Deck 49: Endocrine Regulation
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Match between columns
Premises:
hypothalamus
hypothalamus
hypothalamus
hypothalamus
hypothalamus
hypothalamus
hypothalamus
hypothalamus
kidneys (collecting ducts)
kidneys (collecting ducts)
kidneys (collecting ducts)
kidneys (collecting ducts)
kidneys (collecting ducts)
kidneys (collecting ducts)
kidneys (collecting ducts)
kidneys (collecting ducts)
bone, kidneys, digestive tract
bone, kidneys, digestive tract
bone, kidneys, digestive tract
bone, kidneys, digestive tract
bone, kidneys, digestive tract
bone, kidneys, digestive tract
bone, kidneys, digestive tract
bone, kidneys, digestive tract
liver, adipose tissue
liver, adipose tissue
liver, adipose tissue
liver, adipose tissue
liver, adipose tissue
liver, adipose tissue
liver, adipose tissue
liver, adipose tissue
mammary glands
mammary glands
mammary glands
mammary glands
mammary glands
mammary glands
mammary glands
mammary glands
muscle, blood vessels
muscle, blood vessels
muscle, blood vessels
muscle, blood vessels
muscle, blood vessels
muscle, blood vessels
muscle, blood vessels
muscle, blood vessels
uterus
uterus
uterus
uterus
uterus
uterus
uterus
uterus
bone
bone
bone
bone
bone
bone
bone
bone
Responses:
melatonin
parathyroid hormone
calcitonin
ADH
oxytocin
epinephrine
prolactin
glucagon
melatonin
parathyroid hormone
calcitonin
ADH
oxytocin
epinephrine
prolactin
glucagon
melatonin
parathyroid hormone
calcitonin
ADH
oxytocin
epinephrine
prolactin
glucagon
melatonin
parathyroid hormone
calcitonin
ADH
oxytocin
epinephrine
prolactin
glucagon
melatonin
parathyroid hormone
calcitonin
ADH
oxytocin
epinephrine
prolactin
glucagon
melatonin
parathyroid hormone
calcitonin
ADH
oxytocin
epinephrine
prolactin
glucagon
melatonin
parathyroid hormone
calcitonin
ADH
oxytocin
epinephrine
prolactin
glucagon
melatonin
parathyroid hormone
calcitonin
ADH
oxytocin
epinephrine
prolactin
glucagon
melatonin
parathyroid hormone
calcitonin
ADH
oxytocin
epinephrine
prolactin
glucagon
melatonin
parathyroid hormone
calcitonin
ADH
oxytocin
epinephrine
prolactin
glucagon
melatonin
parathyroid hormone
calcitonin
ADH
oxytocin
epinephrine
prolactin
glucagon
melatonin
parathyroid hormone
calcitonin
ADH
oxytocin
epinephrine
prolactin
glucagon
melatonin
parathyroid hormone
calcitonin
ADH
oxytocin
epinephrine
prolactin
glucagon
melatonin
parathyroid hormone
calcitonin
ADH
oxytocin
epinephrine
prolactin
glucagon
melatonin
parathyroid hormone
calcitonin
ADH
oxytocin
epinephrine
prolactin
glucagon
melatonin
parathyroid hormone
calcitonin
ADH
oxytocin
epinephrine
prolactin
glucagon
Question
Question
Match between columns
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/69
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 49: Endocrine Regulation
1
Figure 49-1 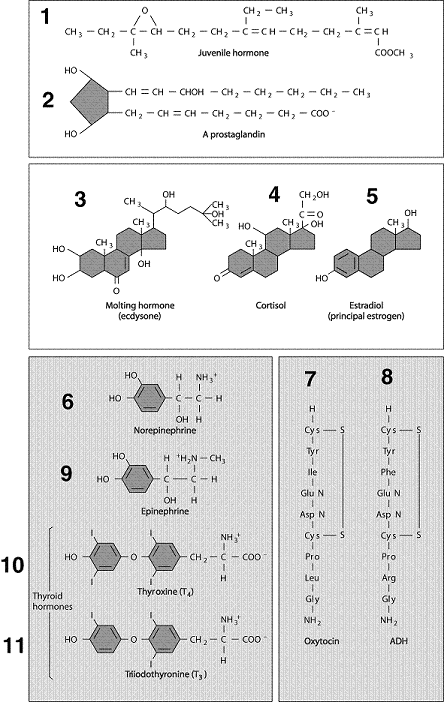 Refer to the accompanying figure. Which of the following hormones is secreted by the adrenal cortex?
Refer to the accompanying figure. Which of the following hormones is secreted by the adrenal cortex?
A) 1
B) 2
C) 4
D) 6
E) 8
 Refer to the accompanying figure. Which of the following hormones is secreted by the adrenal cortex?
Refer to the accompanying figure. Which of the following hormones is secreted by the adrenal cortex?A) 1
B) 2
C) 4
D) 6
E) 8
C
2
Which of the following is the largest group of hormones?
A) steroid hormones
B) polysaccharide hormones
C) amino acid derivatives
D) peptide hormones
E) fatty acid derivatives
A) steroid hormones
B) polysaccharide hormones
C) amino acid derivatives
D) peptide hormones
E) fatty acid derivatives
D
3
Why doesn't every cell in the body respond to every hormone circulating in the bloodstream?
A) Each cell has a limited number of protein channels that shuttle hormones through its membrane.
B) Not all hormones can diffuse through all cell membranes.
C) The concentration of some hormones is too low to stimulate every cell.
D) Each cell has specific surface receptors, which interact only with hormones that they recognize.
E) Although all hormones bind to all cell surfaces, some cells lack second messengers for expression.
A) Each cell has a limited number of protein channels that shuttle hormones through its membrane.
B) Not all hormones can diffuse through all cell membranes.
C) The concentration of some hormones is too low to stimulate every cell.
D) Each cell has specific surface receptors, which interact only with hormones that they recognize.
E) Although all hormones bind to all cell surfaces, some cells lack second messengers for expression.
D
4
Hormones are chemical messengers transported by the ____ that can have ____.
A) blood: stimulatory or inhibitory effects
B) lymph ducts; stimulatory effects
C) ducts; stimulatory or inhibitory effects
D) neurons; stimulatory effects
E) glands; inhibitory effects
A) blood: stimulatory or inhibitory effects
B) lymph ducts; stimulatory effects
C) ducts; stimulatory or inhibitory effects
D) neurons; stimulatory effects
E) glands; inhibitory effects

