Deck 41: Neural Signaling
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Match between columns
Question
Match between columns
Question
Match between columns
Question
Match between columns
Question
Match between columns
Question
Match between columns
Question
Match between columns
Question
Match between columns
Question
Question
Question
Match between columns
Question
Match between columns
Question
Question
Match between columns
Question
Match between columns
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/76
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 41: Neural Signaling
1
Figure 41-1
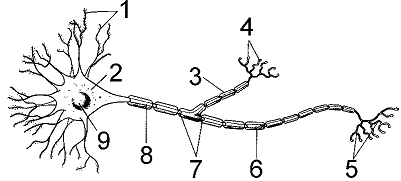
An axon smaller than approximately what diameter is generally unmyelinated?
A) 20 m m
B) 2 m m
C) 200 nm
D) 20 nm
E) 2 nm

An axon smaller than approximately what diameter is generally unmyelinated?
A) 20 m m
B) 2 m m
C) 200 nm
D) 20 nm
E) 2 nm
B
2
Figure 41-1
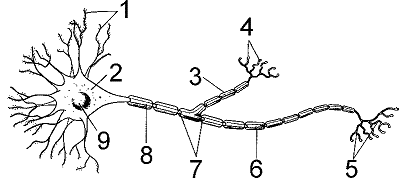
Refer to the accompanying figure. What is the function of the structure labeled as 4?
A) To insulate the axon
B) To release neurotransmitters
C) To synthesize cell body organelles
D) To receive inputs from other neurons
E) To send retrograde signals to the cell body

Refer to the accompanying figure. What is the function of the structure labeled as 4?
A) To insulate the axon
B) To release neurotransmitters
C) To synthesize cell body organelles
D) To receive inputs from other neurons
E) To send retrograde signals to the cell body
B
3
Which of the following is a correct statement regarding the patch clamp technique?
A) The membrane attached to the pipet tip generally contains multiple ion channels.
B) Ion flow cannot be measured.
C) The current flow is constant.
D) The current flow corresponds to opening and closing of the ion channel.
E) The permeability of the channel does not affect the magnitude of the current.
A) The membrane attached to the pipet tip generally contains multiple ion channels.
B) Ion flow cannot be measured.
C) The current flow is constant.
D) The current flow corresponds to opening and closing of the ion channel.
E) The permeability of the channel does not affect the magnitude of the current.
A
4
Which of the following statements about the speed of impulse conduction in a neuron is true?
A) Longer axons can transmit impulses faster than shorter ones.
B) Unmyelinated axons transmit impulses faster than myelinated ones.
C) Shorter axons can transmit impulses faster than longer ones.
D) Nerve impulses travel faster than the speed of light.
E) Unmyelinated axons with larger diameters transmit impulses faster than ones with small diameters.
A) Longer axons can transmit impulses faster than shorter ones.
B) Unmyelinated axons transmit impulses faster than myelinated ones.
C) Shorter axons can transmit impulses faster than longer ones.
D) Nerve impulses travel faster than the speed of light.
E) Unmyelinated axons with larger diameters transmit impulses faster than ones with small diameters.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
Figure 41-2
Which of the following is an INCORRECT characterization of a graded potential?
A) An altered potential in a relatively small region of the plasma membrane
B) Functions as a signal over a very short distance
C) Potential charge varies depending on the strength of the stimulus applied
D) A large stimulus causes a larger change in permeability
E) Is indicative of a serious disease

Which of the following is an INCORRECT characterization of a graded potential?
A) An altered potential in a relatively small region of the plasma membrane
B) Functions as a signal over a very short distance
C) Potential charge varies depending on the strength of the stimulus applied
D) A large stimulus causes a larger change in permeability
E) Is indicative of a serious disease

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
Which neurons integrate information coming into and out of the central nervous system?
A) Afferent neurons
B) Motor neurons
C) Interneurons
D) Efferent neurons
E) Sensory neurons
A) Afferent neurons
B) Motor neurons
C) Interneurons
D) Efferent neurons
E) Sensory neurons

