Deck 4: The Carbohydrates: Sugar, Starch, and Fiberspotlight: Sweet Talk--Alternatives to Sugar
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Match between columns
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/82
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 4: The Carbohydrates: Sugar, Starch, and Fiberspotlight: Sweet Talk--Alternatives to Sugar
1
People with hypoglycemia should eat several snacks throughout the day that are high in complex carbohydrates and lean protein.
True
2
Babies develop the ability to digest lactose when they are about six to nine months old.
False
3
Complex carbohydrates are derived exclusively from plants.
True
4
Sam is interested in eating more whole grains. Which lunch option should he avoid because it lacks a whole-grain component?
A) Ordering brown rice with his Chinese food
B) Eating baked potato chips in place of regular chips
C) Eating a low-fat apple bran muffin for dessert
D) Ordering mushroom barley soup for lunch
E) Ordering an egg salad sandwich on whole rye bread
A) Ordering brown rice with his Chinese food
B) Eating baked potato chips in place of regular chips
C) Eating a low-fat apple bran muffin for dessert
D) Ordering mushroom barley soup for lunch
E) Ordering an egg salad sandwich on whole rye bread

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 82 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
If a person uses up his or her reserve supply of glycogen and still does not eat, the body will break down ____ to provide glucose for the brain.
A) heart
B) liver
C) bloodstream
D) muscle
E) kidneys
A) heart
B) liver
C) bloodstream
D) muscle
E) kidneys

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 82 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
Insoluble fibers help to lower blood cholesterol levels.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 82 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
What is the unusable, or inedible, part of a wheat kernel that provides a protective coating around the kernel?
A) Bran
B) Germ
C) Endosperm
D) Husk
E) Nut
A) Bran
B) Germ
C) Endosperm
D) Husk
E) Nut

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 82 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
What is the condition in which the body is unable or has difficulty digesting dairy products?
A) Lactose deficiency
B) Sugar allergy
C) Lactose intolerance
D) Hyperglycemia
E) Lactase persistence
A) Lactose deficiency
B) Sugar allergy
C) Lactose intolerance
D) Hyperglycemia
E) Lactase persistence

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 82 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
When a person is hungry and needs to replenish blood glucose, she/he should eat ____.
A) predominantly simple sugars
B) carbohydrates, protein, and fats
C) predominantly complex carbohydrates
D) protein only
E) a combination of natural and added sugars
A) predominantly simple sugars
B) carbohydrates, protein, and fats
C) predominantly complex carbohydrates
D) protein only
E) a combination of natural and added sugars

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 82 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
The primary role of carbohydrates in the diet is to provide quick energy.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 82 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
Which hormone raises levels of glucose in the blood by signaling to the liver to break down glycogen stores?
A) Glycogen
B) Insulin
C) Glucagon
D) Adrenaline
E) Dopamine
A) Glycogen
B) Insulin
C) Glucagon
D) Adrenaline
E) Dopamine

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 82 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
What is the major storage form of carbohydrate in the body?
A) Starch
B) Sugar
C) Glucose
D) Glucagon
E) Glycogen
A) Starch
B) Sugar
C) Glucose
D) Glucagon
E) Glycogen

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 82 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
Adding foods sweetened with sugar substitutes to the diet will ensure successful weight loss.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 82 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
What is another name for high blood glucose?
A) Hyperglycemia
B) Depression
C) Hypoglycemia
D) Dysphoria
E) Nephritis
A) Hyperglycemia
B) Depression
C) Hypoglycemia
D) Dysphoria
E) Nephritis

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 82 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
To feel energetic and alert throughout the day an individual should _______.
A) follow a low-carbohydrate eating plan
B) avoid all simple sugars
C) exercise in the morning
D) make an effort to eat so as to maintain blood glucose levels within the normal range
E) eat most carbohydrates in the first half of the day
A) follow a low-carbohydrate eating plan
B) avoid all simple sugars
C) exercise in the morning
D) make an effort to eat so as to maintain blood glucose levels within the normal range
E) eat most carbohydrates in the first half of the day

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 82 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
The protein in a meal stimulates glucagon secretion, which opposes insulin and prevents it from storing glucose.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 82 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
Glucagon can be broken down by the liver to maintain a constant blood glucose level when carbohydrates intake is inadequate.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 82 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
Foods rich in complex carbohydrates should be avoided when trying to lose weight.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 82 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
Fat is used efficiently as fuel by the brain and nerves.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 82 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
Carbohydrate absorption, as well as most carbohydrate digestion, takes place in the small intestine.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 82 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
Which of the following is a disaccharide?
A) Galactose
B) Glucose
C) Glycogen
D) Fructose
E) Maltose
A) Galactose
B) Glucose
C) Glycogen
D) Fructose
E) Maltose

