Deck 14: Aggregate Demand and Supply
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/83
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 14: Aggregate Demand and Supply
1
Nominal wages are assumed fixed in the short run because:
A) workers have wages stated in their contracts.
B) of minimum wage laws.
C) workers are unaware of short-run changes in their real wages.
D) all of the above are true.
E) none of the above are true.
A) workers have wages stated in their contracts.
B) of minimum wage laws.
C) workers are unaware of short-run changes in their real wages.
D) all of the above are true.
E) none of the above are true.
D
2
The short-run aggregate supply curve is upward-sloping because:
A) the quantity of real output supplied is inversely related to aggregate supply.
B) nominal incomes are fixed.
C) of the conjunction between the incremental capital-output ratio and the interbank offer rate.
D) an increase in price will increase the supply of money.
A) the quantity of real output supplied is inversely related to aggregate supply.
B) nominal incomes are fixed.
C) of the conjunction between the incremental capital-output ratio and the interbank offer rate.
D) an increase in price will increase the supply of money.
B
3
In the short run, an increase in the price level causes which of the following:
A) A rightward shift in the aggregate demand curve.
B) A leftward shift in the short-run aggregate supply curve.
C) A rightward shift in the short-run aggregate supply curve.
D) A movement upward along the short-run aggregate supply curve.
A) A rightward shift in the aggregate demand curve.
B) A leftward shift in the short-run aggregate supply curve.
C) A rightward shift in the short-run aggregate supply curve.
D) A movement upward along the short-run aggregate supply curve.
D
4
In the long run, wages and prices are considered to be:
A) fixed.
B) sticky.
C) flexible.
D) unstable.
A) fixed.
B) sticky.
C) flexible.
D) unstable.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 83 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
An aggregate supply curve with a positive slope is associated with an economy in which:
A) input prices and final goods prices always change by the same amount.
B) firms expect output prices to be unaffected by changes in input prices.
C) nominal wages and salaries do not change much in the short run.
D) firms expect consumer demand to be unaffected by changes in prices of final goods.
A) input prices and final goods prices always change by the same amount.
B) firms expect output prices to be unaffected by changes in input prices.
C) nominal wages and salaries do not change much in the short run.
D) firms expect consumer demand to be unaffected by changes in prices of final goods.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 83 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
A short-run aggregate supply curve (SRAS) assumes:
A) the CPI is fixed.
B) each point on the SRAS is potential real GDP.
C) fixed or sticky nominal wages.
D) nominal wages vary directly with price changes.
A) the CPI is fixed.
B) each point on the SRAS is potential real GDP.
C) fixed or sticky nominal wages.
D) nominal wages vary directly with price changes.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 83 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
In the long run, an increase in aggregate demand causes the price level to ____ and the long-run aggregate supply curve to ____.
A) decrease; decrease
B) increase; increase
C) decrease; remain unchanged
D) increase; remain unchanged
A) decrease; decrease
B) increase; increase
C) decrease; remain unchanged
D) increase; remain unchanged

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 83 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
Which of the following explains why higher prices in the goods and services market measured by the CPI leads to an upward-sloping aggregate supply curve?
A) The higher prices will temporarily improve profit margins because the cost of wages and salaries are fixed in the short run.
B) The higher prices will reduce the purchasing power of the fixed quantity of money and, thereby, stimulate additional output.
C) The higher prices will expand the economy's resource base and, thereby, stimulate additional output.
D) The higher prices will improve technology and, thereby, stimulate additional output.
A) The higher prices will temporarily improve profit margins because the cost of wages and salaries are fixed in the short run.
B) The higher prices will reduce the purchasing power of the fixed quantity of money and, thereby, stimulate additional output.
C) The higher prices will expand the economy's resource base and, thereby, stimulate additional output.
D) The higher prices will improve technology and, thereby, stimulate additional output.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 83 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
The short-run aggregate supply curve (SRAS) is the amount of real GDP:
A) produced at various price levels.
B) produced at various savings rate levels.
C) purchased at various price levels.
D) purchased at various saving rate levels.
A) produced at various price levels.
B) produced at various savings rate levels.
C) purchased at various price levels.
D) purchased at various saving rate levels.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 83 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
In the short run, wages are assumed to be:
A) constant.
B) sticky.
C) inflexible.
D) all of the above are true.
A) constant.
B) sticky.
C) inflexible.
D) all of the above are true.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 83 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
If nominal wages and salaries are fixed as firms change product prices, the short-run aggregate supply curve is:
A) vertical.
B) horizontal.
C) negatively sloped.
D) positively sloped.
A) vertical.
B) horizontal.
C) negatively sloped.
D) positively sloped.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 83 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
Which of the following causes a leftward shift in the short-run aggregate supply curve?
A) An increase of goods prices while nominal incomes are unchanged.
B) An increase in nominal incomes.
C) An increase of full-employment real GDP.
D) An increase of personal consumption expenditures while the price level is unchanged.
E) An increase of personal consumption expenditures while full-employment real GDP is unchanged.
A) An increase of goods prices while nominal incomes are unchanged.
B) An increase in nominal incomes.
C) An increase of full-employment real GDP.
D) An increase of personal consumption expenditures while the price level is unchanged.
E) An increase of personal consumption expenditures while full-employment real GDP is unchanged.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 83 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
An explanation for why the short-run aggregate supply curve is upward-sloping is because:
A) the quantity of real output supplied is inversely related to the aggregate supply curve.
B) nominal incomes are fixed.
C) the capital-output ratio is fixed.
D) an increase in price will increase the marginal aggregate output.
A) the quantity of real output supplied is inversely related to the aggregate supply curve.
B) nominal incomes are fixed.
C) the capital-output ratio is fixed.
D) an increase in price will increase the marginal aggregate output.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 83 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
In the long run, a decrease in aggregate demand causes the price level to ____ and the long-run aggregate supply curve to ____.
A) decrease; decrease
B) increase; increase
C) decrease; remain unchanged
D) increase; remain unchanged
A) decrease; decrease
B) increase; increase
C) decrease; remain unchanged
D) increase; remain unchanged

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 83 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
In the short run, a price increase in the goods and services market measured by the CPI will:
A) increase the purchasing power of money.
B) improve producer profits and, thereby, induce suppliers to expand output.
C) increase resource prices, lower profits, and lead to a decline in output.
D) reduce the natural rate of unemployment.
A) increase the purchasing power of money.
B) improve producer profits and, thereby, induce suppliers to expand output.
C) increase resource prices, lower profits, and lead to a decline in output.
D) reduce the natural rate of unemployment.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 83 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
The long-run aggregate supply curve (LRAS) is:
A) a vertical curve that relates the level of real GDP produced to the price level in the long run.
B) an upward sloping curve that relates the level of real GDP produced to the price level in the long run.
C) an infinite curve that relates the level of real GDP produced to the price level in the long run.
D) none of the above are true.
