Deck 9: The Family of Stars
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/105
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 9: The Family of Stars
1
Parallax would be easier to measure if
A) Earth s orbit was larger.
B) the stars were farther away.
C) Earth moved faster along its orbit.
D) all of these
E) none of these
A) Earth s orbit was larger.
B) the stars were farther away.
C) Earth moved faster along its orbit.
D) all of these
E) none of these
Earth s orbit was larger.
2
Spectroscopic binaries are difficult to analyze because
A) we can t measure the radial velocities of each star in the system.
B) we can t see the shape or tilt of the orbit.
C) we can t find the diameters of the stars.
D) we can t determine the luminosities of the stars.
E) the Doppler shift is not measurable.
A) we can t measure the radial velocities of each star in the system.
B) we can t see the shape or tilt of the orbit.
C) we can t find the diameters of the stars.
D) we can t determine the luminosities of the stars.
E) the Doppler shift is not measurable.
we can t see the shape or tilt of the orbit.
3
Red giant stars are
I. more luminous than the sun.
II. larger in diameter than the sun.
III. cooler than B stars.
IV. located above the main sequence stars in the H-R diagram.
A) I II
B) II IV
C) I, II, IV
D) II, III, IV
E) I, II, III, IV
I. more luminous than the sun.
II. larger in diameter than the sun.
III. cooler than B stars.
IV. located above the main sequence stars in the H-R diagram.
A) I II
B) II IV
C) I, II, IV
D) II, III, IV
E) I, II, III, IV
I, II, III, IV
4
The ____ of a star is a measure of the total energy radiated by the star in one second.
A) color
B) apparent visual magnitude
C) luminosity class
D) spectral type
E) luminosity
A) color
B) apparent visual magnitude
C) luminosity class
D) spectral type
E) luminosity

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 105 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
The star named Sheat is of M2 II spectral type and luminosity class. Based on this information, which of the following are true?
I. Sheat has a surface temperature less than the sun.
II. Sheat has a diameter that is greater than that of the sun.
III. Sheat is more luminous than the sun.
IV. Sheat is located near the upper left hand corner in the HR diagram.
A) I II
B) II IV
C) II, III, IV
D) I, II, III
E) I, II, III, IV
I. Sheat has a surface temperature less than the sun.
II. Sheat has a diameter that is greater than that of the sun.
III. Sheat is more luminous than the sun.
IV. Sheat is located near the upper left hand corner in the HR diagram.
A) I II
B) II IV
C) II, III, IV
D) I, II, III
E) I, II, III, IV

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 105 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
We know that giant stars are larger in diameter than the sun because
A) they are more luminous but have about the same temperature.
B) they are less luminous but have about the same temperature.
C) they are hotter but have about the same luminosity.
D) they are cooler but have about the same luminosity.
E) they have a larger absolute magnitude than the sun.
A) they are more luminous but have about the same temperature.
B) they are less luminous but have about the same temperature.
C) they are hotter but have about the same luminosity.
D) they are cooler but have about the same luminosity.
E) they have a larger absolute magnitude than the sun.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 105 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
In a binary system, the more massive star
A) is at the center of mass.
B) is farthest from the center of mass.
C) is nearest the center of mass.
D) follows the largest orbit.
E) shows a larger Doppler shift in its spectral lines.
A) is at the center of mass.
B) is farthest from the center of mass.
C) is nearest the center of mass.
D) follows the largest orbit.
E) shows a larger Doppler shift in its spectral lines.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 105 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
Use the HR diagram below to answer the following question(s). 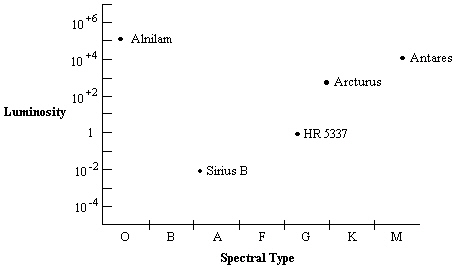 Which star in the diagram has the greatest surface temperature?
Which star in the diagram has the greatest surface temperature?
A) Alnilam
B) Antares
C) Arcturus
D) HR 5337
E) Sirius B
 Which star in the diagram has the greatest surface temperature?
Which star in the diagram has the greatest surface temperature?A) Alnilam
B) Antares
C) Arcturus
D) HR 5337
E) Sirius B

