Deck 52: Animal Behavior
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/91
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 52: Animal Behavior
1
Which of the following is an INCORRECT statement regarding animal behavior?
A) Behavior is defined as what an animal does and how the animal does it.
B) Behavior is usually in response to stimuli in the animal's environment.
C) An example is a bird singing.
D) An animal's behavior is a set of adaptations that equip the animal for survival in a particular environment.
E) What an animal does can be isolated from the way in which the animal lives.
A) Behavior is defined as what an animal does and how the animal does it.
B) Behavior is usually in response to stimuli in the animal's environment.
C) An example is a bird singing.
D) An animal's behavior is a set of adaptations that equip the animal for survival in a particular environment.
E) What an animal does can be isolated from the way in which the animal lives.
E
2
The brief length of time when mammals and birds learn the appearance of a parent is called:
A) imprinting.
B) habituation.
C) classical conditioning.
D) operant conditioning.
E) insight learning.
A) imprinting.
B) habituation.
C) classical conditioning.
D) operant conditioning.
E) insight learning.
A
3
A behavioral pattern can be triggered by a(n):
A) circadian rhythm.
B) environmental stimulus.
C) positive reinforcement.
D) psychological stimulus.
E) sign stimulus.
A) circadian rhythm.
B) environmental stimulus.
C) positive reinforcement.
D) psychological stimulus.
E) sign stimulus.
E
4
Figure 52-1
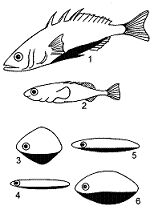
The behavioral response tested using the models in the accompanying figure is:
A) classical conditioning.
B) habituation.
C) imprinting.
D) insight.
E) a sign stimulus.

The behavioral response tested using the models in the accompanying figure is:
A) classical conditioning.
B) habituation.
C) imprinting.
D) insight.
E) a sign stimulus.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
According to the research of Dutch ethologist Niko Tinbergen, which behavior of Philanthus is critical to locating the burrow?
A) Learning landmarks
B) Digging the burrow
C) Covering the burrow
D) Killing bees
E) Capturing bees
A) Learning landmarks
B) Digging the burrow
C) Covering the burrow
D) Killing bees
E) Capturing bees

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
Mothers with small children often do not seem to hear their noisy children. This is an example of:
A) imprinting.
B) habituation.
C) classical conditioning.
D) operant conditioning.
E) insight learning.
A) imprinting.
B) habituation.
C) classical conditioning.
D) operant conditioning.
E) insight learning.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
An animal must be physiologically ready before it can exhibit a behavior pattern. This is NOT illustrated by which of the following?
A) Inability of a newborn human to walk
B) Inability of a newborn bird to fly
C) Inability of a sand wasp pupa to lay eggs
D) Inability of an adult human to locate an address
E) Inability of a newborn sparrow to sing
A) Inability of a newborn human to walk
B) Inability of a newborn bird to fly
C) Inability of a sand wasp pupa to lay eggs
D) Inability of an adult human to locate an address
E) Inability of a newborn sparrow to sing

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
You see an advertisement on the television with a very good-looking person showing off a new, shiny, powerful car. You seriously think about buying that particular car. Therefore, the person in the advertisement could best be described as the:
A) sign stimulus.
B) operant conditioner.
C) imprinter.
D) classic conditioner.
E) negative reinforcer.
A) sign stimulus.
B) operant conditioner.
C) imprinter.
D) classic conditioner.
E) negative reinforcer.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
Reproductive success is measured by the:
A) body mass of an organism.
B) number of viable offspring.
C) longevity of an organism.
D) population size.
E) amount of food it eats.
A) body mass of an organism.
B) number of viable offspring.
C) longevity of an organism.
D) population size.
E) amount of food it eats.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
Which of the following has the strongest influence on the ability of a male white-crowned sparrow to sing at all?
A) Acoustical stimuli
B) Social interaction with any songbird
C) Visual stimuli
D) Social interaction with other white-crowned sparrows
E) Innate behaviors
A) Acoustical stimuli
B) Social interaction with any songbird
C) Visual stimuli
D) Social interaction with other white-crowned sparrows
E) Innate behaviors

