Deck 13: Electrochemistry
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/40
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 13: Electrochemistry
1
Galvanic corrosion may occur only when two different metals are in contact with one another.
True
2
The species undergoing reduction is referred to as the oxidizing agent.
True
3
Copper has a greater tendency to corrode than does zinc.
False
4
Electrolysis involves using an external current to drive an electrochemical reaction in a non-spontaneous direction.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 40 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
All dry cell batteries are rechargeable.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 40 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
In the formation of iron (II) oxide, which species is being reduced?
Fe( s ) + O2( g ) → FeO( s )
A) FeO
B) Fe2O3
C) Fe
D) O2
Fe( s ) + O2( g ) → FeO( s )
A) FeO
B) Fe2O3
C) Fe
D) O2

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 40 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
In the formation of iron (II) oxide, which species is being reduced?
Fe( s ) + O2( g ) → FeO( s )
A) FeO
B) Fe2O3
C) Fe
D) O2
Fe( s ) + O2( g ) → FeO( s )
A) FeO
B) Fe2O3
C) Fe
D) O2

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 40 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
In a redox reaction:
A) there is a transfer of protons from one species to another.
B) electrons are created.
C) electrons are transferred between two species.
D) the reaction always moves in a reverse direction.
A) there is a transfer of protons from one species to another.
B) electrons are created.
C) electrons are transferred between two species.
D) the reaction always moves in a reverse direction.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 40 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
Reduction occurs at the anode of a Galvanic cell.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 40 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
Which phrase best describes the half-reaction as written?
Na+ + e − → Na
A) oxidation 1/2 reaction
B) reduction 1/2 reaction
C) group 2 ionization
D) two electron transfer
Na+ + e − → Na
A) oxidation 1/2 reaction
B) reduction 1/2 reaction
C) group 2 ionization
D) two electron transfer

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 40 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
The standard hydrogen electrode (SHE) involves gaseous HCl at 1 atm being bubbled into water.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 40 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
The Nernst equation describes the pH required to convert electrolytic reactions into spontaneous Galvanic cells.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 40 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
The kinetics of uniform corrosion will speed up considerably in the presence of good electrical conducting salts such as NaCl

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 40 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
A Galvanic cell is an electrochemical cell in which a spontaneous chemical reaction may be used to generate an electrical current.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 40 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
In the decomposition of hydrogen peroxide, which atom is being reduced?
H2O2( aq ) → H2( g ) + O2( g )
A) H
B) O
C) both
D) neither
H2O2( aq ) → H2( g ) + O2( g )
A) H
B) O
C) both
D) neither

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 40 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
Secondary cells are designed to be rechargeable.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 40 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
Electrolysis can be used to electroplate metals onto surfaces.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 40 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
The standard state of an electrochemical cell is measured as 1 atm pressure for all gases and 1.0 M for all aqueous solutions.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 40 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
Species with positive standard reduction potentials are excellent candidates for reduction reactions.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 40 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
In balancing electrochemical half-reactions in acidic media, one can assume an excess of both water and OH-.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 40 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
Using the provided standard reduction potentials, which of the following cells is an example of a Galvanic cell?
A)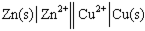
B)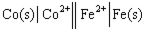
C)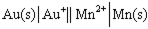
D)
A)
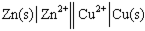
B)
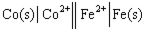
C)
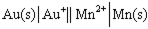
D)


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 40 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
The formation of thin layers of material on the electrodes of a secondary cell will result in:
A) an increase in the EMF of the battery.
B) formation of explosive hydrates.
C) shorter periods of usefulness between recharging sessions.
D) the creation of j-p junction gaps at the electrode surfaces.
A) an increase in the EMF of the battery.
B) formation of explosive hydrates.
C) shorter periods of usefulness between recharging sessions.
D) the creation of j-p junction gaps at the electrode surfaces.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 40 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
What is the oxidation number of Mn in MnO4 − ?
A) 1+
B) 2+
C) 7+
D) 8+
A) 1+
B) 2+
C) 7+
D) 8+

