Deck 14: Chemical Equilibrium
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/212
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 14: Chemical Equilibrium
1
The equilibrium constant for the reaction below is 1.7*1017 at 25 C.
H₂ (g) + Br₂(g)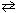 2 HBr (g) K c (25 C) = 1.7*1017
2 HBr (g) K c (25 C) = 1.7*1017
What can be stated about the relative equilibrium distribution for this mixture?
A) The mixture contains predominantly H2 at equilibrium.
B) The mixture contains predominantly Br2 at equilibrium.
C) The mixture contains predominantly HBr at equilibrium.
D) The mixture contains predominantly H2 and Br2 at equilibrium.
E) The mixture contains relatively equal amounts of H2, Br2 and HBr at equilibrium.
H₂ (g) + Br₂(g)
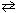 2 HBr (g) K c (25 C) = 1.7*1017
2 HBr (g) K c (25 C) = 1.7*1017 What can be stated about the relative equilibrium distribution for this mixture?
A) The mixture contains predominantly H2 at equilibrium.
B) The mixture contains predominantly Br2 at equilibrium.
C) The mixture contains predominantly HBr at equilibrium.
D) The mixture contains predominantly H2 and Br2 at equilibrium.
E) The mixture contains relatively equal amounts of H2, Br2 and HBr at equilibrium.
The mixture contains predominantly HBr at equilibrium.
2
The equilibrium constant, K c , for the reaction below is 1.2*1045 at 25 C. CO (g) + 1 / 2 O₂(g) 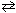 CO₂ (g) What can be stated about the relative equilibrium composition for this mixture?
CO₂ (g) What can be stated about the relative equilibrium composition for this mixture?
A) The mixture contains predominantly CO.
B) The mixture contains predominantly O2.
C) The mixture contains predominantly CO2.
D) The mixture contains predominantly CO and O2.
E) The mixture contains relatively equal amounts of CO, O2 and CO2.
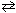 CO₂ (g) What can be stated about the relative equilibrium composition for this mixture?
CO₂ (g) What can be stated about the relative equilibrium composition for this mixture?A) The mixture contains predominantly CO.
B) The mixture contains predominantly O2.
C) The mixture contains predominantly CO2.
D) The mixture contains predominantly CO and O2.
E) The mixture contains relatively equal amounts of CO, O2 and CO2.
The mixture contains predominantly CO2.
3
Consider the following reaction and its corresponding equilibrium constant:
2 ICl (g)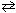 I2 (g) + Cl₂ (g) K c1 = 0.110 What would be the equilibrium constant for the following reaction?
I2 (g) + Cl₂ (g) K c1 = 0.110 What would be the equilibrium constant for the following reaction?
ICl (g)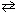 1 / 2 I2 (g) + 1 / 2 Cl₂ (g) K c2 = ??
1 / 2 I2 (g) + 1 / 2 Cl₂ (g) K c2 = ??
A) 0.0121
B) 0.0550
C) 0.110
D) 0.220
E) 0.332
2 ICl (g)
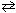 I2 (g) + Cl₂ (g) K c1 = 0.110 What would be the equilibrium constant for the following reaction?
I2 (g) + Cl₂ (g) K c1 = 0.110 What would be the equilibrium constant for the following reaction?ICl (g)
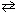 1 / 2 I2 (g) + 1 / 2 Cl₂ (g) K c2 = ??
1 / 2 I2 (g) + 1 / 2 Cl₂ (g) K c2 = ??A) 0.0121
B) 0.0550
C) 0.110
D) 0.220
E) 0.332
0.332
4
When the reversible reaction, N₂+ O₂ 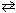 2 NO
2 NO
Has reached a state of dynamic equilibrium , which statement(s) below is(are) true?
I. Both the forward and reverse reactions shut down and no more NO, N₂or O₂are produced.
II. The rate of the forward reaction equals the rate of the reverse reaction.
III. The rate constant of the forward reaction equals the rate constant of the reverse reaction.
A) I only
B) II only
C) III only
D) I and II
E) All of these.
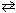 2 NO
2 NOHas reached a state of dynamic equilibrium , which statement(s) below is(are) true?
I. Both the forward and reverse reactions shut down and no more NO, N₂or O₂are produced.
II. The rate of the forward reaction equals the rate of the reverse reaction.
III. The rate constant of the forward reaction equals the rate constant of the reverse reaction.
A) I only
B) II only
C) III only
D) I and II
E) All of these.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 212 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
Consider the following reaction and its corresponding equilibrium constant.
2 O3(g) 3 O₂(g) K c = 5.56*1055 (at 570 K)
3 O₂(g) K c = 5.56*1055 (at 570 K)
What can be stated about the relative proportions of O₂and O3 present at equilibrium?
A) Predominately, O2 exists at equilibrium.
B) Predominately, O3 exists at equilibrium
C) Comparable amounts of O2 and O3 are present at equilibrium.
D) More information is needed to predict relative proportions of O2 and O3.
2 O3(g)
 3 O₂(g) K c = 5.56*1055 (at 570 K)
3 O₂(g) K c = 5.56*1055 (at 570 K)What can be stated about the relative proportions of O₂and O3 present at equilibrium?
A) Predominately, O2 exists at equilibrium.
B) Predominately, O3 exists at equilibrium
C) Comparable amounts of O2 and O3 are present at equilibrium.
D) More information is needed to predict relative proportions of O2 and O3.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 212 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
Given the following two reactions and their corresponding equilibrium constants:
N₂(g) + O₂(g)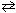 2 NO (g) K c1 = 4.3*10 -25 2 NO₂ (g)
2 NO (g) K c1 = 4.3*10 -25 2 NO₂ (g) 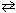 2 NO (g) + O₂(g) K c2 = 1.6 10 - 10 Combine these two reactions in a manner such that they sum to the net reaction that follows and then evaluate its equilibrium constant. N₂(g) + 2 O₂(g)
2 NO (g) + O₂(g) K c2 = 1.6 10 - 10 Combine these two reactions in a manner such that they sum to the net reaction that follows and then evaluate its equilibrium constant. N₂(g) + 2 O₂(g) 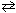 2 NO₂ (g) K net = ??
2 NO₂ (g) K net = ??
A) 6.9×10 - 35
B) 7×10 - 15
C) 6.3×109
D) 3.7×1014
E) 2.3×1024
N₂(g) + O₂(g)
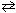 2 NO (g) K c1 = 4.3*10 -25 2 NO₂ (g)
2 NO (g) K c1 = 4.3*10 -25 2 NO₂ (g) 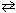 2 NO (g) + O₂(g) K c2 = 1.6 10 - 10 Combine these two reactions in a manner such that they sum to the net reaction that follows and then evaluate its equilibrium constant. N₂(g) + 2 O₂(g)
2 NO (g) + O₂(g) K c2 = 1.6 10 - 10 Combine these two reactions in a manner such that they sum to the net reaction that follows and then evaluate its equilibrium constant. N₂(g) + 2 O₂(g) 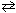 2 NO₂ (g) K net = ??
2 NO₂ (g) K net = ??A) 6.9×10 - 35
B) 7×10 - 15
C) 6.3×109
D) 3.7×1014
E) 2.3×1024

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 212 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
Given the following two reactions and their corresponding equilibrium constants, K c , at 298 K:
1 / 2 N₂(g) + 1 / 2 O₂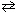 NO (g) K c1 = 6.49*10- 16 2 NO₂ (g)
NO (g) K c1 = 6.49*10- 16 2 NO₂ (g) 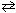 2 NO (g) + O₂(g) K c2 = 4.25*10- 13 What would be the equilibrium constant , K c , for the net reaction given below?
2 NO (g) + O₂(g) K c2 = 4.25*10- 13 What would be the equilibrium constant , K c , for the net reaction given below?
N₂(g) + 2 O₂(g)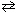 2 NO₂ (g) K c, net = ??
2 NO₂ (g) K c, net = ??
A) 1.79×10 - 43
B) 2.76×10 - 28
C) 9.91×10 - 19
D) 1.53×10 - 3
E) 5.99×104
1 / 2 N₂(g) + 1 / 2 O₂
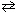 NO (g) K c1 = 6.49*10- 16 2 NO₂ (g)
NO (g) K c1 = 6.49*10- 16 2 NO₂ (g) 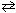 2 NO (g) + O₂(g) K c2 = 4.25*10- 13 What would be the equilibrium constant , K c , for the net reaction given below?
2 NO (g) + O₂(g) K c2 = 4.25*10- 13 What would be the equilibrium constant , K c , for the net reaction given below?N₂(g) + 2 O₂(g)
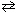 2 NO₂ (g) K c, net = ??
2 NO₂ (g) K c, net = ??A) 1.79×10 - 43
B) 2.76×10 - 28
C) 9.91×10 - 19
D) 1.53×10 - 3
E) 5.99×104

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 212 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
Given the following information, HF (aq) 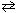 H + (aq) + F - (aq) K c = 6.8*10- 4 H₂ C₂ O4 (aq)
H + (aq) + F - (aq) K c = 6.8*10- 4 H₂ C₂ O4 (aq) 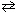 2 H + (aq) + C₂ O4 2 - (aq) K c = 3.8*10- 6 What is the value of the equilibrium constant for the following reaction?
2 H + (aq) + C₂ O4 2 - (aq) K c = 3.8*10- 6 What is the value of the equilibrium constant for the following reaction?
2 HF (aq) + C₂ O4 2 - (aq)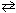 2 F - (aq) + H₂ C₂ O4 (aq) K c = ??
2 F - (aq) + H₂ C₂ O4 (aq) K c = ??
A) - 5.2×10 - 9
B) 2.6×10 - 9
C) 9.9×10 - 8
D) 1.4×10 - 3
E) 0.12
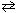 H + (aq) + F - (aq) K c = 6.8*10- 4 H₂ C₂ O4 (aq)
H + (aq) + F - (aq) K c = 6.8*10- 4 H₂ C₂ O4 (aq) 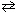 2 H + (aq) + C₂ O4 2 - (aq) K c = 3.8*10- 6 What is the value of the equilibrium constant for the following reaction?
2 H + (aq) + C₂ O4 2 - (aq) K c = 3.8*10- 6 What is the value of the equilibrium constant for the following reaction?2 HF (aq) + C₂ O4 2 - (aq)
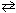 2 F - (aq) + H₂ C₂ O4 (aq) K c = ??
2 F - (aq) + H₂ C₂ O4 (aq) K c = ??A) - 5.2×10 - 9
B) 2.6×10 - 9
C) 9.9×10 - 8
D) 1.4×10 - 3
E) 0.12

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 212 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
The equilibrium constant for the reaction below is 2.5*109 at 25 C.
2 HCl (g) H₂ (g) + Cl₂ (g) K eq (25 C) = 3.2*10- 34
H₂ (g) + Cl₂ (g) K eq (25 C) = 3.2*10- 34
What can be stated about the relative equilibrium distribution for this mixture?
A) The mixture contains predominantly H2.
B) The mixture contains predominantly Cl2.
C) The mixture contains predominantly HCl.
D) The mixture contains predominantly H2 and Cl2.
E) The mixture contains relatively equal amounts of H2, Cl2 and HCl.
2 HCl (g)
 H₂ (g) + Cl₂ (g) K eq (25 C) = 3.2*10- 34
H₂ (g) + Cl₂ (g) K eq (25 C) = 3.2*10- 34 What can be stated about the relative equilibrium distribution for this mixture?
A) The mixture contains predominantly H2.
B) The mixture contains predominantly Cl2.
C) The mixture contains predominantly HCl.
D) The mixture contains predominantly H2 and Cl2.
E) The mixture contains relatively equal amounts of H2, Cl2 and HCl.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 212 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
At 400 C the value of K p for the equilibrium 2 NO (g) + O₂(g)  2 NO₂ (g) is 1.0*106 . What is the value of K p for the equilibrium 2 NO₂ (g)
2 NO₂ (g) is 1.0*106 . What is the value of K p for the equilibrium 2 NO₂ (g)  2 NO (g) + O₂(g)?
2 NO (g) + O₂(g)?
A) 1.0×10 - 6
B) (1.0×106)(RT) - 1
C) (1.0×106)(RT)3
D) 3(1.0×106)/2
E) K p cannot be determined
 2 NO₂ (g) is 1.0*106 . What is the value of K p for the equilibrium 2 NO₂ (g)
2 NO₂ (g) is 1.0*106 . What is the value of K p for the equilibrium 2 NO₂ (g)  2 NO (g) + O₂(g)?
2 NO (g) + O₂(g)?A) 1.0×10 - 6
B) (1.0×106)(RT) - 1
C) (1.0×106)(RT)3
D) 3(1.0×106)/2
E) K p cannot be determined

