Deck 36: Roots and Mineral Nutrition
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/105
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 36: Roots and Mineral Nutrition
1
Which of the following statements about a root cap is false ?
A) It protects the delicate root apical meristem.
B) It secretes lubricating polysaccharides.
C) It orients the root that it grows downward.
D) It loses cells during root growth.
E) It absorbs nutrients.
A) It protects the delicate root apical meristem.
B) It secretes lubricating polysaccharides.
C) It orients the root that it grows downward.
D) It loses cells during root growth.
E) It absorbs nutrients.
E
2
Roots of many plants in arid regions store ______:
A) amino acids
B) water
C) carbon dioxide
D) oxygen
E) fats
A) amino acids
B) water
C) carbon dioxide
D) oxygen
E) fats
B
3
Which of the following protects the delicate cells of the apical meristem?
A) Root hair
B) Root cap
C) Radicle
D) Epidermis
E) Sieve tube
A) Root hair
B) Root cap
C) Radicle
D) Epidermis
E) Sieve tube
B
4
The difference between taproot and fibrous root systems is that a taproot system:
A) consists of many roots of the same size, while a fibrous root system has one main root with lateral roots.
B) consists of one main root with lateral roots, while a fibrous root system has many roots of the same size.
C) is characteristic of most monocots, while a fibrous root system is usually found in eudicots.
D) can be modified for storage, while a fibrous root system cannot.
E) is considered adventitious, while a fibrous root system is not.
A) consists of many roots of the same size, while a fibrous root system has one main root with lateral roots.
B) consists of one main root with lateral roots, while a fibrous root system has many roots of the same size.
C) is characteristic of most monocots, while a fibrous root system is usually found in eudicots.
D) can be modified for storage, while a fibrous root system cannot.
E) is considered adventitious, while a fibrous root system is not.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 105 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
The symplast:
A) greatly increases the surface area of the root.
B) is a waterproof band surrounding the endodermis.
C) is a continuum of living cytoplasm.
D) secretes suberin, which waterproofs the cells.
E) allows nutrient minerals to move against their concentration gradient.
A) greatly increases the surface area of the root.
B) is a waterproof band surrounding the endodermis.
C) is a continuum of living cytoplasm.
D) secretes suberin, which waterproofs the cells.
E) allows nutrient minerals to move against their concentration gradient.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 105 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
The bulk of an herbaceous eudicot root consists of loosely arranged parenchyma cells in the:
A) endodermis.
B) pericycle.
C) epidermis.
D) cortex.
E) periderm.
A) endodermis.
B) pericycle.
C) epidermis.
D) cortex.
E) periderm.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 105 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
In eudicot roots, the last mode of water and mineral transport occurs from the ____ to ______.
A) endodermis; xylem
B) periderm; pericycle
C) cortex; endodermis
D) epidermis; cortex
E) pericycle; xylem
A) endodermis; xylem
B) periderm; pericycle
C) cortex; endodermis
D) epidermis; cortex
E) pericycle; xylem

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 105 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
Which statement concerning the root epidermis is true?
A) It does not secrete a waxy cuticle over the root hairs.
B) It consists of protective tissue several layers thick.
C) It contains large intercellular spaces among the cells.
D) It comprises the bulk of the eudicot root.
E) It is the site of storage of surplus sugars produced in the leaves.
A) It does not secrete a waxy cuticle over the root hairs.
B) It consists of protective tissue several layers thick.
C) It contains large intercellular spaces among the cells.
D) It comprises the bulk of the eudicot root.
E) It is the site of storage of surplus sugars produced in the leaves.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 105 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
Unlike eudicot roots, the center of most monocot roots is occupied by the:
A) cortex.
B) pith.
C) phloem.
D) vascular cambium.
E) xylem.
A) cortex.
B) pith.
C) phloem.
D) vascular cambium.
E) xylem.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 105 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
The seedling's radicle is the origin of roots in a(n) _____ system.
A) adventitious root
B) lateral root
C) taproot
D) fine root
E) indigenous root
A) adventitious root
B) lateral root
C) taproot
D) fine root
E) indigenous root

