Deck 2: The Pursuit of a Healthy Diet
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Match between columns
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/93
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 2: The Pursuit of a Healthy Diet
1
A diet that does not overemphasize any food type or nutrient at the expense of another is following which characteristic of a healthy diet?
A) Adequacy
B) Balance
C) Calorie control
D) Moderation
A) Adequacy
B) Balance
C) Calorie control
D) Moderation
B
2
Dietary Reference Intakes (DRI) should not be used to:
A) estimate nutrient requirements for healthy people.
B) assess dietary nutrient adequacy.
C) plan diets.
D) treat persons with diet-related illnesses.
A) estimate nutrient requirements for healthy people.
B) assess dietary nutrient adequacy.
C) plan diets.
D) treat persons with diet-related illnesses.
D
3
The Acceptable Macronutrient Distribution Ranges (AMDR) set recommendations for which of the following nutrients?
A) Vitamin E, calcium, lipids
B) Fat, carbohydrates, protein
C) Phytochemicals, lipids, fiber
D) Fiber, iron, zinc
A) Vitamin E, calcium, lipids
B) Fat, carbohydrates, protein
C) Phytochemicals, lipids, fiber
D) Fiber, iron, zinc
B
4
Foods with a high nutrient density:
A) are iron rich.
B) contain a mixture of carbohydrate, fat, and protein.
C) carry the USDA nutrition labeling.
D) are rich in nutrients but relatively low in calories.
A) are iron rich.
B) contain a mixture of carbohydrate, fat, and protein.
C) carry the USDA nutrition labeling.
D) are rich in nutrients but relatively low in calories.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
Which of the following statements about the DRI is not correct?
A) They are for healthy people only.
B) They are nutrient requirements that people should meet every day.
C) Separate recommendations are made for different groups of people.
D) They were established by the National Academy of Sciences.
A) They are for healthy people only.
B) They are nutrient requirements that people should meet every day.
C) Separate recommendations are made for different groups of people.
D) They were established by the National Academy of Sciences.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
Which of these snacks would you take to the library if you knew you would be studying for several hours?
A) Fruit rolls
B) Fruit drink
C) Half a peanut butter sandwich
D) Candy bar
A) Fruit rolls
B) Fruit drink
C) Half a peanut butter sandwich
D) Candy bar

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
The concept of nutrient density is most helpful in achieving which principle of diet planning?
A) Variety
B) Moderation
C) Balance
D) Adequacy
E) Calorie control
A) Variety
B) Moderation
C) Balance
D) Adequacy
E) Calorie control

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
Louise would like to lose some weight. How might the exchange lists be helpful to her?
A) Louise can easily compare several brands of a particular food to find the most nutrient-dense version.
B) Louise can identify low-calorie foods rich in each of the essential vitamins and minerals.
C) Louise can mix and match the portion sizes for different foods that provide the same number of calories to plan calorie-controlled meals.
D) Louise can determine which foods will prevent her from developing diabetes if she consumes them on a regular basis as she loses weight.
A) Louise can easily compare several brands of a particular food to find the most nutrient-dense version.
B) Louise can identify low-calorie foods rich in each of the essential vitamins and minerals.
C) Louise can mix and match the portion sizes for different foods that provide the same number of calories to plan calorie-controlled meals.
D) Louise can determine which foods will prevent her from developing diabetes if she consumes them on a regular basis as she loses weight.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
The RDA (Recommended Dietary Allowances) for nutrients are generally:
A) the minimum amounts that average people need.
B) more than twice as high as anyone needs.
C) designed to prevent deficiency diseases in half the population.
D) designed to be adequate for almost all healthy people.
E) the same for all ages for all nutrients.
A) the minimum amounts that average people need.
B) more than twice as high as anyone needs.
C) designed to prevent deficiency diseases in half the population.
D) designed to be adequate for almost all healthy people.
E) the same for all ages for all nutrients.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
The "ABCMV" diet-planning principles are:
A) abundance, balance, conservative, moderation, and variety.
B) adequacy, bone development, correction, moderation, and variety.
C) adequacy, balance, calorie control, moderation, and variety.
D) abundance, better, choices, multiple, and variety.
A) abundance, balance, conservative, moderation, and variety.
B) adequacy, bone development, correction, moderation, and variety.
C) adequacy, balance, calorie control, moderation, and variety.
D) abundance, better, choices, multiple, and variety.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
The FDA has approved health claims on food labels for all of the following conditions except : _____.
A) osteoporosis
B) heart disease
C) tooth decay
D) arthritis
E) all of the above are approved health claims
A) osteoporosis
B) heart disease
C) tooth decay
D) arthritis
E) all of the above are approved health claims

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
For which nutrient is the current U.S. diet closest to meeting the 2010 Dietary Guidelines for Americans intake recommendation?
A) Vitamin D
B) Potassium
C) Calcium
D) Sodium
A) Vitamin D
B) Potassium
C) Calcium
D) Sodium

