Deck 8: Combination Circuits
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/14
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 8: Combination Circuits
1
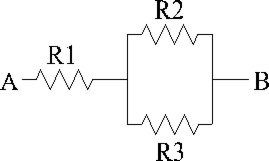
Refer to the diagram above and solve using the values provided.
R1 = 15 Ω , R2 = 300 Ω , and R3 = 900 Ω, and 240 V is applied between A and B. What is the current flow through R1?
1 Α
2
A combination circuit is a circuit that contains _____.
A) only series components
B) only parallel components
C) both series and parallel components
D) both voltage and current sources
A) only series components
B) only parallel components
C) both series and parallel components
D) both voltage and current sources
C
3
In series circuits, the _____ is the same at any point in the circuit.
A) resistance
B) current
C) voltage drop
A) resistance
B) current
C) voltage drop
B
4
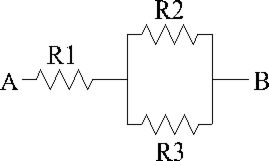
Refer to the diagram above and solve using the values provided.
R1 = 30 Ω , R2 = 600 Ω , and R3 = 1800 Ω, and 240 V is applied between A and B. What is the voltage across R2?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 14 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
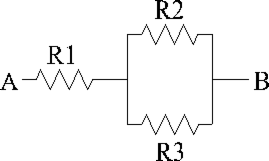
Refer to the diagram above and solve using the values provided.
R1 = 50 Ω , R2 = 200 Ω , and R3 = 600 Ω, and 600 V is applied between A and B. What is the current flow through R3?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 14 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
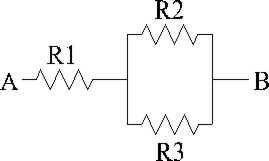
Refer to the diagram above and solve using the values provided.
R1 = 80 Ω , R2 = 100 Ω , and R3 = 400 Ω, and 480 V is applied between A and B. What is the total current flow?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 14 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
Solving combination circuits includes a step in which you _____.
A) enlarge the circuit to several combination circuits
B) eliminate all parallel paths
C) expand the circuit to a more complex circuit
D) reduce the circuit to a simpler circuit
A) enlarge the circuit to several combination circuits
B) eliminate all parallel paths
C) expand the circuit to a more complex circuit
D) reduce the circuit to a simpler circuit

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 14 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
In a series circuit, the _______________ is the sum of the individual resistances.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 14 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
In parallel circuits, the voltage drop across any branch is the same as the _____.
A) applied voltage
B) current
C) resistance
A) applied voltage
B) current
C) resistance

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 14 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
The _______________ in a parallel circuit is equal to the sum of the currents through all of the circuit branches.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 14 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
A series circuit has _____ path(s) for current flow.
A) one
B) two
C) three
D) unlimited
A) one
B) two
C) three
D) unlimited

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 14 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
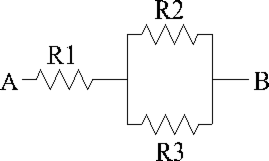
Refer to the diagram above and solve using the values provided.
R1 = 240 Ω , R2 = 300 Ω , and R3 = 1200 Ω .What is the resistance between A and B?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 14 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
In a combination circuit, to identify series and parallel elements, you should _____.
A) trace the current path(s)
B) trace the voltage path(s)
C) calculate the total resistance
D) calculate the total current
A) trace the current path(s)
B) trace the voltage path(s)
C) calculate the total resistance
D) calculate the total current

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 14 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
A junction point of current paths is often called a _____.
A) circuit
B) combination
C) node
A) circuit
B) combination
C) node

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 14 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



