Deck 40: Protection, Support, and Movement
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Match between columns
Question
Question
Match between columns
Question
Match between columns
Question
Question
Question
Match between columns
Question
Question
Question
Question
Match between columns
Question
Match between columns
Question
Question
Match between columns
Question
Match between columns

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/75
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 40: Protection, Support, and Movement
1
Figure 40-3
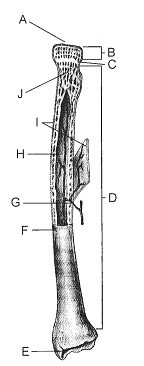
Refer to the accompanying figure. In which portion of the bone is fat stored?
A) B
B) C
C) J
D) H
E) I

Refer to the accompanying figure. In which portion of the bone is fat stored?
A) B
B) C
C) J
D) H
E) I
D
2
What is the major difference between the endoskeleton and the exoskeleton?
A) The endoskeleton is capable of growth.
B) The endoskeleton permits movement.
C) The endoskeleton contains calcium.
D) The endoskeleton is molted more frequently.
E) The endoskeleton provides support.
A) The endoskeleton is capable of growth.
B) The endoskeleton permits movement.
C) The endoskeleton contains calcium.
D) The endoskeleton is molted more frequently.
E) The endoskeleton provides support.
A
3
Figure 40-3
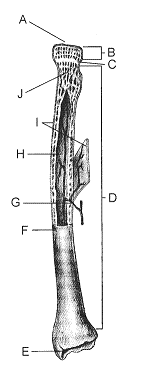
The portion of the bone labeled E in the accompanying figure is called the
A) periosteum.
B) diaphysis.
C) epiphysis.
D) articular cartilage.
E) metaphysis.

The portion of the bone labeled E in the accompanying figure is called the
A) periosteum.
B) diaphysis.
C) epiphysis.
D) articular cartilage.
E) metaphysis.
D
4
Figure 40-1
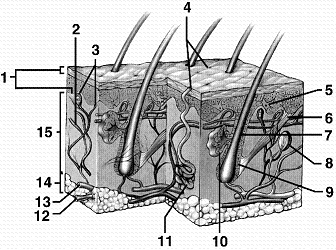
Refer to the accompanying figure. Which structure is the source of sebum, a substance that inhibits bacterial growth on the surface of the skin?
A) 5
B) 7
C) 10
D) 11
E) 12

Refer to the accompanying figure. Which structure is the source of sebum, a substance that inhibits bacterial growth on the surface of the skin?
A) 5
B) 7
C) 10
D) 11
E) 12

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
The difference between spongy bone and compact bone is that spongy bone
A) is found near the surfaces of bone, while compact bone is found interiorly.
B) consists of osteons, while the compact consists of thin strands of bone.
C) is filled with red bone marrow, while compact bone is not
D) occupies the diaphysis, while compact bone occupies the epiphysis.
E) is involved in bone development, while compact bone is not.
A) is found near the surfaces of bone, while compact bone is found interiorly.
B) consists of osteons, while the compact consists of thin strands of bone.
C) is filled with red bone marrow, while compact bone is not
D) occupies the diaphysis, while compact bone occupies the epiphysis.
E) is involved in bone development, while compact bone is not.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
Figure 40-1
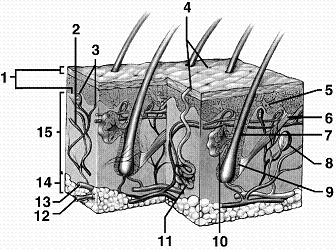
Refer to the accompanying figure. Which region of the skin insulates the body from outside temperature extremes?
A) 1
B) 10
C) 11
D) 14
E) 15

Refer to the accompanying figure. Which region of the skin insulates the body from outside temperature extremes?
A) 1
B) 10
C) 11
D) 14
E) 15

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
The condition that is characterized by a loss of calcium from the bone is called
A) osteitis.
B) osteoporosis.
C) osteopenia.
D) osteoarthritis.
E) osteon disease.
A) osteitis.
B) osteoporosis.
C) osteopenia.
D) osteoarthritis.
E) osteon disease.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
A major function of keratin is to
A) absorb UV radiation.
B) insulate the body.
C) nourish sensory receptors.
D) synthesize fats and waxes.
E) create a diffusion barrier.
A) absorb UV radiation.
B) insulate the body.
C) nourish sensory receptors.
D) synthesize fats and waxes.
E) create a diffusion barrier.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
Figure 40-3
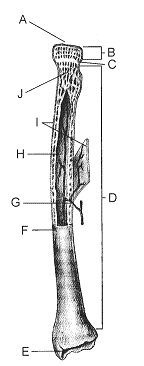
In the accompanying figure, the function of the structure labeled C, particularly in small children, is to
A) produce blood cells.
B) act as a growth center.
C) provide mechanical strength.
D) serve as an attachment site for tendons.
E) nourish the bone tissue.

