Deck 12: Sampling Distributions, Sampling Distribution of the Mean: the Normal Deviate Z Test
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/135
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 12: Sampling Distributions, Sampling Distribution of the Mean: the Normal Deviate Z Test
1
A normally distributed set of population scores has a mean of 65 and a standard deviation of 10.2. The mean, of the sampling distribution of the mean, for samples of size 48 equals _________.
A) 1.35
B) 60
C) 65
D) none of these
A) 1.35
B) 60
C) 65
D) none of these
65
2
As sample size increases, 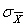 _________.
_________.
A) decreases
B) increases
C) stays the same
D) approaches s
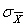 _________.
_________.A) decreases
B) increases
C) stays the same
D) approaches s
decreases
3
If the variability of the raw score population increases and N is held constant,  _________.
_________.
A) decreases
B) increases
C) stays the same
D) need more information
 _________.
_________.A) decreases
B) increases
C) stays the same
D) need more information
increases
4
The sampling distribution of the mean gives _________.
A) all the values the sample mean can take
B) the probability of getting each mean value if sampling is random from the H 0 population
C) all the values the sample standard deviation can take
D) the probability of getting each standard deviation value if sampling is random from the H 0 population
E) all the values the sample mean can take and the probability of getting each mean value if sampling is random from the H 0 population
A) all the values the sample mean can take
B) the probability of getting each mean value if sampling is random from the H 0 population
C) all the values the sample standard deviation can take
D) the probability of getting each standard deviation value if sampling is random from the H 0 population
E) all the values the sample mean can take and the probability of getting each mean value if sampling is random from the H 0 population

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 135 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
The sampling distribution of the mean _________.
A) is always normally distributed
B) is normally distributed if the population raw scores are normally distributed
C) is considered normally distributed if N > 300
D) is normally distributed if the population raw scores are normally distributed and is considered normally distributed if N > 300
A) is always normally distributed
B) is normally distributed if the population raw scores are normally distributed
C) is considered normally distributed if N > 300
D) is normally distributed if the population raw scores are normally distributed and is considered normally distributed if N > 300

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 135 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
Data analysis involving statistical inference basically involves _________.
A) determining the standard deviation of the scores
B) calculating the appropriate statistic
C) evaluating the statistic based on its sampling distribution
D) calculating the appropriate statistic and evaluating the statistic based on its sampling distribution
A) determining the standard deviation of the scores
B) calculating the appropriate statistic
C) evaluating the statistic based on its sampling distribution
D) calculating the appropriate statistic and evaluating the statistic based on its sampling distribution

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 135 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
The normal deviate test is used with _________.
A) a replicated measures design
B) an independent groups design
C) a single sample design
D) a multi-group design
A) a replicated measures design
B) an independent groups design
C) a single sample design
D) a multi-group design

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 135 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
The mean attention span for adults in a certain village is 15 minutes with a standard deviation of 6.4. The mean of all possible samples of size 30, taken from that population equals _________.
A) 15
B) 0.50
C) 30
D) 2.34
A) 15
B) 0.50
C) 30
D) 2.34

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 135 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
The Null Hypothesis Population is an actual or theoretical set of population scores that would result if _________.
A) the experiment were done on the entire population and the independent variable had no effect
B) the experiment were done on the sample and the independent variable had no effect
C) the experiment were done on the entire population and the independent variable had a real effect
D) the subjects in the population believed the null hypothesis was true
A) the experiment were done on the entire population and the independent variable had no effect
B) the experiment were done on the sample and the independent variable had no effect
C) the experiment were done on the entire population and the independent variable had a real effect
D) the subjects in the population believed the null hypothesis was true