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 82 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
Individuals who consume diets rich in whole-grains have improved insulin sensitivity and are ________.
A) less likely to develop metabolic syndrome
B) more likely to develop hypoglycemia
C) less likely to develop lactose intolerance
D) more likely to develop hyperglycemia
E) more likely to develop ketosis
A) less likely to develop metabolic syndrome
B) more likely to develop hypoglycemia
C) less likely to develop lactose intolerance
D) more likely to develop hyperglycemia
E) more likely to develop ketosis

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 82 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
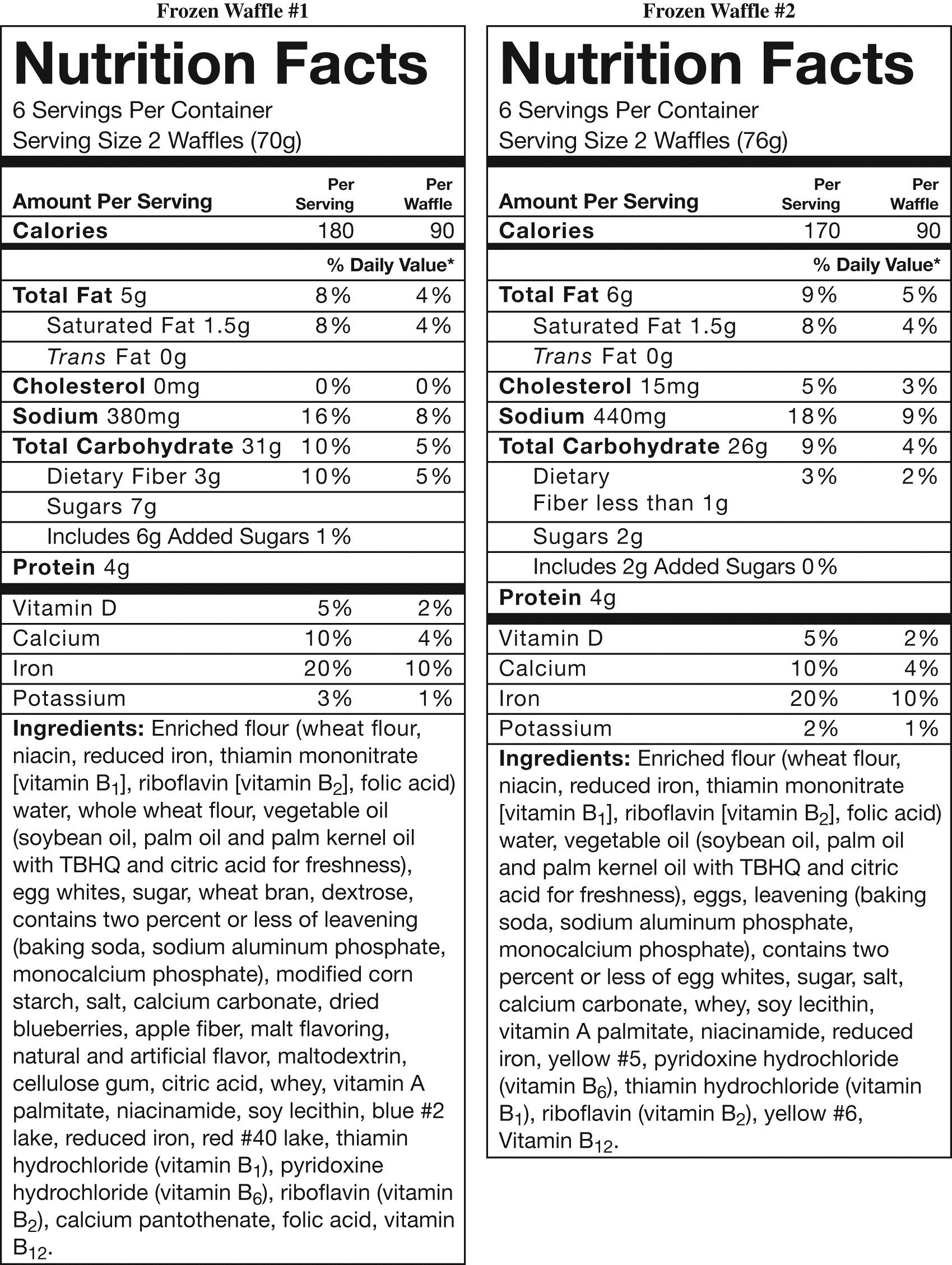 Jack decides to purchase waffle #1 and eats three of the waffles for breakfast. Approximately, what amounts of total fat and total carbohydrates did the waffles contribute to his meal?
Jack decides to purchase waffle #1 and eats three of the waffles for breakfast. Approximately, what amounts of total fat and total carbohydrates did the waffles contribute to his meal?A) 10 grams fat and 62 grams carbohydrates
B) 5 grams fat and 62 grams carbohydrates
C) 10 grams fat and 31 grams carbohydrates
D) 8 grams fat and 46 grams carbohydrates
E) 15 grams fat and 93 grams carbohydrates

