Deck 29: The Fungi
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Match between columns
Question
Match between columns
Question
Match between columns
Question
Question
Match between columns
Question
Match between columns
Question
Match between columns
Question
Question
Question
Match between columns
Question
Match between columns
Question
Question
Question
Match between columns
Question
Question
Match between columns
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/78
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 29: The Fungi
1
Which of the following correctly describes fungal spores?
A) When a spore germinates, it gives rise to sporangia.
B) When a spore germinates, it gives rise to a mycelium, which then develops into hyphae.
C) Most fungal cells do not contain haploid nuclei.
D) They are motile and reproduce sexually only.
E) They are nonmotile and reproduce either sexually or asexually.
A) When a spore germinates, it gives rise to sporangia.
B) When a spore germinates, it gives rise to a mycelium, which then develops into hyphae.
C) Most fungal cells do not contain haploid nuclei.
D) They are motile and reproduce sexually only.
E) They are nonmotile and reproduce either sexually or asexually.
E
2
Which is an example of a member of phylum Zygomycota?
A) Yeast
B) Morels
C) Puffballs
D) Black bread mold
E) Portobella mushrooms
A) Yeast
B) Morels
C) Puffballs
D) Black bread mold
E) Portobella mushrooms
D
3
Designate the hyphae of two different mating types of black bread mold as "+" (plus) and "−" (minus). Mating of these two types is correctly classified as which of the following?
A) Heterozygous
B) Heterothallic
C) Heterotrophic
D) Mycotoxic
E) Coenocytic
A) Heterozygous
B) Heterothallic
C) Heterotrophic
D) Mycotoxic
E) Coenocytic
B
4
The hypha, a filament that makes up the vegetative body of most fungi, serves which of the following functions?
A) Cell division
B) Intercellular communication
C) Cellular locomotion
D) Nutrient absorption
E) Apoptosis
A) Cell division
B) Intercellular communication
C) Cellular locomotion
D) Nutrient absorption
E) Apoptosis

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 78 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
In a fungus, a complex multicellular reproductive structure is called a(n):
A) hypha.
B) gametangium.
C) fruiting body.
D) oogonium.
E) antheridium.
A) hypha.
B) gametangium.
C) fruiting body.
D) oogonium.
E) antheridium.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 78 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
In most fungi, hyphae are divided by cross walls, termed which of the following?
A) Sporocarps
B) Sporangia
C) Zygospores
D) Septa
E) Coenocytes
A) Sporocarps
B) Sporangia
C) Zygospores
D) Septa
E) Coenocytes

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 78 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
Hyphae that contain two genetically distinct, sexually compatible nuclei within each cell are described as:
A) twins.
B) couplets.
C) dikaryotic.
D) polykaryotic.
E) double hyphae.
A) twins.
B) couplets.
C) dikaryotic.
D) polykaryotic.
E) double hyphae.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 78 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
Which unicellular fungus is probably in most kitchens?
A) Mold
B) Mushroom
C) Yeast
D) Rust
E) Dirt
A) Mold
B) Mushroom
C) Yeast
D) Rust
E) Dirt

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 78 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
Figure 29-1
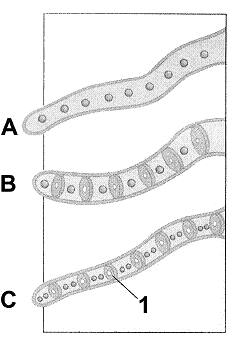
Refer to the accompanying figure. The structure labeled as 1 is a:
A) spore.
B) hypha.
C) conidium.
D) basidium.
E) perforated septum.

Refer to the accompanying figure. The structure labeled as 1 is a:
A) spore.
B) hypha.
C) conidium.
D) basidium.
E) perforated septum.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 78 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
When bread gets moldy with visible black or blue spots, you are looking at masses of the colored:
A) thalli.
B) spores.
C) hyphae.
D) mycelia.
E) ascocarps.
A) thalli.
B) spores.
C) hyphae.
D) mycelia.
E) ascocarps.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 78 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
What makes up most of the mass of an individual mushroom?
A) Underground ascocarp
B) Underground mycelium
C) Above-ground ascocarp
D) Above-ground mycelium
E) Underground fruiting body
A) Underground ascocarp
B) Underground mycelium
C) Above-ground ascocarp
D) Above-ground mycelium
E) Underground fruiting body

