Deck 38: Plant Developmental Responses to External and Internal Signals
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/84
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 38: Plant Developmental Responses to External and Internal Signals
1
The herbicides (weed killers) 2,4-D and 2,4,5-T are examples of synthetic:
A) abscisic acid.
B) auxins.
C) cytokinins.
D) ethylene.
E) gibberellins.
A) abscisic acid.
B) auxins.
C) cytokinins.
D) ethylene.
E) gibberellins.
B
2
You expose a plant to a light that shines on the right side of a plant. Which statement best describes why the plant grows toward the light?
A) Light destroys auxin, and thus the shaded side grows faster.
B) Auxin moves from the shaded side to the lighted side where it stimulates growth.
C) Auxin moves from the lighted side to the shaded side where it stimulates growth.
D) Light destroys auxin and thus the lighted side grows faster.
E) Auxin moves from the shaded side to the lighted side where it inhibits growth.
A) Light destroys auxin, and thus the shaded side grows faster.
B) Auxin moves from the shaded side to the lighted side where it stimulates growth.
C) Auxin moves from the lighted side to the shaded side where it stimulates growth.
D) Light destroys auxin and thus the lighted side grows faster.
E) Auxin moves from the shaded side to the lighted side where it inhibits growth.
C
3
You want to obtain the strongest phototropic response from a shoot. Which wavelength of light should you use?
A) less than 500 nm
B) 660 nm
C) 730 nm
D) 800 nm
E) more than 800 nm
A) less than 500 nm
B) 660 nm
C) 730 nm
D) 800 nm
E) more than 800 nm
A
4
What hormone promotes apical dominance in plants?
A) abscisic acid
B) auxin
C) cytokinin
D) ethylene
E) gibberellin
A) abscisic acid
B) auxin
C) cytokinin
D) ethylene
E) gibberellin

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
Which of the following would be the most likely consequence of removing the apical meristem from a plant?
A) The plant dies.
B) The plant remains alive but will not grow again.
C) The growth of axillary buds is inhibited.
D) The axillary buds die.
E) Some axillary buds grow into branches.
A) The plant dies.
B) The plant remains alive but will not grow again.
C) The growth of axillary buds is inhibited.
D) The axillary buds die.
E) Some axillary buds grow into branches.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
Changing day length, as well as variations in precipitation and temperature, are environmental cues that exert an important influence on:
A) the kinds of genes a plant has.
B) the number of mutations that genes undergo.
C) whether a plant is an annual, biennial, or perennial.
D) which genes will be expressed in a plant.
E) whether a plant reproduces sexually or asexually.
A) the kinds of genes a plant has.
B) the number of mutations that genes undergo.
C) whether a plant is an annual, biennial, or perennial.
D) which genes will be expressed in a plant.
E) whether a plant reproduces sexually or asexually.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
When a plant responds to external stimuli, such as light, gravity, or touch by directional growth, these responses are referred to as:
A) turgor movements.
B) sleep movements.
C) nastic movements.
D) circadian rhythms.
E) tropisms.
A) turgor movements.
B) sleep movements.
C) nastic movements.
D) circadian rhythms.
E) tropisms.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
The photoreceptor that absorbs blue light and triggers a phototropic response is:
A) phototropin.
B) phytochrome.
C) jasmonate.
D) systemin.
E) zeatin.
A) phototropin.
B) phytochrome.
C) jasmonate.
D) systemin.
E) zeatin.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
____ is a synthetic auxin that stimulates root development on stem cuttings and is used extensively in asexual propagation.
A) Indoleacetic acid
B) Indolebutyric acid
C) Naphthalene acetic acid
D) 2,4-D
E) 2,4,5-T
A) Indoleacetic acid
B) Indolebutyric acid
C) Naphthalene acetic acid
D) 2,4-D
E) 2,4,5-T

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
The application of ____ substitutes for low temperature or light requirements for biennial germination.
A) indoleacetic acid
B) indolebutyric acid
C) naphthaleneacetic acid
D) gibberellins
E) ethephon
A) indoleacetic acid
B) indolebutyric acid
C) naphthaleneacetic acid
D) gibberellins
E) ethephon