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 212 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
Given:
2 NO (g) + 2 H₂ (g) N₂(g) + 2 H₂ O (g) K c1 = 6.5*102 What is the equilibrium constant for the following reaction?
N₂(g) + 2 H₂ O (g) K c1 = 6.5*102 What is the equilibrium constant for the following reaction?
1 / 2 N₂(g) + H₂ O (g) NO (g) + H₂ (g) K c2 = ??
NO (g) + H₂ (g) K c2 = ??
A) - 325
B) 2.37×10 - 6
C) 3.92×10 - 2
D) 2.55×101
E) 4.23×105
2 NO (g) + 2 H₂ (g)
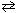 N₂(g) + 2 H₂ O (g) K c1 = 6.5*102 What is the equilibrium constant for the following reaction?
N₂(g) + 2 H₂ O (g) K c1 = 6.5*102 What is the equilibrium constant for the following reaction?1 / 2 N₂(g) + H₂ O (g)
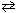 NO (g) + H₂ (g) K c2 = ??
NO (g) + H₂ (g) K c2 = ??A) - 325
B) 2.37×10 - 6
C) 3.92×10 - 2
D) 2.55×101
E) 4.23×105

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 212 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
For the reaction C₂ H₆(g) + 7 / 2 O₂(g) 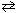 2 CO₂ (g) + 3 H₂ O (g), the expression for K p is
2 CO₂ (g) + 3 H₂ O (g), the expression for K p is
A)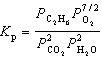
B)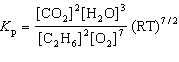
C)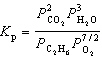
D)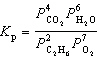
E)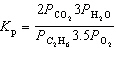
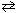 2 CO₂ (g) + 3 H₂ O (g), the expression for K p is
2 CO₂ (g) + 3 H₂ O (g), the expression for K p isA)
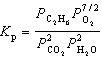
B)
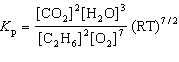
C)
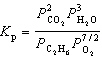
D)
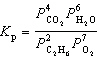
E)
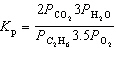

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 212 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
What is the equilibrium constant expression for the following reaction?
2 SO₂ (g) + O₂(g)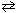 2 SO3(g)
2 SO3(g)
A)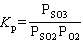
B)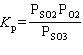
C)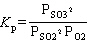
D)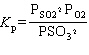
E) K p = PSO22PO2PSO32
2 SO₂ (g) + O₂(g)
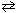 2 SO3(g)
2 SO3(g)A)
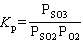
B)
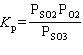
C)
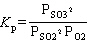
D)
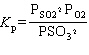
E) K p = PSO22PO2PSO32

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 212 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
For the reaction 2 SO₂ (g) + Cl₂ (g) 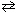 2 SO₂ Cl₂ (g), the expression for K c is
2 SO₂ Cl₂ (g), the expression for K c is
A)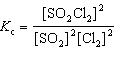
B)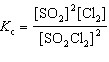
C)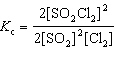
D)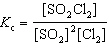
E)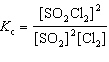
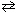 2 SO₂ Cl₂ (g), the expression for K c is
2 SO₂ Cl₂ (g), the expression for K c isA)
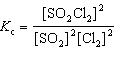
B)
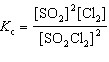
C)
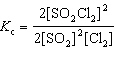
D)
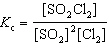
E)
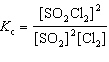

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 212 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
Given:
2 Cl₂ (g) + 2 H₂ O (g)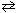 4 HCl (g) + O₂(g) K c (480 C) = 0.0752 What would be the equilibrium constant, K c , for the equation that follows?
4 HCl (g) + O₂(g) K c (480 C) = 0.0752 What would be the equilibrium constant, K c , for the equation that follows?
Cl₂ (g) + H₂ O (g)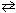 2 HCl (g) + 1 / 2 O₂(g) K c (480 C) = ??
2 HCl (g) + 1 / 2 O₂(g) K c (480 C) = ??
A) 5.66×10 - 3
B) 0.0376
C) 0.0752
D) 0.150
E) 0.274
2 Cl₂ (g) + 2 H₂ O (g)
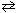 4 HCl (g) + O₂(g) K c (480 C) = 0.0752 What would be the equilibrium constant, K c , for the equation that follows?
4 HCl (g) + O₂(g) K c (480 C) = 0.0752 What would be the equilibrium constant, K c , for the equation that follows?Cl₂ (g) + H₂ O (g)
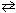 2 HCl (g) + 1 / 2 O₂(g) K c (480 C) = ??
2 HCl (g) + 1 / 2 O₂(g) K c (480 C) = ??A) 5.66×10 - 3
B) 0.0376
C) 0.0752
D) 0.150
E) 0.274

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 212 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
At 700 C, K c = 0.112 for the reaction:
SO₂ (g) + 1 / 2 O₂(g)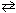 SO3(g) What is the value of the equilibrium constant for the following reaction at 700 C?
SO3(g) What is the value of the equilibrium constant for the following reaction at 700 C?
2 SO₂ (g) + O₂(g)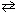 2 SO3(g) K c = ?
2 SO3(g) K c = ?
A) 0.0125
B) 0.0560
C) 0.112
D) 0.224
E) 0.335
SO₂ (g) + 1 / 2 O₂(g)
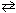 SO3(g) What is the value of the equilibrium constant for the following reaction at 700 C?
SO3(g) What is the value of the equilibrium constant for the following reaction at 700 C?2 SO₂ (g) + O₂(g)
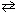 2 SO3(g) K c = ?
2 SO3(g) K c = ?A) 0.0125
B) 0.0560
C) 0.112
D) 0.224
E) 0.335

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 212 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
For the reaction 2 C₂ H₂ (g) + 5 O₂(g) 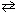 4 CO₂ (g) + 2 H₂ O (g), the expression for K c is
4 CO₂ (g) + 2 H₂ O (g), the expression for K c is
A)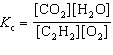
B)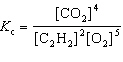
C)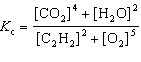
D)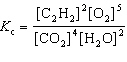
E)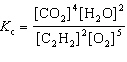
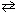 4 CO₂ (g) + 2 H₂ O (g), the expression for K c is
4 CO₂ (g) + 2 H₂ O (g), the expression for K c isA)
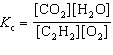
B)
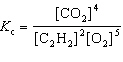
C)
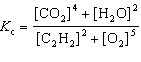
D)
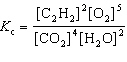
E)
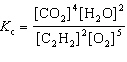

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 212 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
Given:
H₂ O (g) + CO (g)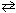 H₂ (g) + CO₂ (g) K c = 1.60 FeO (s) + CO (g)
H₂ (g) + CO₂ (g) K c = 1.60 FeO (s) + CO (g) 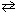 Fe (s) + CO₂ (g) K c = 0.67 What is the equilibrium constant for the following reaction?
Fe (s) + CO₂ (g) K c = 0.67 What is the equilibrium constant for the following reaction?
Fe (s) + H₂ O (g)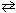 FeO (s) + H₂ (g) K c = ??
FeO (s) + H₂ (g) K c = ??
A) 0.42
B) 0.93
C) 1.07
D) 2.27
E) 2.39
H₂ O (g) + CO (g)
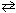 H₂ (g) + CO₂ (g) K c = 1.60 FeO (s) + CO (g)
H₂ (g) + CO₂ (g) K c = 1.60 FeO (s) + CO (g) 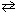 Fe (s) + CO₂ (g) K c = 0.67 What is the equilibrium constant for the following reaction?
Fe (s) + CO₂ (g) K c = 0.67 What is the equilibrium constant for the following reaction?Fe (s) + H₂ O (g)
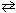 FeO (s) + H₂ (g) K c = ??
FeO (s) + H₂ (g) K c = ??A) 0.42
B) 0.93
C) 1.07
D) 2.27
E) 2.39

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 212 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
Given:
N₂(g) + 3 H₂ (g)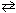 2 NH₃K c (eq 1) = 2.25*10- 6 What is the equilibrium-constant, K c , for the formation of one mole of ammonia from nitrogen and hydrogen at 600 K as shown below?
2 NH₃K c (eq 1) = 2.25*10- 6 What is the equilibrium-constant, K c , for the formation of one mole of ammonia from nitrogen and hydrogen at 600 K as shown below?
1 / 2 N₂(g) + 3 / 2 H₂ (g)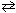 NH₃K c (eq 2) = ??
NH₃K c (eq 2) = ??
A) 2.25×10 - 6 (equilibrium-constants are constant at a given temperature)
B) 1.13×10 - 6
C) 1.5×10 - 3
D) 5.05×10 - 12
E) 4.5×10 - 6
N₂(g) + 3 H₂ (g)
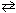 2 NH₃K c (eq 1) = 2.25*10- 6 What is the equilibrium-constant, K c , for the formation of one mole of ammonia from nitrogen and hydrogen at 600 K as shown below?
2 NH₃K c (eq 1) = 2.25*10- 6 What is the equilibrium-constant, K c , for the formation of one mole of ammonia from nitrogen and hydrogen at 600 K as shown below?1 / 2 N₂(g) + 3 / 2 H₂ (g)
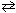 NH₃K c (eq 2) = ??
NH₃K c (eq 2) = ??A) 2.25×10 - 6 (equilibrium-constants are constant at a given temperature)
B) 1.13×10 - 6
C) 1.5×10 - 3
D) 5.05×10 - 12
E) 4.5×10 - 6

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 212 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
The equilibrium constant for the reaction below is 2.5*109 at a particular temperature.
2 SO₂ (g) + O₂(g)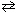 2 SO3(g)
2 SO3(g)
What can be stated about the relative equilibrium distribution for this mixture?
A) The mixture contains predominantly SO3.
B) The mixture contains predominantly O2.
C) The mixture contains predominantly SO2.
D) The mixture contains predominantly SO2 and O2.
E) The mixture contains relatively equal amounts of SO2, O2 and SO3.
2 SO₂ (g) + O₂(g)
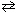 2 SO3(g)
2 SO3(g)What can be stated about the relative equilibrium distribution for this mixture?
A) The mixture contains predominantly SO3.
B) The mixture contains predominantly O2.
C) The mixture contains predominantly SO2.
D) The mixture contains predominantly SO2 and O2.
E) The mixture contains relatively equal amounts of SO2, O2 and SO3.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 212 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
For the reaction 2 H₂ O (g) 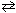 2 H₂ (g) + O₂(g), the relation between K p and K c is:
2 H₂ (g) + O₂(g), the relation between K p and K c is:
A) K p = K c
B) K p = K c(RT)
C) K p = K c(RT)3
D) K p = K c(RT) - 3
E) K p = K c(RT) - 1
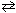 2 H₂ (g) + O₂(g), the relation between K p and K c is:
2 H₂ (g) + O₂(g), the relation between K p and K c is:A) K p = K c
B) K p = K c(RT)
C) K p = K c(RT)3
D) K p = K c(RT) - 3
E) K p = K c(RT) - 1

