Deck 27: The Phillips Curve and Expectations Theory
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/59
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 27: The Phillips Curve and Expectations Theory
1
The long-run Phillips curve:
A) is downward sloping.
B) is upward sloping.
C) shows there is no tradeoff between unemployment and inflation.
D) is horizontal at the natural rate of inflation.
A) is downward sloping.
B) is upward sloping.
C) shows there is no tradeoff between unemployment and inflation.
D) is horizontal at the natural rate of inflation.
C
2
The modern view of the Phillips curve suggests that:
A) when inflation is reduced, unemployment will fall below the natural rate.
B) the Phillips curve is an unstable relationship.
C) systematic demand stimulus policies will be unable to affect prices in the long run.
D) there will be a trade-off between inflation and unemployment in the long run.
A) when inflation is reduced, unemployment will fall below the natural rate.
B) the Phillips curve is an unstable relationship.
C) systematic demand stimulus policies will be unable to affect prices in the long run.
D) there will be a trade-off between inflation and unemployment in the long run.
B
3
Suppose that the economy experiences an increase in the inflation rate at the same time that the unemployment rate decreases. This situation indicates a:
A) shift in the Phillips curve.
B) movement along a vertical Phillips curve.
C) movement along a negatively-sloped Phillips curve.
D) movement along a positively-sloped Phillips curve.
A) shift in the Phillips curve.
B) movement along a vertical Phillips curve.
C) movement along a negatively-sloped Phillips curve.
D) movement along a positively-sloped Phillips curve.
C
4
Under adaptive expectations, the short-term effect of an unanticipated shift to a more expansionary macroeconomic policy will be a:
A) temporary reduction in the unemployment rate.
B) permanent reduction in the unemployment rate.
C) temporary reduction in the inflation rate.
D) permanent reduction in the inflation rate.
A) temporary reduction in the unemployment rate.
B) permanent reduction in the unemployment rate.
C) temporary reduction in the inflation rate.
D) permanent reduction in the inflation rate.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 59 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
According to the Phillips curve, a more expansionary macro-policy that causes inflation to be greater will:
A) place downward pressure on prices.
B) reduce unemployment.
C) reduce output.
D) reduce the natural rate of unemployment.
A) place downward pressure on prices.
B) reduce unemployment.
C) reduce output.
D) reduce the natural rate of unemployment.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 59 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
On a Phillips curve diagram, a decrease in the rate of inflation, other things being equal, is represented by a(n):
A) upward movement along the Phillips curve.
B) downward movement along the Phillips curve.
C) upward shift of the Phillips curve.
D) downward shift of the Phillips curve.
A) upward movement along the Phillips curve.
B) downward movement along the Phillips curve.
C) upward shift of the Phillips curve.
D) downward shift of the Phillips curve.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 59 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
Exhibit 17-1 Inflation and unemployment rates
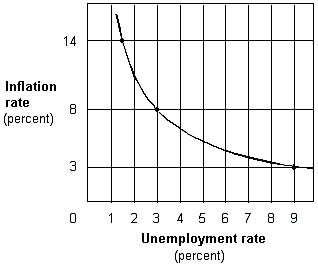
In Exhibit 17-1, when the unemployment rate goes from 9 percent to 1.5 percent, the:
A) level of inflation is unaffected.
B) inflation rate goes from 3 percent to 14 percent.
C) inflation rate goes from 3 percent to 8 percent.
D) inflation rate goes from 8 percent to 14 percent.