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
Compared to the nervous system, the endocrine system responds:
A) more quickly but may have longer-lasting effects.
B) more quickly and may have more short-term effects.
C) more slowly and may have longer-lasting effects.
D) more slowly but may have more short-term effects.
E) about the same and has similar effects.
A) more quickly but may have longer-lasting effects.
B) more quickly and may have more short-term effects.
C) more slowly and may have longer-lasting effects.
D) more slowly but may have more short-term effects.
E) about the same and has similar effects.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
When blood calcium levels are high, ____.
A) neurons may fire more slowly
B) the release of parathyroid hormone would increase
C) neurons may fire spontaneously
D) the release of parathyroid hormone would decrease
E) the reabsorption of calcium from the kidney tubules would increase
A) neurons may fire more slowly
B) the release of parathyroid hormone would increase
C) neurons may fire spontaneously
D) the release of parathyroid hormone would decrease
E) the reabsorption of calcium from the kidney tubules would increase

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
The secretion of which hormone decreases when calcium blood levels increase?
A) calcitonin
B) parathyroid hormone
C) thyroid hormone
D) epinephrine
E) norepinephrine
A) calcitonin
B) parathyroid hormone
C) thyroid hormone
D) epinephrine
E) norepinephrine

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
Which of the following statements about paracrine regulation is TRUE?
A) The hormones released only stimulate the cells that secreted them.
B) The hormones released only inhibit the cells that secreted them.
C) The hormones released act on nearby target cells.
D) The hormones released are transported down axons.
E) The hormones released link the endocrine and nervous systems.
A) The hormones released only stimulate the cells that secreted them.
B) The hormones released only inhibit the cells that secreted them.
C) The hormones released act on nearby target cells.
D) The hormones released are transported down axons.
E) The hormones released link the endocrine and nervous systems.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
What type of endocrine signaling is used predominantly by invertebrates?
A) autocrine signaling
B) paracrine signaling
C) classical endocrine signaling
D) neuroendocrine signaling
E) no endocrine signaling
A) autocrine signaling
B) paracrine signaling
C) classical endocrine signaling
D) neuroendocrine signaling
E) no endocrine signaling

