Deck 45: The Immune System: Internal Defense
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Match between columns
Question
Question
Match between columns
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Match between columns
Question
Match between columns
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/93
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 45: The Immune System: Internal Defense
1
Which statement best describes the relationship between an antibody and an antigen?
A) An antibody is specifically produced in response to an antigen.
B) An antibody is produced by T cells and an antigen is a foreign protein.
C) An antigen is presented by antigen presenting cells to plasma cells, which produce antibodies.
D) An antigen is a disease-causing organism, and antibodies are produced by B cells.
E) An antibody generally induces antigen formation.
A) An antibody is specifically produced in response to an antigen.
B) An antibody is produced by T cells and an antigen is a foreign protein.
C) An antigen is presented by antigen presenting cells to plasma cells, which produce antibodies.
D) An antigen is a disease-causing organism, and antibodies are produced by B cells.
E) An antibody generally induces antigen formation.
A
2
Which of the following is NOT a risk factor for chronic inflammation?
A) Prolonged infections
B) Cigarette smoking
C) Gum disease
D) Obesity
E) Vitamin D deficiency
A) Prolonged infections
B) Cigarette smoking
C) Gum disease
D) Obesity
E) Vitamin D deficiency
E
3
Which statement concerning pathogen-associated molecular patterns (PAMPS) is FALSE?
A) They are features of pathogens recognized by animal cells.
B) They trigger activation of phagocytes.
C) They react with specific receptors on host cells.
D) They are found on all microbes except viruses.
E) The peptidoglycan of gram-positive bacteria is an example.
A) They are features of pathogens recognized by animal cells.
B) They trigger activation of phagocytes.
C) They react with specific receptors on host cells.
D) They are found on all microbes except viruses.
E) The peptidoglycan of gram-positive bacteria is an example.
D
4
The enzyme found in tears that can digest bacterial cell walls is called:
A) protease.
B) lysozyme.
C) interferon.
D) cytokine.
E) defensin.
A) protease.
B) lysozyme.
C) interferon.
D) cytokine.
E) defensin.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
Which of the following is a correct statement regarding innate immunity?
A) They are specific defenses that target distinct macromolecules.
B) They typically lead to the production of antibodies.
C) An important characteristic is immunological memory.
D) They cannot prevent most pathogens from entering the body.
E) Phagocytosis and inflammation are examples.
A) They are specific defenses that target distinct macromolecules.
B) They typically lead to the production of antibodies.
C) An important characteristic is immunological memory.
D) They cannot prevent most pathogens from entering the body.
E) Phagocytosis and inflammation are examples.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
The lymphocytes that are involved in nonspecifically killing altered self-cells, such as tumor cells and virus infected cells, are the:
A) monocytes
B) natural killer cells
C) neutrophils
D) B cells
E) eosinophils
A) monocytes
B) natural killer cells
C) neutrophils
D) B cells
E) eosinophils

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
Which of the following is a group of proteins with actions including antiviral activity?
A) Tumor necrosis factors
B) Chemokines
C) Complement systems
D) Interleukins
E) Interferons
A) Tumor necrosis factors
B) Chemokines
C) Complement systems
D) Interleukins
E) Interferons

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
Which statement about the inflammatory response is FALSE?
A) Histamine causes increased capillary permeability.
B) Type I interferons and neutrophils secrete histamine.
C) Increased blood flow to infected areas brings more phagocytic cells.
D) Swelling results from an increase in the volume of interstitial fluid in the infected area.
E) Edema and certain enzymes in the plasma cause the pain associated with inflammation.
A) Histamine causes increased capillary permeability.
B) Type I interferons and neutrophils secrete histamine.
C) Increased blood flow to infected areas brings more phagocytic cells.
D) Swelling results from an increase in the volume of interstitial fluid in the infected area.
E) Edema and certain enzymes in the plasma cause the pain associated with inflammation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
The basis of the immune system is:
A) direct cell-to-cell contact.
B) distinguishing between self and nonself.
C) communicating between cells.
D) producing antibody action.
E) attacking invading objects.
A) direct cell-to-cell contact.
B) distinguishing between self and nonself.
C) communicating between cells.
D) producing antibody action.
E) attacking invading objects.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
Which of the following is a type of cytokine?
A) Complement protein
B) Mast cell
C) Immunoglobulin
D) Lysozyme
E) Tumor necrosis factor
A) Complement protein
B) Mast cell
C) Immunoglobulin
D) Lysozyme
E) Tumor necrosis factor

