Deck 26: Options and More
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/61
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 26: Options and More
1
You bought a call option with a $35 strike price for $0.25 when the underlying stock was selling for $34.00. Just prior to expiration, the stock was selling for $34.50. What was your gain
Or loss per option share on this transaction?
A)$0.50 loss
B)$35.25 loss
C)$0.25 gain
D)$0.25 loss
Or loss per option share on this transaction?
A)$0.50 loss
B)$35.25 loss
C)$0.25 gain
D)$0.25 loss
$0.25 loss
2
A certain stock is selling for $43.10. What is the minimum amount for which a call option on the stock with a strike price of $40 should sell?
A)$40.00
B)$0
C)$3.10
D)none of the above
A)$40.00
B)$0
C)$3.10
D)none of the above
$3.10
3
A spread involves
A)buying one option and shorting the same type of option on the same stock. The options may have either different strike prices or different expiration dates.
B)buying a call option and shorting a put option on the same stock with the same expiration date but different strike prices.
C)buying a call and buying a put on the same stock. The options typically have the same strike prices and the same expiration dates.
D)buying a put option and shorting a call option on the same stock with different expiration dates, but the same strike prices.
A)buying one option and shorting the same type of option on the same stock. The options may have either different strike prices or different expiration dates.
B)buying a call option and shorting a put option on the same stock with the same expiration date but different strike prices.
C)buying a call and buying a put on the same stock. The options typically have the same strike prices and the same expiration dates.
D)buying a put option and shorting a call option on the same stock with different expiration dates, but the same strike prices.
buying one option and shorting the same type of option on the same stock. The options may have either different strike prices or different expiration dates.
4
A stock is selling for $64.10. A put option on the stock has a strike price of $65. This option is
A)in-the-money.
B)out-of-the-money.
C)far-out-of-the-money.
D)at-the-money.
A)in-the-money.
B)out-of-the-money.
C)far-out-of-the-money.
D)at-the-money.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 61 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
Which of the following would be referred to as a straddle?
A)selling a call and selling a put on the same stock
B)buying a call and shorting a put on the same stock
C)selling a call and buying a put on the same stock
D)none of the above
A)selling a call and selling a put on the same stock
B)buying a call and shorting a put on the same stock
C)selling a call and buying a put on the same stock
D)none of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 61 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
A stock is currently selling for $23.25. What is the minimum amount for which a put option on the stock with a strike price of $25.00 should sell?
A)$3.25
B)$23.25
C)$0
D)$1.75
A)$3.25
B)$23.25
C)$0
D)$1.75

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 61 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
You purchased a stock for $60 a share and simultaneously wrote a covered call with a strike price of $70 on the stock. The call was selling for $0.50 at that time. Just prior to expiration, the
Stock was selling for $72 a share. What was your gain or loss per option share on this
Transaction?
A)$60.50 loss
B)$0.50 loss
C)$10.50 gain
D)$12.50 gain
Stock was selling for $72 a share. What was your gain or loss per option share on this
Transaction?
A)$60.50 loss
B)$0.50 loss
C)$10.50 gain
D)$12.50 gain

