two goods produced by a nation) for the years 1995 and 2003.
Table 5.6

Refer to Table 5.6. Calculate the nominal GDP for 1995.
A) $223,000
B) $254,000
C) $448,000
D) $520,000
E) $110,000
The table given below lists the price per unit and output of computers and calculators (the only two goods produced by a nation) for the years 1995 and 2003.
Table 5.6

Refer to Table 5.6. Calculate the nominal GDP for 1995.
A) $223,000
B) $254,000
C) $448,000
D) $520,000
E) $110,000

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 104 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
NARRBEGIN: Table 5.7
The table given below reports the price of soda over four consecutive years.
Table 5.7

Refer to Table 5.7. By what percentage did the price of soda increase from the third to the fourth year?
A) 15 percent
B) 30 percent
C) 35 percent
D) 18 percent
E) 65 percent
The table given below reports the price of soda over four consecutive years.
Table 5.7

Refer to Table 5.7. By what percentage did the price of soda increase from the third to the fourth year?
A) 15 percent
B) 30 percent
C) 35 percent
D) 18 percent
E) 65 percent

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 104 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
The circular flow diagram validates the fact that the different sectors in the economy are independent.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 104 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72
Which of the following industrial countries experienced a relatively slower growth of real GDP in the latter half of the 1990s?
A) Canada
B) United States
C) Italy
D) France
E) Japan
A) Canada
B) United States
C) Italy
D) France
E) Japan

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 104 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73
In terms of price indexes, what is a COLA?
A) A measure of the quality of living
B) A consumer price adjustment
C) An increase in wages designed to match consumer price increases
D) An estimate of gross domestic product
E) A measure of producer surplus
A) A measure of the quality of living
B) A consumer price adjustment
C) An increase in wages designed to match consumer price increases
D) An estimate of gross domestic product
E) A measure of producer surplus

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 104 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
74
Consider a small country producing only two commodities (coffee beans and corn). Following are the price and output of these two commodities in the year 2008:  Assuming the price level in the economy remains same while the output of both these products increase by 10 percent in 2009, calculate the value of real GDP in this country for the year 2009?
Assuming the price level in the economy remains same while the output of both these products increase by 10 percent in 2009, calculate the value of real GDP in this country for the year 2009?
A) $9,600
B) $10,560
C) $1,056
D) $6,900
E) $10, 960
 Assuming the price level in the economy remains same while the output of both these products increase by 10 percent in 2009, calculate the value of real GDP in this country for the year 2009?
Assuming the price level in the economy remains same while the output of both these products increase by 10 percent in 2009, calculate the value of real GDP in this country for the year 2009?A) $9,600
B) $10,560
C) $1,056
D) $6,900
E) $10, 960

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 104 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
75
NARRBEGIN: Table 5.7
The table given below reports the price of soda over four consecutive years.
Table 5.7

Refer to Table 5.7. Compute the price index for the base year.
A) 130
B) 30
C) 80
D) 100
E) 120
The table given below reports the price of soda over four consecutive years.
Table 5.7

Refer to Table 5.7. Compute the price index for the base year.
A) 130
B) 30
C) 80
D) 100
E) 120

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 104 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
76
The consumer price index:
A) tracks the value of output over time.
B) is not tied to cost-of-living adjustments.
C) doubles every five years in the economy.
D) is a weighted average of consumer prices.
E) is a broader price index measure than the implicit GDP deflator.
A) tracks the value of output over time.
B) is not tied to cost-of-living adjustments.
C) doubles every five years in the economy.
D) is a weighted average of consumer prices.
E) is a broader price index measure than the implicit GDP deflator.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 104 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
77
NARRBEGIN: Table 5.6
The table given below lists the price per unit and output of computers and calculators (the only two goods produced by a nation) for the years 1995 and 2003.
Table 5.6

Refer to Table 5.6. What is the nominal GDP for 2003?
A) $223,000
B) $254,000
C) $376,000
D) $448,000
E) $520,000
The table given below lists the price per unit and output of computers and calculators (the only two goods produced by a nation) for the years 1995 and 2003.
Table 5.6

Refer to Table 5.6. What is the nominal GDP for 2003?
A) $223,000
B) $254,000
C) $376,000
D) $448,000
E) $520,000

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 104 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
78
The price index for the current year is 180. This means that, on average, prices in the current year are:
A) 80 percent of prices in the base year.
B) $1.80 higher than prices in the base year.
C) 180 percent higher than prices in the base year.
D) $0.80 higher than prices in the base year.
E) 80 percent higher than prices in the base year.
A) 80 percent of prices in the base year.
B) $1.80 higher than prices in the base year.
C) 180 percent higher than prices in the base year.
D) $0.80 higher than prices in the base year.
E) 80 percent higher than prices in the base year.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 104 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
79
The producer price index was earlier known as _____.
A) the retail price index
B) the commodity market index
C) the Fischer index
D) the wholesale price index
E) the cost of living index
A) the retail price index
B) the commodity market index
C) the Fischer index
D) the wholesale price index
E) the cost of living index

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 104 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
80
Suppose the current price of DVDs is $16, while its base-year price is $11.50. The value of the price index for the current year is approximately:
A) 139
B) 39
C) 25
D) 160
E) 172
A) 139
B) 39
C) 25
D) 160
E) 172

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 104 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



