Deck 37: Reproduction in Flowering Plants
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Match between columns
Question
Question
Match between columns
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/81
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 37: Reproduction in Flowering Plants
1
Which statement about the megasporocyte is true ?
A) It undergoes meiosis to produce three haploid cells.
B) It is a diploid cell located within an ovule.
C) It divides mitotically to form a male gametophyte.
D) It plays an important role in cross-pollination.
E) It will give rise to the generative cell.
A) It undergoes meiosis to produce three haploid cells.
B) It is a diploid cell located within an ovule.
C) It divides mitotically to form a male gametophyte.
D) It plays an important role in cross-pollination.
E) It will give rise to the generative cell.
B
2
The union of gametes is called ____ and takes place within the ____ of a flower.
A) fertilization; ovary
B) fission; anther
C) meiosis; receptacle
D) mitosis; pistil
E) fusion; stamen
A) fertilization; ovary
B) fission; anther
C) meiosis; receptacle
D) mitosis; pistil
E) fusion; stamen
A
3
Each pollen grain produces two cells, one of which may develop into a(n):
A) polar nucleus.
B) pollen tube.
C) anther.
D) compound pistil.
E) filament.
A) polar nucleus.
B) pollen tube.
C) anther.
D) compound pistil.
E) filament.
B
4
Genes for self-incompatibility usually inhibit:
A) the production of pollen grains.
B) pollination.
C) the growth of the pollen tube.
D) the growth of the style.
E) microspore formation.
A) the production of pollen grains.
B) pollination.
C) the growth of the pollen tube.
D) the growth of the style.
E) microspore formation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
Figure 37-2  The shape of the bill on the bird in the accompanying figure is most likely the result of:
The shape of the bill on the bird in the accompanying figure is most likely the result of:
A) coevolution.
B) pollination.
C) asexual reproduction.
D) pseudocopulation.
E) inbreeding.
 The shape of the bill on the bird in the accompanying figure is most likely the result of:
The shape of the bill on the bird in the accompanying figure is most likely the result of:A) coevolution.
B) pollination.
C) asexual reproduction.
D) pseudocopulation.
E) inbreeding.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
All the sepals of a flower are collectively known as the:
A) calyx.
B) carpel.
C) corolla.
D) pistil.
E) receptacle.
A) calyx.
B) carpel.
C) corolla.
D) pistil.
E) receptacle.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
The diploid portion of a plant life cycle is known as the:
A) parental generation.
B) sporophyte generation.
C) daughter generation.
D) gametophyte generation.
E) reproductive generation.
A) parental generation.
B) sporophyte generation.
C) daughter generation.
D) gametophyte generation.
E) reproductive generation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
In angiosperms, the gametophyte generation:
A) results from the fertilization of two gametes.
B) is dominant.
C) is nutritionally dependent on the sporophyte.
D) produces gametes via meiosis.
E) produces spores by mitosis.
A) results from the fertilization of two gametes.
B) is dominant.
C) is nutritionally dependent on the sporophyte.
D) produces gametes via meiosis.
E) produces spores by mitosis.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
Most flowers are pollinated by which method?
A) wind
B) birds
C) bats
D) water
E) insects
A) wind
B) birds
C) bats
D) water
E) insects

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
Figure 37-1 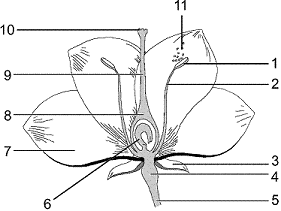 In the accompanying figure, the formation of eggs would occur in the structure labeled as ____.
In the accompanying figure, the formation of eggs would occur in the structure labeled as ____.
A) 1
B) 5
C) 6
D) 9
E) 10
 In the accompanying figure, the formation of eggs would occur in the structure labeled as ____.
In the accompanying figure, the formation of eggs would occur in the structure labeled as ____.A) 1
B) 5
C) 6
D) 9
E) 10

