Deck 57: Biological Diversity and Conservation Biology
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Match between columns
Premises:
contain large portions of different species on the plant
contain large portions of different species on the plant
contain large portions of different species on the plant
contain large portions of different species on the plant
contain large portions of different species on the plant
consists of three zones to protect biodiversity
consists of three zones to protect biodiversity
consists of three zones to protect biodiversity
consists of three zones to protect biodiversity
consists of three zones to protect biodiversity
parks and reserves
parks and reserves
parks and reserves
parks and reserves
parks and reserves
preserves individual species using direct human control
preserves individual species using direct human control
preserves individual species using direct human control
preserves individual species using direct human control
preserves individual species using direct human control
helps isolated habitats maintain more native species
helps isolated habitats maintain more native species
helps isolated habitats maintain more native species
helps isolated habitats maintain more native species
helps isolated habitats maintain more native species
Responses:
ex situ conservation
in situ conservation
biodiversity hotspot
habitat corridors
biosphere reserves
ex situ conservation
in situ conservation
biodiversity hotspot
habitat corridors
biosphere reserves
ex situ conservation
in situ conservation
biodiversity hotspot
habitat corridors
biosphere reserves
ex situ conservation
in situ conservation
biodiversity hotspot
habitat corridors
biosphere reserves
ex situ conservation
in situ conservation
biodiversity hotspot
habitat corridors
biosphere reserves
ex situ conservation
in situ conservation
biodiversity hotspot
habitat corridors
biosphere reserves
ex situ conservation
in situ conservation
biodiversity hotspot
habitat corridors
biosphere reserves
ex situ conservation
in situ conservation
biodiversity hotspot
habitat corridors
biosphere reserves
ex situ conservation
in situ conservation
biodiversity hotspot
habitat corridors
biosphere reserves
ex situ conservation
in situ conservation
biodiversity hotspot
habitat corridors
biosphere reserves
Question
Match between columns
Premises:
in imminent danger of extinction throughout its range
in imminent danger of extinction throughout its range
in imminent danger of extinction throughout its range
not in imminent danger of extinction but has a small population
not in imminent danger of extinction but has a small population
not in imminent danger of extinction but has a small population
dodo bird
dodo bird
dodo bird
Responses:
extinct species
threatened species
endangered species
extinct species
threatened species
endangered species
extinct species
threatened species
endangered species
extinct species
threatened species
endangered species
extinct species
threatened species
endangered species
extinct species
threatened species
endangered species
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/68
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 57: Biological Diversity and Conservation Biology
1
Foreign species that have negative effects on native species are called:
A) prey species.
B) non-native species.
C) invasive species.
D) predator species.
E) endemic species.
A) prey species.
B) non-native species.
C) invasive species.
D) predator species.
E) endemic species.
C
2
An example of an animal already extinct as a result of overhunting is the:
A) rhino.
B) passenger pigeon.
C) macaw.
D) Carolina parakeet.
E) wolf.
A) rhino.
B) passenger pigeon.
C) macaw.
D) Carolina parakeet.
E) wolf.
B
3
When a species dies, the species is said to be:
A) extinct.
B) extant.
C) endangered.
D) threatened.
E) endemic.
A) extinct.
B) extant.
C) endangered.
D) threatened.
E) endemic.
A
4
An unprotected area of naturally occurring plant and animal assemblages that is surrounded by unsuitable territory due to development or habitat destruction is referred to by biologists as:
A) an island.
B) ex situ conservation.
C) a reserve.
D) a park.
E) a refuge.
A) an island.
B) ex situ conservation.
C) a reserve.
D) a park.
E) a refuge.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 68 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
An example of ex situ conservation is a:
A) national park.
B) zoo.
C) reserve.
D) pet store.
E) circus.
A) national park.
B) zoo.
C) reserve.
D) pet store.
E) circus.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 68 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
When the death of species is less imminent, but the population of a particular species is quite small, it is defined as being:
A) extinct.
B) extant.
C) endangered.
D) threatened.
E) endemic.
A) extinct.
B) extant.
C) endangered.
D) threatened.
E) endemic.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 68 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
Which of the following is reported to cause deformities in amphibians in the Sierra Nevadas of California?
A) pesticides
B) pollution
C) trematodes
D) atrazine
E) predators
A) pesticides
B) pollution
C) trematodes
D) atrazine
E) predators