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
The myelin sheath:
A) is a protein covering around dendrites.
B) is responsible for integrating information.
C) is a fatty covering only around axons.
D) stores neurotransmitters in the axon.
E) is a fatty covering only around cell bodies.
A) is a protein covering around dendrites.
B) is responsible for integrating information.
C) is a fatty covering only around axons.
D) stores neurotransmitters in the axon.
E) is a fatty covering only around cell bodies.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
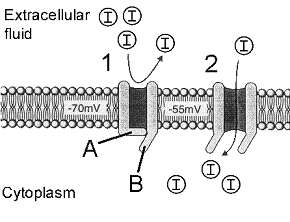
8
Figure 41-2
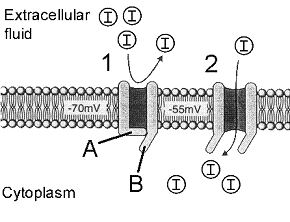
The accompanying figure represents a sequence of events occurring in the neuronal membrane (designated by the numbers 1 and 2). The letter "I" indicates an ion. What event is mostly likely being portrayed in this figure?
A) Activation of voltage-gated sodium channels
B) Activation of voltage-gated potassium channels
C) Activation of voltage-gated chloride channels
D) Activation of sodium-chloride pumps
E) Activation of sodium-potassium pumps

The accompanying figure represents a sequence of events occurring in the neuronal membrane (designated by the numbers 1 and 2). The letter "I" indicates an ion. What event is mostly likely being portrayed in this figure?
A) Activation of voltage-gated sodium channels
B) Activation of voltage-gated potassium channels
C) Activation of voltage-gated chloride channels
D) Activation of sodium-chloride pumps
E) Activation of sodium-potassium pumps

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
Figure 41-2
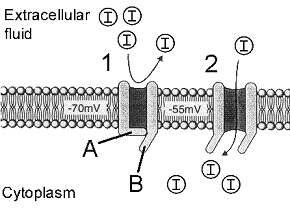
Refer to the accompanying figure. What structure is designated by label B?
A) Activation gate
B) Inactivation gate
C) Modulatory sensor
D) Transport pump
E) Transport sensor

Refer to the accompanying figure. What structure is designated by label B?
A) Activation gate
B) Inactivation gate
C) Modulatory sensor
D) Transport pump
E) Transport sensor

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
Saltatory conduction:
A) does not involve voltage-activated potassium ion channels.
B) can occur in both myelinated and unmyelinated neurons.
C) is slightly slower than continuous conduction.
D) is more energy efficient than continuous conduction.
E) allows nerve impulses to jump from Schwann cell to Schwann cell.
A) does not involve voltage-activated potassium ion channels.
B) can occur in both myelinated and unmyelinated neurons.
C) is slightly slower than continuous conduction.
D) is more energy efficient than continuous conduction.
E) allows nerve impulses to jump from Schwann cell to Schwann cell.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
What axonal characteristic facilitates the propagation of an action potential along a myelinated axon?
A) Voltage-gated Na+ and K+ channels are concentrated in the myelinated axonal segments.
B) Voltage-gated Na+ and K+ channels are concentrated in the unmyelinated axonal segments.
C) Voltage-gated Na+ channels are concentrated in the myelinated axonal segments; voltage-gated K+ channels are concentrated in the unmyelinated axonal segments.
D) Voltage-gated K+ channels are concentrated in the myelinated axonal segments; voltage-gated Na+ channels are concentrated in the unmyelinated axonal segments.
E) Voltage-gated Na+ K+ channels are spread evenly throughout both myelinated and unmyelinated segments.
A) Voltage-gated Na+ and K+ channels are concentrated in the myelinated axonal segments.
B) Voltage-gated Na+ and K+ channels are concentrated in the unmyelinated axonal segments.
C) Voltage-gated Na+ channels are concentrated in the myelinated axonal segments; voltage-gated K+ channels are concentrated in the unmyelinated axonal segments.
D) Voltage-gated K+ channels are concentrated in the myelinated axonal segments; voltage-gated Na+ channels are concentrated in the unmyelinated axonal segments.
E) Voltage-gated Na+ K+ channels are spread evenly throughout both myelinated and unmyelinated segments.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
Figure 41-1
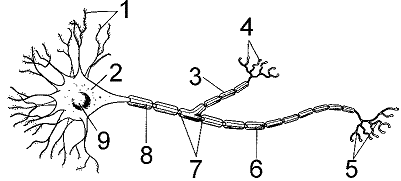
Refer to the accompanying figure. Which structure integrates incoming signals?
A) 2
B) 4
C) 5
D) 6
E) 8