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
The DVs:
A) are nutrient levels set by the FDA.
B) are used in food labeling.
C) serve as a guide for planning diets of individuals or groups.
D) a and b
E) b and c
A) are nutrient levels set by the FDA.
B) are used in food labeling.
C) serve as a guide for planning diets of individuals or groups.
D) a and b
E) b and c

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
Peaches are a food source of vitamins A and C. Why would a raw peach be considered a more nutrient-dense snack than a serving of peaches canned in light syrup?
A) The canned peaches are more processed than the raw peach.
B) The raw peach is brighter in color than the canned peaches.
C) The raw peach contains more vitamins per calorie than the canned peaches.
D) The canned peaches contain more vitamins per calorie than the raw peach.
A) The canned peaches are more processed than the raw peach.
B) The raw peach is brighter in color than the canned peaches.
C) The raw peach contains more vitamins per calorie than the canned peaches.
D) The canned peaches contain more vitamins per calorie than the raw peach.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
The Nutrition Facts panel of the food label must provide information about all of the items listed below except :
A) monounsaturated fat.
B) vitamin A.
C) total fat.
D) fiber.
E) sodium.
A) monounsaturated fat.
B) vitamin A.
C) total fat.
D) fiber.
E) sodium.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
Steven is 9 years old and loves to drink orange juice whenever he can. He often drinks orange juice instead of eating food. Which characteristic of healthy eating is this not in agreement with?
A) Balance
B) Calorie control
C) Moderation
D) Adequacy
A) Balance
B) Calorie control
C) Moderation
D) Adequacy

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
Valerie is eating lunch at the college cafeteria and is determined not to gain weight during her freshman year at college. She realizes that controlling portion size is the key to not over indulging. Which of the following visual references would equal 1 cup of pasta?
A) Four thumbs together
B) Palm of one hand
C) Three clenched fists
D) Two hands, cupped
A) Four thumbs together
B) Palm of one hand
C) Three clenched fists
D) Two hands, cupped

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
Mark is a 5-year-old boy who loves milk. He drinks skim milk all day long. He also loves yogurt and cheese. What type of deficiency is Mark at risk for?
A) Iron
B) Zinc
C) Calcium
D) Vitamin D
A) Iron
B) Zinc
C) Calcium
D) Vitamin D

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
The RDA for a nutrient is set at which point?
A) A point high enough to cover most healthy people
B) A minimum value you are supposed to exceed
C) An average value
D) An upper limit to prevent overdoses
A) A point high enough to cover most healthy people
B) A minimum value you are supposed to exceed
C) An average value
D) An upper limit to prevent overdoses

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
The 2010 Dietary Guidelines for Americans make all of the following suggestions except :
A) eat a variety of vegetables, especially dark-green and red and orange vegetables.
B) use oils to replace solid fats where possible.
C) consume at least half of all grains as whole grains.
D) choose diets that emphasize refined and enriched grain products.
E) increase intake of fat-free or low-fat milk and milk products.
A) eat a variety of vegetables, especially dark-green and red and orange vegetables.
B) use oils to replace solid fats where possible.
C) consume at least half of all grains as whole grains.
D) choose diets that emphasize refined and enriched grain products.
E) increase intake of fat-free or low-fat milk and milk products.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
If you consistently build your diet by choosing mostly nutrient-dense foods that are low in solid fat and added sugars, you may be able to meet your nutrient needs without using your full calorie allowance. In this case, the balance of calories is called your:
A) bonus calorie allowance.
B) daily limit for empty calories.
C) extra calorie allowance.
D) fat and sugar calorie allowance.
A) bonus calorie allowance.
B) daily limit for empty calories.
C) extra calorie allowance.
D) fat and sugar calorie allowance.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
All of the following are equivalent to 1 ounce from the protein foods group except :
A) 1 egg.
B) 1/4 cup cooked dry beans.
C) 3 tbsp peanut butter.
D) 1/2 cup split pea soup.
A) 1 egg.
B) 1/4 cup cooked dry beans.
C) 3 tbsp peanut butter.
D) 1/2 cup split pea soup.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
According to MyPlate, you should avoid fat from
A) fish.
B) nuts.
C) dairy products.
D) vegetable oils.
A) fish.
B) nuts.
C) dairy products.
D) vegetable oils.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
Approximately _____% to _____% of the calories in a balanced diet come from fat.
A) 2, 15
B) 10, 35
C) 20, 35
D) 50, 65
A) 2, 15
B) 10, 35
C) 20, 35
D) 50, 65

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
David wants to lower his risk of heart disease and decides to follow the Mediterranean diet. How often should he consume olive oil?
A) Daily
B) A few times a week
C) A few times a month
D) Never
A) Daily
B) A few times a week
C) A few times a month
D) Never

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
Which of the following is not a nutrient-dense food choice?
A) Bologna
B) Water-packed tuna
C) A baked potato
D) Whole grain bread
E) An orange
A) Bologna
B) Water-packed tuna
C) A baked potato
D) Whole grain bread
E) An orange