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
The site of gravity reception in roots is the:
A) root apical meristem.
B) periderm.
C) root epidermis.
D) root cap.
E) root hair.
A) root apical meristem.
B) periderm.
C) root epidermis.
D) root cap.
E) root hair.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
In barley seed germination, the ____ releases gibberellin, which triggers the synthesis of ____ in the ____.
A) seed coat; α -amylase; embryo
B) endosperm; cellulase; embryo
C) embryo; α -amylase; endosperm
D) embryo; cellulase; seed coat
E) endosperm; β -amylase; embryo
A) seed coat; α -amylase; embryo
B) endosperm; cellulase; embryo
C) embryo; α -amylase; endosperm
D) embryo; cellulase; seed coat
E) endosperm; β -amylase; embryo

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
Auxin sprayed on tomato flowers stimulates the ____ to develop without the formation of ____.
A) roots; root hairs
B) fruit; ovaries
C) seeds; ovaries
D) ovary; seeds
E) seeds; fruits
A) roots; root hairs
B) fruit; ovaries
C) seeds; ovaries
D) ovary; seeds
E) seeds; fruits

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
Which hormone promotes cell division and delays senescence in plants?
A) abscisic acid
B) auxin
C) cytokinin
D) ethylene
E) gibberellin
A) abscisic acid
B) auxin
C) cytokinin
D) ethylene
E) gibberellin

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
____ is growth in response to a mechanical stimulus, such as contact with a solid object.
A) Heliotropism
B) Phototropism
C) Gravitropism
D) Thigmotropism
E) Geotropic bending
A) Heliotropism
B) Phototropism
C) Gravitropism
D) Thigmotropism
E) Geotropic bending

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
A seedling growing toward the source of light is an example of:
A) shade avoidance.
B) a positive hypersensitive response.
C) a negative hypersensitive response.
D) a positive phototropic response.
E) a negative phototropic response.
A) shade avoidance.
B) a positive hypersensitive response.
C) a negative hypersensitive response.
D) a positive phototropic response.
E) a negative phototropic response.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
Which hormone promotes stem elongation and was first discovered while studying the growth of extremely tall and spindly rice plants?
A) abscisic acid
B) auxin
C) cytokinin
D) ethylene
E) gibberellin
A) abscisic acid
B) auxin
C) cytokinin
D) ethylene
E) gibberellin

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
You would like to develop an herbicide that is structurally most similar to cytokinin. Which of the following molecules would you use as starting material?
A) adenine
B) glucose
C) naphthaleneacetic acid
D) α -amylase
E) a steroid
A) adenine
B) glucose
C) naphthaleneacetic acid
D) α -amylase
E) a steroid

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
When a root is placed on its side, what happens to the amyloplasts in the root cap cells?
A) They move away from the direction of gravity.
B) They settle in the direction of gravity
C) They are digested by amylase.
D) They move into the root apical meristem.
E) They move into a root hair.
A) They move away from the direction of gravity.
B) They settle in the direction of gravity
C) They are digested by amylase.
D) They move into the root apical meristem.
E) They move into a root hair.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
____ stimulates rapid elongation of a floral stalk in many plant species.
A) Abscisic acid
B) Gibberellin
C) Cytokinin
D) Ethylene
E) Auxin
A) Abscisic acid
B) Gibberellin
C) Cytokinin
D) Ethylene
E) Auxin

