Deck 5: Biological Membranes
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Match between columns
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/69
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 5: Biological Membranes
1
Which statement about lipid bilayers is false ?
A) They are inflexible.
B) They are self-sealing.
C) They resist forming free ends.
D) They can fuse with other bilayers.
E) They spontaneously form closed vesicles.
A) They are inflexible.
B) They are self-sealing.
C) They resist forming free ends.
D) They can fuse with other bilayers.
E) They spontaneously form closed vesicles.
A
2
In a lipid bilayer, __________ fatty acid tails face each other within the bilayer and form a region that excludes water.
A) hypertonic
B) hyperosmotic
C) hypotonic
D) hydrophilic
E) hydrophobic
A) hypertonic
B) hyperosmotic
C) hypotonic
D) hydrophilic
E) hydrophobic
E
3
How do the phospholipids in vegetable oil differ from those of animal fat?
A) The fatty acid tails bend.
B) The fatty acid tails lack double bonds.
C) The fatty acid tails are a chain of saturated fats.
D) The fatty acid tails solidify at room temperature.
E) The fatty acid tails interact via van der Waals forces.
A) The fatty acid tails bend.
B) The fatty acid tails lack double bonds.
C) The fatty acid tails are a chain of saturated fats.
D) The fatty acid tails solidify at room temperature.
E) The fatty acid tails interact via van der Waals forces.
A
4
Which explanation best describes the asymmetrically oriented structure of the proteins in the cell membrane?
A) Each type of protein has its own function.
B) These proteins are manufactured by free ribosomes.
C) These proteins are initially formed by ribosomes on the rough ER.
D) These proteins pass through the ER membrane into the ER lumen.
E) Enzymes are needed to modify the carbohydrate chains on these proteins.
A) Each type of protein has its own function.
B) These proteins are manufactured by free ribosomes.
C) These proteins are initially formed by ribosomes on the rough ER.
D) These proteins pass through the ER membrane into the ER lumen.
E) Enzymes are needed to modify the carbohydrate chains on these proteins.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
Which of the following statements about phospholipids is false ?
A) They are amphipathic molecules.
B) They contain three fatty acids chains.
C) They contain a polar organic group attached to a phosphate group.
D) They have cylindrical shapes that allow them to associate with water most easily as a bilayer structure.
E) They have two distinct regions, one strongly hydrophobic and the other strongly hydrophilic.
A) They are amphipathic molecules.
B) They contain three fatty acids chains.
C) They contain a polar organic group attached to a phosphate group.
D) They have cylindrical shapes that allow them to associate with water most easily as a bilayer structure.
E) They have two distinct regions, one strongly hydrophobic and the other strongly hydrophilic.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
A transmembrane protein differs from other membrane proteins because it:
A) completely extends through the membrane.
B) is a glycoprotein with carbohydrates attached.
C) is completely embedded within the membrane.
D) is attached to the inside of the membrane by an ionic bond.
E) is covalently linked to the outer surface of the plasma membrane.
A) completely extends through the membrane.
B) is a glycoprotein with carbohydrates attached.
C) is completely embedded within the membrane.
D) is attached to the inside of the membrane by an ionic bond.
E) is covalently linked to the outer surface of the plasma membrane.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
What facilitate the rapid transport of water through the plasma membrane?
A) osmosis
B) uniporters
C) aquaporins
D) channel proteins
E) ABC transporters
A) osmosis
B) uniporters
C) aquaporins
D) channel proteins
E) ABC transporters