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 82 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
Which product is a rich source of starch?
A) Apples
B) Beans
C) Cane sugar
D) Milk
E) Cheese
A) Apples
B) Beans
C) Cane sugar
D) Milk
E) Cheese

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 82 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
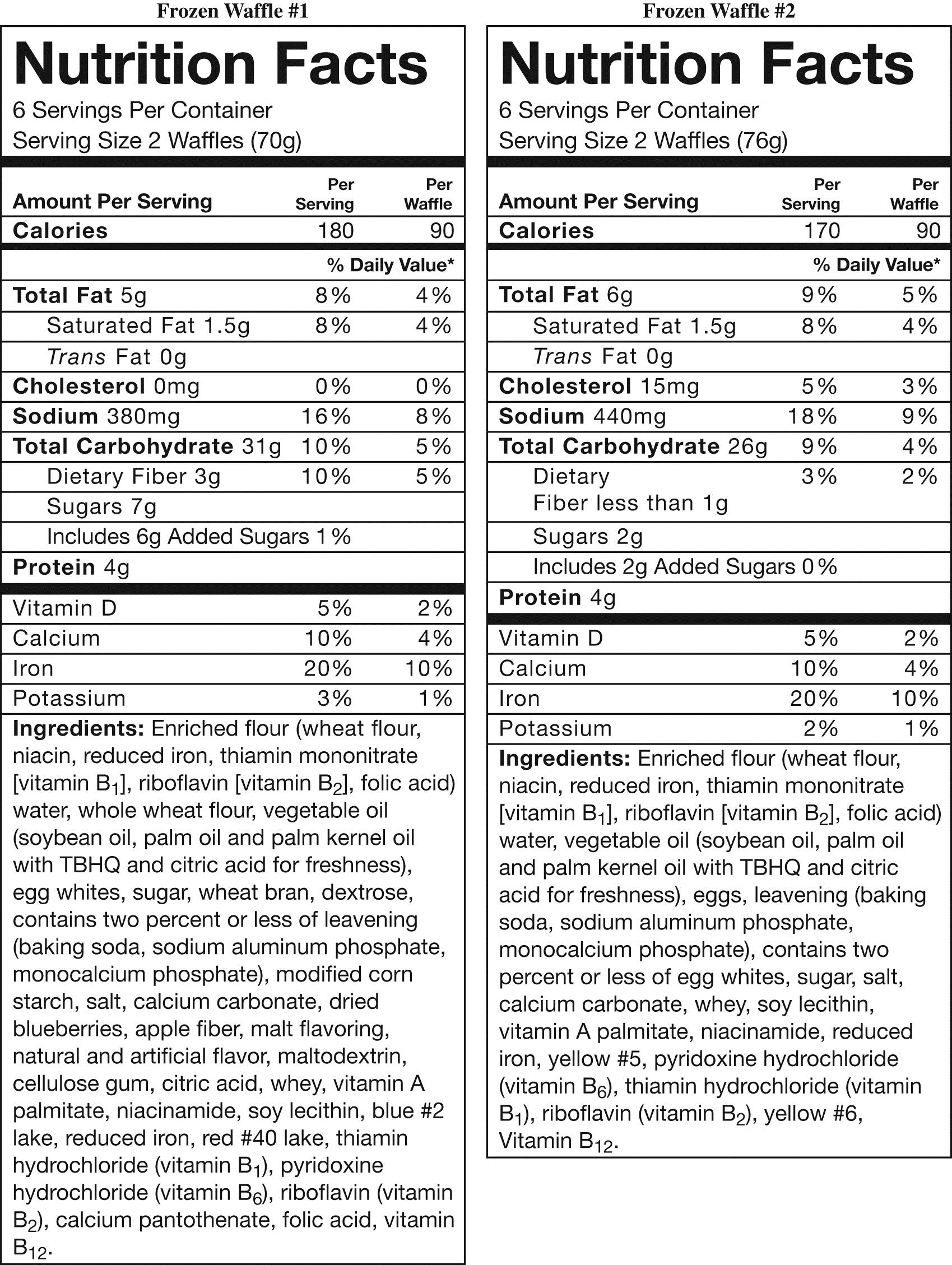 Jack is trying to choose foods that contain whole grains. Which whole grain ingredient is present in waffle #1 that is not found in waffle #2?
Jack is trying to choose foods that contain whole grains. Which whole grain ingredient is present in waffle #1 that is not found in waffle #2?A) Enriched flour
B) Whole wheat flour
C) Modified corn starch
D) Maltodextrin
E) Apple fiber

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 82 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
Eating more higher fiber foods is usually associated with _______.
A) lower intakes of starch
B) higher intakes of added sugars
C) lower intakes of added sugars
D) higher energy intakes
E) lower protein intakes
A) lower intakes of starch
B) higher intakes of added sugars
C) lower intakes of added sugars
D) higher energy intakes
E) lower protein intakes

