Deck 44: Internal Transport
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/90
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 44: Internal Transport
1
Figure 44-1 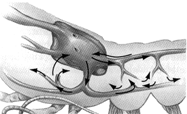 The oxygen transporting pigment found in the system depicted in the accompanying figure is most likely:
The oxygen transporting pigment found in the system depicted in the accompanying figure is most likely:
A) hemoglobin.
B) hemolymph.
C) hemocyanin.
D) globulin.
E) erythropoietin.
 The oxygen transporting pigment found in the system depicted in the accompanying figure is most likely:
The oxygen transporting pigment found in the system depicted in the accompanying figure is most likely:A) hemoglobin.
B) hemolymph.
C) hemocyanin.
D) globulin.
E) erythropoietin.
C
2
Which of the following statements is false ?
A) The tissues of arthropods are bathed with hemolymph, which delivers oxygen to their cells.
B) In an open circulatory system the heart is still responsible for pumping oxygen-rich fluid.
C) Earthworms have a central heart that pumps blood to all their tissues.
D) Blood vessels are found in the open circulatory systems common to some invertebrates.
E) Hemocyanin is the oxygen transport pigment found in the open circulatory system of invertebrates.
A) The tissues of arthropods are bathed with hemolymph, which delivers oxygen to their cells.
B) In an open circulatory system the heart is still responsible for pumping oxygen-rich fluid.
C) Earthworms have a central heart that pumps blood to all their tissues.
D) Blood vessels are found in the open circulatory systems common to some invertebrates.
E) Hemocyanin is the oxygen transport pigment found in the open circulatory system of invertebrates.
C
3
What is a key feature of an open circulatory system?
A) No vessels carry the blood.
B) Open-ended vessels carry the blood.
C) Closed vessels carry the blood.
D) No heart pumps the blood.
E) Hemoglobin is carried in the blood.
A) No vessels carry the blood.
B) Open-ended vessels carry the blood.
C) Closed vessels carry the blood.
D) No heart pumps the blood.
E) Hemoglobin is carried in the blood.
B
4
A vertebrate's circulatory system would include:
A) open blood vessels.
B) closed blood vessels.
C) hemolymph.
D) a hemocoel.
E) hemocyanin.
A) open blood vessels.
B) closed blood vessels.
C) hemolymph.
D) a hemocoel.
E) hemocyanin.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 90 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
Figure 44-1 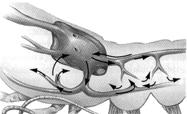 The type of system depicted in the accompanying figure:
The type of system depicted in the accompanying figure:
A) can be found in arthropods.
B) can be found in cephalopods.
C) can be found in annelids.
D) has hemoglobin as the oxygen transporting pigment.
E) can be found in arthropods and annelids.
 The type of system depicted in the accompanying figure:
The type of system depicted in the accompanying figure:A) can be found in arthropods.
B) can be found in cephalopods.
C) can be found in annelids.
D) has hemoglobin as the oxygen transporting pigment.
E) can be found in arthropods and annelids.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 90 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
What is one difference between the erythrocytes of mammals and other vertebrates?
A) Mammal erythrocytes lack nuclei.
B) Mammal erythrocytes respond to changes in water concentration.
C) Mammal erythrocytes are oval with swollen centers.
D) Other vertebrates do not have erythrocytes.
E) Other vertebrates use a respiratory pigment other than hemoglobin.
A) Mammal erythrocytes lack nuclei.
B) Mammal erythrocytes respond to changes in water concentration.
C) Mammal erythrocytes are oval with swollen centers.
D) Other vertebrates do not have erythrocytes.
E) Other vertebrates use a respiratory pigment other than hemoglobin.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 90 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
Figure 44-1 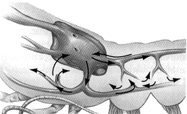 The type of system depicted in the accompanying figure is a(n):
The type of system depicted in the accompanying figure is a(n):
A) open circulatory system.
B) vertebrate circulatory system.
C) closed circulatory system.
D) lymph system.
E) open digestive system.
 The type of system depicted in the accompanying figure is a(n):
The type of system depicted in the accompanying figure is a(n):A) open circulatory system.
B) vertebrate circulatory system.
C) closed circulatory system.
D) lymph system.
E) open digestive system.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 90 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
Which of the below has the largest impact on whether diffusion alone will move nutrients within an organism?
A) shape of organism
B) size of organism
C) environment of organism
D) nutrient being moved
E) atmosphere around organism
A) shape of organism
B) size of organism
C) environment of organism
D) nutrient being moved
E) atmosphere around organism