In Exhibit 17-1, when the unemployment rate goes from 9 percent to 1.5 percent, the:
A) level of inflation is unaffected.
B) inflation rate goes from 3 percent to 14 percent.
C) inflation rate goes from 3 percent to 8 percent.
D) inflation rate goes from 8 percent to 14 percent.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 59 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
Under adaptive expectations theory, people expect the rate of inflation this year to be:
A) zero, regardless of the rate last year.
B) the same as last year.
C) the rate based on predictable and fiscal policies.
D) always higher than last year.
A) zero, regardless of the rate last year.
B) the same as last year.
C) the rate based on predictable and fiscal policies.
D) always higher than last year.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 59 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
The natural rate hypothesis argues that the economy will:
A) self-correct to the natural rate of inflation.
B) require expansionary fiscal policy to reach the natural rate of unemployment.
C) self-correct to the natural rate of unemployment.
D) require expansionary monetary policy to reach the natural rate of unemployment.
A) self-correct to the natural rate of inflation.
B) require expansionary fiscal policy to reach the natural rate of unemployment.
C) self-correct to the natural rate of unemployment.
D) require expansionary monetary policy to reach the natural rate of unemployment.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 59 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
Experience with the Phillips curve since the 1970s has shown that the:
A) curve can be used as a reliable model to guide public policy.
B) relationship between the inflation rate and the unemployment rate moves in a clockwise direction.
C) curve is not stable.
D) inflation rate and the unemployment rate are equal.
A) curve can be used as a reliable model to guide public policy.
B) relationship between the inflation rate and the unemployment rate moves in a clockwise direction.
C) curve is not stable.
D) inflation rate and the unemployment rate are equal.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 59 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
Which of the following statements is true ?
A) The Phillips curve has always been stable.
B) If the Phillips curve shifts outward to the right this illustrates a greater tradeoff between unemployment and inflation.
C) Keynesian economics assumes a vertical Phillips curve.
D) According to the natural rate hypothesis the Phillips curve is downward sloping.
A) The Phillips curve has always been stable.
B) If the Phillips curve shifts outward to the right this illustrates a greater tradeoff between unemployment and inflation.
C) Keynesian economics assumes a vertical Phillips curve.
D) According to the natural rate hypothesis the Phillips curve is downward sloping.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 59 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
Under the natural rate hypothesis, expansionary monetary and fiscal policies can at best produce a:
A) permanent change in the unemployment rate.
B) short-run change in the unemployment rate.
C) permanent change in the inflation rate.
D) short-run change in the long-run Phillips curve.
A) permanent change in the unemployment rate.
B) short-run change in the unemployment rate.
C) permanent change in the inflation rate.
D) short-run change in the long-run Phillips curve.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 59 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
Under adaptive expectations theory, people persistently:
A) underestimate inflation when it is slowing down.
B) overestimate inflation when it is accelerating.
C) underestimate inflation when it is accelerating.
D) adapt to the prevailing inflation rate.
A) underestimate inflation when it is slowing down.
B) overestimate inflation when it is accelerating.
C) underestimate inflation when it is accelerating.
D) adapt to the prevailing inflation rate.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 59 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
On a Phillips curve diagram, a decrease in the rate of inflation, other things being equal, is represented by a(n):
A) upward shift of the Phillips curve.
B) downward movement along Phillips curve.
C) upward movement along the Phillips curve.
D) downward shift of the Phillips curve.
A) upward shift of the Phillips curve.
B) downward movement along Phillips curve.
C) upward movement along the Phillips curve.
D) downward shift of the Phillips curve.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 59 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
The Phillips curve illustrates the relationship between:
A) change in the money supply and change in unemployment.
B) tax rates and tax revenues.
C) the equilibrium level of income and the employment rate.
D) inflation and unemployment.
A) change in the money supply and change in unemployment.
B) tax rates and tax revenues.
C) the equilibrium level of income and the employment rate.
D) inflation and unemployment.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 59 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
According to adaptive expectations theory, expansionary monetary and fiscal policies to reduce the unemployment rate are:
A) useless in the long run.
B) useless in the short run.
C) ineffective on the price level.
D) successful at achieving the desired outcomes.
A) useless in the long run.
B) useless in the short run.
C) ineffective on the price level.
D) successful at achieving the desired outcomes.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 59 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
If the long-run Phillips curve is vertical, then any government policy designed to lower:
A) unemployment will not change the unemployment rate and only increase the inflation rate.
B) unemployment will work leaving the inflation rate unchanged.
C) inflation will cause employment to rise.
D) unemployment will work causing the inflation rate to fall.
A) unemployment will not change the unemployment rate and only increase the inflation rate.
B) unemployment will work leaving the inflation rate unchanged.
C) inflation will cause employment to rise.
D) unemployment will work causing the inflation rate to fall.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 59 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
Exhibit 17-1 Inflation and unemployment rates
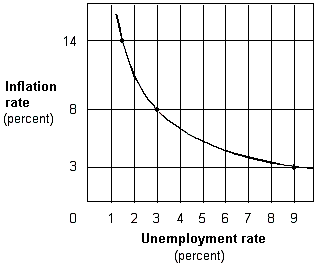
In Exhibit 17-1, when the unemployment rate goes from 3 percent to 9 percent,
A) the level of inflation is unaffected.
B) the inflation rate goes from 8 percent to 14 percent.
C) the inflation rate goes from 8 percent to 3 percent.
D) the inflation rate goes to 0 percent.