A) a vertical curve that relates the level of real GDP produced to the price level in the long run.
B) an upward sloping curve that relates the level of real GDP produced to the price level in the long run.
C) an infinite curve that relates the level of real GDP produced to the price level in the long run.
D) none of the above are true.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 83 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
The adjustment of nominal incomes to changes in the price level (CPI) is fixed because of the:
A) volatility of investment spending.
B) existence of long-term contracts.
C) complete information possessed by workers.
D) all of the above.
A) volatility of investment spending.
B) existence of long-term contracts.
C) complete information possessed by workers.
D) all of the above.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 83 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
The long-run aggregate supply curve is:
A) upward sloping.
B) downward sloping.
C) vertical at full-employment real GDP.
D) horizontal at full-employment real GDP.
A) upward sloping.
B) downward sloping.
C) vertical at full-employment real GDP.
D) horizontal at full-employment real GDP.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 83 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
One reason for the short-run aggregate supply curve (SRAS) is:
A) a fixed CPI market basket.
B) perfect knowledge of workers.
C) fixed-wage contracts.
D) the upward-sloping production function.
A) a fixed CPI market basket.
B) perfect knowledge of workers.
C) fixed-wage contracts.
D) the upward-sloping production function.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 83 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
The short-run aggregate supply curve is:
A) upward-sloping.
B) downward-sloping.
C) horizontal.
D) vertical.
A) upward-sloping.
B) downward-sloping.
C) horizontal.
D) vertical.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 83 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
In the self-correcting AD-AS model, the economy's short-run equilibrium position is indicated by the intersection of which two curves?
A) Short-run aggregate supply and long-run aggregate supply.
B) Short-run aggregate supply and aggregate demand.
C) Long-run aggregate supply and aggregate demand.
D) Long-run aggregate demand and short-run personal consumption expenditures curve.
E) Short-run aggregate demand and long-run personal consumption expenditures curve.
A) Short-run aggregate supply and long-run aggregate supply.
B) Short-run aggregate supply and aggregate demand.
C) Long-run aggregate supply and aggregate demand.
D) Long-run aggregate demand and short-run personal consumption expenditures curve.
E) Short-run aggregate demand and long-run personal consumption expenditures curve.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 83 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
The full-employment level of real GDP is the level which can be produced with:
A) given technology and productive resources.
B) frictional and structural unemployment equal to zero.
C) cyclical unemployment equal to zero.
D) both a and b.
E) both a and c.
A) given technology and productive resources.
B) frictional and structural unemployment equal to zero.
C) cyclical unemployment equal to zero.
D) both a and b.
E) both a and c.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 83 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
Which of the following causes a leftward shift in the short-run aggregate supply curve?
A) An increase of goods prices while nominal incomes are unchanged.
B) An increase in nominal incomes (wages and salaries).
C) An increase of full-employment real GDP.
D) An increase of personal consumption expenditures while the price level is unchanged.
E) An increase of personal consumption expenditures while full-employment real GDP is unchanged.
A) An increase of goods prices while nominal incomes are unchanged.
B) An increase in nominal incomes (wages and salaries).
C) An increase of full-employment real GDP.
D) An increase of personal consumption expenditures while the price level is unchanged.
E) An increase of personal consumption expenditures while full-employment real GDP is unchanged.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 83 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
Which of the following would produce a rightward shift in the short-run aggregate supply curve?
A) An increase in consumption spending.
B) A decrease in investment.
C) A decrease in government spending.
D) A decrease in net exports.
E) None of the above.
A) An increase in consumption spending.
B) A decrease in investment.
C) A decrease in government spending.
D) A decrease in net exports.
E) None of the above.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 83 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
Economic growth is measured by the percentage change in:
A) potential nominal GDP.
B) structural unemployment.
C) the rule of 72.
D) potential real GDP (LRAS).
A) potential nominal GDP.
B) structural unemployment.
C) the rule of 72.
D) potential real GDP (LRAS).

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 83 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
Long-run full-employment equilibrium assumes:
A) a downward-sloping production function.
B) a downward-sloping long-run supply curve (LRAS).
C) the CPI index price level equals the equilibrium wage rate.
D) the CPI equals aggregate demand (AD) equals short-run aggregate supply (SRAS) equals long-run aggregate supply (LRAS).
A) a downward-sloping production function.
B) a downward-sloping long-run supply curve (LRAS).
C) the CPI index price level equals the equilibrium wage rate.
D) the CPI equals aggregate demand (AD) equals short-run aggregate supply (SRAS) equals long-run aggregate supply (LRAS).

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 83 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
In the self-correcting AD-AS model, a point where the economy's long-run AS curve, short-run AS curve, and AD curve all intersect at a single point represents a point where:
A) real GDP is equal to its full-employment level.
B) the conditions of short-run equilibrium are fulfilled.
C) the conditions of long-run equilibrium are fulfilled.
D) all of the above.
E) a and c, but not b.
A) real GDP is equal to its full-employment level.
B) the conditions of short-run equilibrium are fulfilled.
C) the conditions of long-run equilibrium are fulfilled.
D) all of the above.
E) a and c, but not b.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 83 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
If an economy is operating at short-run equilibrium below the level of real GDP, the self-correction model result is that:
A) unemployment increases.
B) unemployment falls.
C) cyclical unemployment increases.
D) frictional and structural unemployment increase.
A) unemployment increases.
B) unemployment falls.
C) cyclical unemployment increases.
D) frictional and structural unemployment increase.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 83 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
Economic growth is represented by a:
A) rightward shift of the rule of 72 curve.
B) movement along a production possibilities curve.
C) rightward shift in potential real GDP (LRAS).
D) leftward shift of the long-run aggregate supply curve (LRAS).
A) rightward shift of the rule of 72 curve.
B) movement along a production possibilities curve.
C) rightward shift in potential real GDP (LRAS).
D) leftward shift of the long-run aggregate supply curve (LRAS).

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 83 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
In long-run full-employment equilibrium, which of the following is true ?
A) The CPI equals AD equals the peak of the production function curve.
B) The horizontal LRAS curve equals the intersection of the demand and supply curves in the labor market.
C) The CPI equals the aggregate production function at the equilibrium wage rates.
D) The CPI equals AD equals SRAS equals LRAS.
A) The CPI equals AD equals the peak of the production function curve.
B) The horizontal LRAS curve equals the intersection of the demand and supply curves in the labor market.
C) The CPI equals the aggregate production function at the equilibrium wage rates.
D) The CPI equals AD equals SRAS equals LRAS.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 83 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
The intersection between the long-run aggregate supply and aggregate demand curves determines the:
A) level of full-employment real GDP.
B) level of prices (CPI).
C) money supply.
D) marginal product.
E) both a and b.
A) level of full-employment real GDP.
B) level of prices (CPI).
C) money supply.
D) marginal product.