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 212 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
One mole of SO₂ , two moles of O₂, and two moles of SO3 are placed in a 1.0 liter flask. If K c for the reaction 2 SO₂ (g) + O₂(g) ![<strong>One mole of SO₂ , two moles of O₂, and two moles of SO<sub>3</sub> are placed in a 1.0 liter flask. If K c for the reaction 2 SO₂ (g) + O₂(g) 2 SO<sub>3</sub>(g) is 0.50 at this temperature, what occurs in the flask as equilibrium is approached?</strong> A) [SO<sub>3</sub>] increases B) [O<sub>2</sub>] increases C) [SO<sub>2</sub>] decreases D) No reaction occurs since the system is at equilibrium. E) The equilibrium concentrations of [O<sub>2</sub>] and [SO<sub>2</sub>] are very small.](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TBX8714/11ebff50_c8b0_84ec_8da6_8fc35af5f8a0_TBX8714_11.jpg) 2 SO3(g) is 0.50 at this temperature, what occurs in the flask as equilibrium is approached?
2 SO3(g) is 0.50 at this temperature, what occurs in the flask as equilibrium is approached?
A) [SO3] increases
B) [O2] increases
C) [SO2] decreases
D) No reaction occurs since the system is at equilibrium.
E) The equilibrium concentrations of [O2] and [SO2] are very small.
![<strong>One mole of SO₂ , two moles of O₂, and two moles of SO<sub>3</sub> are placed in a 1.0 liter flask. If K c for the reaction 2 SO₂ (g) + O₂(g) 2 SO<sub>3</sub>(g) is 0.50 at this temperature, what occurs in the flask as equilibrium is approached?</strong> A) [SO<sub>3</sub>] increases B) [O<sub>2</sub>] increases C) [SO<sub>2</sub>] decreases D) No reaction occurs since the system is at equilibrium. E) The equilibrium concentrations of [O<sub>2</sub>] and [SO<sub>2</sub>] are very small.](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TBX8714/11ebff50_c8b0_84ec_8da6_8fc35af5f8a0_TBX8714_11.jpg) 2 SO3(g) is 0.50 at this temperature, what occurs in the flask as equilibrium is approached?
2 SO3(g) is 0.50 at this temperature, what occurs in the flask as equilibrium is approached?A) [SO3] increases
B) [O2] increases
C) [SO2] decreases
D) No reaction occurs since the system is at equilibrium.
E) The equilibrium concentrations of [O2] and [SO2] are very small.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 212 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
A scientist places 0.0050 mol of H₂ , 0.0020 mol of I2 , and 0.050 mol of HI in a 1.0-L container. K c for H₂ (g) + I2 (g) 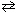 2 HI (g) is 12.5 for this particular experiment. Which statement best describes the results of the experiment?
2 HI (g) is 12.5 for this particular experiment. Which statement best describes the results of the experiment?
A) Some HI (g) will form.
B) Some H2 (g) will form.
C) The system is at equilibrium.
D) The temperature must be known.
E) The pressures must be known.
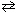 2 HI (g) is 12.5 for this particular experiment. Which statement best describes the results of the experiment?
2 HI (g) is 12.5 for this particular experiment. Which statement best describes the results of the experiment?A) Some HI (g) will form.
B) Some H2 (g) will form.
C) The system is at equilibrium.
D) The temperature must be known.
E) The pressures must be known.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 212 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
What is the partial pressure equilibrium constant, K p , for the following reaction if the concentration equilibrium constant K c = 7.17*1015 at 200 K?
N₂(g) + 3 H₂ (g)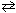 2 NH₃(g)
2 NH₃(g)
A) K p = 7.21×10 - 35
B) K p = 2.66×1013
C) K p = 4.37×1014
D) K p = 1.18×1017
E) K p = 1.93×1018
N₂(g) + 3 H₂ (g)
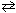 2 NH₃(g)
2 NH₃(g)A) K p = 7.21×10 - 35
B) K p = 2.66×1013
C) K p = 4.37×1014
D) K p = 1.18×1017
E) K p = 1.93×1018

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 212 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
The value of K p is 2.72 at 300 C for the reaction 2 NO (g) + Cl₂ (g) 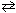 2 NOCl (g). Calculate the value of K c at 300 C.
2 NOCl (g). Calculate the value of K c at 300 C.
A) 5.78×10 - 2
B) 128
C) 67.0
D) 0.110
E) 2.72
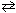 2 NOCl (g). Calculate the value of K c at 300 C.
2 NOCl (g). Calculate the value of K c at 300 C.A) 5.78×10 - 2
B) 128
C) 67.0
D) 0.110
E) 2.72

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 212 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
For the reaction 2 SO₂ (g) + O₂(g) 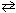 2 SO3(g), K c = 0.15 at 300 K. What is the value of K p for this reaction?
2 SO3(g), K c = 0.15 at 300 K. What is the value of K p for this reaction?
(R = 0.0821 L atm/(mol K)
A) 0.15
B) 6.1×10 - 3
C) 1.6×102
D) 6.7
E) 3.7
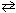 2 SO3(g), K c = 0.15 at 300 K. What is the value of K p for this reaction?
2 SO3(g), K c = 0.15 at 300 K. What is the value of K p for this reaction?(R = 0.0821 L atm/(mol K)
A) 0.15
B) 6.1×10 - 3
C) 1.6×102
D) 6.7
E) 3.7

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 212 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
At 525 C, the equilibrium partial pressures for the substances in the reaction 2 SO₂ (g) + O₂(g) 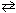 2 SO3(g) were:
2 SO3(g) were:
P SO = 0.0150 atm, P SO = 0.253 atm, and P O = 0.365 atm. The value of K p for this temperature is:
A) 1.28×10 - 3
B) 2.16×10 - 2
C) 46.2
D) 9.63×10 - 3
E) 779
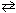 2 SO3(g) were:
2 SO3(g) were:P SO = 0.0150 atm, P SO = 0.253 atm, and P O = 0.365 atm. The value of K p for this temperature is:
A) 1.28×10 - 3
B) 2.16×10 - 2
C) 46.2
D) 9.63×10 - 3
E) 779

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 212 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
An experiment begins when a researcher places 0.020 mol of N₂, 0.050 mol of H₂ and 0.080 mol NH₃, all in the gas phase, in a 1.0-L container. Calculate Q for:
N₂(g) + 3 H₂ (g) 2 NH₃(g)
2 NH₃(g)
A) 1.28×10 - 3
B) 2.16×10 - 2
C) 46.2
D) 3.9×10 - 3
E) 2.6×103
N₂(g) + 3 H₂ (g)
 2 NH₃(g)
2 NH₃(g)A) 1.28×10 - 3
B) 2.16×10 - 2
C) 46.2
D) 3.9×10 - 3
E) 2.6×103

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 212 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
A researcher places 0.10 mol of CO and 0.20 mol of O₂in a 2.0-L container. Calculate Q for:
2 CO₂ (g) 2 CO (g) + O₂(g)
2 CO (g) + O₂(g)
A) 0.
B) 0.00020
C) 0.0020
D) 0.020
E) the result is indeterminably large
2 CO₂ (g)
 2 CO (g) + O₂(g)
2 CO (g) + O₂(g)A) 0.
B) 0.00020
C) 0.0020
D) 0.020
E) the result is indeterminably large

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 212 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
Consider the following system at equilibrium and its corresponding concentration equilibrium constant:
3 O₂(g)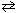 2 O3(g) K c = 1.8*10- 56 at 570 K What is the value of K p for this reaction at 570 K?
2 O3(g) K c = 1.8*10- 56 at 570 K What is the value of K p for this reaction at 570 K?
A) K p = 3.80×10 - 60
B) K p = 3.85×10 - 58
C) K p = 8.42×10 - 55
D) K p = 8.53×10 - 53
E) K p = 1.19×1054
3 O₂(g)
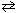 2 O3(g) K c = 1.8*10- 56 at 570 K What is the value of K p for this reaction at 570 K?
2 O3(g) K c = 1.8*10- 56 at 570 K What is the value of K p for this reaction at 570 K?A) K p = 3.80×10 - 60
B) K p = 3.85×10 - 58
C) K p = 8.42×10 - 55
D) K p = 8.53×10 - 53
E) K p = 1.19×1054

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 212 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
If K c for N₂O4 (g) 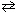 2 NO₂ is 4.5*10- 3 at 25 C, what is the value of K c at 25 C for:
2 NO₂ is 4.5*10- 3 at 25 C, what is the value of K c at 25 C for:
2 NO₂ (g)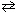 N₂O4 (g)
N₂O4 (g)
A) 2.2×10 - 2
B) 9.0×10 - 3
C) 2.2×102
D) 4.5×10 - 3
E) 4.5×103
 2 NO₂ is 4.5*10- 3 at 25 C, what is the value of K c at 25 C for:
2 NO₂ is 4.5*10- 3 at 25 C, what is the value of K c at 25 C for:2 NO₂ (g)
 N₂O4 (g)
N₂O4 (g)A) 2.2×10 - 2
B) 9.0×10 - 3
C) 2.2×102
D) 4.5×10 - 3
E) 4.5×103

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 212 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
Consider the following reaction at 1200 K:
CH4 (g) + H₂ O (g) CO (g) + 3 H₂ (g) K c = 0.26 What is the pressure equilibrium constant, K p ?
CO (g) + 3 H₂ (g) K c = 0.26 What is the pressure equilibrium constant, K p ?
A) K p = 0.26; K p and K c are always equivalent.
B) K p = 2.7×10 - 5
C) K p = 1.5×10 - 3
D) K p = 6.6×102
E) K p = 2.5×103
CH4 (g) + H₂ O (g)
 CO (g) + 3 H₂ (g) K c = 0.26 What is the pressure equilibrium constant, K p ?
CO (g) + 3 H₂ (g) K c = 0.26 What is the pressure equilibrium constant, K p ?A) K p = 0.26; K p and K c are always equivalent.
B) K p = 2.7×10 - 5
C) K p = 1.5×10 - 3
D) K p = 6.6×102
E) K p = 2.5×103

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 212 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
What is the value of K p for 2 CO (g) + O₂(g) 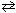 2 CO₂ (g) if K c = 2.24 10 22 ?
2 CO₂ (g) if K c = 2.24 10 22 ?
The temperature is 1273 K.
A) K p = (2.24×1022)(.0821)(1273)
B) K p = (2.24×1022)(.0821)5(1273)5
C) K p = (2.24×1022)(.0821) - 1(1273) - 1
D) K p = (.0821)(1273)(2.24×1022) - 1
E) none of these
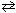 2 CO₂ (g) if K c = 2.24 10 22 ?
2 CO₂ (g) if K c = 2.24 10 22 ?The temperature is 1273 K.
A) K p = (2.24×1022)(.0821)(1273)
B) K p = (2.24×1022)(.0821)5(1273)5
C) K p = (2.24×1022)(.0821) - 1(1273) - 1
D) K p = (.0821)(1273)(2.24×1022) - 1
E) none of these