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
Which statement about plasma membranes is false ?
A) Plasma membranes regulate the passage of materials.
B) Plasma membranes divide the cell into compartments.
C) Plasma membranes serve as surfaces for chemical reactions.
D) Plasma membranes prevent communication with other cells.
E) Plasma membranes transmit signals between the environment and the interior of the cell.
A) Plasma membranes regulate the passage of materials.
B) Plasma membranes divide the cell into compartments.
C) Plasma membranes serve as surfaces for chemical reactions.
D) Plasma membranes prevent communication with other cells.
E) Plasma membranes transmit signals between the environment and the interior of the cell.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
Why can cholesterol act as a "fluidity buffer" in cell membranes?
A) It is slightly amphipathic because of the presence of one hydroxyl group.
B) It is slightly hydrophobic because of the presence of one hydroxyl group.
C) It is slightly hydrophobic because of the presence of one carboxyl group.
D) It is slightly amphipathic because of the presence of one carboxyl group.
E) It is slightly hydrophilic because of the presence of one hydrocarbon group.
A) It is slightly amphipathic because of the presence of one hydroxyl group.
B) It is slightly hydrophobic because of the presence of one hydroxyl group.
C) It is slightly hydrophobic because of the presence of one carboxyl group.
D) It is slightly amphipathic because of the presence of one carboxyl group.
E) It is slightly hydrophilic because of the presence of one hydrocarbon group.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
Which molecule is least likely to cross a cellular membrane by simple diffusion?
A) water
B) oxygen
C) nitrogen
D) potassium ion
E) carbon dioxide
A) water
B) oxygen
C) nitrogen
D) potassium ion
E) carbon dioxide

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
____ are loosely associated with the phospholipid bilayer, whereas ____ are tightly bound to it.
A) Peripheral proteins; integral proteins
B) Integral proteins; peripheral proteins
C) Glycoproteins; peripheral proteins
D) Integral proteins; glycoproteins
E) Glycolipids; glycoproteins
A) Peripheral proteins; integral proteins
B) Integral proteins; peripheral proteins
C) Glycoproteins; peripheral proteins
D) Integral proteins; glycoproteins
E) Glycolipids; glycoproteins

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
How are integral proteins unique in cell membranes?
A) They have no hydrophobic portions.
B) They are weakly bound to the surface of the membrane.
C) They are only located on the inner side of a membrane.
D) They are firmly bound to the membrane and can only be released with a detergent.
E) They are completely embedded within the lipid bilayer with no exposure to the internal cell environment.
A) They have no hydrophobic portions.
B) They are weakly bound to the surface of the membrane.
C) They are only located on the inner side of a membrane.
D) They are firmly bound to the membrane and can only be released with a detergent.
E) They are completely embedded within the lipid bilayer with no exposure to the internal cell environment.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
What does an ABC transporter use to transport larger ions and molecules across the cell membrane?
A) ATP
B) water
C) porins
D) signals
E) tunnels
A) ATP
B) water
C) porins
D) signals
E) tunnels