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 105 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
In the H-R diagram, 90 percent of all stars are
A) in the giant region.
B) in the supergiant region.
C) among the B stars.
D) among the G stars.
E) on the main sequence.
A) in the giant region.
B) in the supergiant region.
C) among the B stars.
D) among the G stars.
E) on the main sequence.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 105 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
Use the HR diagram below to answer the following question(s). 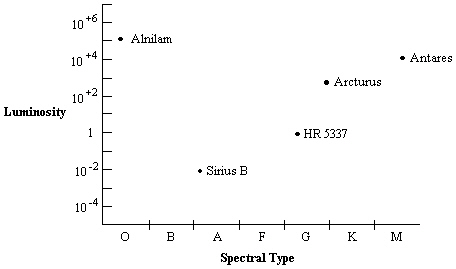 Which of the stars in the diagram has the largest absolute visual magnitude?
Which of the stars in the diagram has the largest absolute visual magnitude?
A) Alnilam
B) Antares
C) Arcturus
D) HR 5337
E) Sirius B
 Which of the stars in the diagram has the largest absolute visual magnitude?
Which of the stars in the diagram has the largest absolute visual magnitude?A) Alnilam
B) Antares
C) Arcturus
D) HR 5337
E) Sirius B

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 105 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
Compared with the spectral lines in the solar spectrum, lines in a supergiant star s spectrum are
A) more narrow.
B) broader.
C) weaker.
D) stronger.
E) b c
A) more narrow.
B) broader.
C) weaker.
D) stronger.
E) b c

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 105 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
An eclipsing binary will
A) be more luminous than a visual binary.
B) also be observed as a spectroscopic binary.
C) give off most of its light in the infrared.
D) show a constant Doppler shift in its spectral lines.
E) show two stars with variable proper motion.
A) be more luminous than a visual binary.
B) also be observed as a spectroscopic binary.
C) give off most of its light in the infrared.
D) show a constant Doppler shift in its spectral lines.
E) show two stars with variable proper motion.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 105 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
The most common stars are
A) supergiants.
B) giants.
C) upper (more luminous) main sequence stars.
D) white dwarfs.
E) lower (less luminous) main sequence stars.
A) supergiants.
B) giants.
C) upper (more luminous) main sequence stars.
D) white dwarfs.
E) lower (less luminous) main sequence stars.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 105 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
To determine the orbital period of a visual binary, we must measure
A) brightness.
B) position on the sky.
C) wavelengths.
D) luminosity.
E) temperature.
A) brightness.
B) position on the sky.
C) wavelengths.
D) luminosity.
E) temperature.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 105 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
Absolute visual magnitude is
A) the apparent magnitude of a star observed from Earth.
B) the luminosity of a star observed from a distance of 1000 pc.
C) the apparent magnitude of a star observed from a distance of 10 pc.
D) the luminosity of a star observed from Earth.
E) c and d
A) the apparent magnitude of a star observed from Earth.
B) the luminosity of a star observed from a distance of 1000 pc.
C) the apparent magnitude of a star observed from a distance of 10 pc.
D) the luminosity of a star observed from Earth.
E) c and d

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 105 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
In an H-R Diagram, stars with the smallest radius are found in the ____ of the diagram.
A) center
B) upper left corner
C) upper right corner
D) lower left corner
E) lower right corner
A) center
B) upper left corner
C) upper right corner
D) lower left corner
E) lower right corner