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 82 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
Complex carbohydrates are found primarily in ____.
A) grains and dairy
B) grains and vegetables
C) fish and vegetables
D) dairy and fruit
E) vegetables and dairy
A) grains and dairy
B) grains and vegetables
C) fish and vegetables
D) dairy and fruit
E) vegetables and dairy

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 82 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
What type of nutrient is starch?
A) Complex carbohydrate
B) Simple carbohydrate
C) Fiber
D) Gluten
E) Monosaccharide
A) Complex carbohydrate
B) Simple carbohydrate
C) Fiber
D) Gluten
E) Monosaccharide

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 82 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
The only animal-derived food that contains significant amounts of carbohydrates is ______.
A) eggs
B) beef
C) milk
D) poultry
E) bacon
A) eggs
B) beef
C) milk
D) poultry
E) bacon

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 82 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
Which component gives fruits their naturally sweet taste?
A) Glucose
B) Fructose
C) Galactose
D) Sucrose
E) Added sugars
A) Glucose
B) Fructose
C) Galactose
D) Sucrose
E) Added sugars

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 82 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
All of the following are health benefits associated with intake of insoluble fiber except ___.
A) helps with weight management
B) reduces risk of constipation and hemorroids
C) lowers risk of colon cancer
D) speeds transit time through intestines
E) slows glucose absorption
A) helps with weight management
B) reduces risk of constipation and hemorroids
C) lowers risk of colon cancer
D) speeds transit time through intestines
E) slows glucose absorption

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 82 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
Which carbohydrate type is mismatched with a major food source for that type?
A) fructose-peaches
B) sucrose-candy bars
C) maltose-barley
D) starch-strawberries
E) galactose-milk
A) fructose-peaches
B) sucrose-candy bars
C) maltose-barley
D) starch-strawberries
E) galactose-milk

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 82 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
When two glucose units are bonded together they form ____.
A) sucrose
B) galactose
C) lactose
D) maltose
E) dextrose
A) sucrose
B) galactose
C) lactose
D) maltose
E) dextrose

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 82 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
Maggie is shopping for a loaf of bread and takes time to review the terms on the label. Which term describes bread that is made using the most nutritious flour?
A) 100 percent wheat
B) Stone ground
C) Whole grain
D) Seven grain
E) Multigrain
A) 100 percent wheat
B) Stone ground
C) Whole grain
D) Seven grain
E) Multigrain

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 82 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
From a health perspective, fruits are better sources of sucrose and fructose than table sugar because they ____.
A) contain higher concentrations of these carbohydrates per unit of weight
B) are more quickly digested than table sugar
C) also provide protein
D) also provide fiber, vitamins, and minerals
E) provide these sugars in a more absorbable form than table sugar
A) contain higher concentrations of these carbohydrates per unit of weight
B) are more quickly digested than table sugar
C) also provide protein
D) also provide fiber, vitamins, and minerals
E) provide these sugars in a more absorbable form than table sugar

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 82 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
According to the Dietary Guidelines , what is the minimum amount of whole-grains that should be consumed if an individual's recommended grain intake each day is 6 ounces?
A) 6 ounces
B) 4 ounces
C) 3 ounces
D) 2 ounces
E) 1 ounce
A) 6 ounces
B) 4 ounces
C) 3 ounces
D) 2 ounces
E) 1 ounce

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 82 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
A refined grain product that is enriched is still lacking some ____ that was lost during processing.
A) iron
B) fiber
C) thiamin
D) folic acid
E) niacin
A) iron
B) fiber
C) thiamin
D) folic acid
E) niacin

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 82 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
Eating too many foods with added sugars usually means getting too many ____.
A) antioxidants
B) empty calories
C) fatty acids
D) complex carbohydrates
E) enzymes
A) antioxidants
B) empty calories
C) fatty acids
D) complex carbohydrates
E) enzymes

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 82 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
In the process of refining wheat into white flour, what part of the kernel is retained?
A) Chaff
B) Endosperm
C) Bran
D) Germ
E) Husk
A) Chaff
B) Endosperm
C) Bran
D) Germ
E) Husk

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 82 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
Diverticulosis is closely associated with a lack of ______ in the diet.
A) starch
B) simple sugars
C) fiber
D) carbohydrates
E) protein
A) starch
B) simple sugars
C) fiber
D) carbohydrates
E) protein

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 82 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
If Steven needs 2400 calories per day to maintain his weight, what is the recommended maximum upper limit of added sugars he should consume each day?
A) 180 calories
B) 240 calories
C) 480 calories
D) 600 calories
E) 750 calories
A) 180 calories
B) 240 calories
C) 480 calories
D) 600 calories
E) 750 calories