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
The term "fluid mosaic model" refers to the:
A) solubility of water in the membrane.
B) method of substance transport across the membrane.
C) movement of surface proteins through the membrane.
D) diffusion of lipid-soluble substances through the lipid bilayer.
E) movement of lipids and integral proteins within the lipid bilayer.
A) solubility of water in the membrane.
B) method of substance transport across the membrane.
C) movement of surface proteins through the membrane.
D) diffusion of lipid-soluble substances through the lipid bilayer.
E) movement of lipids and integral proteins within the lipid bilayer.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
What type of molecule can rapidly cross a plasma membrane?
A) large, polar molecules.
B) small, polar molecules.
C) large, hydrophilic molecules.
D) small, hydrophilic molecules.
E) small, hydrophobic molecules.
A) large, polar molecules.
B) small, polar molecules.
C) large, hydrophilic molecules.
D) small, hydrophilic molecules.
E) small, hydrophobic molecules.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
Peripheral proteins are linked to either surface of the plasma membrane by:
A) covalent disulfide bonds.
B) associating with fatty acids through hydrophobic interactions.
C) associating with glycoproteins on the inner membrane surface.
D) bonding to integral proteins through noncovalent interactions.
E) embedding in one side of the membrane and, thus, not extending through to the other side.
A) covalent disulfide bonds.
B) associating with fatty acids through hydrophobic interactions.
C) associating with glycoproteins on the inner membrane surface.
D) bonding to integral proteins through noncovalent interactions.
E) embedding in one side of the membrane and, thus, not extending through to the other side.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
Proteins that are destined to become associated with the inner surface of the plasma membrane are:
A) made on free ribosomes in the cytoplasm.
B) manufactured in the same way as protein hormones.
C) made on ribosomes located on the rough endoplasmic reticulum.
D) transported to the plasma membrane within a secretory vesicle.
E) manufactured in the same way as proteins destined to become external peripheral proteins.
A) made on free ribosomes in the cytoplasm.
B) manufactured in the same way as protein hormones.
C) made on ribosomes located on the rough endoplasmic reticulum.
D) transported to the plasma membrane within a secretory vesicle.
E) manufactured in the same way as proteins destined to become external peripheral proteins.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
In the experiment in which Frye and Edidin fused the plasma membranes of a mouse and a human cell, what happened to the membrane proteins?
A) They formed a bilayer.
B) They formed a spherical structure.
C) They moved laterally across the cell surface.
D) They flip-flopped from one layer to the other.
E) They reacted with cholesterol molecules on the membrane surface.
A) They formed a bilayer.
B) They formed a spherical structure.
C) They moved laterally across the cell surface.
D) They flip-flopped from one layer to the other.
E) They reacted with cholesterol molecules on the membrane surface.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
Which of the following describes how facilitated diffusion is powered?
A) ATP is required directly.
B) Facilitated diffusion is "free of cost."
C) Facilitated diffusion is powered by endocytosis.
D) The sodium-potassium pump powers facilitated diffusion.
E) Energy is required to do the work of establishing and maintaining a concentration gradient.
A) ATP is required directly.
B) Facilitated diffusion is "free of cost."
C) Facilitated diffusion is powered by endocytosis.
D) The sodium-potassium pump powers facilitated diffusion.
E) Energy is required to do the work of establishing and maintaining a concentration gradient.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
If phospholipids form a spherical structure when placed in water, then which of the following is the most logical conclusion about those phospholipid molecules?
A) They form a bilayer.
B) They are cone-shaped.
C) They are not amphipathic.
D) They have two hydrophilic ends.
E) They contain two fatty acid chains.
A) They form a bilayer.
B) They are cone-shaped.
C) They are not amphipathic.
D) They have two hydrophilic ends.
E) They contain two fatty acid chains.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
You light a scented candle in the guest bathroom. Within a few minutes you can already smell the candle's scent throughout the hallway. What process is occurring?
A) dialysis
B) osmosis
C) simple diffusion
D) active transport
E) facilitated diffusion
A) dialysis
B) osmosis
C) simple diffusion
D) active transport
E) facilitated diffusion

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
A wilted flower placed in a vase of water for several hours became stiff and stood erect. When it was placed in a salt solution, it wilted. From this information, we can say that the cells of the flower are:
A) hypotonic to both fresh water and the salt solution.
B) hypertonic to both the fresh water and the salt solution.
C) hypertonic to fresh water but hypotonic to the salt solution.
D) hypotonic to fresh water but hypertonic to the salt solution.
E) isotonic to fresh water but hypotonic to the salt solution.
A) hypotonic to both fresh water and the salt solution.
B) hypertonic to both the fresh water and the salt solution.
C) hypertonic to fresh water but hypotonic to the salt solution.
D) hypotonic to fresh water but hypertonic to the salt solution.
E) isotonic to fresh water but hypotonic to the salt solution.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
The role of ATP in the sodium-potassium pump is to:
A) transfer NA + to the inside of a cell.
B) assist a NA + to bind to a carbohydrate.
C) transfer NA + to the outside of a cell.
D) assist a cell to release NA + by exocytosis.
E) assist a cell to take up NA + by endocytosis.
A) transfer NA + to the inside of a cell.
B) assist a NA + to bind to a carbohydrate.
C) transfer NA + to the outside of a cell.
D) assist a cell to release NA + by exocytosis.
E) assist a cell to take up NA + by endocytosis.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
The sodium-potassium pump is a carrier protein that maintains a(n) ____ gradient across the plasma membrane.
A) polar
B) nonpolar
C) phosphorous
D) concentration
E) electrochemical
A) polar
B) nonpolar
C) phosphorous
D) concentration
E) electrochemical

