Deck 8: How Cells Make Atp Energy-Releasing Pathways
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Match between columns
Premises:
GDP is phosphorylated
GDP is phosphorylated
GDP is phosphorylated
GDP is phosphorylated
This is the first process that occurs in the mitochondrion.
This is the first process that occurs in the mitochondrion.
This is the first process that occurs in the mitochondrion.
This is the first process that occurs in the mitochondrion.
Pyruvate is an end product.
Pyruvate is an end product.
Pyruvate is an end product.
Pyruvate is an end product.
ATP synthase is a component.
ATP synthase is a component.
ATP synthase is a component.
ATP synthase is a component.
Responses:
electron transport and chemiosmosis
formation of acetyl CoA
citric acid cycle
glycolysis
electron transport and chemiosmosis
formation of acetyl CoA
citric acid cycle
glycolysis
electron transport and chemiosmosis
formation of acetyl CoA
citric acid cycle
glycolysis
electron transport and chemiosmosis
formation of acetyl CoA
citric acid cycle
glycolysis
electron transport and chemiosmosis
formation of acetyl CoA
citric acid cycle
glycolysis
electron transport and chemiosmosis
formation of acetyl CoA
citric acid cycle
glycolysis
electron transport and chemiosmosis
formation of acetyl CoA
citric acid cycle
glycolysis
electron transport and chemiosmosis
formation of acetyl CoA
citric acid cycle
glycolysis
electron transport and chemiosmosis
formation of acetyl CoA
citric acid cycle
glycolysis
electron transport and chemiosmosis
formation of acetyl CoA
citric acid cycle
glycolysis
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/66
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 8: How Cells Make Atp Energy-Releasing Pathways
1
During the citric acid cycle, each acetyl group entering the cycle yields:
A) 1 ATP, 2 NADH, and 3 FADH2.
B) 1 ATP, 3 NADH, and 1 FADH2.
C) 3 ATP, 2 NADH, and 1 FADH2.
D) 4 ATP, 2 NADH, and 1 FADH2.
E) 1 ATP, 2 NADH, and 4 FADH2.
A) 1 ATP, 2 NADH, and 3 FADH2.
B) 1 ATP, 3 NADH, and 1 FADH2.
C) 3 ATP, 2 NADH, and 1 FADH2.
D) 4 ATP, 2 NADH, and 1 FADH2.
E) 1 ATP, 2 NADH, and 4 FADH2.
B
2
The energy released during the chain of electron transport molecules is used to create a(n) ____ gradient across the inner mitochondrial membrane for chemiosmosis.
A) ADP
B) ATP
C) proton
D) oxygen
E) electron
A) ADP
B) ATP
C) proton
D) oxygen
E) electron
C
3
During chemiosmosis, what must be transferred from NADH and FADH2 to electron acceptor molecules?
A) protons
B) electrons
C) ATP molecules
D) ADP molecules
E) water molecules
A) protons
B) electrons
C) ATP molecules
D) ADP molecules
E) water molecules
B
4
After the conversion of pyruvate molecules to acetyl CoA molecules, how many NADH molecules have been produced from one glucose molecule?
A) one
B) two
C) three
D) four
E) five
A) one
B) two
C) three
D) four
E) five

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
A glucose molecule that is metabolized via aerobic respiration has been completely broken down and released as CO2 by the end of:
A) glycolysis.
B) fermentation.
C) the citric acid cycle.
D) the electron transport chain.
E) ATP synthesis in the mitochondria.
A) glycolysis.
B) fermentation.
C) the citric acid cycle.
D) the electron transport chain.
E) ATP synthesis in the mitochondria.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
Which is a product from the first reaction of the citric acid cycle?
A) ATP
B) NAD+
C) citrate
D) phosphate
E) acetyl-CoA
A) ATP
B) NAD+
C) citrate
D) phosphate
E) acetyl-CoA