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 105 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
The star named Circini has the spectral type and luminosity class of O 8.5 V. Based on this information, which of the following are true?
I. Circini has a surface temperature less than the sun.
II. Circini has a diameter that is greater than that of the sun.
III. Circini is more luminous than the sun.
IV. Circini is located near the upper left hand corner in the HR diagram.
A) I II
B) II IV
C) II, III, IV
D) I, II, III
E) I, II, III, IV
I. Circini has a surface temperature less than the sun.
II. Circini has a diameter that is greater than that of the sun.
III. Circini is more luminous than the sun.
IV. Circini is located near the upper left hand corner in the HR diagram.
A) I II
B) II IV
C) II, III, IV
D) I, II, III
E) I, II, III, IV

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 105 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
Use the HR diagram below to answer the following question(s). 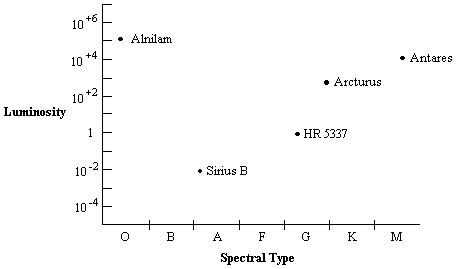 Which star in the diagram is most like the sun?
Which star in the diagram is most like the sun?
A) Alnilam
B) Antares
C) Arcturus
D) HR 5337
E) Sirius B
 Which star in the diagram is most like the sun?
Which star in the diagram is most like the sun?A) Alnilam
B) Antares
C) Arcturus
D) HR 5337
E) Sirius B

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 105 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
A star s luminosity depends only on the star s
A) distance and diameter.
B) temperature and distance.
C) distance.
D) temperature and diameter.
E) apparent magnitude.
A) distance and diameter.
B) temperature and distance.
C) distance.
D) temperature and diameter.
E) apparent magnitude.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 105 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
The hydrogen lines in spectral type A stars
A) are most narrow for supergiants.
B) are most narrow for main sequence stars.
C) can not be used to estimate the luminosity of the star.
D) are very weak and difficult to see.
E) are useful in determining the apparent magnitude of the star.
A) are most narrow for supergiants.
B) are most narrow for main sequence stars.
C) can not be used to estimate the luminosity of the star.
D) are very weak and difficult to see.
E) are useful in determining the apparent magnitude of the star.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 105 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
If a star with an absolute magnitude of - 5 has an apparent magnitude of +5, then its distance is
A) 1 pc.
B) 10 pc.
C) 100 pc.
D) 1000 pc.
E) 10,000 pc.
A) 1 pc.
B) 10 pc.
C) 100 pc.
D) 1000 pc.
E) 10,000 pc.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 105 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
Which of the following kinds of stars is most dense?
A) a supergiant star
B) a main sequence star
C) a giant star
D) a white dwarf
E) the sun
A) a supergiant star
B) a main sequence star
C) a giant star
D) a white dwarf
E) the sun

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 105 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
In the light curve below, what is the period of the eclipsing binary? 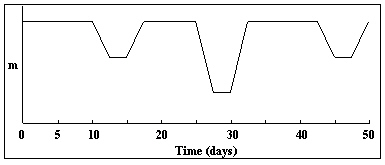
A) 5 days
B) 32.5 days
C) 7.5 days
D) 42.5 days
E) 50 days

A) 5 days
B) 32.5 days
C) 7.5 days
D) 42.5 days
E) 50 days

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 105 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
Use the chart below to answer the following question(s). 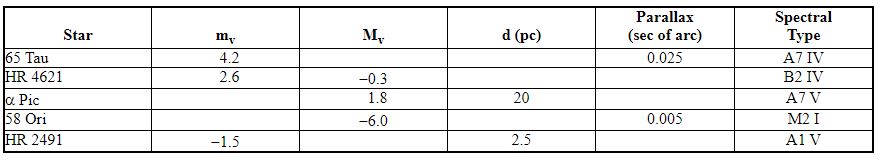
From the data given, which star in the table has the greatest diameter?
A) 65 Tau
B) HR 4621
C) a Pic
D) 58 Ori
E) HR 2491

From the data given, which star in the table has the greatest diameter?
A) 65 Tau
B) HR 4621
C) a Pic
D) 58 Ori
E) HR 2491