E) both a and b.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 83 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
A decrease in nominal incomes cause a:
A) rightward shift in the short-run aggregate supply curve.
B) leftward shift in the short-run aggregate supply curve.
C) rightward shift in the long-run aggregate supply curve.
D) leftward shift in the long-run aggregate supply curve.
A) rightward shift in the short-run aggregate supply curve.
B) leftward shift in the short-run aggregate supply curve.
C) rightward shift in the long-run aggregate supply curve.
D) leftward shift in the long-run aggregate supply curve.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 83 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
Economic growth can be represented by a(n):
A) percentage change in real GDP.
B) rightward shift of the long-run aggregate supply curve (LRAS).
C) outward shift of a production possibilities curve.
D) all of the above.
A) percentage change in real GDP.
B) rightward shift of the long-run aggregate supply curve (LRAS).
C) outward shift of a production possibilities curve.
D) all of the above.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 83 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
If both the price level and nominal incomes change by the same percentage:
A) real GDP will remain constant.
B) the aggregate supply curve will be upward-sloping.
C) profit margins will change in real terms.
D) the long-run aggregate supply curve will be horizontal.
E) both a and d.
A) real GDP will remain constant.
B) the aggregate supply curve will be upward-sloping.
C) profit margins will change in real terms.
D) the long-run aggregate supply curve will be horizontal.
E) both a and d.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 83 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
Long-run full-employment equilibrium assumes:
A) a downward-sloping production function.
B) a downward-sloping long-run supply curve (LRAS).
C) the CPI index price level equals the equilibrium wage rate.
D) the CPI equals aggregate demand (AD) equals short-run aggregate supply (SRAS) equals long-run aggregate supply (LRAS).
A) a downward-sloping production function.
B) a downward-sloping long-run supply curve (LRAS).
C) the CPI index price level equals the equilibrium wage rate.
D) the CPI equals aggregate demand (AD) equals short-run aggregate supply (SRAS) equals long-run aggregate supply (LRAS).

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 83 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
Economic growth is represented by a:
A) leftward shift of a production possibilities curve.
B) rightward shift of the long-run aggregate supply curve (LRAS).
C) horizontal long-run aggregate supply curve (LRAS).
D) downward shift of an aggregate production function.
A) leftward shift of a production possibilities curve.
B) rightward shift of the long-run aggregate supply curve (LRAS).
C) horizontal long-run aggregate supply curve (LRAS).
D) downward shift of an aggregate production function.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 83 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
In an economy where nominal incomes adjust equally to changes in the price level, we would expect the long-run aggregate supply curve to be:
A) vertical.
B) horizontal.
C) unit elastic.
D) negatively sloped.
E) positively sloped.
A) vertical.
B) horizontal.
C) unit elastic.
D) negatively sloped.
E) positively sloped.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 83 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
The long-run aggregate supply curve is:
A) upward-sloping.
B) downward-sloping.
C) horizontal.
D) vertical.
E) none of the above.
A) upward-sloping.
B) downward-sloping.
C) horizontal.
D) vertical.
E) none of the above.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 83 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
The long-run aggregate supply curve (LRAS) is represented by a(n) ____ curve with respect to the CPI.
A) horizontal
B) upward-sloping
C) downward-sloping
D) vertical
A) horizontal
B) upward-sloping
C) downward-sloping
D) vertical

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 83 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
The position of the long-run aggregate supply curve corresponds to the economy's:
A) full-employment real GDP.
B) maximum possible level of employment.
C) natural level of personal consumption expenditure.
D) maximum possible level of personal consumption expenditures.
E) maximum possible price level.
A) full-employment real GDP.
B) maximum possible level of employment.
C) natural level of personal consumption expenditure.
D) maximum possible level of personal consumption expenditures.
E) maximum possible price level.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 83 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
Exhibit 14A-2 Macro AD-AS Model 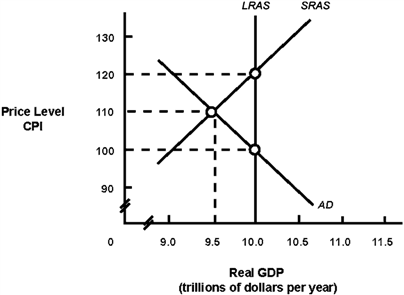 In Exhibit 14A-2, the long-run aggregate supply curve represents:
In Exhibit 14A-2, the long-run aggregate supply curve represents:
A) potential real GDP output for this economy.
B) that the economy is experiencing zero inflation.
C) that the economy is experiencing a recessionary gap.
D) the level of real GDP where the unemployment rate is zero.
 In Exhibit 14A-2, the long-run aggregate supply curve represents:
In Exhibit 14A-2, the long-run aggregate supply curve represents:A) potential real GDP output for this economy.
B) that the economy is experiencing zero inflation.
C) that the economy is experiencing a recessionary gap.
D) the level of real GDP where the unemployment rate is zero.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 83 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
Beginning from a position of long-run equilibrium at the full-employment level of real GDP, the economy's short-run response to an increase in the aggregate demand curve would be:
A) a movement upward along the short-run aggregate supply curve.
B) a movement upward along the long-run aggregate supply curve.
C) a downward shift in the short-run aggregate supply curve.
D) a shift in both the aggregate demand curve and the short-run aggregate supply curve with a movement along the long-run aggregate supply curve.
E) no change, since the economy is already in equilibrium.
A) a movement upward along the short-run aggregate supply curve.
B) a movement upward along the long-run aggregate supply curve.
C) a downward shift in the short-run aggregate supply curve.
D) a shift in both the aggregate demand curve and the short-run aggregate supply curve with a movement along the long-run aggregate supply curve.
E) no change, since the economy is already in equilibrium.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 83 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
Exhibit 14A-1 Aggregate demand and supply model 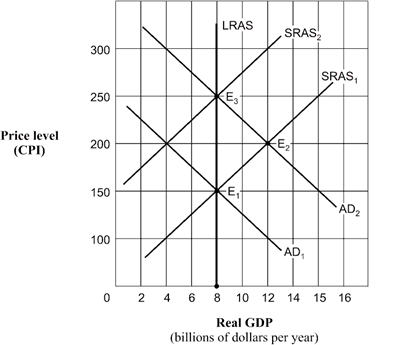 Based on Exhibit 14A-1, when the aggregate demand curve shifts to the position AD2 and the economy is operating at point E2, the economy's position of long-run equilibrium corresponds to point:
Based on Exhibit 14A-1, when the aggregate demand curve shifts to the position AD2 and the economy is operating at point E2, the economy's position of long-run equilibrium corresponds to point:
A) E1.
B) E2.
C) E3.
D) E1 or E3.
 Based on Exhibit 14A-1, when the aggregate demand curve shifts to the position AD2 and the economy is operating at point E2, the economy's position of long-run equilibrium corresponds to point:
Based on Exhibit 14A-1, when the aggregate demand curve shifts to the position AD2 and the economy is operating at point E2, the economy's position of long-run equilibrium corresponds to point:A) E1.