In Exhibit 17-1, when the unemployment rate goes from 3 percent to 9 percent,
A) the level of inflation is unaffected.
B) the inflation rate goes from 8 percent to 14 percent.
C) the inflation rate goes from 8 percent to 3 percent.
D) the inflation rate goes to 0 percent.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 59 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
Under adaptive expectations theory, an increase in the short-run aggregate demand curve ____ the inflation rate and ____ the unemployment rate.
A) increases; increases
B) increases; decreases
C) increases; does not change
D) decreases; increases
A) increases; increases
B) increases; decreases
C) increases; does not change
D) decreases; increases

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 59 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
Which of the following correctly describes the Phillips curve?
A) A curve showing the inverse relationship between interest rates and the quantity of money demanded.
B) A curve showing the direct relationship between interest rates and the quantity of money demanded.
C) A curve showing the direct relationship between the inflation rate and the unemployment rate.
D) A curve showing the inverse relationship between the inflation rate and the unemployment rate.
A) A curve showing the inverse relationship between interest rates and the quantity of money demanded.
B) A curve showing the direct relationship between interest rates and the quantity of money demanded.
C) A curve showing the direct relationship between the inflation rate and the unemployment rate.
D) A curve showing the inverse relationship between the inflation rate and the unemployment rate.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 59 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
The view that individuals weigh all available evidence when they formulate their expectations about economic events (including information concerning the probable effects of current and future economic policy) is called:
A) the adaptive expectations hypothesis.
B) the permanent income hypothesis.
C) the rational expectations hypothesis.
D) the Phillips curve.
A) the adaptive expectations hypothesis.
B) the permanent income hypothesis.
C) the rational expectations hypothesis.
D) the Phillips curve.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 59 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
When people use recent information to gradually adjust their forecasts of inflation, they are said to have:
A) static expectations.
B) adaptive expectations.
C) rational expectations.
D) spiraling expectations.
A) static expectations.
B) adaptive expectations.
C) rational expectations.
D) spiraling expectations.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 59 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
Explain why rational expectations theorists do not support government intervention to alleviate unemployment. Explain their views on the effectiveness of fiscal policy and monetary policy.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 59 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
Under the rational expectations hypothesis, which of the following is the most likely short-run effect of a move to expansionary monetary policy?
A) a higher general level of prices but no change in real output
B) a higher general level of prices and an expansion in real output
C) no change in the general level of prices and a reduction in real output
D) no change in either the general level of prices or real output
A) a higher general level of prices but no change in real output
B) a higher general level of prices and an expansion in real output
C) no change in the general level of prices and a reduction in real output
D) no change in either the general level of prices or real output

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 59 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
According to rational expectations theory, what information do businesses and workers use when they form their expectations regarding inflation?
A) recent events and data
B) Keynesian and monetarist models
C) forecasts by public-and private-sector economists
D) all the relevant information that is available
A) recent events and data
B) Keynesian and monetarist models
C) forecasts by public-and private-sector economists
D) all the relevant information that is available

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 59 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
If the economy is in recession, explain what advice you would give the President, if you were a monetarist economist. What if you were a Keynesian?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 59 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
Exhibit 17-4 Short-run and long-run Phillips curves
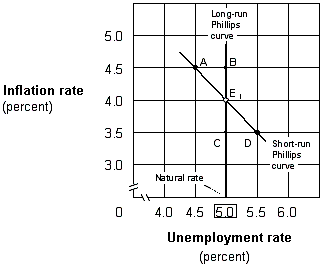
Suppose the economy in Exhibit 17-4 is at point E1, and the Fed increases the money supply. If people have adaptive expectations, then the economy will move:
A) to point A in the short run and point B in the long run.
B) directly to point B.
C) to point C in the short run and point D in the long run.
D) directly to point D.