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 135 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
Which of the following apply to the sampling distribution of the mean?
A)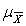 = µ
= µ
B)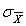 =
= 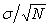
C) the variability of the distribution depends on N
D) the shape of the distribution is always normal
E)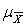 = ,
= , 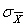 =
= 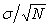 and the variability of the distribution depends on N
and the variability of the distribution depends on N
A)
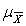 = µ
= µB)
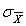 =
= 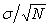
C) the variability of the distribution depends on N
D) the shape of the distribution is always normal
E)
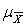 = ,
= , 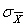 =
= 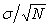 and the variability of the distribution depends on N
and the variability of the distribution depends on N
Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 135 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
For the population and sample size given in question 8, the standard error of the mean equals _________.
A) 4.8
B) 1.47
C) 0.21
D) 65
A) 4.8
B) 1.47
C) 0.21
D) 65

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 135 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
Sampling distributions can be obtained empirically by _________.
A) determining all possible samples of size N that can be formed from the Null Hypothesis Population
B) calculating the statistic for each of the samples
C) calculating the probability of getting each value of the statistic, if chance alone is operating
D) selecting several samples from all possible samples and calculating the statistic for those samples
E) a, b and c
A) determining all possible samples of size N that can be formed from the Null Hypothesis Population
B) calculating the statistic for each of the samples
C) calculating the probability of getting each value of the statistic, if chance alone is operating
D) selecting several samples from all possible samples and calculating the statistic for those samples
E) a, b and c

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 135 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
The mean attention span for adults in a certain village is 15 minutes with a standard deviation of 6.4. What is the probability of randomly selecting a sample of 30 scores from this population that has a mean attention span equal to or greater than 17 minutes?
A) 0.3783
B) 0.0436
C) 0.0446
D) 0.4564
A) 0.3783
B) 0.0436
C) 0.0446
D) 0.4564

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 135 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
The sampling distribution of a statistic _________.
A) gives all the values a statistic can take
B) gives the probability of getting each value of a statistic under the assumption it had resulted due to chance alone
C) is a probability distribution
D) all of these
A) gives all the values a statistic can take
B) gives the probability of getting each value of a statistic under the assumption it had resulted due to chance alone
C) is a probability distribution
D) all of these

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 135 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
We can reject H 0 if _________.
A) z obt = z crit
B) z obt ≥ z crit
C) z obt ≤ z crit
D) | z obt | ≥ | z crit |
A) z obt = z crit
B) z obt ≥ z crit
C) z obt ≤ z crit
D) | z obt | ≥ | z crit |

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 135 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
The mean attention span for adults in a certain village is 15 minutes with a standard deviation of 6.4. If the means of all possible samples of size 30 is taken from this population, 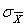 will equal _________.
will equal _________.
A) 3.0
B) 6.4
C) 0.21
D) 1.17
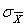 will equal _________.
will equal _________.A) 3.0
B) 6.4
C) 0.21
D) 1.17

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 135 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
Which of the following are true?
A)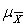 is the mean of the sampling distribution of the mean
is the mean of the sampling distribution of the mean
B)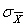 is the standard deviation of the raw scores
is the standard deviation of the raw scores
C) both of these
D) none of these
A)
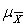 is the mean of the sampling distribution of the mean
is the mean of the sampling distribution of the meanB)
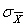 is the standard deviation of the raw scores
is the standard deviation of the raw scoresC) both of these
D) none of these

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 135 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
For the z test, the critical region for rejection of H 0 _________.
A) is determined only by a
B) is determined by a and N
C) allows us to accept the null hypothesis
D) depends on N
A) is determined only by a
B) is determined by a and N
C) allows us to accept the null hypothesis
D) depends on N

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 135 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
A sampling distribution gives all the values a statistic can take, along with _________.
A) the probability of getting each value if sampling is random from the Null Hypothesis Population
B) the probability of getting each value under the assumption that it had resulted due to chance alone
C) the number of samples in the distribution
D) the probability of getting each value if sampling is random from the Null Hypothesis Population and the probability of getting each value under the assumption that it had resulted due to chance alone
A) the probability of getting each value if sampling is random from the Null Hypothesis Population
B) the probability of getting each value under the assumption that it had resulted due to chance alone
C) the number of samples in the distribution
D) the probability of getting each value if sampling is random from the Null Hypothesis Population and the probability of getting each value under the assumption that it had resulted due to chance alone