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
In glycolysis, a phosphorylated sugar (fructose-1, 6-bisphosphate) is split, forming two molecules of:
A) ADP.
B) G3P.
C) glucose.
D) citric acid.
E) acetyl CoA.
A) ADP.
B) G3P.
C) glucose.
D) citric acid.
E) acetyl CoA.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
Where does the citric acid cycle take place in a eukaryotic cell?
A) nucleus
B) cytosol
C) mitochondrial matrix
D) endoplasmic reticulum
E) mitochondrial membrane
A) nucleus
B) cytosol
C) mitochondrial matrix
D) endoplasmic reticulum
E) mitochondrial membrane

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
Glycolysis yields a net energy profit of ____ ATP molecules per molecule of glucose.
A) no
B) one
C) two
D) four
E) six
A) no
B) one
C) two
D) four
E) six

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
What does the oxidative decarboxylation of two pyruvates yield?
A) 2 G3P
B) 2 glucose molecules
C) 2 ATP + 4 CO2 + 2 NADH
D) 1 fructose-1, 6-bisphosphate
E) 2 acetyl CoA + 2 CO2 + 2 NADH
A) 2 G3P
B) 2 glucose molecules
C) 2 ATP + 4 CO2 + 2 NADH
D) 1 fructose-1, 6-bisphosphate
E) 2 acetyl CoA + 2 CO2 + 2 NADH

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
Which reactant of aerobic respiration is oxidized?
A) water
B) oxygen
C) glucose
D) energy
E) carbon dioxide
A) water
B) oxygen
C) glucose
D) energy
E) carbon dioxide

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
During the first phase of glycolysis, because glucose is relatively stable and not easily broken down, two ____ reactions take place to transfer a phosphate group from ATP to the sugar.
A) redox
B) exergonic
C) metabolic
D) hydrolysis
E) phosphorylation
A) redox
B) exergonic
C) metabolic
D) hydrolysis
E) phosphorylation

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
Which reaction is the aerobic respiration of glucose?
A) C6H12O6 + 6 H2O → 6 CO2 + 12 H2 + energy
B) C4H12O4 + 2 H2O + 6 CO2 → 6 O2 + ATP + energy
C) C4H12O4 + 12 O2 + 6 H2O → 6 CO2 + ATP + energy
D) C6H12O6 + 6 O2 + 6 H2O → 6 CO2 + 12 H2O + energy
E) C4H12O2 + 6 O2 + ATP → 6 CO2 + 12 H2O + energy
A) C6H12O6 + 6 H2O → 6 CO2 + 12 H2 + energy
B) C4H12O4 + 2 H2O + 6 CO2 → 6 O2 + ATP + energy
C) C4H12O4 + 12 O2 + 6 H2O → 6 CO2 + ATP + energy
D) C6H12O6 + 6 O2 + 6 H2O → 6 CO2 + 12 H2O + energy
E) C4H12O2 + 6 O2 + ATP → 6 CO2 + 12 H2O + energy

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
What is the chemical reaction illustrated in the figure?
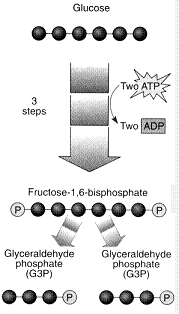
A) fermentation
B) the first step in the citric acid cycle
C) the energy investing phase of glycolysis
D) part of the electron transport chain
E) the energy capture phase of glycolysis

A) fermentation
B) the first step in the citric acid cycle
C) the energy investing phase of glycolysis
D) part of the electron transport chain
E) the energy capture phase of glycolysis

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
In glycolysis, a six-carbon glucose molecule is converted into two three-carbon molecules of:
A) citrate.
B) acetate.
C) pyruvate.
D) oxaloacetate.
E) coenzyme A
A) citrate.
B) acetate.
C) pyruvate.
D) oxaloacetate.
E) coenzyme A