B) E2.
C) E3.
D) E1 or E3.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 83 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
Exhibit 14A-1 Aggregate demand and supply model  Beginning in Exhibit 14A-1 from long-run equilibrium at point E1, the aggregate demand curve shifts to AD2 . The economy's path to a new long-run equilibrium is represented by a movement from:
Beginning in Exhibit 14A-1 from long-run equilibrium at point E1, the aggregate demand curve shifts to AD2 . The economy's path to a new long-run equilibrium is represented by a movement from:
A) E3 to E1 to E2.
B) E1 to E3 to E2.
C) E2 to E1 to E2.
D) E1 to E2 to E3.
 Beginning in Exhibit 14A-1 from long-run equilibrium at point E1, the aggregate demand curve shifts to AD2 . The economy's path to a new long-run equilibrium is represented by a movement from:
Beginning in Exhibit 14A-1 from long-run equilibrium at point E1, the aggregate demand curve shifts to AD2 . The economy's path to a new long-run equilibrium is represented by a movement from:A) E3 to E1 to E2.
B) E1 to E3 to E2.
C) E2 to E1 to E2.
D) E1 to E2 to E3.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 83 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
Which of the following would cause an increase (rightward shift) in the short-run aggregate supply curve (SRAS)?
A) An increase in the long-run aggregate supply curve (LRAS).
B) A decrease in the CPI.
C) An increase in the CPI.
D) A decrease in oil prices.
A) An increase in the long-run aggregate supply curve (LRAS).
B) A decrease in the CPI.
C) An increase in the CPI.
D) A decrease in oil prices.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 83 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
Exhibit 14A-1 Aggregate demand and supply model 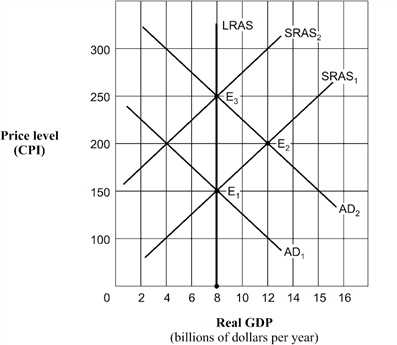 As shown in Exhibit 14A-1 and assuming the aggregate demand curve shifts from AD1 and AD2 , the full-employment level of real GDP is:
As shown in Exhibit 14A-1 and assuming the aggregate demand curve shifts from AD1 and AD2 , the full-employment level of real GDP is:
A) $12 billion.
B) $8 billion.
C) $150 billion.
D) unable to be determined.
 As shown in Exhibit 14A-1 and assuming the aggregate demand curve shifts from AD1 and AD2 , the full-employment level of real GDP is:
As shown in Exhibit 14A-1 and assuming the aggregate demand curve shifts from AD1 and AD2 , the full-employment level of real GDP is:A) $12 billion.
B) $8 billion.
C) $150 billion.
D) unable to be determined.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 83 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
Suppose that the economy is in a position of short-run equilibrium at a point where real GDP is below the full-employment level. Assuming no further change in aggregate demand and self-correction, the movement to a new long-run equilibrium includes a decrease in which of the following?
A) The unemployment rate.
B) The price level (CPI).
C) The level of nominal wages and salaries.
D) All of the above.
A) The unemployment rate.
B) The price level (CPI).
C) The level of nominal wages and salaries.
D) All of the above.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 83 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
Exhibit 14A-1 Aggregate demand and supply model 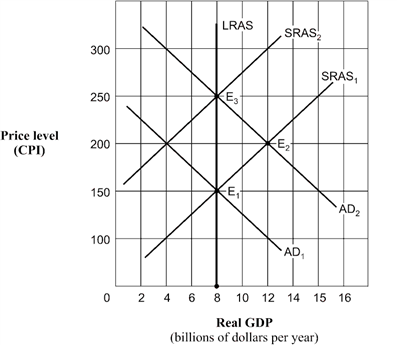 As shown in Exhibit 14A-1, the economy's point of short-run equilibrium, given by the shift of the aggregate demand curve from AD1 to AD2 , is:
As shown in Exhibit 14A-1, the economy's point of short-run equilibrium, given by the shift of the aggregate demand curve from AD1 to AD2 , is:
A) E1.
B) E2.
C) E3.
D) unable to be determined.
 As shown in Exhibit 14A-1, the economy's point of short-run equilibrium, given by the shift of the aggregate demand curve from AD1 to AD2 , is:
As shown in Exhibit 14A-1, the economy's point of short-run equilibrium, given by the shift of the aggregate demand curve from AD1 to AD2 , is:A) E1.
B) E2.
C) E3.
D) unable to be determined.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 83 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
Exhibit 14A-1 Aggregate demand and supply model 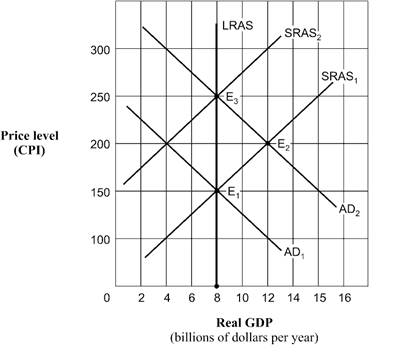 Beginning from short-run equilibrium at point E2 in Exhibit 14A-1, the economy's movement to a new position of long-run equilibrium would best be described as:
Beginning from short-run equilibrium at point E2 in Exhibit 14A-1, the economy's movement to a new position of long-run equilibrium would best be described as:
A) a movement along the AD2 curve with a shift in the SRAS1 curve.
B) a movement along the SRAS2 curve with a shift in the AD2 curve.
C) a shift in the LRAS curve to an intersection at E1.
D) no shift of any kind.
 Beginning from short-run equilibrium at point E2 in Exhibit 14A-1, the economy's movement to a new position of long-run equilibrium would best be described as:
Beginning from short-run equilibrium at point E2 in Exhibit 14A-1, the economy's movement to a new position of long-run equilibrium would best be described as:A) a movement along the AD2 curve with a shift in the SRAS1 curve.
B) a movement along the SRAS2 curve with a shift in the AD2 curve.
C) a shift in the LRAS curve to an intersection at E1.
D) no shift of any kind.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 83 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
Beginning from a position of long-run equilibrium at the full-employment level of real GDP, the economy's short-run response to a decrease in the aggregate demand curve would be a:
A) movement upward along the short-run aggregate supply curve.
B) movement upward along the long-run aggregate supply curve.
C) downward shift in the short-run aggregate supply curve.
D) movement downward along the short-run aggregate supply curve.
A) movement upward along the short-run aggregate supply curve.
B) movement upward along the long-run aggregate supply curve.
C) downward shift in the short-run aggregate supply curve.
