Deck 15: Biosynthesis
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/73
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 15: Biosynthesis
1
Rubisco catalyzes which of the following reactions?
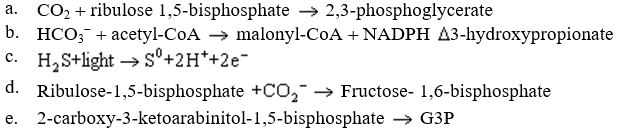
A
2
What types of bacteria perform the reductive pentose phosphate cycle to fix CO₂?
A) cyanobacteria
B) purple phototrophs
C) lithotrophs
D) heterotrophs
E) methanogens
A) cyanobacteria
B) purple phototrophs
C) lithotrophs
D) heterotrophs
E) methanogens
D
3
Which of the following pathways is NOT a route for CO₂ assimilation?
A) reductive acetyl-CoA pathway
B) gluconeogenesis pathway
C) hydroxypropionate cycle
D) reductive pentose phosphate cycle
E) reverse TCA cycle
A) reductive acetyl-CoA pathway
B) gluconeogenesis pathway
C) hydroxypropionate cycle
D) reductive pentose phosphate cycle
E) reverse TCA cycle
B
4
Which of the following statements concerning glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate is FALSE?
A) One G3P is produced by everything three turns of the cycle.
B) Two molecules of G3P condense to form a six-carbon sugar.
C) One more G3P condenses with a sugar to form a larger molecule used for biosynthesis.
D) PGA is reduced to G3P after the PGA moves out of the carboxysome.
E) G3P is reoxidized to carbon dioxide so that the cycle continues.
A) One G3P is produced by everything three turns of the cycle.
B) Two molecules of G3P condense to form a six-carbon sugar.
C) One more G3P condenses with a sugar to form a larger molecule used for biosynthesis.
D) PGA is reduced to G3P after the PGA moves out of the carboxysome.
E) G3P is reoxidized to carbon dioxide so that the cycle continues.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
The enzyme that carries out this reaction shown in the diagram below is ________, and the end product is ________. 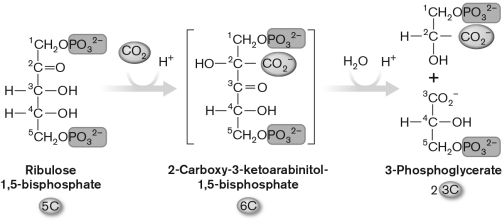
A) 3-phosphoglycerate synthetase; added to another carbon dioxide
B) 3-phosphoglycerate synthetase; reduced to glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate
C) nitrogenase; reduced to glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate
D) Rubisco; reduced to glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate
E) Rubisco; added to another carbon dioxide

A) 3-phosphoglycerate synthetase; added to another carbon dioxide
B) 3-phosphoglycerate synthetase; reduced to glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate
C) nitrogenase; reduced to glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate
D) Rubisco; reduced to glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate
E) Rubisco; added to another carbon dioxide

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
What is the most sensitive method to determine the presence of an isotope such as ¹⁴C in a sample?
A) nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) spectroscopy
B) radioactive decay
C) mass spectroscopy
D) polymerase chain reaction
E) high-performance liquid chromatography
A) nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) spectroscopy
B) radioactive decay
C) mass spectroscopy
D) polymerase chain reaction
E) high-performance liquid chromatography

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
Which of the following are unique in that they fix CO₂ as their sole carbon source?
A) organotrophs and iron oxidizers
B) photoheterotrophs and chemiolithotrophs
C) photoautotrophs and lithotrophs
D) heterotrophs and methanogens
E) methanogens and photoheterotrophs
A) organotrophs and iron oxidizers
B) photoheterotrophs and chemiolithotrophs
C) photoautotrophs and lithotrophs
D) heterotrophs and methanogens
E) methanogens and photoheterotrophs