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 135 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
To use the z test, _________.
A) µ and s must be specified
B) the sampling distribution of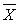 should be normal
should be normal
C) the population of raw scores must be normally distributed
D) and s must be specified and the sampling distribution of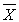 should be normal
should be normal
A) µ and s must be specified
B) the sampling distribution of
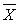 should be normal
should be normalC) the population of raw scores must be normally distributed
D) and s must be specified and the sampling distribution of
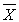 should be normal
should be normal
Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 135 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
An English teacher has been teaching a sixth grade composition class for many years. He has the feeling that over the past several years, the writing ability of students has changed. A national test of proficiency in composition was administered 5 years ago. The resulting distribution of scores was normally shaped, had a mean of 85 and a standard deviation of 10.9. In order to test his feeling, he gives his present class of 43 students the same proficiency test. The resulting mean is 80 and the standard deviation is 8.7. Using the z test with a = 0.05 2 tail , what is your conclusion?
A) reject H 0 ; the present class appears deficient in composition writing
B) retain H 0 ; the present class is not deficient in composition writing
C) accept H 0 ; the present class is not deficient in composition writing
D) reject H 0 ; the present class is not deficient in composition writing
A) reject H 0 ; the present class appears deficient in composition writing
B) retain H 0 ; the present class is not deficient in composition writing
C) accept H 0 ; the present class is not deficient in composition writing
D) reject H 0 ; the present class is not deficient in composition writing

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 135 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
If one draws all possible samples for various values of N from the same population of raw scores, as N increases _________.
A) the mean of the sampling distribution of the mean increases
B) the mean of the sampling distribution of the mean stays the same
C) the mean of the sampling distribution of the mean decreases
D) none of these
A) the mean of the sampling distribution of the mean increases
B) the mean of the sampling distribution of the mean stays the same
C) the mean of the sampling distribution of the mean decreases
D) none of these

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 135 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
If we take all possible samples from a normally distributed population, which of the following sample sizes will yield the smallest variation in the means of the samples?
A) 1
B) 85
C) 120
D) 5
E) 15
A) 1
B) 85
C) 120
D) 5
E) 15

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 135 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
Referring to question 29,how high must N be to be able to detect a µ real = 53 with a power of 0.8000?
A) 158
B) 222
C) 173
D) 248
A) 158
B) 222
C) 173
D) 248

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 135 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
Referring to question 29, the probability of making a Type II error is _________.
A) 0.7764
B) 0.2400
C) 0.2236
D) 0.6459
A) 0.7764
B) 0.2400
C) 0.2236
D) 0.6459

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 135 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
If one draws all possible samples for various values of N from the same population of raw scores, as N increases _________.
A) the standard error of the mean increases
B) the standard error of the mean stays the same
C) the standard error of the mean decreases
D) the standard error of the mean cannot be calculated
A) the standard error of the mean increases
B) the standard error of the mean stays the same
C) the standard error of the mean decreases
D) the standard error of the mean cannot be calculated

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 135 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
An English teacher has been teaching a sixth grade composition class for many years. He has the feeling that over the past several years, the writing ability of students has changed. A national test of proficiency in composition was administered 5 years ago. The resulting distribution of scores was normally shaped, had a mean of 85 and a standard deviation of 10.9. In order to test his feeling, he gives his present class of 43 students the same proficiency test. The resulting mean is 80 and the standard deviation is 8.7. The obtained value of the appropriate statistic for testing H 0 is _________.
A) z obt = - 0.46
B) z obt = +3.01
C) z obt = - 3.01
D) z obt = - 0.45
A) z obt = - 0.46
B) z obt = +3.01
C) z obt = - 3.01
D) z obt = - 0.45

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 135 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
The critical value of the statistic _________.
A) is independent of alpha
B) is equal to alpha
C) is always the same in the z distribution
D) depends on alpha
A) is independent of alpha
B) is equal to alpha
C) is always the same in the z distribution
D) depends on alpha

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 135 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
The critical value for the z distribution using a = 0.05 2 tail is _________.
A) ±1.96
B) ±2.58
C) ±1.64
D) ±2.33
A) ±1.96
B) ±2.58
C) ±1.64
D) ±2.33