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 105 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
Which of the following consists of the interconnected porous cell walls of a plant along which water and mineral ions move freely?
A) Symplast
B) Chloroplast
C) Plasmodesmata
D) Apoplast
E) Endodermis
A) Symplast
B) Chloroplast
C) Plasmodesmata
D) Apoplast
E) Endodermis

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 105 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
The ground tissue lacking in the primary eudicot root is:
A) pith.
B) periderm.
C) cortex.
D) vascular cambium.
E) pericycle.
A) pith.
B) periderm.
C) cortex.
D) vascular cambium.
E) pericycle.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 105 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
The ____ is involved in forming the lateral meristems that produce secondary growth in woody roots.
A) endodermis
B) periderm
C) cortex
D) vascular cambium
E) pericycle
A) endodermis
B) periderm
C) cortex
D) vascular cambium
E) pericycle

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 105 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
The large intercellular spaces, common features of the root cortex, provide:
A) a pathway for water uptake.
B) aeration of the root.
C) structural support.
D) protection.
E) aeration and a pathway for water uptake
A) a pathway for water uptake.
B) aeration of the root.
C) structural support.
D) protection.
E) aeration and a pathway for water uptake

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 105 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
Root hairs are:
A) flattened extensions of epidermal cells.
B) formed once in the area of cell maturation.
C) small in number.
D) located in front of the root tip.
E) short-lived.
A) flattened extensions of epidermal cells.
B) formed once in the area of cell maturation.
C) small in number.
D) located in front of the root tip.
E) short-lived.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 105 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
Minerals move into endodermal cells via:
A) osmosis.
B) simple diffusion.
C) facilitated diffusion.
D) aquaporins.
E) active transport.
A) osmosis.
B) simple diffusion.
C) facilitated diffusion.
D) aquaporins.
E) active transport.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 105 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
The center of a primary eudicot root is known as the:
A) phloem.
B) symplast.
C) cortex.
D) pericycle.
E) stele.
A) phloem.
B) symplast.
C) cortex.
D) pericycle.
E) stele.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 105 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
The thick layers of cells covering and protecting the delicate apical meristem is called the:
A) root cap.
B) root hairs.
C) pericycle.
D) adventitious root.
E) radicle.
A) root cap.
B) root hairs.
C) pericycle.
D) adventitious root.
E) radicle.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 105 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
Which of the following statements about the pericycle is false ?
A) It gives rise to branch roots.
B) It is a single layer of cells inside the endodermis.
C) It is composed of parenchyma cells.
D) Its cells lose their ability to divide upon maturation.
E) It is involved in the formation of lateral meristems.
A) It gives rise to branch roots.
B) It is a single layer of cells inside the endodermis.
C) It is composed of parenchyma cells.
D) Its cells lose their ability to divide upon maturation.
E) It is involved in the formation of lateral meristems.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 105 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
Which is the correct horizontal pathway of water from the soil to the center of the root?
A) Epidermis → root hair → cortex → pericycle → endodermis → xylem
B) Epidermis → cortex → pericycle → endodermis → phloem → xylem
C) Root hair → epidermis → cortex → endodermis → pericycle → xylem
D) Root hair → cortex → endodermis → pericycle → epidermis → xylem
E) Root hair → epidermis → endodermis → cortex → xylem → phloem
A) Epidermis → root hair → cortex → pericycle → endodermis → xylem
B) Epidermis → cortex → pericycle → endodermis → phloem → xylem
C) Root hair → epidermis → cortex → endodermis → pericycle → xylem
D) Root hair → cortex → endodermis → pericycle → epidermis → xylem
E) Root hair → epidermis → endodermis → cortex → xylem → phloem