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 90 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
Figure 44-2 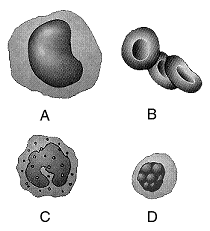 In the accompanying figure, an inadequate supply of which cell may be responsible for anemia?
In the accompanying figure, an inadequate supply of which cell may be responsible for anemia?
A) cell type A only
B) cell type B only
C) cell type C only
D) cell type D only
E) both cell type A and cell type C
 In the accompanying figure, an inadequate supply of which cell may be responsible for anemia?
In the accompanying figure, an inadequate supply of which cell may be responsible for anemia?A) cell type A only
B) cell type B only
C) cell type C only
D) cell type D only
E) both cell type A and cell type C

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 90 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
Why doesn't a flatworm have a circulatory system?
A) The animal is flat enough to permit effective gas exchange by diffusion.
B) There is not enough room for a circulatory system.
C) The animal lacks muscles, so it could not have a heart to pump blood.
D) Only bilaterally symmetrical animals need a circulatory system.
E) Only vertebrates have circulatory systems.
A) The animal is flat enough to permit effective gas exchange by diffusion.
B) There is not enough room for a circulatory system.
C) The animal lacks muscles, so it could not have a heart to pump blood.
D) Only bilaterally symmetrical animals need a circulatory system.
E) Only vertebrates have circulatory systems.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 90 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
Which of the following contributes to an erythrocyte's efficiency in distributing oxygen?
A) presence of mitochondria
B) biconcave shape
C) lobed nuclei
D) granules
E) extraordinarily large size
A) presence of mitochondria
B) biconcave shape
C) lobed nuclei
D) granules
E) extraordinarily large size

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 90 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
Figure 44-1 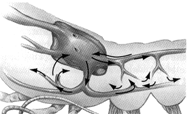 Consider the fluid transported by the system depicted in the accompanying figure. Which statement is FALSE with regard to this system?
Consider the fluid transported by the system depicted in the accompanying figure. Which statement is FALSE with regard to this system?
A) It accumulates in a blood cavity called a hemocoel.
B) It is also called hemolymph.
C) It can be found in grasshoppers.
D) It has hemoglobin as the oxygen transporting pigment.
E) It fills spaces called sinuses.
 Consider the fluid transported by the system depicted in the accompanying figure. Which statement is FALSE with regard to this system?
Consider the fluid transported by the system depicted in the accompanying figure. Which statement is FALSE with regard to this system?A) It accumulates in a blood cavity called a hemocoel.
B) It is also called hemolymph.
C) It can be found in grasshoppers.
D) It has hemoglobin as the oxygen transporting pigment.
E) It fills spaces called sinuses.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 90 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
The ____ proteins in plasma particularly contribute to the blood's osmotic pressure.
A) globulin
B) hemoglobin
C) fibrinogen
D) prothrombin
E) erythropoietin
A) globulin
B) hemoglobin
C) fibrinogen
D) prothrombin
E) erythropoietin

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 90 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
Figure 44-2 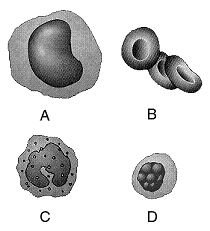 Refer to the accompanying figure. Which cell type or types are primarily responsible for the release of histamine in injured tissues and in allergic responses?
Refer to the accompanying figure. Which cell type or types are primarily responsible for the release of histamine in injured tissues and in allergic responses?
A) A only
B) B only
C) C only
D) D only
E) A and cell type D
 Refer to the accompanying figure. Which cell type or types are primarily responsible for the release of histamine in injured tissues and in allergic responses?
Refer to the accompanying figure. Which cell type or types are primarily responsible for the release of histamine in injured tissues and in allergic responses?A) A only
B) B only
C) C only
D) D only
E) A and cell type D