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
Flowers that are strongly oderiferous and blue or UV purple in color would most likely be pollinated by:
A) insects.
B) birds.
C) bats.
D) wind.
E) small rodents.
A) insects.
B) birds.
C) bats.
D) wind.
E) small rodents.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
Figure 37-1 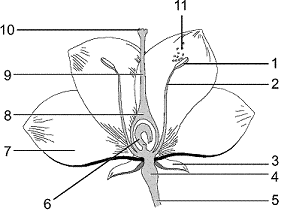 In the accompanying figure, the structure in which you would find microsporocytes is labeled as _____.
In the accompanying figure, the structure in which you would find microsporocytes is labeled as _____.
A) 1
B) 2
C) 6
D) 9
E) 10
 In the accompanying figure, the structure in which you would find microsporocytes is labeled as _____.
In the accompanying figure, the structure in which you would find microsporocytes is labeled as _____.A) 1
B) 2
C) 6
D) 9
E) 10

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
What mechanism is used to prevent self-pollination in angiosperms?
A) separating male and female individuals
B) shedding of pollen when the stigma of that flower is receptive to pollen
C) separating male and female flowers
D) preventing a plant form recognizing its own pollen with self-incompatibility genes
E) stimulating growth of the pollen tube with self-incompatibility genes
A) separating male and female individuals
B) shedding of pollen when the stigma of that flower is receptive to pollen
C) separating male and female flowers
D) preventing a plant form recognizing its own pollen with self-incompatibility genes
E) stimulating growth of the pollen tube with self-incompatibility genes

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
Plants that produce scentless, inconspicuous flowers with enormous amounts of pollen are adapted to which type of pollination?
A) wind
B) birds
C) bats
D) small rodents
E) insects
A) wind
B) birds
C) bats
D) small rodents
E) insects

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
Certain orchids produce flowers and secrete scents that resemble female bees so that male bees will mount these flowers and attempt to copulate with them. This bizarre occurrence is an example of:
A) fertilization.
B) coevolution.
C) apomixis.
D) self-pollination.
E) asexual reproduction.
A) fertilization.
B) coevolution.
C) apomixis.
D) self-pollination.
E) asexual reproduction.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
The female plant structure on which a pollen grain must land for sexual reproduction to occur is the:
A) style.
B) ovary.
C) stigma.
D) anther.
E) style.
A) style.
B) ovary.
C) stigma.
D) anther.
E) style.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
Bat-pollinated, night-blooming flowers would most likely display which two characteristics?
A) blue petals and sticky pollen grains
B) yellow petals and the scent of rotting flesh
C) orange petals and no scent
D) white petals and a strongly sweet scent
E) red petals and sticky pollen grains
A) blue petals and sticky pollen grains
B) yellow petals and the scent of rotting flesh
C) orange petals and no scent
D) white petals and a strongly sweet scent
E) red petals and sticky pollen grains

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
Flower parts are borne on the tip of a stalk referred to as the:
A) calyx.
B) corolla.
C) filament.
D) receptacle.
E) stigma.
A) calyx.
B) corolla.
C) filament.
D) receptacle.
E) stigma.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
Figure 37-2  What type of floral attraction would work best on the pollinator in the accompanying figure?
What type of floral attraction would work best on the pollinator in the accompanying figure?
A) white flowers
B) purple or blue flowers
C) a strong sweet scent
D) a strong carrion-like scent
E) sweet nectar
 What type of floral attraction would work best on the pollinator in the accompanying figure?
What type of floral attraction would work best on the pollinator in the accompanying figure?A) white flowers
B) purple or blue flowers
C) a strong sweet scent
D) a strong carrion-like scent
E) sweet nectar

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
The order of whorls from the flower's periphery to the center is:
A) sepals, petals, stamens, and carpels.
B) carpels, petals, stamens, and sepals.
C) petals, carpels, stamens, and sepals.
D) sepals, carpels, stamens, and calyx.
E) calyx, carpels, stamens, and sepals.
A) sepals, petals, stamens, and carpels.
B) carpels, petals, stamens, and sepals.
C) petals, carpels, stamens, and sepals.
D) sepals, carpels, stamens, and calyx.
E) calyx, carpels, stamens, and sepals.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
Figure 37-4 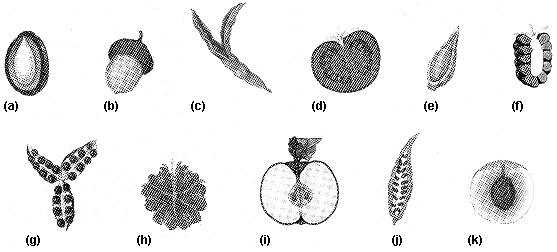 Refer to the accompanying figure. Which of the fruits listed is botanically classified as a berry?
Refer to the accompanying figure. Which of the fruits listed is botanically classified as a berry?
A) c
B) d
C) f
D) g
E) h
 Refer to the accompanying figure. Which of the fruits listed is botanically classified as a berry?
Refer to the accompanying figure. Which of the fruits listed is botanically classified as a berry?A) c
B) d
C) f
D) g
E) h