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
What have studies of glucose transport in liposomes revealed?
A) Glucose is transported against a concentration gradient.
B) Glucose moves readily across the membrane by simple diffusion.
C) Glucose phosphates move readily across the membrane by simple diffusion.
D) The binding of glucose triggers a conformational change in the carrier protein.
E) The transport of solutes via carrier proteins is faster than via channel proteins.
A) Glucose is transported against a concentration gradient.
B) Glucose moves readily across the membrane by simple diffusion.
C) Glucose phosphates move readily across the membrane by simple diffusion.
D) The binding of glucose triggers a conformational change in the carrier protein.
E) The transport of solutes via carrier proteins is faster than via channel proteins.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
What is the passive movement of water along a concentration gradient?
A) osmosis
B) cotransport
C) plasmolysis
D) simple diffusion
E) facilitated diffusion
A) osmosis
B) cotransport
C) plasmolysis
D) simple diffusion
E) facilitated diffusion

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
Figure 5-1 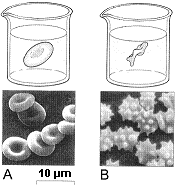 Refer to the accompanying figure. Which best describes what is happening to the red blood cells in Figure A?
Refer to the accompanying figure. Which best describes what is happening to the red blood cells in Figure A?
A) Pinocytosis has occurred.
B) Plasmolysis has occurred.
C) There has been no net water movement.
D) There has been a net flow of water out of the cell.
E) There has been a net flow of water into the cell.
 Refer to the accompanying figure. Which best describes what is happening to the red blood cells in Figure A?
Refer to the accompanying figure. Which best describes what is happening to the red blood cells in Figure A?A) Pinocytosis has occurred.
B) Plasmolysis has occurred.
C) There has been no net water movement.
D) There has been a net flow of water out of the cell.
E) There has been a net flow of water into the cell.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
What is required for facilitated diffusion to take place?
A) energy from ATP
B) a transmembrane protein
C) the transport of large food particles
D) the transport of small nonpolar molecules
E) movement down a concentration gradient
A) energy from ATP
B) a transmembrane protein
C) the transport of large food particles
D) the transport of small nonpolar molecules
E) movement down a concentration gradient

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
What process halts the net movement of water from a hypotonic solution into a plant's cells and often provides the structural support to many plants?
A) plasmolysis
B) turgur pressure
C) osmotic pressure
D) facilitated diffusion
E) dynamic equilibrium
A) plasmolysis
B) turgur pressure
C) osmotic pressure
D) facilitated diffusion
E) dynamic equilibrium

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
Once ligand molecules bind to receptors in coated pits of a plasma membrane, the next step of receptor-mediated endocytisis would be:
A) coating detaches from vesicle
B) coated vesicle forms by endocytosis
C) ligands separate from receptors, which are recycled
D) contents of secondary lysosome are digested and released into the cytosol
E) endosome fuses with primary lysosome, forming secondary lysosome
A) coating detaches from vesicle
B) coated vesicle forms by endocytosis
C) ligands separate from receptors, which are recycled
D) contents of secondary lysosome are digested and released into the cytosol
E) endosome fuses with primary lysosome, forming secondary lysosome

