Deck 50: Reproduction
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/121
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 50: Reproduction
1
Internal fertilization is more advantageous than external fertilization because internal fertilization
A) permits cross-species fertilization.
B) is more open to chance.
C) produces a motile egg.
D) increases the life span of gametes.
E) provides a protective environment.
A) permits cross-species fertilization.
B) is more open to chance.
C) produces a motile egg.
D) increases the life span of gametes.
E) provides a protective environment.
E
2
Where are mitochondria present in the sperm?
A) Acrosome
B) Head
C) Midpiece
D) Tail
E) Throughout the cell
A) Acrosome
B) Head
C) Midpiece
D) Tail
E) Throughout the cell
A
3
Figure 50-1
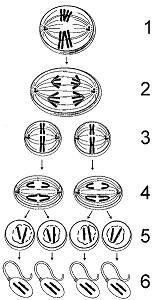
The spermatids are the cells in the accompanying figure labeled as
A) 1
B) 2
C) 3
D) 5
E) 6

The spermatids are the cells in the accompanying figure labeled as
A) 1
B) 2
C) 3
D) 5
E) 6
D
4
Arrange the stages of sperm development in chronological order.
(1) Sperm
(2) Spermatid
(3) Primary spermatocyte
(4) Secondary spermatocyte
(5) Spermatogonium
A) 5 → 2 → 3 → 4 → 1
B) 5 → 3 → 4 → 2 → 1
C) 2 → 3 → 4 → 1 → 5
D) 2 → 5 → 3 → 4 → 1
E) 3 → 4 → 5 → 2 → 1
(1) Sperm
(2) Spermatid
(3) Primary spermatocyte
(4) Secondary spermatocyte
(5) Spermatogonium
A) 5 → 2 → 3 → 4 → 1
B) 5 → 3 → 4 → 2 → 1
C) 2 → 3 → 4 → 1 → 5
D) 2 → 5 → 3 → 4 → 1
E) 3 → 4 → 5 → 2 → 1

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 121 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
Figure 50-2
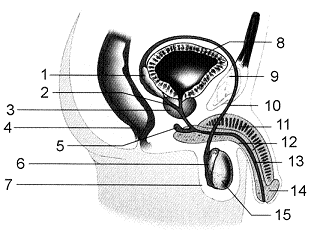
Refer to the accompanying figure. The function of the structure labeled as 3 is to
A) secrete an alkaline fluid that neutralizes the acids of the vagina.
B) produce a nutritive fluid for the sperm.
C) provide a place for maturation and storage of sperm.
D) secrete mucus that lubricates the penis.
E) maintain sperm at a low body temperature.

Refer to the accompanying figure. The function of the structure labeled as 3 is to
A) secrete an alkaline fluid that neutralizes the acids of the vagina.
B) produce a nutritive fluid for the sperm.
C) provide a place for maturation and storage of sperm.
D) secrete mucus that lubricates the penis.
E) maintain sperm at a low body temperature.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 121 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
Sexual reproduction involves which of the following processes?
A) Splitting
B) Budding
C) Fertilization
D) Fragmentation
E) Parthenogenesis
A) Splitting
B) Budding
C) Fertilization
D) Fragmentation
E) Parthenogenesis

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 121 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
The mathematical model developed by Wayne Getz predicts the existence of asexual or sexual reproduction within a population. Which statement best describes this model?
A) The offspring produced by sexual reproduction would be most successful in a stable environment.
B) Clones produced by asexual reproduction would succeed in an unstable environment.
C) Both reproductive strategies would coexist under conditions of moderate change.
D) One assumption is that the offspring of sexual reproduction will use resources in the same way.
E) One assumption is that the offspring of asexual reproduction will use resources differently.
A) The offspring produced by sexual reproduction would be most successful in a stable environment.
B) Clones produced by asexual reproduction would succeed in an unstable environment.
C) Both reproductive strategies would coexist under conditions of moderate change.
D) One assumption is that the offspring of sexual reproduction will use resources in the same way.
E) One assumption is that the offspring of asexual reproduction will use resources differently.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 121 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
Figure 50-2
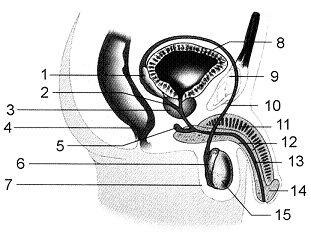
Refer to the accompanying figure. Which of the labeled structures refers to the prostate gland?
A) 1
B) 3
C) 5
D) 7
E) 9