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
Why must the transfer of electrons from glucose to oxygen during aerobic respiration take place in a series of steps?
A) The energy of the protons can be used to make ATP.
B) The energy of the electrons can be used to make ATP.
C) The energy of the electrons can be used to make ADP.
D) It is chemically impossible to transfer electrons directly from glucose to oxygen.
E) The chemical intermediates donate some of their electrons in order to increase the electron pool.
A) The energy of the protons can be used to make ATP.
B) The energy of the electrons can be used to make ATP.
C) The energy of the electrons can be used to make ADP.
D) It is chemically impossible to transfer electrons directly from glucose to oxygen.
E) The chemical intermediates donate some of their electrons in order to increase the electron pool.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
In the electron transport chain, exergonic redox processes drive the endergonic reaction in which:
A) pyruvate is converted to acetyl CoA.
B) ATP is produced by phosphorylation of ADP.
C) G3P is produced from phosphorylation of ADP.
D) ADP is produced by dephosphorylation of ATP.
E) glucose is produced from phosphorylation of ADP.
A) pyruvate is converted to acetyl CoA.
B) ATP is produced by phosphorylation of ADP.
C) G3P is produced from phosphorylation of ADP.
D) ADP is produced by dephosphorylation of ATP.
E) glucose is produced from phosphorylation of ADP.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
During aerobic respiration, nutrients are ____ to carbon dioxide and water.
A) reduced
B) oxidized
C) fermented
D) anabolized
E) catabolized
A) reduced
B) oxidized
C) fermented
D) anabolized
E) catabolized

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
In glycolysis, glucose receives two phosphate groups from ____, thus forming fructose-1, 6-bisphosphate.
A) ADP
B) ATP
C) G3P
D) a bisphosphate group
E) fructose-1, 6-bisphosphate
A) ADP
B) ATP
C) G3P
D) a bisphosphate group
E) fructose-1, 6-bisphosphate

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
What type of reaction is aerobic respiration?
A) redox
B) anabolic
C) hydrolysis
D) glycolysis
E) polymerization
A) redox
B) anabolic
C) hydrolysis
D) glycolysis
E) polymerization

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
Aerobic respiration is regulated by the binding of ATP or AMP to what enzyme?
A) aldolase
B) isomerase
C) hexokinase
D) phosphofructokinase
E) pyruvate dehydrogenase
A) aldolase
B) isomerase
C) hexokinase
D) phosphofructokinase
E) pyruvate dehydrogenase

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
Which of the following statements about the electron transport chain is true?
A) Protons are pumped out of the mitochondria by the complexes of the electron transport chain.
B) The proton gradient established during electron transport is a form of potential energy.
C) The electron transport chain can be found in the mitochondria of aerobic bacteria and other cells.
D) The movement of protons down a concentration gradient is an endergonic process.
E) ATP synthesis associated with the electron transport chain is an example of substrate level phosphorylation.
A) Protons are pumped out of the mitochondria by the complexes of the electron transport chain.
B) The proton gradient established during electron transport is a form of potential energy.
C) The electron transport chain can be found in the mitochondria of aerobic bacteria and other cells.
D) The movement of protons down a concentration gradient is an endergonic process.
E) ATP synthesis associated with the electron transport chain is an example of substrate level phosphorylation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
During aerobic respiration, what molecule is degraded for the formation of acetyl coenzyme A?
A) NAD
B) FADH
C) glucose
D) pyruvate
E) coenzyme A
A) NAD
B) FADH
C) glucose
D) pyruvate
E) coenzyme A

