Deck 13: Students T Test for Single Samples
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/121
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 13: Students T Test for Single Samples
1
As the degrees of freedom increase, the correspondence between the t and z distributions _________.
A) increases
B) decreases
C) remains the same
D) cannot be determined
A) increases
B) decreases
C) remains the same
D) cannot be determined
increases
2
The 95% confidence interval arrived at from a particular experiment is 72-79. This means that _________.
A) the probability is 0.95 that µ falls between 72-79
B) the probability is 0.95 that the interval 72-79 contains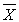
C) the probability is 0.95 that the interval 72-79 contains µ
D) a and c
A) the probability is 0.95 that µ falls between 72-79
B) the probability is 0.95 that the interval 72-79 contains
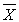
C) the probability is 0.95 that the interval 72-79 contains µ
D) a and c
the probability is 0.95 that the interval 72-79 contains µ
3
The degrees of freedom for the t test for single samples are _________.
A) N
B) N - 1
C) N - 2
D) depends on alpha
A) N
B) N - 1
C) N - 2
D) depends on alpha
N - 1
4
In a correlative study, _________.
A) a value of r ≠ 0 in the sample, means that there is a nonzero correlation in the population
B) a nondirectional alternative hypothesis states that r ≠ 0
C) the null hypothesis for a nondirectional alternative hypothesis states that r = 0
D) a nondirectional alternative hypothesis states that r = 0
E) a nondirectional alternative hypothesis states that r ≠0 and the null hypothesis for a nondirectional alternative hypothesis states that r = 0
A) a value of r ≠ 0 in the sample, means that there is a nonzero correlation in the population
B) a nondirectional alternative hypothesis states that r ≠ 0
C) the null hypothesis for a nondirectional alternative hypothesis states that r = 0
D) a nondirectional alternative hypothesis states that r = 0
E) a nondirectional alternative hypothesis states that r ≠0 and the null hypothesis for a nondirectional alternative hypothesis states that r = 0

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 121 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
| t crit | for any alpha level is _________ | z crit | for N less than infinity.
A) greater than
B) the same as
C) less than
D) none of these
A) greater than
B) the same as
C) less than
D) none of these

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 121 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
In a t test, when the size of the sample is increased, the confidence interval _________.
A) increases
B) decreases
C) stays the same
D) changes shape
A) increases
B) decreases
C) stays the same
D) changes shape

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 121 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
We lose one degree of freedom in calculating _________.
A) s
B)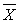
C) t obt (single sample)
D) s and t obt (single sample)
A) s
B)
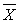
C) t obt (single sample)
D) s and t obt (single sample)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 121 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
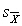 is an estimate of _________.
is an estimate of _________.A) µ
B) s
C)
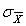
D) s.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 121 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
Which of the characteristics below distinguishes the t statistic from the z statistic?
A) the proportion of area beyond a particular positive t value is equal to the proportion of area below the corresponding negative t
B) the z distribution has a mean of zero while the t distribution does not
C) In the t distribution the area under the curve beyond a value of ±1.96 is greater than that of the normal curve
D) all of these
A) the proportion of area beyond a particular positive t value is equal to the proportion of area below the corresponding negative t
B) the z distribution has a mean of zero while the t distribution does not
C) In the t distribution the area under the curve beyond a value of ±1.96 is greater than that of the normal curve
D) all of these

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 121 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
For a given N , the interval that bounds the population mean at the 99% confidence level is _________ that which bounds the population mean at the 95% confidence level.
A) equal to
B) greater than
C) less than
D) can t be determined without knowing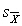
A) equal to
B) greater than
C) less than
D) can t be determined without knowing
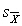

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 121 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
The df associated with evaluating the significance of r obt are _________.
A) N
B) N - 1
C) N - 2
D) need more information
A) N
B) N - 1
C) N - 2
D) need more information

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 121 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
The confidence interval for the population mean is _________.
A) a range of values which probably contains the population mean
B) a range of values which contains the population mean
C) the same from sample-to-sample
D) a range of values which probably contains the population mean and the same from sample-to-sample
A) a range of values which probably contains the population mean
B) a range of values which contains the population mean
C) the same from sample-to-sample
D) a range of values which probably contains the population mean and the same from sample-to-sample