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 82 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
Many nutrition professionals recommend emphasizing "good carbohydrates" in the diet. What does this mean?
A) Choosing foods high in fiber but low in added sugars
B) Avoiding foods with a glycemic index above 70
C) Avoiding foods with a glycemic index below 55
D) Choosing small portions of low-calorie foods
E) Choosing foods that quickly raise blood glucose
A) Choosing foods high in fiber but low in added sugars
B) Avoiding foods with a glycemic index above 70
C) Avoiding foods with a glycemic index below 55
D) Choosing small portions of low-calorie foods
E) Choosing foods that quickly raise blood glucose

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 82 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
In general, changing one's diet by substituting complex carbohydrates in place of refined foods with added sugars typically results in a diet that is ________.
A) higher in calories
B) lower in vitamins and minerals
C) higher in fat
D) higher in fiber
E) lower in natural sugars
A) higher in calories
B) lower in vitamins and minerals
C) higher in fat
D) higher in fiber
E) lower in natural sugars

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 82 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
Foods with a low glycemic index number are digested slowly which may increase ______.
A) satiety
B) hunger
C) glucagon
D) appetite
E) weight gain
A) satiety
B) hunger
C) glucagon
D) appetite
E) weight gain

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 82 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
Jasmine is too busy for lunch and needs a pick-me-up to help her remain alert during her two afternoon classes. Which snack would you recommend?
A) Half a ham and Swiss cheese sandwich on enriched bread
B) Fresh peach with low-fat Greek yogurt and rolled-oat granola
C) Wheat toast with trans fat-free margarine and jelly
D) Baked apple with brown sugar, cinnamon, and canola oil
E) Pretzels and a sport drink
A) Half a ham and Swiss cheese sandwich on enriched bread
B) Fresh peach with low-fat Greek yogurt and rolled-oat granola
C) Wheat toast with trans fat-free margarine and jelly
D) Baked apple with brown sugar, cinnamon, and canola oil
E) Pretzels and a sport drink

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 82 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
Marta tries to avoid sugar because she believes it is responsible for making her overweight, giving her husband diabetes, and causing hyperactivity in her grandchildren. What condition has verifiably been linked to sugar by research studies?
A) Diabetes
B) Heart disease
C) Tooth decay
D) Hyperactivity in children
E) Hyperactivity in some adults
A) Diabetes
B) Heart disease
C) Tooth decay
D) Hyperactivity in children
E) Hyperactivity in some adults

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 82 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
A general principle that can help in choosing carbohydrates (and foods in general) is to choose foods that are __________.
A) whole-food and plant-based
B) high-protein and low-fat
C) enriched-food and varied
D) sugar-free and processed-food
E) low-carbohydrate and nutrient-dense
A) whole-food and plant-based
B) high-protein and low-fat
C) enriched-food and varied
D) sugar-free and processed-food
E) low-carbohydrate and nutrient-dense

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 82 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
The _____ secretes glucagon and insulin in response to changing blood glucose levels.
A) appendix
B) pituitary gland
C) liver
D) pancreas
E) hypothalamus
A) appendix
B) pituitary gland
C) liver
D) pancreas
E) hypothalamus

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 82 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
High intakes of the sugar alternatives sorbitol and mannitol can result in ____.
A) tooth decay
B) diarrhea
C) increased blood cholesterol
D) hypoglycemia
E) increased heart rate
A) tooth decay
B) diarrhea
C) increased blood cholesterol
D) hypoglycemia
E) increased heart rate

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 82 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
When milling whole wheat flour, what components of the wheat kernel are retained?
A) The endosperm and germ
B) The endosperm, germ, and husk
C) The endosperm, germ, and bran
D) The germ
E) The endosperm
A) The endosperm and germ
B) The endosperm, germ, and husk
C) The endosperm, germ, and bran
D) The germ
E) The endosperm

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 82 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
What is the source of stevia?
A) A combination of two amino acids
B) A modification of sucrose molecules
C) A derivative of aspartic acid and phenylalanine
D) A derivative of a plant native to Brazil and Paraguay
E) A modified version of fructose
A) A combination of two amino acids
B) A modification of sucrose molecules
C) A derivative of aspartic acid and phenylalanine
D) A derivative of a plant native to Brazil and Paraguay
E) A modified version of fructose

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 82 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
Sabina is concerned about her children's teeth after their first dental checkups. Her 2-year old already has a cavity and her four-year old needs to brush better. What else should Sabina's children do to prevent tooth decay?
A) Only drink 100 percent fruit juices
B) Eat candy only between meals and not with them
C) Eat crackers and pretzels as snacks and not candy bars
D) Rinse their mouths with water after eating
E) Eat raisins as snacks in place of chocolate candies
A) Only drink 100 percent fruit juices
B) Eat candy only between meals and not with them
C) Eat crackers and pretzels as snacks and not candy bars
D) Rinse their mouths with water after eating
E) Eat raisins as snacks in place of chocolate candies