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
Figure 49-1 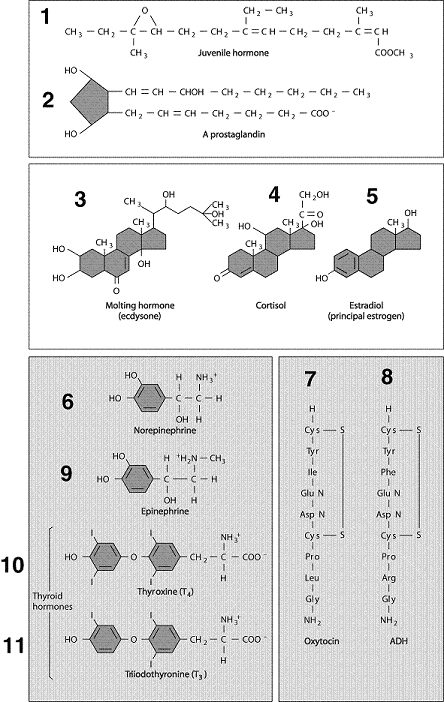 Refer to the accompanying figure. Which of the following is a steroid hormone?
Refer to the accompanying figure. Which of the following is a steroid hormone?
A) 1
B) 3
C) 6
D) 8
E) 10
 Refer to the accompanying figure. Which of the following is a steroid hormone?
Refer to the accompanying figure. Which of the following is a steroid hormone?A) 1
B) 3
C) 6
D) 8
E) 10

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
Figure 49-2 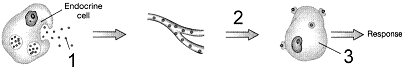 The process illustrated in the accompanying figure is representative of:
The process illustrated in the accompanying figure is representative of:
A) neuroendocrine signaling.
B) paracrine regulation.
C) cAMP as a second messenger.
D) classical endocrine signaling.
E) autocrine regulation.
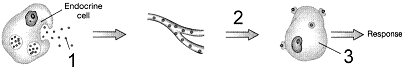 The process illustrated in the accompanying figure is representative of:
The process illustrated in the accompanying figure is representative of:A) neuroendocrine signaling.
B) paracrine regulation.
C) cAMP as a second messenger.
D) classical endocrine signaling.
E) autocrine regulation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
Which of the following is a modified fatty acid?
A) prostaglandin
B) cyclic AMP
C) thyroid hormone
D) epinephrine
E) melatonin
A) prostaglandin
B) cyclic AMP
C) thyroid hormone
D) epinephrine
E) melatonin

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
Anabolic steroids:
A) are removed from the body fairly quickly due to a low concentration of receptor sites.
B) decrease HDL concentration, thereby increasing the risk of cardiovascular disease.
C) are naturally produced hormones typically used by athletes for short-term performance enhancement.
D) have little or no effect on physiology or behavior at very low doses.
E) are metabolized and excreted from the body quickly..
A) are removed from the body fairly quickly due to a low concentration of receptor sites.
B) decrease HDL concentration, thereby increasing the risk of cardiovascular disease.
C) are naturally produced hormones typically used by athletes for short-term performance enhancement.
D) have little or no effect on physiology or behavior at very low doses.
E) are metabolized and excreted from the body quickly..

