Deck 2: Observing the Microbial Cell
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/69
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 2: Observing the Microbial Cell
1
The highest useful magnification for a light microscope is about
A) 100X.
B) 1,000X.
C) 10,000X.
D) 100,000X.
E) 1,000,000X.
A) 100X.
B) 1,000X.
C) 10,000X.
D) 100,000X.
E) 1,000,000X.
C
2
A ball-shaped microbe is referred to as a
A) bacillus.
B) coccus.
C) vibrio.
D) strepto.
E) spirochete.
A) bacillus.
B) coccus.
C) vibrio.
D) strepto.
E) spirochete.
B
3
Resolution is the smallest distance by which two objects can be ________ and still be ________.
A) magnified; seen
B) separated; distinguished
C) magnified; separated
D) distinguished; separated
E) magnified; distinguished
A) magnified; seen
B) separated; distinguished
C) magnified; separated
D) distinguished; separated
E) magnified; distinguished
C
4
Which of these series arranges microbes from smallest to largest?
A) virus bacterium red blood cell paramecium
B) virus red blood cell bacterium paramecium
C) bacterium virus paramecium red blood cell
D) bacterium virus red blood cell paramecium
E) paramecium red blood cell bacterium virus
A) virus bacterium red blood cell paramecium
B) virus red blood cell bacterium paramecium
C) bacterium virus paramecium red blood cell
D) bacterium virus red blood cell paramecium
E) paramecium red blood cell bacterium virus

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
One advantage of a wet mount is
A) low contrast.
B) that the organism is still.
C) viewing in a natural state.
D) high contrast.
E) that the sample does not overheat.
A) low contrast.
B) that the organism is still.
C) viewing in a natural state.
D) high contrast.
E) that the sample does not overheat.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
If aqueous cytoplasm was submerged in a beaker of immersion oil, the slide would be
A) undetectable.
B) brighter than its surroundings.
C) darker than its surroundings.
D) fluorescent.
E) stained.
A) undetectable.
B) brighter than its surroundings.
C) darker than its surroundings.
D) fluorescent.
E) stained.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
The part of the human eye that is MOST involved in resolving an image is the
A) iris.
B) lens.
C) optic nerve.
D) retina.
E) cornea.
A) iris.
B) lens.
C) optic nerve.
D) retina.
E) cornea.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
When two waves are out of phase by ________ wavelength, they produce destructive interference, canceling each other's amplitude and resulting in contrast in the image.
A) one-tenth of a
B) one-eighth of a
C) one-quarter of a
D) one-half of a
E) one
A) one-tenth of a
B) one-eighth of a
C) one-quarter of a
D) one-half of a
E) one

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
Increasing the refractive index of the medium between the object and the objective lens increases
A) refraction.
B) reflection.
C) magnification.
D) resolution.
E) wavelength.
A) refraction.
B) reflection.
C) magnification.
D) resolution.
E) wavelength.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
As lens strength increases, the light cone ________ and the lens must be ________ the object.
A) narrows; nearer to
B) narrows; farther from
C) widens; nearer to
D) widens; farther from
E) widens; touching
A) narrows; nearer to
B) narrows; farther from
C) widens; nearer to
D) widens; farther from
E) widens; touching

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
Label the condenser in the figure below. 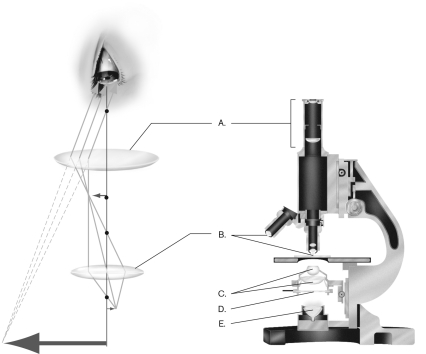
A) A
B) B
C) C
D) D
E) E

A) A
B) B
C) C
D) D
E) E

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
What happens if the wavelength of radiation is larger than the object being viewed?
A) absorption
B) scattering
C) no resolution
D) refraction
E) resolution
A) absorption
B) scattering
C) no resolution
D) refraction
E) resolution