Refer to the accompanying figure. Which of the labeled structures refers to the prostate gland?
A) 1
B) 3
C) 5
D) 7
E) 9

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 121 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
What would occur if humans reproduced by parthenogenesis?
A) Males would need to produce more sperm.
B) External fertilization would be necessary.
C) Number of women in the population would increase.
D) Population would not reproduce asexually.
E) No gametes would be produced.
A) Males would need to produce more sperm.
B) External fertilization would be necessary.
C) Number of women in the population would increase.
D) Population would not reproduce asexually.
E) No gametes would be produced.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 121 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
Figure 50-2
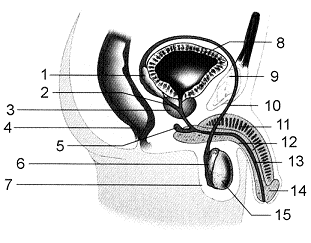
Refer to the accompanying figure. If a cut was made between numbers 6 and 10, ____.
A) seminal fluid would not be produced
B) sperm cells would not be produced
C) sperm maturation would be inhibited
D) the seminal vesicles and the testes would be below the cut
E) sperm cells would not be released

Refer to the accompanying figure. If a cut was made between numbers 6 and 10, ____.
A) seminal fluid would not be produced
B) sperm cells would not be produced
C) sperm maturation would be inhibited
D) the seminal vesicles and the testes would be below the cut
E) sperm cells would not be released

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 121 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
Which statement with regard to Sertoli cells is FALSE?
A) They secrete hormones.
B) They are joined by tight junctions.
C) They form a blood-testis barrier.
D) They phagocytize discarded sperm cytoplasm.
E) They help move the sperm into the blood.
A) They secrete hormones.
B) They are joined by tight junctions.
C) They form a blood-testis barrier.
D) They phagocytize discarded sperm cytoplasm.
E) They help move the sperm into the blood.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 121 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
Figure 50-2
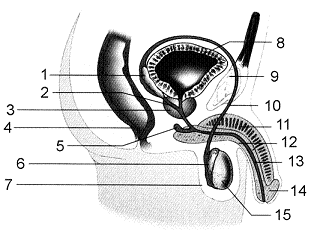
In the accompanying figure, what is the function of the structure that is labeled as 7?
A) Maintaining sperm below body temperature
B) Storing of mature sperm
C) Producing prostaglandins
D) Producing nutritive fluid to support active sperm
E) Producing alkaline fluid to protect sperm in the vagina

In the accompanying figure, what is the function of the structure that is labeled as 7?
A) Maintaining sperm below body temperature
B) Storing of mature sperm
C) Producing prostaglandins
D) Producing nutritive fluid to support active sperm
E) Producing alkaline fluid to protect sperm in the vagina

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 121 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
Figure 50-2
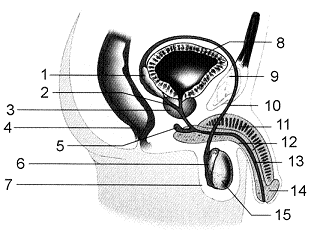
Refer to the accompanying figure. The function of the structure labeled as 6 is to
A) secrete an alkaline fluid that neutralizes the acids of the vagina.
B) produce a nutritive fluid for the sperm.
C) provide a place for maturation and storage of sperm.
D) secrete mucus that lubricates the penis.
E) maintain sperm at a low body temperature.