D) movement downward along the short-run aggregate supply curve.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 83 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
Exhibit 14A-1 Aggregate demand and supply model 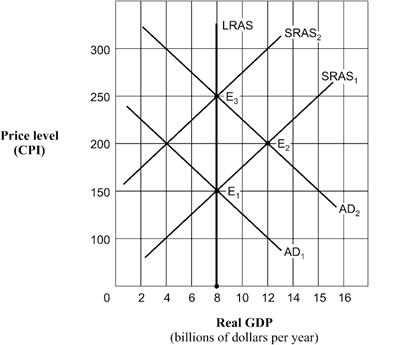 Given the shift of the aggregate demand curve from AD1 to AD2 in Exhibit 14A-1, the real GDP and price level (CPI) in long-run equilibrium will be:
Given the shift of the aggregate demand curve from AD1 to AD2 in Exhibit 14A-1, the real GDP and price level (CPI) in long-run equilibrium will be:
A) $8 billion and 150.
B) $12 billion and 200.
C) $8 billion and 250.
D) $8 billion and 200.
 Given the shift of the aggregate demand curve from AD1 to AD2 in Exhibit 14A-1, the real GDP and price level (CPI) in long-run equilibrium will be:
Given the shift of the aggregate demand curve from AD1 to AD2 in Exhibit 14A-1, the real GDP and price level (CPI) in long-run equilibrium will be:A) $8 billion and 150.
B) $12 billion and 200.
C) $8 billion and 250.
D) $8 billion and 200.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 83 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
Beginning from the full-employment level of real GDP, an increase in one of the components of the aggregate demand curve will increase the:
A) average level of prices (CPI).
B) unemployment rate.
C) natural level of real GDP.
D) level of investment spending.
E) level of government spending.
A) average level of prices (CPI).
B) unemployment rate.
C) natural level of real GDP.
D) level of investment spending.
E) level of government spending.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 83 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
Which of the following would cause a decrease (leftward shift) in the short-run aggregate supply curve (SRAS)?
A) An increase in oil prices.
B) An advance in technology.
C) An increase in the CPI.
D) An increase in the long-run aggregate supply curve (LRAS).
A) An increase in oil prices.
B) An advance in technology.
C) An increase in the CPI.
D) An increase in the long-run aggregate supply curve (LRAS).

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 83 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
Beginning from full-employment macro equilibrium, increase in government spending will cause real GDP to:
A) increase in the short run.
B) decline in the long run.
C) decline in the short run.
D) increase in the long run.
A) increase in the short run.
B) decline in the long run.
C) decline in the short run.
D) increase in the long run.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 83 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
Exhibit 14A-1 Aggregate demand and supply model 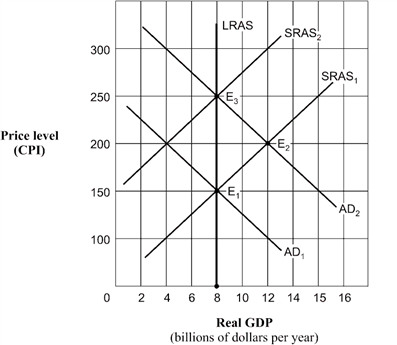 Beginning from long-run equilibrium at point E1 in Exhibit 14A-1, the aggregate demand curve shifts to AD2 . The real GDP and price level (CPI) in short-run equilibrium will be:
Beginning from long-run equilibrium at point E1 in Exhibit 14A-1, the aggregate demand curve shifts to AD2 . The real GDP and price level (CPI) in short-run equilibrium will be:
A) $12 billion and 200.
B) $8 billion and 250.
C) $8 billion and 150.
D) $12 billion and 250.
 Beginning from long-run equilibrium at point E1 in Exhibit 14A-1, the aggregate demand curve shifts to AD2 . The real GDP and price level (CPI) in short-run equilibrium will be:
Beginning from long-run equilibrium at point E1 in Exhibit 14A-1, the aggregate demand curve shifts to AD2 . The real GDP and price level (CPI) in short-run equilibrium will be:A) $12 billion and 200.
B) $8 billion and 250.
C) $8 billion and 150.
D) $12 billion and 250.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 83 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
Along the short-run supply curve (SRAS), a decrease in the aggregate demand curve will decrease:
A) both the price level and real GDP.
B) real GDP without raising the price level.
C) the price level without affecting real GDP.
D) the price level but reduce real GDP.
A) both the price level and real GDP.
B) real GDP without raising the price level.
C) the price level without affecting real GDP.
D) the price level but reduce real GDP.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 83 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
Exhibit 14A-2 Macro AD-AS Model 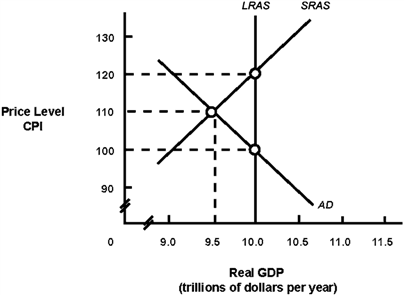 In Exhibit 14A-2, the intersection of AD with SRAS indicates:
In Exhibit 14A-2, the intersection of AD with SRAS indicates:
A) a short-run equilibrium.
B) a long-run equilibrium.
C) that the economy needs policies to reduce unemployment.
D) that the economy is at full employment.
 In Exhibit 14A-2, the intersection of AD with SRAS indicates:
In Exhibit 14A-2, the intersection of AD with SRAS indicates:A) a short-run equilibrium.
B) a long-run equilibrium.
C) that the economy needs policies to reduce unemployment.
D) that the economy is at full employment.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 83 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
Along the short-run aggregate supply curve (SRAS), an increase (rightward shift) in the aggregate demand curve will increase:
A) both the price level and real GDP.
B) real GDP without raising the price level.
C) the price level without affecting real GDP.
D) the price level but reduce real GDP.
A) both the price level and real GDP.
B) real GDP without raising the price level.
C) the price level without affecting real GDP.
D) the price level but reduce real GDP.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 83 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
Beginning from a position of long-run equilibrium, suppose there is an increase in the aggregate demand curve. After adjustment and comparing the economy's new long-run equilibrium with its original long-run position, the result would be an increase in:
A) real GDP.
B) the price level (CPI).
C) the unemployment rate.
D) a and b, but not c.
A) real GDP.
B) the price level (CPI).
C) the unemployment rate.
D) a and b, but not c.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 83 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
A decrease in the aggregate demand curve along the LRAS curve, all other things unchanged, will generate ____ in potential real GDP and ____ in the price level.