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
Which of the following statements is NOT true about Rubisco?
A) It catalyzes the addition of CO2 to ribulose 1,5-bisphosphate.
B) It is present in all organisms that use the Calvin cycle to fix CO2.
C) It is found in the carboxysomes of autotrophic bacteria.
D) All species contain the same number of large and small subunits.
E) Its structure is highly conserved across bacterial groups and chloroplasts.
A) It catalyzes the addition of CO2 to ribulose 1,5-bisphosphate.
B) It is present in all organisms that use the Calvin cycle to fix CO2.
C) It is found in the carboxysomes of autotrophic bacteria.
D) All species contain the same number of large and small subunits.
E) Its structure is highly conserved across bacterial groups and chloroplasts.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
All microorganisms require all of the following for biosynthetic purposes EXCEPT
A) phosphorous.
B) reduction.
C) energy.
D) carbon.
E) nitrogen gas.
A) phosphorous.
B) reduction.
C) energy.
D) carbon.
E) nitrogen gas.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
An association between two Antarctic microorganisms is pictured below. It provides an interaction that supplies ________, made by the ________, to the ________. 
A) amino acids; diatom; bacterium
B) fixed nitrogen; diatom; bacterium
C) fixed nitrogen; bacterium; diatom
D) vitamin B12; diatom; bacterium
E) vitamin B12; bacterium; diatom

A) amino acids; diatom; bacterium
B) fixed nitrogen; diatom; bacterium
C) fixed nitrogen; bacterium; diatom
D) vitamin B12; diatom; bacterium
E) vitamin B12; bacterium; diatom

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
Two strains of E. coli were developed, each of which overproduced an amino acid, either histidine or tryptophan. When grown together in medium with adequate amino acids, they grew but did not associate with each other. When these strains were grown together in medium without histidine and tryptophan, they grew and formed ________ in order to ________.
A) carboxysomes; share the excess of the two amino acids
B) carboxysomes; provide ATP to each other to make the missing amino acids
C) nanotubes; share the excess of the two amino acids
D) nanotubes; provide ATP to each other to make the missing amino acids
E) heterocysts; share the excess of the two amino acids
A) carboxysomes; share the excess of the two amino acids
B) carboxysomes; provide ATP to each other to make the missing amino acids
C) nanotubes; share the excess of the two amino acids
D) nanotubes; provide ATP to each other to make the missing amino acids
E) heterocysts; share the excess of the two amino acids

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
What methods do microorganisms NOT use to minimize energy for biosynthesis?
A) inhibiting or killing competitors by making antimicrobials
B) loss of genes encoding enzymes for a nutrient that can be provided by the environment
C) regulation of gene expression so that molecules are not made if available
D) allosteric control of biosynthetic enzyme activity
E) transport of ATP from the environment into the cell to drive biosynthesis
A) inhibiting or killing competitors by making antimicrobials
B) loss of genes encoding enzymes for a nutrient that can be provided by the environment
C) regulation of gene expression so that molecules are not made if available
D) allosteric control of biosynthetic enzyme activity
E) transport of ATP from the environment into the cell to drive biosynthesis

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
The ________ pathway is utilized for carbon fixation in chloroplasts and cyanobacteria.
A) acetyl-CoA
B) reverse tricarboxylic acid cycle
C) 3-hydroxypropionate cycle
D) reductive pentose phosphate cycle
E) Krebs cycle
A) acetyl-CoA
B) reverse tricarboxylic acid cycle
C) 3-hydroxypropionate cycle
D) reductive pentose phosphate cycle
E) Krebs cycle

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
The structures marked with arrows in the photo below are ________ and are used to ________. 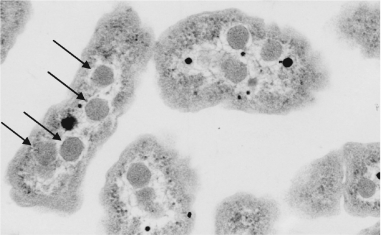
A) polyhydroxyalkanoates; sequester reactions using bicarbonate or carbon dioxide and Rubisco
B) polyhydroxyalkanoates; store carbon for energy
C) carboxysomes; store carbon for energy
D) carboxysomes; sequester reactions using bicarbonate or carbon dioxide and Rubisco
E) heterocysts; sequester reactions using bicarbonate or carbon dioxide and Rubisco

A) polyhydroxyalkanoates; sequester reactions using bicarbonate or carbon dioxide and Rubisco
B) polyhydroxyalkanoates; store carbon for energy
C) carboxysomes; store carbon for energy
D) carboxysomes; sequester reactions using bicarbonate or carbon dioxide and Rubisco
E) heterocysts; sequester reactions using bicarbonate or carbon dioxide and Rubisco