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 121 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
In an independent groups experiment, if we must estimate the population standard deviation to determine the significance of the sample results, the appropriate inference test is the _________.
A) sign test
B) z test
C) t test
D) none of these
A) sign test
B) z test
C) t test
D) none of these

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 121 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
When using the t test, we reject H 0 _________.
A) if t obt ≤ t crit
B) if | t obt | ≥ | t crit |
C) if | t obt | ≤ | t crit |
D) if t obt ≥ t crit
A) if t obt ≤ t crit
B) if | t obt | ≥ | t crit |
C) if | t obt | ≤ | t crit |
D) if t obt ≥ t crit

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 121 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
The mean of the t distribution equals _________.
A) the mean of the population of raw scores
B) 0
C) 1
D) s
A) the mean of the population of raw scores
B) 0
C) 1
D) s

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 121 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
In a correlated groups experiment, if we must estimate the population standard deviation to determine the significance of the sample results, the appropriate statistical test is _________.
A) t test
B) sign test
C) z test
D) none of these
A) t test
B) sign test
C) z test
D) none of these

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 121 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
As the df increases, the t distribution _________.
A) gets more symmetrical
B) approaches the normal distribution
C) stays the same
D) becomes more skewed
A) gets more symmetrical
B) approaches the normal distribution
C) stays the same
D) becomes more skewed

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 121 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
Which of the following represents a sampling distribution?
A) the binomial distribution
B) the z distribution
C) the t distribution
D) all of these
E) the z and t distributions
A) the binomial distribution
B) the z distribution
C) the t distribution
D) all of these
E) the z and t distributions

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 121 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
The t test differs from the z test in that _________.
A) with the t test we estimate s
B) with the t test we estimate µ
C) the z distribution is a family of curves
D) the t distribution is a family of curves
E) with the t test we estimate s and the t distribution is a family of curves
A) with the t test we estimate s
B) with the t test we estimate µ
C) the z distribution is a family of curves
D) the t distribution is a family of curves
E) with the t test we estimate s and the t distribution is a family of curves

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 121 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
With which statistical test do we determine the probability of getting the obtained results or those more extreme assuming the differences in results were due to chance alone?
A) sign test
B) z test
C) t test
D) all of these
A) sign test
B) z test
C) t test
D) all of these

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 121 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
For a given value of alpha, the critical value of t is _______ than the critical value of z .
A) no different
B) less
C) greater
D) none of these
A) no different
B) less
C) greater
D) none of these

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 121 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
As N gets infinitely large, the critical value of t equals the critical value of z .

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 121 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
A researcher believes that women today weigh less than in previous years. To investigate this belief, she randomly samples 41 adult women and records their weights. The scores have a mean of 111 lbs. and a standard deviation of 12.4. A local census taken several years ago shows the mean weight of adult women was 115 lbs. The obtained value of the appropriate statistic for testing H 0 is _________.
A) t obt = - 2.07
B) t obt = +2.07
C) t obt = - 0.32
D) t obt = +0.32
A) t obt = - 2.07
B) t obt = +2.07
C) t obt = - 0.32
D) t obt = +0.32

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 121 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
The sample mean is an example of _________.
A) interval estimation
B) point estimation
C) confidence point
D) confidence numbers
A) interval estimation
B) point estimation
C) confidence point
D) confidence numbers

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 121 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
For N = 20, the degrees of freedom for the test of the significance of the correlation coefficient ( r ) is _________.
A) 20
B) 21
C) 19
D) 18
A) 20
B) 21
C) 19
D) 18

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 121 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
If r = 0.84 and N = 5, the value of t obt for the test of the significance of r is _________.
A) 1.96
B) 2.40
C) 2.68
D) 3.46
A) 1.96
B) 2.40
C) 2.68
D) 3.46