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 82 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
The ______ regulates the amount of glucose circulating in the blood by either synthesizing glycogen or breaking down glycogen.
A) kidneys
B) gallbladder
C) appendix
D) thyroid
E) liver
A) kidneys
B) gallbladder
C) appendix
D) thyroid
E) liver

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 82 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
Which statement is true about hypoglycemia?
A) It is treated with insulin injections.
B) It is aggravated by high-fiber foods.
C) It is classified as a pre-diabetic condition.
D) It is aggravated by high-sugar foods.
E) It is common in teenagers but less so in adults and older adults.
A) It is treated with insulin injections.
B) It is aggravated by high-fiber foods.
C) It is classified as a pre-diabetic condition.
D) It is aggravated by high-sugar foods.
E) It is common in teenagers but less so in adults and older adults.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 82 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
Fletcher's dietary analysis reveals that he is deriving 30% of calories from simple sugars, and he decides to try to cut back. Which item from his food record should Fletcher omit?
A) 1 banana
B) 1/2 cup green grapes
C) 32 fl oz root beer
D) 8 oz orange juice
E) 1/2 cup cooked dried beans
A) 1 banana
B) 1/2 cup green grapes
C) 32 fl oz root beer
D) 8 oz orange juice
E) 1/2 cup cooked dried beans

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 82 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
What factor plays the greatest role in the increase of type 2 diabetes in children and adolescents?
A) Type 2 diabetes is hereditary.
B) Children and adolescents are eating more dairy products.
C) Children and adolescents are becoming obese at an earlier age.
D) Vaccination rates among poor people are very low.
E) Today's diets lack proper levels of vitamins and minerals.
A) Type 2 diabetes is hereditary.
B) Children and adolescents are eating more dairy products.
C) Children and adolescents are becoming obese at an earlier age.
D) Vaccination rates among poor people are very low.
E) Today's diets lack proper levels of vitamins and minerals.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 82 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
How does a balanced meal help keep blood glucose from rising or dropping too quickly?
A) Soluble fibers slow down the rate of digestion so a steady stream of glucose is received.
B) Protein provides a quick source of glucose for the body's cells.
C) Protein stimulates insulin secretion, which prevents rapid glucose storage.
D) Fats accelerate the rate of digestion so that glucose is more quickly received.
E) Starches provide quick energy to the brain, which slows glucose absorption by other body cells.
A) Soluble fibers slow down the rate of digestion so a steady stream of glucose is received.
B) Protein provides a quick source of glucose for the body's cells.
C) Protein stimulates insulin secretion, which prevents rapid glucose storage.
D) Fats accelerate the rate of digestion so that glucose is more quickly received.
E) Starches provide quick energy to the brain, which slows glucose absorption by other body cells.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 82 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
Ketone bodies are produced from the incomplete breakdown of ____ when ____ is unavailable for the brain and nerve cells.
A) fat; glucose
B) carbohydrate; fat
C) glucose; protein
D) protein; glucose
E) fiber; glucose
A) fat; glucose
B) carbohydrate; fat
C) glucose; protein
D) protein; glucose
E) fiber; glucose

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 82 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
What term in the ingredients list indicates added sugars in the product?
A) Pectin
B) Hemicellulose
C) Fruit puree
D) Fruit juice concentrate
E) Vanillin
A) Pectin
B) Hemicellulose
C) Fruit puree
D) Fruit juice concentrate
E) Vanillin

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 82 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
The greatest single source of added sugars in the American diet is ____.
A) fruit drinks
B) cookies
C) candy
D) regular soft drinks
E) ice cream
A) fruit drinks
B) cookies
C) candy
D) regular soft drinks
E) ice cream

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 82 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
Vignette #2 Sam has been overweight since the eighth grade and is diagnosed with type 2 diabetes at his annual checkup. He tells his fiancée, Anna, who is now determined to learn as much as possible about this illness. Sam and Anna have found several reputable sites on the Internet in an attempt to help Sam reverse his condition. Let's ask several questions to see how much they have learned.
Which strategy will help Sam manage his diabetes?
A) Eating a healthful diet
B) Dieting to lose weight rapidly
C) Reducing his exercise level
D) Eating two large meals a day
E) Eliminating all sugar in his diet
Which strategy will help Sam manage his diabetes?
A) Eating a healthful diet
B) Dieting to lose weight rapidly
C) Reducing his exercise level
D) Eating two large meals a day
E) Eliminating all sugar in his diet

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 82 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
Match between columns

