Deck 2: Atoms and Molecules: the Chemical Basis of Life
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Match between columns
Question
Question
Match between columns
Question
Match between columns
Question
Match between columns
Question
Match between columns
Question
Question
Match between columns
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Match between columns
Question
Question
Match between columns

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/75
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 2: Atoms and Molecules: the Chemical Basis of Life
1
What differentiates an organic compound from an inorganic compound?
A) An organic compound lacks isotopes.
B) An organic compound contains carbon.
C) An organic compound lacks valence electrons.
D) An organic compound is basic rather than acidic.
E) An organic compound contains two or more atoms.
A) An organic compound lacks isotopes.
B) An organic compound contains carbon.
C) An organic compound lacks valence electrons.
D) An organic compound is basic rather than acidic.
E) An organic compound contains two or more atoms.
B
2
What is the difference between a stable isotope and a radioisotope?
A) A stable isotope emits light.
B) A radioisotope emits radiation.
C) A stable isotope emits radiation.
D) A stable isotope absorbs radiation.
E) A radioisotope has an unequal number of protons and electrons.
A) A stable isotope emits light.
B) A radioisotope emits radiation.
C) A stable isotope emits radiation.
D) A stable isotope absorbs radiation.
E) A radioisotope has an unequal number of protons and electrons.
B
3
Which substance is a reactant in the following chemical equation? CO2 + H2O ↔ H2CO3
A) water
B) carbon
C) oxygen
D) hydrogen
E) carbonic acid
A) water
B) carbon
C) oxygen
D) hydrogen
E) carbonic acid
A
4
A chlorine atom has 17 protons and 18 neutrons. What is its atomic mass?
A) 1 amu
B) 17 amu
C) 18 amu
D) 35 amu
E) 306 amu
A) 1 amu
B) 17 amu
C) 18 amu
D) 35 amu
E) 306 amu

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
Figure 2-1
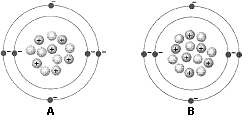
What is the difference between the two atoms in the accompanying figure?
A) their electrical charge
B) the number of electrons
C) the number of protons
D) the number of neutrons
E) the number of valence shells

What is the difference between the two atoms in the accompanying figure?
A) their electrical charge
B) the number of electrons
C) the number of protons
D) the number of neutrons
E) the number of valence shells

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
How many molecules are present in one mole of C6H12O6?
A) 1.7 × 1010 molecules
B) 1.3 × 1010 molecules
C) 24 molecules
D) 1.7 × 1022 molecules
E) 6.02 × 1023 molecules
A) 1.7 × 1010 molecules
B) 1.3 × 1010 molecules
C) 24 molecules
D) 1.7 × 1022 molecules
E) 6.02 × 1023 molecules

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
Sulfur has six valence electrons. How many covalent bonds does a sulfur atom typically form?
A) 3
B) 1
C) 5
D) 2
E) 4
A) 3
B) 1
C) 5
D) 2
E) 4

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
Isotopes differ from each other with respect to the number of:
A) protons only
B) electrons only
C) neutrons only
D) both protons and electrons
E) both neutrons and protons
A) protons only
B) electrons only
C) neutrons only
D) both protons and electrons
E) both neutrons and protons

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
How can we identify a particular element?
A) by its number of protons
B) by its number of electrons
C) by its number of neutrons
D) by its shape of valence shells
E) by its amount of energy levels
A) by its number of protons
B) by its number of electrons
C) by its number of neutrons
D) by its shape of valence shells
E) by its amount of energy levels

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
Figure 2-1
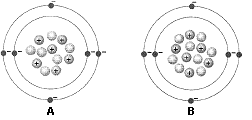
What does the accompanying figure represent?
A) an acid and a base
B) two different ions
C) a cation and an anion
D) two different elements
E) two isotopes of the same element

What does the accompanying figure represent?
A) an acid and a base
B) two different ions
C) a cation and an anion
D) two different elements
E) two isotopes of the same element

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
Figure 2-1
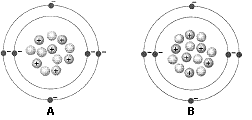
What is the atomic mass of the atom identified as A in the accompanying figure?
A) 2 amu
B) 6 amu
C) 8 amu
D) 12 amu
E) 18 amu

What is the atomic mass of the atom identified as A in the accompanying figure?
A) 2 amu
B) 6 amu
C) 8 amu
D) 12 amu
E) 18 amu

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
The chemical behavior of an atom is determined most directly by the:
A) atomic number
B) atomic weight
C) number of neutrons
D) number protons
E) number of valence electrons
A) atomic number
B) atomic weight
C) number of neutrons
D) number protons
E) number of valence electrons