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 121 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
The 95% confidence interval of the mean for 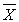 = 13.0, s = 1.6, and N = 21 is _________.
= 13.0, s = 1.6, and N = 21 is _________.
A) 12.01 to 13.99
B) 12.27 to 13.73
C) 11.05 to 15.05
D) 12.95 to 14.95
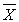 = 13.0, s = 1.6, and N = 21 is _________.
= 13.0, s = 1.6, and N = 21 is _________.A) 12.01 to 13.99
B) 12.27 to 13.73
C) 11.05 to 15.05
D) 12.95 to 14.95

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 121 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
The mean of the t distribution equals _________.
A) 0
B) 1
C) N
D) N - 1
A) 0
B) 1
C) N
D) N - 1

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 121 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
A researcher believes that women today weigh less than in previous years. To investigate this belief, she randomly samples 41 adult women and records their weights. The scores have a mean of 111 lbs. and a standard deviation of 12.4. A local census taken several years ago shows the mean weight of adult women was 115 lbs. The df for determining t crit = _________.
A) 41
B) 40
C) 39
D) need more information
A) 41
B) 40
C) 39
D) need more information

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 121 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
How many t distributions are there?
A) 1
B) 2
C) 30
D) one for each value of df
A) 1
B) 2
C) 30
D) one for each value of df

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 121 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
If the population parameters are known, the t test is _________ powerful than the z test.
A) more
B) less
C) equally
D) need more information
A) more
B) less
C) equally
D) need more information

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 121 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
A researcher believes that women today weigh less than in previous years. To investigate this belief, she randomly samples 41 adult women and records their weights. The scores have a mean of 111 lbs. and a standard deviation of 12.4. A local census taken several years ago shows the mean weight of adult women was 115 lbs. Using a = 0.01 1 tail , the critical value of the appropriate statistic for testing H 0 is _________.
A) - 1.684
B) - 2.423
C) ±1.684
D) ±2.423
A) - 1.684
B) - 2.423
C) ±1.684
D) ±2.423

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 121 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
A researcher believes that women today weigh less than in previous years. To investigate this belief, she randomly samples 41 adult women and records their weights. The scores have a mean of 111 lbs. and a standard deviation of 12.4. A local census taken several years ago shows the mean weight of adult women was 115 lbs. What do you conclude, using the appropriate inference test and a = 0.01 1 tail ?
A) accept H 1
B) accept H 0
C) reject H 0
D) retain H 0
E) accept H 1 and reject H 0
A) accept H 1
B) accept H 0
C) reject H 0
D) retain H 0
E) accept H 1 and reject H 0

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 121 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
As N gets _______, the critical value of t gets _________.
A) larger; larger
B) smaller; smaller
C) larger; smaller
D) smaller; larger
A) larger; larger
B) smaller; smaller
C) larger; smaller
D) smaller; larger

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 121 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
For N = 20, the value of r crit for a = 0.05 2 tail is _________.
A) 0.4329
B) 0.3783
C) 0.4438
D) 0.5614
A) 0.4329
B) 0.3783
C) 0.4438
D) 0.5614

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 121 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
As N increases 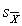 becomes a _________ estimate of
becomes a _________ estimate of 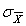 .
.
A) better
B) worse
C) meaningless
D) biased
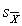 becomes a _________ estimate of
becomes a _________ estimate of 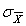 .
.A) better
B) worse
C) meaningless
D) biased

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 121 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
The proper use of the t test requires that _________.
A) the sampling distribution of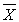 is normal
is normal
B) N ≥ 30
C) the sampling distribution of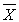 is normal and N ≥30
is normal and N ≥30
D) the sampling distribution of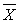 is normal or N ≥30
is normal or N ≥30
A) the sampling distribution of
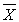 is normal
is normalB) N ≥ 30
C) the sampling distribution of
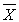 is normal and N ≥30
is normal and N ≥30D) the sampling distribution of
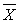 is normal or N ≥30
is normal or N ≥30
Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 121 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
Use the data presented in the text, Chapter 7, question 12. In that question, r obt = - 0.69 and N = 10. Using a = 0.05 2 tail , is this a significant value for r obt ?
A) Yes, df = 9, r crit = ±0.6021
B) Yes, df = 8, r crit = ±0.6319
C) Yes, df = 8, r crit = - 0.6319
D) Yes, df = 8, r crit = +0.6319
A) Yes, df = 9, r crit = ±0.6021
B) Yes, df = 8, r crit = ±0.6319
C) Yes, df = 8, r crit = - 0.6319
D) Yes, df = 8, r crit = +0.6319