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
Fruits that develop from a flower with many separate ovaries are referred to as:
A) accessory fruits.
B) aggregate fruits.
C) dry fruits.
D) multiple fruits.
E) simple fruits.
A) accessory fruits.
B) aggregate fruits.
C) dry fruits.
D) multiple fruits.
E) simple fruits.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
What is an example of a seed dispersed by water?
A) sunflower
B) acorn
C) coconut
D) peach
E) jack fruit
A) sunflower
B) acorn
C) coconut
D) peach
E) jack fruit

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
Which is the correct sequence of embryonic development in eudicots?
A) globular stage embryo → suspensor embryo → proembryo → heart stage embryo
B) heart stage embryo → globular stage embryo → proembryo → torpedo stage embryo
C) torpedo stage embryo → globular stage embryo → heart stage embryo → suspensor
D) proembryo → torpedo stage embryo → heart stage embryo → globular stage embryo
E) proembryo → globular stage embryo → heart stage embryo → torpedo stage embryo
A) globular stage embryo → suspensor embryo → proembryo → heart stage embryo
B) heart stage embryo → globular stage embryo → proembryo → torpedo stage embryo
C) torpedo stage embryo → globular stage embryo → heart stage embryo → suspensor
D) proembryo → torpedo stage embryo → heart stage embryo → globular stage embryo
E) proembryo → globular stage embryo → heart stage embryo → torpedo stage embryo

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
The absorption of water by a dry seed is known as:
A) apical dominance.
B) determinate growth.
C) imbibition.
D) senescence.
E) bolting.
A) apical dominance.
B) determinate growth.
C) imbibition.
D) senescence.
E) bolting.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
Special structures found in seeds that are dispersed by ants are called:
A) glyoxisomes.
B) elaiosomes.
C) peroxisome.
D) elatoir.
E) lysosome.
A) glyoxisomes.
B) elaiosomes.
C) peroxisome.
D) elatoir.
E) lysosome.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
Following double fertilization, the ovule develops into a(n) ____, and the ovary develops into a(n) ____.
A) cotyledon; embryo
B) embryo; seed
C) seed; fruit
D) fruit; seed
E) endosperm; embryo
A) cotyledon; embryo
B) embryo; seed
C) seed; fruit
D) fruit; seed
E) endosperm; embryo

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
The fusion of a sperm cell with two polar nuclei in the ovule forms the:
A) cotyledon.
B) endosperm.
C) fertilized egg.
D) zygote.
E) embryo.
A) cotyledon.
B) endosperm.
C) fertilized egg.
D) zygote.
E) embryo.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
Figure 37-5 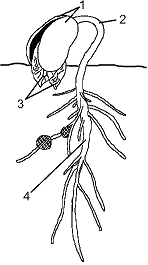 In the accompanying figure, the structure labeled as 2:
In the accompanying figure, the structure labeled as 2:
A) responds to a lack of light.
B) protects the stem tip as it moves through the soil.
C) is the first structure to emerge from the seed during germination.
D) is called the coleoptile.
E) surrounds and protects the young shoot.
 In the accompanying figure, the structure labeled as 2:
In the accompanying figure, the structure labeled as 2:A) responds to a lack of light.
B) protects the stem tip as it moves through the soil.
C) is the first structure to emerge from the seed during germination.
D) is called the coleoptile.
E) surrounds and protects the young shoot.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
Endosperm tissue is:
A) 1/2 n
B) n
C) 2 n
D) 3 n
E) 4 n
A) 1/2 n
B) n
C) 2 n
D) 3 n
E) 4 n