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 78 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
The cell walls of fungi are composed of:
A) lipids.
B) chitin.
C) cellulose.
D) glycogen.
E) chlorophyll.
A) lipids.
B) chitin.
C) cellulose.
D) glycogen.
E) chlorophyll.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 78 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
The sac fungi are characterized by sexual reproductive structures called:
A) asci.
B) basidia.
C) conidia.
D) gemmae.
E) conidiophores.
A) asci.
B) basidia.
C) conidia.
D) gemmae.
E) conidiophores.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 78 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
Fungi that lack septa are called:
A) coenocytic.
B) unicellular.
C) ascomycete.
D) monokaryotic.
E) sporophyllous.
A) coenocytic.
B) unicellular.
C) ascomycete.
D) monokaryotic.
E) sporophyllous.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 78 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
Allomyces has an unusual life cycle in that it spends part of its life as a multicellular haploid thallus and part as a multicellular diploid thallus. This life cycle is known as which of the following?
A) Klepton
B) Parthenocarpy
C) Alternation of generations
D) Cytomixis
E) Apomixis
A) Klepton
B) Parthenocarpy
C) Alternation of generations
D) Cytomixis
E) Apomixis

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 78 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
Figure 29-1
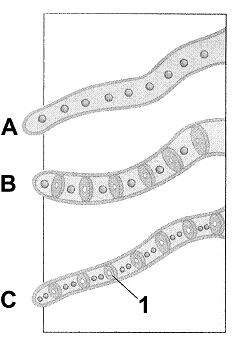
Refer to the accompanying figure. What is missing in the filament labeled as A?
A) Septa
B) Nuclei
C) Spores
D) Hyphae
E) mycelia

Refer to the accompanying figure. What is missing in the filament labeled as A?
A) Septa
B) Nuclei
C) Spores
D) Hyphae
E) mycelia

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 78 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
Which statement about microsporidia is FALSE?
A) They are parasitic.
B) Some divide by binary fission.
C) They are classified with the zygomycetes.
D) They have mitochondria and Golgi complexes.
E) They have a feeding stage and a reproductive stage.
A) They are parasitic.
B) Some divide by binary fission.
C) They are classified with the zygomycetes.
D) They have mitochondria and Golgi complexes.
E) They have a feeding stage and a reproductive stage.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 78 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
Which fungal group is coenocytic and reproduce asexually via blastospores?
A) Zygomycetes
B) Glomeromycetes
C) Basidiomycetes
D) Ascomycetes
E) Chytridiomycetes
A) Zygomycetes
B) Glomeromycetes
C) Basidiomycetes
D) Ascomycetes
E) Chytridiomycetes

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 78 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
Ascomycetes reproduce sexually by forming:
A) asci.
B) basidia.
C) conidia.
D) hyphae.
E) ascospores.
A) asci.
B) basidia.
C) conidia.
D) hyphae.
E) ascospores.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 78 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
Which process marks the start of the dikaryotic stage ( n + n ) in the fungal reproductive cycle?
A) Mitosis
B) Meiosis
C) Karyogamy
D) Fertilization
E) Plasmogamy
A) Mitosis
B) Meiosis
C) Karyogamy
D) Fertilization
E) Plasmogamy

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 78 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
Which of the following is NOT true of lichens?
A) Lichens tolerate extremes of temperature and moisture.
B) Lichens secrete acid.
C) Some lichens produce colored pigments.
D) Lichens can all be seen with an unaided eye.
E) Lichens all grow very slowly.
A) Lichens tolerate extremes of temperature and moisture.
B) Lichens secrete acid.
C) Some lichens produce colored pigments.
D) Lichens can all be seen with an unaided eye.
E) Lichens all grow very slowly.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 78 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
'Which of the following correctly describes basidiomycetes?
A) They are sometimes called "spade fungi."
B) Basidia serve a function that is distinct from that of the asci of ascomycetes.
C) Each basidium undergoes meiosis to form two basidiospores.
D) Basidiospores develop on the inside of the basidium.
E) Hyphae of a primary mycelium consist of monokaryotic cells.
A) They are sometimes called "spade fungi."
B) Basidia serve a function that is distinct from that of the asci of ascomycetes.
C) Each basidium undergoes meiosis to form two basidiospores.
D) Basidiospores develop on the inside of the basidium.
E) Hyphae of a primary mycelium consist of monokaryotic cells.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 78 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
Puffballs and bracket fungi are most closely related to:
A) yeast.
B) molds.
C) truffles.
D) black bread mold.
E) common edible mushrooms.
A) yeast.
B) molds.
C) truffles.
D) black bread mold.
E) common edible mushrooms.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 78 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
Figure 29-2
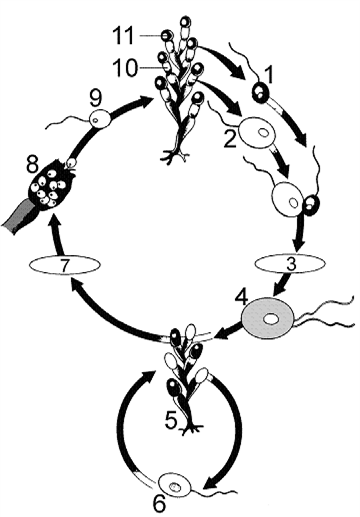
Refer to the accompanying figure. The structure labeled as 4 is a:
A) zygote.
B) gamete.
C) zoospore.
D) sporangium.
E) zoosporangium.