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
How does anaerobic respiration differ from aerobic respiration?
A) Anaerobic respiration produces CO2.
B) Anaerobic respiration produces ATP.
C) Anaerobic respiration involves an electron transport chain.
D) Anaerobic respiration utilizes O2 as the terminal electron acceptor.
E) Anaerobic respiration utilizes NO3 − as the terminal electron acceptor.
A) Anaerobic respiration produces CO2.
B) Anaerobic respiration produces ATP.
C) Anaerobic respiration involves an electron transport chain.
D) Anaerobic respiration utilizes O2 as the terminal electron acceptor.
E) Anaerobic respiration utilizes NO3 − as the terminal electron acceptor.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
Which of the following statements about lactic acid fermentation is FALSE?
A) It uses glucose as a substrate.
B) It is inefficient compared to aerobic respiration.
C) It produces two ATP molecules for every glucose molecule.
D) Oxygen is the final electron acceptor of this pathway.
E) Glycolysis is the only energy-yielding step of this pathway.
A) It uses glucose as a substrate.
B) It is inefficient compared to aerobic respiration.
C) It produces two ATP molecules for every glucose molecule.
D) Oxygen is the final electron acceptor of this pathway.
E) Glycolysis is the only energy-yielding step of this pathway.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
Which of the following is an exploited product of lactate fermentation?
A) butter
B) beer
C) yogurt
D) ice cream
E) loaf of bread
A) butter
B) beer
C) yogurt
D) ice cream
E) loaf of bread

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
The electron transport chain forms a concentration gradient for H+, which diffuses through ATP synthase complexes, producing ____.
A) ATP
B) FAD
C) G3P
D) NADH
E) pyruvate
A) ATP
B) FAD
C) G3P
D) NADH
E) pyruvate

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
In the skeletal muscle cells of vertebrates, as many as ____ ATP molecules are produced from one molecule of glucose, which is less than might be expected because electrons from NADH produced during glycolysis must be shuttled through the ____ mitochondrial membrane at a cost.
A) 2; outer
B) 2; inner
C) 6; outer
D) 36; inner
E) 38; inner
A) 2; outer
B) 2; inner
C) 6; outer
D) 36; inner
E) 38; inner

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
What is the role of the oxygen molecules required for aerobic respiration?
A) To form ATP
B) To produce CO2
C) To accept electrons directly from either NADH or FADH2
D) To accept the low energy electrons at the end of the electron transport chain
E) To store high energy electrons to pass to complex I of the electron transport chain
A) To form ATP
B) To produce CO2
C) To accept electrons directly from either NADH or FADH2
D) To accept the low energy electrons at the end of the electron transport chain
E) To store high energy electrons to pass to complex I of the electron transport chain

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
In chemiosmosis, ATP is produced as hydrogen ions (protons) pass through _____.
A) ATP synthase
B) ATP decarboxylase
C) ATP dehydrogenase
D) a series of electron carriers
E) the outer mitochondrial membrane
A) ATP synthase
B) ATP decarboxylase
C) ATP dehydrogenase
D) a series of electron carriers
E) the outer mitochondrial membrane

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
Saturated fatty acids store more energy than unsaturated fatty acids. Based on your knowledge of aerobic respiration, you draw this conclusion because saturated fatty acids:
A) lack phosphate.
B) are deaminated.
C) contain more ATP.
D) are more highly reduced.
E) contain more ester linkages.
A) lack phosphate.
B) are deaminated.
C) contain more ATP.
D) are more highly reduced.
E) contain more ester linkages.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
Which of the following is an end product of glycolysis?
A) CO2
B) ATP
C) NAD+
D) FADH2
E) acetyl CoA
A) CO2
B) ATP
C) NAD+
D) FADH2
E) acetyl CoA

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
What is the function of coenzyme Q?
A) To reduce glucose
B) To oxidize glucose
C) To transfer electrons
D) To transfer phosphate to ATP
E) To provide energy in the citric acid cycle
A) To reduce glucose
B) To oxidize glucose
C) To transfer electrons
D) To transfer phosphate to ATP
E) To provide energy in the citric acid cycle

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
One gram of ____ contains more than twice the amount of energy of a gram of glucose.
A) starch
B) lipids
C) ATP
D) protein
E) amino acids
A) starch
B) lipids
C) ATP
D) protein
E) amino acids