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
In addition to the five food groups, we need to include a small amount of oil in the diet for the _____ and _____ that oils provide.
A) vitamin K, phytochemicals
B) vitamin E, vitamin C
C) essential fats, vitamin E
D) trans fat, vitamin A
A) vitamin K, phytochemicals
B) vitamin E, vitamin C
C) essential fats, vitamin E
D) trans fat, vitamin A

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
Which of the following is used to describe the maximum daily amount of a nutrient that is unlikely to pose risk of adverse effects?
A) DRI
B) AI
C) DV
D) UL
A) DRI
B) AI
C) DV
D) UL

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
Holly wants to lower her risk of heart disease and decides to follow the Mediterranean diet. How often may she eat red meat?
A) Daily
B) A few times a week
C) A few times per month
D) Never
A) Daily
B) A few times a week
C) A few times per month
D) Never

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
All of the following are major goals from the Dietary Guidelines for Americans 2010 except :
A) reduce health disparities.
B) consume more nutrient-dense foods.
C) balance calories with physical activity to manage weight.
D) consume fewer foods with sodium, saturated fats, trans fats, cholesterol, added sugars, and refined grains.
A) reduce health disparities.
B) consume more nutrient-dense foods.
C) balance calories with physical activity to manage weight.
D) consume fewer foods with sodium, saturated fats, trans fats, cholesterol, added sugars, and refined grains.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
According to the Dietary Reference Intakes (DRI), what percentage of the calories in a balanced diet should come from protein?
A) 2 to 15 percent
B) 10 to 35 percent
C) 35 to 45 percent
D) 45 to 65 percent
A) 2 to 15 percent
B) 10 to 35 percent
C) 35 to 45 percent
D) 45 to 65 percent

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
Joe spends between 30 and 60 minutes a day engaged in moderately intense physical activity, in addition to other daily activities. What activity level would he belong to?
A) Sedentary
B) Moderately active
C) Active
D) Very active
A) Sedentary
B) Moderately active
C) Active
D) Very active

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
Which foods make up the majority of the Mediterranean diet?
A) Eggs, poultry, and fish
B) Fruits, beans, legumes, nuts, and vegetables
C) Cheese, yogurt, and fish
D) Red meat, oil, and sweets
A) Eggs, poultry, and fish
B) Fruits, beans, legumes, nuts, and vegetables
C) Cheese, yogurt, and fish
D) Red meat, oil, and sweets

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
Approximately 45 to 65 percent of the total calories in a balanced diet should come from which of the following?
A) Fats
B) Proteins
C) Carbohydrates
D) Phytochemicals
A) Fats
B) Proteins
C) Carbohydrates
D) Phytochemicals

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
Sue picked up a cereal box and read that one serving provides 15 percent of the DV for total carbohydrate. Which of the following statements is true regarding this cereal?
A) One serving contains 15 percent of its calories from carbohydrates.
B) One serving provides 15 percent of the total carbohydrates that are recommended to be eaten in a day.
C) The contents of the cereal box provide 15 percent of the carbohydrates that should be eaten in a day.
D) One serving provides 15 percent of the starch recommendation only for the day.
A) One serving contains 15 percent of its calories from carbohydrates.
B) One serving provides 15 percent of the total carbohydrates that are recommended to be eaten in a day.
C) The contents of the cereal box provide 15 percent of the carbohydrates that should be eaten in a day.
D) One serving provides 15 percent of the starch recommendation only for the day.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
Juan is of Hispanic origin and enjoys eating native foods. What food group would a corn tortilla belong to?
A) Fruit
B) Vegetable
C) Grains
D) Milk, yogurt and cheese
A) Fruit
B) Vegetable
C) Grains
D) Milk, yogurt and cheese

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
The MyPlate website suggests how much moderate aerobic physical activity to reduce the risk of chronic disease, help prevent weight gain, and help sustain weight loss?
A) 1 hour/week
B) 1 hour and 30 minutes/week
C) 2 hours/week
D) 2 hours and 30 minutes/week
A) 1 hour/week
B) 1 hour and 30 minutes/week
C) 2 hours/week
D) 2 hours and 30 minutes/week

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
Which of the following does not have to appear on the Nutrition Facts panel?
A) Calories
B) Calories from fat
C) Vitamin A
D) Vitamin E
A) Calories
B) Calories from fat
C) Vitamin A
D) Vitamin E

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
All of the following are equivalent to 1 ounce of grains except :
A) 1 slice of bread.
B) 1 English muffin.
C) 3 cups popcorn.
D) 1/2 cup cooked pasta.
A) 1 slice of bread.
B) 1 English muffin.
C) 3 cups popcorn.
D) 1/2 cup cooked pasta.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
All of the following foods contain phytochemicals except :
A) skim milk.
B) mushrooms.
C) canned peas.
D) a frozen tofu burger.
A) skim milk.
B) mushrooms.
C) canned peas.
D) a frozen tofu burger.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
Bill is trying to eat healthier now that he is going to college. He takes a nutrition class, does a diet analysis, and finds out that his salt intake is very high. Which characteristic of a healthy diet is Bill violating?
A) Adequacy
B) Balance
C) Moderation
D) Variety
A) Adequacy
B) Balance
C) Moderation
D) Variety