A) an increase; no change
B) a decrease; no change
C) no change; an increase
D) no change; a decrease
A) an increase; no change
B) a decrease; no change
C) no change; an increase
D) no change; a decrease

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 83 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
Exhibit 14A-6 Aggregate demand and supply model 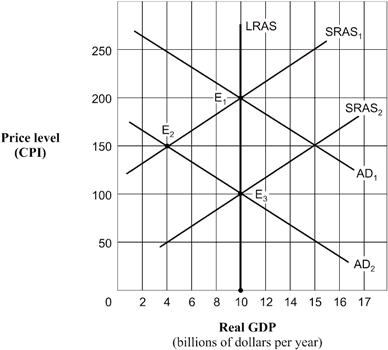 As shown in Exhibit 14A-6, the economy's point of short-run equilibrium, given by the shift of the aggregate demand curve from AD1 to AD2, is:
As shown in Exhibit 14A-6, the economy's point of short-run equilibrium, given by the shift of the aggregate demand curve from AD1 to AD2, is:
A) E1.
B) E2.
C) E3.
D) unable to be determined.
 As shown in Exhibit 14A-6, the economy's point of short-run equilibrium, given by the shift of the aggregate demand curve from AD1 to AD2, is:
As shown in Exhibit 14A-6, the economy's point of short-run equilibrium, given by the shift of the aggregate demand curve from AD1 to AD2, is:A) E1.
B) E2.
C) E3.
D) unable to be determined.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 83 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
Exhibit 14A-4 Macro AD-AS Model 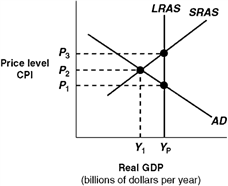 In Exhibit 14A-4, the level of real GDP represented by Yp:
In Exhibit 14A-4, the level of real GDP represented by Yp:
A) would be associated with considerable unemployment.
B) indicates that the economy is experiencing zero inflation.
C) indicates that the economy is experiencing a recessionary gap.
D) is potential real GDP for this economy.
 In Exhibit 14A-4, the level of real GDP represented by Yp:
In Exhibit 14A-4, the level of real GDP represented by Yp:A) would be associated with considerable unemployment.
B) indicates that the economy is experiencing zero inflation.
C) indicates that the economy is experiencing a recessionary gap.
D) is potential real GDP for this economy.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 83 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
Exhibit 14A-6 Aggregate demand and supply model 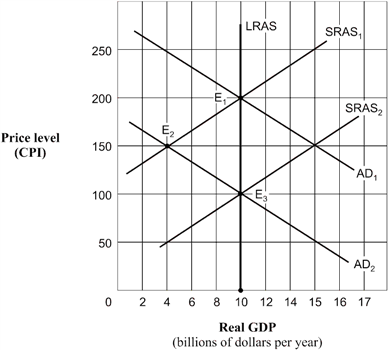 Given the shift of the aggregate demand curve from AD1 to AD2 in Exhibit 14A-6, the real GDP and price level (CPI) in long-run equilibrium will be:
Given the shift of the aggregate demand curve from AD1 to AD2 in Exhibit 14A-6, the real GDP and price level (CPI) in long-run equilibrium will be:
A) $10 billion and 200.
B) $4 billion and 150.
C) $10 billion and 150.
D) $10 billion and 100.
 Given the shift of the aggregate demand curve from AD1 to AD2 in Exhibit 14A-6, the real GDP and price level (CPI) in long-run equilibrium will be:
Given the shift of the aggregate demand curve from AD1 to AD2 in Exhibit 14A-6, the real GDP and price level (CPI) in long-run equilibrium will be:A) $10 billion and 200.
B) $4 billion and 150.
C) $10 billion and 150.
D) $10 billion and 100.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 83 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
Exhibit 14A-4 Macro AD-AS Model 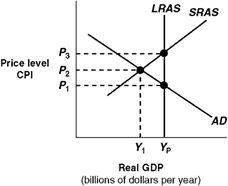 In Exhibit 14A-4, the self-correction argument is that in the long run competition:
In Exhibit 14A-4, the self-correction argument is that in the long run competition:
A) from unemployed workers causes an increase in nominal wages and a leftward shift in SRAS.
B) from unemployed workers causes a rightward shift in SRAS.
C) among firms for workers increases nominal wages and this causes a leftward shift in SRAS.
D) among consumers causes an increase in the CPI and a rightward shift in SRAS.
 In Exhibit 14A-4, the self-correction argument is that in the long run competition:
In Exhibit 14A-4, the self-correction argument is that in the long run competition:A) from unemployed workers causes an increase in nominal wages and a leftward shift in SRAS.
B) from unemployed workers causes a rightward shift in SRAS.
C) among firms for workers increases nominal wages and this causes a leftward shift in SRAS.
D) among consumers causes an increase in the CPI and a rightward shift in SRAS.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 83 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
Exhibit 14A-3 Macro AD-AS Model 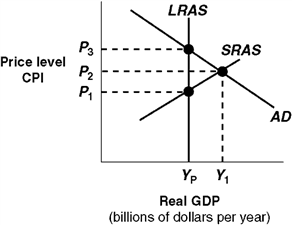 In Exhibit 14A-3, the level of real GDP represented by Yp:
In Exhibit 14A-3, the level of real GDP represented by Yp:
A) is potential real GDP for this economy.
B) indicates that the economy is experiencing zero inflation.
C) indicates that the economy is experiencing a recessionary gap.
D) would be associated with considerable unemployment.
 In Exhibit 14A-3, the level of real GDP represented by Yp:
In Exhibit 14A-3, the level of real GDP represented by Yp:A) is potential real GDP for this economy.
B) indicates that the economy is experiencing zero inflation.
C) indicates that the economy is experiencing a recessionary gap.
D) would be associated with considerable unemployment.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 83 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
Exhibit 14A-5 Macro AD-AS Model 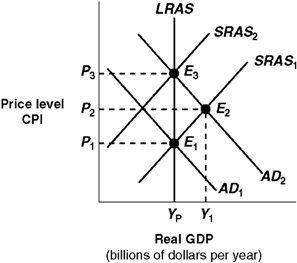 Given the shift of the aggregate demand curve from AD1 to AD2 in Exhibit 14A-5, the real GDP and price level (CPI) in long-run equilibrium will be:
Given the shift of the aggregate demand curve from AD1 to AD2 in Exhibit 14A-5, the real GDP and price level (CPI) in long-run equilibrium will be:
A) P2, Y1.
B) P3, Yp.
C) P2,Yp.
D) P1, Yp.
 Given the shift of the aggregate demand curve from AD1 to AD2 in Exhibit 14A-5, the real GDP and price level (CPI) in long-run equilibrium will be:
Given the shift of the aggregate demand curve from AD1 to AD2 in Exhibit 14A-5, the real GDP and price level (CPI) in long-run equilibrium will be:A) P2, Y1.
B) P3, Yp.
C) P2,Yp.