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 68 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
Which animal is incorrectly matched with its desired product?
A) tiger − fur
B) bear − gallbladder
C) anteaters − bush meat
D) rhinos − horns
E) cheetah-liver
A) tiger − fur
B) bear − gallbladder
C) anteaters − bush meat
D) rhinos − horns
E) cheetah-liver

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 68 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
Animals that are being hunted (often illegally) for body parts thought to have medicinal value include:
A) rhinos and bears.
B) cheetahs and snow leopards.
C) snow leopards and bears.
D) wolves and mountain lions.
E) mountain lions and black-footed ferrets.
A) rhinos and bears.
B) cheetahs and snow leopards.
C) snow leopards and bears.
D) wolves and mountain lions.
E) mountain lions and black-footed ferrets.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 68 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
Biological diversity is an index of the variety of living organisms in an ecosystem, and includes:
A) species richness only.
B) species richness, genetic diversity, and ecosystem diversity.
C) species richness, biosphere diversity, and ecosystem diversity.
D) population diversity and ecosystem diversity.
E) genetic diversity only.
A) species richness only.
B) species richness, genetic diversity, and ecosystem diversity.
C) species richness, biosphere diversity, and ecosystem diversity.
D) population diversity and ecosystem diversity.
E) genetic diversity only.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 68 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
The introduction of a foreign species into an area where it is not native is called:
A) parasitization.
B) infestation.
C) fragmentation.
D) biotic pollution.
E) commercial harvest.
A) parasitization.
B) infestation.
C) fragmentation.
D) biotic pollution.
E) commercial harvest.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 68 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
Biotic pollution has been particularly harmful to native species:
A) in deserts.
B) in tundra.
C) on islands.
D) in tropical rain forests.
E) in grasslands.
A) in deserts.
B) in tundra.
C) on islands.
D) in tropical rain forests.
E) in grasslands.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 68 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
Today, the major danger to species is:
A) hunting by humans.
B) introduction of exotic species.
C) destruction of habitats.
D) predator control.
E) commercial harvesting.
A) hunting by humans.
B) introduction of exotic species.
C) destruction of habitats.
D) predator control.
E) commercial harvesting.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 68 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
The breakup of large areas of habitat into small, isolated patches is called:
A) extinction.
B) habitat fragmentation.
C) invasive species.
D) unsuitable territory.
E) habitat endangerment.
A) extinction.
B) habitat fragmentation.
C) invasive species.
D) unsuitable territory.
E) habitat endangerment.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 68 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
Estimates vary, but reasonable numbers for extinction rates suggest that extinction is occurring at a rate approximately ____ times above the normal background rate.
A) 10
B) 100
C) 1000
D) 10,000
E) 1,000,000
A) 10
B) 100
C) 1000
D) 10,000
E) 1,000,000