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
Mary is comparing light potato chips to regular potato chips. What is the difference?
A) The light potato chips are lower in calories.
B) The light potato chips are lighter in color.
C) The light potato chips are lighter in texture.
D) The light potato chips are lower in weight.
A) The light potato chips are lower in calories.
B) The light potato chips are lighter in color.
C) The light potato chips are lighter in texture.
D) The light potato chips are lower in weight.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
Joe picks up a package of low-fat hot dogs in the supermarket. He can be confident that this food has:
A) no more than 10 grams of fat per serving.
B) no more than 3 grams of fat per serving.
C) no saturated fat.
D) no cholesterol.
A) no more than 10 grams of fat per serving.
B) no more than 3 grams of fat per serving.
C) no saturated fat.
D) no cholesterol.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
An unhealthful aspect of the traditional Mexican diet is the frequent consumption of:
A) tomatoes, chilis, and onions.
B) flour tortillas, chorizo, and eggs.
C) corn tortillas, amaranth, and rice.
D) pinto beans, jicama, and avocado.
A) tomatoes, chilis, and onions.
B) flour tortillas, chorizo, and eggs.
C) corn tortillas, amaranth, and rice.
D) pinto beans, jicama, and avocado.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
Which style of Chinese cooking is characterized by steaming and stir-frying, and therefore tends to be the lowest in fat?
A) Cantonese
B) Peking
C) Shanghai
D) Szechwan or Hunan
A) Cantonese
B) Peking
C) Shanghai
D) Szechwan or Hunan

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
Which of the following does not equal 1 tsp from the "Oils" group?
A) 1 tbsp low-fat mayonnaise
B) 2 tbsp light salad dressing
C) 1 oz peanuts
D) 1 tbsp soft margarine
A) 1 tbsp low-fat mayonnaise
B) 2 tbsp light salad dressing
C) 1 oz peanuts
D) 1 tbsp soft margarine

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
All of the following are forms of added sugar except :
A) molasses.
B) high-fructose corn syrup.
C) levulose.
D) niacinamide.
A) molasses.
B) high-fructose corn syrup.
C) levulose.
D) niacinamide.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
The % Daily Values for vitamins and minerals on labels represent the _____ of all the DRI values.
A) lowest
B) average
C) highest
D) It is different for different nutrients.
A) lowest
B) average
C) highest
D) It is different for different nutrients.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
Which are the only vitamins that must appear on a food label?
A) Vitamins D and E
B) Folate and niacin
C) Riboflavin and vitamin C
D) Vitamins C and A
A) Vitamins D and E
B) Folate and niacin
C) Riboflavin and vitamin C
D) Vitamins C and A

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
If a cup of skim milk has 8 grams of protein and the Daily Value for protein is 50 grams, what percentage of the DV is this?
A) 6%
B) 8%
C) 16%
D) 625%
A) 6%
B) 8%
C) 16%
D) 625%

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
A food label can make a health claim for soluble fiber. Which disease is this nutrient associated with a lower risk of?
A) Heart disease
B) Cancer
C) Tooth decay
D) High blood pressure
A) Heart disease
B) Cancer
C) Tooth decay
D) High blood pressure

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
Plain, low-fat yogurt with fresh blueberries:
A) is a good snack choice because it provides a mixture of energy nutrients.
B) is a poor snack choice because it combines two food groups.
C) is a good snack choice because it is low in carbohydrate and high in protein.
D) is a poor snack choice because it contains fat.
A) is a good snack choice because it provides a mixture of energy nutrients.
B) is a poor snack choice because it combines two food groups.
C) is a good snack choice because it is low in carbohydrate and high in protein.
D) is a poor snack choice because it contains fat.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
Which of the following foods provides empty calories?
A) Roasted skinless turkey breast
B) Whole-wheat bread
C) Frozen peaches
D) Reduced-fat milk
A) Roasted skinless turkey breast
B) Whole-wheat bread
C) Frozen peaches
D) Reduced-fat milk

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
Tulley is a 38-year-old man who successfully lost 50 lb. of excess weight. According to MyPlate recommendations, how much physical activity does he need to maintain his weight loss when he doesn't exceed his calorie needs?
A) At least 90 minutes of moderate activity per week
B) At least 30-60 minutes vigorous activity per week
C) At least 150 minutes of moderate activity per week
D) At least 180 minutes of vigorous activity per week
A) At least 90 minutes of moderate activity per week
B) At least 30-60 minutes vigorous activity per week
C) At least 150 minutes of moderate activity per week
D) At least 180 minutes of vigorous activity per week

