Deck 9: Energy and Chemistry
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/45
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 9: Energy and Chemistry
1
In the context of the second law of thermodynamics, one can say that :
A)it is impossible to completely convert heat to work.
B)every action has an equal and opposite reaction.
C)fire can never burn to completion.
D)force is equal to mass multiplied by acceleration.
A)it is impossible to completely convert heat to work.
B)every action has an equal and opposite reaction.
C)fire can never burn to completion.
D)force is equal to mass multiplied by acceleration.
it is impossible to completely convert heat to work.
2
A proton accelerated to a velocity of 3.81 × 10 3 m\s will have more energy than an electron accelerated to the same velocity .
True
3
When you drive your car, your location is a state function, but the distance that you have traveled to get there is not .
True
4
The amount of heat required to raise the temperature of one gram of a material by 1 ° C is the _____ of that material.
A)electron affinity
B)specific heat capacity
C)molar heat capacity
D)calorimetric constant
A)electron affinity
B)specific heat capacity
C)molar heat capacity
D)calorimetric constant

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 45 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
As the velocity of a moving object doubles, the kinetic energy of the object doubles .

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 45 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
The complicated multi-part system designed to balance the demand for electricity with its production is referred to as the electrical grid.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 45 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
In the context of chemical reactions, bond formation is always _____.
A)exothermic
B)endothermic
C)eutectic
D)eutectoid
A)exothermic
B)endothermic
C)eutectic
D)eutectoid

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 45 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
Thermochemistry is the study of the energetic consequences of chemistry.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 45 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
All energy flow is either heat or work.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 45 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
In the United States of America, the largest component of energy use in the year 2016 was _____.
A)residential
B)commercial
C)industrial
D)transportation
A)residential
B)commercial
C)industrial
D)transportation

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 45 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
The study of chemical energy and the transfer of this energy provide a crucial link between chemistry and engineering.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 45 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
Stored energy or energy due to position is known as _____.
A)kinetic energy
B)thermal energy
C)electrical energy
D)potential energy
A)kinetic energy
B)thermal energy
C)electrical energy
D)potential energy

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 45 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
The United States relies upon crude oil and related petroleum products as its primary energy source.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 45 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
Thermal energy is directly related to the motion of atoms and molecules.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 45 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
_____ is the transfer of energy accomplished by a force moving a mass some distance against resistance .
A)Heat
B)Momentum
C)Work
D)Power
A)Heat
B)Momentum
C)Work
D)Power

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 45 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
A state function is a variable whose value depends only on the current state of the system.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 45 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
What term is used to most accurately describe the energy flow from a warm object to a cooler one?
A)Heat
B)Work
C)Cascade
D)Acceleration
A)Heat
B)Work
C)Cascade
D)Acceleration

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 45 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
A chemical reaction that transfers heat from the system (the reaction)to the surroundings is always _____.
A)exothermic
B)endothermic
C)spontaneous
D)electrically charged
A)exothermic
B)endothermic
C)spontaneous
D)electrically charged

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 45 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
The molecular formula of octane is _____.
A)C2H6
B)C6H14
C)C 8 H 18
D)C9H20
A)C2H6
B)C6H14
C)C 8 H 18
D)C9H20

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 45 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
Power stations, which use fossil fuels to produce electrical energy, rely upon _____.
A)endothermic chemical reactions
B)nuclear fusion reactions
C)exothermic chemical reactions
D)nuclear fission reactions
A)endothermic chemical reactions
B)nuclear fusion reactions
C)exothermic chemical reactions
D)nuclear fission reactions

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 45 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
Under constant volume conditions, the change in internal energy equals the _____.
A)entropy
B)insulation capacity
C)transduction
D)heat flow
A)entropy
B)insulation capacity
C)transduction
D)heat flow

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 45 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
Deposition refers to the phase transition from _____.
A)liquid to gas
B)gas to liquid
C)gas to solid
D)solid to gas
A)liquid to gas
B)gas to liquid
C)gas to solid
D)solid to gas

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 45 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
What amount of heat is required to convert a 1.5 kg block of ice at − 15.0 ° C to steam at 150.0 ° C? Assume the specific heat of water to be 4.18 J\g ° C, specific heat of ice to be 2.108 J\g ° C, specific heat of steam to be 1.996 J\g ° C, Δ H fus = 333.55 J\g, and Δ H vap = 2.26 kJ\g.
A)94.1 kJ
B)1,035 kJ
C)6,371 kJ
D)4,711 kJ
A)94.1 kJ
B)1,035 kJ
C)6,371 kJ
D)4,711 kJ

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 45 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
During the phase change from liquid water to gaseous water (steam), the temperature of the water _____.
A)increases proportional to the volume of the water
B)remains the same
C)decreases
D)increases proportional to the mass of the water
A)increases proportional to the volume of the water
B)remains the same
C)decreases
D)increases proportional to the mass of the water