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 135 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
The area under the critical region for rejection must _________.
A) equal alpha
B) be less than alpha
C) be greater than alpha
D) equal one-half of alpha
A) equal alpha
B) be less than alpha
C) be greater than alpha
D) equal one-half of alpha

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 135 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
A set of sample scores from an experiment has an N = 28 and a mean = 52. H 1 is directional, predicting an effect of the independent variable which decreases the magnitude of the dependent variable. H 0 asserts the sample is a random sample from a population of scores where µ = 55 and s = 12. a = 0.051 tail. Using the z test to analyze the data, what is the correct conclusion regarding H 0 ?
A) reject H 0 ; the independent variable has a real effect
B) retain H 0 ; we cannot conclude that the independent variable has a real effect
C) accept H 0 ; the independent variable has no effect
D) reject H 0 ; the independent variable has no effect
A) reject H 0 ; the independent variable has a real effect
B) retain H 0 ; we cannot conclude that the independent variable has a real effect
C) accept H 0 ; the independent variable has no effect
D) reject H 0 ; the independent variable has no effect

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 135 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
An English teacher has been teaching a sixth grade composition class for many years. He has the feeling that over the past several years, the writing ability of students has changed. A national test of proficiency in composition was administered 5 years ago. The resulting distribution of scores was normally shaped, had a mean of 85 and a standard deviation of 10.9. In order to test his feeling, he gives his present class of 43 students the same proficiency test. The resulting mean is 80 and the standard deviation is 8.7. Using the z test with a = 0.05 2 tail , the appropriate critical value is _________.
A) z crit = - 1.645
B) z crit = ±1.96
C) z crit = - 1.96
D) z crit = ± 1.645
A) z crit = - 1.645
B) z crit = ±1.96
C) z crit = - 1.96
D) z crit = ± 1.645

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 135 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
A set of sample scores from an experiment has an N = 28 and a mean = 52. H 1 is directional, predicting an effect of the independent variable which decreases the magnitude of the dependent variable. H 0 asserts the sample is a random sample from a population of scores where µ = 55 and s = 12. a = 0.051 tail. Using the z test to analyze the data, the power of the experiment to detect a real effect such that µ real = 53 is _________.
A) 0.3541
B) 0.7764
C) 0.7600
D) 0.2236
A) 0.3541
B) 0.7764
C) 0.7600
D) 0.2236

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 135 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
A set of sample scores from an experiment has an N = 28 and a mean = 52. H 1 is directional, predicting an effect of the independent variable which decreases the magnitude of the dependent variable. H 0 asserts the sample is a random sample from a population of scores where µ = 55 and s = 12. a = 0.051 tail. Using the z test to analyze the data, z obt = _________.
A) - 1.322
B) - 0.250
C) - 7.000
D) - 0.132
A) - 1.322
B) - 0.250
C) - 7.000
D) - 0.132

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 135 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
Power increases with _________.
A) increasing N
B) increasing magnitude of the effect of the independent variable
C) increasing a level
D) the magnitude of the difference between µ real and µ null
E) all of these
A) increasing N
B) increasing magnitude of the effect of the independent variable
C) increasing a level
D) the magnitude of the difference between µ real and µ null
E) all of these

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 135 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
A set of sample scores from an experiment has an N = 28 and a mean = 52. H 1 is directional, predicting an effect of the independent variable which decreases the magnitude of the dependent variable. H 0 asserts the sample is a random sample from a population of scores where µ = 55 and s = 12. a = 0.051 tail. Using the z test to analyze the data, z crit = _________.
A) +1.96
B) - 1.96
C) - 1.645
D) +1.645
A) +1.96
B) - 1.96
C) - 1.645
D) +1.645

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 135 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
Referring to question 29, if N is increased to 90, power = _________ to detect a real effect such that µ real = 53.
A) 0.8524
B) 0.9103
C) 0.4761
D) 0.5142
A) 0.8524
B) 0.9103
C) 0.4761
D) 0.5142