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
Cyanobacteria are believed to generate the majority of oxygen gas in Earth's atmosphere. What allows them to produce oxygen?
A) photosynthesis in which H2S is the electron source
B) photosynthesis in which water photolysis produces H+, e-, and O2
C) bacteriorhodopsin-based photosynthesis
D) being near the surface of a pond where more oxygen is available
E) possession of a variety of chlorophylls to absorb a wide range of wavelengths of light
A) photosynthesis in which H2S is the electron source
B) photosynthesis in which water photolysis produces H+, e-, and O2
C) bacteriorhodopsin-based photosynthesis
D) being near the surface of a pond where more oxygen is available
E) possession of a variety of chlorophylls to absorb a wide range of wavelengths of light

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
The catalytic site of Rubisco is located in
A) the large subunit.
B) the small subunit.
C) a cavity that forms between an LSU and an SSU.
D) the chloroplast.
E) the chlorosome.
A) the large subunit.
B) the small subunit.
C) a cavity that forms between an LSU and an SSU.
D) the chloroplast.
E) the chlorosome.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
Which of the following molecules links glycolysis with the TCA cycle, and also serves as a precursor for many biosynthetic products?
A) malate
B) citrate
C) oxaloacetate
D) acetyl-CoA
E) succinate
A) malate
B) citrate
C) oxaloacetate
D) acetyl-CoA
E) succinate

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
Which technique did Melvin Calvin use to elucidate the intermediates of phototrophic carbon fixation in the chloroplasts of Chlorella?
A) HPLC
B) gel electrophoresis
C) paper chromatography
D) column chromatography
E) mass spectroscopy
A) HPLC
B) gel electrophoresis
C) paper chromatography
D) column chromatography
E) mass spectroscopy

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
The Calvin cycle is essentially
A) started by the oxygen capture by Rubisco.
B) a reductive pentose phosphate cycle.
C) the reductive, or reverse, tricarboxylic acid cycle.
D) a pathway to synthesize fatty acids but not sugars.
E) a pathway that is used only when light is present.
A) started by the oxygen capture by Rubisco.
B) a reductive pentose phosphate cycle.
C) the reductive, or reverse, tricarboxylic acid cycle.
D) a pathway to synthesize fatty acids but not sugars.
E) a pathway that is used only when light is present.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
How many turns of the Calvin cycle does it take to provide one molecule of glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate into the biosynthesis of glucose?
A) 1
B) 2
C) 3
D) 6
E) 5
A) 1
B) 2
C) 3
D) 6
E) 5

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
Which of the following is NOT correct regarding unsaturation in certain fatty acids?
A) Temperature regulates fatty acid composition.
B) The plasma membrane must maintain a certain degree of flexibility.
C) Low temperature induces expression of fabA, which encodes a dehydratase enzyme.
D) Low temperatures favor fewer unsaturated fatty acids.
E) Temperature has no effect.
A) Temperature regulates fatty acid composition.
B) The plasma membrane must maintain a certain degree of flexibility.
C) Low temperature induces expression of fabA, which encodes a dehydratase enzyme.
D) Low temperatures favor fewer unsaturated fatty acids.
E) Temperature has no effect.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
In the reductive TCA cycle, four or five ATPs are used to produce one oxaloacetate. How many molecules of CO₂ are fixed in this cycle?
A) two
B) three
C) four
D) five
E) six
A) two
B) three
C) four
D) five
E) six

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
Biological nitrogen fixation is energetically expensive. Assuming that NADPH is used as the reducing equivalent, how many ATPs are used in the enzymatic conversion of N₂ to NH₃?
A) 16
B) 32
C) 48
D) 64
E) none; only GTP is used
A) 16
B) 32
C) 48
D) 64
E) none; only GTP is used