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
Which statement best describes the activity of the sodium-potassium pump?
A) It transports hydrogen ions out of the cell.
B) It transports water directly out of the cell.
C) It transports 2 sodium ions into the cell in exchange for 3 potassium ions.
D) It transports 3 sodium ions out of the cell in exchange for 2 potassium ions.
E) It transports 2 sodium ions out of the cell in exchange for 2 potassium ions.
A) It transports hydrogen ions out of the cell.
B) It transports water directly out of the cell.
C) It transports 2 sodium ions into the cell in exchange for 3 potassium ions.
D) It transports 3 sodium ions out of the cell in exchange for 2 potassium ions.
E) It transports 2 sodium ions out of the cell in exchange for 2 potassium ions.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
Although glucose molecules constantly diffuse into a red blood cell along their concentration gradient, equilibrium is never reached and a steep concentration gradient is continually maintained. What causes this?
A) The active transport of glucose
B) The very fast turnover rate of glucose metabolism
C) The ability of the cell to engulf glucose by pinocytosis
D) The continuous excretion of glucose from other parts of the cell
E) The rapid and continuous addition of phosphates onto the glucose molecules
A) The active transport of glucose
B) The very fast turnover rate of glucose metabolism
C) The ability of the cell to engulf glucose by pinocytosis
D) The continuous excretion of glucose from other parts of the cell
E) The rapid and continuous addition of phosphates onto the glucose molecules

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
Since sodium-potassium pumps transport sodium ions out of a cell and potassium ions into a cell, what type of carrier proteins are they?
A) ion pumps
B) uniporters
C) symporters
D) antiporters
E) ABC transporter
A) ion pumps
B) uniporters
C) symporters
D) antiporters
E) ABC transporter

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
When the net movement of water in and out a cell is zero, that solution is said to be:
A) osmotic
B) isotonic
C) hypotonic
D) hypertonic
E) pressurized
A) osmotic
B) isotonic
C) hypotonic
D) hypertonic
E) pressurized

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
Figure 5-1 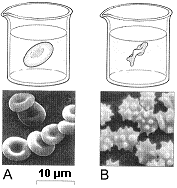 Refer to the accompanying figure. Which best describes the red blood cells in Figure B?
Refer to the accompanying figure. Which best describes the red blood cells in Figure B?
A) These red blood cells have been placed in an isotonic solution.
B) These red blood cells have swollen in response to a hypertonic external solution.
C) These red blood cells have swollen in response to a hypotonic external solution.
D) These red blood cells have shrunken in response to a hypertonic external solution.
E) These red blood cells have shrunken in response to a hypotonic external solution.
 Refer to the accompanying figure. Which best describes the red blood cells in Figure B?
Refer to the accompanying figure. Which best describes the red blood cells in Figure B?A) These red blood cells have been placed in an isotonic solution.
B) These red blood cells have swollen in response to a hypertonic external solution.
C) These red blood cells have swollen in response to a hypotonic external solution.
D) These red blood cells have shrunken in response to a hypertonic external solution.
E) These red blood cells have shrunken in response to a hypotonic external solution.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
If the concentration of solutes in a cell is less than the concentration of solutes in the surrounding fluid, then the extracellular fluid is said to be:
A) stable.
B) isotonic.
C) hypotonic.
D) hypertonic.
E) amphipathic.
A) stable.
B) isotonic.
C) hypotonic.
D) hypertonic.
E) amphipathic.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
In cells that are constantly involved in secretion, an equivalent amount of membrane must be returned to the interior of the cell for each vesicle that fuses with the plasma membrane; if this does not occur, then what would happen?
A) The cell surface would shrivel.
B) The cell surface will keep expanding.
C) The surface area would remain constant.
D) The number of membrane receptor proteins would decrease.
E) The ratio of cell surface would decrease, compared to cell volume.
A) The cell surface would shrivel.
B) The cell surface will keep expanding.
C) The surface area would remain constant.
D) The number of membrane receptor proteins would decrease.
E) The ratio of cell surface would decrease, compared to cell volume.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
What happens during the cotransport of glucose and sodium ions?
A) The transport of glucose powers the transport of sodium.
B) ATP causes a conformational change in the carrier protein.
C) Both D and E
D) Glucose molecules are transported against their concentration gradient.
E) Sodium ions are transported against their concentration gradient.
A) The transport of glucose powers the transport of sodium.
B) ATP causes a conformational change in the carrier protein.
C) Both D and E
D) Glucose molecules are transported against their concentration gradient.
E) Sodium ions are transported against their concentration gradient.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
What will happen to a plant cell if placed in a hypertonic solution?
A) The cell will swell slightly.
B) The cell will undergo lysis.
C) The cell will become crenated.
D) The cell will remain unchanged.
E) The cell will undergo plasmolysis.
A) The cell will swell slightly.
B) The cell will undergo lysis.
C) The cell will become crenated.
D) The cell will remain unchanged.
E) The cell will undergo plasmolysis.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
A patient who has had a severe hemorrhage accidentally receives a large transfusion of distilled water directly into a major blood vessel. What effect will this have on the patient?
A) It will have no unfavorable effect as long as the water is free of bacteria.
B) It will have serious, perhaps fatal consequences because there would be too much fluid to pump.
C) It will have serious, perhaps fatal consequences because the red blood cells could shrink.
D) It will have serious, perhaps fatal consequences because the red blood cells could swell and burst.
E) It will have no serious effect because the kidney could quickly eliminate excess water.
A) It will have no unfavorable effect as long as the water is free of bacteria.
B) It will have serious, perhaps fatal consequences because there would be too much fluid to pump.
C) It will have serious, perhaps fatal consequences because the red blood cells could shrink.
D) It will have serious, perhaps fatal consequences because the red blood cells could swell and burst.
E) It will have no serious effect because the kidney could quickly eliminate excess water.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
Osmotic pressure of a solution is the amount of pressure exerted on the side of the selectively permeable containing a higher concentration of solute to prevent diffusion of solute . __________________