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
Which of the following is a large group of molecules involved in signaling and regulation of defense responses?
A) Complement
B) Prostaglandins
C) Opsonins
D) Cytokines
E) Histamines
A) Complement
B) Prostaglandins
C) Opsonins
D) Cytokines
E) Histamines

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
Which of the following is a function of activated complement proteins?
A) Producing antibodies
B) Reducing inflammation
C) Coating skin with more mucus
D) Attracting white blood cells to infection sites
E) Decreasing capillary permeability to minimize edema
A) Producing antibodies
B) Reducing inflammation
C) Coating skin with more mucus
D) Attracting white blood cells to infection sites
E) Decreasing capillary permeability to minimize edema

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
Natural killer cells destroy target cells by:
A) releasing antibiotics, which break down the cell membranes.
B) releasing cytokines and enzymes that trigger apoptosis.
C) releasing histamine, which signals other blood cells to aggregate.
D) phagocytosis, after the cells are targeted by antibodies.
E) releasing lysosomal enzymes, which digest the target cells.
A) releasing antibiotics, which break down the cell membranes.
B) releasing cytokines and enzymes that trigger apoptosis.
C) releasing histamine, which signals other blood cells to aggregate.
D) phagocytosis, after the cells are targeted by antibodies.
E) releasing lysosomal enzymes, which digest the target cells.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
Which of the following are large phagocytes that develop from monocytes?
A) Eosinophils
B) Macrophages
C) Neutrophils
D) Dendritic cells
E) Basophils
A) Eosinophils
B) Macrophages
C) Neutrophils
D) Dendritic cells
E) Basophils

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
Which of the following statements concerning tumor necrosis factor (TNF) is FALSE?
A) TNF can be secreted by macrophages.
B) TNF may stimulate the inflammatory response.
C) The release of large amounts of TNF brings down a high fever.
D) TNF kills cancer cells.
E) TNF can be secreted by lymphocytes.
A) TNF can be secreted by macrophages.
B) TNF may stimulate the inflammatory response.
C) The release of large amounts of TNF brings down a high fever.
D) TNF kills cancer cells.
E) TNF can be secreted by lymphocytes.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
Which regulatory protein is mismatched with its function?
A) Type I interferons-inhibit viral replication
B) interleukin-1-resets body's thermostat, resulting in fever
C) tumor necrosis factor-kills tumor cells
D) cytokines-secrete antibodies
E) Type II interferons-stimulate macrophages to destroy tumor cells
A) Type I interferons-inhibit viral replication
B) interleukin-1-resets body's thermostat, resulting in fever
C) tumor necrosis factor-kills tumor cells
D) cytokines-secrete antibodies
E) Type II interferons-stimulate macrophages to destroy tumor cells

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
Which of the following are the most powerful antigens?
A) Proteins
B) Polysaccharides
C) Lipids
D) DNA
E) RNA
A) Proteins
B) Polysaccharides
C) Lipids
D) DNA
E) RNA

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
Which of the following is a specific defense mechanisms or barrier used by an animal?
A) Acid secretions of the stomach
B) Inflammation
C) Antibodies
D) Mucus in the respiratory tract
E) Skin
A) Acid secretions of the stomach
B) Inflammation
C) Antibodies
D) Mucus in the respiratory tract
E) Skin

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
Which of the following are active against tumor cells and cells infected with some types of viruses?
A) Natural killer cells
B) Plasma cells
C) Macrophages
D) T helper cells
E) Cytotoxic T cells
A) Natural killer cells
B) Plasma cells
C) Macrophages
D) T helper cells
E) Cytotoxic T cells

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
Which of the following immune system components has been identified in almost all organisms studied?
A) Bone marrow
B) Phagocytes
C) Antimicrobial peptides
D) T-cells
E) Memory cells
A) Bone marrow
B) Phagocytes
C) Antimicrobial peptides
D) T-cells
E) Memory cells