D) P1, Yp.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 83 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
Exhibit 14A-6 Aggregate demand and supply model 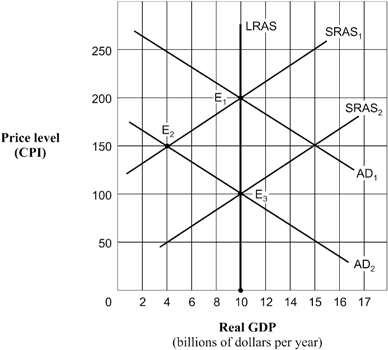 As shown in Exhibit 14A-6, and assuming the aggregate demand curve shifts from AD1 to AD2, the full-employment level of real GDP is:
As shown in Exhibit 14A-6, and assuming the aggregate demand curve shifts from AD1 to AD2, the full-employment level of real GDP is:
A) $10 billion.
B) $4 billion.
C) $100 billion.
D) unable to be determined.
 As shown in Exhibit 14A-6, and assuming the aggregate demand curve shifts from AD1 to AD2, the full-employment level of real GDP is:
As shown in Exhibit 14A-6, and assuming the aggregate demand curve shifts from AD1 to AD2, the full-employment level of real GDP is:A) $10 billion.
B) $4 billion.
C) $100 billion.
D) unable to be determined.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 83 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
Exhibit 14A-4 Macro AD-AS Model 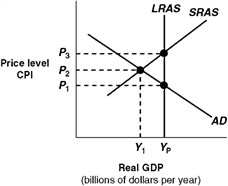 In Exhibit 14A-4, point P2, Y1 represents:
In Exhibit 14A-4, point P2, Y1 represents:
A) that the economy needs policies to reduce unemployment.
B) a long-run equilibrium.
C) a short-run equilibrium.
D) that the economy is at full employment.
 In Exhibit 14A-4, point P2, Y1 represents:
In Exhibit 14A-4, point P2, Y1 represents:A) that the economy needs policies to reduce unemployment.
B) a long-run equilibrium.
C) a short-run equilibrium.
D) that the economy is at full employment.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 83 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
Exhibit 14A-3 Macro AD-AS Model 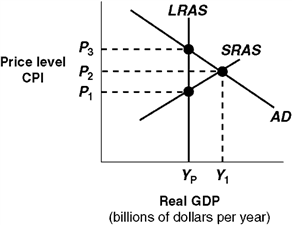 In Exhibit 14A-3, the self-correction argument is that in the long run competition:
In Exhibit 14A-3, the self-correction argument is that in the long run competition:
A) from unemployed workers causes an increase in nominal wages and a leftward shift in SRAS.
B) from unemployment workers causes a rightward shift in LRAS.
C) among firms for workers increases nominal wages and this causes a leftward shift in SRAS.
D) among consumers causes an increase in the CPI and a rightward shift in SRAS.
 In Exhibit 14A-3, the self-correction argument is that in the long run competition:
In Exhibit 14A-3, the self-correction argument is that in the long run competition:A) from unemployed workers causes an increase in nominal wages and a leftward shift in SRAS.
B) from unemployment workers causes a rightward shift in LRAS.
C) among firms for workers increases nominal wages and this causes a leftward shift in SRAS.
D) among consumers causes an increase in the CPI and a rightward shift in SRAS.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 83 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
Exhibit 14A-5 Macro AD-AS Model 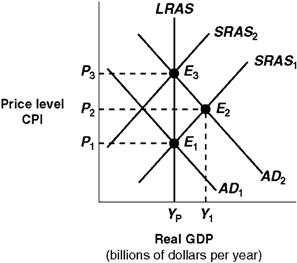 Beginning in Exhibit 14A-5 from long-run equilibrium at point E1, the aggregate demand curve shifts to AD2. The economy's path to a new long-run equilibrium is represented by a movement from:
Beginning in Exhibit 14A-5 from long-run equilibrium at point E1, the aggregate demand curve shifts to AD2. The economy's path to a new long-run equilibrium is represented by a movement from:
A) E1 to E2 to E3.
B) E3 to E2 to E2.
C) E1 to E3 to E2.
D) E2 to E1 to E2.
 Beginning in Exhibit 14A-5 from long-run equilibrium at point E1, the aggregate demand curve shifts to AD2. The economy's path to a new long-run equilibrium is represented by a movement from:
Beginning in Exhibit 14A-5 from long-run equilibrium at point E1, the aggregate demand curve shifts to AD2. The economy's path to a new long-run equilibrium is represented by a movement from:A) E1 to E2 to E3.
B) E3 to E2 to E2.
C) E1 to E3 to E2.
D) E2 to E1 to E2.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 83 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
Exhibit 14A-2 Macro AD-AS Model 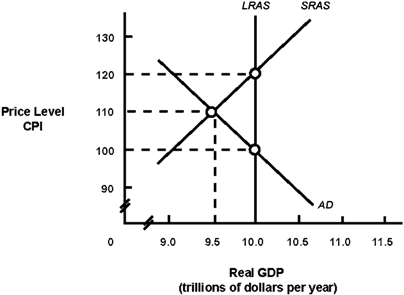 In Exhibit 14A-2, the short-run equilibrium depicts an economy:
In Exhibit 14A-2, the short-run equilibrium depicts an economy:
A) with an inflationary gap.
B) with a recessionary gap.
C) producing at full employment.
D) None of the above answers are correct.
 In Exhibit 14A-2, the short-run equilibrium depicts an economy:
In Exhibit 14A-2, the short-run equilibrium depicts an economy:A) with an inflationary gap.
B) with a recessionary gap.
C) producing at full employment.
D) None of the above answers are correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 83 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72
Exhibit 14A-6 Aggregate demand and supply model 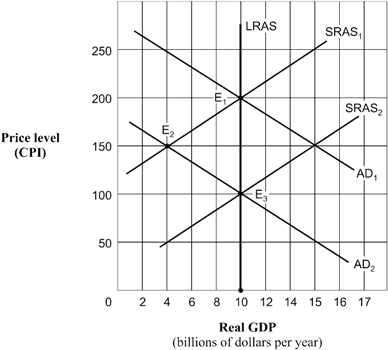 Beginning from long-run equilibrium at point E1 in Exhibit 14A-6, the aggregate demand curve shifts to AD2. The real GDP and price level (CPI) in short-run equilibrium will be:
Beginning from long-run equilibrium at point E1 in Exhibit 14A-6, the aggregate demand curve shifts to AD2. The real GDP and price level (CPI) in short-run equilibrium will be:
A) $10 billion and 200.
B) $10 billion and 150.
C) $10 billion and 100.
D) $4 billion and 150.
 Beginning from long-run equilibrium at point E1 in Exhibit 14A-6, the aggregate demand curve shifts to AD2. The real GDP and price level (CPI) in short-run equilibrium will be:
Beginning from long-run equilibrium at point E1 in Exhibit 14A-6, the aggregate demand curve shifts to AD2. The real GDP and price level (CPI) in short-run equilibrium will be:A) $10 billion and 200.
B) $10 billion and 150.
C) $10 billion and 100.