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
Figure 5-2 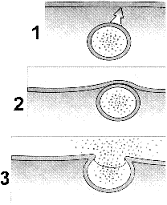 Consider the cellular process illustrated in the accompanying figure. What substance would most likely be used to transport?
Consider the cellular process illustrated in the accompanying figure. What substance would most likely be used to transport?
A) glucose
B) bacteria
C) hormones
D) potassium ions
E) carbon dioxide
 Consider the cellular process illustrated in the accompanying figure. What substance would most likely be used to transport?
Consider the cellular process illustrated in the accompanying figure. What substance would most likely be used to transport?A) glucose
B) bacteria
C) hormones
D) potassium ions
E) carbon dioxide

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
Biological membranes are one dimensional fluids.
__________________
__________________

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
In cell membranes cholesterol and glycoproteins are exposed to the extracellular surface for cell recognition and adhesion to other cells.
__________________
__________________

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
Mutations to ABC transporter genes contribute to cystic fibrosis.
__________________
__________________

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
Using correct terminology, describe what would happen to a red blood cell placed in a solution of 0.5% sodium chloride.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
If solution of A is hypotonic to B, then the direction of net movement of water is B to A .
__________________
__________________

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
During phagocytosis, what may fuse with the vacuole to further degrade the ingested material?
A) ligand
B) receptor
C) lysosome
D) phosphate
E) desmosome
A) ligand
B) receptor
C) lysosome
D) phosphate
E) desmosome

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
Compare and contrast the structure and functions of three of the following four intercellular junctions: desmosomes, gap junctions, tight junctions, and plasmodesmata.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
Identify and discuss three different roles for membrane proteins.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
What method does a human white blood cell employ to engulf a bacterial cell?
A) osmosis
B) exocytosis
C) pinocytosis
D) phagocytosis
E) facilitated diffusion
A) osmosis
B) exocytosis
C) pinocytosis
D) phagocytosis
E) facilitated diffusion