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 121 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
The _______ confidence interval for the population mean is always wider than the _______ confidence interval for the population mean.
A) 99%; 95%
B) 95%; 99%
C) both of these
D) none of these
A) 99%; 95%
B) 95%; 99%
C) both of these
D) none of these

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 121 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
If = 30, s = 5.2, 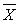 = 28.0, s = 6.1 and N = 13, the value of the most powerful statistic to test the significance of the sample mean is _________.
= 28.0, s = 6.1 and N = 13, the value of the most powerful statistic to test the significance of the sample mean is _________.
A) - 1.18
B) 1.96
C) 2.18
D) - 1.39
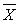 = 28.0, s = 6.1 and N = 13, the value of the most powerful statistic to test the significance of the sample mean is _________.
= 28.0, s = 6.1 and N = 13, the value of the most powerful statistic to test the significance of the sample mean is _________.A) - 1.18
B) 1.96
C) 2.18
D) - 1.39

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 121 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
Which of the following are not characteristics of the t distribution?
A) has a mean = 0.
B) has a standard deviation greater than 1.00 for df less than infinity.
C) varies with df.
D) has no negative values.
E) all of these are characteristics of the t distribution.
A) has a mean = 0.
B) has a standard deviation greater than 1.00 for df less than infinity.
C) varies with df.
D) has no negative values.
E) all of these are characteristics of the t distribution.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 121 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
The t distribution is a family of curves that vary with the degrees of freedom.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 121 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
"Degrees of freedom" for any statistic is defined as _________.
A) N
B) N - 1
C) the number of scores that are free to vary in calculating the statistic
D) N - 1and the number of scores that are free to vary in calculating the statistic
A) N
B) N - 1
C) the number of scores that are free to vary in calculating the statistic
D) N - 1and the number of scores that are free to vary in calculating the statistic

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 121 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
The degrees of freedom equal N - 1 for the t test for single samples.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 121 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
The t test requires that the sampling distribution of t be normally distributed.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 121 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
There are two values for t crit when H 1 is directional.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 121 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
To test the significance of r obt , the df = N - 2.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 121 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
In general, the z test is more powerful than the t test because _________.
A) with the z test, the sample mean is closer to the population mean than with the t test
B) with the t test we lose a degree of freedom
C) the standard deviation of the sample raw scores is larger with the t test
D) with the z test, we know ó , whereas with the t test, we must estimate it.
A) with the z test, the sample mean is closer to the population mean than with the t test
B) with the t test we lose a degree of freedom
C) the standard deviation of the sample raw scores is larger with the t test
D) with the z test, we know ó , whereas with the t test, we must estimate it.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 121 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
The 95% confidence interval is defined as _________.
A) an interval such that we are 95% confident that the population value lies within the interval
B) an interval such that the probability is 0.95 that the interval contains the population value
C) an interval such that we can reject H 0 at á = 0.05
D) a and b
A) an interval such that we are 95% confident that the population value lies within the interval
B) an interval such that the probability is 0.95 that the interval contains the population value
C) an interval such that we can reject H 0 at á = 0.05
D) a and b

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 121 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
The sampling distribution of t differs from the sampling distribution of z in that _________.
A) there is only one sampling distribution of z (the normal distribution) for all N , while there are many sampling distributions for t , depending on sample size.
B) the sampling distribution of z is more narrow, except when N equals infinity.
C) the means of the two distributions are different
D) all of these
E) a and b
A) there is only one sampling distribution of z (the normal distribution) for all N , while there are many sampling distributions for t , depending on sample size.
B) the sampling distribution of z is more narrow, except when N equals infinity.
C) the means of the two distributions are different
D) all of these
E) a and b