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 61 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
Which of the following statements about put options is true?
A)The writer of a put option is exposed to limitless losses, theoretically at least.
B)A put option is the opposite of a call option. That is, when someone wants to buy a call option, another investor must be willing to invest in a put option with the same
Characteristics.
C)You might purchase a put if you believe the price of the underlying stock will increase.
D)You might write a put if you believe the price of the underlying stock will increase.
A)The writer of a put option is exposed to limitless losses, theoretically at least.
B)A put option is the opposite of a call option. That is, when someone wants to buy a call option, another investor must be willing to invest in a put option with the same
Characteristics.
C)You might purchase a put if you believe the price of the underlying stock will increase.
D)You might write a put if you believe the price of the underlying stock will increase.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 61 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
A stock is currently selling for $32 a share. You write a naked call with a strike price of $30 on the stock and receive $2.50 per option share. What is the maximum amount of money you
Could lose on this position?
A)$32.50
B)$4.50
C)$2.50
D)Your losses are, theoretically, limitless.
Could lose on this position?
A)$32.50
B)$4.50
C)$2.50
D)Your losses are, theoretically, limitless.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 61 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
A stock is selling for $33.13. A call option on the stock has a strike price of $40. This option is
A)out-of-the-money.
B)at-the-money.
C)far-in-the-money.
D)in-the-money.
A)out-of-the-money.
B)at-the-money.
C)far-in-the-money.
D)in-the-money.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 61 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
The writer of a put option
A)has the right, but not the obligation, to sell shares of the underlying asset.
B)has the right, but not the obligation, to buy shares of the underlying asset.
C)is obliged to buy shares of the underlying asset if the put holder chooses to exercise the option.
D)is obliged to sell shares of the underlying asset if the put holder chooses to exercise the option.
A)has the right, but not the obligation, to sell shares of the underlying asset.
B)has the right, but not the obligation, to buy shares of the underlying asset.
C)is obliged to buy shares of the underlying asset if the put holder chooses to exercise the option.
D)is obliged to sell shares of the underlying asset if the put holder chooses to exercise the option.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 61 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
You purchase a stock for $53 and simultaneously buy a put option on the stock with a strike price of $60 for $8.50. Just prior to expiration, the stock is selling for $62.50. What is your gain
Or loss on your position?
A)$1.50 loss
B)$18.00 gain
C)$1.00 gain
D)$9.50 gain
Or loss on your position?
A)$1.50 loss
B)$18.00 gain
C)$1.00 gain
D)$9.50 gain

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 61 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
A call option
A)gives the owner of the option the right to buy the underlying asset for a specified price within a specified period of time if the owner wishes to exercise his option.
B)obligates the owner of the option to buy the underlying asset for a specified price at a specified point in time unless the owner closes out his position.
C)gives the owner of the option the right to sell the underlying asset at a specified price within a specified period of time if the owner wishes to exercise his option.
D)obligates the owner of the option to sell the underlying asset for a specified price at a specified point in time unless the owner closes out his position.
A)gives the owner of the option the right to buy the underlying asset for a specified price within a specified period of time if the owner wishes to exercise his option.
B)obligates the owner of the option to buy the underlying asset for a specified price at a specified point in time unless the owner closes out his position.
C)gives the owner of the option the right to sell the underlying asset at a specified price within a specified period of time if the owner wishes to exercise his option.
D)obligates the owner of the option to sell the underlying asset for a specified price at a specified point in time unless the owner closes out his position.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 61 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
If an investor believes that the price of a stock will fall, he might
A)buy a call option on the stock.
B)write a put option on the stock.
C)buy a put option on the stock.
D)Either A or C would be an appropriate position to take.
A)buy a call option on the stock.
B)write a put option on the stock.
C)buy a put option on the stock.
D)Either A or C would be an appropriate position to take.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 61 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
If an investor believes that the price of a stock will increase, he might
A)buy a call option on the stock.
B)buy a put option on the stock.
C)write a put option on the stock.
D)Either A or C would be an appropriate position to take.
A)buy a call option on the stock.
B)buy a put option on the stock.
C)write a put option on the stock.
D)Either A or C would be an appropriate position to take.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 61 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
A certain stock is selling for $36.40. What is the minimum amount for which a call option on the stock with a strike price of $35 should sell?
A)$1.40
B)$0
C)$35.00
D)none of the above
A)$1.40
B)$0
C)$35.00
D)none of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 61 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
An American option
A)can be exercised only at expiration.
B)can be exercised any time prior to expiration.
C)sells only on the U.S. exchanges.
D)Both A and B are true.
A)can be exercised only at expiration.
B)can be exercised any time prior to expiration.
C)sells only on the U.S. exchanges.
D)Both A and B are true.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 61 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
A stock is currently selling for $51.00. What is the minimum amount for which a put option on the stock with a strike price of $50.00 should sell?
A)$50.00
B)$1.00
C)-$1.00
D)$0
A)$50.00
B)$1.00
C)-$1.00
D)$0