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
Zach eats a 2000-calorie diet and therefore should eat no more than 65 grams of fat per day. While at the mall he had a soft pretzel (6 grams of fat) and a mocha coffee drink (20 grams of fat). How many more grams of fat can Zach have to stay within his fat "budget"?
A) 26
B) 39
C) 91
D) There is not enough information provided.
A) 26
B) 39
C) 91
D) There is not enough information provided.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
Nicole is reading a food label on a bag of broccoli and sees that it says it is "high in vitamin C." What exactly does this mean?
A) A serving provides 20% or more of the Daily Value for vitamin C.
B) The bag contains 20% or more of the Daily Value for vitamin C.
C) A serving contains more vitamin C than is normally found in broccoli.
D) A serving provides 50% of the Daily Value for vitamin C.
A) A serving provides 20% or more of the Daily Value for vitamin C.
B) The bag contains 20% or more of the Daily Value for vitamin C.
C) A serving contains more vitamin C than is normally found in broccoli.
D) A serving provides 50% of the Daily Value for vitamin C.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
In the typical Mexican diet, which of the following would provide the most phytochemicals?
A) Salsa
B) Tortilla shells
C) Chorizo
D) Vegetable oil
A) Salsa
B) Tortilla shells
C) Chorizo
D) Vegetable oil

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
A food label can make a health claim for sugar alcohols. Which disease is this nutrient associated with a lower risk of?
A) Heart disease
B) Cancer
C) Tooth decay
D) Liver disease
A) Heart disease
B) Cancer
C) Tooth decay
D) Liver disease

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
Which statement below is true?
A) Indian cuisines are noted for their very mild, almost bland flavors.
B) Women in India typically eat more meat than men do.
C) Fish is avoided by people in India, even those residing in coastal areas.
D) Vegetarianism has been practiced in India for thousands of years.
A) Indian cuisines are noted for their very mild, almost bland flavors.
B) Women in India typically eat more meat than men do.
C) Fish is avoided by people in India, even those residing in coastal areas.
D) Vegetarianism has been practiced in India for thousands of years.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
Vignette #1 Carly is an overweight 21 year old who is committed to good health after taking a nutrition course. She realizes that being a savvy shopper is part of the process and decides to learn how to look more critically at food labels. She picks up two different boxes of ready-to-eat breakfast cereal and sees the food labels shown in Figure 1. Help Carly evaluate these 2 breakfast cereals. 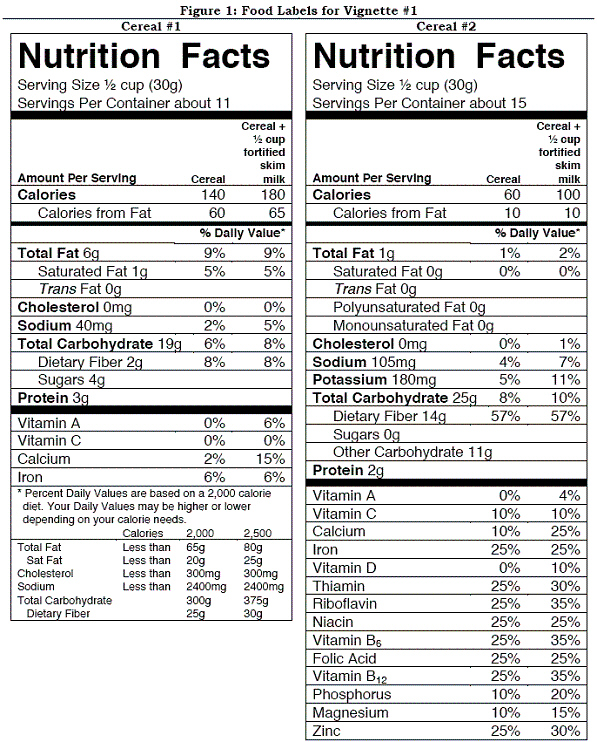 Which cereal would provide the fewest calories per serving?
Which cereal would provide the fewest calories per serving?
A) Cereal #1
B) Cereal #2
C) Both cereals have the same calories per serving.
D) It is impossible to determine from the information provided.
 Which cereal would provide the fewest calories per serving?
Which cereal would provide the fewest calories per serving?A) Cereal #1
B) Cereal #2
C) Both cereals have the same calories per serving.
D) It is impossible to determine from the information provided.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
Vignette #2 Julia and David are new parents of a 13-year-old girl, Zoe. They want to make sure they are feeding her the most nutritious diet possible. Julia makes an appointment with a registered dietitian at Zoe's pediatrician's office. The first thing David asks the dietitian is "Please help us figure out what foods to feed Zoe that will help prevent chronic diseases in her future." Julia seems concerned about how to make sure Zoe gets enough essential nutrients. Imagine you are the dietitian. Thinking about the Dietary Guidelines for Americans 2010 and the MyPlate tool, answer the following questions. Which of the following food recommendations would you expect the dietitian to make?
A) Consume 2 cups per day of milk or its equivalent.
B) Consume more refined grains.
C) Eat fresh fruit as snacks.
D) Choose foods with more saturated fat and less monounsaturated fat.
A) Consume 2 cups per day of milk or its equivalent.
B) Consume more refined grains.
C) Eat fresh fruit as snacks.
D) Choose foods with more saturated fat and less monounsaturated fat.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
According to MyPlate, one egg is equivalent to 1 ounce of cooked lean meat.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
Vignette #1 Carly is an overweight 21 year old who is committed to good health after taking a nutrition course. She realizes that being a savvy shopper is part of the process and decides to learn how to look more critically at food labels. She picks up two different boxes of ready-to-eat breakfast cereal and sees the food labels shown in Figure 1. Help Carly evaluate these 2 breakfast cereals. 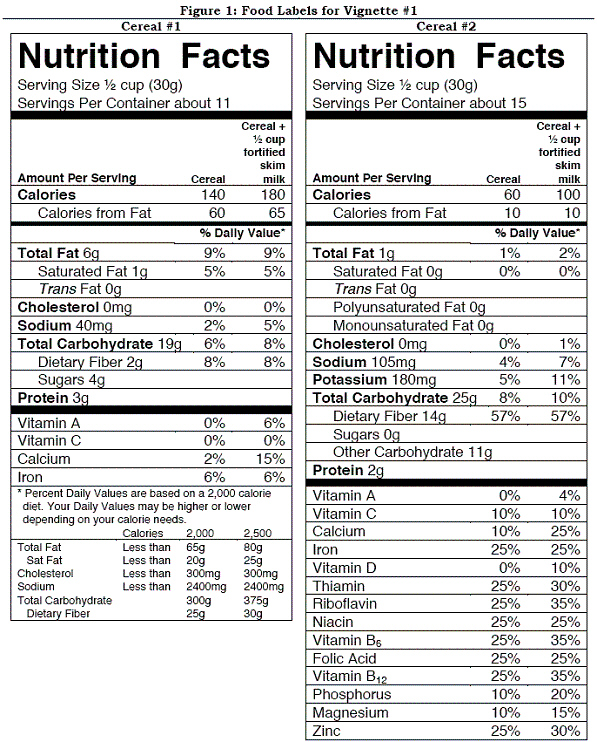 What is the percentage of calories from fat in cereal #1?
What is the percentage of calories from fat in cereal #1?
A) 9%
B) 43%
C) 60%
D) 65%
 What is the percentage of calories from fat in cereal #1?
What is the percentage of calories from fat in cereal #1?A) 9%
B) 43%
C) 60%
D) 65%