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
Which of the following is an anaerobic pathway?
A) chemiosmosis
B) fermentation
C) citric acid cycle
D) aerobic respiration
E) electron transport chain
A) chemiosmosis
B) fermentation
C) citric acid cycle
D) aerobic respiration
E) electron transport chain

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
Peter Mitchell demonstrated ATP production by aerobic bacteria to prove what process?
A) glycolysis
B) hydrolysis
C) fermentation
D) chemiosmosis
E) citric acid cycle
A) glycolysis
B) hydrolysis
C) fermentation
D) chemiosmosis
E) citric acid cycle

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
Which of the following steps in the citric acid cycle directly produces a molecule of ATP (or GTP)?
A) citrate → isocitrate
B) succinate → fumarate
C) malate → oxaloacetate
D) succinyl CoA → succinate
E) isocitrate → α -ketoglutarate
A) citrate → isocitrate
B) succinate → fumarate
C) malate → oxaloacetate
D) succinyl CoA → succinate
E) isocitrate → α -ketoglutarate

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
Which of the following molecules can be used as a substrate for cellular respiration?
A) glucose only
B) glucose and lipids only
C) glucose and proteins only
D) glucose, lipids, and proteins only
E) glucose, lipids, proteins, and fatty acids
A) glucose only
B) glucose and lipids only
C) glucose and proteins only
D) glucose, lipids, and proteins only
E) glucose, lipids, proteins, and fatty acids

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
In eukaryotes, where does glycolysis occur?
A) cytosol
B) lysosomes
C) Golgi complex
D) mitochondrial matrix
E) mitochondrial inner membrane
A) cytosol
B) lysosomes
C) Golgi complex
D) mitochondrial matrix
E) mitochondrial inner membrane

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
The complete aerobic metabolism of one molecule of glucose yields a maximum of how many ATPs?
A) 2
B) 4
C) 18
D) 32 to 34
E) 36 to 38
A) 2
B) 4
C) 18
D) 32 to 34
E) 36 to 38

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
Which molecule contains the least stored chemical energy?
A) ethyl alcohol
B) pyruvate
C) glucose
D) lactate
E) oxygen
A) ethyl alcohol
B) pyruvate
C) glucose
D) lactate
E) oxygen

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
If yeast cells are incubated under anaerobic conditions, the pyruvate they produce is converted to lactate .
__________________
__________________

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
Identify and briefly describe the process(es) of cellular respiration that occur in the mitochondria. Indicate the amount of ATP, NADH, and FADH2 produced in each process.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
In liver cells, each NADH produced via glycolysis results in two ATP molecules in the electron transport chain.
__________________
__________________

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
Explain how proteins can be metabolized by the same pathways that oxidize glucose.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
What is chemiosmosis, and how is it used to synthesize ATP? Use the following terms in your explanation: inner mitochondria membrane, mitochondrial matrix, endergonic, exergonic, ADP, Pi, and NADH/FADH2.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
The reactions of the citric acid cycle take place in the matrix of the mitochondrion.
__________________
__________________

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
If yeasts are grown under anaerobic conditions, pyruvate is converted first to ____ and then to ____.
A) citrate; oxaloacetate
B) acetaldehyde; lactate
C) lactate; carbon dioxide
D) acetaldehyde; ethyl alcohol
E) acetyl coenzyme A; citrate
A) citrate; oxaloacetate
B) acetaldehyde; lactate
C) lactate; carbon dioxide
D) acetaldehyde; ethyl alcohol
E) acetyl coenzyme A; citrate

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
Phosphofructokinase is stimulated by high levels of ATP.
__________________
__________________