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 61 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
You bought a call option with a $40 strike price for $2.25 when the underlying stock was selling for $39.00. Just prior to expiration, the stock was selling for $44.00. What was your gain
Or loss per option share on this transaction?
A)$1.75 gain
B)$2.75 gain
C)$2.75 loss
D)$2.25 loss
Or loss per option share on this transaction?
A)$1.75 gain
B)$2.75 gain
C)$2.75 loss
D)$2.25 loss

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 61 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
One option contract is typically an option to buy or sell
A)100 shares of the underlying stock.
B)500 shares of the underlying stock.
C)200 shares of the underlying stock.
D)50 shares of the underlying stock.
A)100 shares of the underlying stock.
B)500 shares of the underlying stock.
C)200 shares of the underlying stock.
D)50 shares of the underlying stock.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 61 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
Assume an investor buys a call option with strike price, 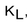 , and sells a call option on the same stock with a strike price,
, and sells a call option on the same stock with a strike price, 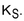 Assume, too, that
Assume, too, that 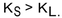 If the stock price,
If the stock price, 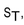 is greater than
is greater than 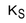 at expiration, which of the following represents the total payoff to the investor?
at expiration, which of the following represents the total payoff to the investor?
A)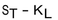
B)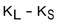
C)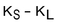
D)0
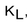 , and sells a call option on the same stock with a strike price,
, and sells a call option on the same stock with a strike price, 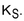 Assume, too, that
Assume, too, that 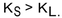 If the stock price,
If the stock price, 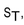 is greater than
is greater than 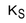 at expiration, which of the following represents the total payoff to the investor?
at expiration, which of the following represents the total payoff to the investor?A)
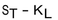
B)
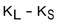
C)
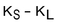
D)0

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 61 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
Explain how you could duplicate a short position in a stock by using options.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 61 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
An investor can create a synthetic call option by
A)taking a long position in a stock, simultaneously buying a put option on the stock, and investing the present value of the strike price in Treasury securities.
B)taking a long position in a stock, and simultaneously buying a put option on the stock.
C)short selling the stock and using the proceeds to buy a put option on the stock and investing the rest in Treasury securities.
D)borrowing money at the risk-free rate and using the funds to invest in the stock itself.
A)taking a long position in a stock, simultaneously buying a put option on the stock, and investing the present value of the strike price in Treasury securities.
B)taking a long position in a stock, and simultaneously buying a put option on the stock.
C)short selling the stock and using the proceeds to buy a put option on the stock and investing the rest in Treasury securities.
D)borrowing money at the risk-free rate and using the funds to invest in the stock itself.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 61 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
CUMULATIVE NORMAL DISTRIBUTION TABLE 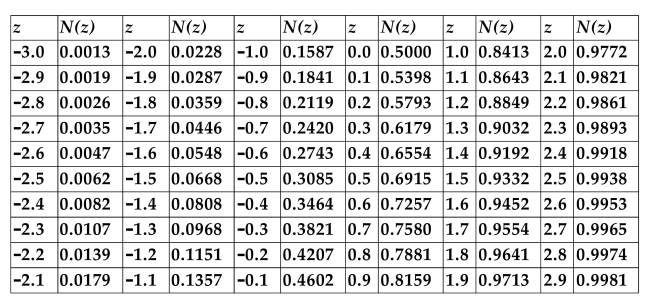
Refer to the information above. Calculate the value of a call option on a stock that is
currently selling for $88 if the strike price is $90, the option expires in 3 months, the
implied volatility of the underlying stock returns is 22%, and the annualized risk-free
rate is 4%.