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
Staining helps to visualize bacteria by increasing the
A) size of the cells.
B) motility of the cells.
C) contrast of the image.
D) magnification of the image.
E) aberration of the image.
A) size of the cells.
B) motility of the cells.
C) contrast of the image.
D) magnification of the image.
E) aberration of the image.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
Which of these arranges the steps of the Gram stain into the correct order?
A) iodine crystal violet decolorizer safranin
B) safranin decolorizer crystal violet iodine
C) crystal violet decolorizer iodine safranin
D) crystal violet decolorizer safranin iodine
E) crystal violet iodine decolorizer safranin
A) iodine crystal violet decolorizer safranin
B) safranin decolorizer crystal violet iodine
C) crystal violet decolorizer iodine safranin
D) crystal violet decolorizer safranin iodine
E) crystal violet iodine decolorizer safranin

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
Malachite green is commonly used to stain
A) eukaryotic cells.
B) Gram-negative cells.
C) Gram-positive cells.
D) bacterial endospores.
E) acid-fast cells.
A) eukaryotic cells.
B) Gram-negative cells.
C) Gram-positive cells.
D) bacterial endospores.
E) acid-fast cells.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
Chlamydia trachomatis transmits infection to a new cell via
A) a membrane vesicle.
B) elementary bodies.
C) amoeba.
D) host membranes.
E) the human cell.
A) a membrane vesicle.
B) elementary bodies.
C) amoeba.
D) host membranes.
E) the human cell.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
What is the MOST important property that enables a lens to magnify an image?
A) absorption
B) fluorescence
C) reflection
D) refraction
E) scattering
A) absorption
B) fluorescence
C) reflection
D) refraction
E) scattering

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
Wavelength interference results in small observed objects (like bacteria) being surrounded by
A) a capsule.
B) a membrane.
C) concentric rings.
D) a dark field.
E) a cell wall.
A) a capsule.
B) a membrane.
C) concentric rings.
D) a dark field.
E) a cell wall.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
What would happen if a lens had the same refractive index as air?
A) Light would not pass through the lens.
B) The image would be magnified more than with a glass lens.
C) The image would be magnified, but the resolution would be less than with a glass lens.
D) The image would be magnified, and the resolution would be greater than with a glass lens.
E) The image would not be magnified.
A) Light would not pass through the lens.
B) The image would be magnified more than with a glass lens.
C) The image would be magnified, but the resolution would be less than with a glass lens.
D) The image would be magnified, and the resolution would be greater than with a glass lens.
E) The image would not be magnified.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
A(n) ________ acts to vary the diameter of the light column in a light microscope.
A) condenser
B) objective
C) ocular
D) diaphragm
E) lens
A) condenser
B) objective
C) ocular
D) diaphragm
E) lens

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
Which of the following is best visualized using a negative stain?
A) Gram-negative cell wall
B) acid-fast cell wall
C) capsule
D) endospores
E) flagella
A) Gram-negative cell wall
B) acid-fast cell wall
C) capsule
D) endospores
E) flagella

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
Which of these techniques can be used to localize the DNA sequence at the origin of replication in a bacterial cell?
A) fluorescence microscopy
B) phase contrast
C) X-ray diffraction
D) atomic force microscopy
E) cryo-EM
A) fluorescence microscopy
B) phase contrast
C) X-ray diffraction
D) atomic force microscopy
E) cryo-EM

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
Which type of microscopy is used to identify the 3-D structure of biofilms?
A) phase-contrast
B) dark-field
C) florescent
D) bright-field
E) confocal
A) phase-contrast
B) dark-field
C) florescent
D) bright-field
E) confocal

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
What is the total magnification of a light microscope when using a 25X ocular and 40X objective lens?
A) 15X
B) 65X
C) 400X
D) 1,000X
E) 1,200X
A) 15X
B) 65X
C) 400X
D) 1,000X
E) 1,200X

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
What is the best explanation for a Gram-positive bacterium appearing pink after performing a Gram stain?
A) The crystal violet was left on for too long.
B) The iodine was left on for too long.
C) The decolorizer was left on for too long.
D) The safranin was left on for too long.
E) The stain was properly performed.
A) The crystal violet was left on for too long.
B) The iodine was left on for too long.
C) The decolorizer was left on for too long.
D) The safranin was left on for too long.
E) The stain was properly performed.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
In which type of microscopy do dust particles interfere the MOST?
A) bright-field
B) dark-field
C) phase-contrast
D) interference
E) fluorescence
A) bright-field
B) dark-field
C) phase-contrast
D) interference
E) fluorescence