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 90 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
Which of the following are agranular leukocytes?
A) neutrophils and basophils
B) basophils and eosinophils
C) monocytes and lymphocytes
D) eosinophils and lymphocytes
E) neutrophils and monocytes
A) neutrophils and basophils
B) basophils and eosinophils
C) monocytes and lymphocytes
D) eosinophils and lymphocytes
E) neutrophils and monocytes

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 90 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
Platelets in mammals are functionally the same as ____ in other vertebrates.
A) neutrophils
B) eosinophils
C) thrombocytes
D) monocytes
E) lymphocytes
A) neutrophils
B) eosinophils
C) thrombocytes
D) monocytes
E) lymphocytes

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 90 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
In which animals would diffusion alone not be an effective transport mechanism for gas exchange?
A) nematodes
B) sponges
C) cnidarians
D) annelids
E) flatworms
A) nematodes
B) sponges
C) cnidarians
D) annelids
E) flatworms

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 90 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
Mammalian red blood cells:
A) are phagocytic.
B) contain a lobed nucleus.
C) have a one-day lifespan.
D) are produced in the liver.
E) are produced in response to erythropoietin.
A) are phagocytic.
B) contain a lobed nucleus.
C) have a one-day lifespan.
D) are produced in the liver.
E) are produced in response to erythropoietin.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 90 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
An open circulatory system usually consists of which of the following?
A) blood
B) pumping organ
C) arteries
D) veins
E) hemocoel
A) blood
B) pumping organ
C) arteries
D) veins
E) hemocoel

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 90 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
Figure 44-2 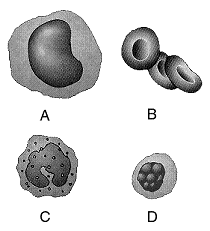 Refer to the accompanying figure. Which cell type is the source of antibodies?
Refer to the accompanying figure. Which cell type is the source of antibodies?
A) A only
B) B only
C) C only
D) D only
E) both A and B
 Refer to the accompanying figure. Which cell type is the source of antibodies?
Refer to the accompanying figure. Which cell type is the source of antibodies?A) A only
B) B only
C) C only
D) D only
E) both A and B

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 90 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
Which of the following depicts the correct sequence of protein activity in clot formation?
A) thrombin → prothrombin → fibrinogen → fibrin
B) prothrombin → thrombin → fibrinogen → fibrin
C) prothrombin → thrombin → fibrin → fibrinogen
D) prothrombin → thrombin → fibrin
E) prothrombin → thrombin → fibrinogen → erythrocytes
A) thrombin → prothrombin → fibrinogen → fibrin
B) prothrombin → thrombin → fibrinogen → fibrin
C) prothrombin → thrombin → fibrin → fibrinogen
D) prothrombin → thrombin → fibrin
E) prothrombin → thrombin → fibrinogen → erythrocytes

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 90 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
Which plasma protein(s) will be important immediately following a small cut on your finger?
A) serum
B) high-density lipoproteins
C) beta globulins
D) fibrinogen
E) gamma globulin
A) serum
B) high-density lipoproteins
C) beta globulins
D) fibrinogen
E) gamma globulin

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 90 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
Choose the correct order of the chambers through which oxygen-poor blood flows in an amphibian heart.
A) atrium → ventricle → sinus venosus → conus arteriosus
B) atrium → conus arteriosus → ventricle → sinus venosus
C) sinus venosus → atrium → ventricle → conus arteriosus
D) conus arteriosus → atrium → sinus venosus → ventricle
E) ventricle → atrium → conus arteriosus → sinus venosus
A) atrium → ventricle → sinus venosus → conus arteriosus
B) atrium → conus arteriosus → ventricle → sinus venosus
C) sinus venosus → atrium → ventricle → conus arteriosus
D) conus arteriosus → atrium → sinus venosus → ventricle
E) ventricle → atrium → conus arteriosus → sinus venosus