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 135 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
A raw score distribution that is negatively skewed will produce a sampling distribution of the mean for N = 4 which is _________.
A) also negatively skewed
B) normally distributed
C) positively skewed
D) cannot be determined
A) also negatively skewed
B) normally distributed
C) positively skewed
D) cannot be determined

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 135 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
In cases where N > 1, the relationship between the raw score population standard deviation and the standard error is _________.
A) the standard error is greater than the standard deviation
B) the standard error is less than the standard deviation
C) the standard error equals the standard deviation
D) the standard error is the standard deviation
A) the standard error is greater than the standard deviation
B) the standard error is less than the standard deviation
C) the standard error equals the standard deviation
D) the standard error is the standard deviation

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 135 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
A raw score distribution which has a moderate negative skew will result in a sampling distribution of the mean for N = 42 that is _________.
A) also negatively distributed
B) normally distributed
C) positively skewed
D) cannot be determined
A) also negatively distributed
B) normally distributed
C) positively skewed
D) cannot be determined

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 135 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
The sampling distribution of the mean varies with the size of the sample.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 135 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
If one draws two samples of size N from a distribution of raw scores (with replacement), then the means of the two samples will _________.
A) be equal
B) perhaps be equal but not necessarily
C) be equal to the standard error
D) be equal to 1.0
A) be equal
B) perhaps be equal but not necessarily
C) be equal to the standard error
D) be equal to 1.0

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 135 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
The sampling distribution of z varies with the size of the sample.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 135 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
To use the z test the data _________.
A) must be normally distributed
B) must be sampled from a normal distribution
C) should be sampled from a normal distribution if sample size is 10
D) can be any shape if N = 10
E) should be normal distributed if sample size is 10
A) must be normally distributed
B) must be sampled from a normal distribution
C) should be sampled from a normal distribution if sample size is 10
D) can be any shape if N = 10
E) should be normal distributed if sample size is 10

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 135 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
If the population standard deviation is 19.0 and the sample size is 19, then the standard error equals _________.
A) 19.00
B) 1.00
C) 4.36
D) cannot be determined; need to know population mean
A) 19.00
B) 1.00
C) 4.36
D) cannot be determined; need to know population mean

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 135 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
The sampling distribution of the mean is always normally distributed.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 135 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
What we are testing with the z test in this chapter is _________.
A) the sample mean
B) the population mean
C) the sample error
D) the standard error
A) the sample mean
B) the population mean
C) the sample error
D) the standard error

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 135 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
The symbol for the standard error of the mean is 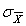 .
.
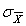 .
.
Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 135 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
A health psychologist knows the smoking population at the hospital where she works smokes an average of 18 cigarettes per day with a standard deviation of 7. She plans to conduct a program to reduce smoking. If she has 25 persons in her program, what is the power to detect a real effect of the program such that cigarette consumption is reduced, on the average, by 5 cigarettes? Assume population normality and use a = 0.05 1 tail .
A) Insufficient information
B) 0.9732
C) 0.9463
D) 0.8925
A) Insufficient information
B) 0.9732
C) 0.9463
D) 0.8925

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 135 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
Could the following sample reasonably have been drawn from a normal population with a mean of 20 and standard deviation of 1.5 using a = 0.01 2 tail ? X : 21, 21, 21, 20, 22, 20, 22?
A) yes
B) no
C) cannot be tested with z test
D) The correct answer cannot be determined from the information provided.
A) yes
B) no
C) cannot be tested with z test
D) The correct answer cannot be determined from the information provided.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 135 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
The symbol for the mean of the sampling distribution of the mean is 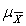 .
.
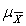 .
.
Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 135 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
The sampling distribution of z must be normally distributed to use the z test.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 135 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
The critical value for the z distribution using a = 0.01 2 tail is _________.
A) ±1.96
B) ±2.58
C) ±1.64
D) ±2.33
A) ±1.96
B) ±2.58
C) ±1.64
D) ±2.33