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
The representation H−O−H is known as a(n):
A) structural formula
B) simplest formula
C) molecular formula
D) Lewis structure
E) orbital diagram
A) structural formula
B) simplest formula
C) molecular formula
D) Lewis structure
E) orbital diagram

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
Which statement best describes the product of a chemical reaction?
A) It is joined by an ionic bond only.
B) It is always in equilibrium with the reactants.
C) It is the substance that initiates the reaction.
D) It is generally written on the left side of the equation.
E) It is the substance generated by the reaction.
A) It is joined by an ionic bond only.
B) It is always in equilibrium with the reactants.
C) It is the substance that initiates the reaction.
D) It is generally written on the left side of the equation.
E) It is the substance generated by the reaction.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
Nitrogen has five electrons in its valence shell. How many electrons does it need to gain to complete its valence shell?
A) one
B) two
C) three
D) seven
E) eight
A) one
B) two
C) three
D) seven
E) eight

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
Which statement best describes an atom?
A) A substance that cannot burn.
B) A substance that is soluble in both acid and base
C) A substance that is held together by covalent bonds
D) A substance that is composed of more than one kind of atom
E) A substance that cannot be broken into a simpler substance
A) A substance that cannot burn.
B) A substance that is soluble in both acid and base
C) A substance that is held together by covalent bonds
D) A substance that is composed of more than one kind of atom
E) A substance that cannot be broken into a simpler substance

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
What is the atomic mass of the most common isotope of carbon?
A) 12.01 amu
B) 20.18 amu
C) 16.01 amu
D) 1.01 amu
E) 14.01 amu
A) 12.01 amu
B) 20.18 amu
C) 16.01 amu
D) 1.01 amu
E) 14.01 amu

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
Which of the following atoms can form five covalent bonds?
A) oxygen
B) phosphorus
C) hydrogen
D) carbon
E) nitrogen
A) oxygen
B) phosphorus
C) hydrogen
D) carbon
E) nitrogen

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
Which element activates many enzymes and is needed in blood and other tissues of animals?
A) magnesium
B) iron
C) sulfur
D) chlorine
E) sodium
A) magnesium
B) iron
C) sulfur
D) chlorine
E) sodium

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
Which of the following is a covalent compound?
A) potassium chloride
B) methane
C) lithium bromide
D) magnesium oxide
E) sodium fluoride
A) potassium chloride
B) methane
C) lithium bromide
D) magnesium oxide
E) sodium fluoride

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
Which of the following would most likely form electrolytes in water?
A) glucose
B) ethanol
C) an organic compound
D) an inorganic compound
E) a nonionic compound
A) glucose
B) ethanol
C) an organic compound
D) an inorganic compound
E) a nonionic compound

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
As water boils and turns to steam, what happens to the hydrogen bonds?
A) The hydrogen bonds break.
B) The hydrogen bonds strengthen.
C) The hydrogen bonds generate additional bonds.
D) The hydrogen bonds form a crystalline lattice structure.
E) The hydrogen bonds continually break and rejoin.
A) The hydrogen bonds break.
B) The hydrogen bonds strengthen.
C) The hydrogen bonds generate additional bonds.
D) The hydrogen bonds form a crystalline lattice structure.
E) The hydrogen bonds continually break and rejoin.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
Which component becomes oxidized in the following chemical reaction? 4 Fe + 3 O2 → 2 Fe2O3
A) rust
B) iron
C) water
D) oxygen
E) hydrogen
A) rust
B) iron
C) water
D) oxygen
E) hydrogen

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
Which statement about van der Waal interactions is false ?
A) They are very strong.
B) They are attractive forces.
C) They operate over very short distances.
D) They form between nonpolar molecules.
E) They involve transient regions of positive and negative charges.
A) They are very strong.
B) They are attractive forces.
C) They operate over very short distances.
D) They form between nonpolar molecules.
E) They involve transient regions of positive and negative charges.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
Which of the following is a common oxidizing agent?
A) carbon monoxide
B) lithium
C) oxygen
D) zinc
E) iron
A) carbon monoxide
B) lithium
C) oxygen
D) zinc
E) iron

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
The cohesiveness between water molecules is due largely to _________.
A) ionic bonds
B) hydrogen bonds
C) polar covalent bonds
D) nonpolar covalent bonds
E) hydrophobic interactions
A) ionic bonds
B) hydrogen bonds
C) polar covalent bonds
D) nonpolar covalent bonds
E) hydrophobic interactions