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
In the embryonic development of flowering plants, the basal cell develops into the:
A) apical cell.
B) apical meristem.
C) suspensor.
D) integuments.
E) endosperm.
A) apical cell.
B) apical meristem.
C) suspensor.
D) integuments.
E) endosperm.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
Figure 37-3 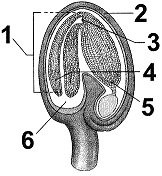 In the accompanying figure, the part of the embryo that contains most of the food used by the embryonic plant during germination is labeled with the number:
In the accompanying figure, the part of the embryo that contains most of the food used by the embryonic plant during germination is labeled with the number:
A) 2
B) 3
C) 4
D) 5
E) 6
 In the accompanying figure, the part of the embryo that contains most of the food used by the embryonic plant during germination is labeled with the number:
In the accompanying figure, the part of the embryo that contains most of the food used by the embryonic plant during germination is labeled with the number:A) 2
B) 3
C) 4
D) 5
E) 6

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
Figure 37-4 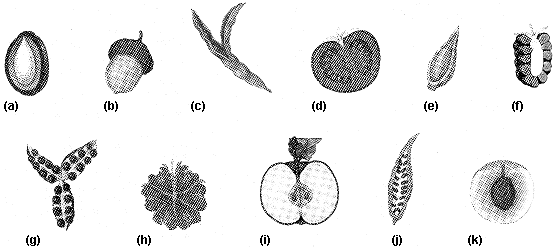 On Figure 37-4, which of the fruit listed is formed by the fusion of ovaries from many flowers?
On Figure 37-4, which of the fruit listed is formed by the fusion of ovaries from many flowers?
A) f
B) g
C) h
D) i
E) j
 On Figure 37-4, which of the fruit listed is formed by the fusion of ovaries from many flowers?
On Figure 37-4, which of the fruit listed is formed by the fusion of ovaries from many flowers?A) f
B) g
C) h
D) i
E) j

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
Which of the following is a structure adapted for seed dispersal by animals?
A) light, feathery plumes
B) thick, indigestible seed coats
C) air spaces and cork
D) turgor pressure within fruits
E) winged fruits
A) light, feathery plumes
B) thick, indigestible seed coats
C) air spaces and cork
D) turgor pressure within fruits
E) winged fruits

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
The function of cotyledons in many plants is to:
A) enclose and protect the seed.
B) act as a short embryonic root.
C) produce pollen.
D) store food reserves.
E) aid in seed dispersal.
A) enclose and protect the seed.
B) act as a short embryonic root.
C) produce pollen.
D) store food reserves.
E) aid in seed dispersal.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
Corn and other grasses have a unique sheath of cells known as the ____ that surrounds and protects the young shoot.
A) coleoptile
B) coleorhizum
C) cotyledon
D) endosperm
E) radicle
A) coleoptile
B) coleorhizum
C) cotyledon
D) endosperm
E) radicle

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
Figure 37-4 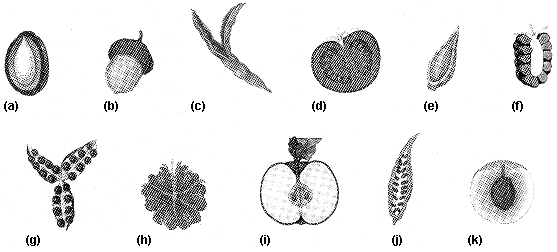 Refer to the accompanying figure. Which of the fruits listed would be classified as an accessory fruit?
Refer to the accompanying figure. Which of the fruits listed would be classified as an accessory fruit?
A) a
B) b
C) e
D) i
E) k
 Refer to the accompanying figure. Which of the fruits listed would be classified as an accessory fruit?
Refer to the accompanying figure. Which of the fruits listed would be classified as an accessory fruit?A) a
B) b
C) e
D) i
E) k