D) $4 billion and 150.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 83 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73
The short-run aggregate supply curve (SRAS) is based on the theory that wages are flexible.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 83 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
74
The long-run aggregate supply curve (LRAS) corresponds to full-employment real GDP with zero frictional and structural unemployment.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 83 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
75
Exhibit 14A-6 Aggregate demand and supply model 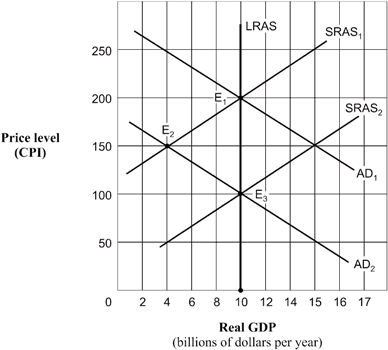 Beginning in Exhibit 14A-6 from long-run equilibrium at point E1, the aggregate demand curve shifts to AD2. The economy's path to a new long-run equilibrium is represented by a movement from:
Beginning in Exhibit 14A-6 from long-run equilibrium at point E1, the aggregate demand curve shifts to AD2. The economy's path to a new long-run equilibrium is represented by a movement from:
A) E3 to E1 to E2.
B) E1 to E3 to E2.
C) E2 to E1 to E2.
D) E1 to E2 to E3.
 Beginning in Exhibit 14A-6 from long-run equilibrium at point E1, the aggregate demand curve shifts to AD2. The economy's path to a new long-run equilibrium is represented by a movement from:
Beginning in Exhibit 14A-6 from long-run equilibrium at point E1, the aggregate demand curve shifts to AD2. The economy's path to a new long-run equilibrium is represented by a movement from:A) E3 to E1 to E2.
B) E1 to E3 to E2.
C) E2 to E1 to E2.
D) E1 to E2 to E3.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 83 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
76
Exhibit 14A-5 Macro AD-AS Model 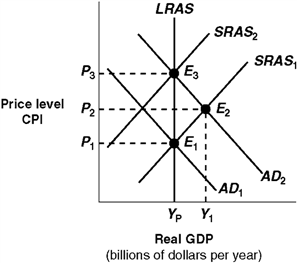 Economic growth is represented in Exhibit 14A-5 by a:
Economic growth is represented in Exhibit 14A-5 by a:
A) leftward shift in the long-run aggregate supply curve (LRAS).
B) inward shift of the production possibilities curve.
C) rightward shift in the long-run aggregate supply curve (LRAS).
D) movement along the long-run aggregate supply curve (LRAS).
 Economic growth is represented in Exhibit 14A-5 by a:
Economic growth is represented in Exhibit 14A-5 by a:A) leftward shift in the long-run aggregate supply curve (LRAS).
B) inward shift of the production possibilities curve.
C) rightward shift in the long-run aggregate supply curve (LRAS).
D) movement along the long-run aggregate supply curve (LRAS).

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 83 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
77
Exhibit 14A-3 Macro AD-AS Model 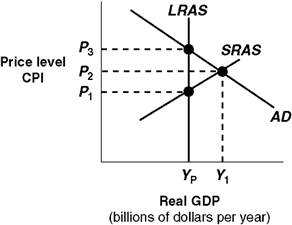 In Exhibit 14A-3, the intersection of AD with SRAS indicates:
In Exhibit 14A-3, the intersection of AD with SRAS indicates:
A) a short-run equilibrium.
B) a long-run equilibrium.
C) that the economy needs policies to reduce unemployment.
D) that the economy is at full employment.
 In Exhibit 14A-3, the intersection of AD with SRAS indicates:
In Exhibit 14A-3, the intersection of AD with SRAS indicates:A) a short-run equilibrium.
B) a long-run equilibrium.
C) that the economy needs policies to reduce unemployment.
D) that the economy is at full employment.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 83 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
78
Exhibit 14A-3 Macro AD-AS Model 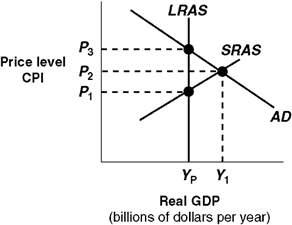 In Exhibit 14A-3, the level of real GDP associated with Y1:
In Exhibit 14A-3, the level of real GDP associated with Y1:
A) is equal to potential real GDP.
B) is an inflationary gap real GDP.
C) is a long-run equilibrium.
D) is caused by flexible wages and prices.
 In Exhibit 14A-3, the level of real GDP associated with Y1:
In Exhibit 14A-3, the level of real GDP associated with Y1:A) is equal to potential real GDP.
B) is an inflationary gap real GDP.
C) is a long-run equilibrium.
D) is caused by flexible wages and prices.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 83 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
79
Exhibit 14A-6 Aggregate demand and supply model 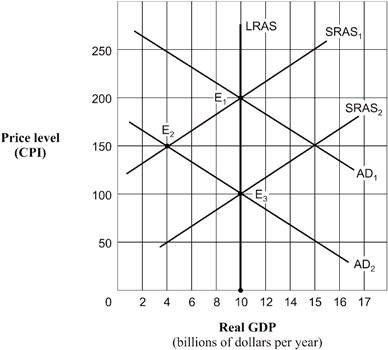 Beginning from a point of short-run equilibrium at point E2 in Exhibit 14A-6, the economy's movement to a new position of long-run equilibrium from that point would best be described as:
Beginning from a point of short-run equilibrium at point E2 in Exhibit 14A-6, the economy's movement to a new position of long-run equilibrium from that point would best be described as:
A) a movement along the AD2 curve caused by a shift in the SRAS1 curve to SRAS2.
B) a movement along the SRAS2 curve with a shift in the AD2 curve.
C) a shift in the LRAS curve to an intersection at E3.
D) no shift of any kind.
 Beginning from a point of short-run equilibrium at point E2 in Exhibit 14A-6, the economy's movement to a new position of long-run equilibrium from that point would best be described as:
Beginning from a point of short-run equilibrium at point E2 in Exhibit 14A-6, the economy's movement to a new position of long-run equilibrium from that point would best be described as:A) a movement along the AD2 curve caused by a shift in the SRAS1 curve to SRAS2.
B) a movement along the SRAS2 curve with a shift in the AD2 curve.
C) a shift in the LRAS curve to an intersection at E3.
D) no shift of any kind.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 83 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
80
Exhibit 14A-6 Aggregate demand and supply model  Based on Exhibit 14A-6, when the aggregate demand curve is in the position AD1, the economy's position of long-run equilibrium corresponds to point:
Based on Exhibit 14A-6, when the aggregate demand curve is in the position AD1, the economy's position of long-run equilibrium corresponds to point:
A) E1.
B) E2.
C) E3.
D) E1 or E2.
 Based on Exhibit 14A-6, when the aggregate demand curve is in the position AD1, the economy's position of long-run equilibrium corresponds to point:
Based on Exhibit 14A-6, when the aggregate demand curve is in the position AD1, the economy's position of long-run equilibrium corresponds to point:A) E1.
B) E2.
C) E3.
D) E1 or E2.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 83 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