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
Which statement concerning the auxin F-box protein is false ?
A) It is located in the nucleus.
B) It is a type of receptor.
C) It is involved in catalyzing the addition of ubiquitin tags.
D) Plants have about 700 of these.
E) An example is the transport inhibitor response 1 protein.
A) It is located in the nucleus.
B) It is a type of receptor.
C) It is involved in catalyzing the addition of ubiquitin tags.
D) Plants have about 700 of these.
E) An example is the transport inhibitor response 1 protein.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
The movement of auxin downward from its site of production is referred to as:
A) gravitropism.
B) apical dominance.
C) nonpolar transport.
D) polar transport.
E) turgor movement.
A) gravitropism.
B) apical dominance.
C) nonpolar transport.
D) polar transport.
E) turgor movement.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
The "stress hormone" involved in stomatal closure during water stress is:
A) abscisic acid.
B) auxin.
C) cytokinin.
D) ethylene.
E) gibberellin.
A) abscisic acid.
B) auxin.
C) cytokinin.
D) ethylene.
E) gibberellin.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
Unripe green fruits ripen quickly in supermarkets or commercial storage facilities after exposure to:
A) abscisic acid.
B) auxin.
C) cytokinin.
D) ethylene.
E) gibberellin.
A) abscisic acid.
B) auxin.
C) cytokinin.
D) ethylene.
E) gibberellin.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
Which hormone promotes cell elongation by changing plant cell walls so they can expand due to the force of turgor pressure?
A) abscisic acid
B) auxin
C) cytokinin
D) ethylene
E) gibberellin
A) abscisic acid
B) auxin
C) cytokinin
D) ethylene
E) gibberellin

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
Brassinosteroids differ from other plant hormones in that they are:
A) peptides.
B) steroids.
C) derivatives of adenine.
D) derivatives of aspirin.
E) derivatives of prostaglandins.
A) peptides.
B) steroids.
C) derivatives of adenine.
D) derivatives of aspirin.
E) derivatives of prostaglandins.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
Figure 38-1  One conclusion that can be drawn from the accompanying figure is that a low ratio of auxin to cytokinin:
One conclusion that can be drawn from the accompanying figure is that a low ratio of auxin to cytokinin:
A) stimulates root development.
B) stimulates shoot development.
C) results in undifferentiated growth.
D) stimulates the formation of an entire plant.
E) results in no growth.
 One conclusion that can be drawn from the accompanying figure is that a low ratio of auxin to cytokinin:
One conclusion that can be drawn from the accompanying figure is that a low ratio of auxin to cytokinin:A) stimulates root development.
B) stimulates shoot development.
C) results in undifferentiated growth.
D) stimulates the formation of an entire plant.
E) results in no growth.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
In the mechanism of action for auxin, after auxin binds with its receptor, which of the following happens next?
A) Proteins are targeted for destruction.
B) Genes are activated.
C) Ubiquitin attaches to repressor proteins.
D) Transcription occurs.
E) The cell wall loosens.
A) Proteins are targeted for destruction.
B) Genes are activated.
C) Ubiquitin attaches to repressor proteins.
D) Transcription occurs.
E) The cell wall loosens.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
What hypothetical hormone promotes flowering but has never been successfully isolated?
A) florigen
B) ubiquitin
C) jasmonic acid
D) brassinosteroids
E) methyl salicylate
A) florigen
B) ubiquitin
C) jasmonic acid
D) brassinosteroids
E) methyl salicylate

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
Which of the following would be characteristic of a plant exhibiting shade avoidance?
A) stem elongation
B) more leaves
C) higher quantity of storage products
D) more reproductive tissue
E) more branches
A) stem elongation
B) more leaves
C) higher quantity of storage products
D) more reproductive tissue
E) more branches