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 82 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
What are the potential hazards of consuming too much fiber?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 82 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
Explain what makes an added sugar different from natural sugars, and give two examples of foods that contain added sugars.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 82 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
Vignette #2 Sam has been overweight since the eighth grade and is diagnosed with type 2 diabetes at his annual checkup. He tells his fiancée, Anna, who is now determined to learn as much as possible about this illness. Sam and Anna have found several reputable sites on the Internet in an attempt to help Sam reverse his condition. Let's ask several questions to see how much they have learned.
Which of the following is not usually a recommendation for someone with Sam's condition?
A) Lose weight
B) Eat balanced meals at regular intervals
C) Exercise
D) Follow a high-protein diet
E) Choose complex carbohydrates
Which of the following is not usually a recommendation for someone with Sam's condition?
A) Lose weight
B) Eat balanced meals at regular intervals
C) Exercise
D) Follow a high-protein diet
E) Choose complex carbohydrates

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 82 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
Vignette #1 You and your friend Karen are having lunch out and you order an iced tea. Karen sees you reach for the pink packet of Sweet 'N Low, stops your hand, and says, "Don't you know that stuff is bad for you? I read that it causes cancer, and I also know people who say that Equal, another nonnutritive sweetener, gives them headaches." As your conversation continues, let's show Karen how well informed you are concerning nonnutritive sweeteners by answering the following questions:
The chemical name for the nonnutritive sweetener in the pink packet is _____, which the chemical name for the nonnutritive sweetener in the blue packet is ______.
A) aspartame; saccharin
B) saccharin; aspartame
C) neotame; aspartame
D) sucralose; saccharin
E) sorbitol; sucralose
The chemical name for the nonnutritive sweetener in the pink packet is _____, which the chemical name for the nonnutritive sweetener in the blue packet is ______.
A) aspartame; saccharin
B) saccharin; aspartame
C) neotame; aspartame
D) sucralose; saccharin
E) sorbitol; sucralose

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 82 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
List four recommendations of the American Dental Association for optimal dental health.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 82 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
Eunice is a 60-year-old woman who is trying to increase the amount of fiber in her diet in order to meet the Dietary Guidelines . What change would be best for her to make?
A) Increase her intake of yogurt
B) Choose white rice or scalloped potatoes instead of beans to go with dinner
C) Eat pretzels made from wheat flour instead of fruit with her lunch
D) Replace her morning enriched-flour croissant with a wheat bagel
E) Eat air-popped popcorn in place of chips for an evening snack
A) Increase her intake of yogurt
B) Choose white rice or scalloped potatoes instead of beans to go with dinner
C) Eat pretzels made from wheat flour instead of fruit with her lunch
D) Replace her morning enriched-flour croissant with a wheat bagel
E) Eat air-popped popcorn in place of chips for an evening snack

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 82 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
What are the nutrient advantages of using whole grains over enriched, refined grains?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 82 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
Vignette #2 Sam has been overweight since the eighth grade and is diagnosed with type 2 diabetes at his annual checkup. He tells his fiancée, Anna, who is now determined to learn as much as possible about this illness. Sam and Anna have found several reputable sites on the Internet in an attempt to help Sam reverse his condition. Let's ask several questions to see how much they have learned.
What problem is most responsible for Sam's type 2 diabetes?
A) Sam's kidneys don't excrete blood glucose efficiently.
B) A virus has triggered the destruction of pancreatic cells that produce insulin.
C) Sam's gallbladder fails to secrete bile when needed.
D) The cells in Sam's body do not respond to insulin secreted by his pancreas.
E) The pancreas is producing insufficient levels of glucagon.
What problem is most responsible for Sam's type 2 diabetes?
A) Sam's kidneys don't excrete blood glucose efficiently.
B) A virus has triggered the destruction of pancreatic cells that produce insulin.
C) Sam's gallbladder fails to secrete bile when needed.
D) The cells in Sam's body do not respond to insulin secreted by his pancreas.
E) The pancreas is producing insufficient levels of glucagon.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 82 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
Discuss the difference between type 1 and type 2 diabetes in regard to incidence, risk factors, cause, and treatment.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 82 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72
Vignette #2 Sam has been overweight since the eighth grade and is diagnosed with type 2 diabetes at his annual checkup. He tells his fiancée, Anna, who is now determined to learn as much as possible about this illness. Sam and Anna have found several reputable sites on the Internet in an attempt to help Sam reverse his condition. Let's ask several questions to see how much they have learned.
Anna is still confused about the difference between type 1 and type 2 diabetes. Which statement is characteristic of type 1 diabetes only?
A) It causes weight gain.
B) Treatment always involves insulin injections.
C) It is also called hyperglycemia.
D) It is typically associated with insulin resistance.
E) Its incidence is increasing in the United States.
Anna is still confused about the difference between type 1 and type 2 diabetes. Which statement is characteristic of type 1 diabetes only?
A) It causes weight gain.
B) Treatment always involves insulin injections.
C) It is also called hyperglycemia.
D) It is typically associated with insulin resistance.
E) Its incidence is increasing in the United States.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 82 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73
Vignette #1 You and your friend Karen are having lunch out and you order an iced tea. Karen sees you reach for the pink packet of Sweet 'N Low, stops your hand, and says, "Don't you know that stuff is bad for you? I read that it causes cancer, and I also know people who say that Equal, another nonnutritive sweetener, gives them headaches." As your conversation continues, let's show Karen how well informed you are concerning nonnutritive sweeteners by answering the following questions:
Neotame is a derivative of which two amino acids?
A) Alanine and cysteine
B) Aspartic acid and phenylalanine
C) Tryptophan and leucine
D) Lysine and glutamic acid
E) Asparagine and glutamine
Neotame is a derivative of which two amino acids?
A) Alanine and cysteine
B) Aspartic acid and phenylalanine
C) Tryptophan and leucine
D) Lysine and glutamic acid
E) Asparagine and glutamine

