Deck 2: Validating an Xml Document
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/91
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 2: Validating an Xml Document
1
Attribute-list declarations can be located anywhere within the document type declaration.
True
2
An attribute declared using the NAME token must have a value equal to the value of an ID attribute located somewhere in the same document.
False
3
Generally, elements contain parsed character data or child elements.
True
4
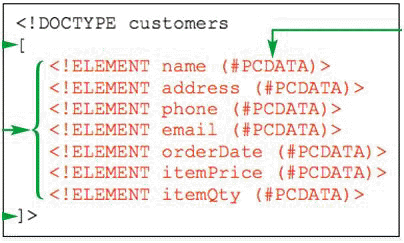
An element declaration employing the #PCDATA content model shown in the accompanying figure does not allow for child elements.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
An XML element is not limited to either parsed character data or child elements.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
A modifying symbol is placed directly before the element it modifies.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7

As shown in the accompanying figure, the external subset would define some basic rules for all of the documents, and the internal subset would define rules that are specific to each document.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
In a valid document, at least two elements must be declared in the DTD.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
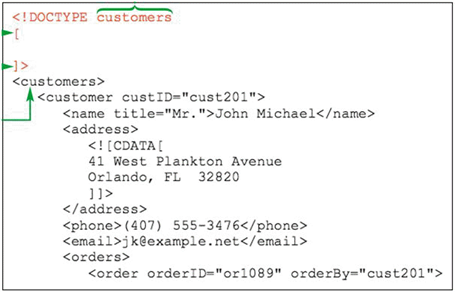
The DOCTYPE declaration has to be added to a document epilog as shown in the accompanying figure.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
If a processor encounters more than one declaration for the same attribute, it ignores the first statement.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
Entities can reference content found either in an external file or within the DTD itself.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
A(n) notation must supply a name for the data type and provide clues about how applications should handle the data.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
To test for validity, an XML parser must be able to compare the XML document with the rules established in the DTD.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
A DTD can be used to enforce a specific data structure on document content.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
One way to create a valid document is to design a document type definition, or DTD, for the document.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
It is best not to work with mixed content if you want a tightly structured document.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
The #FIXED attribute default is used to indicate that the use of an attribute is optional.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
An entity whose content is found within the DTD is known as a(n) external entity.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
For a DTD to validate either binary data, such as images or video clips, or character data that is not well formed, you need to work with parsed entities.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
Attribute values do not allow you to control the format of the character data.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
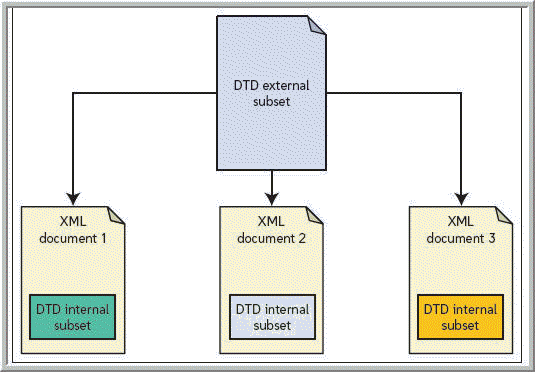
The locations of external subsets like that shown in the accompanying figure can be defined using _____ types of identifiers.
A) two
B) three
C) four
D) six

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
The content-model value can be one of _____ specific keywords or one of two content descriptions.
A) five
B) four
C) three
D) two
A) five
B) four
C) three
D) two

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
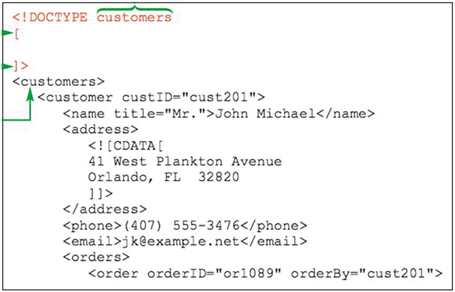
The DOCTYPE declaration has to be added to the document _____, after the XML declaration and before the document's root element, as shown in the accompanying figure.
A) prolog
B) epilog
C) body
D) any of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
The _____ content model is reserved for elements that store no content.
A) NULL
B) NONE
C) EMPTY
D) VOID
A) NULL
B) NONE
C) EMPTY
D) VOID