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
You place a coleoptile in unidirectional light and then immediately cover the tip. Which of the following will happen?
A) The coleoptile would bend toward the light.
B) The coleoptile would not bend.
C) The coleoptile would bend away from the light.
D) The coleoptile would die.
E) The coleoptile would grow in a spiral pattern.
A) The coleoptile would bend toward the light.
B) The coleoptile would not bend.
C) The coleoptile would bend away from the light.
D) The coleoptile would die.
E) The coleoptile would grow in a spiral pattern.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
Figure 38-1 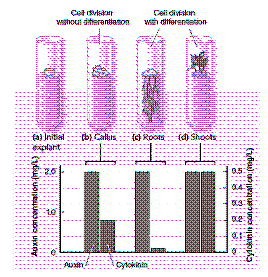 Based on the data in the accompanying figure, the condition that results in root development is:
Based on the data in the accompanying figure, the condition that results in root development is:
A) a high ratio of auxin to cytokinin.
B) a low ratio of auxin to cytokinin.
C) a relatively equal proportion of auxin to cytokinin.
D) cytokinin levels of at least 0.2 mg/L.
E) auxin concentrations of 0.5 mg/L.
 Based on the data in the accompanying figure, the condition that results in root development is:
Based on the data in the accompanying figure, the condition that results in root development is:A) a high ratio of auxin to cytokinin.
B) a low ratio of auxin to cytokinin.
C) a relatively equal proportion of auxin to cytokinin.
D) cytokinin levels of at least 0.2 mg/L.
E) auxin concentrations of 0.5 mg/L.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
The purification and elucidation of the primary auxin's chemical structure were accomplished by:
A) Charles Darwin.
B) Francis Darwin.
C) Frits Went.
D) Kenneth Thimann.
E) F. Skoog.
A) Charles Darwin.
B) Francis Darwin.
C) Frits Went.
D) Kenneth Thimann.
E) F. Skoog.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
Which hormone stimulates both leaf abscission and fruit ripening?
A) abscisic acid
B) auxin
C) cytokinin
D) ethylene
E) gibberellin
A) abscisic acid
B) auxin
C) cytokinin
D) ethylene
E) gibberellin

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
You plant two gardens, one in the sun and one in the shade. The plants grown in the shade will most likely be ____ because neighboring leaves absorb more ____.
A) shorter; far-red light than red light
B) shorter; red light than far-red light
C) taller; red light than far-red light
D) taller; far-red light than red light
E) shorter; cryptochrome than phytochrome
A) shorter; far-red light than red light
B) shorter; red light than far-red light
C) taller; red light than far-red light
D) taller; far-red light than red light
E) shorter; cryptochrome than phytochrome

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
The most common and physiologically important auxin is:
A) indoleacetic acid.
B) indolebutyric acid.
C) naphthaleneacetic acid.
D) 2,4-D.
E) 2,4,5-T.
A) indoleacetic acid.
B) indolebutyric acid.
C) naphthaleneacetic acid.
D) 2,4-D.
E) 2,4,5-T.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
Which of the following statements about plant hormones is false ?
A) They are organic compounds that act as a highly specific chemical signal.
B) They are effective in extremely small amounts.
C) They elicit many different responses.
D) They may stimulate a response at one concentration and inhibit that same response at a different concentration.
E) They currently can be categorized into seven major classes.
A) They are organic compounds that act as a highly specific chemical signal.
B) They are effective in extremely small amounts.
C) They elicit many different responses.
D) They may stimulate a response at one concentration and inhibit that same response at a different concentration.
E) They currently can be categorized into seven major classes.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
A plant growth response to mechanical stress, such as rain and contact with passing animals, is known as:
A) phototropism.
B) gravitropism.
C) thigmomorphogensis.
D) a circadian rhythm.
E) thigmotropism.
A) phototropism.
B) gravitropism.
C) thigmomorphogensis.
D) a circadian rhythm.
E) thigmotropism.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
____ is believed to be produced in the leaves and transported to the phloem in the shoot apical meristem.
A) Jasmonic acid
B) Florigen
C) Brassinosteroid
D) Abscisic acid
E) Ethylene
A) Jasmonic acid
B) Florigen
C) Brassinosteroid
D) Abscisic acid
E) Ethylene

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
____ used tiny blocks of agar to show that auxin is made in the tip of coleoptiles and still capable of influencing bending of the coleoptile.
A) Charles Darwin
B) Francis Darwin
C) Frits Went
D) Kenneth Thimann
E) Frits Skoog
A) Charles Darwin
B) Francis Darwin
C) Frits Went
D) Kenneth Thimann
E) Frits Skoog