Refer to the information above. Calculate the value of a call option on a stock that is
currently selling for $88 if the strike price is $90, the option expires in 3 months, the
implied volatility of the underlying stock returns is 22%, and the annualized risk-free
rate is 4%.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 61 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
Under what two conditions might an American option be worth more than an
otherwise identical European option? Explain.
otherwise identical European option? Explain.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 61 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
You purchase both a call option and a put option on a stock. Both options have a strike
price of $50 and have the same expiration. Develop a payoff table for this combination,
using stock prices from $0 to $150, in increments of $25.
price of $50 and have the same expiration. Develop a payoff table for this combination,
using stock prices from $0 to $150, in increments of $25.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 61 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
An investor can duplicate the payoffs generated by taking a long position in a stock by
A)buying a put option on the stock and simultaneously selling a call option on the stock and investing the proceeds in Treasury securities.
B)buying a put and a call on the same stock with the same expiration date, but different strike prices.
C)buying a call option on the stock, simultaneously selling a put option on the stock, and investing the present value of the strike price in Treasury securities.
D)buying a call option on the stock and simultaneously selling a call option on the stock with the same expiration date, but a different strike price.
A)buying a put option on the stock and simultaneously selling a call option on the stock and investing the proceeds in Treasury securities.
B)buying a put and a call on the same stock with the same expiration date, but different strike prices.
C)buying a call option on the stock, simultaneously selling a put option on the stock, and investing the present value of the strike price in Treasury securities.
D)buying a call option on the stock and simultaneously selling a call option on the stock with the same expiration date, but a different strike price.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 61 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
The volatility smile
A)suggests that the prices for far-out-of-the-money options calculated using the Black-Scholes formula are lower than they are in reality.
B)is the result of plotting the Black-Scholes implied volatilities as a function of the stock price.
C)is the result of plotting the Black-Scholes strike prices as a function of the stock price.
D)suggests that prices for at-the-money options calculated using the Black-Scholes formula are higher than they are in reality.
A)suggests that the prices for far-out-of-the-money options calculated using the Black-Scholes formula are lower than they are in reality.
B)is the result of plotting the Black-Scholes implied volatilities as a function of the stock price.
C)is the result of plotting the Black-Scholes strike prices as a function of the stock price.
D)suggests that prices for at-the-money options calculated using the Black-Scholes formula are higher than they are in reality.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 61 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
If there is to be no arbitrage possibility, which of the following is a requirement for the price of an option?
A)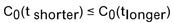
B)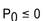
C)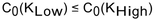
D)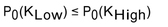
A)
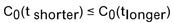
B)
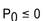
C)
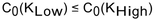
D)
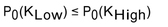

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 61 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
A European call option on a stock has an exercise price of $100 and expires in 5 months. The option is currently selling for $3.80 per option share. A European put option on the same stock
With the same exercise price and time to expiration is selling for $22.20. The stock itself is
Selling for $80.81. The annualized risk-free rate is 2.25%. According to the put-call parity
Model,
A)the call option is underpriced relative to the put option by $0.13.
B)the put option is overpriced relative to the call option by $0.59.
C)the put option is overpriced relative to the call option by $0.13.
D)the put and the call are correctly priced relative to one another, but we do not know whether either is fairly priced.
With the same exercise price and time to expiration is selling for $22.20. The stock itself is
Selling for $80.81. The annualized risk-free rate is 2.25%. According to the put-call parity
Model,
A)the call option is underpriced relative to the put option by $0.13.
B)the put option is overpriced relative to the call option by $0.59.
C)the put option is overpriced relative to the call option by $0.13.
D)the put and the call are correctly priced relative to one another, but we do not know whether either is fairly priced.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 61 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
An investor buys a call with a strike price of $40 and sells a call on the same stock and with the same expiration date that has a strike price of $35. What will the total payoff for this strategy
Be if the price of the stock is $43 when the options expire?
A)+$5.00
B)+$2.00
C)-$5.00
D)-$2.00
Be if the price of the stock is $43 when the options expire?
A)+$5.00
B)+$2.00
C)-$5.00
D)-$2.00