In the accompanying figure, the function of the structure labeled C, particularly in small children, is to
A) produce blood cells.
B) act as a growth center.
C) provide mechanical strength.
D) serve as an attachment site for tendons.
E) nourish the bone tissue.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
Which process is a specialized function carried out by epithelial tissue?
A) Exchange of gases
B) Production of hormones
C) Regulation of heart rate
D) Facilitation of muscle contraction
E) Insulation of nerve fibers
A) Exchange of gases
B) Production of hormones
C) Regulation of heart rate
D) Facilitation of muscle contraction
E) Insulation of nerve fibers

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
Adipose tissue is found in which layer of the skin?
A) Epidermis
B) Dermis
C) Subcutaneous tissue
D) Stratum basale
E) Stratum corneum
A) Epidermis
B) Dermis
C) Subcutaneous tissue
D) Stratum basale
E) Stratum corneum

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
Which class of bones is part of the appendicular skeletal division?
A) Skull
B) Vertebral column
C) Ribs
D) Pelvis
E) Sternum
A) Skull
B) Vertebral column
C) Ribs
D) Pelvis
E) Sternum

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
The components of the pectoral girdle are
A) three fused hipbones.
B) the clavicles and the scapula.
C) the ribs and the clavicles.
D) the ribs and the sternum.
E) the ribs and the digits.
A) three fused hipbones.
B) the clavicles and the scapula.
C) the ribs and the clavicles.
D) the ribs and the sternum.
E) the ribs and the digits.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
Large, multinucleate cells that break down bone are called
A) osteoblasts.
B) chondrocytes.
C) osteocytes.
D) chondroblasts.
E) osteoclasts.
A) osteoblasts.
B) chondrocytes.
C) osteocytes.
D) chondroblasts.
E) osteoclasts.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
When the ______ cannot absorb all the UV rays, the skin becomes ______.
A) Melatonin; suntanned
B) melanin; suntanned
C) melanin; sunburned
D) melatonin; sunburned
E) melanin; cancerous
A) Melatonin; suntanned
B) melanin; suntanned
C) melanin; sunburned
D) melatonin; sunburned
E) melanin; cancerous

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
Figure 40-1
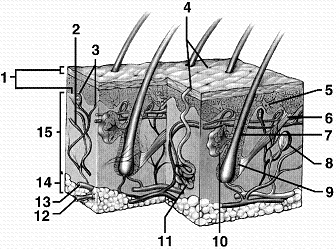
Refer to the accompanying figure. Which region of the skin is composed mainly of collagen fibers?
A) 1
B) 6
C) 11
D) 14
E) 15

Refer to the accompanying figure. Which region of the skin is composed mainly of collagen fibers?
A) 1
B) 6
C) 11
D) 14
E) 15

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
Figure 40-3
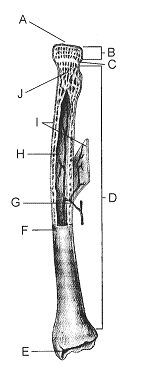
The portion of the bone labeled I in the accompanying figure is called the
A) periosteum.
B) lacunae.
C) epiphysis.
D) osteon.
E) metaphysis.

The portion of the bone labeled I in the accompanying figure is called the
A) periosteum.
B) lacunae.
C) epiphysis.
D) osteon.
E) metaphysis.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
Which of the following groups of vertebrae is located farthest from the head?
A) Sacral
B) Thoracic
C) Cervical
D) Coccygeal
E) Cranial
A) Sacral
B) Thoracic
C) Cervical
D) Coccygeal
E) Cranial