Refer to the accompanying figure. The structure labeled as 4 is a:
A) zygote.
B) gamete.
C) zoospore.
D) sporangium.
E) zoosporangium.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 78 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
Asomycetes are NOT used for which of the following applications?
A) Flavor cheese
B) Bake bread
C) Prepare vinegar
D) Produce antibiotics
E) Biological research
A) Flavor cheese
B) Bake bread
C) Prepare vinegar
D) Produce antibiotics
E) Biological research

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 78 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
Like fungi, chytrid cell walls contain which of the following?
A) Chitin
B) Chitobiose
C) Lorica
D) Sporopollenin
E) Tectin
A) Chitin
B) Chitobiose
C) Lorica
D) Sporopollenin
E) Tectin

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 78 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
What is an example of a plant disease caused by a basiodiomycete?
A) Wheat rust
B) Ergot of rye
C) Chestnut blight
D) Dutch elm disease
E) Verticillium wilt on potatoes
A) Wheat rust
B) Ergot of rye
C) Chestnut blight
D) Dutch elm disease
E) Verticillium wilt on potatoes

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 78 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
Figure 29-2
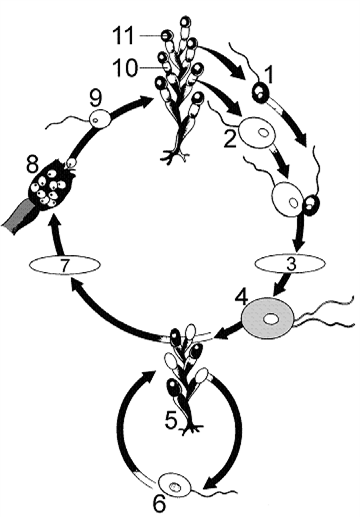
What is the process occurring at point 3 in the accompanying figure?
A) Asexual reproduction
B) Zygote germination
C) Fertilization
D) Meiosis
E) Mitosis

What is the process occurring at point 3 in the accompanying figure?
A) Asexual reproduction
B) Zygote germination
C) Fertilization
D) Meiosis
E) Mitosis

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 78 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
Figure 29-2
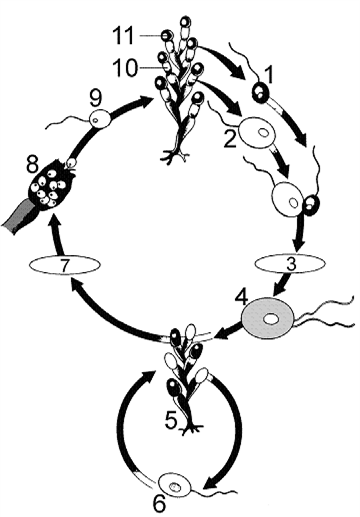
The structure labeled as 9 in the accompanying figure was produced by:
A) the fertilization of two zygotes.
B) meiosis in the zoosporangium.
C) mitosis in the zoosporangium.
D) mitosis in the resting sporangium.
E) meiosis in the resting sporangium.

The structure labeled as 9 in the accompanying figure was produced by:
A) the fertilization of two zygotes.
B) meiosis in the zoosporangium.
C) mitosis in the zoosporangium.
D) mitosis in the resting sporangium.
E) meiosis in the resting sporangium.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 78 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
One ancestral characteristic remaining in representatives of the Chytridiomycota is:
A) both sexual and asexual reproduction.
B) gametes formed by mitosis.
C) alternation of generations.
D) flagellated cells.
E) cell walls.
A) both sexual and asexual reproduction.
B) gametes formed by mitosis.
C) alternation of generations.
D) flagellated cells.
E) cell walls.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 78 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
Lichens reproduce mainly by asexual means, usually by which of the following?
A) Budding
B) Fission
C) Vegetative propagation
D) Fragmentation
E) Sporogenesis
A) Budding
B) Fission
C) Vegetative propagation
D) Fragmentation
E) Sporogenesis