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 105 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
Which statement with regard to pore spaces is false ?
A) Minerals are removed from soil via leaching.
B) Water is held in the smaller pores, and air is found in the larger pores.
C) They occupy approximately 50% of a soil's volume.
D) They typically contain more carbon dioxide than found in the atmosphere.
E) Immediately after a heavy rain, most pore spaces remain filled with air.
A) Minerals are removed from soil via leaching.
B) Water is held in the smaller pores, and air is found in the larger pores.
C) They occupy approximately 50% of a soil's volume.
D) They typically contain more carbon dioxide than found in the atmosphere.
E) Immediately after a heavy rain, most pore spaces remain filled with air.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 105 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
In low nitrogen soils, rhizobacteria secrete ____ to help root hairs recognize them.
A) cytokin
B) flavonoids
C) nod factors
D) calcium
E) water
A) cytokin
B) flavonoids
C) nod factors
D) calcium
E) water

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 105 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
What group of organisms secretes acids into soil?
A) Bacteria
B) Earthworms
C) Fungi
D) Lichens
E) Algae
A) Bacteria
B) Earthworms
C) Fungi
D) Lichens
E) Algae

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 105 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
Which of the following plants would have photosynthetic roots?
A) Palm trees
B) Orchids
C) Corn
D) Mangrove trees
E) Mistletoe
A) Palm trees
B) Orchids
C) Corn
D) Mangrove trees
E) Mistletoe

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 105 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
Water enters endodermal cells by _____ directly across the lipid and through integral membrane proteins called ____.
A) osmosis; aquaporins
B) countertransport; exchangers
C) osmosis; ATP pumps
D) active transport; ATP pumps
E) carrier-mediated transport; cotransporters
A) osmosis; aquaporins
B) countertransport; exchangers
C) osmosis; ATP pumps
D) active transport; ATP pumps
E) carrier-mediated transport; cotransporters

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 105 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
Plants connected by mycorrhizal fungi:
A) must be of the same species.
B) can only exchange carbon dioxide in one direction.
C) are an excellent example of a parasitic relationship.
D) compete for light.
E) exchange organic materials in both directions.
A) must be of the same species.
B) can only exchange carbon dioxide in one direction.
C) are an excellent example of a parasitic relationship.
D) compete for light.
E) exchange organic materials in both directions.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 105 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
Prop roots are more common in:
A) annuals.
B) eudicots.
C) monocots.
D) epiphytes.
E) parasitic plants.
A) annuals.
B) eudicots.
C) monocots.
D) epiphytes.
E) parasitic plants.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 105 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
Rhizobia take ____ from the air and convert it into ____.
A) N2; NH3
B) CO2; C6H12O6
C) O2; H2O
D) NH3; NO3
E) P; ATP
A) N2; NH3
B) CO2; C6H12O6
C) O2; H2O
D) NH3; NO3
E) P; ATP

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 105 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
In the establishment of rhizobia in a legume, infection threads are found in the:
A) stele.
B) cortex.
C) root hairs.
D) xylem.
E) phloem.
A) stele.
B) cortex.
C) root hairs.
D) xylem.
E) phloem.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 105 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
The most abundant organisms in soil are:
A) earthworms.
B) fungi.
C) algae.
D) protozoa.
E) bacteria.
A) earthworms.
B) fungi.
C) algae.
D) protozoa.
E) bacteria.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 105 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
Roots that arise from branches or vertical stems, and that are used to support a plant in an upright position, are referred to as:
A) prop roots.
B) contractile roots.
C) pneumatophores.
D) lateral roots.
E) tap roots.
A) prop roots.
B) contractile roots.
C) pneumatophores.
D) lateral roots.
E) tap roots.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 105 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
Figure 36-1 Use the figure to answer the corresponding question(s).
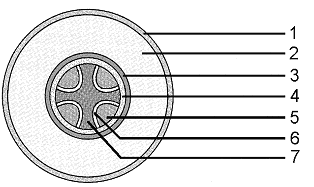
Refer to the accompanying figure. During the development of secondary vascular tissues, which of the following structures is replaced by periderm?
A) 1
B) 3
C) 5
D) 6
E) 7