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 61 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
CUMULATIVE NORMAL DISTRIBUTION TABLE 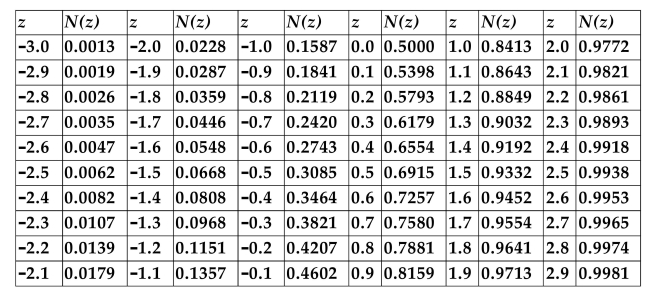
Refer to the information above. A stock is currently selling for $60. The stock pays no dividends. An American call option on the stock has a strike price of $55 and has 3 months to
Expiration. The standard deviation of the continuously compounded rate of return of the stock
Is 30%, and the annualized risk-free rate is 3%. Use the Black-Scholes formula to calculate the
Fair value of this option.
A)$7.66
B)$6.79
C)$7.03
D)The Black-Scholes formula cannot be used to determine the fair value of an American call option.

Refer to the information above. A stock is currently selling for $60. The stock pays no dividends. An American call option on the stock has a strike price of $55 and has 3 months to
Expiration. The standard deviation of the continuously compounded rate of return of the stock
Is 30%, and the annualized risk-free rate is 3%. Use the Black-Scholes formula to calculate the
Fair value of this option.
A)$7.66
B)$6.79
C)$7.03
D)The Black-Scholes formula cannot be used to determine the fair value of an American call option.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 61 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
The value of the right to exercise an American call option early, assuming the underlying stock pays no dividends, is
A)equal to the difference in the strike prices of the American call and the European call.
B)equal to zero.
C)equal to the call option premium.
D)equal to the strike price of the option.
A)equal to the difference in the strike prices of the American call and the European call.
B)equal to zero.
C)equal to the call option premium.
D)equal to the strike price of the option.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 61 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
What is the difference between writing a covered call and writing a naked call? Which
one is riskier? Why?
one is riskier? Why?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 61 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
A European call option on a stock has an exercise price of $50, is selling for $6.50, and has 3 months to expiration. The stock itself is currently selling for $53.38. The annualized risk-free
Rate is 3%. If the call option is fairly priced, what is the fair price of a European put option on
This stock that has the same strike price and time to expiration?
A)$1.66
B)$2.75
C)$11.34
D)$10.25
Rate is 3%. If the call option is fairly priced, what is the fair price of a European put option on
This stock that has the same strike price and time to expiration?
A)$1.66
B)$2.75
C)$11.34
D)$10.25

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 61 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
Which of the following values can not be obtained by applying the Black-Scholes formula and/or the put-call parity model?
A)the value of a European call
B)the value of an American put
C)the value of an American call on a non-dividend paying stock
D)the value of a European put
A)the value of a European call
B)the value of an American put
C)the value of an American call on a non-dividend paying stock
D)the value of a European put

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 61 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
CUMULATIVE NORMAL DISTRIBUTION TABLE 
Refer to the information above. A stock is currently selling for $42. The stock pays no dividends. An American call option on the stock has a strike price of $45 and has 6 months to
Expiration. The standard deviation of the continuously compounded rate of return of the stock
Is 25%, and the annualized risk-free rate is 3%. Use the Black-Scholes formula to calculate the
Fair value of this option.
A)$2.33
B)$2.01
C)$2.25
D)The Black-Scholes formula cannot be used to determine the fair value of an American call option.