Refer to the accompanying figure. Which structure integrates incoming signals?
A) 2
B) 4
C) 5
D) 6
E) 8

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
Which of the following are typically short, highly branched processes specialized to receive stimuli and send signals to the nerve cell body?
A) Dendrites
B) Axons
C) Schwann cells
D) Myelin sheath
E) Nodes of Ranvier
A) Dendrites
B) Axons
C) Schwann cells
D) Myelin sheath
E) Nodes of Ranvier

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
Which neural signaling process is correctly paired with its function?
A) Integration: sort and interpret sensory information
B) Reception: sort and interpret sensory information
C) Transmission: sort and interpret sensory information
D) Integration: detect a stimulus
E) Transmission: detect a stimulus
A) Integration: sort and interpret sensory information
B) Reception: sort and interpret sensory information
C) Transmission: sort and interpret sensory information
D) Integration: detect a stimulus
E) Transmission: detect a stimulus

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
What happens when the membrane potential of a neuron reaches the threshold level?
A) Voltage-gated sodium channels open, and sodium diffuses out of the cell.
B) Voltage-gated potassium channels open for a very brief period.
C) Voltage-gated sodium channels close, so sodium cannot diffuse out of the cell.
D) The sodium channel protein changes its shape to open the gates of the channel.
E) The membrane potential is more negative than when at rest.
A) Voltage-gated sodium channels open, and sodium diffuses out of the cell.
B) Voltage-gated potassium channels open for a very brief period.
C) Voltage-gated sodium channels close, so sodium cannot diffuse out of the cell.
D) The sodium channel protein changes its shape to open the gates of the channel.
E) The membrane potential is more negative than when at rest.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
Neural signaling typically involves four processes. What is the correct order of those processes?
A) Integration, reception, action by effectors, and transmission
B) Reception, transmission, integration, and action by effectors
C) Integration, transmission, reception, and action by effectors
D) Action by effectors, transmission, integration, and reception
E) Reception, integration, action by effectors, and transmission
A) Integration, reception, action by effectors, and transmission
B) Reception, transmission, integration, and action by effectors
C) Integration, transmission, reception, and action by effectors
D) Action by effectors, transmission, integration, and reception
E) Reception, integration, action by effectors, and transmission

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
Which of the following is a neuronal attribute that contributes to the resting membrane potential?
A) Potassium is kept at a high concentration outside the cell compared with the inside.
B) Sodium is kept at a high concentration inside the cell compared with the outside.
C) Neurons are more permeable to sodium than they are to potassium.
D) The cytosol contains large molecules that have a net positive charge.
E) The cytosol contains large molecules that have a net negative charge.
A) Potassium is kept at a high concentration outside the cell compared with the inside.
B) Sodium is kept at a high concentration inside the cell compared with the outside.
C) Neurons are more permeable to sodium than they are to potassium.
D) The cytosol contains large molecules that have a net positive charge.
E) The cytosol contains large molecules that have a net negative charge.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
In multiple sclerosis, a patient:
A) loses coordination due to the replacement of myelin with scar tissue.
B) accumulates neurofibrillary tangles in the brain resulting in dementia.
C) suffers tremors due to overly rapid and spontaneous firing of neural impulses.
D) loses the ability to move because of motor neuron degeneration.
E) suffers depression due to abnormal secretion of neurotransmitters.
A) loses coordination due to the replacement of myelin with scar tissue.
B) accumulates neurofibrillary tangles in the brain resulting in dementia.
C) suffers tremors due to overly rapid and spontaneous firing of neural impulses.
D) loses the ability to move because of motor neuron degeneration.
E) suffers depression due to abnormal secretion of neurotransmitters.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
The function of the sodium-potassium pump is to actively move:
A) sodium into the cell and potassium out of the cell.
B) sodium out of the cell and potassium into the cell.
C) sodium out of the cell and to block potassium movement.
D) both sodium and potassium out of the cell.
E) both sodium and potassium into the cell.
A) sodium into the cell and potassium out of the cell.
B) sodium out of the cell and potassium into the cell.
C) sodium out of the cell and to block potassium movement.
D) both sodium and potassium out of the cell.
E) both sodium and potassium into the cell.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
Figure 41-1
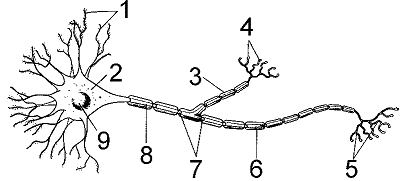
Refer to the accompanying figure. The absence of structures represented by label 6 would result in:
A) increased speed of impulse transmission.
B) decreased speed of impulse transmission.
C) enhanced saltatory conduction.
D) complete loss of impulse transmission.
E) complete loss of neurotransmitter release.