Suppose the economy in Exhibit 17-4 is at point E1, and the Fed increases the money supply. If people have adaptive expectations, then the economy will move:
A) to point A in the short run and point B in the long run.
B) directly to point B.
C) to point C in the short run and point D in the long run.
D) directly to point D.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 59 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
Which of the following best describes the idea of a political business cycle?
A) Politicians have a bias to cut taxes and increase government spending.
B) Special interests result in alternating federal deficits.
C) Politicians will use fiscal and monetary policy to cause output, real incomes, and employment to be rising prior to elections.
D) Good intentions of politicians influence the business cycle.
A) Politicians have a bias to cut taxes and increase government spending.
B) Special interests result in alternating federal deficits.
C) Politicians will use fiscal and monetary policy to cause output, real incomes, and employment to be rising prior to elections.
D) Good intentions of politicians influence the business cycle.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 59 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
The proponents of rational expectations believe that:
A) there will be a substantial time lag before people anticipate the eventual effects of a shift to a more expansionary macro-policy.
B) macro-policies that stimulate demand and place upward pressure on the general level if prices will temporarily increase output and employment.
C) the inflationary side effects of expansionary policies will be anticipated quickly, and therefore, even their short-run effects on real output and employment will be minimal.
D) discretionary changes in macro-policy can be made in a manner that will reduce the economic ups and downs of a market economy.
A) there will be a substantial time lag before people anticipate the eventual effects of a shift to a more expansionary macro-policy.
B) macro-policies that stimulate demand and place upward pressure on the general level if prices will temporarily increase output and employment.
C) the inflationary side effects of expansionary policies will be anticipated quickly, and therefore, even their short-run effects on real output and employment will be minimal.
D) discretionary changes in macro-policy can be made in a manner that will reduce the economic ups and downs of a market economy.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 59 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
Starting from an initial long-run equilibrium, under the rational expectations hypothesis, an anticipated shift to a more expansionary policy will increase:
A) prices but not real output in the short run.
B) real output but not prices in the short run.
C) real output in the long run but not in the short run.
D) real output in both the long run and the short run.
A) prices but not real output in the short run.
B) real output but not prices in the short run.
C) real output in the long run but not in the short run.
D) real output in both the long run and the short run.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 59 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
If people behave according to rational expectations theory, people would expect the rate of inflation this year to be:
A) the same as last year.
B) zero, regardless of the rate last year.
C) the rate based on predictable monetary and fiscal policies.
D) always higher than last year.
A) the same as last year.
B) zero, regardless of the rate last year.
C) the rate based on predictable monetary and fiscal policies.
D) always higher than last year.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 59 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
What is the difference between the Keynesian and rational expectations theories concerning the success of stabilization policy?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 59 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
According to rational expectations theory, predictable expansionary monetary and fiscal policies to reduce the unemployment rate are:
A) desirable because the result is to lower inflation.
B) harmful because the only result is higher inflation.
C) ineffective on the price level.
D) successful in reducing unemployment in the long run.
A) desirable because the result is to lower inflation.
B) harmful because the only result is higher inflation.
C) ineffective on the price level.
D) successful in reducing unemployment in the long run.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 59 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
The rational expectations theory indicates that expansionary policy will:
A) stimulate real output in the long run but not in the short run.
B) expand real output and employment if the public quickly anticipates the effects of the expansionary policy.
C) equalize real and nominal interest rates during lengthy periods of inflation.
D) fail to increase employment because individuals will anticipate it and take actions that will offset its impact.
A) stimulate real output in the long run but not in the short run.
B) expand real output and employment if the public quickly anticipates the effects of the expansionary policy.
C) equalize real and nominal interest rates during lengthy periods of inflation.
D) fail to increase employment because individuals will anticipate it and take actions that will offset its impact.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 59 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
Which of the following models emphasizes the importance of credible, predictable government policies for maintaining full employment with low inflation?
A) the monetarist model
B) the Keynesian model
C) the supply-side model
D) the rational expectations model
A) the monetarist model
B) the Keynesian model
C) the supply-side model
D) the rational expectations model

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 59 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
If the government accelerates money supply growth and enlarges the budget deficit to stimulate aggregate demand, the rational expectations hypothesis indicates that decision makers will:
A) ignore the policy until it exerts an observable impact on prices, output, and employment.
B) quickly take steps to adjust their decision making in light of the more expansionary policies.
C) be fooled at the outset but eventually adjust their decision making in accordance with the change in policy.
D) be unaware that this policy change has been implemented until a higher rate of inflation is observed.
A) ignore the policy until it exerts an observable impact on prices, output, and employment.
B) quickly take steps to adjust their decision making in light of the more expansionary policies.
C) be fooled at the outset but eventually adjust their decision making in accordance with the change in policy.
D) be unaware that this policy change has been implemented until a higher rate of inflation is observed.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 59 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
Exhibit 17-4 Short-run and long-run Phillips curves
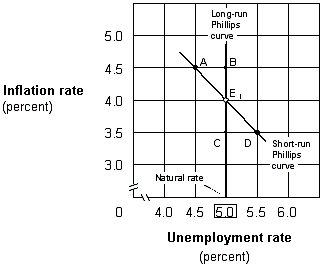
Suppose the economy in Exhibit 17-4 is at point E1, and the Fed increases the money supply. If people have rational expectations, then the economy will move:
A) to point A in the short run and point B in the long run.
B) directly to point B.
C) to point C in the short run and point D in the long run.
D) directly to point D.