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 105 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
If we can solve the orbital motion of an eclipsing binary, we can find
A) the mass of each star.
B) the diameter of each star.
C) the distance to the binary.
D) all of the above
E) both a and b
A) the mass of each star.
B) the diameter of each star.
C) the distance to the binary.
D) all of the above
E) both a and b

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 105 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
At what point in the light curve below is the cooler star in front of the hotter star? 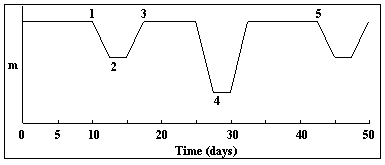
A) 1
B) 2
C) 3
D) 4
E) 5

A) 1
B) 2
C) 3
D) 4
E) 5

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 105 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
The star Algol is
A) an astrometric binary.
B) a spectroscopic binary.
C) a visual binary.
D) an eclipsing binary.
E) both b and d
A) an astrometric binary.
B) a spectroscopic binary.
C) a visual binary.
D) an eclipsing binary.
E) both b and d

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 105 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
Use the chart below to answer the following question(s). 
From the data given, which star in the table has the greatest surface temperature?
A) 65 Tau
B) HR 4621
C) a Pic
D) 58 Ori
E) HR 2491

From the data given, which star in the table has the greatest surface temperature?
A) 65 Tau
B) HR 4621
C) a Pic
D) 58 Ori
E) HR 2491

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 105 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
Use the chart below to answer the following question(s). 
From the data given, which star in the table has the greatest luminosity?
A) 65 Tau
B) HR 4621
C) a Pic
D) 58 Ori
E) HR 2491

From the data given, which star in the table has the greatest luminosity?
A) 65 Tau
B) HR 4621
C) a Pic
D) 58 Ori
E) HR 2491

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 105 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
Stars on the main sequence with the greatest mass
A) are spectral type M stars.
B) are spectral type O stars.
C) are located at the bottom of the main sequence in the HR diagram.
D) have masses very similar to the sun.
E) both b and c
A) are spectral type M stars.
B) are spectral type O stars.
C) are located at the bottom of the main sequence in the HR diagram.
D) have masses very similar to the sun.
E) both b and c

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 105 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
Use the chart below to answer the following question(s). 
From the data given,which star in the table is the closest to Earth?
A) 65 Tau
B) HR 4621
C) a Pic
D) 58 Ori
E) HR 2491

From the data given,which star in the table is the closest to Earth?
A) 65 Tau
B) HR 4621
C) a Pic
D) 58 Ori
E) HR 2491

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 105 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
The diagram below shows the radial velocity curve of a double-line spectroscopic binary. Based on this radial velocity curve, which of the following statements is correct? 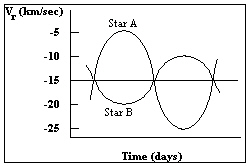
A) Star A is twice the mass of star B.
B) Star B is twice the mass of star A.
C) Star A is ten times the mass of star B.
D) Star B is ten times the mass of star A.
E) Star A and Star B have the same mass.

A) Star A is twice the mass of star B.
B) Star B is twice the mass of star A.
C) Star A is ten times the mass of star B.
D) Star B is ten times the mass of star A.
E) Star A and Star B have the same mass.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 105 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
The diagram below illustrates two stars in a visual binary system and the center of mass of this system. Based on this diagram, what is the ratio of the mass of star A to the mass of star B? 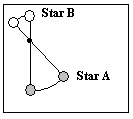
A) 2 to 1
B) 1 to 2
C) 2 to 3
D) 3 to 2
E) 1 to 3