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 212 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
Two moles of SO₂ , two moles of O₂, and two moles of SO3 are placed in a one liter flask. If K c for the reaction 2 SO₂ (g) + O₂(g) ![<strong>Two moles of SO₂ , two moles of O₂, and two moles of SO<sub>3</sub> are placed in a one liter flask. If K c for the reaction 2 SO₂ (g) + O₂(g) 2 SO<sub>3</sub>(g) is 0.50 at this temperature, what occurs in the flask as equilibrium is approached?</strong> A) [SO<sub>3</sub>] increases B) [O<sub>2</sub>] increases C) [SO<sub>2</sub>] increases D) All concentrations remain constant since the system is at equilibrium. E) The equilibrium concentrations of [O<sub>2</sub>] and [SO<sub>2</sub>] are very small.](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TBX8714/11ebff50_c8b0_84ed_8da6_9fb30ba8a877_TBX8714_11.jpg) 2 SO3(g) is 0.50 at this temperature, what occurs in the flask as equilibrium is approached?
2 SO3(g) is 0.50 at this temperature, what occurs in the flask as equilibrium is approached?
A) [SO3] increases
B) [O2] increases
C) [SO2] increases
D) All concentrations remain constant since the system is at equilibrium.
E) The equilibrium concentrations of [O2] and [SO2] are very small.
![<strong>Two moles of SO₂ , two moles of O₂, and two moles of SO<sub>3</sub> are placed in a one liter flask. If K c for the reaction 2 SO₂ (g) + O₂(g) 2 SO<sub>3</sub>(g) is 0.50 at this temperature, what occurs in the flask as equilibrium is approached?</strong> A) [SO<sub>3</sub>] increases B) [O<sub>2</sub>] increases C) [SO<sub>2</sub>] increases D) All concentrations remain constant since the system is at equilibrium. E) The equilibrium concentrations of [O<sub>2</sub>] and [SO<sub>2</sub>] are very small.](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TBX8714/11ebff50_c8b0_84ed_8da6_9fb30ba8a877_TBX8714_11.jpg) 2 SO3(g) is 0.50 at this temperature, what occurs in the flask as equilibrium is approached?
2 SO3(g) is 0.50 at this temperature, what occurs in the flask as equilibrium is approached?A) [SO3] increases
B) [O2] increases
C) [SO2] increases
D) All concentrations remain constant since the system is at equilibrium.
E) The equilibrium concentrations of [O2] and [SO2] are very small.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 212 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
What is the value of the concentration equilibrium constant, K c (@1000 K), for the following reaction?
CO (g) + Cl₂ (g)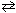 COCl₂ (g) K p = 3.9*10- 2 (@ 1000 K)
COCl₂ (g) K p = 3.9*10- 2 (@ 1000 K)
A) K c = 4.75×10 - 4
B) K c = 3.9×10 - 2
C) K c = 0.312
D) K c = 3.20
E) K c = 324
CO (g) + Cl₂ (g)
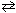 COCl₂ (g) K p = 3.9*10- 2 (@ 1000 K)
COCl₂ (g) K p = 3.9*10- 2 (@ 1000 K)A) K c = 4.75×10 - 4
B) K c = 3.9×10 - 2
C) K c = 0.312
D) K c = 3.20
E) K c = 324

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 212 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
For the reaction I2 (g) + Cl₂ (g) 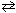 2 ICl (g), the relation between K p and K c is:
2 ICl (g), the relation between K p and K c is:
A) K p = K c
B) K p = K c(RT)2
C) K p = K c(RT) - 2
D) K c = K p(RT)4
E) K p = K c(RT)4
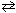 2 ICl (g), the relation between K p and K c is:
2 ICl (g), the relation between K p and K c is:A) K p = K c
B) K p = K c(RT)2
C) K p = K c(RT) - 2
D) K c = K p(RT)4
E) K p = K c(RT)4

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 212 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
Two (2.00) moles of NO, one (1.00) mole of Cl₂ , and two (2.00) moles of NOCl are placed in a 1.00 liter flask. If K c for 2 NO (g) + Cl₂ (g) ![<strong>Two (2.00) moles of NO, one (1.00) mole of Cl₂ , and two (2.00) moles of NOCl are placed in a 1.00 liter flask. If K c for 2 NO (g) + Cl₂ (g) 2 NOCl (g) is 2.72 at this temperature, what occurs in the flask as equilibrium is approached?</strong> A) The reaction is at equilibrium, so no reaction occurs. B) The [NO] increases. C) The [Cl<sub>2</sub>] decreases until [Cl<sub>2</sub>] = 0. D) The [NOCl] increases. E) The [NO] decreases while [Cl<sub>2</sub>] increases.](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TBX8714/11ebff50_c8b0_84ee_8da6_b7c0e8e9b340_TBX8714_11.jpg) 2 NOCl (g) is 2.72 at this temperature, what occurs in the flask as equilibrium is approached?
2 NOCl (g) is 2.72 at this temperature, what occurs in the flask as equilibrium is approached?
A) The reaction is at equilibrium, so no reaction occurs.
B) The [NO] increases.
C) The [Cl2] decreases until [Cl2] = 0.
D) The [NOCl] increases.
E) The [NO] decreases while [Cl2] increases.
![<strong>Two (2.00) moles of NO, one (1.00) mole of Cl₂ , and two (2.00) moles of NOCl are placed in a 1.00 liter flask. If K c for 2 NO (g) + Cl₂ (g) 2 NOCl (g) is 2.72 at this temperature, what occurs in the flask as equilibrium is approached?</strong> A) The reaction is at equilibrium, so no reaction occurs. B) The [NO] increases. C) The [Cl<sub>2</sub>] decreases until [Cl<sub>2</sub>] = 0. D) The [NOCl] increases. E) The [NO] decreases while [Cl<sub>2</sub>] increases.](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TBX8714/11ebff50_c8b0_84ee_8da6_b7c0e8e9b340_TBX8714_11.jpg) 2 NOCl (g) is 2.72 at this temperature, what occurs in the flask as equilibrium is approached?
2 NOCl (g) is 2.72 at this temperature, what occurs in the flask as equilibrium is approached?A) The reaction is at equilibrium, so no reaction occurs.
B) The [NO] increases.
C) The [Cl2] decreases until [Cl2] = 0.
D) The [NOCl] increases.
E) The [NO] decreases while [Cl2] increases.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 212 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
At a certain temperature K c = 9.0 for the equilibrium N₂O4 (g) 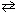 2 NO₂ . What is K c at the same temperature for:
2 NO₂ . What is K c at the same temperature for:
NO₂ (g)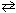 1 / 2 N₂O4 (g)
1 / 2 N₂O4 (g)
A) 1.1
B) 3.0
C) 0.33
D) 9.0
E) none of these
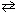 2 NO₂ . What is K c at the same temperature for:
2 NO₂ . What is K c at the same temperature for:NO₂ (g)
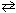 1 / 2 N₂O4 (g)
1 / 2 N₂O4 (g)A) 1.1
B) 3.0
C) 0.33
D) 9.0
E) none of these

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 212 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
For the reaction 4 NH₃(g) + 7 O₂(g) 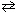 2 N₂O4 (g) + 6 H₂ O (g), the relation between K p and K c is:
2 N₂O4 (g) + 6 H₂ O (g), the relation between K p and K c is:
A) K p = K c
B) K p = K c(RT) - 3
C) K c = K p(RT) - 3
D) K p = K c(RT) - 9
E) none of these
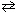 2 N₂O4 (g) + 6 H₂ O (g), the relation between K p and K c is:
2 N₂O4 (g) + 6 H₂ O (g), the relation between K p and K c is:A) K p = K c
B) K p = K c(RT) - 3
C) K c = K p(RT) - 3
D) K p = K c(RT) - 9
E) none of these