Refer to the accompanying figure. The function of the structure labeled as 6 is to
A) secrete an alkaline fluid that neutralizes the acids of the vagina.
B) produce a nutritive fluid for the sperm.
C) provide a place for maturation and storage of sperm.
D) secrete mucus that lubricates the penis.
E) maintain sperm at a low body temperature.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 121 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
Mature sperm are stored in the ______.
A) abdominal wall.
B) scrotum.
C) epididymis.
D) ejaculatory duct.
E) vas deferens.
A) abdominal wall.
B) scrotum.
C) epididymis.
D) ejaculatory duct.
E) vas deferens.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 121 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
One advantage of sexual reproduction over asexual reproduction is that
A) sexual reproduction is faster.
B) sexual reproduction is less difficult to achieve.
C) sexual reproduction is particularly effective for sessile animals.
D) sexual reproduction promotes genetic diversity.
E) sexual reproduction produces genetically identical offspring.
A) sexual reproduction is faster.
B) sexual reproduction is less difficult to achieve.
C) sexual reproduction is particularly effective for sessile animals.
D) sexual reproduction promotes genetic diversity.
E) sexual reproduction produces genetically identical offspring.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 121 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
Figure 50-1
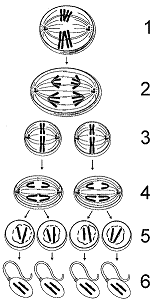
Based on the accompanying figure, which label describes diploid cells?
A) 2
B) 3
C) 4
D) 5
E) 6

Based on the accompanying figure, which label describes diploid cells?
A) 2
B) 3
C) 4
D) 5
E) 6

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 121 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
In an adult male, the ____ extends through the inguinal canal.
A) scrotum
B) ejaculatory duct
C) vas deferens
D) seminal vesicles
E) urethra
A) scrotum
B) ejaculatory duct
C) vas deferens
D) seminal vesicles
E) urethra

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 121 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
The function of the bulbourethral gland is to
A) secrete an alkaline fluid that neutralizes the acids of the vagina.
B) produce a nutritive fluid for the sperm.
C) provide a place for maturation and storage of sperm.
D) secrete mucus that lubricates the penis.
E) maintain sperm at a low body temperature.
A) secrete an alkaline fluid that neutralizes the acids of the vagina.
B) produce a nutritive fluid for the sperm.
C) provide a place for maturation and storage of sperm.
D) secrete mucus that lubricates the penis.
E) maintain sperm at a low body temperature.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 121 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
Which group can reproduce asexually?
A) Amphibians
B) Insects
C) Gastropods
D) Fishes
E) Cnidarians
A) Amphibians
B) Insects
C) Gastropods
D) Fishes
E) Cnidarians

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 121 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
Which structure connects to the scrotum?
A) An acrosome
B) A flagellum
C) A head
D) An inguinal canal
E) A midpiece
A) An acrosome
B) A flagellum
C) A head
D) An inguinal canal
E) A midpiece

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 121 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
Which hormone stimulates masculine physical characteristics?
A) Inhibin
B) Follicle-stimulating hormone
C) Interstitial cell stimulating hormone
D) Luteinizing hormone
E) Testosterone
A) Inhibin
B) Follicle-stimulating hormone
C) Interstitial cell stimulating hormone
D) Luteinizing hormone
E) Testosterone

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 121 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
Figure 50-4
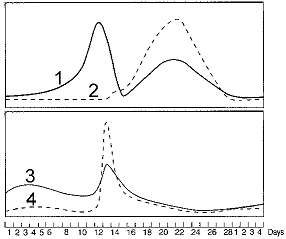
Refer to the accompanying figure. On which day of a 28-day menstrual cycle would you predict that estrogen levels would peak?
A) 10
B) 12
C) 16
D) 19
E) 22

Refer to the accompanying figure. On which day of a 28-day menstrual cycle would you predict that estrogen levels would peak?
A) 10
B) 12
C) 16
D) 19
E) 22