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
You shine light having a wavelength of 660 nm on a plant. Which of the following will most likely happen next?
A) Pfr is stored for later use.
B) Pr is synthesized.
C) Pr is converted to Pfr.
D) Pfr is converted to Pr.
E) Pr is degraded.
A) Pfr is stored for later use.
B) Pr is synthesized.
C) Pr is converted to Pfr.
D) Pfr is converted to Pr.
E) Pr is degraded.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
Figure 38-2 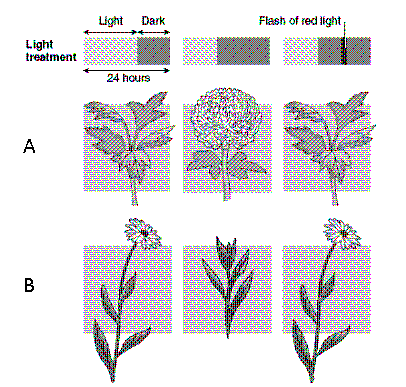 The plant in Row B of the accompanying figure demonstrates a photoperiodic response characteristic of:
The plant in Row B of the accompanying figure demonstrates a photoperiodic response characteristic of:
A) short-day plants.
B) day-neutral plants.
C) long-day plants.
D) long-night plants.
E) intermediate-day plants.
 The plant in Row B of the accompanying figure demonstrates a photoperiodic response characteristic of:
The plant in Row B of the accompanying figure demonstrates a photoperiodic response characteristic of:A) short-day plants.
B) day-neutral plants.
C) long-day plants.
D) long-night plants.
E) intermediate-day plants.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
An example of a long-day plant is:
A) poinsettia.
B) florist's chrysanthemum.
C) sunflower.
D) black-eyed Susan.
E) sugarcane.
A) poinsettia.
B) florist's chrysanthemum.
C) sunflower.
D) black-eyed Susan.
E) sugarcane.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
Plants compete for light, a response known as ____, in which plants tend to grow taller when closely surrounded by other plants.
A) epinasty
B) phototropism
C) shade avoidance
D) shade tolerance
E) thigmotropism
A) epinasty
B) phototropism
C) shade avoidance
D) shade tolerance
E) thigmotropism

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
Which statement concerning phytochrome-induced responses is false ?
A) All responses are very rapid and short-term.
B) Red light causes potassium channels to open.
C) The absorption of light by one part of the phytochrome molecule triggers a conformational change in another part.
D) Phytochrome activates transcription of the gene for a subunit of rubisco.
E) Far-red light causes potassium channels to close.
A) All responses are very rapid and short-term.
B) Red light causes potassium channels to open.
C) The absorption of light by one part of the phytochrome molecule triggers a conformational change in another part.
D) Phytochrome activates transcription of the gene for a subunit of rubisco.
E) Far-red light causes potassium channels to close.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
Which statement about the internal biological clock is false ?
A) It is known as a circadian rhythm.
B) It relates to the opening and closing of stomata.
C) It includes the sleep movements observed in some plants, such as beans.
D) It may involve both phytochrome and cryptochrome.
E) It disappears totally if it is not reset by the rising and setting sun.
A) It is known as a circadian rhythm.
B) It relates to the opening and closing of stomata.
C) It includes the sleep movements observed in some plants, such as beans.
D) It may involve both phytochrome and cryptochrome.
E) It disappears totally if it is not reset by the rising and setting sun.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
Pr is located in the ____, and after it absorbs red light, the resulting Pfr moves to the ____.
A) endoplasmic reticulum; plasma membrane
B) cytoplasm; nucleus
C) plasma membrane; cytoplasm
D) cytoplasm; plasma membrane
E) nucleus; cytoplasm
A) endoplasmic reticulum; plasma membrane
B) cytoplasm; nucleus
C) plasma membrane; cytoplasm
D) cytoplasm; plasma membrane
E) nucleus; cytoplasm