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
Many of the antibiotics and other pharmaceutical agents isolated from Streptomyces species are
A) amides.
B) polyketides.
C) thioesters.
D) fatty acids.
E) lipids.
A) amides.
B) polyketides.
C) thioesters.
D) fatty acids.
E) lipids.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
Denitrification is the
A) conversion of nitrate or nitrite to N2 by anaerobic respirers.
B) oxidation of NH4+ to nitrate or nitrite by lithotrophs.
C) conversion of N2 to NH4+.
D) removal of nitro groups from organic molecules.
E) removal of amino groups from organic molecules.
A) conversion of nitrate or nitrite to N2 by anaerobic respirers.
B) oxidation of NH4+ to nitrate or nitrite by lithotrophs.
C) conversion of N2 to NH4+.
D) removal of nitro groups from organic molecules.
E) removal of amino groups from organic molecules.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
The most ancient CO₂ fixation pathway in methanogens is the
A) reverse TCA cycle.
B) 3-hydroxypropionate cycle.
C) Calvin cycle.
D) reductive acetyl-CoA pathway.
E) Krebs cycle.
A) reverse TCA cycle.
B) 3-hydroxypropionate cycle.
C) Calvin cycle.
D) reductive acetyl-CoA pathway.
E) Krebs cycle.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
The cell diagrammed below provides an overview of some regulation of the Calvin cycle. Which of the following is NOT involved in this regulation? 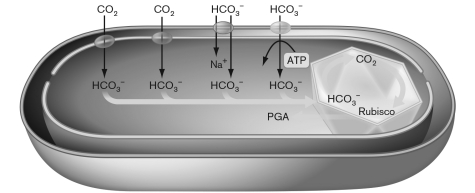




Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
What kind of reaction is the formation of oxaloacetate from phosphoenolpyruvate?
A) catabolic
B) anaplerotic
C) decarboxylation
D) dehydrogenation
E) co-factor induced
A) catabolic
B) anaplerotic
C) decarboxylation
D) dehydrogenation
E) co-factor induced

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
In the mechanism of nitrogen reduction, ________ directly takes the place of the H₂ in the FeMo subunit of the enzyme nitrogenase.
A) NH3
B) N2
C) HN=NH
D) H2N-NH2
E) NADPH
A) NH3
B) N2
C) HN=NH
D) H2N-NH2
E) NADPH

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
Why do most fatty acids contain an even number of carbon atoms?
A) The priming reaction involves condensation of the acetyl-CoA with ACP.
B) A C3-intermediate (malonyl-CoA) is carboxylated during chain elongation to yield an even number of carbons.
C) Fatty acid biosynthesis incorporates succinyl-CoA.
D) Fatty acids do not have an even number of carbons.
E) It is now easier to add double bonds.
A) The priming reaction involves condensation of the acetyl-CoA with ACP.
B) A C3-intermediate (malonyl-CoA) is carboxylated during chain elongation to yield an even number of carbons.
C) Fatty acid biosynthesis incorporates succinyl-CoA.
D) Fatty acids do not have an even number of carbons.
E) It is now easier to add double bonds.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
Which of the following is NOT correct regarding nitrogen assimilation into biomass?
A) Different oxidation states of nitrogen require different amounts of reducing energy.
B) It is easy for living organisms to assimilate nitrogen due to its great stability.
C) Nitrogen forms must be fully reduced to NH3.
D) Only bacteria and archaea can assimilate elemental nitrogen.
E) It is expensive, requiring reducing energy and ATP.
A) Different oxidation states of nitrogen require different amounts of reducing energy.
B) It is easy for living organisms to assimilate nitrogen due to its great stability.
C) Nitrogen forms must be fully reduced to NH3.
D) Only bacteria and archaea can assimilate elemental nitrogen.
E) It is expensive, requiring reducing energy and ATP.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
In anaplerotic reactions
A) intermediates in a pathway are regenerated.
B) nutrients are imported from the environment.
C) molecules targeted for breakdown are salvaged for anabolism.
D) the reactions are thermodynamically impossible.
E) large amounts of ATP are generated.
A) intermediates in a pathway are regenerated.
B) nutrients are imported from the environment.
C) molecules targeted for breakdown are salvaged for anabolism.
D) the reactions are thermodynamically impossible.
E) large amounts of ATP are generated.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
How does the reductive (reverse) TCA cycle participate in carbon fixation?
A) Some of the TCA reactions occur in reverse, assimilating small amounts of CO2.
B) CO2 assimilation uses up TCA intermediates for anabolic pathways.
C) Reverse TCA regenerates succinyl-CoA, which may enter gluconeogenesis.
D) A large amount of ATP is generated.
E) All reactions take place in a carboxysome.
A) Some of the TCA reactions occur in reverse, assimilating small amounts of CO2.
B) CO2 assimilation uses up TCA intermediates for anabolic pathways.
C) Reverse TCA regenerates succinyl-CoA, which may enter gluconeogenesis.
D) A large amount of ATP is generated.
E) All reactions take place in a carboxysome.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
Which pair is NOT matched correctly?
A) NtrC-regulates nitrogenase gene expression in response to NH4+ concentration
B) NtrB-phosphorylates NtrC when NH4+ concentration is low
C) NifL-forms a two-component signal transduction system with NtrC
D) NifA-acts in concert with factor s -54
E) NifHDKTY-components of nitrogenase
A) NtrC-regulates nitrogenase gene expression in response to NH4+ concentration
B) NtrB-phosphorylates NtrC when NH4+ concentration is low
C) NifL-forms a two-component signal transduction system with NtrC
D) NifA-acts in concert with factor s -54
E) NifHDKTY-components of nitrogenase