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 40 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
Balance the following electrochemical reaction in acid:
MnO4 − ( aq ) + Zr( s ) ↔ Mn2+( aq ) + Zr2+( aq )
A) 2 MnO4 − ( aq ) + 16H+( aq ) + 5 Zr( s ) → 2 Mn2+( aq ) + 5 Zr2+( aq ) + 8 H2O( l )
B) 2 MnO4 − ( aq ) + 5 Zr( s ) → 2 Mn2+( aq ) + 5 Zr2+( aq )
C) MnO4 − ( aq ) + Zr( s ) → Mn2+( aq )+ Zr2+( aq ) + 5 e −
D) 2 MnO4 − ( aq ) + 8H+( aq ) + 5 Zr( s ) → 2 Mn2+( aq ) + 5 Zr2+( aq ) + 8 H2O( l )
MnO4 − ( aq ) + Zr( s ) ↔ Mn2+( aq ) + Zr2+( aq )
A) 2 MnO4 − ( aq ) + 16H+( aq ) + 5 Zr( s ) → 2 Mn2+( aq ) + 5 Zr2+( aq ) + 8 H2O( l )
B) 2 MnO4 − ( aq ) + 5 Zr( s ) → 2 Mn2+( aq ) + 5 Zr2+( aq )
C) MnO4 − ( aq ) + Zr( s ) → Mn2+( aq )+ Zr2+( aq ) + 5 e −
D) 2 MnO4 − ( aq ) + 8H+( aq ) + 5 Zr( s ) → 2 Mn2+( aq ) + 5 Zr2+( aq ) + 8 H2O( l )

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 40 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
How many grams of silver are deposited at a platinum cathode in the electrolysis of AgNO3 (aq) by 5.30 amps of electric current in 4.0 hours?
A) 85.3 g
B) 42.6 g
C) 121 g
D) 188 g
A) 85.3 g
B) 42.6 g
C) 121 g
D) 188 g

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 40 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
What is the oxidation number of Cl in HClO4?
A) 1+
B) 2+
C) 7+
D) 8+
A) 1+
B) 2+
C) 7+
D) 8+

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 40 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
Which mechanism is most energy efficient?
A) internal combustion motor
B) a voltaic fuel cell
C) electricity from coal fired plants
A) internal combustion motor
B) a voltaic fuel cell
C) electricity from coal fired plants

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 40 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
What is the E0 value for the Galvanic cell formed from these two half-reactions?

A) −1 .43 V
B) +1.43 V
C) −0 .93 V
D) +0.93 V

A) −1 .43 V
B) +1.43 V
C) −0 .93 V
D) +0.93 V

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 40 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
How long will it take to collect 1.0 L of H2 (g) at STP in the electrolysis of 2.0 M HCl with a current of 4.25 A?
A) 15 min
B) 34 min
C) 2.8 hr
D) 11 hr
A) 15 min
B) 34 min
C) 2.8 hr
D) 11 hr

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 40 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
Given a Galvanic cell: 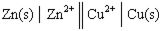 , the right-hand side of this notation represents the:
, the right-hand side of this notation represents the:
A) spontaneous half of the reaction.
B) oxidation 1/2 reaction.
C) anode of the cell.
D) reduction 1/2 reaction.
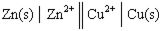 , the right-hand side of this notation represents the:
, the right-hand side of this notation represents the:A) spontaneous half of the reaction.
B) oxidation 1/2 reaction.
C) anode of the cell.
D) reduction 1/2 reaction.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 40 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
What is the E value for the Galvanic cell formed from these two half-reactions at these concentrations?
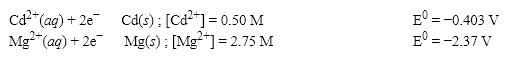
A) 1.90 V
B) 1.95 V
C) 1.99 V
D) 2.20 V
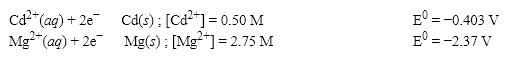
A) 1.90 V
B) 1.95 V
C) 1.99 V
D) 2.20 V