Refer to the accompanying figure. During the development of secondary vascular tissues, which of the following structures is replaced by periderm?
A) 1
B) 3
C) 5
D) 6
E) 7

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 105 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
The partly decayed organic portion of soil is called:
A) silt.
B) clay.
C) sand.
D) humus.
E) castings.
A) silt.
B) clay.
C) sand.
D) humus.
E) castings.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 105 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
Plants that are adapted to growing in flooded soils that are depleted of oxygen have:
A) aerial roots.
B) contractile roots.
C) pneumatophores.
D) prop roots.
E) buttress roots.
A) aerial roots.
B) contractile roots.
C) pneumatophores.
D) prop roots.
E) buttress roots.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 105 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
Which list correctly orders soil particles in increasing diameter?
A) Clay, sand, silt
B) Clay, silt, sand
C) Silt, sand, clay
D) Silt, clay, sand
E) sand, silt, clay
A) Clay, sand, silt
B) Clay, silt, sand
C) Silt, sand, clay
D) Silt, clay, sand
E) sand, silt, clay

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 105 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
Which pair demonstrates a mutualistic relationship?
A) Orchid and its host
B) Rhizobia and strawberry plants
C) Soil fungus and soil bacteria
D) Mistletoe and its host
E) Mychorrhizae and roots
A) Orchid and its host
B) Rhizobia and strawberry plants
C) Soil fungus and soil bacteria
D) Mistletoe and its host
E) Mychorrhizae and roots

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 105 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
Figure 36-1 Use the figure to answer the corresponding question(s).
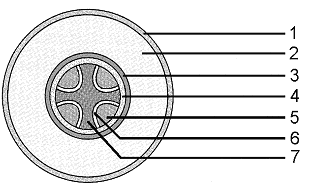
Refer to the accompanying figure. The endodermis is the structure labeled as:
A) 3
B) 4
C) 5
D) 6
E) 7

Refer to the accompanying figure. The endodermis is the structure labeled as:
A) 3
B) 4
C) 5
D) 6
E) 7

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 105 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
The ideal agricultural soil is:
A) loam.
B) silt.
C) sand.
D) clay.
E) dry.
A) loam.
B) silt.
C) sand.
D) clay.
E) dry.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 105 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
Epiphytes have ____ that anchor the plants to the surface on which they grow.
A) pneumatophores
B) buttress roots
C) prop roots
D) aerial roots
E) root hairs
A) pneumatophores
B) buttress roots
C) prop roots
D) aerial roots
E) root hairs

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 105 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
Which of the following statements about soil pH is true ?
A) Aluminum is more soluble at high pH.
B) Calcium phosphate becomes less soluble at low pH.
C) Acidic soil can be found in Pygmy forest in California.
D) Soils in Death Valley California are acidic.
E) Manganese is more soluble at low pH.
A) Aluminum is more soluble at high pH.
B) Calcium phosphate becomes less soluble at low pH.
C) Acidic soil can be found in Pygmy forest in California.
D) Soils in Death Valley California are acidic.
E) Manganese is more soluble at low pH.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 105 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
Cation exchange between soil particles and root hairs is the process in which:
A) protons are exchanged for positively charged mineral ions.
B) electrons are exchanged for positively charged mineral ions.
C) protons are exchanged for negatively charged mineral ions.
D) electrons are exchanged for negatively charged mineral ions.
E) water is exchanged for positively charged mineral ions.
A) protons are exchanged for positively charged mineral ions.
B) electrons are exchanged for positively charged mineral ions.
C) protons are exchanged for negatively charged mineral ions.
D) electrons are exchanged for negatively charged mineral ions.
E) water is exchanged for positively charged mineral ions.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 105 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
Which element is correctly matched with its major function in plants?
A) Phosphorus-alters membrane permeability
B) Sulfur-essential part of chlorophyll
C) Potassium-opens and closes stomata
D) Carbon-maintains turgidity of cells
E) Calcium-involved in nitrogen fixation
A) Phosphorus-alters membrane permeability
B) Sulfur-essential part of chlorophyll
C) Potassium-opens and closes stomata
D) Carbon-maintains turgidity of cells
E) Calcium-involved in nitrogen fixation