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 90 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
When a blood vessel is cut, why does vasoconstriction take place?
A) To expose collagen fibers to which platelets can adhere
B) To trigger the release of platelets from the surrounding tissues
C) To initiate the activation of thrombin
D) To entrap white blood cells
E) To reduce the flow of blood
A) To expose collagen fibers to which platelets can adhere
B) To trigger the release of platelets from the surrounding tissues
C) To initiate the activation of thrombin
D) To entrap white blood cells
E) To reduce the flow of blood

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 90 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
One advantage of a four-chambered heart is that it ____.
A) prevents mixing of oxygenated and deoxygenated blood
B) prevents deoxygenated blood from entering the heart
C) allows for better flow of blood to the tissues
D) prevents mixing of oxygenated and deoxygenated blood and allows tissues to be bypassed
E) prevents mixing of oxygenated and deoxygenated blood and allows better flow of blood to the tissues
A) prevents mixing of oxygenated and deoxygenated blood
B) prevents deoxygenated blood from entering the heart
C) allows for better flow of blood to the tissues
D) prevents mixing of oxygenated and deoxygenated blood and allows tissues to be bypassed
E) prevents mixing of oxygenated and deoxygenated blood and allows better flow of blood to the tissues

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 90 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
When impulses are conducted through the heart, transmission is delayed at the ____ so that the____ may contract before the ____.
A) sinoatrial node; atria; ventricles
B) sinoatrial node; ventricles; atria
C) atrioventricular bundle; atria; ventricles
D) atrioventricular node; ventricles; atria
E) atrioventricular node; atria; ventricles
A) sinoatrial node; atria; ventricles
B) sinoatrial node; ventricles; atria
C) atrioventricular bundle; atria; ventricles
D) atrioventricular node; ventricles; atria
E) atrioventricular node; atria; ventricles

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 90 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
A vein always carries:
A) blood to the heart.
B) blood from the heart.
C) oxygen-rich blood.
D) oxygen-poor blood.
E) blood rich in carbon dioxide.
A) blood to the heart.
B) blood from the heart.
C) oxygen-rich blood.
D) oxygen-poor blood.
E) blood rich in carbon dioxide.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 90 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
Chordae tendineae:
A) hold the AV valves in place.
B) contract when the heart contracts.
C) are one part of the conductance system of the heart.
D) regulate blood flow into the ventricles.
E) are stretched during ventricular systole.
A) hold the AV valves in place.
B) contract when the heart contracts.
C) are one part of the conductance system of the heart.
D) regulate blood flow into the ventricles.
E) are stretched during ventricular systole.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 90 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
Adding a fibrinogen inactivator to blood would prevent:
A) the formation of thrombin.
B) platelet formation.
C) the blood from clotting.
D) constriction of the blood vessels.
E) hemoglobin synthesis.
A) the formation of thrombin.
B) platelet formation.
C) the blood from clotting.
D) constriction of the blood vessels.
E) hemoglobin synthesis.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 90 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
Blood is routed through the capillary beds through the action of ____ at the metarterioles.
A) epithelium
B) precapillary sphincters
C) cartilage
D) fibrous connective tissue
E) skeletal muscle
A) epithelium
B) precapillary sphincters
C) cartilage
D) fibrous connective tissue
E) skeletal muscle

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 90 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
Which of the following structures is considered to be the pacemaker of the heart?
A) atrioventricular node
B) sinoatrial node
C) atrioventricular bundle
D) Purkinje fibers
E) intercalated discs
A) atrioventricular node
B) sinoatrial node
C) atrioventricular bundle
D) Purkinje fibers
E) intercalated discs

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 90 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
The component with the highest concentration in plasma is ____.
A) water
B) plasma proteins
C) erythrocytes
D) leukocytes
E) salts
A) water
B) plasma proteins
C) erythrocytes
D) leukocytes
E) salts

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 90 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
Which of the following is a component of plasma?
A) erythrocytes
B) hemoglobin
C) dissolved gases
D) leukocytes
E) histamine
A) erythrocytes
B) hemoglobin
C) dissolved gases
D) leukocytes
E) histamine

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 90 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
Which chemical, contained in the granules of basophils, helps prevent blood clot formation?
A) histamine
B) leukotrienes
C) prostaglandins
D) heparin
E) SRS-A
A) histamine
B) leukotrienes
C) prostaglandins
D) heparin
E) SRS-A