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
The enzyme nitrogenase is inhibited by oxygen. Which of the following does NOT protect nitrogenase from oxygen?
A) special thick-walled cells (heterocysts) in filamentous cyanobacteria, such as Anabaena
B) special nitrogenase-protecting proteins in Azotobacter species
C) temporal separation of nitrogen fixation (at night) and photosynthesis (during the day) in some species of cyanobacteria
D) growth under aerobic conditions
E) growth under anaerobic conditions
A) special thick-walled cells (heterocysts) in filamentous cyanobacteria, such as Anabaena
B) special nitrogenase-protecting proteins in Azotobacter species
C) temporal separation of nitrogen fixation (at night) and photosynthesis (during the day) in some species of cyanobacteria
D) growth under aerobic conditions
E) growth under anaerobic conditions

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
Industrial nitrogen fixation is achieved through the Haber process
A) in which N2 is reduced catalytically by H2 at ambient temperature.
B) in which N2 is hydrogenated by CH4 at extreme temperature and pressure.
C) in which nitrate and nitrite are chemically converted to NH at ambient temperature.
D) which requires little energy.
E) which is carried out by purified enzymes in a reactor.
A) in which N2 is reduced catalytically by H2 at ambient temperature.
B) in which N2 is hydrogenated by CH4 at extreme temperature and pressure.
C) in which nitrate and nitrite are chemically converted to NH at ambient temperature.
D) which requires little energy.
E) which is carried out by purified enzymes in a reactor.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
The most ancient CO₂ fixation pathway in anaerobic phototrophic bacteria and archaea is the
A) reverse TCA cycle.
B) 3-hydroxypropionate cycle.
C) Calvin cycle.
D) reductive acetyl-CoA pathway.
E) glyoxylate bypass.
A) reverse TCA cycle.
B) 3-hydroxypropionate cycle.
C) Calvin cycle.
D) reductive acetyl-CoA pathway.
E) glyoxylate bypass.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
Which of the following is the reducing agent in the saturation step of polyketide biosynthesis?
A) NADH
B) NADPH
C) ferredoxin
D) H2
E) O2
A) NADH
B) NADPH
C) ferredoxin
D) H2
E) O2