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 121 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
Which accessory gland produces prostaglandins?
A) Seminal vesicles
B) Prostate gland
C) Bulbourethral glands
D) Vas deferens
E) Testes
A) Seminal vesicles
B) Prostate gland
C) Bulbourethral glands
D) Vas deferens
E) Testes

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 121 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
An example of a primary sex characteristic in males is
A) growth of facial hair.
B) growth of body hair.
C) spermatogenesis.
D) muscle development.
E) increase in length of vocal cords.
A) growth of facial hair.
B) growth of body hair.
C) spermatogenesis.
D) muscle development.
E) increase in length of vocal cords.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 121 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
Organize the sequence of structures through which sperm must pass upon ejaculation. (1) Urethra
(2) Ejaculatory duct
(3) Epididymis
(4) Vas deferens
A) 3 → 2 → 1 → 4
B) 3 → 4 → 2 → 1
C) 2 → 3 → 4 → 1
D) 2 → 4 → 3 → 1
E) 4 → 3 → 2 → 1
(2) Ejaculatory duct
(3) Epididymis
(4) Vas deferens
A) 3 → 2 → 1 → 4
B) 3 → 4 → 2 → 1
C) 2 → 3 → 4 → 1
D) 2 → 4 → 3 → 1
E) 4 → 3 → 2 → 1

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 121 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
Fertility is impaired when a male's sperm count drops below ____ sperm per milliliter of semen, and the male is considered sterile if his sperm count drops below ____ sperm per milliliter of semen.
A) 500 million; 200 million
B) 100 million; 50 million
C) 35 million; 20 million
D) 2 million; 1 million
E) 500,000; 100,000
A) 500 million; 200 million
B) 100 million; 50 million
C) 35 million; 20 million
D) 2 million; 1 million
E) 500,000; 100,000

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 121 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
In males, gonadotropin-releasing hormone stimulates the ____ to secrete ____.
A) anterior pituitary; inhibin
B) anterior pituitary; FSH and LH
C) anterior pituitary; testosterone
D) posterior pituitary; FSH and LH
E) posterior pituitary; testosterone
A) anterior pituitary; inhibin
B) anterior pituitary; FSH and LH
C) anterior pituitary; testosterone
D) posterior pituitary; FSH and LH
E) posterior pituitary; testosterone

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 121 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
Figure 50-4
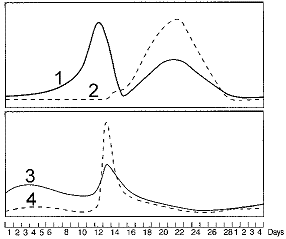
Refer to the accompanying figure. Which statement about the corpus luteum is FALSE?
A) It is responsible for the second peak in the line labeled as 1.
B) It is responsible for the second peak in the line labeled as 2.
C) It is responsible for the first peak in the line labeled as 1.
D) It develops from the empty follicle following ovulation.
E) It is most active between days 18 and 26.

Refer to the accompanying figure. Which statement about the corpus luteum is FALSE?
A) It is responsible for the second peak in the line labeled as 1.
B) It is responsible for the second peak in the line labeled as 2.
C) It is responsible for the first peak in the line labeled as 1.
D) It develops from the empty follicle following ovulation.
E) It is most active between days 18 and 26.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 121 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
One secondary spermatocyte ultimately produces
A) one mature sperm.
B) two mature sperm.
C) four mature sperm.
D) eight mature sperm.
E) an indeterminate number of sperm.
A) one mature sperm.
B) two mature sperm.
C) four mature sperm.
D) eight mature sperm.
E) an indeterminate number of sperm.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 121 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
Figure 50-4
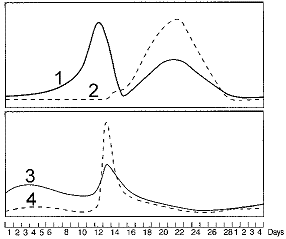
Refer to the accompanying figure. The peak in ____ around day 21 corresponds with ____.
A) luteinizing hormone; ovulation
B) follicle-stimulating hormone; the development of the follicle
C) estrogen; breakdown of the endometrium
D) progesterone; continuing to build up the endometrium
E) estrogen; ovulation