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 90 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
The characteristic that enables efficient gas exchange in capillaries is:
A) the very short total length of the capillaries.
B) their proximity to the heart.
C) thick walls of connective and muscle tissue.
D) thin walls that are only one cell wide.
E) the long total length of the capillaries.
A) the very short total length of the capillaries.
B) their proximity to the heart.
C) thick walls of connective and muscle tissue.
D) thin walls that are only one cell wide.
E) the long total length of the capillaries.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 90 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
Platelets are formed by:
A) cells division in the spleen.
B) disruption of a phagocyte.
C) fragmentation of the cytoplasm of a B lymphocyte.
D) small pieces pinching from very large cells in the bone marrow.
E) the release of granules from a neutrophil.
A) cells division in the spleen.
B) disruption of a phagocyte.
C) fragmentation of the cytoplasm of a B lymphocyte.
D) small pieces pinching from very large cells in the bone marrow.
E) the release of granules from a neutrophil.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 90 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
Smooth muscle in the arteriole walls can vasoconstrict or vasodilate, which:
A) helps to regulate blood pressure.
B) helps to accelerate the flow of blood through the vessels.
C) prevents the back flow of blood into the tissues.
D) squeezes oxygen out of the blood.
E) adds strength to the blood vessels.
A) helps to regulate blood pressure.
B) helps to accelerate the flow of blood through the vessels.
C) prevents the back flow of blood into the tissues.
D) squeezes oxygen out of the blood.
E) adds strength to the blood vessels.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 90 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
The four-chambered heart first evolved among the:
A) arthropods.
B) birds.
C) nonavian reptiles.
D) mammals.
E) fishes.
A) arthropods.
B) birds.
C) nonavian reptiles.
D) mammals.
E) fishes.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 90 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
The rapid onset of overproduction of immature white blood cells is known as:
A) anemia.
B) hemolytic anemia.
C) leukemia.
D) thrombocytopenia.
E) pernicious anemia.
A) anemia.
B) hemolytic anemia.
C) leukemia.
D) thrombocytopenia.
E) pernicious anemia.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 90 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
____ are leukocytes that produce antibodies.
A) Lymphocytes
B) Basophils
C) Eosinophils
D) Monocytes
E) Neutrophils
A) Lymphocytes
B) Basophils
C) Eosinophils
D) Monocytes
E) Neutrophils

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 90 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
Figure 44-3 Use the figure to answer the corresponding question(s). 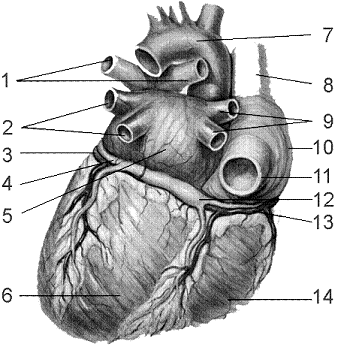 (Posterior View)
(Posterior View)
Refer to the accompanying figure. The function of the structure labeled as 14 is to:
A) stimulate the ventricles to contract.
B) pump blood to the lungs.
C) pump blood into the systemic circulation.
D) receive blood from the systemic circulation.
E) receive blood from the pulmonary circulation.
 (Posterior View)
(Posterior View)Refer to the accompanying figure. The function of the structure labeled as 14 is to:
A) stimulate the ventricles to contract.
B) pump blood to the lungs.
C) pump blood into the systemic circulation.
D) receive blood from the systemic circulation.
E) receive blood from the pulmonary circulation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 90 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
An electrocardiogram (ECG, EKG) is a measure of the heart's:
A) electrical system.
B) blood flow to the body.
C) contraction rate.
D) blood flow to heart muscle.
E) pumping ability.
A) electrical system.
B) blood flow to the body.
C) contraction rate.
D) blood flow to heart muscle.
E) pumping ability.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 90 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
To be diagnosed as having hypertension, you consistently will have a diastolic pressure of ____ mm Hg and a systolic pressure of ____ mm Hg.
A) 120; 80
B) 80; 120
C) 90; 140
D) 140; 90
E) 120; 73
A) 120; 80
B) 80; 120
C) 90; 140
D) 140; 90
E) 120; 73