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 135 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
The normal deviate test uses the mean of the sample as a basic statistic.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 135 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
What would one conclude about the null hypothesis that a sample of N = 46 with a mean of 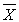 = 104 could reasonably have been drawn from a population with the parameters of = 100 and s = 8? Use a = 0.05 2 tail .
= 104 could reasonably have been drawn from a population with the parameters of = 100 and s = 8? Use a = 0.05 2 tail .
A) accept H0
B) reject H1
C) reject H0
D) retain H0
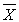 = 104 could reasonably have been drawn from a population with the parameters of = 100 and s = 8? Use a = 0.05 2 tail .
= 104 could reasonably have been drawn from a population with the parameters of = 100 and s = 8? Use a = 0.05 2 tail .A) accept H0
B) reject H1
C) reject H0
D) retain H0

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 135 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
If z obt had a value of 4.50 in the direction opposite from that predicted by the directional H 1 and z crit was 2.58, one would _________.
A) accept H0
B) reject the alternative hypothesis
C) retain H0
D) reject H0
A) accept H0
B) reject the alternative hypothesis
C) retain H0
D) reject H0

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 135 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
Generally speaking, if the sampling distribution of a statistic is indeterminate (impossible to determine), the statistic cannot be used for inference.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 135 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
Assuming that the population mean is 47.2 and the population deviation is 6.4, what is the z obt value for a sample mean of 52.1 if N = 8?
A) 1.96
B) 2.17
C) 1.73
D) 0.77
A) 1.96
B) 2.17
C) 1.73
D) 0.77

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 135 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
Which of the following statements is(are) false?
A) The sampling distribution of a statistic gives (1) all the values that the statistic can take and (2) the probability of getting each value if sampling is random from the null hypothesis population.
B) The sampling distribution of a statistic gives (1) all the values that the statistic can take and (2) the probability of getting each value under the assumption that it resulted from chance alone.
C) The critical region for rejection of the null hypothesis is 1 - (the area under the curve that contains all the values of the statistic that allow rejection of the null hypothesis).
D) They are all true.
A) The sampling distribution of a statistic gives (1) all the values that the statistic can take and (2) the probability of getting each value if sampling is random from the null hypothesis population.
B) The sampling distribution of a statistic gives (1) all the values that the statistic can take and (2) the probability of getting each value under the assumption that it resulted from chance alone.
C) The critical region for rejection of the null hypothesis is 1 - (the area under the curve that contains all the values of the statistic that allow rejection of the null hypothesis).
D) They are all true.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 135 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
The sampling distribution of z is always normally distributed.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 135 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
Power + Beta = 1.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 135 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
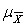 = , regardless of the shape of the sampling distribution of the mean.
= , regardless of the shape of the sampling distribution of the mean.
Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 135 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
The critical value of a statistic is the value of the statistic that bounds the critical region for rejection of H 0 .

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 135 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
Increasing N increases the real effect of the independent variable.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 135 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
A sampling distribution is based on the assumption that the independent variable has an effect on the dependent variable.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 135 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
In general, Alpha + Beta = 1.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 135 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
The z test does not depend on the shape of the sampling distribution of 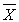 .
.
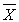 .
.
Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 135 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
If H 0 is false, a high level of power increases the probability we will reject it.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 135 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
To use the z test, µ and s must be specified.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 135 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
Power is the sensitivity of the experiment to detect a real effect of the independent variable, if there is one.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 135 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
Power and Beta are directly related.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 135 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72
Alpha and Beta are inversely related.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 135 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73
Only one sampling distribution can apply to any given problem or experiment.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 135 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
74
The power of the z test increases with sample variability.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 135 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
75
The sampling distribution of the mean is made up of mean scores.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 135 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
76
High power is desirable in an experiment.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 135 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
77
Using the sample standard deviation as an estimate for the population standard deviation is an example of interval estimation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 135 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
78
The critical region for rejection of H 0 is the area under the curve that contains all the values of the statistic that fail to allow rejection of H 0 .

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 135 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
79
As N increases, the variability of the sampling distribution of the mean increases.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 135 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
80
The binomial distribution is an example of a sampling distribution.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 135 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