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
A nursing baby:
A) lacks cell-mediated immunity.
B) lacks antibody-mediated immunity.
C) lacks an adaptive immune response.
D) receives active immunity via the breast milk.
E) receives passive immunity via the breast milk.
A) lacks cell-mediated immunity.
B) lacks antibody-mediated immunity.
C) lacks an adaptive immune response.
D) receives active immunity via the breast milk.
E) receives passive immunity via the breast milk.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
Which cells stimulate B cells to divide and produce antibodies?
A) Mast cells
B) Macrophages
C) NK cells
D) TC cells
E) TH cells
A) Mast cells
B) Macrophages
C) NK cells
D) TC cells
E) TH cells

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
T cells that react with self-antigens are destroyed through:
A) cytokinesis.
B) macrophages.
C) perforins.
D) apoptosis.
E) receptor mediated endocytosis.
A) cytokinesis.
B) macrophages.
C) perforins.
D) apoptosis.
E) receptor mediated endocytosis.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
The part of the antibody that binds an antigen:
A) is known as the Fc fragment.
B) is called an epitope.
C) makes up the tail of the Y-shaped molecule.
D) is known as the Fab fragments.
E) is known as the constant segment.
A) is known as the Fc fragment.
B) is called an epitope.
C) makes up the tail of the Y-shaped molecule.
D) is known as the Fab fragments.
E) is known as the constant segment.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
In antibody-mediated immunity, what happens immediately after B cells are activated?
A) The foreign antigen-MHC complex is displayed on the cell surfaces.
B) Activated T helper cells interact with the B cells.
C) The B cells are cloned.
D) Antibodies combine with antigens on the pathogen surface.
E) The B cells becomes plasma cells.
A) The foreign antigen-MHC complex is displayed on the cell surfaces.
B) Activated T helper cells interact with the B cells.
C) The B cells are cloned.
D) Antibodies combine with antigens on the pathogen surface.
E) The B cells becomes plasma cells.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
In cell-mediated immunity, what happens immediately after the infected cell displays the antigen-MHC complex?
A) A virus invades the cell.
B) Specific T cytotoxic cells are activated.
C) Effector T cytotoxic cells migrate to the infection site.
D) Cytokines are released by T helper cells.
E) Enzymes destroy the target cells.
A) A virus invades the cell.
B) Specific T cytotoxic cells are activated.
C) Effector T cytotoxic cells migrate to the infection site.
D) Cytokines are released by T helper cells.
E) Enzymes destroy the target cells.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
Cell-mediated immunity is directed by:
A) B cells, which secrete antibodies.
B) T cells, which secrete antibodies.
C) macrophages, which produce histamines.
D) B cells, which react with APCs.
E) T cells, which react with APCs.
A) B cells, which secrete antibodies.
B) T cells, which secrete antibodies.
C) macrophages, which produce histamines.
D) B cells, which react with APCs.
E) T cells, which react with APCs.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
Which statement about the immune system is correct?
A) Memory cells are involved in a primary immune response.
B) Dendritic cells were first identified in the nervous system.
C) Interferons are specific proteins that block cell replication at the level of mitosis.
D) Natural killer cells are involved in both specific and nonspecific immune responses.
E) Defensins are one type of protective protein synthesized by T helper cells.
A) Memory cells are involved in a primary immune response.
B) Dendritic cells were first identified in the nervous system.
C) Interferons are specific proteins that block cell replication at the level of mitosis.
D) Natural killer cells are involved in both specific and nonspecific immune responses.
E) Defensins are one type of protective protein synthesized by T helper cells.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
Which of the following are "professional" antigen-presenting cells, which are pertinent to the major histocompatibility complex?
A) Macrophages, dendritic cells, and B cells
B) Mast cells, dendritic cells, and B cells
C) Macrophages, dendritic cells, and T cells
D) Macrophages, natural killer cells, and T cells
E) Mast cells, B cells, and T cells
A) Macrophages, dendritic cells, and B cells
B) Mast cells, dendritic cells, and B cells
C) Macrophages, dendritic cells, and T cells
D) Macrophages, natural killer cells, and T cells
E) Mast cells, B cells, and T cells