A) 2 to 1
B) 1 to 2
C) 2 to 3
D) 3 to 2
E) 1 to 3

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 105 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
The total mass of a binary system can be calculated from
A) the ratio of the angular separation from the center of mass of each of the stars.
B) the distance to the binary and its radial velocity.
C) the semi major axis and period of the orbit.
D) the radial velocities of the two stars.
E) the time required for the small star to eclipse the larger star.
A) the ratio of the angular separation from the center of mass of each of the stars.
B) the distance to the binary and its radial velocity.
C) the semi major axis and period of the orbit.
D) the radial velocities of the two stars.
E) the time required for the small star to eclipse the larger star.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 105 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
What is the total mass of a binary star system with P = 20 yr and a = 10 AU?
A) 2 solar masses
B) 2.5 solar masses
C) 0.5 solar mass
D) 80 solar masses
E) 0.4 solar mass
A) 2 solar masses
B) 2.5 solar masses
C) 0.5 solar mass
D) 80 solar masses
E) 0.4 solar mass

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 105 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
Which of the following kinds of stars best obey the mass-luminosity relation?
A) main sequence stars
B) giant stars
C) supergiant stars
D) white dwarfs
E) all of the above
A) main sequence stars
B) giant stars
C) supergiant stars
D) white dwarfs
E) all of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 105 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
Use the chart below to answer the following question(s). 
From the data given, which star in the table would appear the faintest in the night sky?
A) 65 Tau
B) HR 4621
C) a Pic
D) 58 Ori
E) HR 2491

From the data given, which star in the table would appear the faintest in the night sky?
A) 65 Tau
B) HR 4621
C) a Pic
D) 58 Ori
E) HR 2491

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 105 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
A spectroscopic binary shows periodic variations in its
A) radial velocity.
B) proper motion.
C) brightness.
D) mass.
E) spectral type.
A) radial velocity.
B) proper motion.
C) brightness.
D) mass.
E) spectral type.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 105 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
If a star has a parallax of 0.02 seconds of arc, then its distance is
A) 20 pc
B) 50 pc
C) 2 pc
D) 5 pc
E) 500 pc
A) 20 pc
B) 50 pc
C) 2 pc
D) 5 pc
E) 500 pc

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 105 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
An eclipsing binary has been analyzed and it has been determined that the ratio of the mass of star A to the mass of star B is 6 and the total mass of the two stars is 26 solar masses. What are the masses of star A and star B?
A) Star A has a mass of 1 solar mass and star B has a mass of 6 solar masses.
B) Star A has a mass of 20 solar mass and star B has a mass of 6 solar masses.
C) Star A has a mass of 31.2 solar mass and star B has a mass of 5.2 solar masses.
D) Star A has a mass of 22.3 solar mass and star B has a mass of 3.7 solar masses.
E) The masses of star A and star B cannot be determined from the information given.
A) Star A has a mass of 1 solar mass and star B has a mass of 6 solar masses.
B) Star A has a mass of 20 solar mass and star B has a mass of 6 solar masses.
C) Star A has a mass of 31.2 solar mass and star B has a mass of 5.2 solar masses.
D) Star A has a mass of 22.3 solar mass and star B has a mass of 3.7 solar masses.
E) The masses of star A and star B cannot be determined from the information given.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 105 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
Use the chart below to answer the following question(s). 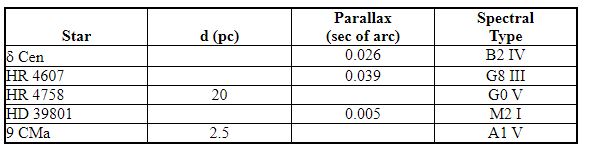
Which star in the table has the greatest diameter?
A) d Cen
B) HR 4607
C) HR 4758
D) HD 39801
E) 9 CMa

Which star in the table has the greatest diameter?
A) d Cen
B) HR 4607
C) HR 4758
D) HD 39801
E) 9 CMa

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 105 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
The most accurate way to determine the surface temperature of a star is to study
A) the pattern of absorption lines from various atoms.
B) the relative intensities of light measured through different photometric filters.
C) the peak wavelength of the star s continuum blackbody spectrum.
D) pattern of emission lines that are on the star s spectrum.
A) the pattern of absorption lines from various atoms.
B) the relative intensities of light measured through different photometric filters.
C) the peak wavelength of the star s continuum blackbody spectrum.
D) pattern of emission lines that are on the star s spectrum.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 105 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
Stars in the upper right part of the Hertzsprung-Russell diagram are always ____ when compared to stars near the middle of the diagram.
A) cooler
B) brighter as seen from Earth
C) larger
D) smaller
E) more massive
A) cooler
B) brighter as seen from Earth
C) larger
D) smaller
E) more massive