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
People who undergo radiation therapy sometimes develop anemia resulting from a decreased production of red blood cells. This is because radiation affects
A) spongy bone.
B) osteoblasts.
C) osteoclasts.
D) lacunae.
E) metaphysis.
A) spongy bone.
B) osteoblasts.
C) osteoclasts.
D) lacunae.
E) metaphysis.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
Figure 40-1
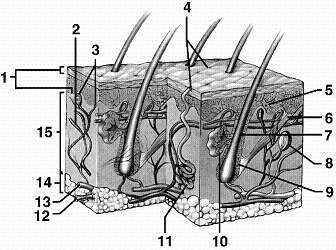
Refer to the accompanying figure. Which structure of the skin represents the sweat gland?
A) 1
B) 6
C) 11
D) 14
E) 15

Refer to the accompanying figure. Which structure of the skin represents the sweat gland?
A) 1
B) 6
C) 11
D) 14
E) 15

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
To begin the actual contraction, calcium ions must first bind to ____ in the muscle cell.
A) actin
B) myosin
C) troponin
D) sarcoplasmic reticulum
E) T tubules
A) actin
B) myosin
C) troponin
D) sarcoplasmic reticulum
E) T tubules

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
What is the primary cause of the symptoms associated with rheumatoid arthritis?
A) Degeneration of osteoblasts
B) Degeneration of osteoclasts
C) Accumulation of synovial fluid
D) Accumulation of articular cartilage
E) Thickening of bone tissue
A) Degeneration of osteoblasts
B) Degeneration of osteoclasts
C) Accumulation of synovial fluid
D) Accumulation of articular cartilage
E) Thickening of bone tissue

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
The immediate source of energy for muscle contraction is ____.
A) ATP
B) Creatine phosphate
C) Glycogen
D) Lactic acid
E) Carbon monoxide
A) ATP
B) Creatine phosphate
C) Glycogen
D) Lactic acid
E) Carbon monoxide

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
Which process is an example of a function carried out by the skeletal system?
A) Transmission of mechanical forces
B) Conduction of nerve impulses
C) Regulation of body temperature
D) Transportation of hemoglobin
E) Contraction of muscle fibers
A) Transmission of mechanical forces
B) Conduction of nerve impulses
C) Regulation of body temperature
D) Transportation of hemoglobin
E) Contraction of muscle fibers

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
The function of synovial fluid is to
A) store calcium.
B) reduce friction.
C) produce marrow.
D) carry nutrients.
E) resorb bone.
A) store calcium.
B) reduce friction.
C) produce marrow.
D) carry nutrients.
E) resorb bone.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
Figure 40-2
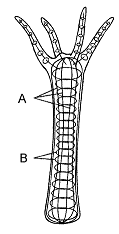
The type of support illustrated in the accompanying figure is a(n)
A) hydrostatic skeleton.
B) exoskeleton.
C) integumentary system.
D) epidermal skeleton.
E) endoskeleton.

The type of support illustrated in the accompanying figure is a(n)
A) hydrostatic skeleton.
B) exoskeleton.
C) integumentary system.
D) epidermal skeleton.
E) endoskeleton.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
Helena's doctor has advised her to take calcium supplements to help prevent
A) osteitis.
B) osteoporosis.
C) osteopenia.
D) osteoarthritis.
E) osteon disease.
A) osteitis.
B) osteoporosis.
C) osteopenia.
D) osteoarthritis.
E) osteon disease.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
Bands of fibrous connective tissue that connect bones and limit movement at the joint are called ____.
A) tendons
B) ligaments
C) sutures
D) osteobands
E) cartilage
A) tendons
B) ligaments
C) sutures
D) osteobands
E) cartilage

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
Figure 40-4 Use the figure to answer the corresponding question(s).
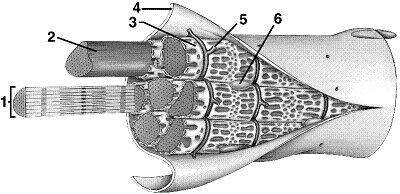
Refer to the accompanying figure. In which part of the muscle fiber are calcium ions stored?
A) 2
B) 3
C) 4
D) 5
E) 6

Refer to the accompanying figure. In which part of the muscle fiber are calcium ions stored?
A) 2
B) 3
C) 4
D) 5
E) 6