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
Changes in behavior that result from environmental experiences are called:
A) instincts.
B) learned behaviors.
C) proximate causes.
D) ultimate causes.
E) innate behaviors.
A) instincts.
B) learned behaviors.
C) proximate causes.
D) ultimate causes.
E) innate behaviors.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
A bird is born and raised in captivity. Immediately after release, the bird carries nesting materials underneath the feathers. After three years, the bird starts to consistently carry nesting materials in the bill. This is an example of which of the following?
A) Innate behavior
B) Learned behavior
C) Direct fitness
D) Proximate behavior
E) Ultimate behavior
A) Innate behavior
B) Learned behavior
C) Direct fitness
D) Proximate behavior
E) Ultimate behavior

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
If the benefits of a behavior are greater than the costs, the behavior is known as which of the following?
A) Proximate
B) Ultimate
C) Positive
D) Direct
E) Adaptive
A) Proximate
B) Ultimate
C) Positive
D) Direct
E) Adaptive

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
Which of the following terms is most closely associated with ultimate causes of behavior?
A) Physiological changes
B) Genetic causes
C) Evolutionary pressures
D) Developmental processes
E) Climatic pressures
A) Physiological changes
B) Genetic causes
C) Evolutionary pressures
D) Developmental processes
E) Climatic pressures

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
Figure 52-1
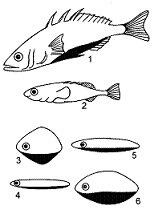
Which model in the accompanying figure would elicit an attack response from another male stickleback?
A) 1 and 2
B) 1, 2, 4, and 5
C) 2, 3, and 5
D) 1, 3, 4, 5, and 6
E) 1 through 6

Which model in the accompanying figure would elicit an attack response from another male stickleback?
A) 1 and 2
B) 1, 2, 4, and 5
C) 2, 3, and 5
D) 1, 3, 4, 5, and 6
E) 1 through 6

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
Which of the following is an organ that is NOT a primary influencer of animal behavior?
A) Thyroid gland
B) Adrenal gland
C) Thymus
D) Cerebellum
E) Spinal cord
A) Thyroid gland
B) Adrenal gland
C) Thymus
D) Cerebellum
E) Spinal cord

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
Which term most applies to learned behavior?
A) Inborn
B) Environmentally influenced
C) Genetically programmed
D) Instinctive
E) Inherited
A) Inborn
B) Environmentally influenced
C) Genetically programmed
D) Instinctive
E) Inherited

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
The study of behavior in natural environments from an evolutionary perspective is called:
A) ethology.
B) animal behavior.
C) behavioral ecology.
D) behavioral ethology.
E) direct fitness.
A) ethology.
B) animal behavior.
C) behavioral ecology.
D) behavioral ethology.
E) direct fitness.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
The ability of an infant organism to be able to keep track of the location of its mother is an example of:
A) classical conditioning.
B) habituation.
C) imprinting.
D) insight.
E) operant conditioning.
A) classical conditioning.
B) habituation.
C) imprinting.
D) insight.
E) operant conditioning.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
A squirrel is born and raised in captivity. Once released into the wild, it immediately begins to bury nuts. This is an example of:
A) direct fitness.
B) learning.
C) innate behavior.
D) learned behavior.
E) habituation.
A) direct fitness.
B) learning.
C) innate behavior.
D) learned behavior.
E) habituation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
A rat had one bad experience with a poisoned food that caused it to become sick. This rat will now avoid that food due to a behavior known as:
A) classical conditioning.
B) habituation.
C) imprinting.
D) insight.
E) operant conditioning.
A) classical conditioning.
B) habituation.
C) imprinting.
D) insight.
E) operant conditioning.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
Figure 52-2

Refer to the accompanying figure. In this sequence of events, the bell is serving as:
A) a motor stimulus.
B) the conditioned stimulus.
C) a cognition stimulus.
D) a sign stimulus.
E) the unconditioned stimulus.