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
Element names can contain which of the following?
A) reserved symbols
B) spaces
C) numbers
D) All of these are correct.
A) reserved symbols
B) spaces
C) numbers
D) All of these are correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
A DTD is entered into the document in a statement called a document _____ declaration.
A) basis
B) element
C) index
D) type
A) basis
B) element
C) index
D) type

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
To create a parsed entity that references content from an external file using a system _____, you use the declaration .
A) identifier
B) qualifier
C) index
D) locator
A) identifier
B) qualifier
C) index
D) locator

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
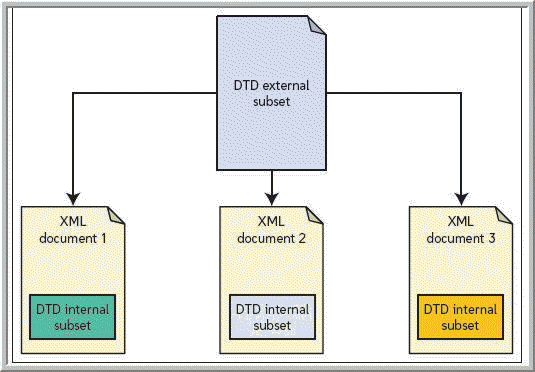
Which of the following is a part into which a DTD like the one in the accompanying figure can be divided?
A) internal subset
B) system identifier
C) root element
D) public identifier

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
The _____ value for the content model in an element declaration means an element cannot store any content.
A) EMPTY
B) NULL
C) NONE
D) mixed
A) EMPTY
B) NULL
C) NONE
D) mixed

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
The _____ value for the content model in an element declaration means the element can contain only parsed character data.
A) parsed
B) mixed
C) #PCDATA
D) elements
A) parsed
B) mixed
C) #PCDATA
D) elements

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
How many DOCTYPE declarations can there be in an XML document?
A) 1
B) 2
C) 3
D) There is no limit.
A) 1
B) 2
C) 3
D) There is no limit.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
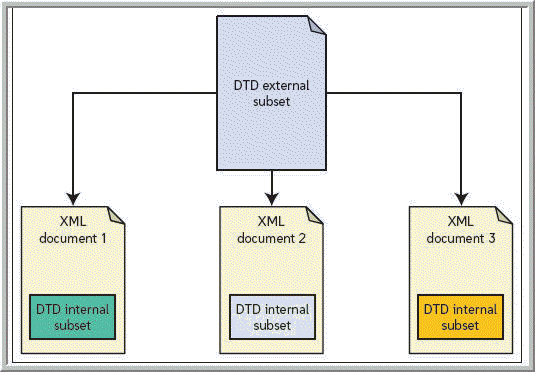
Which of the following is a type of identifier for the location of an external subset like the one in the accompanying figure?
A) internal
B) undeclared
C) qualified
D) system

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
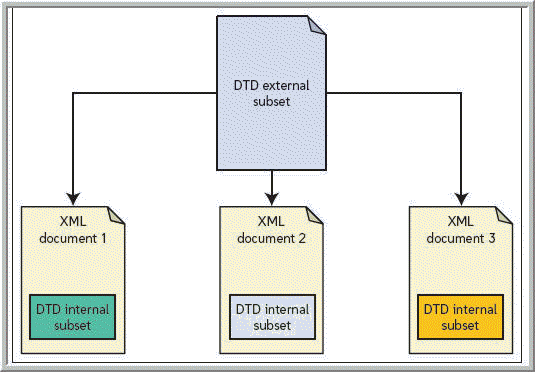
Which of the following is a part into which a DTD like the one in the accompanying figure can be divided?
A) element declaration
B) strict declaration
C) external subset
D) root element

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
You can divide a DTD into _____ parts.
A) two
B) three
C) five
D) seven
A) two
B) three
C) five
D) seven

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
One way to create a valid document is to design a(n) _____ for the document.
A) data structure
B) DTD
C) XMLNS
D) validity glossary
A) data structure
B) DTD
C) XMLNS
D) validity glossary

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
The _____ value for the content model in an element declaration means the element can contain both parsed character data and child elements.
A) mixed
B) elements
C) #PCDATA with sequence
D) BOTH
A) mixed
B) elements
C) #PCDATA with sequence
D) BOTH

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
An element _____ declaration specifies an element's name and indicates what kind of content the element can contain.
A) content
B) model
C) type
D) detail
A) content
B) model
C) type
D) detail