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
What is the difference between endocrine and exocrine glands?
A) Endocrine glands are discrete structures, while exocrine glands may be specialized cells in other tissues.
B) Exocrine glands produce hormones, while endocrine glands do not.
C) Endocrine glands only affect cells in the immediate area, while exocrine glands do not.
D) Endocrine glands secrete into the interstitial fluid, while exocrine glands release secretions into ducts.
E) Exocrine glands secrete neurohormones, while endocrine glands do not.
A) Endocrine glands are discrete structures, while exocrine glands may be specialized cells in other tissues.
B) Exocrine glands produce hormones, while endocrine glands do not.
C) Endocrine glands only affect cells in the immediate area, while exocrine glands do not.
D) Endocrine glands secrete into the interstitial fluid, while exocrine glands release secretions into ducts.
E) Exocrine glands secrete neurohormones, while endocrine glands do not.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
The products of an endocrine gland:
A) only affect their own tissues.
B) can have a digestive function.
C) always stimulate the target tissue.
D) generally have to travel to reach the target tissue.
E) are not produced by cells in organs, such as the heart.
A) only affect their own tissues.
B) can have a digestive function.
C) always stimulate the target tissue.
D) generally have to travel to reach the target tissue.
E) are not produced by cells in organs, such as the heart.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
Figure 49-2 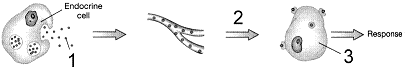 The second messenger for the hormone mechanism in the accompanying figure is:
The second messenger for the hormone mechanism in the accompanying figure is:
A) ATP.
B) G protein.
C) cAMP.
D) calmodulin.
E) Ca2+.
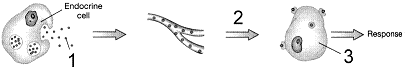 The second messenger for the hormone mechanism in the accompanying figure is:
The second messenger for the hormone mechanism in the accompanying figure is:A) ATP.
B) G protein.
C) cAMP.
D) calmodulin.
E) Ca2+.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
Hormones are synthesized from cholesterol are part of the ____ group of hormones.
A) fatty acid derivatives
B) steroid hormones
C) amino acid derivatives
D) peptide hormones
E) protein hormones
A) fatty acid derivatives
B) steroid hormones
C) amino acid derivatives
D) peptide hormones
E) protein hormones

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
In which type of regulation do hormones act on the cells that produce it?
A) classical endocrine signaling
B) neuroendocrine signaling
C) paracrine signaling
D) autocrine signaling
E) pheromone signaling
A) classical endocrine signaling
B) neuroendocrine signaling
C) paracrine signaling
D) autocrine signaling
E) pheromone signaling

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
Figure 49-1 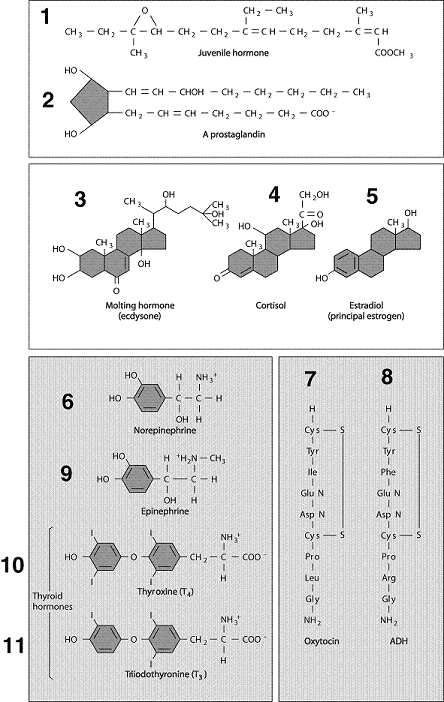 Refer to the accompanying figure. Insulin-like growth factor would be included with which of the following pairs?
Refer to the accompanying figure. Insulin-like growth factor would be included with which of the following pairs?
A) 1, 2
B) 3, 4
C) 6, 9
D) 7, 8
E) 10, 11
 Refer to the accompanying figure. Insulin-like growth factor would be included with which of the following pairs?
Refer to the accompanying figure. Insulin-like growth factor would be included with which of the following pairs?A) 1, 2
B) 3, 4
C) 6, 9
D) 7, 8
E) 10, 11

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
Which of the following is a peptide hormone?
A) adrenaline
B) ACTH
C) progesterone
D) melatonin
E) prostaglandin
A) adrenaline
B) ACTH
C) progesterone
D) melatonin
E) prostaglandin