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 90 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
The semilunar valves prevent blood from moving:
A) from the atria back into the veins.
B) from the ventricles back into the atria.
C) from the arteries back into the ventricles.
D) moving backwards in the capillaries.
E) moving backward in the arteries.
A) from the atria back into the veins.
B) from the ventricles back into the atria.
C) from the arteries back into the ventricles.
D) moving backwards in the capillaries.
E) moving backward in the arteries.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 90 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
Figure 44-3 Use the figure to answer the corresponding question(s). 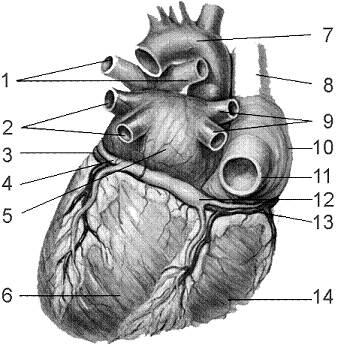 (Posterior View)
(Posterior View)
Refer to the accompanying figure. Which structure would carry blood to the systemic (body) circulation?
A) 1
B) 2
C) 6
D) 7
E) 14
 (Posterior View)
(Posterior View)Refer to the accompanying figure. Which structure would carry blood to the systemic (body) circulation?
A) 1
B) 2
C) 6
D) 7
E) 14

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 90 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
The ____ valve guards the opening between the right atrium and the right ventricle.
A) tricuspid
B) bicuspid
C) semilunar
D) atrial
E) mitral
A) tricuspid
B) bicuspid
C) semilunar
D) atrial
E) mitral

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 90 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
Figure 44-3 Use the figure to answer the corresponding question(s). 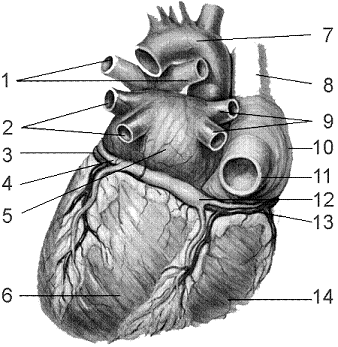 (Posterior View)
(Posterior View)
Refer to the accompanying figure. A semilunar valve regulates blood flow into which structures?
A) 1 and 2
B) 1 and 5
C) 1 and 7
D) 2 and 7
E) 7 and 11
 (Posterior View)
(Posterior View)Refer to the accompanying figure. A semilunar valve regulates blood flow into which structures?
A) 1 and 2
B) 1 and 5
C) 1 and 7
D) 2 and 7
E) 7 and 11

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 90 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
Due to recent changes in blood pressure guidelines, a reading of 120/80 is now considered to be:
A) a low normal reading.
B) a high normal reading.
C) prehypertensive.
D) hypotensive..
E) hypertensive.
A) a low normal reading.
B) a high normal reading.
C) prehypertensive.
D) hypotensive..
E) hypertensive.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 90 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
Starling's law of the heart states that the heart pumps:
A) more forcefully when more blood is delivered to it.
B) more rapidly when less blood is delivered to it.
C) less forcefully when oxygen-rich blood is delivered to it.
D) slower when more blood is delivered to it.
E) slower when norepinephrine is secreted.
A) more forcefully when more blood is delivered to it.
B) more rapidly when less blood is delivered to it.
C) less forcefully when oxygen-rich blood is delivered to it.
D) slower when more blood is delivered to it.
E) slower when norepinephrine is secreted.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 90 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
Blood pressure is greatest in the:
A) veins.
B) arteries.
C) capillaries.
D) venules.
E) arterioles.
A) veins.
B) arteries.
C) capillaries.
D) venules.
E) arterioles.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 90 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
The fluid-filled space that helps reduce the friction of a beating heart is called the:
A) endocardium.
B) pericardial cavity.
C) interventricular septum.
D) fossa ovalis.
E) auricle.
A) endocardium.
B) pericardial cavity.
C) interventricular septum.
D) fossa ovalis.
E) auricle.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 90 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
Figure 44-3 Use the figure to answer the corresponding question(s). 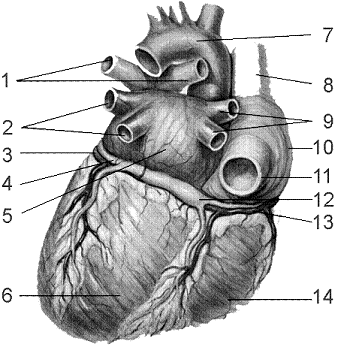 (Posterior View)
(Posterior View)
Refer to the accompanying figure. The structure labeled as 7 is called the:
A) superior vena cava.
B) aorta.
C) pulmonary veins.
D) right atrium.
E) right ventricle.
 (Posterior View)
(Posterior View)Refer to the accompanying figure. The structure labeled as 7 is called the:
A) superior vena cava.
B) aorta.
C) pulmonary veins.
D) right atrium.
E) right ventricle.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 90 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
The hepatic portal system is a special blood circuit between the ____ and ____.
A) liver; spleen
B) kidney; liver
C) liver; intestine
D) kidney; heart
E) spleen; heart
A) liver; spleen
B) kidney; liver
C) liver; intestine
D) kidney; heart
E) spleen; heart