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
During fermentation, the immediate fate of the electrons in NADH is that they:
A) are transferred to the electron transport chain.
B) are transferred to an organic molecule.
C) are transferred to O2.
D) are used to make CO2.
E) are used to form H2O.
A) are transferred to the electron transport chain.
B) are transferred to an organic molecule.
C) are transferred to O2.
D) are used to make CO2.
E) are used to form H2O.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
Both alcohol fermentation and lactate fermentation are highly ____ because the fuel is only partially ____.
A) efficient; reduced
B) efficient; oxidized
C) inefficient; reduced
D) inefficient; oxidized
E) efficient; metabolized
A) efficient; reduced
B) efficient; oxidized
C) inefficient; reduced
D) inefficient; oxidized
E) efficient; metabolized

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
Substrate level phosphorylation reactions occur in the process of chemiosmosis.
__________________
__________________

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
An example of a(n) anabolic reaction is the splitting of a polysaccharide into monosaccharides.
__________________
__________________

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
The stage of cellular respiration in which most of the ATP is produced is the citric acid cycle. __________________

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
Alcohol is the end product of fermentation by what type of organism?
A) cow
B) algae
C) yeast
D) protist
E) bacteria
A) cow
B) algae
C) yeast
D) protist
E) bacteria

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
In the tricarboxylic acid cycle, oxaloacetate reacts with acetyl CoA forming citrate .
__________________
__________________

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
For each glucose molecule that begins cellular respiration, the citric acid cycle must turn once .
__________________
__________________

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
For each acetyl CoA molecule that enters the citric acid cycle, two CO2 molecules are produced.
__________________
__________________

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
The downhill flow of protons through the ATP synthase complex powers the production of ATP.
__________________
__________________

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
Compare and contrast aerobic and anaerobic pathways used by cells to extract energy from organic molecules. Include the mechanism of ATP formation, the final electron acceptor, and the end products in your comparison.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
Match between columns
Premises:
GDP is phosphorylated
GDP is phosphorylated
GDP is phosphorylated
GDP is phosphorylated
This is the first process that occurs in the mitochondrion.
This is the first process that occurs in the mitochondrion.
This is the first process that occurs in the mitochondrion.
This is the first process that occurs in the mitochondrion.
Pyruvate is an end product.
Pyruvate is an end product.
Pyruvate is an end product.
Pyruvate is an end product.
ATP synthase is a component.
ATP synthase is a component.
ATP synthase is a component.
ATP synthase is a component.
Responses:
electron transport and chemiosmosis
formation of acetyl CoA
citric acid cycle
glycolysis
electron transport and chemiosmosis
formation of acetyl CoA
citric acid cycle
glycolysis
electron transport and chemiosmosis
formation of acetyl CoA
citric acid cycle
glycolysis
electron transport and chemiosmosis
formation of acetyl CoA
citric acid cycle
glycolysis
electron transport and chemiosmosis
formation of acetyl CoA
citric acid cycle
glycolysis
electron transport and chemiosmosis
formation of acetyl CoA
citric acid cycle
glycolysis
electron transport and chemiosmosis
formation of acetyl CoA
citric acid cycle
glycolysis
electron transport and chemiosmosis
formation of acetyl CoA
citric acid cycle
glycolysis
electron transport and chemiosmosis
formation of acetyl CoA
citric acid cycle
glycolysis
electron transport and chemiosmosis
formation of acetyl CoA
citric acid cycle
glycolysis

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
Although our muscle cells contain mitochondria and normally undergo aerobic respiration, during strenuous activity, lactate is formed, which contributes to cramps in our muscles. What is the evolutionary advantage of lactate production in our cells?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
What is the major difference between substrate-level phosphorylation and oxidative phosphorylation?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
In the process of aerobic respiration, nitrate can function as the terminal electron acceptor in the electron transport chain.
__________________
__________________

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
Describe how cells can regulate aerobic respiration at the level of the conversion of glucose-6-phosphate to fructose-1, 6-bisphosphate as catalyzed by phosphofructokinase (PFK).

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
Explain why fermentation is a highly inefficient process.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