Suppose the economy in Exhibit 17-4 is at point E1, and the Fed increases the money supply. If people have rational expectations, then the economy will move:
A) to point A in the short run and point B in the long run.
B) directly to point B.
C) to point C in the short run and point D in the long run.
D) directly to point D.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 59 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
The political business cycle refers to the possibility that:
A) incumbent politicians will be reelected regardless of the state of the economy.
B) politicians will manipulate the economy to enhance their chances of being reelected.
C) there are more recessions prior to elections.
D) recessions coincide with election years.
A) incumbent politicians will be reelected regardless of the state of the economy.
B) politicians will manipulate the economy to enhance their chances of being reelected.
C) there are more recessions prior to elections.
D) recessions coincide with election years.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 59 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
"Preannounced, stable policies to achieve a low and constant money supply growth and a balanced federal budget are therefore the best way to lower the inflation rate." This statement best illustrates the:
A) Keynesian theory.
B) rational expectations theory.
C) incomes policy.
D) supply-side theory.
A) Keynesian theory.
B) rational expectations theory.
C) incomes policy.
D) supply-side theory.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 59 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
Under adaptive expectations theory, a decrease in the short-run aggregate demand curve ____ the inflation rate and ____ the unemployment rate.
A) increases; increases
B) increases; decreases
C) decreases; increases
D) decreases; decreases
A) increases; increases
B) increases; decreases
C) decreases; increases
D) decreases; decreases

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 59 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
Which of the following is not an example of an incomes policy?
A) presidential jawboning
B) unemployment insurance
C) wage and price guidelines
D) wage and price controls
A) presidential jawboning
B) unemployment insurance
C) wage and price guidelines
D) wage and price controls

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 59 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
In the United States, the most recent use of wage and price controls occurred during the:
A) Nixon administration.
B) Carter administration.
C) Reagan administration.
D) Clinton administration.
A) Nixon administration.
B) Carter administration.
C) Reagan administration.
D) Clinton administration.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 59 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
Which of the following groups believes that government policy is undermined by people's incorporation of the anticipated consequences of the policy into their present decisions?
A) monetarist school
B) Keynesian school
C) supply-side school
D) rational expectations school
A) monetarist school
B) Keynesian school
C) supply-side school
D) rational expectations school

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 59 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
Exhibit 17-2 Aggregate demand and aggregate supply curves
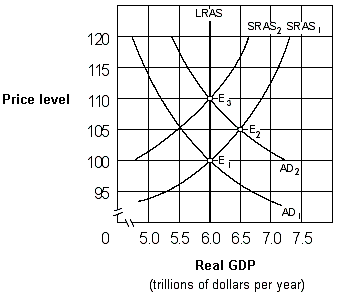
As shown in Exhibit 17-2, if people behave according to rational expectations theory, an increase in the aggregate demand curve from AD1 to AD2 will cause the price level to move:
A) directly from 100 to 105 and then remain at 105.
B) directly from 100 to 110 and then remain at 110.
C) from 100 to 105 initially and then eventually move back to 100.
D) from 100 to 105 initially and then eventually move to 110.

As shown in Exhibit 17-2, if people behave according to rational expectations theory, an increase in the aggregate demand curve from AD1 to AD2 will cause the price level to move:
A) directly from 100 to 105 and then remain at 105.
B) directly from 100 to 110 and then remain at 110.
C) from 100 to 105 initially and then eventually move back to 100.
D) from 100 to 105 initially and then eventually move to 110.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 59 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
Exhibit 17-2 Aggregate demand and aggregate supply curves
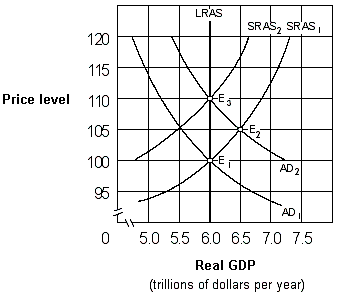
As shown in Exhibit 17-2, if people behave according to rational expectations theory, an increase in the aggregate demand curve from AD1 to AD2 will cause:
A) labor to adjust nominal wages sluggishly.
B) the aggregate supply curve to remain at SRAS1.
C) the price level to eventually rise from 100 to 110.
D) the price level to rise directly from 100 to 110 and GDP to remain constant at $6 trillion.