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
After a steroid hormone binds its receptor, the hormone-receptor complex then:
A) activates a G protein.
B) activates a protein kinase.
C) activates adenylyl cyclase.
D) activates calmodulin.
E) binds DNA.
A) activates a G protein.
B) activates a protein kinase.
C) activates adenylyl cyclase.
D) activates calmodulin.
E) binds DNA.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
During stressful situations, epinephrine initiates:
A) the dilation of the blood vessels to the kidneys.
B) the constriction of the blood vessels to the heart.
C) the dilation of the blood vessels to the brain.
D) the dilation of the blood vessels to the skin.
E) a decrease in blood glucose levels.
A) the dilation of the blood vessels to the kidneys.
B) the constriction of the blood vessels to the heart.
C) the dilation of the blood vessels to the brain.
D) the dilation of the blood vessels to the skin.
E) a decrease in blood glucose levels.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
Insulin promotes the storage of glucose by:
A) stimulating protein synthesis.
B) increasing the use of fatty acids as fuel.
C) promoting the liver to release glucose.
D) stimulating fatty acid release by adipose tissue.
E) inhibiting glycogen formation.
A) stimulating protein synthesis.
B) increasing the use of fatty acids as fuel.
C) promoting the liver to release glucose.
D) stimulating fatty acid release by adipose tissue.
E) inhibiting glycogen formation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
What is the difference between type 1 and type 2 diabetes?
A) One causes hyperglycemia, while the other causes hypoglycemia.
B) One demonstrates protein breakdown, while the other demonstrates protein synthesis.
C) One leads to blindness, while the other leads to kidney disorder.
D) One has insulin hypersecretion, while the other has insulin hyposecretion.
E) One has insulin deficiency, while the other has insulin resistance.
A) One causes hyperglycemia, while the other causes hypoglycemia.
B) One demonstrates protein breakdown, while the other demonstrates protein synthesis.
C) One leads to blindness, while the other leads to kidney disorder.
D) One has insulin hypersecretion, while the other has insulin hyposecretion.
E) One has insulin deficiency, while the other has insulin resistance.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
Type 2 diabetes is caused by:
A) too much insulin in the blood.
B) too little insulin in the blood.
C) too much glucagon in the blood.
D) too little glucagon in the blood.
E) receptors being insensitive to insulin.
A) too much insulin in the blood.
B) too little insulin in the blood.
C) too much glucagon in the blood.
D) too little glucagon in the blood.
E) receptors being insensitive to insulin.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
Which pair of hormones regulates the calcium levels of the blood?
A) thyroxin and parathyroid hormone
B) adrenocorticotropic hormone and thyroid stimulating hormone
C) prolactin and oxytocin
D) parathyroid hormone and calcitonin
E) calcitonin and thyroxin
A) thyroxin and parathyroid hormone
B) adrenocorticotropic hormone and thyroid stimulating hormone
C) prolactin and oxytocin
D) parathyroid hormone and calcitonin
E) calcitonin and thyroxin

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
In a signal transduction pathway involving cAMP as a second messenger, after a G protein is activated, the activated G protein then activates:
A) phospholipase C.
B) adenylyl cyclase.
C) calmodulin.
D) protein kinase.
E) diacylglycerol.
A) phospholipase C.
B) adenylyl cyclase.
C) calmodulin.
D) protein kinase.
E) diacylglycerol.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
In a signal transduction pathway involving phospholipid products as second messengers, after a G protein is activated, the activated G protein then activates:
A) IP2.
B) IP3.
C) protein kinase C.
D) phospholipase C.
E) adenylyl cyclase.
A) IP2.
B) IP3.
C) protein kinase C.
D) phospholipase C.
E) adenylyl cyclase.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
Hypothyroidism during infancy and childhood can lead to a condition of retarded mental and physical development called:
A) dwarfism.
B) gigantism.
C) acromegaly.
D) myxedema.
E) cretinism.
A) dwarfism.
B) gigantism.
C) acromegaly.
D) myxedema.
E) cretinism.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
Chronic stress:
A) is associated with elevated levels of glucocorticoids.
B) may lead to the excessive stimulation of neurons.
C) increases blood flow to the brain, especially the hippocampus.
D) results in lower levels of epinephrine and norepinephrine.
E) promotes the linear growth of the skeleton.
A) is associated with elevated levels of glucocorticoids.
B) may lead to the excessive stimulation of neurons.
C) increases blood flow to the brain, especially the hippocampus.
D) results in lower levels of epinephrine and norepinephrine.
E) promotes the linear growth of the skeleton.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
Which types of hormones can enter cells and turn specific genes on and off?
A) steroid and peptide hormones
B) steroid and thyroid hormones
C) thyroid and peptide hormones
D) peptide and phospholipid hormones
E) steroid and phospholipid hormones
A) steroid and peptide hormones
B) steroid and thyroid hormones
C) thyroid and peptide hormones
D) peptide and phospholipid hormones
E) steroid and phospholipid hormones