Refer to the accompanying figure. The peak in ____ around day 21 corresponds with ____.
A) luteinizing hormone; ovulation
B) follicle-stimulating hormone; the development of the follicle
C) estrogen; breakdown of the endometrium
D) progesterone; continuing to build up the endometrium
E) estrogen; ovulation

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 121 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
Spermatogenesis takes place in which of the following structures?
A) Seminiferous tubules
B) Seminal vesicles
C) Prostate gland
D) Bulbourethral glands
E) Glans
A) Seminiferous tubules
B) Seminal vesicles
C) Prostate gland
D) Bulbourethral glands
E) Glans

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 121 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
What does prostate-specific antigen (PS A) do?
A) Clots semen in the vagina
B) Lubricates the penis for penetration
C) Provides nutrition for sperm while in the vagina
D) Unclots semen in the vagina
E) Neutralizes acids in the vagina
A) Clots semen in the vagina
B) Lubricates the penis for penetration
C) Provides nutrition for sperm while in the vagina
D) Unclots semen in the vagina
E) Neutralizes acids in the vagina

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 121 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
Which cells in the testes secrete testosterone?
A) Sertoli cells
B) Luteinizing cells
C) Glycoprotein cells
D) Interstitial cells
E) Sperm cells
A) Sertoli cells
B) Luteinizing cells
C) Glycoprotein cells
D) Interstitial cells
E) Sperm cells

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 121 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
Sperm pass through several stages during their development. The earliest stage in which the cell becomes haploid is the
A) sperm.
B) spermatid.
C) primary spermatocyte.
D) secondary spermatocyte.
E) spermatogonium.
A) sperm.
B) spermatid.
C) primary spermatocyte.
D) secondary spermatocyte.
E) spermatogonium.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 121 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
Both male and female gonads function to produce _____, _____, and _______.
A) gametes; erections; secondary sexual characteristics
B) gametes; hormones; secondary sexual characteristics
C) gametes; embryos; primary sexual characteristics
D) gametes; hormones; sex drive
E) hormones; secondary sexual characteristics; sex drive
A) gametes; erections; secondary sexual characteristics
B) gametes; hormones; secondary sexual characteristics
C) gametes; embryos; primary sexual characteristics
D) gametes; hormones; sex drive
E) hormones; secondary sexual characteristics; sex drive

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 121 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
Which substance inhibits FSH production in males?
A) Testosterone
B) Epinephrine
C) Inhibin
D) Estrogen
E) Viagra
A) Testosterone
B) Epinephrine
C) Inhibin
D) Estrogen
E) Viagra

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 121 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
Which of the following sequences is correct ?
A) Males: inhibin: secreted by sperm cells
B) Males: Luteinizing hormone: stimulate production of androgen binding protein
C) Males: gonadotropin-releasing hormone: stimulate LH and FSH secretion
D) Females: progesterone: stimulate ovulation
E) Females: inhibin: decreased secretion of FSH
A) Males: inhibin: secreted by sperm cells
B) Males: Luteinizing hormone: stimulate production of androgen binding protein
C) Males: gonadotropin-releasing hormone: stimulate LH and FSH secretion
D) Females: progesterone: stimulate ovulation
E) Females: inhibin: decreased secretion of FSH

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 121 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
______ blocks the action of an enzyme that breaks down the signaling molecule that sustains erection.
A) Epinephrine
B) Lipitor
C) Viagra
D) Elequis
E) Ibuprofen
A) Epinephrine
B) Lipitor
C) Viagra
D) Elequis
E) Ibuprofen