Refer to the information above. A stock is currently selling for $42. The stock pays no dividends. An American call option on the stock has a strike price of $45 and has 6 months to
Expiration. The standard deviation of the continuously compounded rate of return of the stock
Is 25%, and the annualized risk-free rate is 3%. Use the Black-Scholes formula to calculate the
Fair value of this option.
A)$2.33
B)$2.01
C)$2.25
D)The Black-Scholes formula cannot be used to determine the fair value of an American call option.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 61 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
Using 5 years of historical daily stock returns, you have determined the standard deviation of the returns to be 1.3%. This means that the annual standard deviation of the returns (rounded
To the nearest tenth of a percent)is
A)3.3%
B)24.8%
C)20.8%.
D)4.7%.
To the nearest tenth of a percent)is
A)3.3%
B)24.8%
C)20.8%.
D)4.7%.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 61 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
A European put option on a certain stock has an exercise price of $32.50 and expires in one month. The put option is fairly priced at $4.02 per option share. The stock itself is currently
Selling for $32.31 a share. If the annualized risk-free rate is 6.5%, what should the price of a
European call option on this stock, with the same exercise price and expiration date, be?
A)$5.81
B)$4.00
C)$2.05
D)none of the above
Selling for $32.31 a share. If the annualized risk-free rate is 6.5%, what should the price of a
European call option on this stock, with the same exercise price and expiration date, be?
A)$5.81
B)$4.00
C)$2.05
D)none of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 61 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
A call option with 6 months to expiration has a strike price of $30 and costs $2. A share
of the underlying stock is currently selling for $28.50. The annualized risk-free rate is
4%. If this option is fairly priced, what should the value of a put option with the same
strike price and expiration be? If it is currently selling for $4.00, how could you earn
arbitrage profits?
of the underlying stock is currently selling for $28.50. The annualized risk-free rate is
4%. If this option is fairly priced, what should the value of a put option with the same
strike price and expiration be? If it is currently selling for $4.00, how could you earn
arbitrage profits?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 61 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
Inmar Corporation is a mail-order company that imports a lot of its products from Switzerland. The firm must place its order six months in advance and must pay upon
Delivery. If the CFO is concerned that the dollar will depreciate relative to the Swiss franc, she
Could execute a hedge by
A)buying put options on the Swiss franc.
B)writing put options on the Swiss franc.
C)writing call options on the Swiss franc.
D)buying call options on the Swiss franc.
Delivery. If the CFO is concerned that the dollar will depreciate relative to the Swiss franc, she
Could execute a hedge by
A)buying put options on the Swiss franc.
B)writing put options on the Swiss franc.
C)writing call options on the Swiss franc.
D)buying call options on the Swiss franc.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 61 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
The change in the price of the option as the time to expiration changes is called
A)rho.
B)gamma.
C)delta.
D)theta.
A)rho.
B)gamma.
C)delta.
D)theta.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 61 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
The price of a call option will be lower,
A)the higher the interest rates.
B)the less time to expiration it has.
C)the lower the strike price is.
D)the greater the volatility of the stock returns.
A)the higher the interest rates.
B)the less time to expiration it has.
C)the lower the strike price is.
D)the greater the volatility of the stock returns.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 61 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
CUMULATIVE NORMAL DISTRIBUTION TABLE 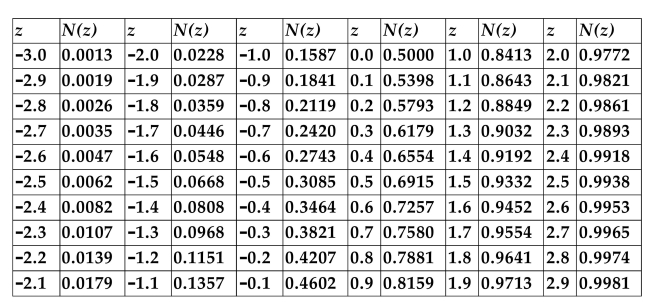
Refer to the information above. A stock is currently selling for $60. The stock pays no dividends. A call option on the stock has a strike price of $55 and has 3 months to expiration.
The implied volatility is 30%, and the annualized risk-free rate is 3%. What is the option's
Hedge ratio, rounded to the nearest hundredth?
A)0.55
B)0.71
C)0.76
D)0.70