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
Which of the following is NOT correct about fatty acid biosynthesis?
A) It involves successive condensations of malonyl-ACP.
B) A dehydratase is used to generate an unsaturated bond.
C) It is regulated by the stringent response of carbon starvation.
D) NADPH is generally involved in hydrogenation.
E) Many single-component enzymes are involved.
A) It involves successive condensations of malonyl-ACP.
B) A dehydratase is used to generate an unsaturated bond.
C) It is regulated by the stringent response of carbon starvation.
D) NADPH is generally involved in hydrogenation.
E) Many single-component enzymes are involved.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
Gene expression of nitrogenase through NtrC is downregulated in high concentrations of
A) carbon dioxide.
B) nitrogen.
C) nitrate.
D) ammonium.
E) FeMo protein.
A) carbon dioxide.
B) nitrogen.
C) nitrate.
D) ammonium.
E) FeMo protein.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
How does the reductive or reverse TCA cycle differ from the regular TCA cycle?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
Which of the following is NOT correct regarding the biosynthesis of purines and pyrimidines?
A) 5-phosphoribosyl-1-pyrophosphate (PRPP) is a precursor to both purines and pyrimidines.
B) The pyrimidine ring is synthesized first and then linked to 5-phosphoribosyl-1-pyrophosphate.
C) The purine ring is built around the C1 of 5-phosphoribosyl-1-pyrophosphate.
D) Both purines and pyrimidines use inosine monophosphate as a precursor.
E) Both purines and pyrimidines are built by adding carbon components to ribose 5-phosphate.
A) 5-phosphoribosyl-1-pyrophosphate (PRPP) is a precursor to both purines and pyrimidines.
B) The pyrimidine ring is synthesized first and then linked to 5-phosphoribosyl-1-pyrophosphate.
C) The purine ring is built around the C1 of 5-phosphoribosyl-1-pyrophosphate.
D) Both purines and pyrimidines use inosine monophosphate as a precursor.
E) Both purines and pyrimidines are built by adding carbon components to ribose 5-phosphate.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
Nitrogenase is diagrammed below. This particular enzyme is shown in the format just before it begins a cycle of nitrogen reduction. This goal is accomplished in four steps. What is the first step? 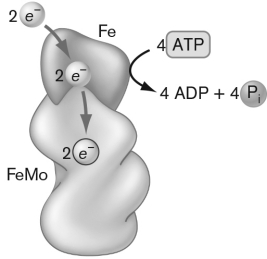
A) N2 gas binds to the active site on the FeMo protein.
B) NADPH binds to the active site in order to reduce it prior to N2 binding.
C) Two e - are transferred to the Fe protein and then to the FeMo protein, which are used to reduce H+ to H2 prior to N2 binding.
D) The preexisitng NH4+ is removed prior to N2 binding.
E) Fe and Mo are bound to the active sites and then released prior to the next cycle.

A) N2 gas binds to the active site on the FeMo protein.
B) NADPH binds to the active site in order to reduce it prior to N2 binding.
C) Two e - are transferred to the Fe protein and then to the FeMo protein, which are used to reduce H+ to H2 prior to N2 binding.
D) The preexisitng NH4+ is removed prior to N2 binding.
E) Fe and Mo are bound to the active sites and then released prior to the next cycle.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
What technique was used to demonstrate that gene expression of the CO₂-concentrating mechanism (CCM) transporters is induced by low levels of CO₂? Briefly explain the basis of the technique.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
Which of the following molecules provides a way to simultaneously assimilate one carbon atom and one nitrogen atom during purine biosynthesis?
A) acetyl-CoA
B) acetyl-ACP
C) malonyl-ACP
D) carbamoyl phosphate
E) NADPH
A) acetyl-CoA
B) acetyl-ACP
C) malonyl-ACP
D) carbamoyl phosphate
E) NADPH

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
Briefly discuss how carbon molecules of different sizes can be made for biosynthesis. What else is needed and how is it obtained?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
Describe the 3-hydroxypropionate cycle; give examples of microorganisms that use this CO₂ fixation mechanism.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
What techniques and technical advances allowed Melvin Calvin to study carbon fixation? Why did he choose the unicellular alga Chlorella?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
Briefly describe the reductive acetyl-CoA pathway. What is its relevance for methanogens?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
Chorismate is used in a branched pathway to synthesize
A) fatty acids.
B) polyketide antibiotics
C) purines and pyrimidines
D) aromatic amino acids
E) tetrapyrroles
A) fatty acids.
B) polyketide antibiotics
C) purines and pyrimidines
D) aromatic amino acids
E) tetrapyrroles

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
Which molecules use 5-phosphoribosyl-1-pyrophosphate (PRPP) in their biosynthesis?
A) amino acids
B) nucleotides
C) fatty acids
D) tetrapyrrole
E) nonribosomal peptide antibiotics
A) amino acids
B) nucleotides
C) fatty acids
D) tetrapyrrole
E) nonribosomal peptide antibiotics

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
Which of the following is NOT a tetrapyrrole?
A) cytochrome
B) chlorophyll
C) vitamin B12
D) tryptophan
E) hemoglobin
A) cytochrome
B) chlorophyll
C) vitamin B12
D) tryptophan
E) hemoglobin