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
The effect of red light on plants is to:
A) inactivate phytochrome.
B) convert Pfr to Pr.
C) inhibit germination in some seeds.
D) initiate shade avoidance responses.
E) impact the equilibrium between Pr and Pfr.
A) inactivate phytochrome.
B) convert Pfr to Pr.
C) inhibit germination in some seeds.
D) initiate shade avoidance responses.
E) impact the equilibrium between Pr and Pfr.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
PhyB may inhibit flowering in:
A) day-neutral plants.
B) vernalized plants.
C) long-day plants.
D) senescing plants.
E) short-day plants.
A) day-neutral plants.
B) vernalized plants.
C) long-day plants.
D) senescing plants.
E) short-day plants.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
The photorecepter ____ was first discovered in plants but later found to also be present in fruit flies and mice.
A) Pfr
B) Pr
C) phytochrome
D) cryptochrome
E) PIF3
A) Pfr
B) Pr
C) phytochrome
D) cryptochrome
E) PIF3

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
An example of a short-day plant is:
A) poinsettia.
B) sunflower.
C) spinach.
D) coleus.
E) corn.
A) poinsettia.
B) sunflower.
C) spinach.
D) coleus.
E) corn.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
In a hypersensitive response, ____.
A) long-lasting resistance is built up throughout the plan.
B) the axillary buds break dormancy
C) cryptochrome is synthesized
D) jasmonic acid activates enzymes
E) the infected area is sealed off by necrotic lesions
A) long-lasting resistance is built up throughout the plan.
B) the axillary buds break dormancy
C) cryptochrome is synthesized
D) jasmonic acid activates enzymes
E) the infected area is sealed off by necrotic lesions

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
____ is a lipid-derived hormone produced in response to the presence of insect pests.
A) Cytokinin
B) Abscisic acid
C) Jasmonic acid
D) Gibberellin
E) Auxin
A) Cytokinin
B) Abscisic acid
C) Jasmonic acid
D) Gibberellin
E) Auxin

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
During the day, the leaves of bean plants are ____, and at night they are ____.
A) horizontal; wilted
B) horizontal; vertical
C) horizontal; horizontal
D) vertical; vertical
E) vertical; horizontal
A) horizontal; wilted
B) horizontal; vertical
C) horizontal; horizontal
D) vertical; vertical
E) vertical; horizontal

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
Which of the following sequences correctly represents the phytochrome signal transduction pathway?
A) red light → PIF3 activation → PIF3 into nucleus → light-responsive gene switched off
B) red light → Pfr to Pr → Pr into nucleus → Pr-PIF3 complex → light-responsive gene regulation
C) UV light → PIF3 into nucleus → light responsive gene produces phytochrome → Pr to Pfr
D) blue light → Pfr into nucleus → Pfr-PIF3 complex → light-responsive gene regulation
E) red light → Pr to Pfr → Pfr into nucleus → Pfr-PIF3 complex → light-responsive gene regulation
A) red light → PIF3 activation → PIF3 into nucleus → light-responsive gene switched off
B) red light → Pfr to Pr → Pr into nucleus → Pr-PIF3 complex → light-responsive gene regulation
C) UV light → PIF3 into nucleus → light responsive gene produces phytochrome → Pr to Pfr
D) blue light → Pfr into nucleus → Pfr-PIF3 complex → light-responsive gene regulation
E) red light → Pr to Pfr → Pfr into nucleus → Pfr-PIF3 complex → light-responsive gene regulation