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 105 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
Which of the following statements about acid precipitation is false ?
A) It can decrease soil pH.
B) It is implicated in forest decline.
C) It drops sulfuric and nitric acids on the Earth.
D) It is caused by human activities.
E) It prevents the leaching of essential cations.
A) It can decrease soil pH.
B) It is implicated in forest decline.
C) It drops sulfuric and nitric acids on the Earth.
D) It is caused by human activities.
E) It prevents the leaching of essential cations.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 105 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
Which list of elements below is present in all biomolecules in plants?
A) Sulfur, silicon, and calcium
B) Oxygen, hydrogen, and carbon
C) Chlorine, iron, and zinc
D) Phosphorus, nitrogen, and carbon
E) Potassium, oxygen, and magnesium
A) Sulfur, silicon, and calcium
B) Oxygen, hydrogen, and carbon
C) Chlorine, iron, and zinc
D) Phosphorus, nitrogen, and carbon
E) Potassium, oxygen, and magnesium

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 105 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
While working in a soil-testing laboratory, you are given a sample of a "typical" soil to analyze. Which of the following do you correctly conclude is present in the largest amount?
A) Water
B) Inorganic mineral particles
C) Rocks
D) Air
E) Organic material
A) Water
B) Inorganic mineral particles
C) Rocks
D) Air
E) Organic material

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 105 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
Which element is a micronutrient in plants?
A) Chlorine
B) Hydrogen
C) Potassium
D) Calcium
E) Magnesium
A) Chlorine
B) Hydrogen
C) Potassium
D) Calcium
E) Magnesium

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 105 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
The water balance problem of plants living in salty soil is the result of:
A) water moving out of plant roots by osmosis.
B) extensive leaching.
C) a low soil pH.
D) low concentrations of micronutrients.
E) excessive run off.
A) water moving out of plant roots by osmosis.
B) extensive leaching.
C) a low soil pH.
D) low concentrations of micronutrients.
E) excessive run off.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 105 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
Which crops can be easily grown hydroponically?
A) Potatoes
B) Carrots
C) Corn
D) Lettuce
E) Zucchini
A) Potatoes
B) Carrots
C) Corn
D) Lettuce
E) Zucchini

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 105 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
What three elements are most often limiting factors for plant growth?
A) Carbon, potassium, and magnesium
B) Carbon, oxygen, and nitrogen
C) Hydrogen, magnesium, and oxygen
D) Sulfur, calcium, and nitrogen
E) Nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium
A) Carbon, potassium, and magnesium
B) Carbon, oxygen, and nitrogen
C) Hydrogen, magnesium, and oxygen
D) Sulfur, calcium, and nitrogen
E) Nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 105 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
The two major factors that contribute to the weathering of rock are climate and:
A) inorganic minerals.
B) atmospheric carbon dioxide.
C) organisms.
D) aeration.
E) atmospheric oxygen..
A) inorganic minerals.
B) atmospheric carbon dioxide.
C) organisms.
D) aeration.
E) atmospheric oxygen..

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 105 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
Explain how you would distinguish a monocot from a eudicot by looking at the anatomy of their roots.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 105 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
What are secondary tissues and how are they formed?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 105 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
Water, wind, and ice are agents of:
A) erosion.
B) decomposition.
C) mineralization.
D) salinization.
E) soil pH.
A) erosion.
B) decomposition.
C) mineralization.
D) salinization.
E) soil pH.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 105 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
Irrigation can cause salt to accumulate in the soil, a process known as:
A) erosion.
B) decomposition.
C) mineralization.
D) salinization.
E) weathering.
A) erosion.
B) decomposition.
C) mineralization.
D) salinization.
E) weathering.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 105 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
_______ and _____ are particularly effective in moving soil from one place to another.
A) Plants; wind
B) Water; acidic soil pH
C) Wind; temperature
D) Water: wind
E) Plants; water
A) Plants; wind
B) Water; acidic soil pH
C) Wind; temperature
D) Water: wind
E) Plants; water