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
The amino acid biosynthetic pathways are designated as families. The ________ family generates only one amino acid.
A) aspartate
B) serine
C) pyruvate
D) aromatic
E) histidine
A) aspartate
B) serine
C) pyruvate
D) aromatic
E) histidine

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
Based on the number of enzymes involved in its biosynthesis, which of the following is the most complex amino acid specified by the genetic code?
A) tryptophan
B) tyrosine
C) phenylalanine
D) leucine
E) isoleucine
A) tryptophan
B) tyrosine
C) phenylalanine
D) leucine
E) isoleucine

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
Which amino acid is NOT one of the first amino acids produced by ancient cells?
A) glutamate
B) tyrosine
C) glycine
D) valine
E) asparate
A) glutamate
B) tyrosine
C) glycine
D) valine
E) asparate

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
Which of the following molecules CANNOT freely cross biological membranes?
A) O2
B) CO2
C) NH4+
D) N2
E) H2O
A) O2
B) CO2
C) NH4+
D) N2
E) H2O

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
The incorporation of NH₄⁺ into 2-oxoglutarate is the first step in nitrogen assimilation in bacterial cells. This reaction is catalyzed by the enzyme ________ and produces ________.
A) glutamate dehydrogenase (GDH); glutamate
B) glutamine synthase (GS); glutamine
C) glutamate synthase (GOGAT); glutamate
D) 2-oxoglutarate aminase (2-OA); glutamine
E) 2-oxoglutarate dehydrogenase (2-ODH); glutamine
A) glutamate dehydrogenase (GDH); glutamate
B) glutamine synthase (GS); glutamine
C) glutamate synthase (GOGAT); glutamate
D) 2-oxoglutarate aminase (2-OA); glutamine
E) 2-oxoglutarate dehydrogenase (2-ODH); glutamine

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
Which of the following does NOT serve as an intermediate in the biosynthesis of amino acids?
A) citrate
B) 2-oxoglutarate
C) pyruvate
D) 3-phosphoglycerate
E) pentose phosphate
A) citrate
B) 2-oxoglutarate
C) pyruvate
D) 3-phosphoglycerate
E) pentose phosphate

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
Which of the following drugs is a nonribosomal peptide antibiotic?
A) erythromycin
B) penicillin
C) tetracycline
D) vancomycin
E) ciprofloxacin
A) erythromycin
B) penicillin
C) tetracycline
D) vancomycin
E) ciprofloxacin

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
It is thought that the Calvin cycle appeared after the divergence of the three domains of life. What supports this hypothesis?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
How do ammonium and oxygen regulate the expression of nitrogen fixation genes?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
Certain amino acids are more energetically expensive than others (tryptophan versus glutamate). Thus, when proteins are moved to the cell surface, extended outside the surface, or secreted out of the cell, there is a potential harm. Why is this potentially harmful, and what adaptations do bacteria have for this potential loss? Give an example.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
Tryptophan is among the so-called essential amino acids for humans, as we cannot produce it ourselves. Briefly describe tryptophan biosynthesis in bacteria. Why is it so energetically expensive to synthesize this aromatic amino acid?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
What are polyalkanoates, and what are bacterially produced polyalkanoates used for? Why are they of ecological and medical interest?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
What are nonribosomal peptide antibiotics? How are they synthesized?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
How do cyanobacteria benefit from their heterocysts attracting heterotrophic bacteria?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
What is the health risk of having nitrates in drinking water? What conditions favor the accumulation of nitrates and nitrites in bodies of water?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
How is fatty acid biosynthesis regulated in bacteria?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
The bacterial enzyme nitrogenase performs the reduction of N₂ gas using a large amount of energy and reducing power. Describe the nitrogen reduction steps during nitrogenase activity and write the overall reaction.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
Describe how modular enzymes function in polyketide biosynthesis. Why might this be of use medically?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
Briefly describe how NH₄⁺ is assimilated into biomass by bacteria.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72
Discuss evidence that supports the idea that glutamate, aspartate, alanine, glycine, and valine were the first amino acids produced by ancient cells.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73
Briefly describe the biosynthetic pathway for arginine.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