Refer to the accompanying figure. In this sequence of events, the bell is serving as:
A) a motor stimulus.
B) the conditioned stimulus.
C) a cognition stimulus.
D) a sign stimulus.
E) the unconditioned stimulus.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
Which statement concerning play is FALSE?
A) It may be an example of imprinting.
B) It may be a way of learning to coordinate movements.
C) It may help animals learn social skills.
D) It may be a way to practice adult behavior.
E) It may function as a means of exercise.
A) It may be an example of imprinting.
B) It may be a way of learning to coordinate movements.
C) It may help animals learn social skills.
D) It may be a way to practice adult behavior.
E) It may function as a means of exercise.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
Figure 52-2

The sequence in the accompanying figure illustrates:
A) classical conditioning.
B) habituation.
C) imprinting.
D) insight.
E) operant conditioning.

The sequence in the accompanying figure illustrates:
A) classical conditioning.
B) habituation.
C) imprinting.
D) insight.
E) operant conditioning.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
Which term describes an animal whose behavior is tied to phases of the moon?
A) Diurnal
B) Lunar
C) Parasitic
D) Reptilian
E) Nocturnal
A) Diurnal
B) Lunar
C) Parasitic
D) Reptilian
E) Nocturnal

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
As the sun is setting, you notice bats coming out of a cave to begin a period of heavy activity. In the very early morning, several days later, you notice them entering the cave to sleep. Which circadian rhythm would best explain this observation?
A) Crepuscular
B) Nocturnal
C) Diurnal
D) Lunar
E) Asynchronous
A) Crepuscular
B) Nocturnal
C) Diurnal
D) Lunar
E) Asynchronous

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
What is the best definition of learning?
A) A conditioned response to a repetitive stimulus
B) A long-term change in behavior due to experience
C) A trial-and-error response to negative feedback
D) The ability to ignore unwanted or irrelevant stimuli
E) Communication with another member of a society for mutual benefit
A) A conditioned response to a repetitive stimulus
B) A long-term change in behavior due to experience
C) A trial-and-error response to negative feedback
D) The ability to ignore unwanted or irrelevant stimuli
E) Communication with another member of a society for mutual benefit

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
Loggerhead sea turtles use which of the following to travel across the Atlantic Ocean, mate, and lay their eggs?
A) Compass sense only
B) Map sense only
C) Both compass sense and map sense
D) Neither compass sense nor map sense
E) Circadian rhythms
A) Compass sense only
B) Map sense only
C) Both compass sense and map sense
D) Neither compass sense nor map sense
E) Circadian rhythms

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
Which of the following animal behaviors generates a great deal of controversy in scientific research because it may approximate human thought processes?
A) Habituation
B) Classical conditioning
C) Operant conditioning
D) Cognition
E) Imprinting
A) Habituation
B) Classical conditioning
C) Operant conditioning
D) Cognition
E) Imprinting

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
Which statement about biological clocks is FALSE?
A) They are limited to vertebrates.
B) They are regulated by clock proteins that act both within and outside the nervous system.
C) They have complex feedback loops.
D) They are controlled by genes.
E) They are capable of sustaining biological rhythms independently of environmental cues.
A) They are limited to vertebrates.
B) They are regulated by clock proteins that act both within and outside the nervous system.
C) They have complex feedback loops.
D) They are controlled by genes.
E) They are capable of sustaining biological rhythms independently of environmental cues.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
When some birds mature, they migrate long distances to their breeding grounds or to escape harsh weather. A signal for this type of behavior is often:
A) a conditioned stimulus.
B) day length.
C) negative reinforcement.
D) a sign stimulus.
E) territoriality.
A) a conditioned stimulus.
B) day length.
C) negative reinforcement.
D) a sign stimulus.
E) territoriality.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
A human urban dweller reports that she does not sleep well in a rural area. This is most clearly an example of which of the following?
A) Habituation
B) Classical conditioning
C) Operant conditioning
D) Cognition
E) Imprinting
A) Habituation
B) Classical conditioning
C) Operant conditioning
D) Cognition
E) Imprinting