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
Vignette #2 Julia and David are new parents of a 13-year-old girl, Zoe. They want to make sure they are feeding her the most nutritious diet possible. Julia makes an appointment with a registered dietitian at Zoe's pediatrician's office. The first thing David asks the dietitian is "Please help us figure out what foods to feed Zoe that will help prevent chronic diseases in her future." Julia seems concerned about how to make sure Zoe gets enough essential nutrients. Imagine you are the dietitian. Thinking about the Dietary Guidelines for Americans 2010 and the MyPlate tool, answer the following questions. You show Julia and David the MyPlate graphic. What important principle can you best demonstrate to them using this graphic?
A) Adequacy-include at least 4 different foods on your plate at each meal
B) Proportionality-fill at least half your plate with fruits and vegetables
C) Food safety-avoid mixing dairy foods with other foods on your plate
D) Moderation-limit added sugars and solid fats on your plate
A) Adequacy-include at least 4 different foods on your plate at each meal
B) Proportionality-fill at least half your plate with fruits and vegetables
C) Food safety-avoid mixing dairy foods with other foods on your plate
D) Moderation-limit added sugars and solid fats on your plate

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
Match between columns

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
Phytochemicals do not provide energy or building materials.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
Vignette #2 Julia and David are new parents of a 13-year-old girl, Zoe. They want to make sure they are feeding her the most nutritious diet possible. Julia makes an appointment with a registered dietitian at Zoe's pediatrician's office. The first thing David asks the dietitian is "Please help us figure out what foods to feed Zoe that will help prevent chronic diseases in her future." Julia seems concerned about how to make sure Zoe gets enough essential nutrients. Imagine you are the dietitian. Thinking about the Dietary Guidelines for Americans 2010 and the MyPlate tool, answer the following questions. Julia and David like to have a beer or glass of wine when they get home from work. The beer and wine contribute _____ to their diets.
A) no calories
B) sweets
C) oils
D) empty calories
A) no calories
B) sweets
C) oils
D) empty calories