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 212 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
A researcher begins an experiment by adding 0.050 mol of CO₂ and 0.010 mol of H₂ in a 10.0-L container. Under the appropriate conditions, a reaction occurs:
CO₂ (g) + H₂ (g)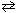 CO (g) + H₂ O (g) Previous experiments show that K p for this reaction is 0.030 under these conditions. Which statement best describes the results of the experiment?
CO (g) + H₂ O (g) Previous experiments show that K p for this reaction is 0.030 under these conditions. Which statement best describes the results of the experiment?
A) Some CO2 (g) will form.
B) Some CO (g) will form.
C) Some H2 (g) will form.
D) The temperature must be known.
E) The pressures must be known.
CO₂ (g) + H₂ (g)
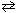 CO (g) + H₂ O (g) Previous experiments show that K p for this reaction is 0.030 under these conditions. Which statement best describes the results of the experiment?
CO (g) + H₂ O (g) Previous experiments show that K p for this reaction is 0.030 under these conditions. Which statement best describes the results of the experiment?A) Some CO2 (g) will form.
B) Some CO (g) will form.
C) Some H2 (g) will form.
D) The temperature must be known.
E) The pressures must be known.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 212 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
The reaction of chlorine and water vapor was allowed to reach equilibrium at 25 C:
2 Cl₂ (g) + 2 H₂ O (g)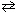 4 HCl (g) + O₂(g)
4 HCl (g) + O₂(g)
The volume of the reactor increased so that the pressure in the reaction chamber at equilibrium decreased from 5 atm to 1 atm. Choose the correct statement below.
A) The number of moles of Cl2 increase.
B) The number of moles of HCl decrease.
C) The number of moles of H2O increase.
D) The number of moles of O2 increase.
E) The number of moles of all substances remain unchanged.
2 Cl₂ (g) + 2 H₂ O (g)
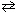 4 HCl (g) + O₂(g)
4 HCl (g) + O₂(g)The volume of the reactor increased so that the pressure in the reaction chamber at equilibrium decreased from 5 atm to 1 atm. Choose the correct statement below.
A) The number of moles of Cl2 increase.
B) The number of moles of HCl decrease.
C) The number of moles of H2O increase.
D) The number of moles of O2 increase.
E) The number of moles of all substances remain unchanged.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 212 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
Consider the reaction:
PCl 3 (g) + Cl₂ (g)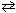 PCl5 (g) K c = 4.2*10- 2
PCl5 (g) K c = 4.2*10- 2
A chemist charged a 1.00 liter reaction vessel with 0.125 moles of PCl5 , 0.250 moles of Cl₂ and 0.375 moles of PCl 3 . If the equilibrium constant, K c , for this reaction is 4.2 10 - 2 , what is the reaction quotient, Q c , and what can be stated about the direction in which this reaction is occurring?
A) Q c = 0.75 and the reaction is proceeding from left to right as written.
B) Q c = 0.75 and the reaction is proceeding from right to left as written.
C) Q c = 0.75 and the reaction is at equilibrium.
D) Q c = 1.33 and the reaction is proceeding from left to right as written.
E) Q c = 1.33 and the reaction is proceeding from right to left as written.
PCl 3 (g) + Cl₂ (g)
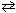 PCl5 (g) K c = 4.2*10- 2
PCl5 (g) K c = 4.2*10- 2A chemist charged a 1.00 liter reaction vessel with 0.125 moles of PCl5 , 0.250 moles of Cl₂ and 0.375 moles of PCl 3 . If the equilibrium constant, K c , for this reaction is 4.2 10 - 2 , what is the reaction quotient, Q c , and what can be stated about the direction in which this reaction is occurring?
A) Q c = 0.75 and the reaction is proceeding from left to right as written.
B) Q c = 0.75 and the reaction is proceeding from right to left as written.
C) Q c = 0.75 and the reaction is at equilibrium.
D) Q c = 1.33 and the reaction is proceeding from left to right as written.
E) Q c = 1.33 and the reaction is proceeding from right to left as written.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 212 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
Given:
N₂(g) + 3 H₂ (g)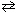 2 NH₃(g) K p (450 C) = 4.51*10- 5 At a single moment, if the partial pressure values for these three components were:
2 NH₃(g) K p (450 C) = 4.51*10- 5 At a single moment, if the partial pressure values for these three components were:
PH 2= 129 atm P N2 = 38 atm P NH3 = 171 atm What can be stated about the reaction quotient , Q , and the direction that the reaction is preceding?
A) Q = 3.49×10 - 2 and the reaction is preceding from left to right as written.
B) Q = 3.49×10 - 2 and the reaction is preceding from right to left as written.
C) Q = 3.58×10 - 4 and the reaction is preceding from left to right as written.
D) Q = 3.58×10 - 4 and the reaction is preceding from right to left as written.
E) Q = 4.51×10 - 5 and the reaction is at equilibrium.
N₂(g) + 3 H₂ (g)
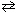 2 NH₃(g) K p (450 C) = 4.51*10- 5 At a single moment, if the partial pressure values for these three components were:
2 NH₃(g) K p (450 C) = 4.51*10- 5 At a single moment, if the partial pressure values for these three components were:PH 2= 129 atm P N2 = 38 atm P NH3 = 171 atm What can be stated about the reaction quotient , Q , and the direction that the reaction is preceding?
A) Q = 3.49×10 - 2 and the reaction is preceding from left to right as written.
B) Q = 3.49×10 - 2 and the reaction is preceding from right to left as written.
C) Q = 3.58×10 - 4 and the reaction is preceding from left to right as written.
D) Q = 3.58×10 - 4 and the reaction is preceding from right to left as written.
E) Q = 4.51×10 - 5 and the reaction is at equilibrium.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 212 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
Consider the following reaction at 730 K:
H₂ (g) + I2 (g)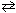 2 HI (g) In one experiment, the following partial pressures were observed at a single moment in time:
2 HI (g) In one experiment, the following partial pressures were observed at a single moment in time:
PH 2= 0.250 atm P I2 = 0.370 atm P HI = 2.13 atm After calculating the reaction quotient, Q p , what can be stated about the reaction above, given K p = 49 at 730 K?
A) Q p K p and the reaction is proceeding left to right as written.
B) Q p K p and the reaction is proceeding right to left as written.
C) Q p > K p and the reaction is proceeding left to right as written.
D) Q p > K p and the reaction is proceeding right to left as written.
E) Q p = K p and the reaction is at equilibrium.
H₂ (g) + I2 (g)
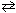 2 HI (g) In one experiment, the following partial pressures were observed at a single moment in time:
2 HI (g) In one experiment, the following partial pressures were observed at a single moment in time:PH 2= 0.250 atm P I2 = 0.370 atm P HI = 2.13 atm After calculating the reaction quotient, Q p , what can be stated about the reaction above, given K p = 49 at 730 K?
A) Q p K p and the reaction is proceeding left to right as written.
B) Q p K p and the reaction is proceeding right to left as written.
C) Q p > K p and the reaction is proceeding left to right as written.
D) Q p > K p and the reaction is proceeding right to left as written.
E) Q p = K p and the reaction is at equilibrium.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 212 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
The system is in equilibrium with the concentrations as shown at 222 C:
2 NH₃(g)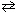 N₂(g) + 3 H₂ (g) Equilibrium pressure 0.4 atm 0.2 atm 0.6 atm By means of a cold trap, ammonia is removed until its equilibrium partial pressure is 0.1 atm. As this change occurs:
N₂(g) + 3 H₂ (g) Equilibrium pressure 0.4 atm 0.2 atm 0.6 atm By means of a cold trap, ammonia is removed until its equilibrium partial pressure is 0.1 atm. As this change occurs:
A) the position of equilibrium will shift to the right.
B) the value of the equilibrium constant will increase.
C) both answers a and b are correct.
D) the position of equilibrium will not be affected.
E) the partial pressure of hydrogen will decrease.
2 NH₃(g)
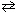 N₂(g) + 3 H₂ (g) Equilibrium pressure 0.4 atm 0.2 atm 0.6 atm By means of a cold trap, ammonia is removed until its equilibrium partial pressure is 0.1 atm. As this change occurs:
N₂(g) + 3 H₂ (g) Equilibrium pressure 0.4 atm 0.2 atm 0.6 atm By means of a cold trap, ammonia is removed until its equilibrium partial pressure is 0.1 atm. As this change occurs:A) the position of equilibrium will shift to the right.
B) the value of the equilibrium constant will increase.
C) both answers a and b are correct.
D) the position of equilibrium will not be affected.
E) the partial pressure of hydrogen will decrease.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 212 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
Consider the following chemical reaction at equilibrium:
2 CH4 (g) + O₂(g) 2 CO (g) + 4 H₂ (g) What is the effect of adding more O₂to this system at equilibrium?
2 CO (g) + 4 H₂ (g) What is the effect of adding more O₂to this system at equilibrium?
A) The system momentarily proceeds from the left side to the right side until equilibrium is re-established.
B) The system momentarily proceeds from the right side to the left side until equilibrium is re-established.
C) There is no effect. Equilibrium has already been established.
D) The system proceeds from the right side to the left side until all of the O2 is consumed.
2 CH4 (g) + O₂(g)
 2 CO (g) + 4 H₂ (g) What is the effect of adding more O₂to this system at equilibrium?
2 CO (g) + 4 H₂ (g) What is the effect of adding more O₂to this system at equilibrium?A) The system momentarily proceeds from the left side to the right side until equilibrium is re-established.
B) The system momentarily proceeds from the right side to the left side until equilibrium is re-established.
C) There is no effect. Equilibrium has already been established.
D) The system proceeds from the right side to the left side until all of the O2 is consumed.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 212 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
For the reaction I2 (g) + Cl₂ (g)  2 ICl (g) at equilibrium, an increase in the volume of the reaction vessel would:
2 ICl (g) at equilibrium, an increase in the volume of the reaction vessel would:
A) increase the mole amount of ICl
B) increase the mole amount of I2
C) decrease the mole amount of Cl2
D) decrease the mole amount of ICl
E) leave the mole amount of ICl, Cl2, and I2 unchanged
 2 ICl (g) at equilibrium, an increase in the volume of the reaction vessel would:
2 ICl (g) at equilibrium, an increase in the volume of the reaction vessel would:A) increase the mole amount of ICl
B) increase the mole amount of I2
C) decrease the mole amount of Cl2
D) decrease the mole amount of ICl
E) leave the mole amount of ICl, Cl2, and I2 unchanged

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 212 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
For the reaction
2 NO (g) + 2 CO (g)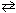 N₂(g) + 2 CO₂ (g)
N₂(g) + 2 CO₂ (g)
At equilibrium, an increase in the volume of the reaction vessel would:
A) decrease the number of moles of both NO and CO.
B) increase the number of moles of both N2 and CO2.
C) decrease the number of moles of both NO and CO2.
D) increase the number of moles of both NO and CO2.
E) increase the number of moles of both NO and CO.
2 NO (g) + 2 CO (g)
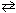 N₂(g) + 2 CO₂ (g)
N₂(g) + 2 CO₂ (g)At equilibrium, an increase in the volume of the reaction vessel would:
A) decrease the number of moles of both NO and CO.
B) increase the number of moles of both N2 and CO2.
C) decrease the number of moles of both NO and CO2.
D) increase the number of moles of both NO and CO2.
E) increase the number of moles of both NO and CO.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 212 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
At 1000 K, the value of the K eq for the following reaction equals 0.338.
2 SO3(g)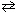 2 SO₂ (g) + O₂(g) K c = 0.338
2 SO₂ (g) + O₂(g) K c = 0.338
If the partial pressure values for these three components at a single moment were:
P SO3 = 0.16 atm P SO2 = 0.41 atm PO2 = 2.5 atm What can be stated about the reaction quotient , Q , and the direction that the reaction is preceding?
A) Q = 16.4 and the reaction is preceding from left to right as written.
B) Q = 16.4 and the reaction is preceding from right to left as written.
C) Q = 6.4 and the reaction is preceding from left to right as written.
D) Q = 6.4 and the reaction preceding from right to left as written.
E) Q = 6.4 and the reaction is at equilibrium.
2 SO3(g)
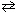 2 SO₂ (g) + O₂(g) K c = 0.338
2 SO₂ (g) + O₂(g) K c = 0.338If the partial pressure values for these three components at a single moment were:
P SO3 = 0.16 atm P SO2 = 0.41 atm PO2 = 2.5 atm What can be stated about the reaction quotient , Q , and the direction that the reaction is preceding?
A) Q = 16.4 and the reaction is preceding from left to right as written.
B) Q = 16.4 and the reaction is preceding from right to left as written.
C) Q = 6.4 and the reaction is preceding from left to right as written.
D) Q = 6.4 and the reaction preceding from right to left as written.
E) Q = 6.4 and the reaction is at equilibrium.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 212 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
Under what conditions does changing the pressure have no effect upon the position of equilibrium?
I. When the total pressure is changed by adding an inert gas.
II. When the total number of moles of gas on the reactant side equals the total number of moles of gas on the product side.
III. When all substances present at equilibrium are aqueous phases.
A) I only
B) II only
C) III only
D) I and II
E) all of these
I. When the total pressure is changed by adding an inert gas.
II. When the total number of moles of gas on the reactant side equals the total number of moles of gas on the product side.
III. When all substances present at equilibrium are aqueous phases.
A) I only
B) II only
C) III only
D) I and II
E) all of these