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
An element declaration can specify which of the following?
A) an element's name
B) what kind of content the element can contain
C) the order in which elements appear in the document
D) All of the these are correct.
A) an element's name
B) what kind of content the element can contain
C) the order in which elements appear in the document
D) All of the these are correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
Most standard XML vocabularies have _____ identifiers.
A) public
B) strict
C) system
D) master
A) public
B) strict
C) system
D) master

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
A(n) _____ is a collection of rules that define the content and structure of an XML document.
A) data structure
B) DTD
C) XMLNS
D) validity glossary
A) data structure
B) DTD
C) XMLNS
D) validity glossary

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
The _____ attribute default means that the attribute must appear with every occurrence of the element.
A) #MANDATED
B) #FIXED
C) #REQUIRED
D) #IMPLIED
A) #MANDATED
B) #FIXED
C) #REQUIRED
D) #IMPLIED

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
To test for validity, an XML parser must be able to compare your XML document with the _____ rules you set up in the DTD.
A) validity
B) integration
C) persistence
D) interpolation
A) validity
B) integration
C) persistence
D) interpolation

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
The attributes of the attribute value type _____ contain a list of entities separated by white space.
A) ENTITY
B) enumerated list
C) ENTITIES
D) ID
A) ENTITY
B) enumerated list
C) ENTITIES
D) ID

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
The attributes of the attribute value type _____ contain an accepted XML name.
A) ID
B) NMTOKEN
C) IDREF
D) ENTITY
A) ID
B) NMTOKEN
C) IDREF
D) ENTITY

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
Once an ID value has been declared in a document, other attribute values can refer to it using the _____ token.
A) name
B) entity
C) IDREF
D) value
A) name
B) entity
C) IDREF
D) value

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
Content referenced by an entity can be either _____ .
A) persistent or consistent
B) parsed or unparsed
C) static or dynamic
D) well-formed or unique
A) persistent or consistent
B) parsed or unparsed
C) static or dynamic
D) well-formed or unique

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
In a DTD, a _____ symbol specifies the number of occurrences of each element.
A) specifying
B) quantifier
C) count
D) modifying
A) specifying
B) quantifier
C) count
D) modifying

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
XML parsers interpret the _____ symbol as a reference to another entity and attempt to resolve the reference.
A) &
B) %
C) #
D) !
A) &
B) %
C) #
D) !

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
The _____ symbol is used for inserting parameter entities.
A) &
B) %
C) #
D) !
A) &
B) %
C) #
D) !

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
The _____ symbol indicates that an element occurs at least once.
A) ^
B) ?
C) +
D) &
A) ^
B) ?
C) +
D) &

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
The _____ content model allows an element to store any type of content.
A) OPEN
B) mixed
C) #PCDATA
D) ANY
A) OPEN
B) mixed
C) #PCDATA
D) ANY

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
An entity that references content that cannot be interpreted by the XML parser is a(n) _____ entity.
A) internal
B) well-formed
C) unparsed
D) dynamic
A) internal
B) well-formed
C) unparsed
D) dynamic

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
The syntax for creating a conditional section is _____.
A) ]}>
B) }}>
C) ]]>
D) ]]>
A) ]}>
B) }}>
C) ]]>
D) ]]>

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
The declaration _____ would permit this element in an XML document: Lea Ziegler .
A)
B)
C)
D)
A)
B)
C)
D)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
The NMTOKEN data types cannot contain _____ .
A) hyphens
B) colons
C) white space
D) Any of the above.
A) hyphens
B) colons
C) white space
D) Any of the above.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
If an entity's content is found within the DTD, the entity is known as a(n) _____ entity.
A) internal
B) persistent
C) contained
D) consistent
A) internal
B) persistent
C) contained
D) consistent

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
While very flexible, elements with _____ content do not add much defined structure to a document.
A) dynamic
B) mixed
C) static
D) integrated
A) dynamic
B) mixed
C) static
D) integrated

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
Any attribute that has been declared by the data type ID is a candidate for an ID _____.
A) property
B) element
C) link
D) reference
A) property
B) element
C) link
D) reference

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
Which of the following is accomplished by an attribute-list declaration?
A) It lists the names of all the attributes associated with a specific element.
B) It specifies the data type of each attribute.
C) It indicates whether each attribute is required or optional.
D) All of these are correct.
A) It lists the names of all the attributes associated with a specific element.
B) It specifies the data type of each attribute.
C) It indicates whether each attribute is required or optional.
D) All of these are correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
When the _____ symbol is used with a choice list, the element can contain any number of occurrences of child elements or PCDATA, or it can contain no content at all.
A) +
B) *
C) ?
D) ^
A) +
B) *
C) ?
D) ^