Refer to the accompanying figure. The absence of structures represented by label 6 would result in:
A) increased speed of impulse transmission.
B) decreased speed of impulse transmission.
C) enhanced saltatory conduction.
D) complete loss of impulse transmission.
E) complete loss of neurotransmitter release.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
In a neuron, a graded potential:
A) does not vary in magnitude.
B) becomes stronger as it propagates.
C) only generates slow action potentials.
D) fades out within a few millimeters.
E) propagates only along unmyelinated axons.
A) does not vary in magnitude.
B) becomes stronger as it propagates.
C) only generates slow action potentials.
D) fades out within a few millimeters.
E) propagates only along unmyelinated axons.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
Many neurotransmitter receptors are chemically activated ion channels known as:
A) ligand-gated channels.
B) metabotropic channels.
C) voltage-gated channels.
D) G protein-coupled channels.
E) neurotransmitter-selective channels.
A) ligand-gated channels.
B) metabotropic channels.
C) voltage-gated channels.
D) G protein-coupled channels.
E) neurotransmitter-selective channels.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
In Alzheimer's disease, neurons that secrete which neurotransmitter are particularly affected?
A) Epinephrine
B) Dopamine
C) Serotonin
D) Acetylcholine
E) GABA
A) Epinephrine
B) Dopamine
C) Serotonin
D) Acetylcholine
E) GABA

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
Which molecule is the major excitatory neurotransmitter in the brain?
A) GABA
B) Glutamate
C) Serotonin
D) Dopamine
E) Acetylcholine
A) GABA
B) Glutamate
C) Serotonin
D) Dopamine
E) Acetylcholine

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
Which of the following is a characteristic of the all-or-none response?
A) If a stimulus is strong enough, all axons in a nerve bundle will fire simultaneously.
B) A neuron will only produce an action potential if it has been depolarized to its threshold level.
C) All neurons of a nerve bundle discharge impulses at the same frequency.
D) A neuron can create an action potential of varying intensities.
E) Either all or none of the neurons of a brain region will fire impulses when stimulated.
A) If a stimulus is strong enough, all axons in a nerve bundle will fire simultaneously.
B) A neuron will only produce an action potential if it has been depolarized to its threshold level.
C) All neurons of a nerve bundle discharge impulses at the same frequency.
D) A neuron can create an action potential of varying intensities.
E) Either all or none of the neurons of a brain region will fire impulses when stimulated.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
THC, the main psychoactive ingredient of cannabis, decreases release of which of the following neurotransmitters?
A) Glutamate
B) Dopamine
C) Norepinephrine
D) "Substance P"
E) Nitric oxide
A) Glutamate
B) Dopamine
C) Norepinephrine
D) "Substance P"
E) Nitric oxide

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
Which molecule acts as a retrograde messenger at many synapses?
A) GABA
B) Glycine
C) Serotonin
D) Substance P
E) Nitric oxide
A) GABA
B) Glycine
C) Serotonin
D) Substance P
E) Nitric oxide