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 121 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
The seminal vesicles secrete
A) fructose, which nourishes the developing embryo.
B) a basic fluid, which neutralizes the acidic environment of the vagina.
C) mucus, which lubricates the penis.
D) sperm, which fertilize the ovum.
E) prostaglandins, which stimulate contraction of the uterus.
A) fructose, which nourishes the developing embryo.
B) a basic fluid, which neutralizes the acidic environment of the vagina.
C) mucus, which lubricates the penis.
D) sperm, which fertilize the ovum.
E) prostaglandins, which stimulate contraction of the uterus.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 121 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
The erectile tissue in the penis includes the
A) epididymis.
B) mons pubis.
C) cavernous bodies.
D) seminal vesicles.
E) vas deferens.
A) epididymis.
B) mons pubis.
C) cavernous bodies.
D) seminal vesicles.
E) vas deferens.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 121 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
Which hormone that signals the mother's corpus luteum to continue to function?
A) Estrogen
B) Progesterone
C) Human chorionic gonadotropin
D) LH
E) FSH
A) Estrogen
B) Progesterone
C) Human chorionic gonadotropin
D) LH
E) FSH

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 121 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
The lining of the uterus is called the
A) diaphragm.
B) endothelium.
C) endometrium.
D) hymen.
E) cervix.
A) diaphragm.
B) endothelium.
C) endometrium.
D) hymen.
E) cervix.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 121 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
Figure 50-3
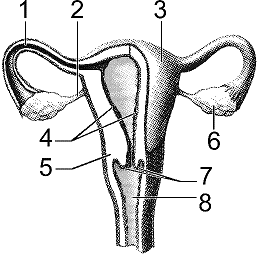
In the accompanying figure, fertilization occurs within which of the labeled structures?
A) 1
B) 2
C) 4
D) 7
E) 8

In the accompanying figure, fertilization occurs within which of the labeled structures?
A) 1
B) 2
C) 4
D) 7
E) 8

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 121 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
Figure 50-3
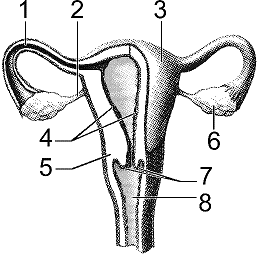
Which structure in the accompanying figure is responsible for the production of hormones?
A) 1
B) 3
C) 4
D) 6
E) 7

Which structure in the accompanying figure is responsible for the production of hormones?
A) 1
B) 3
C) 4
D) 6
E) 7

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 121 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
Figure 50-3
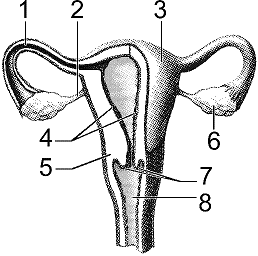
Refer to the accompanying figure. The cervix is labeled
A) 3
B) 4
C) 5
D) 7
E) 8

Refer to the accompanying figure. The cervix is labeled
A) 3
B) 4
C) 5
D) 7
E) 8

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 121 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
After fertilization, which hormone is secreted by the developing embryo to maintain the function of the corpus luteum?
A) GnRH
B) FSH
C) hCG
D) ACTH
E) LH
A) GnRH
B) FSH
C) hCG
D) ACTH
E) LH

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 121 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
Which of the following hormones stimulates ovulation?
A) Gonadotropin-releasing hormone
B) Luteinizing hormone
C) Follicle-stimulating hormone
D) Estrogen
E) Progesterone
A) Gonadotropin-releasing hormone
B) Luteinizing hormone
C) Follicle-stimulating hormone
D) Estrogen
E) Progesterone

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 121 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
Which technique is most routine for breast cancer screening?
A) Breast MRI
B) Breast CT scan
C) Mammogram
D) Serum PSA assay
E) Genetic testing for BRCA1 or BRCA2 mutations
A) Breast MRI
B) Breast CT scan
C) Mammogram
D) Serum PSA assay
E) Genetic testing for BRCA1 or BRCA2 mutations

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 121 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
Fertilization normally occurs in the ____.
A) vagina
B) oviducts
C) uterus
D) labia major
E) cervix
A) vagina
B) oviducts
C) uterus
D) labia major
E) cervix