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
Any response of a plant to the relative lengths of light and darkness is referred to as:
A) gravitropism.
B) photoperiodism.
C) phototropism.
D) thigmotropism.
E) thigmomorphogenesis.
A) gravitropism.
B) photoperiodism.
C) phototropism.
D) thigmotropism.
E) thigmomorphogenesis.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
Figure 38-2 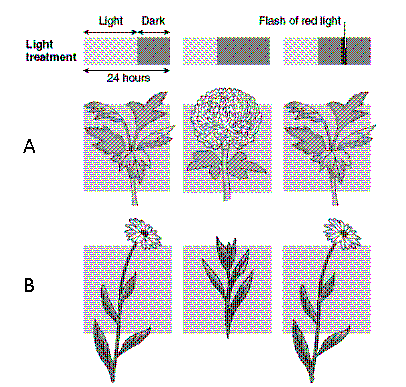 Refer to the accompanying figure. What does the photoperiodic response of the plant in Row A suggest?
Refer to the accompanying figure. What does the photoperiodic response of the plant in Row A suggest?
A) A brief dark period is the light cue that induces flowering.
B) A brief daylight period is the light cue that induces flowering.
C) A long uninterrupted daylight period is the light cue that induces flowering.
D) A long uninterrupted dark period is the light cue that induces flowering.
E) A determination cannot be made from the data provided.
 Refer to the accompanying figure. What does the photoperiodic response of the plant in Row A suggest?
Refer to the accompanying figure. What does the photoperiodic response of the plant in Row A suggest?A) A brief dark period is the light cue that induces flowering.
B) A brief daylight period is the light cue that induces flowering.
C) A long uninterrupted daylight period is the light cue that induces flowering.
D) A long uninterrupted dark period is the light cue that induces flowering.
E) A determination cannot be made from the data provided.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
Which statement about cryptochrome is false ?
A) It is implicated in resetting the biological clock.
B) It is a "clock protein."
C) It absorbs green light.
D) Its counterparts are found in fruit flies and mice.
E) It sometimes interacts with phytochrome.
A) It is implicated in resetting the biological clock.
B) It is a "clock protein."
C) It absorbs green light.
D) Its counterparts are found in fruit flies and mice.
E) It sometimes interacts with phytochrome.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
What happens after the sun goes down?
A) The level of Pfr increases.
B) The level of Pfr remains constant.
C) Pfr is converted to Pr.
D) Pfr is degraded.
E) Pr is converted to Pfr.
A) The level of Pfr increases.
B) The level of Pfr remains constant.
C) Pfr is converted to Pr.
D) Pfr is degraded.
E) Pr is converted to Pfr.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
The photoreceptor for photoperiodism and some other light-initiated plant responses is a group of blue-green pigments named:
A) xanthophyll.
B) carotene.
C) chlorophyll.
D) phytochrome.
E) phycocyanin.
A) xanthophyll.
B) carotene.
C) chlorophyll.
D) phytochrome.
E) phycocyanin.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
Describe the evidence for the existence of a flowering promoter and also for the existence of a flowering inhibitor.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
Jasmonic acid is structurally similar to prostaglandins .

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
Methyl salicylate triggers the genes that code for the systemic acquired resistance pathway .

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
A long day plant will flower when exposed to short nights.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
A circadian rhythm has a period that approximates a(n) 12-hour cycle.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
Write a one-sentence explanation for the role of each of the following plant hormonelike signaling molecules: methyl salicylate and jasmonic acid.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
The site of gravity perception in roots is the root apical meristem .

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
In three sentences or less, explain why a plant placed in a window grows toward the light.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
Pr strongly absorbs light having a wavelength of 730 nm.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
Ethylene stimulates the ripening of fruits.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
____ helps defend plants against viral infection.
A) Systemin
B) Jasmonates
C) Brassinosteroids
D) Methyl salicylate
E) Oligosaccharins
A) Systemin
B) Jasmonates
C) Brassinosteroids
D) Methyl salicylate
E) Oligosaccharins

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72
When cytokinins are sprayed on leaves of a cut stem, the leaves become, or remain, yellow .

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73
Phototropins are light-activated kinases .

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
74
Summarize the effects of each of the six classes of plant hormones.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
75
Differentiate between circadian rhythms and photoperiodism. Give examples of each. What regulates these responses?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
76
Auxin produced by the apical meristem inhibits the germination of lateral buds.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
77
The twining of tendrils around a support is an example of thigmomorphogenesis .

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
78
Cryptochrome absorbs blue light.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
79
Summarize the experiment by Darwin that provided the first evidence for auxins.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
80
When Pfr absorbs far-red light, the Pfr is converted to Pr.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