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 78 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
The club fungi typically reproduce by producing:
A) asci.
B) basidia.
C) zygospores.
D) ascospores.
E) mycorrhizae.
A) asci.
B) basidia.
C) zygospores.
D) ascospores.
E) mycorrhizae.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 78 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
Yeasts reproduce asexually by:
A) meiosis.
B) budding.
C) ascospores.
D) binary fission.
E) forming a secondary mycelium.
A) meiosis.
B) budding.
C) ascospores.
D) binary fission.
E) forming a secondary mycelium.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 78 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
Which one of the following is mismatched?
A) Sac fungi−ascomycetes
B) Bread mold−zygomycetes
C) Mushrooms-basidiomycetes
D) Allomyces -chytridiomycetes
E) Dutch elm disease-glomeromycetes
A) Sac fungi−ascomycetes
B) Bread mold−zygomycetes
C) Mushrooms-basidiomycetes
D) Allomyces -chytridiomycetes
E) Dutch elm disease-glomeromycetes

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 78 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
Which process takes place within the young basidia on the gills of the mushroom?
A) Mitosis
B) Meiosis
C) Karyogamy
D) Fertilization
E) Plasmogamy
A) Mitosis
B) Meiosis
C) Karyogamy
D) Fertilization
E) Plasmogamy

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 78 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
Which statement about mycorrhizae is FALSE?
A) They are symbiotic associations between a fungus and a plant root.
B) They increase the uptake of nutrient minerals by the plant.
C) Arbuscular mycorrhizae are extracellular.
D) Endomycorrhizae are intracellular.
E) Members of the Glomeromycota may be involved.
A) They are symbiotic associations between a fungus and a plant root.
B) They increase the uptake of nutrient minerals by the plant.
C) Arbuscular mycorrhizae are extracellular.
D) Endomycorrhizae are intracellular.
E) Members of the Glomeromycota may be involved.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 78 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
Chytrids produce which of the following cells at some point during their life cycle, which is an indicator of fungal evolution?
A) Flagellate
B) Spores
C) Hyphae
D) Ascocarps
E) Conidia
A) Flagellate
B) Spores
C) Hyphae
D) Ascocarps
E) Conidia

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 78 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
Mushrooms that we eat are technically referred to as:
A) basidiospores.
B) basidiocarps.
C) myceliae.
D) hyphae.
E) gills.
A) basidiospores.
B) basidiocarps.
C) myceliae.
D) hyphae.
E) gills.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 78 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
How do mycorrhizae benefit plants?
A) Mycorrhizae increase a plant's flowering.
B) Mycorrhizae increase the surface area of the leaves.
C) Mycorrhizae increase a plant's rate of photosynthetic.
D) Mycorrhizae increase a plant's absorptive surface area of roots.
E) Mycorrhizae increase the number of chloroplasts within a plant.
A) Mycorrhizae increase a plant's flowering.
B) Mycorrhizae increase the surface area of the leaves.
C) Mycorrhizae increase a plant's rate of photosynthetic.
D) Mycorrhizae increase a plant's absorptive surface area of roots.
E) Mycorrhizae increase the number of chloroplasts within a plant.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 78 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
Of the following, which would be predicted to grow at the slowest rate?
A) Yeasts
B) Lichens
C) Sac fungi
D) Mushrooms
E) Bread molds
A) Yeasts
B) Lichens
C) Sac fungi
D) Mushrooms
E) Bread molds

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 78 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
Lichens are currently thought to be an example of which of the following?
A) Inhibition
B) Mutualism
C) Controlled parasitism
D) A fungus and a chemoautotroph
E) An algae and a photoautotroph
A) Inhibition
B) Mutualism
C) Controlled parasitism
D) A fungus and a chemoautotroph
E) An algae and a photoautotroph

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 78 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
What is a fungal chemical that shows promise as an anticancer agent because of its ability to inhibit the formation of new blood vessels?
A) Penicillin
B) Fumigallin
C) Aflatoxin
D) Psilocybin
E) Ergot compounds
A) Penicillin
B) Fumigallin
C) Aflatoxin
D) Psilocybin
E) Ergot compounds