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 68 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
Some animals are facing extinction as a direct result of deliberate efforts to exterminate them because of their perceived harm to economically useful species. Examples of these include:
A) cheetahs and rhinos.
B) passenger pigeons and cheetahs.
C) prairie dogs and rhinos.
D) rhinos and macaws.
E) mountain lions and wolves.
A) cheetahs and rhinos.
B) passenger pigeons and cheetahs.
C) prairie dogs and rhinos.
D) rhinos and macaws.
E) mountain lions and wolves.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 68 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
Building roads, parking lots, buildings and bridges all contribute to:
A) biotic pollution.
B) commercial harvest.
C) habitat destruction.
D) ex situ conservation.
E) restoration ecology.
A) biotic pollution.
B) commercial harvest.
C) habitat destruction.
D) ex situ conservation.
E) restoration ecology.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 68 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
The ability to meet humanity's current needs without compromising the ability of future generations to meet their needs is:
A) environmental sustainability.
B) species richness.
C) biosphere diversity.
D) resource conservation.
E) habitat regeneration.
A) environmental sustainability.
B) species richness.
C) biosphere diversity.
D) resource conservation.
E) habitat regeneration.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 68 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
A species' numbers are so severely reduced that it is in imminent danger of extinction throughout all or a significant part of its range. This species would be considered:
A) extinct.
B) extant.
C) endangered.
D) threatened.
E) endemic.
A) extinct.
B) extant.
C) endangered.
D) threatened.
E) endemic.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 68 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
Harmful introduced species usually come into an area by:
A) human beings.
B) the species themselves.
C) hurricanes.
D) floods.
E) parasites.
A) human beings.
B) the species themselves.
C) hurricanes.
D) floods.
E) parasites.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 68 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
A biodiversity hotspot is a(n):
A) protected area with few humans present.
B) type of island from which humans are leaving.
C) an area rich in endemic species and high in human population.
D) a type of corridor to which humans are rapidly migrating.
E) an area poor in endemic species in a tropical location.
A) protected area with few humans present.
B) type of island from which humans are leaving.
C) an area rich in endemic species and high in human population.
D) a type of corridor to which humans are rapidly migrating.
E) an area poor in endemic species in a tropical location.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 68 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
The problems associated with slash-and-burn agriculture are most closely related to:
A) greed by international corporations.
B) subsistence agriculture.
C) consumption by highly developed countries.
D) cattle ranching.
E) timber for export.
A) greed by international corporations.
B) subsistence agriculture.
C) consumption by highly developed countries.
D) cattle ranching.
E) timber for export.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 68 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
Commercial logging:
A) cuts trees primarily for use by developing countries.
B) cuts trees for subsistence farmers.
C) cuts trees primarily for export.
D) is a very sustainable practice in the tropics.
E) is most prevalent in temperate deciduous forests.
A) cuts trees primarily for use by developing countries.
B) cuts trees for subsistence farmers.
C) cuts trees primarily for export.
D) is a very sustainable practice in the tropics.
E) is most prevalent in temperate deciduous forests.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 68 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
Which of the following is a predicted effect of continued global warming?
A) greater impact on plant species in particular
B) thermal contraction of a cooler ocean
C) increased precipitation and flooding in mid-latitude continental interiors
D) decreased frequency and intensity of storms
E) overall increase in agricultural productivity
A) greater impact on plant species in particular
B) thermal contraction of a cooler ocean
C) increased precipitation and flooding in mid-latitude continental interiors
D) decreased frequency and intensity of storms
E) overall increase in agricultural productivity

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 68 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
Which of the following will prevent the further buildup of greenhouse gases?
A) Choose furniture made from exotic hardwoods.
B) Use your automobile less, and ride a bicycle more.
C) Produce more waste that goes to landfills.
D) Buy an air conditioner that uses chlorofluorocarbons.
E) Buy an automobile with poor fuel-efficient.
A) Choose furniture made from exotic hardwoods.
B) Use your automobile less, and ride a bicycle more.
C) Produce more waste that goes to landfills.
D) Buy an air conditioner that uses chlorofluorocarbons.
E) Buy an automobile with poor fuel-efficient.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 68 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
In situ conservation includes:
A) zoos.
B) aquaria.
C) parks and reserves.
D) seed storage banks.
E) sperm banks.
A) zoos.
B) aquaria.
C) parks and reserves.
D) seed storage banks.
E) sperm banks.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 68 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
What bird, due to human efforts, has been removed from the endangered species list and is now listed as threatened?
A) passenger pigeon
B) dusky seaside sparrow
C) hyacinth macaw
D) bald eagle
E) Carolina parakeet
A) passenger pigeon
B) dusky seaside sparrow
C) hyacinth macaw
D) bald eagle
E) Carolina parakeet

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 68 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
Climate change occurs because greenhouse gases absorb ____ radiation.
A) UVA
B) UVB
C) visible
D) infrared
E) cosmic
A) UVA
B) UVB
C) visible
D) infrared
E) cosmic