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 90 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
The first heart sound (lub) is produced by the closing of the ____ and ____ valves.
A) aortic semilunar; pulmonary semilunar
B) right atrioventricular; aortic semilunar
C) left atrioventricular; pulmonary semilunar
D) right atrioventricular; left atrioventricular
E) mitral; left atrioventricular
A) aortic semilunar; pulmonary semilunar
B) right atrioventricular; aortic semilunar
C) left atrioventricular; pulmonary semilunar
D) right atrioventricular; left atrioventricular
E) mitral; left atrioventricular

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 90 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
You enjoy a lot of salt on your food. One of the long-term effects will be an increase in blood volume. This increase in blood volume will eventually result in a(n):
A) decrease in cardiac output.
B) increase in blood pressure.
C) decrease in stroke volume.
D) decrease in the force of contraction of the heart.
E) increase in body temperature.
A) decrease in cardiac output.
B) increase in blood pressure.
C) decrease in stroke volume.
D) decrease in the force of contraction of the heart.
E) increase in body temperature.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 90 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
The foramen ovale functions to:
A) permit blood to bypass the non-functional lungs in a fetus.
B) establish the basic heart rate.
C) prevent blood from flowing backward.
D) carry blood to the lungs in a fetus.
E) transport poorly oxygenated blood.
A) permit blood to bypass the non-functional lungs in a fetus.
B) establish the basic heart rate.
C) prevent blood from flowing backward.
D) carry blood to the lungs in a fetus.
E) transport poorly oxygenated blood.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 90 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
During ventricular systole (contraction):
A) the ventricles relax.
B) blood flows from the ventricles into the atria.
C) the tricuspid and mitral valves are open.
D) blood flows from the ventricles to the pulmonary artery and aorta.
E) the atria contract.
A) the ventricles relax.
B) blood flows from the ventricles into the atria.
C) the tricuspid and mitral valves are open.
D) blood flows from the ventricles to the pulmonary artery and aorta.
E) the atria contract.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 90 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
Blood pressure depends on:
A) the height and weight of an individual.
B) atrial volume and stroke rate.
C) blood flow and resistance of blood against the vessel walls.
D) total blood volume.
E) heart rate.
A) the height and weight of an individual.
B) atrial volume and stroke rate.
C) blood flow and resistance of blood against the vessel walls.
D) total blood volume.
E) heart rate.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 90 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
Cardiac output is determined by:
A) blood volume.
B) venous return.
C) blood volume and venous return.
D) stroke volume only.
E) stroke volume and heart rate.
A) blood volume.
B) venous return.
C) blood volume and venous return.
D) stroke volume only.
E) stroke volume and heart rate.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 90 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
What is the correct order for the following events that follow a nerve impulse along a sympathetic neuron to innervate the heart?
1) G protein activates adenylyl cyclase
2) Neuron releases norepinephrine
3) Cyclic AMP activates protein kinase
4) Receptor activates G protein
5) Protein kinase phosphorylates Ca2+ channels
6) Receptors activated on the membrane of the cardiac muscle
A) 1, 3, 4, 5, 2, 6
B) 5, 3, 4, 1, 2, 6
C) 6, 2, 4, 1, 3, 5
D) 2, 6, 4, 1, 3, 5
E) 2, 3, 4, 1, 6, 5
1) G protein activates adenylyl cyclase
2) Neuron releases norepinephrine
3) Cyclic AMP activates protein kinase
4) Receptor activates G protein
5) Protein kinase phosphorylates Ca2+ channels
6) Receptors activated on the membrane of the cardiac muscle
A) 1, 3, 4, 5, 2, 6
B) 5, 3, 4, 1, 2, 6
C) 6, 2, 4, 1, 3, 5
D) 2, 6, 4, 1, 3, 5
E) 2, 3, 4, 1, 6, 5