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 105 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
Use the chart below to answer the following question(s). 
Which star in the table is the closest to Earth?
A) d Cen
B) HR 4607
C) HR 4758
D) HD 39801
E) 9 CMa

Which star in the table is the closest to Earth?
A) d Cen
B) HR 4607
C) HR 4758
D) HD 39801
E) 9 CMa

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 105 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
Use the chart below to answer the following question(s). 
Which star in the table has the greatest surface temperature?
A) d Cen
B) HR 4607
C) HR 4758
D) HD 39801
E) 9 CMa

Which star in the table has the greatest surface temperature?
A) d Cen
B) HR 4607
C) HR 4758
D) HD 39801
E) 9 CMa

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 105 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
____________________ can be used to determine the distance to a star when the spectrum of the star can be used to determine its spectral type and luminosity class.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 105 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
From the mass-luminosity relation, a 2 solar mass star on the main sequence would have a luminosity of approximately ____ solar luminosities.
A) 2
B) 4
C) 11
D) 0.5
E) 0.25
A) 2
B) 4
C) 11
D) 0.5
E) 0.25

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 105 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
If the orbital velocity of an eclipsing binary is 97 km/sec and the smaller star is completely eclipsed in 2 hours, what is the diameter of the smaller star?
A) 175,000 km
B) 350,000 km
C) 194 km
D) 700,000 km
E) 4656 km
A) 175,000 km
B) 350,000 km
C) 194 km
D) 700,000 km
E) 4656 km

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 105 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
We can determine the surface temperature of a star from
A) studying its continuous spectrum.
B) studying its line absorption spectrum.
C) measuring the star s luminosity.
D) Both a and c
E) All of a, b, and c
A) studying its continuous spectrum.
B) studying its line absorption spectrum.
C) measuring the star s luminosity.
D) Both a and c
E) All of a, b, and c

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 105 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
How do humans use their eyes to measure relative distance by parallax?
A) By continuously focusing our eyes on distant objects we can determine distance.
B) Since our eyes are separated the brain interprets the relative look angles of these eyes in terms of distance to the object viewed.
C) Our eyes can measure the time it takes light to travel from an object and from this we get distance.
D) By moving our heads from side to side our brain compares look angles from each of these positions to obtain the distance to the object viewed.
A) By continuously focusing our eyes on distant objects we can determine distance.
B) Since our eyes are separated the brain interprets the relative look angles of these eyes in terms of distance to the object viewed.
C) Our eyes can measure the time it takes light to travel from an object and from this we get distance.
D) By moving our heads from side to side our brain compares look angles from each of these positions to obtain the distance to the object viewed.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 105 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
On the HR diagram below, indicate the location of the white dwarf stars. 