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
What class of antibodies is normally found in the mucosa of the respiratory tract?
A) IgA
B) IgD
C) IgE
D) IgG
E) IgM
A) IgA
B) IgD
C) IgE
D) IgG
E) IgM

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
Which of the following is the predominant antibody in a secondary immune response?
A) IgA
B) IgD
C) IgE
D) IgG
E) IgM
A) IgA
B) IgD
C) IgE
D) IgG
E) IgM

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
B cells:
A) are produced in the adult spleen.
B) lyse bacterial cell walls by secreting digestive enzymes.
C) can become plasma cells, which produce interleukins.
D) undergo clonal reproduction once activated.
E) stimulate apoptosis.
A) are produced in the adult spleen.
B) lyse bacterial cell walls by secreting digestive enzymes.
C) can become plasma cells, which produce interleukins.
D) undergo clonal reproduction once activated.
E) stimulate apoptosis.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
A baby born without a thymus:
A) would not have an antibody mediated immune response.
B) would not produce lymphocytes.
C) would not produce immunocompetent T cells.
D) will lack the ability to mount an immune response.
E) will lack antigen presenting cells.
A) would not have an antibody mediated immune response.
B) would not produce lymphocytes.
C) would not produce immunocompetent T cells.
D) will lack the ability to mount an immune response.
E) will lack antigen presenting cells.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
Which of the following cell types is long lived and continues to produce antibody?
A) Cytotoxic T cells
B) Memory B cells
C) T helper cells
D) Plasma cells
E) Macrophages
A) Cytotoxic T cells
B) Memory B cells
C) T helper cells
D) Plasma cells
E) Macrophages

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
Which of the following cells secrete cytokines that activate B cells, T cells, and macrophages?
A) T helper cells
B) regulatory T cells
C) T cytotoxic cells
D) dendritic cells
E) natural killer cells
A) T helper cells
B) regulatory T cells
C) T cytotoxic cells
D) dendritic cells
E) natural killer cells

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
The main antigen presenting cells of the body are:
A) macrophages and B cells only.
B) macrophages and dendritic cell only.
C) dendritic cells and B cells only.
D) dendritic cells and plasma cells only.
E) macrophages, B cells and dendritic cells.
A) macrophages and B cells only.
B) macrophages and dendritic cell only.
C) dendritic cells and B cells only.
D) dendritic cells and plasma cells only.
E) macrophages, B cells and dendritic cells.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
T cells mature in which of the following glands?
A) Thymus
B) Thyroid
C) Apocrine
D) Parotid
E) Lumbar
A) Thymus
B) Thyroid
C) Apocrine
D) Parotid
E) Lumbar

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
Fever helps the body fight infection in which of the following ways?
A) Increased body temperature decreases phagocytosis.
B) Fever causes the creation of lysosomes.
C) Fever inhibits the growth of some microorganisms.
D) Fever reduces lymphocyte activity.
E) Fever increases capillary permeability.
A) Increased body temperature decreases phagocytosis.
B) Fever causes the creation of lysosomes.
C) Fever inhibits the growth of some microorganisms.
D) Fever reduces lymphocyte activity.
E) Fever increases capillary permeability.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
You had a cold last month and you caught another one this month from your daughter. What is the most likely cause of this?
A) Memory cells were not formed as a response to the first cold.
B) The antibodies formed as a response to the first cold were degraded.
C) The two cold viruses are significantly different.
D) Your T cells are not working properly.
E) Your antigen-presenting cells do not recognize the second cold virus.
A) Memory cells were not formed as a response to the first cold.
B) The antibodies formed as a response to the first cold were degraded.
C) The two cold viruses are significantly different.
D) Your T cells are not working properly.
E) Your antigen-presenting cells do not recognize the second cold virus.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
Which cells complete their maturation in the thymus gland?
A) T cytotoxic cells only
B) T helper cells only
C) B cells only
D) Both T cytotoxic and T helper cells
E) T cytotoxic cells, T helper cells, and B cells
A) T cytotoxic cells only
B) T helper cells only
C) B cells only
D) Both T cytotoxic and T helper cells
E) T cytotoxic cells, T helper cells, and B cells