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
Attributes that are limited to a set of possible values are known as _____ types.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
Case-based Critical Thinking Questions Case 2-2
Rosalind wants to add attribute declarations to her DTD, and she turns to you for information about the possible attribute types.
Rosalind wants to declare a "coursenum" attribute, the values of which will be unique within the document. Which attribute type should she use?
A) CDATA
B) UNIQUE
C) ID
D) IDREF
Rosalind wants to add attribute declarations to her DTD, and she turns to you for information about the possible attribute types.
Rosalind wants to declare a "coursenum" attribute, the values of which will be unique within the document. Which attribute type should she use?
A) CDATA
B) UNIQUE
C) ID
D) IDREF

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
Case-based Critical Thinking Questions Case 2-1
Casey is using XML to store information about the students in the science classes that he teaches. He wants to design a DTD that he can use to validate the XML documents that he uses for this purpose, and he comes to you for help.
You tell Casey that he must declare the DTD using a DOCTYPE statement. Where should the DOCTYPE go?
A) before the XML declaration
B) within the XML declaration
C) after the XML declaration and before the document's root element
D) after the document's root element
Casey is using XML to store information about the students in the science classes that he teaches. He wants to design a DTD that he can use to validate the XML documents that he uses for this purpose, and he comes to you for help.
You tell Casey that he must declare the DTD using a DOCTYPE statement. Where should the DOCTYPE go?
A) before the XML declaration
B) within the XML declaration
C) after the XML declaration and before the document's root element
D) after the document's root element

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
Case-based Critical Thinking Questions Case 2-2
Rosalind wants to add attribute declarations to her DTD, and she turns to you for information about the possible attribute types.
You tell Rosalind about the CDATA attribute type. Which of the following attribute values would NOT be allowed for an attribute of this type?
A) 25.99
B) New York, NY
C) Bob & Jenny
D) yellow
Rosalind wants to add attribute declarations to her DTD, and she turns to you for information about the possible attribute types.
You tell Rosalind about the CDATA attribute type. Which of the following attribute values would NOT be allowed for an attribute of this type?
A) 25.99
B) New York, NY
C) Bob & Jenny
D) yellow

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
In a(n) _____ subset, the declarations are placed in an external file that is accessed from the XML document.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
A(n) _____ is added to the DOCTYPE declaration to provide information about the DTD to the XML parser.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
DTDs use more general numbering with a(n) _____ symbol, which specifies the number of occurrences of each element.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
Case-based Critical Thinking Questions Case 2-2
Rosalind wants to add attribute declarations to her DTD, and she turns to you for information about the possible attribute types.
You help Rosalind write the declaration of an attribute named "credits" of an element named "course." This optional attribute should contain character data, and a value of 4 should be used if an attribute value is not specified. Which of the following is an appropriate declaration of this attribute?
A)
B)
C)
D)
Rosalind wants to add attribute declarations to her DTD, and she turns to you for information about the possible attribute types.
You help Rosalind write the declaration of an attribute named "credits" of an element named "course." This optional attribute should contain character data, and a value of 4 should be used if an attribute value is not specified. Which of the following is an appropriate declaration of this attribute?
A)
B)
C)
D)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
_____ content allows an element to contain both parsed character data and child elements.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
Case-based Critical Thinking Questions Case 2-1
Casey is using XML to store information about the students in the science classes that he teaches. He wants to design a DTD that he can use to validate the XML documents that he uses for this purpose, and he comes to you for help.
Casey needs to declare an "address" element that can be used to store a student's address. If he intends to store the address as parsed character data, which of the following is an appropriate declaration for this element?
A)
B)
C)
D)
Casey is using XML to store information about the students in the science classes that he teaches. He wants to design a DTD that he can use to validate the XML documents that he uses for this purpose, and he comes to you for help.
Casey needs to declare an "address" element that can be used to store a student's address. If he intends to store the address as parsed character data, which of the following is an appropriate declaration for this element?
A)
B)
C)
D)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
External DTDs work the same way as _____ style sheets.
A) dynamic
B) external
C) embedded
D) inline
A) dynamic
B) external
C) embedded
D) inline

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72
A(n) _____ content model is a list of child elements that follow a defined order.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73
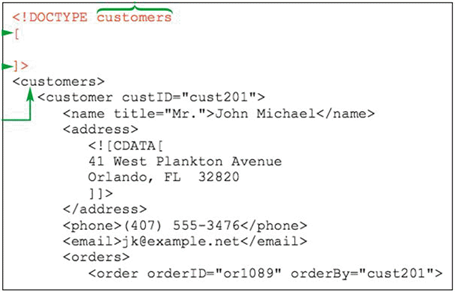
A DOCTYPE declaration like the one in the accompanying figure is also known as a(n) _____ .