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 90 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
All arteries, with the exception of the ____, contain oxygen-rich blood.
A) aorta
B) carotid arteries
C) coronary arteries
D) pulmonary arteries
E) mesenteric arteries
A) aorta
B) carotid arteries
C) coronary arteries
D) pulmonary arteries
E) mesenteric arteries

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 90 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
The amphibian heart consists of two atria and two ventricle(s).

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 90 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
One purpose of the lymphatic system is to:
A) transport nutrients and oxygen.
B) returns interstitial fluid to the blood.
C) block the transport of blood proteins.
D) produce red blood cells.
E) deliver carbon dioxide to the heart.
A) transport nutrients and oxygen.
B) returns interstitial fluid to the blood.
C) block the transport of blood proteins.
D) produce red blood cells.
E) deliver carbon dioxide to the heart.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 90 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
Eosinophils are filled with hemoglobin.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 90 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
Compare and contrast internal transportation as conducted by an open and closed circulatory system. Also, identify two animals representative of each type of circulatory system.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 90 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
The pacemaker is located in the atrioventricular node.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 90 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
Compare the structure and function of three of the following types of blood vessels: arteries, arterioles, veins, venules and capillaries.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 90 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
The blood pressure in the veins of your toe is most likely higher than the blood pressure in the arteries of your little finger.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 90 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
The tricuspid valve is located between the right atrium and the right ventricle.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 90 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
Serum is plasma without the proteins involved in clotting.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 90 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
In the clotting process, fibrinogen is converted to fibrin.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 90 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72
An example of a(n) granular leucocyte is a monocyte.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 90 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73
Identify two hormones that are involved in regulating blood pressure and briefly describe the role of each.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 90 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
74
Interstitial fluid enters the lymphatic capillaries:
A) by diffusion.
B) by pinocytosis.
C) through pores in the lymph vessel walls.
D) due to the hydrostatic pressure of blood.
E) through pressure-controlled openings between endothelial cells.
A) by diffusion.
B) by pinocytosis.
C) through pores in the lymph vessel walls.
D) due to the hydrostatic pressure of blood.
E) through pressure-controlled openings between endothelial cells.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 90 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
75
Cardiac output is obtained by multiplying stroke volume by heart rate.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 90 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
76
Metarterioles directly link arterioles with venules.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 90 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
77
The coronary sinus drains blood directly into the:
A) inferior vena cava.
B) superior vena cava.
C) left atrium.
D) right atrium.
E) coronary arteries.
A) inferior vena cava.
B) superior vena cava.
C) left atrium.
D) right atrium.
E) coronary arteries.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 90 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
78
By definition, an animal having a(n) closed circulatory system will also have a hemocoel.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 90 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
79
Describe the structure of representative vertebrate hearts from fish through mammals. Briefly explain the circulation pattern supported by one type of non-mammalian vertebrate heart.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 90 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
80
A blocked coronary sinus would block blood flow:
A) into the superior vena cava.
B) into the inferior vena cava.
C) into the pulmonary arteries.
D) returning from the pulmonary arteries.
E) returning from the coronary circulation.
A) into the superior vena cava.
B) into the inferior vena cava.
C) into the pulmonary arteries.
D) returning from the pulmonary arteries.
E) returning from the coronary circulation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 90 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