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 212 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
The reaction NO (g) + O3(g)  NO₂ (g) + O₂(g) reaches equilibrium at 310 K. Some of the NO₂ gas is then removed from the reaction chamber. Which of the following statements correctly describes the change that would result when equilibrium is restored?
NO₂ (g) + O₂(g) reaches equilibrium at 310 K. Some of the NO₂ gas is then removed from the reaction chamber. Which of the following statements correctly describes the change that would result when equilibrium is restored?
A) The concentration of NO increases.
B) The concentration of O2 decreases.
C) The concentration of NO remains the same.
D) The concentration of O3 decreases.
E) The equilibrium constant decreases.
 NO₂ (g) + O₂(g) reaches equilibrium at 310 K. Some of the NO₂ gas is then removed from the reaction chamber. Which of the following statements correctly describes the change that would result when equilibrium is restored?
NO₂ (g) + O₂(g) reaches equilibrium at 310 K. Some of the NO₂ gas is then removed from the reaction chamber. Which of the following statements correctly describes the change that would result when equilibrium is restored?A) The concentration of NO increases.
B) The concentration of O2 decreases.
C) The concentration of NO remains the same.
D) The concentration of O3 decreases.
E) The equilibrium constant decreases.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 212 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
At 100 C, the equilibrium constant for the reaction below is 6.71 10 - 9 . COCl₂ (g)  CO (g) + Cl₂ (g) At a particular moment, the following partial pressures were observed:
CO (g) + Cl₂ (g) At a particular moment, the following partial pressures were observed:
P COCl2 = 6.12 10 - 2 atm P CO = 1.01 10 - 4 atm P Cl2 = 2.03*10- 4atm After calculating the reaction quotient , what can be stated about the direction in which this reaction is proceeding?
A) Not enough information is provided to make an assessment.
B) This reaction is proceeding left to right as written. (reactants to products)
C) This reaction is proceeding right to left as written. (product to reactants)
D) This reaction is at a state of chemical equilibrium.
 CO (g) + Cl₂ (g) At a particular moment, the following partial pressures were observed:
CO (g) + Cl₂ (g) At a particular moment, the following partial pressures were observed:P COCl2 = 6.12 10 - 2 atm P CO = 1.01 10 - 4 atm P Cl2 = 2.03*10- 4atm After calculating the reaction quotient , what can be stated about the direction in which this reaction is proceeding?
A) Not enough information is provided to make an assessment.
B) This reaction is proceeding left to right as written. (reactants to products)
C) This reaction is proceeding right to left as written. (product to reactants)
D) This reaction is at a state of chemical equilibrium.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 212 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
At 700 C, the equilibrium constant ( K c ) for the reaction
N₂(g) + 3 H₂ (g) 2 NH₃(g) is 2.37 10 - 3 .
2 NH₃(g) is 2.37 10 - 3 .
If 0.683 mol of N₂, 8.80 mol of H₂ and 0.744 mole of NH₃are mixed in a 1.00 L container at 700 C:
A) the value of Q is unknown.
B) the value of Q is greater than K c.
C) the value of Q is equal to K c.
D) the reaction is at equilibrium.
E) the value of Q is less than K c.
N₂(g) + 3 H₂ (g)
 2 NH₃(g) is 2.37 10 - 3 .
2 NH₃(g) is 2.37 10 - 3 .If 0.683 mol of N₂, 8.80 mol of H₂ and 0.744 mole of NH₃are mixed in a 1.00 L container at 700 C:
A) the value of Q is unknown.
B) the value of Q is greater than K c.
C) the value of Q is equal to K c.
D) the reaction is at equilibrium.
E) the value of Q is less than K c.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 212 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
The reaction of chlorine and water vapor was allowed to reach equilibrium at 125 C:
2 Cl₂ (g) + 2 H₂ O (g) 4 HCl (g) + O₂(g) If the volume of the reaction chamber were suddenly doubled, at equilibrium:
4 HCl (g) + O₂(g) If the volume of the reaction chamber were suddenly doubled, at equilibrium:
A) the number of moles of O2 would decrease.
B) the number of moles of Cl2 would increase.
C) the number of moles of H2O would decrease.
D) the number of moles of all gases would be unchanged.
E) cannot be determined from information.
2 Cl₂ (g) + 2 H₂ O (g)
 4 HCl (g) + O₂(g) If the volume of the reaction chamber were suddenly doubled, at equilibrium:
4 HCl (g) + O₂(g) If the volume of the reaction chamber were suddenly doubled, at equilibrium:A) the number of moles of O2 would decrease.
B) the number of moles of Cl2 would increase.
C) the number of moles of H2O would decrease.
D) the number of moles of all gases would be unchanged.
E) cannot be determined from information.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 212 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
For the reaction 2 NH₃(g) 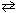 N₂(g) + 3 H₂ (g), what would you expect if 0.6 atm of inert neon gas is added at constant volume to the equilibrium mixture of gases?
N₂(g) + 3 H₂ (g), what would you expect if 0.6 atm of inert neon gas is added at constant volume to the equilibrium mixture of gases?
A) Since neon is more dense than hydrogen, it would suppress the reverse reaction; thus, more hydrogen would be formed.
B) The position of equilibrium would shift to the left.
C) Because neon does not react with any of the other chemical species, it cannot change the equilibrium partial pressures of the reactants or products; therefore, the position of equilibrium will remain the same.
D) Because neon is isoelectronic with ammonia, it would compete with ammonia in the forward reaction; therefore, the equilibrium would shift to the right.
E) Neon acts as a catalyst for the reaction thereby lowering the activation energy for the forward reaction.
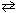 N₂(g) + 3 H₂ (g), what would you expect if 0.6 atm of inert neon gas is added at constant volume to the equilibrium mixture of gases?
N₂(g) + 3 H₂ (g), what would you expect if 0.6 atm of inert neon gas is added at constant volume to the equilibrium mixture of gases?A) Since neon is more dense than hydrogen, it would suppress the reverse reaction; thus, more hydrogen would be formed.
B) The position of equilibrium would shift to the left.
C) Because neon does not react with any of the other chemical species, it cannot change the equilibrium partial pressures of the reactants or products; therefore, the position of equilibrium will remain the same.
D) Because neon is isoelectronic with ammonia, it would compete with ammonia in the forward reaction; therefore, the equilibrium would shift to the right.
E) Neon acts as a catalyst for the reaction thereby lowering the activation energy for the forward reaction.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 212 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
The reaction 2 NO (g) + 2 CO (g) ![<strong>The reaction 2 NO (g) + 2 CO (g) N₂(g) + 2 CO₂ (g) was allowed to reach equilibrium. Additional NO gas was then injected into the reaction chamber and equilibrium was restored. Choose the correct statement below.</strong> A) All concentrations remain the same. B) A new equilibrium is obtained such that [CO] decreases. C) A new equilibrium is obtained such that [N<sub>2</sub>] decreases. D) The value of K <sub>c</sub> increases. E) A new equilibrium is obtained such that both [CO] and [N<sub>2</sub>] decrease.](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TBX8714/11ebff50_c8b1_4847_8da6_e17851fe54ba_TBX8714_11.jpg) N₂(g) + 2 CO₂ (g) was allowed to reach equilibrium. Additional NO gas was then injected into the reaction chamber and equilibrium was restored. Choose the correct statement below.
N₂(g) + 2 CO₂ (g) was allowed to reach equilibrium. Additional NO gas was then injected into the reaction chamber and equilibrium was restored. Choose the correct statement below.
A) All concentrations remain the same.
B) A new equilibrium is obtained such that [CO] decreases.
C) A new equilibrium is obtained such that [N2] decreases.
D) The value of K c increases.
E) A new equilibrium is obtained such that both [CO] and [N2] decrease.
![<strong>The reaction 2 NO (g) + 2 CO (g) N₂(g) + 2 CO₂ (g) was allowed to reach equilibrium. Additional NO gas was then injected into the reaction chamber and equilibrium was restored. Choose the correct statement below.</strong> A) All concentrations remain the same. B) A new equilibrium is obtained such that [CO] decreases. C) A new equilibrium is obtained such that [N<sub>2</sub>] decreases. D) The value of K <sub>c</sub> increases. E) A new equilibrium is obtained such that both [CO] and [N<sub>2</sub>] decrease.](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TBX8714/11ebff50_c8b1_4847_8da6_e17851fe54ba_TBX8714_11.jpg) N₂(g) + 2 CO₂ (g) was allowed to reach equilibrium. Additional NO gas was then injected into the reaction chamber and equilibrium was restored. Choose the correct statement below.
N₂(g) + 2 CO₂ (g) was allowed to reach equilibrium. Additional NO gas was then injected into the reaction chamber and equilibrium was restored. Choose the correct statement below.A) All concentrations remain the same.
B) A new equilibrium is obtained such that [CO] decreases.
C) A new equilibrium is obtained such that [N2] decreases.
D) The value of K c increases.
E) A new equilibrium is obtained such that both [CO] and [N2] decrease.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 212 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
Which of the following reactions would shift to the right to favor the product side upon increasing the pressure (through a reduction in the volume of the reaction vessel)?
I. H₂ (g) + C₂ N₂(g)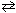 2 HCN (g)
2 HCN (g)
II. CO (g) + Br₂(g)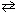 CO Br₂(g)
CO Br₂(g)
III. 6 CO₂ (g) + 6 H₂ O ( )
)  C6 H12 O6 (s) + 6 O₂(g)
C6 H12 O6 (s) + 6 O₂(g)
A) I only
B) II only
C) III only
D) I and III
E) II and III
I. H₂ (g) + C₂ N₂(g)
 2 HCN (g)
2 HCN (g)II. CO (g) + Br₂(g)
 CO Br₂(g)
CO Br₂(g)III. 6 CO₂ (g) + 6 H₂ O (
 )
)  C6 H12 O6 (s) + 6 O₂(g)
C6 H12 O6 (s) + 6 O₂(g)A) I only
B) II only
C) III only
D) I and III
E) II and III

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 212 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
Consider the following reaction:
2 HBr (g) H₂ (g) + Br₂(g) In one experiment, the following partial pressures were observed at a single moment in time:
H₂ (g) + Br₂(g) In one experiment, the following partial pressures were observed at a single moment in time:
P HBr = 0.25 atm PH 2= 0.100 atm PBr2 = 0.019 atm After calculating the reaction quotient, Q p , what can be stated about the reaction above, given K p = 4.18*10 - 9 ?
A) Q p K p and the reaction is proceeding left to right as written.
B) Q p K p and the reaction is proceeding right to left as written.
C) Q p > K p and the reaction is proceeding left to right as written.
D) Q p > K p and the reaction is proceeding right to left as written.
E) Q p = K p and the reaction is at equilibrium.
2 HBr (g)
 H₂ (g) + Br₂(g) In one experiment, the following partial pressures were observed at a single moment in time:
H₂ (g) + Br₂(g) In one experiment, the following partial pressures were observed at a single moment in time:P HBr = 0.25 atm PH 2= 0.100 atm PBr2 = 0.019 atm After calculating the reaction quotient, Q p , what can be stated about the reaction above, given K p = 4.18*10 - 9 ?
A) Q p K p and the reaction is proceeding left to right as written.
B) Q p K p and the reaction is proceeding right to left as written.
C) Q p > K p and the reaction is proceeding left to right as written.
D) Q p > K p and the reaction is proceeding right to left as written.
E) Q p = K p and the reaction is at equilibrium.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 212 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
For the reaction CO₂ (g) + H₂ (g) ![<strong>For the reaction CO₂ (g) + H₂ (g) H₂ O (g) + CO (g) at equilibrium, increasing the volume of the reaction vessel will:</strong> A) increase [H<sub>2</sub>O] B) increase both [H<sub>2</sub>O] and [CO] C) change K <sub>c</sub> D) cause no change in the number of moles of each substance E) increase both [CO<sub>2</sub>] and [H<sub>2</sub>]](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TBX8714/11ebff50_c8b1_966c_8da6_ad26389fc06d_TBX8714_11.jpg) H₂ O (g) + CO (g) at equilibrium, increasing the volume of the reaction vessel will:
H₂ O (g) + CO (g) at equilibrium, increasing the volume of the reaction vessel will:
A) increase [H2O]
B) increase both [H2O] and [CO]
C) change K c
D) cause no change in the number of moles of each substance
E) increase both [CO2] and [H2]
![<strong>For the reaction CO₂ (g) + H₂ (g) H₂ O (g) + CO (g) at equilibrium, increasing the volume of the reaction vessel will:</strong> A) increase [H<sub>2</sub>O] B) increase both [H<sub>2</sub>O] and [CO] C) change K <sub>c</sub> D) cause no change in the number of moles of each substance E) increase both [CO<sub>2</sub>] and [H<sub>2</sub>]](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TBX8714/11ebff50_c8b1_966c_8da6_ad26389fc06d_TBX8714_11.jpg) H₂ O (g) + CO (g) at equilibrium, increasing the volume of the reaction vessel will:
H₂ O (g) + CO (g) at equilibrium, increasing the volume of the reaction vessel will:A) increase [H2O]
B) increase both [H2O] and [CO]
C) change K c
D) cause no change in the number of moles of each substance
E) increase both [CO2] and [H2]