As shown in Exhibit 17-2, if people behave according to rational expectations theory, an increase in the aggregate demand curve from AD1 to AD2 will cause:
A) labor to adjust nominal wages sluggishly.
B) the aggregate supply curve to remain at SRAS1.
C) the price level to eventually rise from 100 to 110.
D) the price level to rise directly from 100 to 110 and GDP to remain constant at $6 trillion.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 59 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
According to rational expectations theory, which of the following is the best approach to lower the inflation rate?
A) preannounced stable government policies
B) unpredictable government policies
C) first predictable and then unpredictable government policies
D) None of these.
A) preannounced stable government policies
B) unpredictable government policies
C) first predictable and then unpredictable government policies
D) None of these.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 59 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
Exhibit 17-2 Aggregate demand and aggregate supply curves
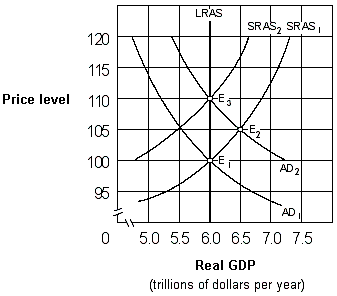
As shown in Exhibit 17-2, if people behave according to adaptive expectations theory, an increase in the aggregate demand curve from AD1 to AD2 will cause the economy to move:
A) directly from E1 to E3 and then remain at E3.
B) directly from E1 to E2 and then remain at E2.
C) from E1 to E2 initially and then eventually move back to E1.
D) from E1 to E2 initially and then eventually move to E3.

As shown in Exhibit 17-2, if people behave according to adaptive expectations theory, an increase in the aggregate demand curve from AD1 to AD2 will cause the economy to move:
A) directly from E1 to E3 and then remain at E3.
B) directly from E1 to E2 and then remain at E2.
C) from E1 to E2 initially and then eventually move back to E1.
D) from E1 to E2 initially and then eventually move to E3.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 59 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
Exhibit 17-3 Aggregate demand and aggregate supply curves
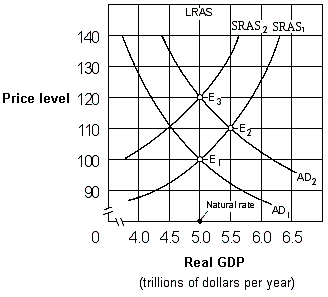
As shown in Exhibit 17-3, if people behave according to adaptive expectations theory, an increase in the aggregate demand curve from AD1 to AD2 will cause the economy to move:
A) from E1 to E2 initially and then eventually move back to E1.
B) directly from E1 to E2 and then remain at E2.
C) directly from E1 to E3 and then remain at E3.
D) from E1 to E2 initially and then eventually move to E3.

As shown in Exhibit 17-3, if people behave according to adaptive expectations theory, an increase in the aggregate demand curve from AD1 to AD2 will cause the economy to move:
A) from E1 to E2 initially and then eventually move back to E1.
B) directly from E1 to E2 and then remain at E2.
C) directly from E1 to E3 and then remain at E3.
D) from E1 to E2 initially and then eventually move to E3.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 59 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
Exhibit 17-3 Aggregate demand and aggregate supply curves
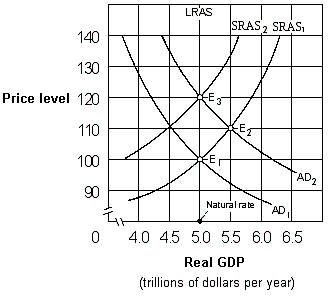
As shown in Exhibit 17-3, if people behave according to adaptive expectations theory, an increase in the aggregate demand curve from AD1 to AD2 will cause the price level to move:
A) from 100 to 110 initially and then eventually move back to 100.
B) directly from 100 to 110 and then remain at 110.
C) directly from 100 to 120 and then remain at 120.
D) from 100 to 110 initially and then eventually move to 120.