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
Most joints found in the human body are
A) synovial.
B) immovable.
C) slightly movable.
D) freely movable.
E) cartilaginous.
A) synovial.
B) immovable.
C) slightly movable.
D) freely movable.
E) cartilaginous.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
What is the correct order of events that occur during muscle contraction? 1) Muscle shortens
2) Calcium binds to troponin
3) Filaments slide
4) T tubules are depolarized
5) Acetylcholine is released
6) ATP molecule is split
A) 4 → 5 → 2 → 1 → 3 → 6
B) 4 → 2 → 5 → 6 → 1 → 3
C) 5 → 2 → 4 → 1 → 6 → 3
D) 6 → 2 → 5 → 4 → 3 → 1
E) 5 → 4 → 2 → 6 → 3 → 1
2) Calcium binds to troponin
3) Filaments slide
4) T tubules are depolarized
5) Acetylcholine is released
6) ATP molecule is split
A) 4 → 5 → 2 → 1 → 3 → 6
B) 4 → 2 → 5 → 6 → 1 → 3
C) 5 → 2 → 4 → 1 → 6 → 3
D) 6 → 2 → 5 → 4 → 3 → 1
E) 5 → 4 → 2 → 6 → 3 → 1

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
Figure 40-4 Use the figure to answer the corresponding question(s).
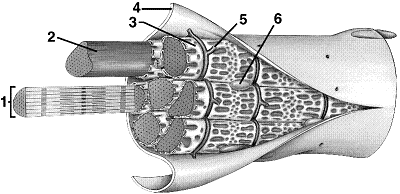
Refer to the accompanying figure. An action potential spreads and triggers Ca2+ release through the structure labeled as
A) 2
B) 3
C) 4
D) 5
E) 6

Refer to the accompanying figure. An action potential spreads and triggers Ca2+ release through the structure labeled as
A) 2
B) 3
C) 4
D) 5
E) 6

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
The condition that is characterized by loss of bone mineral is called
A) osteitis.
B) osteoporosis.
C) osteopenia.
D) osteoarthritis.
E) osteon disease.
A) osteitis.
B) osteoporosis.
C) osteopenia.
D) osteoarthritis.
E) osteon disease.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
Why are delicate movements difficult in a hydrostatic skeleton?
A) Force tends to be transmitted equally in all directions throughout the entire fluid-filled body of the animal.
B) Force tends to be transmitted anteriorly in fluid-filled body of the animal.
C) Force tends to be transmitted posteriorly in fluid-filled body of the animal.
D) Force tends to be transmitted radially in fluid-filled body of the animal.
E) Force tends to be transmitted ventrally in fluid-filled body of the animal.
A) Force tends to be transmitted equally in all directions throughout the entire fluid-filled body of the animal.
B) Force tends to be transmitted anteriorly in fluid-filled body of the animal.
C) Force tends to be transmitted posteriorly in fluid-filled body of the animal.
D) Force tends to be transmitted radially in fluid-filled body of the animal.
E) Force tends to be transmitted ventrally in fluid-filled body of the animal.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
Muscles act _____ to one another, which means that the movement produced by one can be reversed by another.
A) agonistically
B) retroactively
C) proactively
D) antagonistically
E) acrimoniously
A) agonistically
B) retroactively
C) proactively
D) antagonistically
E) acrimoniously

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
Troponin and tropomyosin regulate
A) calcium storage and release.
B) actin and myosin interactions.
C) action potential transmission.
D) acetylcholine storage and release.
E) rate of muscle fiber division.
A) calcium storage and release.
B) actin and myosin interactions.
C) action potential transmission.
D) acetylcholine storage and release.
E) rate of muscle fiber division.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
The basic unit of muscle contraction is known as the
A) sarcoplasmic reticulum.
B) transverse tubule.
C) sarcomere.
D) sarcolemma.
E) motor unit.
A) sarcoplasmic reticulum.
B) transverse tubule.
C) sarcomere.
D) sarcolemma.
E) motor unit.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
What is a disadvantage of the exoskeleton?
A) It cannot be replaced if damaged.
B) It must be shed to accommodate growth.
C) It is easily penetrated by predators.
D) It requires high ATP levels for continuous growth.
E) It does not permit movement of the organism.
A) It cannot be replaced if damaged.
B) It must be shed to accommodate growth.
C) It is easily penetrated by predators.
D) It requires high ATP levels for continuous growth.
E) It does not permit movement of the organism.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
Figure 40-2
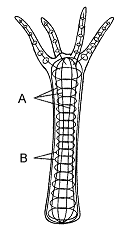
Contraction of the fibers labeled A in the accompanying figure results in
A) elongation of the body.
B) elongation of the tentacles.
C) elongation of the gastrovascular cavity.
D) shortening of the body.
E) expansion of the pedal disk.