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 68 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
In ____, fertilized eggs from a rare species may be implanted in a related and less rare species.
A) host mothering
B) captive breeding
C) artificial insemination
D) commercial harvesting
E) sperm banking
A) host mothering
B) captive breeding
C) artificial insemination
D) commercial harvesting
E) sperm banking

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 68 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
The collection of sperm from a male and the use of that sperm to impregnate a female of the same species is called:
A) host mothering.
B) artificial insemination.
C) in situ conservation.
D) in vitro fertilization.
E) ex situ conservation.
A) host mothering.
B) artificial insemination.
C) in situ conservation.
D) in vitro fertilization.
E) ex situ conservation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 68 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
Figure 57-1 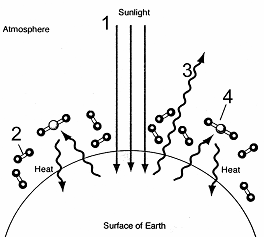 In the accompanying figure, the process labeled as 3 illustrates an action that is reduced by greenhouse gas accumulation. What is this action?
In the accompanying figure, the process labeled as 3 illustrates an action that is reduced by greenhouse gas accumulation. What is this action?
A) heat redirection to the surface
B) heat radiation into space
C) heat reflection into space
D) heat trapping on the surface
E) heat generation by the surface
 In the accompanying figure, the process labeled as 3 illustrates an action that is reduced by greenhouse gas accumulation. What is this action?
In the accompanying figure, the process labeled as 3 illustrates an action that is reduced by greenhouse gas accumulation. What is this action?A) heat redirection to the surface
B) heat radiation into space
C) heat reflection into space
D) heat trapping on the surface
E) heat generation by the surface

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 68 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
Deforestation in the boreal forests is due primarily to:
A) commercial logging for rare woods to be used in furniture.
B) commercial logging subsistence agriculture.
C) clear-cut logging for industrial wood.
D) slash-and-burn agriculture for farming
E) slash-and-burn agriculture for cattle ranching.
A) commercial logging for rare woods to be used in furniture.
B) commercial logging subsistence agriculture.
C) clear-cut logging for industrial wood.
D) slash-and-burn agriculture for farming
E) slash-and-burn agriculture for cattle ranching.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 68 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
In the United States, the largest group of endangered species is:
A) mammals.
B) flowering plants.
C) insects.
D) birds.
E) amphibians.
A) mammals.
B) flowering plants.
C) insects.
D) birds.
E) amphibians.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 68 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
Which action best illustrates in situ conservation?
A) breeding captive species in zoos
B) collecting eggs from nature
C) participating in artificial insemination
D) breeding captive species and collecting eggs from nature
E) designating a large area as a national reserve
A) breeding captive species in zoos
B) collecting eggs from nature
C) participating in artificial insemination
D) breeding captive species and collecting eggs from nature
E) designating a large area as a national reserve

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 68 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
Figure 57-1 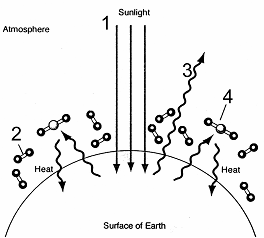 According to the accompanying figure, global warming would result from an increase in which of the labeled components?
According to the accompanying figure, global warming would result from an increase in which of the labeled components?
A) 1 and 2
B) 2
C) 2 and 3
D) 3
E) 4
 According to the accompanying figure, global warming would result from an increase in which of the labeled components?
According to the accompanying figure, global warming would result from an increase in which of the labeled components?A) 1 and 2
B) 2
C) 2 and 3
D) 3
E) 4