As shown in Exhibit 17-3, if people behave according to adaptive expectations theory, an increase in the aggregate demand curve from AD1 to AD2 will cause the price level to move:
A) from 100 to 110 initially and then eventually move back to 100.
B) directly from 100 to 110 and then remain at 110.
C) directly from 100 to 120 and then remain at 120.
D) from 100 to 110 initially and then eventually move to 120.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 59 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
Exhibit 17-5 Short-run and long-run Phillips curve
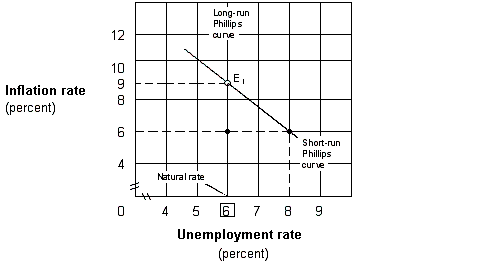
Suppose the government shown in Exhibit 17-5 uses contractionary monetary policy to reduce inflation from 9 to 6 percent. If people have rational expectations, then:
A) the economy will remain stuck at point E1.
B) the natural rate will permanently increase to 8 percent.
C) unemployment will rise to 8 percent in the short run.
D) unemployment will remain at 6 percent as the inflation rate falls.

Suppose the government shown in Exhibit 17-5 uses contractionary monetary policy to reduce inflation from 9 to 6 percent. If people have rational expectations, then:
A) the economy will remain stuck at point E1.
B) the natural rate will permanently increase to 8 percent.
C) unemployment will rise to 8 percent in the short run.
D) unemployment will remain at 6 percent as the inflation rate falls.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 59 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
Which of the following statements is true ?
A) A political business cycle is one created by the incentive for politicians to make policies in accordance with benefit-cost analysis.
B) Adaptive expectations theory argues that the best indicator of the future is all of the available information.
C) Incomes policies tend to be very effective over time.
D) Incomes policies include jawboning, wage-price guidelines, and wage-price controls.
A) A political business cycle is one created by the incentive for politicians to make policies in accordance with benefit-cost analysis.
B) Adaptive expectations theory argues that the best indicator of the future is all of the available information.
C) Incomes policies tend to be very effective over time.
D) Incomes policies include jawboning, wage-price guidelines, and wage-price controls.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 59 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
Exhibit 17-2 Aggregate demand and aggregate supply curves
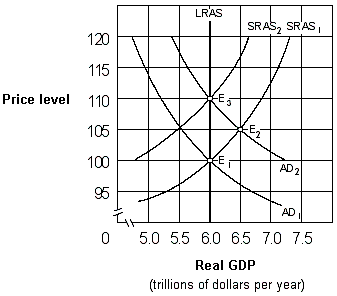
As shown in Exhibit 17-2, if people behave according to adaptive expectations theory, an increase in the aggregate demand curve from AD1 to AD2 will cause:
A) labor to adjust nominal wages immediately.
B) the aggregate supply curve to shift from SRAS1 to SRAS2
C) the price level to eventually fall from 110 to 100.
D) real GDP to rise from $6 trillion to $6.5 trillion permanently.

As shown in Exhibit 17-2, if people behave according to adaptive expectations theory, an increase in the aggregate demand curve from AD1 to AD2 will cause:
A) labor to adjust nominal wages immediately.
B) the aggregate supply curve to shift from SRAS1 to SRAS2
C) the price level to eventually fall from 110 to 100.
D) real GDP to rise from $6 trillion to $6.5 trillion permanently.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 59 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
According to adaptive expectations theory, which of the following would be the result of expansionary monetary and fiscal policies?
A) The economy self-corrects to the natural rate of unemployment.
B) There is a long-run trade off between inflation and unemployment.
C) The inflation rate falls.
D) These policies can succeed in reducing the unemployment rate.
A) The economy self-corrects to the natural rate of unemployment.
B) There is a long-run trade off between inflation and unemployment.
C) The inflation rate falls.
D) These policies can succeed in reducing the unemployment rate.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 59 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
Wage and price controls imposed for an extended period of time are likely to result in:
A) surpluses.
B) efficient markets.
C) black markets.
D) lower inflation rates once the controls are lifted.
A) surpluses.
B) efficient markets.
C) black markets.
D) lower inflation rates once the controls are lifted.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 59 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
Under the adaptive expectations hypothesis, which of the following is the effect of a shift to a more expansionary monetary policy?
A) In the short run, the real rate of output will be unaffected, but in the long run, it will increase.
B) In the short run, the unemployment rate will decrease, but in the long run, it will self correct to the natural rate of unemployment.
C) There will be a permanent increase in the real rate of output, but the inflation rate will also be a little higher.
D) In the short run, the impact on the real rate of output is uncertain, but in the long run, output will increase.
A) In the short run, the real rate of output will be unaffected, but in the long run, it will increase.
B) In the short run, the unemployment rate will decrease, but in the long run, it will self correct to the natural rate of unemployment.
C) There will be a permanent increase in the real rate of output, but the inflation rate will also be a little higher.
D) In the short run, the impact on the real rate of output is uncertain, but in the long run, output will increase.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 59 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
Exhibit 17-2 Aggregate demand and aggregate supply curves
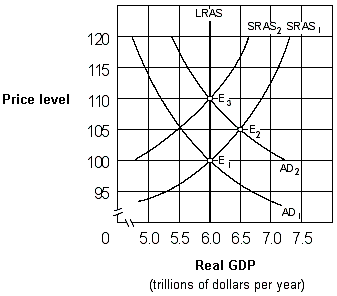
As shown in Exhibit 17-2, if people behave according to rational expectations theory, an increase in the aggregate demand curve from AD1 to AD2 will cause the economy to move:
A) directly from E1 to E3 and then remain at E3.
B) directly from E1 to E2 and then remain at E2.
C) from E1 to E2 initially and then eventually move back to E1.
D) from E1 to E2 initially and then eventually move to E3.