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
Glucagon raises blood glucose levels by:
A) stimulating the liver to take up glucose.
B) inhibiting gluconeogenesis.
C) stimulating gluconeogenesis.
D) inhibiting fatty acid mobilization.
E) inhibiting amino acid mobilization.
A) stimulating the liver to take up glucose.
B) inhibiting gluconeogenesis.
C) stimulating gluconeogenesis.
D) inhibiting fatty acid mobilization.
E) inhibiting amino acid mobilization.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
Calcium ions may act with phospholipid second messengers by binding to ____, which then regulates other proteins.
A) adenylyl cyclase
B) cyclic AMP
C) calmodulin
D) phosphodiesterase
E) protein kinase
A) adenylyl cyclase
B) cyclic AMP
C) calmodulin
D) phosphodiesterase
E) protein kinase

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
An adult who is suffering from hyperthyroidism:
A) is always tired.
B) is often hungry.
C) is overweight.
D) is mentally slow.
E) shows a lack of emotions.
A) is always tired.
B) is often hungry.
C) is overweight.
D) is mentally slow.
E) shows a lack of emotions.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
Insulin is produced by the:
A) beta cells of the islets of Langerhans.
B) alpha cells of the islets of Langerhans.
C) cortical cells of the adrenal gland.
D) neurons in the hypothalamus.
E) lobules of the liver.
A) beta cells of the islets of Langerhans.
B) alpha cells of the islets of Langerhans.
C) cortical cells of the adrenal gland.
D) neurons in the hypothalamus.
E) lobules of the liver.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
The principal mineralocorticoid is:
A) ADH.
B) epinephrine.
C) growth hormone.
D) aldosterone.
E) ACTH.
A) ADH.
B) epinephrine.
C) growth hormone.
D) aldosterone.
E) ACTH.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
Once a hormone activates the enzyme adenylyl cyclase, ATP is converted to cAMP, which in turn:
A) activates protein kinase.
B) inhibits phosphodiesterase.
C) initiates more cAMP production.
D) initiates protein synthesis.
E) inhibits protein synthesis.
A) activates protein kinase.
B) inhibits phosphodiesterase.
C) initiates more cAMP production.
D) initiates protein synthesis.
E) inhibits protein synthesis.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
Arrange the following events in the correct sequence.
1) thyroid gland secretes less hormone
2) homeostasis
3) high concentration of thyroid hormones
4) anterior pituitary secretes less TSH
A) 2 → 1 → 4 → 3
B) 2 → 3 → 4 → 1
C) 3 → 4 → 1 → 2
D) 4 → 3 → 1 → 2
E) 1 → 4 → 3 → 2
1) thyroid gland secretes less hormone
2) homeostasis
3) high concentration of thyroid hormones
4) anterior pituitary secretes less TSH
A) 2 → 1 → 4 → 3
B) 2 → 3 → 4 → 1
C) 3 → 4 → 1 → 2
D) 4 → 3 → 1 → 2
E) 1 → 4 → 3 → 2

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
The function of corticotropin-releasing factor (CRF) is to stimulate:
A) the release of adrenocorticotropic hormone.
B) gluconeogenesis.
C) adrenaline release.
D) glycogen synthesis.
E) the inflammatory response.
A) the release of adrenocorticotropic hormone.
B) gluconeogenesis.
C) adrenaline release.
D) glycogen synthesis.
E) the inflammatory response.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
Which hormone stimulates insect growth and molting?
A) ecdysiotropin
B) juvenile hormone
C) histamine
D) pheromone
E) ecdysone
A) ecdysiotropin
B) juvenile hormone
C) histamine
D) pheromone
E) ecdysone

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
Exocrine glands have no ducts and secrete their hormones into the surrounding interstial fluid or blood.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
____ is produced by the anterior lobe of the pituitary.
A) Oxytocin
B) Melatonin
C) Growth hormone
D) ADH
E) Epinephrine
A) Oxytocin
B) Melatonin
C) Growth hormone
D) ADH
E) Epinephrine