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 68 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
The use of the principles of ecology to return a degraded environment to as close as possible of a functional state is called:
A) in situ conservation.
B) ex situ conservation.
C) conservation biology.
D) restoration ecology.
E) corridor formation.
A) in situ conservation.
B) ex situ conservation.
C) conservation biology.
D) restoration ecology.
E) corridor formation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 68 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
Perhaps the biggest problem associated with the Endangered Species Act as it currently stands is that it:
A) tends to protect a limited number of organisms.
B) tends to protect plants and some animals, but often under-represents mammals and insects.
C) protects animals whose populations are currently on the increase.
D) currently protects ecosystem diversity.
E) has not been amended since its passage in 1962.
A) tends to protect a limited number of organisms.
B) tends to protect plants and some animals, but often under-represents mammals and insects.
C) protects animals whose populations are currently on the increase.
D) currently protects ecosystem diversity.
E) has not been amended since its passage in 1962.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 68 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
Deforestation:
A) retards soil erosion.
B) releases carbon dioxide that may contribute to global warming.
C) has no effect on the extinction of biological species.
D) promotes the preservation of tropical birds.
E) is only a threat to tropical rain forests.
A) retards soil erosion.
B) releases carbon dioxide that may contribute to global warming.
C) has no effect on the extinction of biological species.
D) promotes the preservation of tropical birds.
E) is only a threat to tropical rain forests.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 68 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
Slash-and-burn agriculture:
A) is practiced by international corporations.
B) is practiced by large scale cattle ranchers.
C) includes fuel wood consumption.
D) is practiced by many people in highly developed countries.
E) is practiced by subsistence farmers.
A) is practiced by international corporations.
B) is practiced by large scale cattle ranchers.
C) includes fuel wood consumption.
D) is practiced by many people in highly developed countries.
E) is practiced by subsistence farmers.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 68 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
What is a practice in which a family produces enough food to feed itself, accounting for nearly 50% of tropical deforestation?
A) monoculture
B) subsistence agriculture
C) slash-and-burn agriculture
D) cattle ranching
E) subsistence ranching.
A) monoculture
B) subsistence agriculture
C) slash-and-burn agriculture
D) cattle ranching
E) subsistence ranching.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 68 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
A(n) threatened species is a species in imminent danger of extinction.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 68 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
Which of the following has increased as a direct result of stratospheric ozone depletion?
A) CO2
B) UVB
C) CFCs
D) nitrous oxides
E) sulfur oxides
A) CO2
B) UVB
C) CFCs
D) nitrous oxides
E) sulfur oxides

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 68 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
By definition, a(n) endemic species is a species that is not found anywhere else in the world.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 68 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
The Montreal Protocol:
A) has not yet resulted in measurable decreases in the quantity of global warming chemicals.
B) has not yet been ratified by the U.S. Senate.
C) banned global use of CFCs by 1998.
D) was signed by all 50 states.
E) limited production of CFCs.
A) has not yet resulted in measurable decreases in the quantity of global warming chemicals.
B) has not yet been ratified by the U.S. Senate.
C) banned global use of CFCs by 1998.
D) was signed by all 50 states.
E) limited production of CFCs.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 68 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
Habitat corridors allow animals to move from one habitat fragment to another.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 68 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
Differentiate between the problems and effects of global warming and ozone depletion.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 68 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
Host mothering is technique important in in situ conservation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 68 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
In slash-and-burn agriculture, the yield from the first crop is usually quite high .

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 68 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
Identify three greenhouse gases and briefly explain how these gases are contributing to global warming.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 68 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
The term species richness refers to the number of species in a specific location.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 68 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
An example of ex situ conservation is a national park.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 68 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
An example of a(n) ecosystem service is the boreal forest contributing to the proper functioning of the global nitrogen cycle.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 68 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
Which of the following is not a predicted outcome of climate change?
A) change in precipitation patterns
B) inability of some organisms to adapt
C) profound health effect on people in developing countries
D) increased problems for agriculture
E) global average sea level decreasing
A) change in precipitation patterns
B) inability of some organisms to adapt
C) profound health effect on people in developing countries
D) increased problems for agriculture
E) global average sea level decreasing

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 68 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
Stratospheric ozone is important because it:
A) traps reradiated heat from Earth.
B) prevents heat penetration from the sun.
C) replenishes the surface ozone layer.
D) dissipates the surface ozone layer.
E) blocks solar UV radiation.
A) traps reradiated heat from Earth.
B) prevents heat penetration from the sun.
C) replenishes the surface ozone layer.
D) dissipates the surface ozone layer.
E) blocks solar UV radiation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 68 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
Which of the following is considered a key human made contributor to global warming?
A) carbon dioxide
B) hydrochlorofluorocarbons
C) nitrous oxide
D) ethane
E) surface ozone
A) carbon dioxide
B) hydrochlorofluorocarbons
C) nitrous oxide
D) ethane
E) surface ozone