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
The resting potential of a neuron results from a:
A) neutral charge in the cytosolic and extracellular fluids.
B) negative cytosolic charge relative to the extracellular fluid.
C) positive cytosolic charge relative to the extracellular fluid.
D) fluctuating cytosolic charge and constant extracellular charge.
E) constant cytosolic charge and fluctuating extracellular charge.
A) neutral charge in the cytosolic and extracellular fluids.
B) negative cytosolic charge relative to the extracellular fluid.
C) positive cytosolic charge relative to the extracellular fluid.
D) fluctuating cytosolic charge and constant extracellular charge.
E) constant cytosolic charge and fluctuating extracellular charge.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
Which of the following has giant unmyelinated axons, up to 1 mm in diameter, that enable rapid response when escaping from predators?
A) Horses
B) Lizards
C) Squirrels
D) Birds
E) Squids
A) Horses
B) Lizards
C) Squirrels
D) Birds
E) Squids

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
Which of the following is an INCORRECT statement regarding the equilibrium potential?
A) It is a steady state in which opposing chemical and electrical flows are equal and there is no net movement of the ion.
B) The equilibrium potential for K+ in a typical neuron is −90 mV.
C) The equilibrium potential for Na+ in a typical neuron is +60 mV.
D) The resting potential of a neuron is approximately −70 mV.
E) The membrane is much more permeable to Na+ than to K+.
A) It is a steady state in which opposing chemical and electrical flows are equal and there is no net movement of the ion.
B) The equilibrium potential for K+ in a typical neuron is −90 mV.
C) The equilibrium potential for Na+ in a typical neuron is +60 mV.
D) The resting potential of a neuron is approximately −70 mV.
E) The membrane is much more permeable to Na+ than to K+.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
Most axons transmit impulses at approximately which of the following rates?
A) 10-100 m/s
B) 1-10 m/s
C) 100-1,000 mm/s
D) 10-100 mm/s
E) 1-10 mm/s
A) 10-100 m/s
B) 1-10 m/s
C) 100-1,000 mm/s
D) 10-100 mm/s
E) 1-10 mm/s

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
Passive ion channels do NOT permit the passage of which of the following ions?
A) Na+
B) K+
C) Cl−
D) Ca2+
E) Hg2+
A) Na+
B) K+
C) Cl−
D) Ca2+
E) Hg2+

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
Figure 41-3
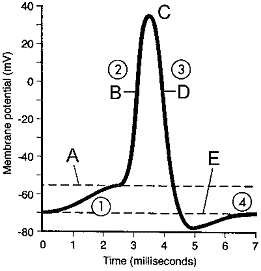
Step 2 in the accompanying figure is accomplished by an influx of:
A) Ca2+.
B) Na2+.
C) K+.
D) Na2+.
E) K+.

Step 2 in the accompanying figure is accomplished by an influx of:
A) Ca2+.
B) Na2+.
C) K+.
D) Na2+.
E) K+.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
Charybdotoxin, produced by scorpions, blocks K+ channels. This has which of the following effects?
A) Hyperexcites the nervous system
B) Dampens the nervous system
C) Depolarizes axons
D) Repolarizes axons
E) Demyelinates axons
A) Hyperexcites the nervous system
B) Dampens the nervous system
C) Depolarizes axons
D) Repolarizes axons
E) Demyelinates axons

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
"Substance P" is a neurotransmitter that functions in which of the following biological processes?
A) Learning and memory
B) Mood and sleep
C) Transmits pain signals
D) Regulates food intake
E) Inhibits cardiac muscle
A) Learning and memory
B) Mood and sleep
C) Transmits pain signals
D) Regulates food intake
E) Inhibits cardiac muscle