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
Which statement about HIV is FALSE?
A) HIV infection results in a dramatic decline in the T helper cell population.
B) The first cells targeted by HIV are dendritic cells.
C) T cytotoxic cells are the main cells that attack HIV.
D) Dendritic cells transport HIV from the mucosa to the lymph nodes.
E) HIV attaches to the CD4 component of TH cells.
A) HIV infection results in a dramatic decline in the T helper cell population.
B) The first cells targeted by HIV are dendritic cells.
C) T cytotoxic cells are the main cells that attack HIV.
D) Dendritic cells transport HIV from the mucosa to the lymph nodes.
E) HIV attaches to the CD4 component of TH cells.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
Figure 45-1
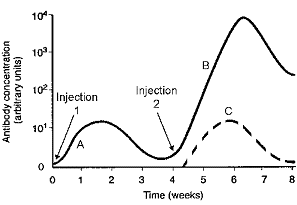
Based on the accompanying graph, which statement is accurate?
A) The primary response to the initial injection subsides after seven weeks.
B) The primary response to the initial injection peaks at 102 antibody units.
C) The primary response to the initial injection is faster, but not as intense as the secondary response.
D) The secondary response to the initial antigen is both faster and more intense than the primary response.
E) The primary and secondary responses to the initial antigen are about equal.

Based on the accompanying graph, which statement is accurate?
A) The primary response to the initial injection subsides after seven weeks.
B) The primary response to the initial injection peaks at 102 antibody units.
C) The primary response to the initial injection is faster, but not as intense as the secondary response.
D) The secondary response to the initial antigen is both faster and more intense than the primary response.
E) The primary and secondary responses to the initial antigen are about equal.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
Figure 45-1
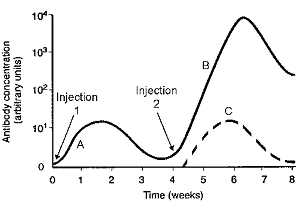
The response represented by the dashed line in the accompanying figure indicates a:
A) secondary response to the initial antigen.
B) primary response to the initial antigen.
C) secondary response to an antigen distinctly different from the initial antigen.
D) primary response to an antigen distinctly different from the initial antigen.
E) secondary response equivalent to a primary response

The response represented by the dashed line in the accompanying figure indicates a:
A) secondary response to the initial antigen.
B) primary response to the initial antigen.
C) secondary response to an antigen distinctly different from the initial antigen.
D) primary response to an antigen distinctly different from the initial antigen.
E) secondary response equivalent to a primary response

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
Figure 45-1
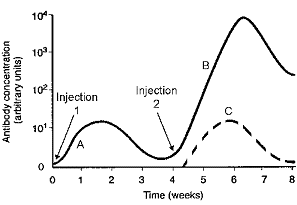
The immune system component with a principal role at point B in the accompanying figure is:
A) memory cells.
B) IgM antibodies.
C) IgG antibodies.
D) cytotoxic T cells.
E) antibody IgA.

The immune system component with a principal role at point B in the accompanying figure is:
A) memory cells.
B) IgM antibodies.
C) IgG antibodies.
D) cytotoxic T cells.
E) antibody IgA.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
What must happen in order for a donor organ to not be rejected by the recipient?
A) The MHC complexes need to match as closely as possible.
B) The recipient's plasma cells will be inactivated.
C) The recipient's passive immunity pathway will be activated.
D) The NK cells of the recipient will be inactivated.
E) The cytotoxic T cells will be inactivated.
A) The MHC complexes need to match as closely as possible.
B) The recipient's plasma cells will be inactivated.
C) The recipient's passive immunity pathway will be activated.
D) The NK cells of the recipient will be inactivated.
E) The cytotoxic T cells will be inactivated.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
An immunization against cow pox should protect an individual:
A) by increasing the production of lymphocytes by the bone marrow.
B) through the production of diverse antibodies.
C) by initiating a secondary immune response.
D) against other antigens with the same antigenic determinants.
E) against other bacterial infections.
A) by increasing the production of lymphocytes by the bone marrow.
B) through the production of diverse antibodies.
C) by initiating a secondary immune response.
D) against other antigens with the same antigenic determinants.
E) against other bacterial infections.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
Which of the following vaccines are NOT produced by long-term culturing in nonhuman cells, rendering the pathogen unable to cause disease in humans?
A) Sabin polio
B) Measles
C) Mumps
D) Rubella
E) Tetanus
A) Sabin polio
B) Measles
C) Mumps
D) Rubella
E) Tetanus