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 121 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
t crit must always be positive.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 121 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
If we have to estimate s , we should use the z test.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 121 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
If N t test, the population of raw scores should be normally distributed.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 121 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
Confidence interval is defined as _________.
A) a range of values that probably contains the population value
B) a range of values that probably contains the population mean
C) a range of values that probably contain the population standard deviation
D) all of these
A) a range of values that probably contains the population value
B) a range of values that probably contains the population mean
C) a range of values that probably contain the population standard deviation
D) all of these

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 121 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
The 99% confidence interval is defined as _________.
A) an interval such that we are 99% confident that the population value lies within the interval
B) an interval such that the probability is 0.99 that the interval contains the population value
C) an interval such that we can reject H 0 at á = 0.01
D) an interval such that we are 99% confident that the population value lies within the interval and an interval such that the probability is 0.99 that the interval contains the population value
A) an interval such that we are 99% confident that the population value lies within the interval
B) an interval such that the probability is 0.99 that the interval contains the population value
C) an interval such that we can reject H 0 at á = 0.01
D) an interval such that we are 99% confident that the population value lies within the interval and an interval such that the probability is 0.99 that the interval contains the population value

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 121 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
Confidence limits are defined as _________.
A) the highest and lowest score in the sample set of scores
B) the values that lie outside of the confidence interval
C) the values that bound the confidence interval
D) the values that lie within the confidence interval
A) the highest and lowest score in the sample set of scores
B) the values that lie outside of the confidence interval
C) the values that bound the confidence interval
D) the values that lie within the confidence interval

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 121 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
As the degrees of freedom increase, the t distribution becomes more like the z distribution.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 121 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
Generally speaking, the more confidence we have that the interval contains the population mean, the larger is the interval.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 121 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
The t test is more sensitive than the z test.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 121 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
The sampling distribution of t _________.
A) gives all possible different t values of size N and the probability of getting each value if sampling is random from the null-hypothesis population
B) is defined as a probability distribution of the t values that would occur if all possible different samples of size N were drawn from the null hypothesis population
C) varies uniquely with N
D) all of these
E) a and b
A) gives all possible different t values of size N and the probability of getting each value if sampling is random from the null-hypothesis population
B) is defined as a probability distribution of the t values that would occur if all possible different samples of size N were drawn from the null hypothesis population
C) varies uniquely with N
D) all of these
E) a and b

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 121 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
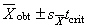 determines the confidence interval for the population mean.
determines the confidence interval for the population mean.
Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 121 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
For a two-tailed test, if | t obt | ≥ | t crit |, reject H 0.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 121 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
If r obt is not equal to zero, r cannot equal zero.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 121 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
If | r obt | > | r crit |, we reject the assumption that r = 0.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 121 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
The t test is more powerful than the z test.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 121 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
The 99% confidence limit is always wider than the 95% confidence interval.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 121 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
In the t test s is used to estimate s .

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 121 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
The t test for single samples is used when the population parameters µ and s are unknown.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 121 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
The t test requires that the sampling distribution of 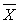 is normal.
is normal.
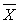 is normal.
is normal.
Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 121 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
If r > 0.50, then there must be a nonzero correlation in the population.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 121 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
The t distribution is the same for all sample sizes.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 121 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72
In general t crit is greater than z crit at the same a level.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 121 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73
The mean of the t distribution equals 0 for all sample sizes.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 121 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
74
The 95% confidence interval means that 95% of the time 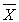 = .
= .
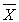 = .
= .
Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 121 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
75
The confidence interval is one example of point estimation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 121 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
76
When df = ¥ the t distribution is identical to the z distribution.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 121 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
77
In general, if r = 0, then r = 0.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 121 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
78
The t test can only be applied to a nondirectional alternative hypothesis.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 121 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
79
In general, if r ≠ 0, then r must not equal 0.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 121 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
80
By definition the degrees of freedom for all statistical tests equals N - 1.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 121 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