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
What event triggers the release of neurotransmitters?
A) Calcium induces the fusion of synaptic vesicles with the presynaptic membrane.
B) Sodium induces the fusion of synaptic vesicles with the presynaptic membrane.
C) Potassium induces the fusion of synaptic vesicles with the presynaptic membrane.
D) Calcium activates enzymes that degrade synaptic vesicles.
E) Sodium activates enzymes that degrade synaptic vesicles.
A) Calcium induces the fusion of synaptic vesicles with the presynaptic membrane.
B) Sodium induces the fusion of synaptic vesicles with the presynaptic membrane.
C) Potassium induces the fusion of synaptic vesicles with the presynaptic membrane.
D) Calcium activates enzymes that degrade synaptic vesicles.
E) Sodium activates enzymes that degrade synaptic vesicles.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
Figure 41-3
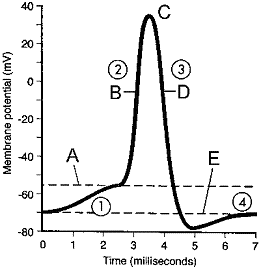
Refer to the accompanying figure. Depolarization is indicated by the label:
A) A.
B) B.
C) C.
D) D.
E) E.

Refer to the accompanying figure. Depolarization is indicated by the label:
A) A.
B) B.
C) C.
D) D.
E) E.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
What did Alan Hodgkin and Andrew Huxley conclude from their squid axon experiments?
A) The passage of Na+ ions into a neuron and K+ ions out of a neuron results in an action potential.
B) The passage of K+ ions into a neuron and Na+ ions out of a neuron results in an action potential.
C) The passage of K+ ions into a neuron and Ca+ ions out of a neuron results in an action potential.
D) The passage of Cl− ions into a neuron and K+ ions out of a neuron results in an action potential.
E) The passage of Cl− ions into a neuron and Ca+ ions out of a neuron results in an action potential.
A) The passage of Na+ ions into a neuron and K+ ions out of a neuron results in an action potential.
B) The passage of K+ ions into a neuron and Na+ ions out of a neuron results in an action potential.
C) The passage of K+ ions into a neuron and Ca+ ions out of a neuron results in an action potential.
D) The passage of Cl− ions into a neuron and K+ ions out of a neuron results in an action potential.
E) The passage of Cl− ions into a neuron and Ca+ ions out of a neuron results in an action potential.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
Glutamate is a neurotransmitter that functions in which of the following biological processes?
A) Learning and memory
B) Mood and sleep
C) Transmits pain signals
D) Regulates food intake
E) Inhibits cardiac muscle
A) Learning and memory
B) Mood and sleep
C) Transmits pain signals
D) Regulates food intake
E) Inhibits cardiac muscle

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
Figure 41-3
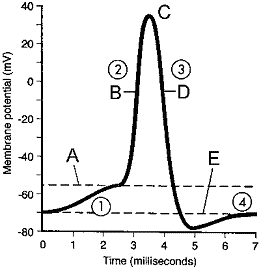
In the accompanying figure, label A represents:
A) resting state.
B) repolarization
C) threshold level.
D) equilibrium potential.
E) hyperpolarization.

In the accompanying figure, label A represents:
A) resting state.
B) repolarization
C) threshold level.
D) equilibrium potential.
E) hyperpolarization.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
During the absolute refractory period, the axon membrane cannot transmit another action potential.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
Arrange the events of a second messenger system in the correct order.
1) Protein kinase is activated.
2) G protein is activated.
3) The neurotransmitter binds to its receptor.
4) The protein closes the potassium channel.
5) Cyclic AMP is produced.
6) Phosphorylation takes place.
A) 1 → 2 → 5 → 6 → 4 → 3
B) 3 → 5 → 6 → 1 → 2 → 4
C) 5 → 2 → 6 → 1 → 3 → 4
D) 3 → 2 → 5 → 1 → 6 → 4
E) 5 → 2 → 6 → 1 → 4 → 3
1) Protein kinase is activated.
2) G protein is activated.
3) The neurotransmitter binds to its receptor.
4) The protein closes the potassium channel.
5) Cyclic AMP is produced.
6) Phosphorylation takes place.
A) 1 → 2 → 5 → 6 → 4 → 3
B) 3 → 5 → 6 → 1 → 2 → 4
C) 5 → 2 → 6 → 1 → 3 → 4
D) 3 → 2 → 5 → 1 → 6 → 4
E) 5 → 2 → 6 → 1 → 4 → 3