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
Insulin-like growth factors can induce which of the following?
A) promoting exponential growth of the skeleton
B) stimulating degradation of cartilage
C) promoting protein synthesis
D) promoting the mobilization of fat
E) decreasing organ size
A) promoting exponential growth of the skeleton
B) stimulating degradation of cartilage
C) promoting protein synthesis
D) promoting the mobilization of fat
E) decreasing organ size

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
What is a symptom of Cushing's disease?
A) loss of ability to cope with stress
B) mild infection
C) abnormally large face and hands
D) fat deposition around the trunk
E) intellectual disability
A) loss of ability to cope with stress
B) mild infection
C) abnormally large face and hands
D) fat deposition around the trunk
E) intellectual disability

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
Neuroendocrine cells release neurohormones which are transported through contact or diffuse through interstitial fluid.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
The posterior lobe of the pituitary gland secretes:
A) ADH.
B) ACTH.
C) TSH.
D) FSH.
E) LH.
A) ADH.
B) ACTH.
C) TSH.
D) FSH.
E) LH.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
Nonsteroid anti-inflammatory drugs such as aspirin and ibuprofen reduce fever and decrease inflammation and pain by directly inhibiting cAMP synthesis.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
Pituitary dwarfism is caused by:
A) hypersecretion of thyroxine during childhood.
B) hyposecretion of thyroxine during childhood.
C) hypersecretion of growth hormone during childhood.
D) hyposecretion of growth hormone during childhood.
E) hypersecretion of epinephrine during childhood.
A) hypersecretion of thyroxine during childhood.
B) hyposecretion of thyroxine during childhood.
C) hypersecretion of growth hormone during childhood.
D) hyposecretion of growth hormone during childhood.
E) hypersecretion of epinephrine during childhood.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
The anterior lobe of the pituitary gland releases hormones produced by the hypothalamus.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
The function of oxytocin is to:
A) stimulate uterine contractions
B) stimulate the cells of the mammary glands to produce milk
C) regulate the permeability of the collecting tubules of the kidney
D) stimulate ovulation
E) stimulate the growth of the ovarian follicles
A) stimulate uterine contractions
B) stimulate the cells of the mammary glands to produce milk
C) regulate the permeability of the collecting tubules of the kidney
D) stimulate ovulation
E) stimulate the growth of the ovarian follicles

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
Compare and contrast the mechanism of action of a steroid and a protein-type hormone at the cellular level.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
Use a specific example to explain how a negative feedback mechanism may be used to regulate the function of endocrine glands.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
G protein-linked receptors are transmembrane proteins that convert a(n) extracellular hormone signal into an intracellular signal that affects certain cell processes.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
The ____ gland stores and releases hormones produced by the hypothalamus.
A) pancreas
B) pineal
C) pituitary
D) thyroid
E) parathyroid
A) pancreas
B) pineal
C) pituitary
D) thyroid
E) parathyroid

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
The ____ produce(s) ____, which influences biological rhythms and the onset of sleep.
A) pituitary gland; thyroid stimulating hormone
B) pituitary gland; adrenocorticotropic hormone
C) pineal gland; melatonin
D) adrenal cortex; cortisol
E) parathyroid glands; parathyroid hormone
A) pituitary gland; thyroid stimulating hormone
B) pituitary gland; adrenocorticotropic hormone
C) pineal gland; melatonin
D) adrenal cortex; cortisol
E) parathyroid glands; parathyroid hormone

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
Which gland is considered to be the master gland of the body?
A) pineal gland
B) adrenal gland
C) pituitary gland
D) thyroid gland
E) parathyroid gland
A) pineal gland
B) adrenal gland
C) pituitary gland
D) thyroid gland
E) parathyroid gland