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 40 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
An oxidation occurs at the ____ of a Galvanic cell.
A) intersection
B) anode
C) p-n junction
D) cathode
A) intersection
B) anode
C) p-n junction
D) cathode

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 40 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
The salt bridge between 1/2 reactions maintains the electrical balance of a Galvanic cell. This bridge is filled with:
A) strong electrolytes.
B) inert carbon.
C) weak electrolytes.
D) interstitial membranes.
A) strong electrolytes.
B) inert carbon.
C) weak electrolytes.
D) interstitial membranes.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 40 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
What is the E value for the Galvanic cell formed from these two half-reactions at these concentrations?
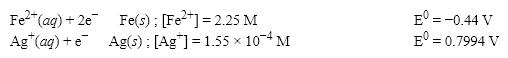
A) 1.00 V
B) 1.12 V
C) 1.24 V
D) 0.36 V
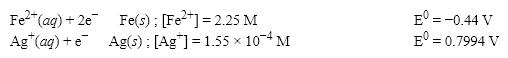
A) 1.00 V
B) 1.12 V
C) 1.24 V
D) 0.36 V

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 40 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
The SHE is assigned a voltage of ____ V.
A) − 1.000
B) 1.000
C) 0.150
D) 0.000
A) − 1.000
B) 1.000
C) 0.150
D) 0.000

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 40 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
What is the E0 value for the Galvanic cell formed from these two half-reactions?
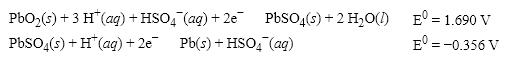
A) +1.334 V
B) − 2.046 V
C) +2.046 V
D) +2.758 V
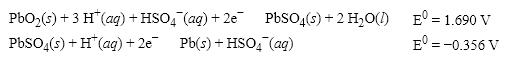
A) +1.334 V
B) − 2.046 V
C) +2.046 V
D) +2.758 V

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 40 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
Single use, non-rechargeable batteries are referred to as:
A) primary cells
B) secondary cells
C) tertiary cells
D) electrolytic cells
A) primary cells
B) secondary cells
C) tertiary cells
D) electrolytic cells

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 40 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
What is the E0 value for the Galvanic cell formed from these two half-reactions?

A) − 2.31 V
B) +4.33 V
C) − 1.32 V
D) +2.00 V

A) − 2.31 V
B) +4.33 V
C) − 1.32 V
D) +2.00 V

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 40 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
Identify the correct balanced chemical equation for the cell: 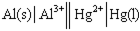
A) Al( s ) + Hg2+( aq ) → Al3+( aq ) + Hg( l )
B) 2 Al( s ) + Hg2+( aq ) → 2 Al3+( aq ) + Hg( l )
C) Al( s ) + 3 Hg2+( aq ) → Al3+( aq ) + 3 Hg( l )
D) 2 Al( s ) + 3 Hg2+( aq ) → 2 Al3+( aq ) + 3 Hg( l )
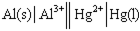
A) Al( s ) + Hg2+( aq ) → Al3+( aq ) + Hg( l )
B) 2 Al( s ) + Hg2+( aq ) → 2 Al3+( aq ) + Hg( l )
C) Al( s ) + 3 Hg2+( aq ) → Al3+( aq ) + 3 Hg( l )
D) 2 Al( s ) + 3 Hg2+( aq ) → 2 Al3+( aq ) + 3 Hg( l )

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 40 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
The rusting witnessed in the sheet metal of a '65 Impala is an example of:
A) uniform corrosion.
B) galvanic corrosion.
C) electrolysis.
D) compounding corrosion.
A) uniform corrosion.
B) galvanic corrosion.
C) electrolysis.
D) compounding corrosion.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 40 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