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
Figure 37-5 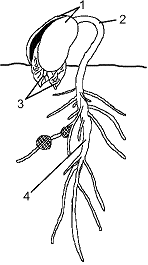 The process illustrated in the accompanying figure is:
The process illustrated in the accompanying figure is:
A) imbibition.
B) germination in a monocot.
C) apomixis.
D) abscission.
E) germination in a eudicot.
 The process illustrated in the accompanying figure is:
The process illustrated in the accompanying figure is:A) imbibition.
B) germination in a monocot.
C) apomixis.
D) abscission.
E) germination in a eudicot.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
Figure 37-3 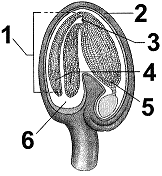 Which of the following is false concerning the structures labeled as 4 in the accompanying figure?
Which of the following is false concerning the structures labeled as 4 in the accompanying figure?
A) They are known as cotyledons.
B) They indicate that this plant is a eudicot.
C) They are part of the maturing embryo.
D) They are surrounded by endosperm.
E) They are derived from the integuments.
 Which of the following is false concerning the structures labeled as 4 in the accompanying figure?
Which of the following is false concerning the structures labeled as 4 in the accompanying figure?A) They are known as cotyledons.
B) They indicate that this plant is a eudicot.
C) They are part of the maturing embryo.
D) They are surrounded by endosperm.
E) They are derived from the integuments.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
The difference between a drupe and a berry is that a drupe:
A) is an accessory fruit, while a berry is a multiple fruit.
B) is formed from a single carpel, while a berry is formed from many carpels.
C) has a stony pit around a single seed, while a berry is fleshy throughout with many seeds.
D) is a dry fruit, while a berry is a fleshy one.
E) splits open along two sutures, while a berry splits open along one suture.
A) is an accessory fruit, while a berry is a multiple fruit.
B) is formed from a single carpel, while a berry is formed from many carpels.
C) has a stony pit around a single seed, while a berry is fleshy throughout with many seeds.
D) is a dry fruit, while a berry is a fleshy one.
E) splits open along two sutures, while a berry splits open along one suture.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
____ is an example of a plant that produces detachable plantlets in notches along their leaf margins.
A) Pineapple
B) Kalanchoe
C) Chlorophytum
D) Pepperomia
E) Spathiphyllum
A) Pineapple
B) Kalanchoe
C) Chlorophytum
D) Pepperomia
E) Spathiphyllum

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
Diagram a flower, labeling the parts and identify the function of each labeled part from the following list: a) reproduction male, b) reproduction female, c) attracting a pollinator, d) point of attachment of flower parts, and e) protection for a bud.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
What is a fruit species that can be propagated by apomixis?
A) apple
B) peach
C) citrus
D) pear
E) peach
A) apple
B) peach
C) citrus
D) pear
E) peach

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
Rhizomes, tubers, corms, and stolons are examples of modified:
A) leaves.
B) flowers.
C) roots.
D) bulbs.
E) stems.
A) leaves.
B) flowers.
C) roots.
D) bulbs.
E) stems.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
Sexual reproduction results in:
A) the preservation of the parental genotypes.
B) low death rates among offspring.
C) genetic similarity among offspring.
D) genetic diversity among offspring.
E) offspring with fitness equal to that of their parents.
A) the preservation of the parental genotypes.
B) low death rates among offspring.
C) genetic similarity among offspring.
D) genetic diversity among offspring.
E) offspring with fitness equal to that of their parents.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
Aboveground shoots that develop from adventitious buds on roots are called:
A) corms.
B) crowns.
C) plantlets.
D) suckers.
E) culms.
A) corms.
B) crowns.
C) plantlets.
D) suckers.
E) culms.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
What is the first part of the seedling to come out during germination?
A) plumule
B) radicle
C) cotyledons
D) leaves
E) coleoptile
A) plumule
B) radicle
C) cotyledons
D) leaves
E) coleoptile

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
The prolonged low temperature exposure required for the germination of some seeds:
A) is typical of coconuts.
B) provides an alternative to the process of imbibition.
C) prevents them from growing in flooded, anaerobic soils.
D) allows the seeds to conserve limited food stores.
E) ensures that the seeds germinate in spring, rather than in fall.
A) is typical of coconuts.
B) provides an alternative to the process of imbibition.
C) prevents them from growing in flooded, anaerobic soils.
D) allows the seeds to conserve limited food stores.
E) ensures that the seeds germinate in spring, rather than in fall.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
Apomixis is often found in ____ plants with different degrees of sterility.
A) haploid
B) diploid
C) polyploid
D) injured
E) dessicated
A) haploid
B) diploid
C) polyploid
D) injured
E) dessicated