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
In mammals, the master clock is located in the:
A) pineal gland.
B) suprachiasmatic nucleus.
C) crepuscular gland.
D) biological clock.
E) pituitary gland.
A) pineal gland.
B) suprachiasmatic nucleus.
C) crepuscular gland.
D) biological clock.
E) pituitary gland.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
Which paired terms are incorrectly matched?
A) Classical conditioning−extinction
B) Habituation−relevant stimuli
C) Imprinting−behavioral bonding
D) Insight−trial and error
E) Operant conditioning−reward
A) Classical conditioning−extinction
B) Habituation−relevant stimuli
C) Imprinting−behavioral bonding
D) Insight−trial and error
E) Operant conditioning−reward

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
Animals, like fiddler crabs, that are busiest at dawn or dusk are known as:
A) crepuscular.
B) nocturnal.
C) diurnal.
D) lunar.
E) asynchronous.
A) crepuscular.
B) nocturnal.
C) diurnal.
D) lunar.
E) asynchronous.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
Which of the following is a correct statement regarding biological clocks?
A) They simply respond to environmental cues.
B) They are incapable of sustaining biological rhythms independently.
C) They have been identified in only a few eukaryotes.
D) They are controlled by genes.
E) The principal clock is located in specific areas of the peripheral nervous system.
A) They simply respond to environmental cues.
B) They are incapable of sustaining biological rhythms independently.
C) They have been identified in only a few eukaryotes.
D) They are controlled by genes.
E) The principal clock is located in specific areas of the peripheral nervous system.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
Figure 52-2

The first panel of the sequence in the accompanying figure reflects:
A) trial-and-error.
B) negative reinforcement.
C) an irrelevant stimulus.
D) the conditioned response.
E) the unconditioned response.

The first panel of the sequence in the accompanying figure reflects:
A) trial-and-error.
B) negative reinforcement.
C) an irrelevant stimulus.
D) the conditioned response.
E) the unconditioned response.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
You place ant traps around the house. You notice after a period of time that the ants do not enter the traps and the population size is greater than it was originally. This experience would best be explained by:
A) classical conditioning.
B) habituation.
C) proximate cause.
D) innate behavior.
E) operant conditioning.
A) classical conditioning.
B) habituation.
C) proximate cause.
D) innate behavior.
E) operant conditioning.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
Which of the following is used by loggerhead turtles as a guide for navigation?
A) Gravity
B) Odors
C) Magnetic fields
D) Temperature
E) Stars
A) Gravity
B) Odors
C) Magnetic fields
D) Temperature
E) Stars

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
Which of the following changes is an example of a proximate cause of animal migration?
A) Temperature
B) Availability of food resources
C) Safe nesting sites
D) Rainfall
E) Day length
A) Temperature
B) Availability of food resources
C) Safe nesting sites
D) Rainfall
E) Day length