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
An excitatory postsynaptic potential (EPSP):
A) results in partial depolarization of the neuron.
B) always causes a neuron to fire.
C) prevents a neuron from firing.
D) results in partial hyperpolarization of the neuron.
E) changes the action potential threshold level.
A) results in partial depolarization of the neuron.
B) always causes a neuron to fire.
C) prevents a neuron from firing.
D) results in partial hyperpolarization of the neuron.
E) changes the action potential threshold level.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
The resting potential of a typical neuron is approximately +70 mV.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
The action potential either occurs or it does not. No variation exists in the strength of a single impulse.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
In convergence, a single neuron is controlled by signals from two or more presynaptic neurons. ____________________

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
Draw a diagram of a typical neuron, label its parts, and list the function of each labeled structure.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
What is/are the characteristic(s) of EPSPs and IPSPs?
A) EPSPs and IPSPs do not influence action potentials.
B) EPSPs and IPSPs are graded potentials.
C) EPSPs and IPSPs occur via an all-or-none response.
D) EPSPs are fast action potentials; IPSPs are slow action potentials.
E) EPSPs occur in myelinated axons; IPSPs occur in unmyelinated axons.
A) EPSPs and IPSPs do not influence action potentials.
B) EPSPs and IPSPs are graded potentials.
C) EPSPs and IPSPs occur via an all-or-none response.
D) EPSPs are fast action potentials; IPSPs are slow action potentials.
E) EPSPs occur in myelinated axons; IPSPs occur in unmyelinated axons.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
The sodium-potassium pump transports two Na+ out of the cell for every two K+ transported in.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
In divergence, one neuron:
A) is controlled by several neurons.
B) is controlled by several neurotransmitter substances.
C) contains several different types of ion channels.
D) controls several other neurons.
E) contains several different types of receptors.
A) is controlled by several neurons.
B) is controlled by several neurotransmitter substances.
C) contains several different types of ion channels.
D) controls several other neurons.
E) contains several different types of receptors.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
Nitric oxide, carbon monoxide, and hydrogen sulfide are all neurotransmitters.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
Most neural integrations take place in the PNS.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
Ependymal cells are a type of macrophage.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
Acetylcholine is a neurotransmitter released from motor neurons.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
Compare and contrast the production and transmission of a graded potential with those of an action potential.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
Spatial summation is characterized by:
A) several presynaptic neurons releasing neurotransmitters simultaneously.
B) several presynaptic neurons releasing neurotransmitters in a sequential pattern.
C) several postsynaptic neurons receiving sequential inputs from several presynaptic neurons.
D) a single presynaptic neuron firing multiple times in rapid succession.
E) a single presynaptic neuron directly contacting several postsynaptic neurons.
A) several presynaptic neurons releasing neurotransmitters simultaneously.
B) several presynaptic neurons releasing neurotransmitters in a sequential pattern.
C) several postsynaptic neurons receiving sequential inputs from several presynaptic neurons.
D) a single presynaptic neuron firing multiple times in rapid succession.
E) a single presynaptic neuron directly contacting several postsynaptic neurons.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
A neuronal axon transmits neural impulses toward its cell body.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
Astrocytes are glia that provide nutrients for neurons.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
Define summation and explain the difference between temporal and spatial summation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
The arrival of an action potential at a synaptic terminal causes voltage-gated potassium channels to open.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
Match between columns

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
Match between columns

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
Match between columns

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
Match between columns

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
Match between columns

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
Match between columns

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
Match between columns

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
Match between columns

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
How is summation related to IPSPs and EPSPs? What is the difference between temporal summation and spatial summation?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
Although the effects of an EPSP are subliminal, explain how EPSPs affect membrane potential.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
Match between columns

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72
Match between columns

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73
Explain the difference between convergence and divergence, and outline why each is important in neural circuit functioning.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
74
Match between columns

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
75
Match between columns

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
76
Explain the difference between an absolute and a relative refractory period.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