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
It takes one calorie of heat to raise the temperature of one gram of water by one degree Celsius at sea level. This is referred to as the ____ of water.
A) specific heat
B) heat of fusion
C) homeostasis
D) vaporization
E) heat of transformation
A) specific heat
B) heat of fusion
C) homeostasis
D) vaporization
E) heat of transformation

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
Which of the following solutions has a pH value of 9.0?
A) Beer
B) Blood
C) Bleach
D) Seawater
E) Rainwater
A) Beer
B) Blood
C) Bleach
D) Seawater
E) Rainwater

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
___________ in the muscle cell are required for muscle contraction.
A) Sodium ions
B) Potassium ions
C) Calcium ions
D) Chloride ions
E) Magnesium ions
A) Sodium ions
B) Potassium ions
C) Calcium ions
D) Chloride ions
E) Magnesium ions

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
Water molecules have a strong tendency to stick to one another, a property known as ___________.
A) adhesion
B) capillary action
C) cohesion
D) surface tension
E) osmosis
A) adhesion
B) capillary action
C) cohesion
D) surface tension
E) osmosis

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
Consider the aquatic insects pictured in the accompanying figure. Which characteristic of water molecules directly contributes to their remarkable "water walking" success?
A) ionic bonds
B) capillary action
C) hydrogen bonds
D) adhesive forces
E) nonpolar covalent bonds

A) ionic bonds
B) capillary action
C) hydrogen bonds
D) adhesive forces
E) nonpolar covalent bonds

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
Which component is the oxidizing agent in the following chemical reaction? 4 Fe + 3 O2 → 2 Fe2O3
A) rust
B) iron
C) water
D) oxygen
E) hydrogen
A) rust
B) iron
C) water
D) oxygen
E) hydrogen

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
Which event illustrates evaporative cooling?
A) a tea kettle whistling
B) sweat evaporating from the skin
C) ice cubes floating in a glass of water
D) a fish not freezing in an ice-covered pond
E) salt dissolving in a pot of water with potatoes
A) a tea kettle whistling
B) sweat evaporating from the skin
C) ice cubes floating in a glass of water
D) a fish not freezing in an ice-covered pond
E) salt dissolving in a pot of water with potatoes

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
What is the specific heat of water?
A) 0.5 cal/g of water per degree Celsius
B) 0.75 cal/g of water per degree Celsius
C) 3 cal/g of water per degree Celsius
D) 1 cal/g of water per degree Celsius
E) 2 cal/g of water per degree Celsius
A) 0.5 cal/g of water per degree Celsius
B) 0.75 cal/g of water per degree Celsius
C) 3 cal/g of water per degree Celsius
D) 1 cal/g of water per degree Celsius
E) 2 cal/g of water per degree Celsius

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
Sugar dissolves readily in water because it is a(n) ____ substance.
A) adhesive
B) cohesive
C) hydrophilic
D) hydrophobic
E) evaporative
A) adhesive
B) cohesive
C) hydrophilic
D) hydrophobic
E) evaporative

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
Which atom would most likely be involved in an ionic bond?
A) hydrogen
B) oxygen
C) sodium
D) nitrogen
E) helium
A) hydrogen
B) oxygen
C) sodium
D) nitrogen
E) helium

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
What is the difference between an electrically neutral atom and an ion?
A) An ion has an unequal number of protons and electrons, while a neutral atom has an equal number.
B) An ion has an equal number of protons and electrons, while an atom has an unequal number.
C) An atom has an unequal number of neutrons and protons, while an ion has an equal number.
D) An atom has its electrons in orbitals, while an ion has its electrons in its nucleus.
E) An atom must have an equal number of neutrons and electrons, while an ion does not.
A) An ion has an unequal number of protons and electrons, while a neutral atom has an equal number.
B) An ion has an equal number of protons and electrons, while an atom has an unequal number.
C) An atom has an unequal number of neutrons and protons, while an ion has an equal number.
D) An atom has its electrons in orbitals, while an ion has its electrons in its nucleus.
E) An atom must have an equal number of neutrons and electrons, while an ion does not.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
A base is defined as a(n) _____ acceptor.
A) neutron
B) electron
C) proton
D) anion
E) cation
A) neutron
B) electron
C) proton
D) anion
E) cation

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
The covalent bond between a hydrogen atom and the oxygen atom in water is formed when:
A) hydrogen gains an electron from oxygen
B) hydrogen and oxygen share an electron pair
C) hydrogen and oxygen both lose electrons from their outer shells
D) hydrogen and oxygen both gain electrons in their outer shells
E) hydrogen loses an electron from oxygen
A) hydrogen gains an electron from oxygen
B) hydrogen and oxygen share an electron pair
C) hydrogen and oxygen both lose electrons from their outer shells
D) hydrogen and oxygen both gain electrons in their outer shells
E) hydrogen loses an electron from oxygen