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
Dominance hierarchies:
A) are limited to primate societies.
B) are only characteristic of males defending territories.
C) are never passed from one generation to the next.
D) are always passed from one generation to the next.
E) may vary between the sexes in some species.
A) are limited to primate societies.
B) are only characteristic of males defending territories.
C) are never passed from one generation to the next.
D) are always passed from one generation to the next.
E) may vary between the sexes in some species.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
The difference between a society and an aggregation is that aggregations are characterized by:
A) communication between all animals present.
B) individuals present only for breeding.
C) a lack of intentional interaction between those animals present.
D) confinement; while in a society the individuals are free to enter and exit.
E) genetically determined behavioral responses required to bring these individuals together.
A) communication between all animals present.
B) individuals present only for breeding.
C) a lack of intentional interaction between those animals present.
D) confinement; while in a society the individuals are free to enter and exit.
E) genetically determined behavioral responses required to bring these individuals together.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
Males of some animal species have a display area where they compete for reproductively available females. This area is known as a:
A) lek.
B) home range.
C) pride.
D) territory.
E) hive.
A) lek.
B) home range.
C) pride.
D) territory.
E) hive.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
Sexual selection:
A) is the basis for establishing elaborate societies.
B) leads to a reproductive advantage for some individuals over others of the same sex and species.
C) favors monogamous mating systems.
D) leads to the investment of parental care of offspring.
E) is not a type of natural selection.
A) is the basis for establishing elaborate societies.
B) leads to a reproductive advantage for some individuals over others of the same sex and species.
C) favors monogamous mating systems.
D) leads to the investment of parental care of offspring.
E) is not a type of natural selection.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
Figure 52-3
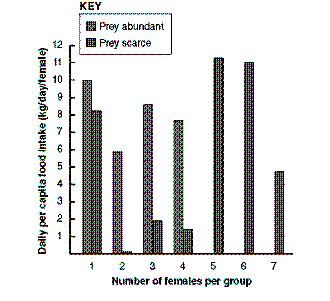
Which of the following is an INCORRECT statement regarding optimal foraging?
A) It is defined as the most efficient means of animal to obtain food.
B) When animals forage, they maximize their energy intake per unit of foraging time.
C) Optimal foraging may maximize an animal's reproductive success.
D) Avoiding predators while foraging is also a factor in determining optimal foraging strategies.
E) Animals can always afford to be selective when obtaining food items.
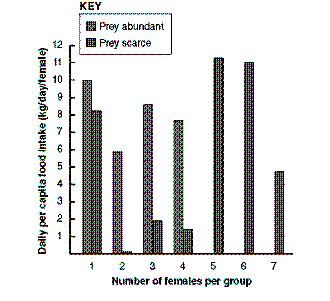
Which of the following is an INCORRECT statement regarding optimal foraging?
A) It is defined as the most efficient means of animal to obtain food.
B) When animals forage, they maximize their energy intake per unit of foraging time.
C) Optimal foraging may maximize an animal's reproductive success.
D) Avoiding predators while foraging is also a factor in determining optimal foraging strategies.
E) Animals can always afford to be selective when obtaining food items.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
Dominance, sexual behavior, and territoriality can all be related in song birds. This is because:
A) the establishment of a territory by singing tends to reduce conflict.
B) the establishment of a territory encourages use of the entire habitat and regulates the size of the breeding area.
C) competing species are eliminated.
D) only individuals that successfully defend their territory can mate.
E) females sing but males do not.
A) the establishment of a territory by singing tends to reduce conflict.
B) the establishment of a territory encourages use of the entire habitat and regulates the size of the breeding area.
C) competing species are eliminated.
D) only individuals that successfully defend their territory can mate.
E) females sing but males do not.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
A soldier ant dies defending the ant colony from invading termites. Which term best describes this event?
A) Suprachiasmatic protection
B) Sociobiology
C) Ultimate cause
D) Inclusive fitness
E) Altruism
A) Suprachiasmatic protection
B) Sociobiology
C) Ultimate cause
D) Inclusive fitness
E) Altruism

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
Which of the following animals are NOT sensitive to Earth's magnetic field and do NOT use it as a guide?
A) Birds
B) Sea turtles
C) Honeybees
D) Some fishes
E) Ants
A) Birds
B) Sea turtles
C) Honeybees
D) Some fishes
E) Ants

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
Mammals detect pheromones with specialized cells in which of the following organs?
A) Vomeronasal
B) Jejunum
C) Thymus
D) Spleen
E) Cochlea
A) Vomeronasal
B) Jejunum
C) Thymus
D) Spleen
E) Cochlea