As shown in Exhibit 17-2, if people behave according to rational expectations theory, an increase in the aggregate demand curve from AD1 to AD2 will cause the economy to move:
A) directly from E1 to E3 and then remain at E3.
B) directly from E1 to E2 and then remain at E2.
C) from E1 to E2 initially and then eventually move back to E1.
D) from E1 to E2 initially and then eventually move to E3.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 59 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
Exhibit 17-5 Short-run and long-run Phillips curve
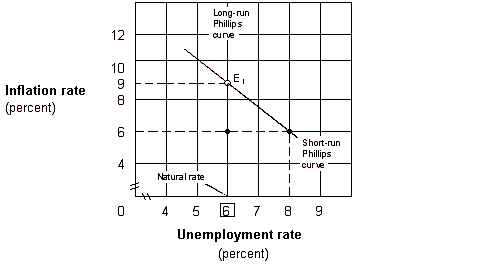
Suppose the government shown in Exhibit 17-5 uses contractionary monetary policy to reduce inflation from 9 to 6 percent. If people have adaptive expectations, then:
A) the economy will remain stuck at point E1.
B) the natural rate will permanently increase to 8 percent.
C) unemployment will rise to 8 percent in the short run.
D) unemployment will remain at 6 percent as the inflation rate falls.

Suppose the government shown in Exhibit 17-5 uses contractionary monetary policy to reduce inflation from 9 to 6 percent. If people have adaptive expectations, then:
A) the economy will remain stuck at point E1.
B) the natural rate will permanently increase to 8 percent.
C) unemployment will rise to 8 percent in the short run.
D) unemployment will remain at 6 percent as the inflation rate falls.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 59 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
Most economists consider the case for jawboning to control inflation is strongest when this policy is used:
A) for an extended period of time.
B) in combination with a credible threat against a firm's profits.
C) by a president who has no credible threat against a firm's profits.
D) to increase the minimum wage.
A) for an extended period of time.
B) in combination with a credible threat against a firm's profits.
C) by a president who has no credible threat against a firm's profits.
D) to increase the minimum wage.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 59 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
Exhibit 17-2 Aggregate demand and aggregate supply curves
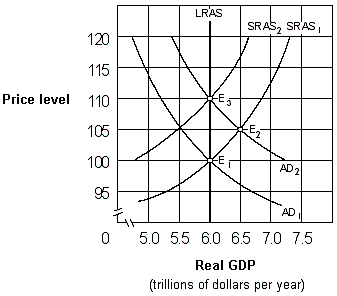
As shown in Exhibit 17-2, if people behave according to adaptive expectations theory, an increase in the aggregate demand curve from AD1 to AD2 will cause the price level to move:
A) directly from 100 to 110 and then remain at 110.
B) directly from 100 to 105 and then remain at 105.
C) from 100 to 105 initially and then eventually move back to 100.
D) from 100 to 105 initially and then eventually move to 110.

As shown in Exhibit 17-2, if people behave according to adaptive expectations theory, an increase in the aggregate demand curve from AD1 to AD2 will cause the price level to move:
A) directly from 100 to 110 and then remain at 110.
B) directly from 100 to 105 and then remain at 105.
C) from 100 to 105 initially and then eventually move back to 100.
D) from 100 to 105 initially and then eventually move to 110.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 59 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