Contraction of the fibers labeled A in the accompanying figure results in
A) elongation of the body.
B) elongation of the tentacles.
C) elongation of the gastrovascular cavity.
D) shortening of the body.
E) expansion of the pedal disk.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
Generally, movements are accomplished by
A) a single muscle exerting a pulling force only.
B) a single muscle exerting a pushing force only.
C) groups of muscles opposing the actions of one another.
D) groups of muscles collectively exerting pulling forces only.
E) groups of muscles collectively exerting pushing forces only.
A) a single muscle exerting a pulling force only.
B) a single muscle exerting a pushing force only.
C) groups of muscles opposing the actions of one another.
D) groups of muscles collectively exerting pulling forces only.
E) groups of muscles collectively exerting pushing forces only.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
The exoskeleton of arthropods is composed of chitin.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
How is the structure of insect flight muscles adapted to their function?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
The collagen fibers in bone are secreted by osteoblasts.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
Calcium ions are stored in the sarcoplasmic reticulum.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
Describe the three major types of skeletal muscle fibers found in vertebrates.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
The repeating units of muscle contraction are called myofibrils.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
Keratin is a mixture of fats and waxes that inhibits growth of harmful bacteria.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
The axial skeleton of vertebrates consists of the bones of the limbs, the pectoral girdle, and most of the pelvic girdle.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
The Z line consists of parts of actin filaments on two adjacent sarcomeres.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
The deepest layer of the epidermis is the stratum corneum.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
Identify the two main divisions of the vertebrate skeleton and identify the bones that are representative of each division.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
Joint capsules are typically reinforced by ligaments.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
How does smooth muscle differ from skeletal muscle?
A) Smooth muscle attaches to bones via tendons.
B) Smooth muscle has a striated appearance.
C) Smooth muscle undergoes quick contractions.
D) Smooth muscles are connected via gap junctions.
E) Smooth muscle cross bridges form transiently.
A) Smooth muscle attaches to bones via tendons.
B) Smooth muscle has a striated appearance.
C) Smooth muscle undergoes quick contractions.
D) Smooth muscles are connected via gap junctions.
E) Smooth muscle cross bridges form transiently.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
The body of a cnidarian is supported by a hydrostatic skeleton.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
Many insects must warm up before they fly in order to
A) generate hemolymph.
B) increase ATP synthesis.
C) enhance gas exchange.
D) elevate actin synthesis.
E) diminish muscle rigidity.
A) generate hemolymph.
B) increase ATP synthesis.
C) enhance gas exchange.
D) elevate actin synthesis.
E) diminish muscle rigidity.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
The main shaft of a long bone is known as the epiphysis.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
Endoskeletons are shed in the process of ecdysis.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
The breast muscle of geese have ____, while those of chickens have _____.
A) white fibers; red fibers
B) slow-oxidative fibers; fast-glycolytic fibers
C) red fibers; fast-oxidative fibers
D) red fibers; slow-oxidative fibers
E) slow-oxidative fibers; fast-oxidative fibers
A) white fibers; red fibers
B) slow-oxidative fibers; fast-glycolytic fibers
C) red fibers; fast-oxidative fibers
D) red fibers; slow-oxidative fibers
E) slow-oxidative fibers; fast-oxidative fibers

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
A smooth, sustained contraction of skeletal muscle is called a
A) simple twitch.
B) tetanus.
C) pulse contraction.
D) red fiber contraction.
E) white fiber contraction.
A) simple twitch.
B) tetanus.
C) pulse contraction.
D) red fiber contraction.
E) white fiber contraction.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
The plasma membrane of a muscle fiber is called the sarcolemma.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
Match between columns

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
When a motor neuron transmits a message, it releases the neurotransmitter serotonin.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
Match between columns

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
Match between columns

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
Cardiac muscle fibers are electrically coupled by junctions called intercalated discs.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
Explain why rigor mortis occurs following death.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
Match between columns

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
During the process of muscle contraction, Ca2+ binds tropomyosin.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
Briefly describe the sequence of events that take place in muscle contraction.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
Compare and contrast the function of the external epithelium and its derivatives in invertebrates and vertebrates.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
Match between columns

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72
Match between columns

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73
What are joints? Describe the main types of vertebrate joints and provide examples.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
74
Match between columns

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
75
Match between columns

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