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
Vignette #2 Julia and David are new parents of a 13-year-old girl, Zoe. They want to make sure they are feeding her the most nutritious diet possible. Julia makes an appointment with a registered dietitian at Zoe's pediatrician's office. The first thing David asks the dietitian is "Please help us figure out what foods to feed Zoe that will help prevent chronic diseases in her future." Julia seems concerned about how to make sure Zoe gets enough essential nutrients. Imagine you are the dietitian. Thinking about the Dietary Guidelines for Americans 2010 and the MyPlate tool, answer the following questions. Which of the following snacks would be the best for Zoe and her parents?
A) Half a bagel with 1 tablespoon of peanut butter
B) One cup cereal with skim or soy milk
C) An apple and low-fat cheddar cheese
D) All these are smart snacks.
A) Half a bagel with 1 tablespoon of peanut butter
B) One cup cereal with skim or soy milk
C) An apple and low-fat cheddar cheese
D) All these are smart snacks.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
A healthy diet should consist of 3 meals a day without any snacking.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
The only vitamins that must appear on a food label are vitamins C and A.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
The EAR for nutrients is set at a point high enough to cover most healthy people.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72
Vignette #1 Carly is an overweight 21 year old who is committed to good health after taking a nutrition course. She realizes that being a savvy shopper is part of the process and decides to learn how to look more critically at food labels. She picks up two different boxes of ready-to-eat breakfast cereal and sees the food labels shown in Figure 1. Help Carly evaluate these 2 breakfast cereals. 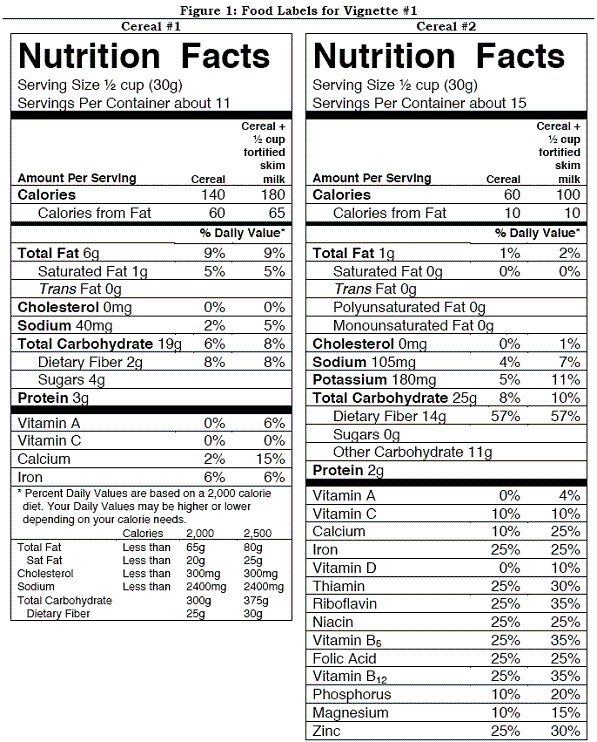 If both cereals cost the same amount, which cereal is a better economic value?
If both cereals cost the same amount, which cereal is a better economic value?
A) Cereal #1
B) Cereal #2
C) Both have the same value.
D) Not enough information is provided.
 If both cereals cost the same amount, which cereal is a better economic value?
If both cereals cost the same amount, which cereal is a better economic value?A) Cereal #1
B) Cereal #2
C) Both have the same value.
D) Not enough information is provided.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73
Vignette #1 Carly is an overweight 21 year old who is committed to good health after taking a nutrition course. She realizes that being a savvy shopper is part of the process and decides to learn how to look more critically at food labels. She picks up two different boxes of ready-to-eat breakfast cereal and sees the food labels shown in Figure 1. Help Carly evaluate these 2 breakfast cereals. 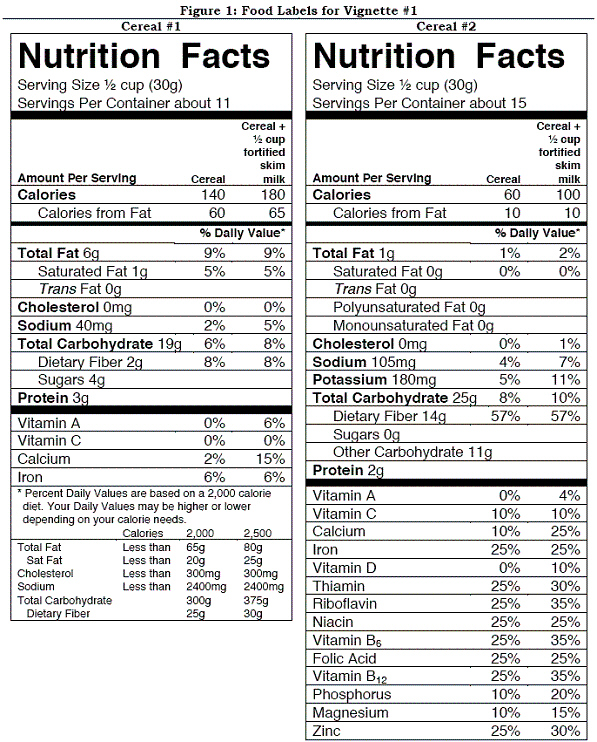 Carly wants to also stay healthy and decides to purchase the cereal that may help prevent heart disease and cancer. Which cereal would she buy and why?
Carly wants to also stay healthy and decides to purchase the cereal that may help prevent heart disease and cancer. Which cereal would she buy and why?
A) Cereal #1 because it contains more protein per serving.
B) Cereal #2 because it has less sugar.
C) Cereal #2 because it contains more fiber.
D) Both cereals would be equally effective because they both contain no cholesterol.