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 82 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
74
Vignette #1 You and your friend Karen are having lunch out and you order an iced tea. Karen sees you reach for the pink packet of Sweet 'N Low, stops your hand, and says, "Don't you know that stuff is bad for you? I read that it causes cancer, and I also know people who say that Equal, another nonnutritive sweetener, gives them headaches." As your conversation continues, let's show Karen how well informed you are concerning nonnutritive sweeteners by answering the following questions:
Which nonnutritive sweetener should be entirely avoided by individuals with phenylketonuria (PKU)?
A) Aspartame
B) Saccharin
C) Neotame
D) Sucralose
E) Xylitol
Which nonnutritive sweetener should be entirely avoided by individuals with phenylketonuria (PKU)?
A) Aspartame
B) Saccharin
C) Neotame
D) Sucralose
E) Xylitol

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 82 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
75
Vignette #1 You and your friend Karen are having lunch out and you order an iced tea. Karen sees you reach for the pink packet of Sweet 'N Low, stops your hand, and says, "Don't you know that stuff is bad for you? I read that it causes cancer, and I also know people who say that Equal, another nonnutritive sweetener, gives them headaches." As your conversation continues, let's show Karen how well informed you are concerning nonnutritive sweeteners by answering the following questions:
Although some studies in the past may have found that saccharin can cause bladder cancer in lab rats, why would it be considered safe today to continue using it?
A) The research used extremely high doses of saccharin that are not relevant for humans.
B) What occurs in rats is unlikely to occur in humans.
C) The American Medical Association's Council on Scientific Affairs has stated that saccharin increases the risk of bladder cancer, but only if consumed in soft drinks.
D) There are known hazards that are more important to avoid if you want to reduce your risk of cancer.
E) Saccharin is allowed in other countries around the world, so should be considered safe in U.S. food products.
Although some studies in the past may have found that saccharin can cause bladder cancer in lab rats, why would it be considered safe today to continue using it?
A) The research used extremely high doses of saccharin that are not relevant for humans.
B) What occurs in rats is unlikely to occur in humans.
C) The American Medical Association's Council on Scientific Affairs has stated that saccharin increases the risk of bladder cancer, but only if consumed in soft drinks.
D) There are known hazards that are more important to avoid if you want to reduce your risk of cancer.
E) Saccharin is allowed in other countries around the world, so should be considered safe in U.S. food products.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 82 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
76
The Dietary Guidelines for Americans recommend that you "reduce the intake of calories from added sugars." Identity the specific recommendation for added sugar consumption, and list six tips offered in the textbook that help with this task while still catering to the sweet tooth.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 82 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
77
Explain how the hormones insulin and glucagon regulate blood glucose in a healthy individual following digestion of a meal and then several hours after that meal when nothing additional has been consumed.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 82 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
78
Sucrose is composed of ______.
A) two fructose units
B) one glucose and one fructose unit
C) one glucose and one galactose unit
D) one galactose and one fructose unit
E) two galactose units
A) two fructose units
B) one glucose and one fructose unit
C) one glucose and one galactose unit
D) one galactose and one fructose unit
E) two galactose units

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 82 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
79
Vignette #2 Sam has been overweight since the eighth grade and is diagnosed with type 2 diabetes at his annual checkup. He tells his fiancée, Anna, who is now determined to learn as much as possible about this illness. Sam and Anna have found several reputable sites on the Internet in an attempt to help Sam reverse his condition. Let's ask several questions to see how much they have learned.
Which statement is correct concerning type 2 diabetes?
A) Its incidence is decreasing due to greater awareness.
B) It is less common than type 1 diabetes.
C) It is characterized by too much glucose getting into the cells.
D) Generally insulin injections are not required.
E) Infrequent urination is a typical response.
Which statement is correct concerning type 2 diabetes?
A) Its incidence is decreasing due to greater awareness.
B) It is less common than type 1 diabetes.
C) It is characterized by too much glucose getting into the cells.
D) Generally insulin injections are not required.
E) Infrequent urination is a typical response.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 82 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
80
Your mother has been recently diagnosed with type 2 diabetes. She is now afraid to eat anything with sugar in it. What advice would you give her to help her understand her condition?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 82 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