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
The pituitary gland is regulated most directly by the:
A) pineal gland.
B) hypothalamus.
C) thymus gland.
D) adrenal gland.
E) thyroid gland.
A) pineal gland.
B) hypothalamus.
C) thymus gland.
D) adrenal gland.
E) thyroid gland.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
Briefly discuss the complementary functional roles of insulin and glucagon.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
Steroid hormones bind with G-protein linked receptors in plasma membranes of target cells.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
Hypersecretion of growth hormone in adulthood leads to enlarged hands, face, and feet, a condition known as:
A) dwarfism.
B) gigantism.
C) acromegaly.
D) goiter.
E) cretinism.
A) dwarfism.
B) gigantism.
C) acromegaly.
D) goiter.
E) cretinism.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
Match between columns
Premises:
hypothalamus
hypothalamus
hypothalamus
hypothalamus
hypothalamus
hypothalamus
hypothalamus
hypothalamus
kidneys (collecting ducts)
kidneys (collecting ducts)
kidneys (collecting ducts)
kidneys (collecting ducts)
kidneys (collecting ducts)
kidneys (collecting ducts)
kidneys (collecting ducts)
kidneys (collecting ducts)
bone, kidneys, digestive tract
bone, kidneys, digestive tract
bone, kidneys, digestive tract
bone, kidneys, digestive tract
bone, kidneys, digestive tract
bone, kidneys, digestive tract
bone, kidneys, digestive tract
bone, kidneys, digestive tract
liver, adipose tissue
liver, adipose tissue
liver, adipose tissue
liver, adipose tissue
liver, adipose tissue
liver, adipose tissue
liver, adipose tissue
liver, adipose tissue
mammary glands
mammary glands
mammary glands
mammary glands
mammary glands
mammary glands
mammary glands
mammary glands
muscle, blood vessels
muscle, blood vessels
muscle, blood vessels
muscle, blood vessels
muscle, blood vessels
muscle, blood vessels
muscle, blood vessels
muscle, blood vessels
uterus
uterus
uterus
uterus
uterus
uterus
uterus
uterus
bone
bone
bone
bone
bone
bone
bone
bone
Responses:
melatonin
parathyroid hormone
calcitonin
ADH
oxytocin
epinephrine
prolactin
glucagon
melatonin
parathyroid hormone
calcitonin
ADH
oxytocin
epinephrine
prolactin
glucagon
melatonin
parathyroid hormone
calcitonin
ADH
oxytocin
epinephrine
prolactin
glucagon
melatonin
parathyroid hormone
calcitonin
ADH
oxytocin
epinephrine
prolactin
glucagon
melatonin
parathyroid hormone
calcitonin
ADH
oxytocin
epinephrine
prolactin
glucagon
melatonin
parathyroid hormone
calcitonin
ADH
oxytocin
epinephrine
prolactin
glucagon
melatonin
parathyroid hormone
calcitonin
ADH
oxytocin
epinephrine
prolactin
glucagon
melatonin
parathyroid hormone
calcitonin
ADH
oxytocin
epinephrine
prolactin
glucagon
melatonin
parathyroid hormone
calcitonin
ADH
oxytocin
epinephrine
prolactin
glucagon
melatonin
parathyroid hormone
calcitonin
ADH
oxytocin
epinephrine
prolactin
glucagon
melatonin
parathyroid hormone
calcitonin
ADH
oxytocin
epinephrine
prolactin
glucagon
melatonin
parathyroid hormone
calcitonin
ADH
oxytocin
epinephrine
prolactin
glucagon
melatonin
parathyroid hormone
calcitonin
ADH
oxytocin
epinephrine
prolactin
glucagon
melatonin
parathyroid hormone
calcitonin
ADH
oxytocin
epinephrine
prolactin
glucagon
melatonin
parathyroid hormone
calcitonin
ADH
oxytocin
epinephrine
prolactin
glucagon
melatonin
parathyroid hormone
calcitonin
ADH
oxytocin
epinephrine
prolactin
glucagon

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
Prolactin appears to help us recognize familiar faces and trust other people.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
Match between columns

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
Calcitonin works synergistically to parathyroid hormone.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
Since hormones are present in such small amounts, how can their signals be amplified enough to regulate so many physiological processes?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
When thyroid hormone concentration is low the anterior pituitary secretes less TSH.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
What effects do hypothyroidism and hyperthyroidism have on metabolism?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
Based on Berthold's methods, how do researchers today determine a tissue to be endocrine in nature?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
When blood glucose concentration is high, pancreatic beta cells secrete insulin, and consequently blood glucose concentration is increased.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