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
Which of the following present antigens to T cells, stimulating them to produce interferons, which have an antitumor effect?
A) Natural killer cells
B) Macrophages
C) Dendritic cells
D) Tc cells
E) Mast cells
A) Natural killer cells
B) Macrophages
C) Dendritic cells
D) Tc cells
E) Mast cells

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
Which of the following is NOT a disease that can result from a failure in self-tolerance?
A) Rheumatoid arthritis
B) Systemic lupus erythematosus
C) Shingles
D) Insulin-dependent diabetes
E) Multiple sclerosis
A) Rheumatoid arthritis
B) Systemic lupus erythematosus
C) Shingles
D) Insulin-dependent diabetes
E) Multiple sclerosis

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
Which of the following combinations could result in Rh incompatibility?
A) Rh-positive mother, Rh-negative father
B) Rh-positive mother, Rh-positive father
C) Rh-negative mother, Rh-positive father
D) Rh-negative mother, Rh-negative father
E) More than one of the above.
A) Rh-positive mother, Rh-negative father
B) Rh-positive mother, Rh-positive father
C) Rh-negative mother, Rh-positive father
D) Rh-negative mother, Rh-negative father
E) More than one of the above.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
Arrange the steps of an allergic reaction in the proper order.
1) Allergic symptoms appear.
2) The allergen binds with IgE.
3) IgE combines with mast cell receptors.
4) The mast cell releases histamine.
5) Plasma cells are sensitized.
A) 5 → 3 → 2 → 4 → 1
B) 1 → 5 → 2 → 4 → 3
C) 5 → 2 → 4 → 3 → 1
D) 1 → 4 → 5 → 2 → 3
E) 4 → 5 → 2 → 3 → 1
1) Allergic symptoms appear.
2) The allergen binds with IgE.
3) IgE combines with mast cell receptors.
4) The mast cell releases histamine.
5) Plasma cells are sensitized.
A) 5 → 3 → 2 → 4 → 1
B) 1 → 5 → 2 → 4 → 3
C) 5 → 2 → 4 → 3 → 1
D) 1 → 4 → 5 → 2 → 3
E) 4 → 5 → 2 → 3 → 1

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
Protease inhibitors:
A) inhibit the action of reverse transcriptase.
B) are glycoproteins found in saliva.
C) result in viral copies that cannot infect new cells.
D) can cure AIDS patients.
E) destroy helper T cells.
A) inhibit the action of reverse transcriptase.
B) are glycoproteins found in saliva.
C) result in viral copies that cannot infect new cells.
D) can cure AIDS patients.
E) destroy helper T cells.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
Which of the following results from the combination of antibodies and antigens?
A) Activation of the pathogen
B) Formation of cytotoxic T cells
C) Stimulation of phagocytosis
D) Activation of toxins
E) Inactivation of the complement system
A) Activation of the pathogen
B) Formation of cytotoxic T cells
C) Stimulation of phagocytosis
D) Activation of toxins
E) Inactivation of the complement system

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
During a specific defense, the process of increasing the numbers of the selected cells is called:
A) mitotic expansion.
B) clonal selection.
C) divisional activation.
D) lymphocytic activation.
E) memory establishment.
A) mitotic expansion.
B) clonal selection.
C) divisional activation.
D) lymphocytic activation.
E) memory establishment.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
Which of the following is an INCORRECT statement regarding allergic asthma?
A) An allergen-IgE response occurs in the bronchioles of the lungs.
B) Mast cells release substances that cause smooth muscle to contract.
C) Mast cells secrete compounds that cause inflammation.
D) It cannot be treated with steroids.
E) It can be treated with monoclonal antibodies to IgE.
A) An allergen-IgE response occurs in the bronchioles of the lungs.
B) Mast cells release substances that cause smooth muscle to contract.
C) Mast cells secrete compounds that cause inflammation.
D) It cannot be treated with steroids.
E) It can be treated with monoclonal antibodies to IgE.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
In many kinds of allergic reactions, distinctive immunoglobins of which type are produced?
A) IgA
B) IgD
C) IgE
D) IgG
E) IgM
A) IgA
B) IgD
C) IgE
D) IgG
E) IgM