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 212 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
Consider the Haber process for preparing ammonia from nitrogen and hydrogen as shown below and the reaction s corresponding equilibrium constant at 532 C.
N₂(g) + 3 H₂ (g) 2 NH₃(g) K eq (532 C) = 0.19
2 NH₃(g) K eq (532 C) = 0.19
At a particular moment, the following equilibrium concentrations were observed:
N₂= 0.079 M, H₂ = 0.12 M and NH₃= 0.0051 M. After calculating the reaction quotient , Q , what can be stated about the direction in which this reaction is proceeding?
A) Not enough information is provided to make an assessment.
B) This reaction is proceeding left to right as written. (reactants to products)
C) This reaction is proceeding right to left as written. (product to reactants)
D) This reaction is at a state of chemical equilibrium.
N₂(g) + 3 H₂ (g)
 2 NH₃(g) K eq (532 C) = 0.19
2 NH₃(g) K eq (532 C) = 0.19At a particular moment, the following equilibrium concentrations were observed:
N₂= 0.079 M, H₂ = 0.12 M and NH₃= 0.0051 M. After calculating the reaction quotient , Q , what can be stated about the direction in which this reaction is proceeding?
A) Not enough information is provided to make an assessment.
B) This reaction is proceeding left to right as written. (reactants to products)
C) This reaction is proceeding right to left as written. (product to reactants)
D) This reaction is at a state of chemical equilibrium.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 212 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
At 125 C, K p = 5.2*10- 9 and at 500 C, K p = 0.10 for the reaction:
2 Cl₂ (g) + 2 H₂ O (g)![<strong>At 125 C, K p = 5.2*10<sup>- 9</sup> and at 500 C, K p = 0.10 for the reaction: 2 Cl₂ (g) + 2 H₂ O (g) 4 HCl (g) + O₂(g) Choose the correct statement.</strong> A) The reaction is endothermic. B) The reaction is exothermic. C) K <sub>c</sub> is independent of temperature. D) The [O<sub>2</sub>] decreases with increasing temperature. E) K <sub>p</sub> is directly proportional to the temperature.](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TBX8714/11ebff50_c8b2_a6f7_8da6_5f3e7bb94018_TBX8714_11.jpg) 4 HCl (g) + O₂(g) Choose the correct statement.
4 HCl (g) + O₂(g) Choose the correct statement.
A) The reaction is endothermic.
B) The reaction is exothermic.
C) K c is independent of temperature.
D) The [O2] decreases with increasing temperature.
E) K p is directly proportional to the temperature.
2 Cl₂ (g) + 2 H₂ O (g)
![<strong>At 125 C, K p = 5.2*10<sup>- 9</sup> and at 500 C, K p = 0.10 for the reaction: 2 Cl₂ (g) + 2 H₂ O (g) 4 HCl (g) + O₂(g) Choose the correct statement.</strong> A) The reaction is endothermic. B) The reaction is exothermic. C) K <sub>c</sub> is independent of temperature. D) The [O<sub>2</sub>] decreases with increasing temperature. E) K <sub>p</sub> is directly proportional to the temperature.](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TBX8714/11ebff50_c8b2_a6f7_8da6_5f3e7bb94018_TBX8714_11.jpg) 4 HCl (g) + O₂(g) Choose the correct statement.
4 HCl (g) + O₂(g) Choose the correct statement.A) The reaction is endothermic.
B) The reaction is exothermic.
C) K c is independent of temperature.
D) The [O2] decreases with increasing temperature.
E) K p is directly proportional to the temperature.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 212 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
Which of the following reactions is product favored by a higher temperature ?
I. N₂(g) + 2 O₂+ Heat 2 NO₂ (g)
2 NO₂ (g)
II. 2 N₂(g) + 6 H₂ O (g) 4 NH₃(g) + 3 O₂(g) (endothermic reaction)
4 NH₃(g) + 3 O₂(g) (endothermic reaction)
III. C₂ H4 (g) + 3 O₂(g)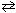 2 CO₂ (g) + 2 H₂ O (g) ( D H 0)
2 CO₂ (g) + 2 H₂ O (g) ( D H 0)
A) I only
B) II only
C) III only
D) I and II
E) I and III
I. N₂(g) + 2 O₂+ Heat
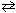 2 NO₂ (g)
2 NO₂ (g)II. 2 N₂(g) + 6 H₂ O (g)
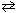 4 NH₃(g) + 3 O₂(g) (endothermic reaction)
4 NH₃(g) + 3 O₂(g) (endothermic reaction)III. C₂ H4 (g) + 3 O₂(g)
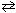 2 CO₂ (g) + 2 H₂ O (g) ( D H 0)
2 CO₂ (g) + 2 H₂ O (g) ( D H 0)A) I only
B) II only
C) III only
D) I and II
E) I and III

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 212 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
Which system at equilibrium shifts right ?
I. Increasing the pressure by compression for:
H₂ (g) + I2 (g) 2 HI (g)
2 HI (g)
II. Increasing the pressure by compression for:
PCl 3 (g) + Cl₂ (g) PCl5 (g)
PCl5 (g)
III. Increasing the pressure by addition of Argon, an inert gas:
N₂(g) + 3 H₂ (g) 2 NH₃(g)
2 NH₃(g)
A) I only
B) II only
C) I and II
D) I and III
E) All of these
I. Increasing the pressure by compression for:
H₂ (g) + I2 (g)
 2 HI (g)
2 HI (g)II. Increasing the pressure by compression for:
PCl 3 (g) + Cl₂ (g)
 PCl5 (g)
PCl5 (g)III. Increasing the pressure by addition of Argon, an inert gas:
N₂(g) + 3 H₂ (g)
 2 NH₃(g)
2 NH₃(g)A) I only
B) II only
C) I and II
D) I and III
E) All of these

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 212 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
For the high temperature equilibrium system, 2 H₂ O (g)  2 H₂ (g) + O₂(g), what will be the effect on the equilibrium concentration of O₂(g) upon:
2 H₂ (g) + O₂(g), what will be the effect on the equilibrium concentration of O₂(g) upon:
(1) adding H₂ O (g) and (2) decreasing the pressure of the system?
A) (1) and (2) increase the concentration of O2
B) (1) increases while (2) decreases the concentration of O2
C) (1) decreases while (2) increases the concentration of O2
D) (1) and (2) decrease the concentration of O2
E) none of these
 2 H₂ (g) + O₂(g), what will be the effect on the equilibrium concentration of O₂(g) upon:
2 H₂ (g) + O₂(g), what will be the effect on the equilibrium concentration of O₂(g) upon:(1) adding H₂ O (g) and (2) decreasing the pressure of the system?
A) (1) and (2) increase the concentration of O2
B) (1) increases while (2) decreases the concentration of O2
C) (1) decreases while (2) increases the concentration of O2
D) (1) and (2) decrease the concentration of O2
E) none of these

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 212 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
Which system at equilibrium shifts right upon heating?
I. PCl 3 (g) + Cl₂ (g) PCl5 (g) + 111 kJ
PCl5 (g) + 111 kJ
II. N₂(g) + 3 H₂ (g) 2 NH₃(g) (exothermic)
2 NH₃(g) (exothermic)
III. N₂(g) + O₂(g) 2 NO ( D H 0)
2 NO ( D H 0)
A) I only
B) II only
C) III only
D) I and II
E) I and III
I. PCl 3 (g) + Cl₂ (g)
 PCl5 (g) + 111 kJ
PCl5 (g) + 111 kJII. N₂(g) + 3 H₂ (g)
 2 NH₃(g) (exothermic)
2 NH₃(g) (exothermic)III. N₂(g) + O₂(g)
 2 NO ( D H 0)
2 NO ( D H 0)A) I only
B) II only
C) III only
D) I and II
E) I and III

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 212 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
Consider the following endothermic reaction at equilibrium:
2 N₂(g) + 6 H₂ O 4 NH₃(g) + 3 O₂(g) Which statement is true?
4 NH₃(g) + 3 O₂(g) Which statement is true?
A) Heat shows up as a product in this reaction and supplying heat favors shifting the direction of the reaction to the reactants.
B) Heat shows up as a product in this reaction and supplying heat favors shifting the direction of the reaction to the products.
C) Heat shows up as a reactant in this reaction and supplying heat favors shifting the direction of the reaction to the reactants.
D) Heat shows up as a reactant in this reaction and supplying heat favors shifting the direction of the reaction to the products.
2 N₂(g) + 6 H₂ O
 4 NH₃(g) + 3 O₂(g) Which statement is true?
4 NH₃(g) + 3 O₂(g) Which statement is true?A) Heat shows up as a product in this reaction and supplying heat favors shifting the direction of the reaction to the reactants.
B) Heat shows up as a product in this reaction and supplying heat favors shifting the direction of the reaction to the products.
C) Heat shows up as a reactant in this reaction and supplying heat favors shifting the direction of the reaction to the reactants.
D) Heat shows up as a reactant in this reaction and supplying heat favors shifting the direction of the reaction to the products.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 212 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
The only factor that causes a change in the numerical value of an equilibrium constant is a(n):
A) change in volume.
B) change in pressure.
C) change in concentrations.
D) addition of a catalyst.
E) change in temperature.
A) change in volume.
B) change in pressure.
C) change in concentrations.
D) addition of a catalyst.
E) change in temperature.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 212 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
Which of the following reactions is product favored by a higher temperature ?
I. N₂(g) + 2 O₂ 2 NO₂ (g) (endothermic reaction)
2 NO₂ (g) (endothermic reaction)
II. 4 NH₃(g) + 3 O₂(g) 2 N₂(g) + 6 H₂ O (g) ( D H 0)
2 N₂(g) + 6 H₂ O (g) ( D H 0)
III. 2 CO₂ (g) + 2 H₂ O (g) C₂ H4 (g) + 3 O₂(g) + heat
C₂ H4 (g) + 3 O₂(g) + heat
A) I only
B) II only
C) III only
D) I and III
E) II and III
I. N₂(g) + 2 O₂
 2 NO₂ (g) (endothermic reaction)
2 NO₂ (g) (endothermic reaction)II. 4 NH₃(g) + 3 O₂(g)
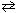 2 N₂(g) + 6 H₂ O (g) ( D H 0)
2 N₂(g) + 6 H₂ O (g) ( D H 0)III. 2 CO₂ (g) + 2 H₂ O (g)
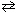 C₂ H4 (g) + 3 O₂(g) + heat
C₂ H4 (g) + 3 O₂(g) + heatA) I only
B) II only
C) III only
D) I and III
E) II and III

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 212 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
At 500 C, K p = 4.9*10- 5 for the exothermic reaction:
N₂(g) + 3 H₂ (g)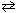 2 NH₃(g) The value of K p at 1000 C is:
2 NH₃(g) The value of K p at 1000 C is:
A) greater than 4.9×10 - 5
B) less than 4.9×10 - 5
C) equal tO4.9×10 - 5
D) equal to 0.00
E) insufficient information to reach a conclusion
N₂(g) + 3 H₂ (g)
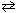 2 NH₃(g) The value of K p at 1000 C is:
2 NH₃(g) The value of K p at 1000 C is:A) greater than 4.9×10 - 5
B) less than 4.9×10 - 5
C) equal tO4.9×10 - 5
D) equal to 0.00
E) insufficient information to reach a conclusion

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 212 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
What is the effect upon addition of Argon (an inert gas) to the equilibrium reaction shown below?
N₂O4 (g) 2 NO₂ (g)
2 NO₂ (g)
A) No effect
B) The reaction shifts to the right.
C) The reaction shifts to the left.
D) More information is needed.
N₂O4 (g)
 2 NO₂ (g)
2 NO₂ (g)A) No effect
B) The reaction shifts to the right.
C) The reaction shifts to the left.
D) More information is needed.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 212 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
Which of the following reaction(s) at equilibrium would shift to the right upon subjecting it to the conditions stated?
I. Increasing the total pressure of the following reaction mixture by introducing an inert gas such as helium:
2 SO₂ (g) + O₂(g) 2 SO3 .
2 SO3 .
II. Increasing the pressure of the following reaction mixture through a reduction in volume of the reaction vessel:
H₂ (g) + I2 (g) 2 HI (g).
2 HI (g).
III. Decreasing the pressure of the following reaction mixture through an expansion in volume of the reaction vessel:
Co(H₂ O) 6 2+ (aq) + 4 Cl - (aq) CoCl42 - (aq) + 6 H₂ O (
CoCl42 - (aq) + 6 H₂ O (  )
)
A) I only
B) II only
C) III only
D) I and II
E) none of these
I. Increasing the total pressure of the following reaction mixture by introducing an inert gas such as helium:
2 SO₂ (g) + O₂(g)
 2 SO3 .
2 SO3 .II. Increasing the pressure of the following reaction mixture through a reduction in volume of the reaction vessel:
H₂ (g) + I2 (g)
 2 HI (g).
2 HI (g).III. Decreasing the pressure of the following reaction mixture through an expansion in volume of the reaction vessel:
Co(H₂ O) 6 2+ (aq) + 4 Cl - (aq)
 CoCl42 - (aq) + 6 H₂ O (
CoCl42 - (aq) + 6 H₂ O (  )
)A) I only
B) II only
C) III only
D) I and II
E) none of these