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 105 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
Which element is a macronutrient in plants?
A) Sodium
B) Calcium
C) Manganese
D) Zinc
E) Copper
A) Sodium
B) Calcium
C) Manganese
D) Zinc
E) Copper

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 105 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
Figure 36-2
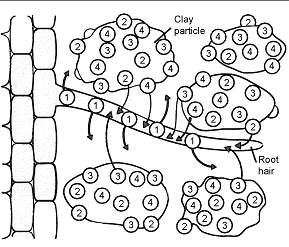
Refer to the accompanying figure. Absorption of positively charged mineral ions by the root is facilitated by the movement of:
A) clay particles into the root hair.
B) water into the root hair.
C) protons into the root hair.
D) protons out of the root hair.
E) Mg+ out of the root hair.

Refer to the accompanying figure. Absorption of positively charged mineral ions by the root is facilitated by the movement of:
A) clay particles into the root hair.
B) water into the root hair.
C) protons into the root hair.
D) protons out of the root hair.
E) Mg+ out of the root hair.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 105 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
Diagram and label a cross section of a primary eudicot root. Identify the function of three of the labeled tissues.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 105 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
The formation of soil by gradually breaking rock into smaller particles by biological, chemical, and physical processes is known as:
A) erosion.
B) inorganic synthesis.
C) cation exchange.
D) salinization.
E) weathering.
A) erosion.
B) inorganic synthesis.
C) cation exchange.
D) salinization.
E) weathering.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 105 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
Figure 36-2
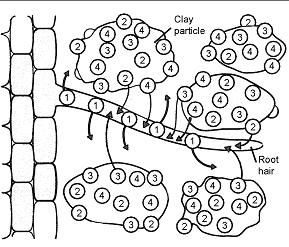
The process illustrated in the accompanying figure is known as:
A) humus formation.
B) weathering.
C) cation exchange.
D) soil erosion.
E) salinization.

The process illustrated in the accompanying figure is known as:
A) humus formation.
B) weathering.
C) cation exchange.
D) soil erosion.
E) salinization.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 105 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
Buttress roots help trees obtain oxygen from flooded soil.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 105 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
A root hair is an extension of an endodermal cell.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 105 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
The outermost layer of the stele is the pericycle.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 105 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
Water flowing inward through the endodermis moves next into the pericycle.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 105 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
The removal of dissolved materials from soil by percolating water is called illuviation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 105 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
The root cortex is composed mostly of collenchyma cells.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 105 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
Identify two plant macronutrients and two micronutrients and provide a physiological role for each.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 105 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
An example of a micronutrient is phosphorus.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 105 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
Hydroponics refers to the growing of plants in aerated water rather than soil.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 105 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
The nodules found in the roots of legumes characteristically contain mycorrhizae.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 105 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
In woody plants, the root epidermis is replaced by periderm.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 105 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72
Lateral roots arise from cells of the cortex.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 105 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73
The symplast is the continuum of living cytoplasm.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 105 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
74
Explain the process of soil formation by weathering.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 105 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
75
The roots of certain epiphytes are photosynthetic.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 105 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
76
An adventitious root is one that occurs in an unusual location.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 105 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
77
Root hair development is under the control of two genes that code for transcription factors.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 105 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
78
A typical soil is composed mostly of humus.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 105 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
79
Differentiate between the following specialized roots.
A. Prop root
B. Buttress root
C. Pneumatophore
D. Storage root
E. Photosynthetic root
A. Prop root
B. Buttress root
C. Pneumatophore
D. Storage root
E. Photosynthetic root

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 105 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
80
The portion of a mycorrhizal fungus that penetrates the cell walls of the root cortex is called an arbuscule.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 105 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