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
What molecule is shown below? 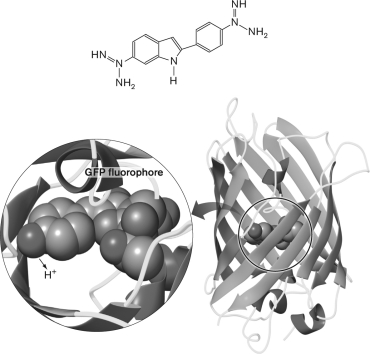
A) GFP
B) FM4-64
C) DNA
D) RNA
E) DAPI

A) GFP
B) FM4-64
C) DNA
D) RNA
E) DAPI

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
Which type of microscopy gives a "false 3-D image"?
A) Gram stain
B) nuclear magnetic resonance
C) scanning electron
D) negative stain
E) differential interference contrast
A) Gram stain
B) nuclear magnetic resonance
C) scanning electron
D) negative stain
E) differential interference contrast

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
Which two components of the Gram stain form a complex that is retained by Gram-positive cells?
A) crystal violet and iodine
B) safranin and iodine
C) crystal violet and safranin
D) alcohol and safranin
E) alcohol and iodine
A) crystal violet and iodine
B) safranin and iodine
C) crystal violet and safranin
D) alcohol and safranin
E) alcohol and iodine

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
Fluorescent microscopy that absorbs light at 260m would MOST likely fluoresce at
A) 100 nm.
B) 200 nm.
C) 260 nm.
D) 400 nm.
E) 800 nm.
A) 100 nm.
B) 200 nm.
C) 260 nm.
D) 400 nm.
E) 800 nm.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
What is the best explanation for a Gram-negative bacterium appearing purple after performing a Gram stain?
A) The safranin was not applied.
B) The decolorizer was not applied.
C) The iodine was not applied.
D) The crystal violet was not applied.
E) The stain was properly performed.
A) The safranin was not applied.
B) The decolorizer was not applied.
C) The iodine was not applied.
D) The crystal violet was not applied.
E) The stain was properly performed.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
A useful application of dark-field optics is the study of bacterial
A) motility.
B) surfaces.
C) interiors.
D) shape.
E) structure.
A) motility.
B) surfaces.
C) interiors.
D) shape.
E) structure.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
What happens to an electron when excited by light at the excitation wavelength?
A) It remains in the same orbital.
B) It moves to a lower energy orbital.
C) It moves to a higher energy orbital.
D) It emits a photon.
E) It is filtered.
A) It remains in the same orbital.
B) It moves to a lower energy orbital.
C) It moves to a higher energy orbital.
D) It emits a photon.
E) It is filtered.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
Which of the following techniques are based upon wave interference?
A) X-ray diffraction and phase contrast microscopy
B) phase contrast and dark-field microscopy
C) bright-field and dark-field microscopy
D) X-ray diffraction and atomic force microscopy
E) scanning and transmission electron microscopy
A) X-ray diffraction and phase contrast microscopy
B) phase contrast and dark-field microscopy
C) bright-field and dark-field microscopy
D) X-ray diffraction and atomic force microscopy
E) scanning and transmission electron microscopy

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
Which of the following is an advantage of using chemical imaging microscopy?
A) observing an organism in its living environment
B) displaying plankton
C) measuring pH within a cell
D) showing distribution of chemicals in a cell
E) pinpointing a protein location
A) observing an organism in its living environment
B) displaying plankton
C) measuring pH within a cell
D) showing distribution of chemicals in a cell
E) pinpointing a protein location

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
Which type of microscopy is used to view the internal structures of a specimen?
A) light
B) atomic force
C) scanning electron
D) transmission electron
E) confocal fluorescence
A) light
B) atomic force
C) scanning electron
D) transmission electron
E) confocal fluorescence