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
Which statement about a secondary immune response is FALSE?
A) It is a response to an antigen.
B) It may occur years after a primary response.
C) It involves memory cells.
D) It has a longer latent period than a primary response.
E) It is stimulated by less antigen than a primary response.
A) It is a response to an antigen.
B) It may occur years after a primary response.
C) It involves memory cells.
D) It has a longer latent period than a primary response.
E) It is stimulated by less antigen than a primary response.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
Which of the following binds with receptors on phagocytes and other cells of the immune system, and also binds with molecules of the complement system?
A) IgG
B) IgM
C) Heavy chain
D) Light chain
E) Fc fragment
A) IgG
B) IgM
C) Heavy chain
D) Light chain
E) Fc fragment

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
Which statement about cancer defense is FALSE?
A) Natural killer and T cytotoxic cells destroy cancer cells.
B) Cancer antigens stimulate a strong immune response.
C) Monoclonal antibodies can deliver toxic drugs to cancer cells.
D) T cells produce interleukins, which defend against cancer.
E) Macrophages produce tumor necrosis factor, which inhibits tumor growth.
A) Natural killer and T cytotoxic cells destroy cancer cells.
B) Cancer antigens stimulate a strong immune response.
C) Monoclonal antibodies can deliver toxic drugs to cancer cells.
D) T cells produce interleukins, which defend against cancer.
E) Macrophages produce tumor necrosis factor, which inhibits tumor growth.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
Monoclonal antibodies:
A) have been linked as causative agents in some types of cancer.
B) are only produced by harvesting B cells from mice exposed to particular antigens.
C) include hCG, a component of commonly used home pregnancy tests.
D) are very specific for their target antigen, but are somewhat difficult to purify.
E) are produced by millions of genes.
A) have been linked as causative agents in some types of cancer.
B) are only produced by harvesting B cells from mice exposed to particular antigens.
C) include hCG, a component of commonly used home pregnancy tests.
D) are very specific for their target antigen, but are somewhat difficult to purify.
E) are produced by millions of genes.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
Type II interferon inhibits viral replication and activates natural killer cells.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
Active immunity occurs after transfer of antibodies from mother to fetus.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
Contrast cell-mediated and antibody-mediated immunity and give a brief overview of each process.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
Nonspecific cell responses depend on the actions of lymphocytes, natural killer cells, and dendritic cells.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
Match between columns

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
Select one of the options below and compare and contrast the paired terms:
A. Primary and secondary immune response
B. Passive and active immunity
C. Artificial and natural immunity
A. Primary and secondary immune response
B. Passive and active immunity
C. Artificial and natural immunity

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
Match between columns

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
Explain the events that occur during the inflammatory response and how this response is a protective mechanism.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
Class II MHC genes encode glycoproteins on the surface of cells that bind with antigens originating from intracellular pathogens.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
Interleukins activate and direct the movement of white blood cells from the blood to the tissues.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
Identify the following as participants in either specific or nonspecific immune responses, and provide a one-sentence explanation of the function or role of each one.
A. Macrophages
B. Natural killer cells
C. Memory cells
A. Macrophages
B. Natural killer cells
C. Memory cells

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72
Specific immune responses are also referred to as innate immunity.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73
Describe the sequence of events that occur during cell-mediated immunity.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
74
Describe the differences in the functions of the five immunoglobulin classes.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
75
Match between columns

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
76
Match between columns

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
77
Animal cells recognize common types of pathogen-associated molecules and activate the production of antimicrobial peptides.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
78
Cell walls and cytokines of bacteria are examples of the evolution of resistance to the host immune response.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
79
Each T cytotoxic cell expresses CD8 and 50,000 identical T cell receptors on its surface.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
80
Normally, complement proteins are active until the body is exposed to antigen.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