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 105 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
A G2 I star is ____________________ in diameter and ____________________ luminous than the sun.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 105 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
The two most abundant elements in the sun are
A) nitrogen and oxygen.
B) hydrogen and helium.
C) sulfur and iron.
D) carbon and hydrogen.
E) carbon and nitrogen.
A) nitrogen and oxygen.
B) hydrogen and helium.
C) sulfur and iron.
D) carbon and hydrogen.
E) carbon and nitrogen.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 105 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
How can we tell that some stars are relatively close to us in the sky?
A) Some stars are occasionally eclipsed by the Moon, so they must be nearby.
B) Some stars vary in brightness caused by sunspots we can see because they are so close.
C) Some stars appear to be extremely bright and must therefore be very close to us.
D) Some stars appear to move periodically back and forth against the background stars because of the Earth s movement around the Sun.
A) Some stars are occasionally eclipsed by the Moon, so they must be nearby.
B) Some stars vary in brightness caused by sunspots we can see because they are so close.
C) Some stars appear to be extremely bright and must therefore be very close to us.
D) Some stars appear to move periodically back and forth against the background stars because of the Earth s movement around the Sun.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 105 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
The parallax of the star 75 Leo is 0.10 and its apparent visual magnitude is +5.18. The absolute visual magnitude of 75 Leo is ____________________.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 105 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
If you compare two stars,
A) the one with the larger radius will always have the greater luminosity.
B) the one with the higher surface temperature will always have the greater luminosity.
C) the one with the smaller absolute magnitude will always have the greater luminosity.
D) the one with the larger surface area has the greater energy flux from its surface.
A) the one with the larger radius will always have the greater luminosity.
B) the one with the higher surface temperature will always have the greater luminosity.
C) the one with the smaller absolute magnitude will always have the greater luminosity.
D) the one with the larger surface area has the greater energy flux from its surface.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 105 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
How is a luminosity class assigned to a star?
A) By combining the apparent magnitude with the star s parallax.
B) By measuring the period of variability in the star s apparent magnitude.
C) By studying the absorption line width in the spectrum of the star.
D) By observing the angular size of the star s image in a photograph or digital image.
A) By combining the apparent magnitude with the star s parallax.
B) By measuring the period of variability in the star s apparent magnitude.
C) By studying the absorption line width in the spectrum of the star.
D) By observing the angular size of the star s image in a photograph or digital image.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 105 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
Which stars always have large positive absolute magnitude?
A) Stars of high luminosity.
B) Stars of low luminosity.
C) Nearby stars.
D) Distant stars.
E) Not enough information given.
A) Stars of high luminosity.
B) Stars of low luminosity.
C) Nearby stars.
D) Distant stars.
E) Not enough information given.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 105 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
Luminosity class IV objects are known as ____________________.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 105 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
If two stars are emitting the same amount of light, the star that is farther will appear
A) brighter.
B) dimmer.
C) redder.
D) bluer.
E) They will have the same brightness as seen from Earth.
A) brighter.
B) dimmer.
C) redder.
D) bluer.
E) They will have the same brightness as seen from Earth.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 105 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
For stars on the main sequence, the luminosity can be estimated by the formula L = ____________________.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 105 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
To observe a visual binary, we must measure radial velocities.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 105 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
To observe a spectroscopic binary, we must be able to see both stars individually.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 105 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
Below is a radial velocity curve for a spectroscopic binary. Which of the stars is most massive? ____________________ 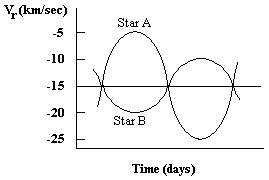


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 105 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
Giant stars are members of luminosity class III.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 105 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
The absolute magnitude of a star is the apparent magnitude it would have if it were 10 pc from Earth.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 105 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
Absorption lines in the spectra of supergiant stars are broader than the same spectral lines in main sequence stars of the same spectral type.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 105 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
If we divide the mass of a star by its volume we calculate the star s ____________________.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 105 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
If a star is twice as hot as the sun and only half the sun s diameter, it will be less luminous than the sun.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 105 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
Most stars on the H-R diagram are on the ____________________.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 105 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
The most common kinds of stars are low-luminosity stars.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 105 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72
If a binary system has a period of 4 years and a separation of 5 AU, then the total mass is 7.8 solar masses.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 105 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73
The largest of the red stars are the ____________________ stars.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 105 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
74
White dwarfs have such a low luminosity that even the nearest white dwarfs are not visible to the naked eye.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 105 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
75
Supergiants are about as common as the sun.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 105 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
76
A star whose parallax is 0.01 seconds arc is at a distance of 1000 pc.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 105 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
77
The location of a star in the HR diagram indicates its temperature and intrinsic brightness.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 105 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
78
The more massive star in a binary system is always farthest from the center of mass.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 105 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
79
The method of spectroscopic parallax cannot be applied to stars beyond about 100 pc.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 105 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
80
The masses and diameters of each star in the binary can be determined from ____________________ binaries.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 105 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