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
The knife used to cut embedded specimens for observation by transmission electron microscopy is called a
A) crystallographer.
B) microtome.
C) grid.
D) polymer.
E) scalpel.
A) crystallographer.
B) microtome.
C) grid.
D) polymer.
E) scalpel.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
Fluorescence microscopy using labeled antibodies is referred to as
A) immunofluorescence.
B) autofluorescence.
C) confocal microscopy.
D) phase-contrast microscopy.
E) dark-field microscopy.
A) immunofluorescence.
B) autofluorescence.
C) confocal microscopy.
D) phase-contrast microscopy.
E) dark-field microscopy.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
Atomic force microscopy measures ________ between a probe and an object to map the three-dimensional topography of a cell.
A) hydrogen bonds
B) covalent interactions
C) van der Waals forces
D) pH changes
E) magnetic interactions
A) hydrogen bonds
B) covalent interactions
C) van der Waals forces
D) pH changes
E) magnetic interactions

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
Which of these numeric aperture and light combinations would give the best resolution?
A) numeric aperture = 0.8, wavelength = 600 nm
B) numeric aperture = 0.8, wavelength = 500 nm
C) numeric aperture = 1.0, wavelength = 700 nm
D) numeric aperture = 1.0, wavelength = 600 nm
E) numeric aperture = 0.8, wavelength = 400 nm
A) numeric aperture = 0.8, wavelength = 600 nm
B) numeric aperture = 0.8, wavelength = 500 nm
C) numeric aperture = 1.0, wavelength = 700 nm
D) numeric aperture = 1.0, wavelength = 600 nm
E) numeric aperture = 0.8, wavelength = 400 nm

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
Which of these techniques would provide the best resolution of an enzyme's structure?
A) scanning electron microscopy
B) transmission electron microscopy
C) cryo-EM
D) X-ray diffraction analysis
E) atomic force microscopy
A) scanning electron microscopy
B) transmission electron microscopy
C) cryo-EM
D) X-ray diffraction analysis
E) atomic force microscopy

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
The spots recorded on film during X-ray diffraction analyses are due to
A) artifacts.
B) scattering.
C) wave interference.
D) absorption.
E) fluorescence.
A) artifacts.
B) scattering.
C) wave interference.
D) absorption.
E) fluorescence.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
Cryo-electron microscopy (cryo-EM) is differentiated from transmission electron microscopy because it
A) requires making thin slices of the sample to be viewed.
B) does not require staining with heavy metals.
C) may be used to view living tissues.
D) uses a weaker electron beam.
E) can provide a color image of the microbial cell.
A) requires making thin slices of the sample to be viewed.
B) does not require staining with heavy metals.
C) may be used to view living tissues.
D) uses a weaker electron beam.
E) can provide a color image of the microbial cell.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
Describe three conditions that are necessary for electromagnetic radiation to resolve an object.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
If your eyes had photoreceptors packed as closely as an eagle's (about eight times greater than humans), would you be able to resolve a virus (100 nm in size) using a light microscope? Why or why not?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
Compare and contrast the radiation sources, lenses, and image-capturing devices used in light microscopy and transmission electron microscopy.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
Compare and contrast a simple stain (like methylene blue) with the Gram stain. What information about a microbial sample can be collected with each?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
Which type of microscopy is particularly useful to study the surfaces of live bacteria?
A) atomic force
B) scanning electron
C) transmission electron
D) dark-field
E) bright-field
A) atomic force
B) scanning electron
C) transmission electron
D) dark-field
E) bright-field

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
What color are Gram-positive and Gram-negative cells when properly Gram stained? For each step of the Gram-stain procedure, predict the colors of a Gram-positive or Gram-negative cell if that step were omitted during staining. Explain your reasoning.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
Which of the following techniques can visualize bacteria without focusing electromagnetic radiation?
A) cryo-electron microscopy
B) phase-contrast microscopy
C) dark-field microscopy
D) atomic force microscopy
E) X-ray diffraction
A) cryo-electron microscopy
B) phase-contrast microscopy
C) dark-field microscopy
D) atomic force microscopy
E) X-ray diffraction

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
Microbes were detected long before the invention of the microscope. How could this be?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
Transmission electron microscopy commonly has a resolution of ________ the highest resolution possible for light microscopy.
A) 10X
B) 100X
C) 1,000X
D) 10,000X
E) 1,000,000X
A) 10X
B) 100X
C) 1,000X
D) 10,000X
E) 1,000,000X