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
For an animal to respond to a pheromone, it must:
A) have a specific receptor.
B) be able to see it coming.
C) be able to smell it with its nose.
D) have a thin epidermis or hair so it can penetrate.
E) be of the opposite sex of the individual from which it was produced.
A) have a specific receptor.
B) be able to see it coming.
C) be able to smell it with its nose.
D) have a thin epidermis or hair so it can penetrate.
E) be of the opposite sex of the individual from which it was produced.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
Which of the following is an example of intersexual selection?
A) An elaborate ornamental display to establish dominance
B) Physical combat
C) Producing a large number of eggs
D) Discouraging a competitor by having large antlers
E) A courtship ritual
A) An elaborate ornamental display to establish dominance
B) Physical combat
C) Producing a large number of eggs
D) Discouraging a competitor by having large antlers
E) A courtship ritual

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
Which of the following is NOT a cost of social behavior?
A) Increased competition for food and habitat
B) Increased risk of attracting predators
C) Increased risk of transmitting disease
D) Time and energy invested in gaining and maintaining social status
E) Increased time to locate prey
A) Increased competition for food and habitat
B) Increased risk of attracting predators
C) Increased risk of transmitting disease
D) Time and energy invested in gaining and maintaining social status
E) Increased time to locate prey

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
Figure 52-3
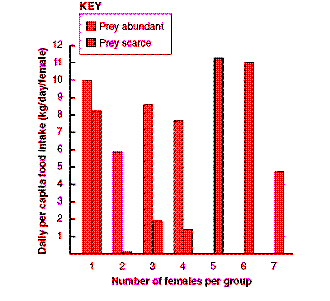
Which statement accurately reflects the data in the accompanying figure?
A) Successful foraging is independent of prey density.
B) Hunting groups of two to three individuals are more effective at low prey densities.
C) Larger hunting groups are more effective at low prey densities.
D) Hunting groups of two to three individuals are more effective at all prey densities.
E) Successful foraging is independent of hunting group size.
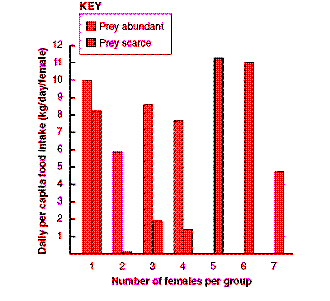
Which statement accurately reflects the data in the accompanying figure?
A) Successful foraging is independent of prey density.
B) Hunting groups of two to three individuals are more effective at low prey densities.
C) Larger hunting groups are more effective at low prey densities.
D) Hunting groups of two to three individuals are more effective at all prey densities.
E) Successful foraging is independent of hunting group size.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
In some animals, such as the marsh wren, one male bird mates with several females. This is known as:
A) polygyny.
B) polyandry.
C) monogamy.
D) a dominance hierarchy.
E) codominance.
A) polygyny.
B) polyandry.
C) monogamy.
D) a dominance hierarchy.
E) codominance.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
Parental care of offspring:
A) for many animals has a lower cost than benefit.
B) results in a decreased probability that each offspring will survive.
C) is more common in species in which the female produces two or more times during a breeding season.
D) is more common among male animals than among females.
E) is more common among male fishes than among females.
A) for many animals has a lower cost than benefit.
B) results in a decreased probability that each offspring will survive.
C) is more common in species in which the female produces two or more times during a breeding season.
D) is more common among male animals than among females.
E) is more common among male fishes than among females.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
Which factor is most critical for organisms to facilitate social behavior?
A) There must be a large population.
B) All present must be of the same species.
C) All present must have the same genetic imprinting.
D) There must be a mechanism for communication.
E) No outsiders can be allowed to enter the group.
A) There must be a large population.
B) All present must be of the same species.
C) All present must have the same genetic imprinting.
D) There must be a mechanism for communication.
E) No outsiders can be allowed to enter the group.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
Some members of an animal society may have greater success at reproduction as a result of:
A) dominance hierarchy.
B) sexual selection.
C) reproductive isolating mechanisms.
D) reproductive isolating mechanisms along with sexual selection.
E) dominance hierarchy along with sexual selection and reproductive isolating mechanisms.
A) dominance hierarchy.
B) sexual selection.
C) reproductive isolating mechanisms.
D) reproductive isolating mechanisms along with sexual selection.
E) dominance hierarchy along with sexual selection and reproductive isolating mechanisms.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
The field of sociobiology was much expanded by the book, Sociobiology: The New Synthesis , written by:
A) K. Lorenz.
B) N. Tinbergen.
C) W. Hamilton.
D) W. Dilger.
E) E. O. Wilson.
A) K. Lorenz.
B) N. Tinbergen.
C) W. Hamilton.
D) W. Dilger.
E) E. O. Wilson.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
Many organisms have different reproductive strategies. Which of the following most accurately reflects altruistic behavior?
A) Courtship rituals
B) Dominance hierarchy
C) Optimal foraging strategies
D) Adult care of related offspring
E) Territoriality
A) Courtship rituals
B) Dominance hierarchy
C) Optimal foraging strategies
D) Adult care of related offspring
E) Territoriality