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 45 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
The formation reaction for NaF( s )is _____.
A)Na( s )+ F( g )→ NaF( s )
B)2 Na( s )+ F 2 ( g )→ 2 NaF( s )
C)Na( s )+ F 2 ( g )→ NaF( s )
D)2Na( s )+ 2F( s )→ 2NaF( s )
A)Na( s )+ F( g )→ NaF( s )
B)2 Na( s )+ F 2 ( g )→ 2 NaF( s )
C)Na( s )+ F 2 ( g )→ NaF( s )
D)2Na( s )+ 2F( s )→ 2NaF( s )

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 45 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
If a 136.51 g Al rod (c = 0.900 J\g ° C)is at 100.0 ° C and placed into 250.0 g of water at 21.8 ° C, what is the temperature of the system (rod + water)at equilibrium assuming no losses to the surroundings? Assume the specific heat of water to be 4.18 J\g ° C.
A)18 ° C
B)206 ° C
C)30 ° C
D)46 ° C
A)18 ° C
B)206 ° C
C)30 ° C
D)46 ° C

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 45 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
What are the primary products in the complete combustion of a hydrocarbon?
A)H2and O2
B)C and H2
C)H2O and CO2
D)CO and H2O
A)H2and O2
B)C and H2
C)H2O and CO2
D)CO and H2O

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 45 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
What is the kinetic energy of a single He atom traveling at 2.0 × 104m\s?
A)1.3 × 10 − 18 J
B)6.4 × 10 − 18 J
C)2.6 × 10 − 18 J
D)7.7 × 10 − 1 8 J
A)1.3 × 10 − 18 J
B)6.4 × 10 − 18 J
C)2.6 × 10 − 18 J
D)7.7 × 10 − 1 8 J

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 45 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
The synthesis of ammonia via the Haber reaction follows the balanced equation:
3 H2( g )+ N2( g )→ 2 NH3( g )Δ H = − 99.22 kJ
How much heat is created from the synthesis of 7.38 metric tons (1 metric ton = 1000 kg)of ammonia?
A)− 8.37 × 107kJ
B)− 4.43 × 108kJ
C)− 1.95 × 106kJ
D)− 2.15 × 107kJ
3 H2( g )+ N2( g )→ 2 NH3( g )Δ H = − 99.22 kJ
How much heat is created from the synthesis of 7.38 metric tons (1 metric ton = 1000 kg)of ammonia?
A)− 8.37 × 107kJ
B)− 4.43 × 108kJ
C)− 1.95 × 106kJ
D)− 2.15 × 107kJ

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 45 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
The heat required to melt a substance is the _____.
A)specific heat capacity
B)heat of vaporization
C)heat of condensation
D)heat of fusion
A)specific heat capacity
B)heat of vaporization
C)heat of condensation
D)heat of fusion

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 45 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
An iron piston in a compressor has a mass of 3.62 kg. If the specific heat of iron is 0.449 J\g ° C, how much heat is required to raise the temperature of the piston from 12.0 ° C to 111.0 ° C?
A)1.61 × 102J
B)7.08 × 108J
C)1.61 × 105J
D)4.35 × 105J
A)1.61 × 102J
B)7.08 × 108J
C)1.61 × 105J
D)4.35 × 105J

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 45 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
The chemical reaction by which one mole of a compound is formed from its elements in their standard states is best described as a(n)_____.
A)aldol condensation reaction
B)formation reaction
C)thermodynamic equivalent
D)addition reaction
A)aldol condensation reaction
B)formation reaction
C)thermodynamic equivalent
D)addition reaction

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 45 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
The formation reaction for carbon monoxide is _____.
A)C( s )+ O( g )→ CO( g )
B)2C( s )+ O2( g )→ 2 CO( g )
C)CO( g )→ C( s )+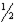 O2( g )
O2( g )
D)C( s )+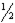 O2( g )→ CO( g )
O2( g )→ CO( g )
A)C( s )+ O( g )→ CO( g )
B)2C( s )+ O2( g )→ 2 CO( g )
C)CO( g )→ C( s )+
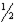 O2( g )
O2( g )D)C( s )+
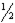 O2( g )→ CO( g )
O2( g )→ CO( g )
Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 45 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
What is the kinetic energy of a 22,500 lb truck traveling at 55 mi\hr?
A)6.2 × 106J
B)3.1 × 103J
C)6.2 × 108J
D)3.1 × 106J
A)6.2 × 106J
B)3.1 × 103J
C)6.2 × 108J
D)3.1 × 106J

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 45 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
Given the following heat of formation values, calculate the heat of reaction for:
Na( s )+ Cl 2 ( g )→ NaCl( s ).
Δ H f value in kJ\mol for Na( s )is 0, for Na( g )is 108.7, for Cl 2 ( g )is 0, and for NaCl( s )is − 411.0.
A)− 411.0 kJ
B)+411.0 kJ
C)− 302.3 kJ
D)+519.7 kJ
Na( s )+ Cl 2 ( g )→ NaCl( s ).
Δ H f value in kJ\mol for Na( s )is 0, for Na( g )is 108.7, for Cl 2 ( g )is 0, and for NaCl( s )is − 411.0.
A)− 411.0 kJ
B)+411.0 kJ
C)− 302.3 kJ
D)+519.7 kJ