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
What is the OH− concentration of a solution having a pH of 2?
A) 1 × 10-12
B) 1 × 10-10
C) 1 × 10-7
D) 1 × 10-2
E) 1 × 10-1
A) 1 × 10-12
B) 1 × 10-10
C) 1 × 10-7
D) 1 × 10-2
E) 1 × 10-1

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
When a small amount of hydrochloric acid (HCl) is added to a solution of Na2HPO4, the pH of the solution does not change markedly. The pH also does not change drastically when a small amount of sodium hydroxide (NaOH) is added to this same solution. Based on these observations, the compound Na2HPO4 is:
A) acting as a buffer
B) acting as a solvent
C) able to donate hydrogen atoms to HCl
D) able to remove hydrogen ions from the OH− of NaOH
E) an enzyme facilitating the reaction between HCl and NaOH
A) acting as a buffer
B) acting as a solvent
C) able to donate hydrogen atoms to HCl
D) able to remove hydrogen ions from the OH− of NaOH
E) an enzyme facilitating the reaction between HCl and NaOH

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
Diagram and carefully label two water molecules using an appropriately sized ball for each atom. Then, use a dashed line on this diagram to show how hydrogen bonds form between the two water molecules.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
The atomic mass determines the identity of an element.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
When atoms react to form an ionic bond, electrons are shared between those atoms.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
An inorganic compound is one that contains carbon.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
A salt is a compound in which the hydrogen ion of ____ is replaced by some other cation.
A) water
B) a base
C) an acid
D) an anion
E) a hydroxide ion
A) water
B) a base
C) an acid
D) an anion
E) a hydroxide ion

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
An atom that has a filled valence shell is stable and unreactive.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
An example of an anion is K+.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
List four of the principal chemical elements found in living organisms and identify an important biological function of each element.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
Oxidation occurs when an atom gains one or more electrons.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
Identify and compare the properties of the bond between sodium and chloride (NaCl) with the bond between carbon and hydrogen in methane (CH4).

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
A chemical formula shows the types and numbers of atoms in a molecule and their arrangement.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
What is the approximate pH of ammonia?
A) 2
B) 4
C) 7
D) 8
E) 11
A) 2
B) 4
C) 7
D) 8
E) 11

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
The tetrahedron shape of a methane molecule is the result of orbital hybridization.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
Which substance is an example of a very strong acid?
A) milk
B) coffee
C) bleach
D) seawater
E) lemon juice
A) milk
B) coffee
C) bleach
D) seawater
E) lemon juice

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
Which element forms the backbone of organic molecules?
A) magnesium
B) iron
C) chlorine
D) sodium
E) carbon
A) magnesium
B) iron
C) chlorine
D) sodium
E) carbon

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
The valence shell of hydrogen or helium is unstable when it contains two electrons.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
A liquid with a pH of 7 is considered a(n) ____ solution.
A) basic
B) acidic
C) neutral
D) hydrophilic
E) hydrochloric
A) basic
B) acidic
C) neutral
D) hydrophilic
E) hydrochloric

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
Explain how the number and arrangement of valence electrons is related to the chemical properties of an atom. Use two specific examples in your explanation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
What is the purpose of a buffer?
A) To convert an acid to a base
B) To minimize the change in pH
C) To measure the acidity of a solution
D) To form a stable bond between atoms
E) To maintain a constant internal temperature
A) To convert an acid to a base
B) To minimize the change in pH
C) To measure the acidity of a solution
D) To form a stable bond between atoms
E) To maintain a constant internal temperature

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
Match between columns

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
A solution having a pH of 8 is slightly acidic .

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
Match between columns

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
Match between columns

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
Match between columns

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
Match between columns

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
A calorie is the amount of heat energy required to raise the temperature of 1 g of water 1 degree Celsius (C).

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
Match between columns

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
Specific heat refers to the amount of energy required to change 1 gram of a substance from the liquid phase to the vapor phase.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
Explain and identify the mechanism of how carbon dioxide maintains blood pH levels.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
A combination of adhesive and cohesive forces accounts for surface tension.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72
As a researcher, you are charged with determining the effects of a new drug. From previous observations, you suspect that this drug reduces the rate of DNA production (replication) in the skin cells of patients using the drug. With the following materials, design an experiment that would determine the effect of the drug on DNA replication. You know that DNA contains phosphate groups. You have radioactive isotopes of phosphate (32P), skin cell cultures from different patients, the drug in question, and a device that measures radioactivity.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73
Match between columns

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
74
The hydrogen bonds of water play an important role in the ability of plants to transport water (via capillary action). Explain how this occurs.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
75
Match between columns

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