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
Sketch and label a typical cell membrane. Provide a brief explanation for each of the labeled structures.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
Figure 5-3  In the accompanying figure, what is the role of the structures between the membranes?
In the accompanying figure, what is the role of the structures between the membranes?
A) They provide structure to plant cells.
B) They provide anchorage points between adjacent cells.
C) They allow passage of materials through intercellular spaces.
D) They prevent the passage of materials through intercellular spaces.
E) They allow the transport of small molecules and ions between adjacent cells.
 In the accompanying figure, what is the role of the structures between the membranes?
In the accompanying figure, what is the role of the structures between the membranes?A) They provide structure to plant cells.
B) They provide anchorage points between adjacent cells.
C) They allow passage of materials through intercellular spaces.
D) They prevent the passage of materials through intercellular spaces.
E) They allow the transport of small molecules and ions between adjacent cells.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
A person has a genetic disease that prevents the phospholipids in the plasma membrane of the white blood cells from freely fusing with the other membranes within the cell. How would this disease affect phagocytosis?
A) Endocytosis would not occur.
B) Lysosomes would not be formed.
C) Facilitated diffusion would not occur.
D) Lysosomes would be formed lacking hydrolytic enzymes.
E) The phagocytic vacuole would not fuse with the lysosome.
A) Endocytosis would not occur.
B) Lysosomes would not be formed.
C) Facilitated diffusion would not occur.
D) Lysosomes would be formed lacking hydrolytic enzymes.
E) The phagocytic vacuole would not fuse with the lysosome.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
How do gap junctions differ from desmosomes?
A) A gap junction bridges the space between cells.
B) A gap junction is a much larger space between cells.
C) A gap junction provides communication between cells.
D) A gap junction can control the passage of materials between cells.
E) A gap junction requires the use of ATP to open and close its channels.
A) A gap junction bridges the space between cells.
B) A gap junction is a much larger space between cells.
C) A gap junction provides communication between cells.
D) A gap junction can control the passage of materials between cells.
E) A gap junction requires the use of ATP to open and close its channels.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
Figure 5-3 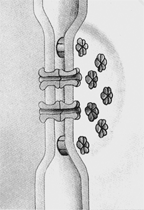 In the accompanying figure, what is the form of cellular junction?
In the accompanying figure, what is the form of cellular junction?
A) desmosomes
B) gap junctions
C) tight junctions
D) plasmodesmata
E) adhering junctions
 In the accompanying figure, what is the form of cellular junction?
In the accompanying figure, what is the form of cellular junction?A) desmosomes
B) gap junctions
C) tight junctions
D) plasmodesmata
E) adhering junctions

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
Figure 5-2 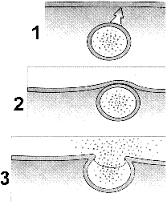 What cellular process is represented in the accompanying figure?
What cellular process is represented in the accompanying figure?
A) lysis
B) exocytosis
C) cotransport
D) pinocytosis
E) facilitated diffusion
 What cellular process is represented in the accompanying figure?
What cellular process is represented in the accompanying figure?A) lysis
B) exocytosis
C) cotransport
D) pinocytosis
E) facilitated diffusion

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
Compare and contrast simple diffusion, osmosis, and facilitated diffusion.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
Plasmodesmata of plant cells are functionally equivalent to the ____ of animal cells.
A) vesicles
B) gap junctions
C) tight junctions
D) anchoring junctions
E) cell surface receptors
A) vesicles
B) gap junctions
C) tight junctions
D) anchoring junctions
E) cell surface receptors

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
What type of cellular junction cements cells together that use cadherins as a belt around each cell?
A) desmosomes
B) gap junctions
C) tight junctions
D) plasmodesmata
E) adhering junctions
A) desmosomes
B) gap junctions
C) tight junctions
D) plasmodesmata
E) adhering junctions

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
Match between columns

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
Compare and contrast the processes of facilitated diffusion and active transport.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
In the sodium-potassium pump, sodium ion release causes two K+ ions to be released into the cell.
__________________
__________________

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
Describe some of the various activities performed by membrane proteins in multicellular organisms.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
Plasmolysis occurs in plant cells when the soil or water contains low concentration of salts or fertilizers.
__________________
__________________

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
LDL cholesterol is taken into the cell by receptor-mediated endocytosis .
__________________
__________________

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
Sodium-potassium pumps maintain a(n) electrochemical gradient.
__________________
__________________

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
Cotransport systems directly provide energy for active transport of solutes.
__________________
__________________

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
Compare and contrast the mechanisms of the sodium-potassium pump and glucose-sodium cotransport systems.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