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
List and describe three common shapes of bacteria.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
List and briefly describe four ways that light interacts with objects.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
List three different differential stains used in microbiology. What can be detected with each?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
Which of the following would be MOST appropriate to visualize viral particles being assembled inside an infected bacterial cell?
A) dark-field microscopy
B) atomic force microscopy
C) fluorescence microscopy
D) scanning electron microscopy
E) transmission electron microscopy
A) dark-field microscopy
B) atomic force microscopy
C) fluorescence microscopy
D) scanning electron microscopy
E) transmission electron microscopy

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
Are all bacilli Bacillus? Explain.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
The digitally combined images of cryo-EM can achieve resolution comparable to that of
A) scanning electron microscopy.
B) transmission electron microscopy.
C) interference microscopy.
D) X-ray crystallography.
E) dark-field microscopy.
A) scanning electron microscopy.
B) transmission electron microscopy.
C) interference microscopy.
D) X-ray crystallography.
E) dark-field microscopy.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
Why do some bacteria appear purple after being Gram stained, while others appear pink?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
Which of the following methods is used to generate the structure shown below? 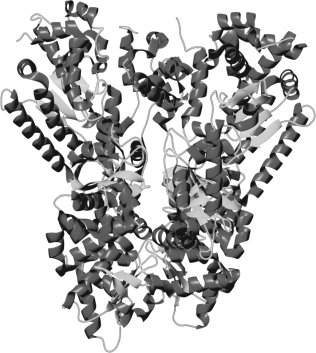
A) scanning probe microscopy
B) scanning electron microscopy
C) transmission electron microscopy
D) confocal microscopy
E) X-ray crystallography

A) scanning probe microscopy
B) scanning electron microscopy
C) transmission electron microscopy
D) confocal microscopy
E) X-ray crystallography

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
The figure below shows the Gram-staining process. Describe what is happening at step number 3 relative to bacterial cell walls.
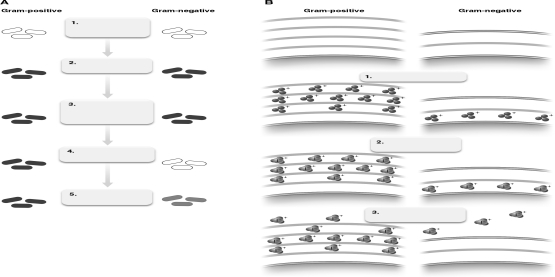


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
Explain why components from thermophilic bacteria take less X-ray damage than other bacteria.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
The figure below displays absorption and emission spectra for a fluorophore. Describe the difference between absorption and emission and how this is reflected in the figure.


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
Using the figure below, explain how the visualization of molecules occurs through X-ray crystallography.
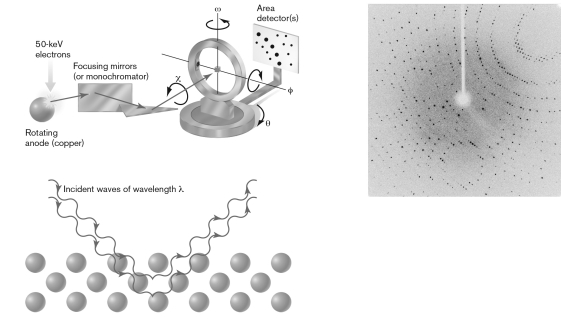


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
Define a fluorophore and give three examples of how it can be used to label cells.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
Why are stains used in microscopy? Compare and contrast the stains used in light versus electron microscopy.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
Give a few reasons why living organisms may not be observed by transmission electron microscopy (TEM) or scanning electron microscopy (SEM).

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
Most electron micrographs in microbiology textbooks are in color. Is this normal for an electron micrograph? Why or why not?

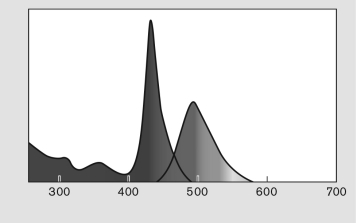
Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
Describe three methods of sample preparation for electron microscopy. Which method would cause the fewest artifacts? Why?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