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
Figure 52-3
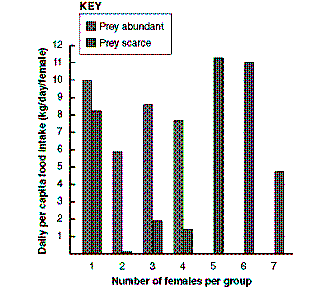
Based on the accompanying figure, when prey are abundant, the most effective hunting group size is:
A) 1
B) 3
C) 4
D) 5
E) 7
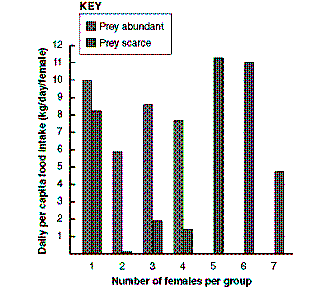
Based on the accompanying figure, when prey are abundant, the most effective hunting group size is:
A) 1
B) 3
C) 4
D) 5
E) 7

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
Imprinting is a type of social learning based on an early experience.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
When the food supply is far from a beehive, the scout bee will perform a waggle dance.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
Which vertebrate has a social structure most closely resembling social insects?
A) The phalarope
B) Lions
C) The naked mole rats
D) Siberian tigers
E) Chimpanzees
A) The phalarope
B) Lions
C) The naked mole rats
D) Siberian tigers
E) Chimpanzees

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
By definition, pheromones are chemical signals secreted into the bloodstream.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
Identify two different types of mating systems and list the advantages and disadvantages of each.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
Briefly describe the ways animals communicate. List some benefits of the different methods.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
Instinct is another name for innate behavior.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
Hansen's rule is a mathematical model dealing with altruism.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
In polygyny , one female mates with several males.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
Develop a scenario different from that in the book that demonstrates a survival benefit of each of the following types of learning: classical conditioning, operant conditioning habituation, imprinting, and insight.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
In the mammalian biological clock, the "master clock" is located in the pineal gland.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72
The egg rolling behavior in the European graylag goose is an example of a motor program.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73
Distinguish between diurnal, nocturnal, and crepuscular animals, and provide an example of each.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
74
Aposematic coloration is also called habituation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
75
In a honeybee society, the worker bees are all male.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
76
The salivating response to a bell is what Pavlov called an unconditioned response.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
77
In classical conditioning, an animal must do something to gain a reward or avoid punishment.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
78
Proximate causes of behavior have evolutionary explanations.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
79
Diurnal animals are most active at night.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
80
Navigation requires both compass sense and map sense.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