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 121 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
Figure 50-3
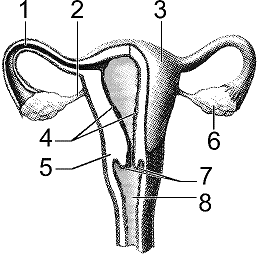
Which structure in the accompanying figure is a common site of cancer that can usually be detected by a Pap smear?
A) 4
B) 5
C) 6
D) 7
E) 8

Which structure in the accompanying figure is a common site of cancer that can usually be detected by a Pap smear?
A) 4
B) 5
C) 6
D) 7
E) 8

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 121 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
In the female, ____ stimulates ovulation.
A) GnRH
B) LH
C) FSH
D) estrogen
E) progesterone
A) GnRH
B) LH
C) FSH
D) estrogen
E) progesterone

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 121 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
In the female, the____ serves as a temporary endocrine gland and secretes ____.
A) pituitary; luteinizing hormone and follicle-stimulating hormone
B) ovaries; testosterone and luteinizing hormone
C) endometrium; estrogen and follicle-stimulating hormone
D) corpus luteum; progesterone and estrogen
E) uterus; luteinizing hormone and follicle-stimulating hormone
A) pituitary; luteinizing hormone and follicle-stimulating hormone
B) ovaries; testosterone and luteinizing hormone
C) endometrium; estrogen and follicle-stimulating hormone
D) corpus luteum; progesterone and estrogen
E) uterus; luteinizing hormone and follicle-stimulating hormone

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 121 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
Arrange the following stages of oogenesis in sequential order.
(1) Secondary oocyte
(2) Oogonium
(3) Ovum
(4) Primary oocyte
A) 4 → 1 → 2 → 3
B) 4 → 3 → 2 → 1
C) 3 → 2 → 4 → 1
D) 2 → 3 → 4 → 1
E) 2 → 4 → 1 → 3
(1) Secondary oocyte
(2) Oogonium
(3) Ovum
(4) Primary oocyte
A) 4 → 1 → 2 → 3
B) 4 → 3 → 2 → 1
C) 3 → 2 → 4 → 1
D) 2 → 3 → 4 → 1
E) 2 → 4 → 1 → 3

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 121 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
Which of the following is part of the vulva?
A) Urethra
B) Vestibule of the vagina
C) Cervix
D) Endometrium
E) Mons pubis
A) Urethra
B) Vestibule of the vagina
C) Cervix
D) Endometrium
E) Mons pubis

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 121 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
One function of the developing follicle is to
A) stimulate ovulation.
B) secrete progesterone.
C) secrete estrogens.
D) secrete prolactin.
E) secrete glycoproteins.
A) stimulate ovulation.
B) secrete progesterone.
C) secrete estrogens.
D) secrete prolactin.
E) secrete glycoproteins.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 121 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
The female erectile structure analogous to the male glans penis is the
A) vulva.
B) labia majora.
C) mons pubis.
D) hymen.
E) clitoris.
A) vulva.
B) labia majora.
C) mons pubis.
D) hymen.
E) clitoris.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 121 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
Which hormone causes contraction of the uterus?
A) Cortisol
B) Oxytocin
C) Prostaglandins
D) Progesterone
E) Estrogen
A) Cortisol
B) Oxytocin
C) Prostaglandins
D) Progesterone
E) Estrogen

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 121 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
Which hormone is secreted by the ovary after ovulation, but not before?
A) LH
B) FSH
C) Estrogen
D) Progesterone
E) hCG
A) LH
B) FSH
C) Estrogen
D) Progesterone
E) hCG

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 121 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
The ____ develops into a corpus luteum.
A) zona pellucida
B) uterine wall
C) primary oocyte
D) secondary oocyte
E) follicle
A) zona pellucida
B) uterine wall
C) primary oocyte
D) secondary oocyte
E) follicle