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 212 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72
Inert helium gas was injected into a reaction vessel of fixed volume containing an equilibrium mixture of 2 SO₂ (g) + O₂(g) ![<strong>Inert helium gas was injected into a reaction vessel of fixed volume containing an equilibrium mixture of 2 SO₂ (g) + O₂(g) 2 SO<sub>3</sub>(g). The pressure was increased from 1.0 atm to 2.0 atm by the adding helium. Which of the following statements describes the new equilibrium system?</strong> A) [SO<sub>3</sub>] increases B) [SO<sub>2</sub>] increases C) [SO<sub>3</sub>] decreases D) [O<sub>2</sub>] increases E) [SO<sub>3</sub>], [SO<sub>2</sub>], and [O<sub>2</sub>] remain unchanged](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TBX8714/11ebff50_c8b2_32b7_8da6_91435ed1c22b_TBX8714_11.jpg) 2 SO3(g). The pressure was increased from 1.0 atm to 2.0 atm by the adding helium. Which of the following statements describes the new equilibrium system?
2 SO3(g). The pressure was increased from 1.0 atm to 2.0 atm by the adding helium. Which of the following statements describes the new equilibrium system?
A) [SO3] increases
B) [SO2] increases
C) [SO3] decreases
D) [O2] increases
E) [SO3], [SO2], and [O2] remain unchanged
![<strong>Inert helium gas was injected into a reaction vessel of fixed volume containing an equilibrium mixture of 2 SO₂ (g) + O₂(g) 2 SO<sub>3</sub>(g). The pressure was increased from 1.0 atm to 2.0 atm by the adding helium. Which of the following statements describes the new equilibrium system?</strong> A) [SO<sub>3</sub>] increases B) [SO<sub>2</sub>] increases C) [SO<sub>3</sub>] decreases D) [O<sub>2</sub>] increases E) [SO<sub>3</sub>], [SO<sub>2</sub>], and [O<sub>2</sub>] remain unchanged](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TBX8714/11ebff50_c8b2_32b7_8da6_91435ed1c22b_TBX8714_11.jpg) 2 SO3(g). The pressure was increased from 1.0 atm to 2.0 atm by the adding helium. Which of the following statements describes the new equilibrium system?
2 SO3(g). The pressure was increased from 1.0 atm to 2.0 atm by the adding helium. Which of the following statements describes the new equilibrium system?A) [SO3] increases
B) [SO2] increases
C) [SO3] decreases
D) [O2] increases
E) [SO3], [SO2], and [O2] remain unchanged

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 212 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73
Which of the following reactions is product favored by a higher temperature ?
I. Co(H₂ O) 6 2+ (aq) + 4 Cl - (aq) + heat CoCl42 - (aq) + 6 H₂ O (
CoCl42 - (aq) + 6 H₂ O (  )
)
II. 2 SO₂ (g) + O₂(g) 2 SO3(D H 0)
2 SO3(D H 0)
III. 6 CO₂ (g) + 6 H₂ O (g) C6 H12 O6 (s) + 6 O₂(g) (endothermic reaction)
C6 H12 O6 (s) + 6 O₂(g) (endothermic reaction)
A) I only
B) II only
C) III only
D) I and III
E) All of these
I. Co(H₂ O) 6 2+ (aq) + 4 Cl - (aq) + heat
 CoCl42 - (aq) + 6 H₂ O (
CoCl42 - (aq) + 6 H₂ O (  )
)II. 2 SO₂ (g) + O₂(g)
 2 SO3(D H 0)
2 SO3(D H 0)III. 6 CO₂ (g) + 6 H₂ O (g)
 C6 H12 O6 (s) + 6 O₂(g) (endothermic reaction)
C6 H12 O6 (s) + 6 O₂(g) (endothermic reaction)A) I only
B) II only
C) III only
D) I and III
E) All of these

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 212 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
74
The equilibrium governed by the reaction 4 NH₃(g) + 5 O₂(g)  4 NO (g) + 6 H₂ O (g) undergoes a change in volume from 1.0 L to 2.0 L at 600 C. Choose the correct statement below.
4 NO (g) + 6 H₂ O (g) undergoes a change in volume from 1.0 L to 2.0 L at 600 C. Choose the correct statement below.
A) The number of moles of H2O decreases.
B) The number of moles of NO remains the same.
C) The number of moles of NH3 decreases.
D) The value of K c increases.
E) The number of moles of both H2O and O2 decrease.
 4 NO (g) + 6 H₂ O (g) undergoes a change in volume from 1.0 L to 2.0 L at 600 C. Choose the correct statement below.
4 NO (g) + 6 H₂ O (g) undergoes a change in volume from 1.0 L to 2.0 L at 600 C. Choose the correct statement below.A) The number of moles of H2O decreases.
B) The number of moles of NO remains the same.
C) The number of moles of NH3 decreases.
D) The value of K c increases.
E) The number of moles of both H2O and O2 decrease.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 212 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
75
Which of the following reactions is product favored by increasing the temperature of the reaction mixture?
I. 2 NO₂ (g) N₂(g) + 2 O₂(g) (exothermic)
N₂(g) + 2 O₂(g) (exothermic)
II. 2 CO₂ (g) + 2 H₂ O (g) + heat C₂ H4 (g) + 3 O₂(g)
C₂ H4 (g) + 3 O₂(g)
III. 2 KCl (s) + 3 O₂(g) 2 KClO3(s) ( D H 0)
2 KClO3(s) ( D H 0)
A) I only
B) II only
C) I and III
D) II and III
E) All of these
I. 2 NO₂ (g)
 N₂(g) + 2 O₂(g) (exothermic)
N₂(g) + 2 O₂(g) (exothermic)II. 2 CO₂ (g) + 2 H₂ O (g) + heat
 C₂ H4 (g) + 3 O₂(g)
C₂ H4 (g) + 3 O₂(g)III. 2 KCl (s) + 3 O₂(g)
 2 KClO3(s) ( D H 0)
2 KClO3(s) ( D H 0)A) I only
B) II only
C) I and III
D) II and III
E) All of these

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 212 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
76
At constant volume, helium gas was injected into an equilibrium mixture of 2 SO3(g) ![<strong>At constant volume, helium gas was injected into an equilibrium mixture of 2 SO<sub>3</sub>(g) 2 SO₂ (g) + O₂(g) The total pressure increased from 1.0 atm to 10.0 atm. Which of the following statements is correct?</strong> A) The concentrations of the reacting gases are unchanged. B) [SO<sub>3</sub>] increases C) [SO<sub>2</sub>] increases D) [O<sub>2</sub>] increases E) [SO<sub>2</sub>] and [O<sub>2</sub>] decrease](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TBX8714/11ebff50_c8b2_0ba6_8da6_cf8a4ebc94c0_TBX8714_11.jpg) 2 SO₂ (g) + O₂(g) The total pressure increased from 1.0 atm to 10.0 atm. Which of the following statements is correct?
2 SO₂ (g) + O₂(g) The total pressure increased from 1.0 atm to 10.0 atm. Which of the following statements is correct?
A) The concentrations of the reacting gases are unchanged.
B) [SO3] increases
C) [SO2] increases
D) [O2] increases
E) [SO2] and [O2] decrease
![<strong>At constant volume, helium gas was injected into an equilibrium mixture of 2 SO<sub>3</sub>(g) 2 SO₂ (g) + O₂(g) The total pressure increased from 1.0 atm to 10.0 atm. Which of the following statements is correct?</strong> A) The concentrations of the reacting gases are unchanged. B) [SO<sub>3</sub>] increases C) [SO<sub>2</sub>] increases D) [O<sub>2</sub>] increases E) [SO<sub>2</sub>] and [O<sub>2</sub>] decrease](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TBX8714/11ebff50_c8b2_0ba6_8da6_cf8a4ebc94c0_TBX8714_11.jpg) 2 SO₂ (g) + O₂(g) The total pressure increased from 1.0 atm to 10.0 atm. Which of the following statements is correct?
2 SO₂ (g) + O₂(g) The total pressure increased from 1.0 atm to 10.0 atm. Which of the following statements is correct?A) The concentrations of the reacting gases are unchanged.
B) [SO3] increases
C) [SO2] increases
D) [O2] increases
E) [SO2] and [O2] decrease

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 212 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
77
For the reaction H₂ (g) + I2 (g)  2 HI (g) with D H 0, which of the following stresses when applied to an equilibrium mixture will not increase the amount of HI when equilibrium is reestablished?
2 HI (g) with D H 0, which of the following stresses when applied to an equilibrium mixture will not increase the amount of HI when equilibrium is reestablished?
A) Add 3 moles of H2 (g) at constant volume.
B) Lower the temperature at constant volume.
C) Increase the volume of the mixture.
D) Add 1 mole of I2 (g) at constant pressure.
E) All of these increase the amount of HI.
 2 HI (g) with D H 0, which of the following stresses when applied to an equilibrium mixture will not increase the amount of HI when equilibrium is reestablished?
2 HI (g) with D H 0, which of the following stresses when applied to an equilibrium mixture will not increase the amount of HI when equilibrium is reestablished?A) Add 3 moles of H2 (g) at constant volume.
B) Lower the temperature at constant volume.
C) Increase the volume of the mixture.
D) Add 1 mole of I2 (g) at constant pressure.
E) All of these increase the amount of HI.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 212 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
78
At equilibrium, the endothermic reaction N₂(g) + O₂(g)  2 NO (g) produces a maximum amount of NO for which of the following conditions?
2 NO (g) produces a maximum amount of NO for which of the following conditions?
A) high P
B) high T
C) low P
D) low T
E) a combination of low P and low T
 2 NO (g) produces a maximum amount of NO for which of the following conditions?
2 NO (g) produces a maximum amount of NO for which of the following conditions?A) high P
B) high T
C) low P
D) low T
E) a combination of low P and low T

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 212 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
79
At 600 C, K p = 0.57 for the endothermic reaction:
CO₂ (g) + H₂ (g) CO (g) + H₂ O (g) The value of K p at 300 C is:
CO (g) + H₂ O (g) The value of K p at 300 C is:
A) greater than 0.57
B) equal to 0.57
C) less than 0.57
D) equal to 0.00
E) insufficient information to reach a conclusion
CO₂ (g) + H₂ (g)
 CO (g) + H₂ O (g) The value of K p at 300 C is:
CO (g) + H₂ O (g) The value of K p at 300 C is:A) greater than 0.57
B) equal to 0.57
C) less than 0.57
D) equal to 0.00
E) insufficient information to reach a conclusion

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 212 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
80
Which reaction shown below is shifted in the direction of the products (to the right) by increasing the pressure of the reaction mixture?
A) H₂ (g) + C₂ N₂(g) 2 HCN (g)
2 HCN (g)
B) CO (g) + Br₂(g) CO Br₂(g)
CO Br₂(g)
C) CH4 (g) + 2 H₂ S (g) C S2(g) + 4 H₂ (g)
C S2(g) + 4 H₂ (g)
D) 2 Na2 O (s) 4 Na (
4 Na (  ) + O₂(g)
) + O₂(g)
E) None of these.
A) H₂ (g) + C₂ N₂(g)
 2 HCN (g)
2 HCN (g)B) CO (g) + Br₂(g)
 CO Br₂(g)
CO Br₂(g)C) CH4 (g) + 2 H₂ S (g)
 C S2(g) + 4 H₂ (g)
C S2(g) + 4 H₂ (g)D) 2 Na2 O (s)
 4 Na (
4 Na (  ) + O₂(g)
) + O₂(g)E) None of these.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 212 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