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
Asexual reproduction in flowering plants does not usually involve the formation of:
A) plantlets, stolons, or seeds.
B) suckers, corms, or rhizomes.
C) flowers, seeds, or fruits.
D) bulbs, rhizomes, or seeds.
E) flowers, bulbs, or stolons.
A) plantlets, stolons, or seeds.
B) suckers, corms, or rhizomes.
C) flowers, seeds, or fruits.
D) bulbs, rhizomes, or seeds.
E) flowers, bulbs, or stolons.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
The petals constitute the outermost whorl of flower parts.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
Which of the following is an example of a modified underground bud with fleshy leaves for storage?
A) onion
B) white potato
C) gladiolus
D) ginger
E) strawberry
A) onion
B) white potato
C) gladiolus
D) ginger
E) strawberry

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
Provide a one sentence explanation of how each of the following structures can be used to propagate plants asexually: suckers, corms, stolons. BONUS: Identify one representative plant that is capable of each type of reproduction identified.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
Sometimes plants produce embryos in seeds without meiosis and fusion of gametes. This process is known as:
A) coevolution.
B) apomixis.
C) self-pollination.
D) mitosis.
E) suckering.
A) coevolution.
B) apomixis.
C) self-pollination.
D) mitosis.
E) suckering.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
The term for physical damage to a seed coat that induces germination is:
A) imbibition.
B) scarification.
C) bolting.
D) vernalization.
E) thigmomorphogenesis.
A) imbibition.
B) scarification.
C) bolting.
D) vernalization.
E) thigmomorphogenesis.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
Identify two environmental factors that affect the germination of seeds. Then list the adaptation(s) of seeds to deal with each environmental factor.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
A ____ is an underground stem that is greatly enlarged for food storage.
A) sucker
B) runner
C) plantlet
D) stolon
E) tuber
A) sucker
B) runner
C) plantlet
D) stolon
E) tuber

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
Compare and contrast the processes of pollination and fertilization.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
Which statement about asexual reproduction is true?
A) The advantage of asexual reproduction is that it results in new gene combinations.
B) Two parents are required for successful asexual reproduction.
C) The process of meiosis takes place in the parent and results in four haploid cells.
D) The offspring of asexual reproduction are genetically identical to the parent.
E) Asexual reproduction requires the fusion of two haploid gametes.
A) The advantage of asexual reproduction is that it results in new gene combinations.
B) Two parents are required for successful asexual reproduction.
C) The process of meiosis takes place in the parent and results in four haploid cells.
D) The offspring of asexual reproduction are genetically identical to the parent.
E) Asexual reproduction requires the fusion of two haploid gametes.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
Explain the significance of apomixis in propagation of plants. Cite two examples of commercial significance.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
The male gametophyte is also called an embryo sac.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
Match between columns

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
Imbibition is the process by which a seed takes in oxygen from the environment.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
Match between columns

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
An ovule usually develops directly into a(n) fruit .

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
Nicotine can be found in nectaries.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
When the generative cell divides, the daughter cells are sperm cells.
____________________
____________________

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
A rhizome is a horizontal aboveground stem.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
An example of a(n) drupe is an olive.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
What is the significance of double fertilization in flowering plants?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
The integuments develop into the seed coat.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72
During embryonic development, the proembryo develops from the basal cell.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73
Endosperm is usually triploid .

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
74
Give examples of how plants and animal pollinators have coevolved.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
75
When a microsporocyte divides, its daughter cells are diploid.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
76
In double fertilization, one sperm fuses with the egg, and the other sperm fuses with the two antipodal nuclei.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
77
The hypocotyl connects the radicle with the cotyledons.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
78
Plants that are wind-pollinated characteristically have conspicuous flowers.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
79
What are the advantages and disadvantages of both sexual and asexual reproduction?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
80
Apomixis refers to a type of sexual reproduction.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