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 45 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
If a lighter contains 4.0 mL of liquid butane (density of butane = 0.8 g\cm 3 ), how much potential energy does the lighter contain according to the combustion of butane?
2 C 4 H 10 ( g )+ 13 O 2 ( g )→ 8 CO 2 ( g )+ 10 H 2 O( l )Δ H = − 5.75 × 10 3 kJ
A)− 5 × 102kJ
B)− 1.6 × 10 2 kJ
C)− 8 × 102kJ
D)+4.8 × 103kJ
2 C 4 H 10 ( g )+ 13 O 2 ( g )→ 8 CO 2 ( g )+ 10 H 2 O( l )Δ H = − 5.75 × 10 3 kJ
A)− 5 × 102kJ
B)− 1.6 × 10 2 kJ
C)− 8 × 102kJ
D)+4.8 × 103kJ

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 45 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
Given the following heat of formation values, calculate the heat of reaction for the following:
C 3 H 8 ( g )+ O 2 ( g )→ CO 2 ( g )+ H 2 O( l ).
Δ H f value in kJ\mol for C 3 H 8 ( g )is − 103.8, for O 2 ( g )is 0, for CO 2 ( g )is − 393.5, and for H 2 O( l )is − 285.8.
A)3.613 × 102kJ
B)− 5.755 × 102kJ
C)1.413 × 102kJ
D)− 2.220 × 103kJ
C 3 H 8 ( g )+ O 2 ( g )→ CO 2 ( g )+ H 2 O( l ).
Δ H f value in kJ\mol for C 3 H 8 ( g )is − 103.8, for O 2 ( g )is 0, for CO 2 ( g )is − 393.5, and for H 2 O( l )is − 285.8.
A)3.613 × 102kJ
B)− 5.755 × 102kJ
C)1.413 × 102kJ
D)− 2.220 × 103kJ

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 45 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
How much energy is required to increase the temperature of 175 mL of water from 18.5 ° C to 85.0 ° C? Assume the specific heat of water to be 4.18 J\g ° C.
A)821,000 J
B)48.6 kJ
C)52.8 kJ
D)48,645 J
A)821,000 J
B)48.6 kJ
C)52.8 kJ
D)48,645 J

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 45 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
A new alloy is designed for use in a car radiator. If the 17.6 kg radiator required 8.69 × 105J of heat to warm from 22.1 ° C to 155.8 ° C, what is the specific heat of the new alloy?
A)0.369 J\g ° C
B)8.27 J\g ° C
C)0.00491 J\g ° C
D)1.70 J\g ° C
A)0.369 J\g ° C
B)8.27 J\g ° C
C)0.00491 J\g ° C
D)1.70 J\g ° C

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 45 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
A hungry engineering student reaches for his favorite granola bar while working on a statics assignment. If the granola bar contains 240 "calories" (1 food calorie = 1kcal), how much energy (in joules)will the student receive from the bar?
A)3.1 × 103J
B)1.0 × 106J
C)1.0 × 103J
D)2.6 × 106J
A)3.1 × 103J
B)1.0 × 106J
C)1.0 × 103J
D)2.6 × 106J

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 45 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
The specific heat is a physical property of a material that measures how much heat is required to raise the temperature of 1 mole of that material by 1°C.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 45 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
Chemical bond breaking is always endothermic.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 45 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
A calorimeter is used to compare the energy content of some fuels. During the calibration of the calorimeter, an electrical resistance heater supplies 120 J of heat and a temperature increase of 0.920°C is observed. Then, 0.3 g of a particular fuel is burned in this same calorimeter, and the temperature increases by 6.15°C. What is the amount of energy liberated per gram of fuel burned?
A)2.7 kJ\g
B)3.2 kJ\g
C)4.1 kJ\g
D)5.7 kJ\g
A)2.7 kJ\g
B)3.2 kJ\g
C)4.1 kJ\g
D)5.7 kJ\g

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 45 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
Potential energy of a moving body is directly proportional to its velocity.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 45 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
The following reaction can be characterized as a(n)_____.
CH 4 ( g )+ 2 O 2 ( g )→ CO 2 ( g )+ 2 H 2 O( l ) Δ H = − 890.4 kJ
A)endothermic reaction
B)exothermic reaction
C)reduction reaction
D)displacement reaction
CH 4 ( g )+ 2 O 2 ( g )→ CO 2 ( g )+ 2 H 2 O( l ) Δ H = − 890.4 kJ
A)endothermic reaction
B)exothermic reaction
C)reduction reaction
D)displacement reaction

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 45 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