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
74
A(n) _____ specifies an element's name and indicates what kind of content it can contain.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
75
Case-based Critical Thinking Questions Case 2-2
Rosalind wants to add attribute declarations to her DTD, and she turns to you for information about the possible attribute types.
Rosalind wants to define a required attribute called "semester" of an element named "course." She wants to ensure that this attribute takes on one of three values: fall, spring, or summer. Which type of attribute should she use?
A) CDATA
B) an enumerated type
C) a tokenized type
D) a value-list type
Rosalind wants to add attribute declarations to her DTD, and she turns to you for information about the possible attribute types.
Rosalind wants to define a required attribute called "semester" of an element named "course." She wants to ensure that this attribute takes on one of three values: fall, spring, or summer. Which type of attribute should she use?
A) CDATA
B) an enumerated type
C) a tokenized type
D) a value-list type

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
76
Case-based Critical Thinking Questions Case 2-1
Casey is using XML to store information about the students in the science classes that he teaches. He wants to design a DTD that he can use to validate the XML documents that he uses for this purpose, and he comes to you for help.
Casey next wants to write a declaration for an element named "advanced" that he will use to record the fact that a student is advanced. This element will not contain any content. Which of the following is an appropriate element declaration for this element?
A)
B)
C)
D)
Casey is using XML to store information about the students in the science classes that he teaches. He wants to design a DTD that he can use to validate the XML documents that he uses for this purpose, and he comes to you for help.
Casey next wants to write a declaration for an element named "advanced" that he will use to record the fact that a student is advanced. This element will not contain any content. Which of the following is an appropriate element declaration for this element?
A)
B)
C)
D)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
77
Case-based Critical Thinking Questions Case 2-1
Casey is using XML to store information about the students in the science classes that he teaches. He wants to design a DTD that he can use to validate the XML documents that he uses for this purpose, and he comes to you for help.
After you teach Casey about declarations for elements with child elements, he constructs the element declaration . Given this declaration, which of the following is NOT a valid "class" element?
A)Beginner Drawing
B)One-on-One Painting
C)Oil Painting brushstrokes
D)Working with Clay
Casey is using XML to store information about the students in the science classes that he teaches. He wants to design a DTD that he can use to validate the XML documents that he uses for this purpose, and he comes to you for help.
After you teach Casey about declarations for elements with child elements, he constructs the element declaration . Given this declaration, which of the following is NOT a valid "class" element?
A)
B)
C)
D)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
78
Case-based Critical Thinking Questions Case 2-1
Casey is using XML to store information about the students in the science classes that he teaches. He wants to design a DTD that he can use to validate the XML documents that he uses for this purpose, and he comes to you for help.
Casey wants to include a declaration for an element named "note" that can contain any type of content. Which of the following is an appropriate element declaration for this element?
A)
B)
C)
D)
Casey is using XML to store information about the students in the science classes that he teaches. He wants to design a DTD that he can use to validate the XML documents that he uses for this purpose, and he comes to you for help.
Casey wants to include a declaration for an element named "note" that can contain any type of content. Which of the following is an appropriate element declaration for this element?
A)
B)
C)
D)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
79
The chunks into which a DTD can be broken with parameter entities are known as _____ .
A) components
B) blurbs
C) links
D) modules
A) components
B) blurbs
C) links
D) modules

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
80
Case-based Critical Thinking Questions Case 2-2
Rosalind wants to add attribute declarations to her DTD, and she turns to you for information about the possible attribute types.
You help Rosalind write the declaration of the "semester" attribute described in the previous problem. Which of the following is an appropriate declaration for this attribute?
A)
B)
C)
D)
Rosalind wants to add attribute declarations to her DTD, and she turns to you for information about the possible attribute types.
You help Rosalind write the declaration of the "semester" attribute described in the previous problem. Which of the following is an appropriate declaration for this attribute?
A)
B)
C)
D)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