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 78 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
Thrush, a painful yeast infection of the mouth, throat and vagina, is caused by a member of the genus:
A) Aspergillus.
B) Candida.
C) Claviceps.
D) Penicillium.
E) Psilocybe.
A) Aspergillus.
B) Candida.
C) Claviceps.
D) Penicillium.
E) Psilocybe.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 78 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
Identify the parts of a typical fungal body plan and briefly explain the function of each of the structures you identified.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 78 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
Describe the importance of fungi as decomposer.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 78 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
List the major types of foods and beverages for which fungi are responsible, and give an example of the particular fungus involved in each.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 78 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
What are the two main types of mycorrhizae, and how do they differ? List three ways in which mycorrhizal associations are beneficial to plants.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 78 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
Which of the following is NOT a correct statement regarding fungal infections of plants?
A) Fungi are responsible for about 70% of all major crop diseases.
B) Fungal infections often result in complete crop failure.
C) All plants are apparently susceptible to some fungal infection.
D) Damage is always systemic and spread throughout the plant.
E) A plant often becomes infected through a pore or a wound.
A) Fungi are responsible for about 70% of all major crop diseases.
B) Fungal infections often result in complete crop failure.
C) All plants are apparently susceptible to some fungal infection.
D) Damage is always systemic and spread throughout the plant.
E) A plant often becomes infected through a pore or a wound.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 78 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
List the characteristics suggesting that fungi should be assigned to the opisthokont clade.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 78 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
Conidia are asexual spores.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 78 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
Microsporidia are unicellular parasites of animals.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 78 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
Chytrids produce spores that lack a flagellum.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 78 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
Consuming even a single mushroom of the genus ____ can be fatal.
A) Agaricus
B) Shiitake
C) Portobello
D) Amanita
E) Oyster
A) Agaricus
B) Shiitake
C) Portobello
D) Amanita
E) Oyster

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 78 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
Which genus is used to produce beer and wine?
A) Agaricus
B) Aspergillus
C) Amanita
D) Rhizopus
E) Saccharomyces
A) Agaricus
B) Aspergillus
C) Amanita
D) Rhizopus
E) Saccharomyces

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 78 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
Which of the following is NOT an example of an animal disease caused by an ascomycete?
A) Histoplasmosis
B) Ringworm
C) Aspergillosis
D) Tuberculosis
E) Sick-building syndrome
A) Histoplasmosis
B) Ringworm
C) Aspergillosis
D) Tuberculosis
E) Sick-building syndrome

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 78 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
In zygomycetes such as Rhizopus , the zygospore is haploid.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 78 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
The fungus that causes black stem rust of wheat belongs to which fungal group?
A) Ascomycetes
B) Zygomycetes
C) Basidiomycetes
D) Chytridiomycetes
E) Glomeromycetes
A) Ascomycetes
B) Zygomycetes
C) Basidiomycetes
D) Chytridiomycetes
E) Glomeromycetes

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 78 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
Saccharomyces cerevisiae are useful for which of the following?
A) Baking
B) Penicillin production
C) Cheese flavoring
D) Soybean fermentation
E) Inducing hallucinations
A) Baking
B) Penicillin production
C) Cheese flavoring
D) Soybean fermentation
E) Inducing hallucinations

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 78 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
Lichens are most typically formed by the symbiotic association of an alga or cyanobacterium and a(n):
A) zygomycete.
B) ascomycete.
C) basidiomycete.
D) glomeromycete.
E) chytridiomycete.
A) zygomycete.
B) ascomycete.
C) basidiomycete.
D) glomeromycete.
E) chytridiomycete.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 78 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
The cell walls of fungi are composed of cellulose.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 78 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
Match between columns

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 78 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
Match between columns

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 78 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
Match between columns

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 78 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
Endomycorrhizal fungi penetrate the plasma membranes of root cells.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 78 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
Match between columns

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 78 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
Match between columns

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 78 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
Match between columns

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 78 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
Discuss the sexual and asexual reproduction of Rhizopus , the black bread mold. Include the names of the structures involved.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 78 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
What are some way in which the relationship between a plant root and a mycorrihizal fungus is mutualistic?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 78 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
Match between columns

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 78 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
Match between columns

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 78 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72
What is the economic importance of fungi? Name at least 10 products made utilizing fungi.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 78 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73
The primary mycelium of basidiomycetes is dikaryotic.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 78 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
74
Match between columns

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 78 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
75
A lichen is a combination of a fungus and a photoautotroph.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 78 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
76
Match between columns

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 78 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
77
In mushrooms, karyogamy occurs within the basidium.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 78 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
78
Blastospores are produced by glomeromycetes.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 78 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