Refer to the information above. A stock is currently selling for $60. The stock pays no dividends. A call option on the stock has a strike price of $55 and has 3 months to expiration.
The implied volatility is 30%, and the annualized risk-free rate is 3%. What is the option's
Hedge ratio, rounded to the nearest hundredth?
A)0.55
B)0.71
C)0.76
D)0.70

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 61 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
If the hedge ratio for a call option is 0.5 and you own 100 shares of the underlying stock, which of the following actions would result in a risk-free hedge?
A)Buy 200 calls on the stock.
B)Sell 100 calls on the stock.
C)Sell 200 calls on the stock.
D)Buy 50 calls on the stock.
A)Buy 200 calls on the stock.
B)Sell 100 calls on the stock.
C)Sell 200 calls on the stock.
D)Buy 50 calls on the stock.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 61 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
In which of the following corporate applications would the Black-Scholes formula not be of much use?
A)risk management
B)valuing corporate stocks and bonds
C)valuing real options
D)The Black-Scholes formula would be very useful for all of the above applications.
A)risk management
B)valuing corporate stocks and bonds
C)valuing real options
D)The Black-Scholes formula would be very useful for all of the above applications.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 61 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
Indicate how the indicated change in each of the inputs in the table below will affect
the value of a call option, all else equal. Use "+" for increase, "-" for decrease, and "0"
for no change.
the value of a call option, all else equal. Use "+" for increase, "-" for decrease, and "0"
for no change.


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 61 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
All else equal, what effect will an increase in the risk-free rate of interest have on the
hedge ratio? Explain.
hedge ratio? Explain.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 61 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
Assume that a stock is currently selling for $33, and that its price is equally likely to increase by 10% or decrease by 5% in the next instant. Assume that bonds increase at the risk-free rate of 1
+ 0.2% each instant. Determine the current value of a call option on this stock that will expire
In one instant and has a strike price of $35. Round your answer to the nearest cent.
A)$0.45
B)$0.00
C)$2.00
D)$1.82
+ 0.2% each instant. Determine the current value of a call option on this stock that will expire
In one instant and has a strike price of $35. Round your answer to the nearest cent.
A)$0.45
B)$0.00
C)$2.00
D)$1.82

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 61 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
Which of the following statements is false?
A)If the underlying stock does not pay dividends, an investor should never exercise an American call option early.
B)The Black-Scholes formula can be used to determine the value of American call options on non-dividend paying stocks.
C)The Black-Scholes formula can be used only to calculate the values of call option; it does not apply to put options.
D)The Black-Scholes formula was developed using European options and, therefore, can calculate the value of an American call option only on its final expiration date.
A)If the underlying stock does not pay dividends, an investor should never exercise an American call option early.
B)The Black-Scholes formula can be used to determine the value of American call options on non-dividend paying stocks.
C)The Black-Scholes formula can be used only to calculate the values of call option; it does not apply to put options.
D)The Black-Scholes formula was developed using European options and, therefore, can calculate the value of an American call option only on its final expiration date.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 61 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
Another name for the hedge ratio is the
A)delta.
B)rho.
C)vega.
D)theta.
A)delta.
B)rho.
C)vega.
D)theta.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 61 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
Which of the following statements about employee stock options (ESOPs)is true?
A)When initially issued, the strike price on the option is typically established such that the option will be far-out-of-the-money.
B)ESOPs are worth less to the employees who receive them than they would be to third parties.
C)ESOPs should rarely be exercised early, but instead should be held to expiration.
D)They do not have the dilutive effect on earnings and ownership that the exercise of a regular option has.
A)When initially issued, the strike price on the option is typically established such that the option will be far-out-of-the-money.
B)ESOPs are worth less to the employees who receive them than they would be to third parties.
C)ESOPs should rarely be exercised early, but instead should be held to expiration.
D)They do not have the dilutive effect on earnings and ownership that the exercise of a regular option has.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 61 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
Which of the following terms in the Black-Scholes formula represents the amount by which the price of a call option will change with each dollar change in the price of the underlying asset?
A)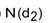
B)
C)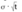
D)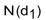
A)
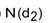
B)

C)
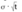
D)
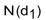

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 61 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
List five differences between regular stock options and employee stock options
(ESOPs).
(ESOPs).