 Carly wants to also stay healthy and decides to purchase the cereal that may help prevent heart disease and cancer. Which cereal would she buy and why?
Carly wants to also stay healthy and decides to purchase the cereal that may help prevent heart disease and cancer. Which cereal would she buy and why?A) Cereal #1 because it contains more protein per serving.
B) Cereal #2 because it has less sugar.
C) Cereal #2 because it contains more fiber.
D) Both cereals would be equally effective because they both contain no cholesterol.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
74
Dry beans are fattening and should only be eaten occasionally.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
75
The Mediterranean Diet recommends eating meat a few times a week.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
76
Vignette #1 Carly is an overweight 21 year old who is committed to good health after taking a nutrition course. She realizes that being a savvy shopper is part of the process and decides to learn how to look more critically at food labels. She picks up two different boxes of ready-to-eat breakfast cereal and sees the food labels shown in Figure 1. Help Carly evaluate these 2 breakfast cereals. 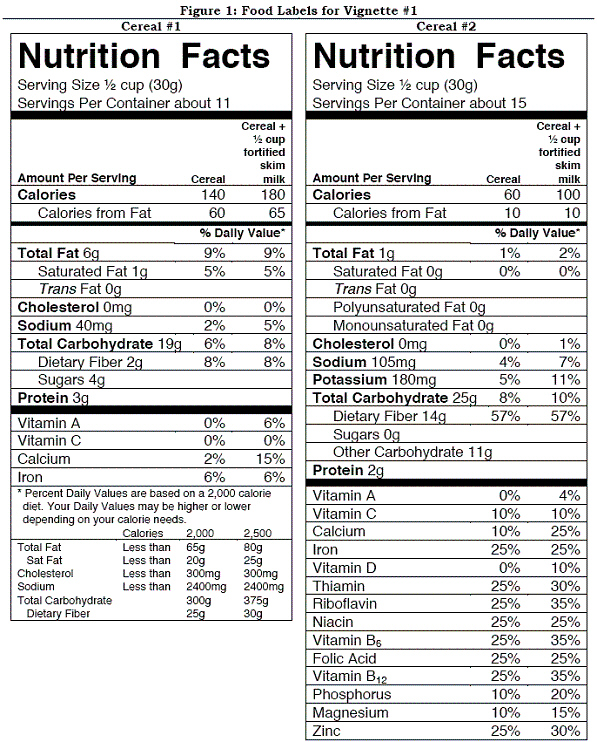 Which of the following statements is incorrect about the two cereals?
Which of the following statements is incorrect about the two cereals?
A) A serving of either cereal provides the same amount of vitamin A.
B) Only cereal #1 can be labeled as being a good source of fiber.
C) Cereal #1 provides less fiber and more protein than cereal #2.
D) Both cereals can be labeled as low in sodium .
 Which of the following statements is incorrect about the two cereals?
Which of the following statements is incorrect about the two cereals?A) A serving of either cereal provides the same amount of vitamin A.
B) Only cereal #1 can be labeled as being a good source of fiber.
C) Cereal #1 provides less fiber and more protein than cereal #2.
D) Both cereals can be labeled as low in sodium .

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
77
Vignette #2 Julia and David are new parents of a 13-year-old girl, Zoe. They want to make sure they are feeding her the most nutritious diet possible. Julia makes an appointment with a registered dietitian at Zoe's pediatrician's office. The first thing David asks the dietitian is "Please help us figure out what foods to feed Zoe that will help prevent chronic diseases in her future." Julia seems concerned about how to make sure Zoe gets enough essential nutrients. Imagine you are the dietitian. Thinking about the Dietary Guidelines for Americans 2010 and the MyPlate tool, answer the following questions. To prevent the risk of chronic disease in adulthood, what would be recommended?
A) Reduce time in sedentary behaviors
B) Increase solid fats and reduce oils
C) Eat a variety of vegetables
D) a and c
A) Reduce time in sedentary behaviors
B) Increase solid fats and reduce oils
C) Eat a variety of vegetables
D) a and c

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
78
The ingredients on a food label are listed in alphabetical order.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
79
The need for setting Tolerable Upper Intake Levels (UL) for nutrients is the result of more people using large doses of supplements and fortified foods.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
80
Chinese food served in American Chinese restaurants usually is very similar to food eaten by rural Chinese people in China.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