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 121 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
Granulosa cells surround a
A) primary oocyte.
B) secondary oocyte.
C) primary spermatocyte.
D) secondary spermatocyte.
E) Sertoli cell.
A) primary oocyte.
B) secondary oocyte.
C) primary spermatocyte.
D) secondary spermatocyte.
E) Sertoli cell.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 121 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
What occurs during the second stage of labor?
A) The cervix begins to dilate.
B) The cervix becomes effaced.
C) The fetus is "delivered."
D) The uterus begins to contract.
E) The amnion breaks.
A) The cervix begins to dilate.
B) The cervix becomes effaced.
C) The fetus is "delivered."
D) The uterus begins to contract.
E) The amnion breaks.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 121 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
The acrosome contains enzymes that
A) digest the zona pellucida.
B) digest the endometrium.
C) stimulate ovulation.
D) stimulate sperm motility.
E) inhibit premature ejaculation.
A) digest the zona pellucida.
B) digest the endometrium.
C) stimulate ovulation.
D) stimulate sperm motility.
E) inhibit premature ejaculation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 121 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
Testosterone is produced by the interstitial cells.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 121 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
In females, a primary oocyte completes meiosis II at the time of fertilization.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 121 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
Parthenogenesis is a form of sexual reproduction.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 121 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
Acrosomes contain nutrients for the developing sperm cells, and they also secrete hormones and other signaling molecules.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 121 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
What are the advantages and disadvantages of asexual and sexual reproduction?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 121 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
Afterbirth refers collectively to the
A) fetus and the placenta.
B) fetus and the surrounding fetal membranes.
C) fetus and the umbilical cord.
D) placenta and the fetal membranes.
E) fetus, the umbilical cord, and the placenta.
A) fetus and the placenta.
B) fetus and the surrounding fetal membranes.
C) fetus and the umbilical cord.
D) placenta and the fetal membranes.
E) fetus, the umbilical cord, and the placenta.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 121 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
Spermatogenesis takes place in the epididymis.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 121 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
For sexually active females, which method of contraception is most reliable?
A) Tubal ligation
B) IUD
C) Injectable contraceptives
D) Oral contraceptives
E) Condom/spermicide combination
A) Tubal ligation
B) IUD
C) Injectable contraceptives
D) Oral contraceptives
E) Condom/spermicide combination

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 121 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
Which of the following is the phase of maximum physical sensation?
A) Orgasm
B) Stimulation
C) Resolution
D) Plateau
E) Sexual excitement
A) Orgasm
B) Stimulation
C) Resolution
D) Plateau
E) Sexual excitement

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 121 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72
Identify two different types of contraception, one chemical and one surgical. Discuss the mode of action, effectiveness, advantages, and disadvantages of each method identified.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 121 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73
Sperm travel from the epididymis directly into the vas deferens.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 121 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
74
An example of a secondary sexual characteristic in males is spermatogenesis.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 121 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
75
In hermaphroditism, a single individual produces both sperm and eggs.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 121 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
76
Which of the following is the least effective method of contraception?
A) Progestin
B) Tubal ligation
C) IUDs
D) Rhythm method
E) Spermicidal foam
A) Progestin
B) Tubal ligation
C) IUDs
D) Rhythm method
E) Spermicidal foam

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 121 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
77
Secondary spermatocytes are produced in the first meiotic division.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 121 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
78
Identify two sexually transmitted diseases, listing the symptoms, effects, and treatments for each.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 121 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
79
The bulbourethral glands secrete a fluid containing fructose and prostaglandins.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 121 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
80
A laparoscope is used to guide the transfer of eggs into a woman's oviduct in
A) intrauterine insemination.
B) host mothering.
C) in vitro fertilization.
D) gamete intrafallopian transfer.
E) zygote intrafallopian transfer.
A) intrauterine insemination.
B) host mothering.
C) in vitro fertilization.
D) gamete intrafallopian transfer.
E) zygote intrafallopian transfer.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 121 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