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 61 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
If the hedge ratio for a call option is 0.4 and you are short 100 shares of the underlying stock, which of the following actions would result in a risk-free hedge?
A)Buy 400 calls on the stock.
B)Buy 40 calls on the stock.
C)Buy 250 calls on the stock.
D)Sell 400 calls on the stock.
A)Buy 400 calls on the stock.
B)Buy 40 calls on the stock.
C)Buy 250 calls on the stock.
D)Sell 400 calls on the stock.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 61 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
You purchased a home worth $400,000, with the help of a $300,000 mortgage. Your levered equity ownership is, in effect,
A)a put option with a strike price of $300,000.
B)a put option with a strike price of $400,000.
C)a call option with a strike price of $300,000.
D)a call option with a strike price of $100,000.
A)a put option with a strike price of $300,000.
B)a put option with a strike price of $400,000.
C)a call option with a strike price of $300,000.
D)a call option with a strike price of $100,000.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 61 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
The price of a call option will be higher,
A)the higher the strike price is.
B)the greater the volatility of the stock returns.
C)the less time to expiration it has.
D)the lower the interest rates.
A)the higher the strike price is.
B)the greater the volatility of the stock returns.
C)the less time to expiration it has.
D)the lower the interest rates.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 61 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
Assume that a stock is currently selling for $18, and that its price is equally likely to increase by 20% or decrease by 6% in the next instant. Assume that bonds increase at the risk-free rate of 1
+ 0.1% each instant. Determine the current value of a call option on this stock that will expire
In one instant and has a strike price of $20. Round your answer to the nearest cent.
A)$0.37
B)$0.00
C)$2.00
D)none of the above
+ 0.1% each instant. Determine the current value of a call option on this stock that will expire
In one instant and has a strike price of $20. Round your answer to the nearest cent.
A)$0.37
B)$0.00
C)$2.00
D)none of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 61 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
Which of the following is not necessary to know in order to calculate the price of a call option?
A)the expected rate of return on the underlying stock
B)the strike price of the option
C)the risk-free interest rate
D)All of the above are necessary inputs in calculating the price of a call option.
A)the expected rate of return on the underlying stock
B)the strike price of the option
C)the risk-free interest rate
D)All of the above are necessary inputs in calculating the price of a call option.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 61 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
Being a corporate bondholder is, in effect,
A)like owning a risk-free bond and selling a put option on the firm to the stockholders.
B)like selling a risk-free bond and buying a call option on the firm from the stockholders.
C)like owning a risk-free bond and buying a put option on the firm.
D)like owning a risk-free bond and selling a call option on the firm to the stockholders.
A)like owning a risk-free bond and selling a put option on the firm to the stockholders.
B)like selling a risk-free bond and buying a call option on the firm from the stockholders.
C)like owning a risk-free bond and buying a put option on the firm.
D)like owning a risk-free bond and selling a call option on the firm to the stockholders.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 61 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
Assume that a stock is currently selling for $46 and that its price is equally likely to
increase by 10% or decrease by 5% in the next instant. Assume that bonds increase at
the risk-free rate of 1 + 0.1% each instant. Find the value of a put that will expire in
one instant and has a strike price of $50.
increase by 10% or decrease by 5% in the next instant. Assume that bonds increase at
the risk-free rate of 1 + 0.1% each instant. Find the value of a put that will expire in
one instant and has a strike price of $50.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 61 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