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 68 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
Differentiate between the following terms: threatened species, endangered species, and extinct species.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 68 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
An example of in situ conservation is a zoo.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 68 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
Increased exposure to UV radiation is expected to increase rates of ____ in humans.
A) cataracts
B) glaucoma
C) psoriasis
D) shingles
E) alopecia
A) cataracts
B) glaucoma
C) psoriasis
D) shingles
E) alopecia

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 68 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
An example of commercial harvest is the introduction of a foreign species into an area where it is not native.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 68 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
Greenhouse gases contribute to global warming by absorbing UV radiation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 68 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
Match between columns
Premises:
contain large portions of different species on the plant
contain large portions of different species on the plant
contain large portions of different species on the plant
contain large portions of different species on the plant
contain large portions of different species on the plant
consists of three zones to protect biodiversity
consists of three zones to protect biodiversity
consists of three zones to protect biodiversity
consists of three zones to protect biodiversity
consists of three zones to protect biodiversity
parks and reserves
parks and reserves
parks and reserves
parks and reserves
parks and reserves
preserves individual species using direct human control
preserves individual species using direct human control
preserves individual species using direct human control
preserves individual species using direct human control
preserves individual species using direct human control
helps isolated habitats maintain more native species
helps isolated habitats maintain more native species
helps isolated habitats maintain more native species
helps isolated habitats maintain more native species
helps isolated habitats maintain more native species
Responses:
ex situ conservation
in situ conservation
biodiversity hotspot
habitat corridors
biosphere reserves
ex situ conservation
in situ conservation
biodiversity hotspot
habitat corridors
biosphere reserves
ex situ conservation
in situ conservation
biodiversity hotspot
habitat corridors
biosphere reserves
ex situ conservation
in situ conservation
biodiversity hotspot
habitat corridors
biosphere reserves
ex situ conservation
in situ conservation
biodiversity hotspot
habitat corridors
biosphere reserves
ex situ conservation
in situ conservation
biodiversity hotspot
habitat corridors
biosphere reserves
ex situ conservation
in situ conservation
biodiversity hotspot
habitat corridors
biosphere reserves
ex situ conservation
in situ conservation
biodiversity hotspot
habitat corridors
biosphere reserves
ex situ conservation
in situ conservation
biodiversity hotspot
habitat corridors
biosphere reserves
ex situ conservation
in situ conservation
biodiversity hotspot
habitat corridors
biosphere reserves

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 68 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
Match between columns
Premises:
in imminent danger of extinction throughout its range
in imminent danger of extinction throughout its range
in imminent danger of extinction throughout its range
not in imminent danger of extinction but has a small population
not in imminent danger of extinction but has a small population
not in imminent danger of extinction but has a small population
dodo bird
dodo bird
dodo bird
Responses:
extinct species
threatened species
endangered species
extinct species
threatened species
endangered species
extinct species
threatened species
endangered species
extinct species
threatened species
endangered species
extinct species
threatened species
endangered species
extinct species
threatened species
endangered species

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 68 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
The greenhouse gas presently at highest concentration in the Earth's atmosphere is methane .

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 68 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
Give examples of at least two species that are either extinct or facing extinction due to each of the following: 1) destruction of habitat, 2) biotic pollution, 3) unregulated hunting and poaching, 4) deliberate pest or predator control, and 5) commercial harvesting.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 68 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
List four reasons for deforestation in the tropics. Which of these are associated with consumption by persons in highly developed countries? Which are associated with overpopulation of indigenous persons?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 68 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
Give several examples of in situ and ex situ conservation. What are advantages and disadvantages of each approach to conservation?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 68 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
Ozone molecules in the stratosphere shield the Earth from damaging UV radiation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 68 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
An example of an atom or molecule that directly breaks down O3 is CFC .

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 68 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



