Deck 14: Students T Test for Correlated and Independent Groups
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/145
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 14: Students T Test for Correlated and Independent Groups
1
If the homogeneity of variance assumption is violated in an experiment using the t test for independent groups, this means _________.
A) the populations from which the samples were drawn have different variances
B) the power of the t test will be reduced
C) t the test can still be used, if the violation is a moderate one
D) the t test should not be used
E) the populations from which the samples were drawn have different variances and t the test can still be used, if the violation is a moderate one
A) the populations from which the samples were drawn have different variances
B) the power of the t test will be reduced
C) t the test can still be used, if the violation is a moderate one
D) the t test should not be used
E) the populations from which the samples were drawn have different variances and t the test can still be used, if the violation is a moderate one
the populations from which the samples were drawn have different variances
2
Assuming large between subject variability, which of the following tests is usually the most sensitive ( N held constant)?
A) t test for correlated groups
B) sign test
C) t test for independent groups
D) they are all equal in sensitivity
A) t test for correlated groups
B) sign test
C) t test for independent groups
D) they are all equal in sensitivity
t test for correlated groups
3
Which of the following increase(s) the power of the t test?
A) increasing N
B) increasing the sample variance(s)
C) increasing the effect of the independent variable
D) all of these
E) increasing N and increasing the effect of the independent variable
A) increasing N
B) increasing the sample variance(s)
C) increasing the effect of the independent variable
D) all of these
E) increasing N and increasing the effect of the independent variable
increasing N and increasing the effect of the independent variable
4
The t test for correlated groups requires that _________.
A) the sampling distribution of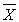 is normally distributed
is normally distributed
B) N ≥ 30
C) the population raw scores are normally distributed
D) the sampling distribution of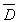 is normally is normally distributed
is normally is normally distributed
A) the sampling distribution of
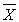 is normally distributed
is normally distributedB) N ≥ 30
C) the population raw scores are normally distributed
D) the sampling distribution of
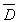 is normally is normally distributed
is normally is normally distributed
Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 145 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
Student's t test for correlated groups is _________.
A) more powerful than the sign test because it uses both the magnitude and direction of the scores
B) less powerful than the sign test because it uses only the magnitude of the scores
C) impractical because we need to know s
D) generally less powerful than Student's t test for independent groups
A) more powerful than the sign test because it uses both the magnitude and direction of the scores
B) less powerful than the sign test because it uses only the magnitude of the scores
C) impractical because we need to know s
D) generally less powerful than Student's t test for independent groups

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 145 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
Which of the following is (are) major advantage(s) of a two condition experiment over a single sample design?
A) A lack of dependence on population values which may be inappropriate
B) no need to know any parameters of the raw score population
C) creates ability to control for other variables which may affect the results
D) all of these
A) A lack of dependence on population values which may be inappropriate
B) no need to know any parameters of the raw score population
C) creates ability to control for other variables which may affect the results
D) all of these

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 145 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
One employs a correlated groups design _________.
A) to eliminate random error
B) to simplify calculations
C) for prediction
D) to reduce the effects of individual differences among subjects
A) to eliminate random error
B) to simplify calculations
C) for prediction
D) to reduce the effects of individual differences among subjects

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 145 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
In an experiment using the independent groups design, there are 10 subjects in one group and 12 subjects in the other group. The sampling distribution of t that is appropriate for that experiment is identical to the t distribution that is appropriate for a single sample design with _________ subjects.
A) 22
B) 21
C) 20
D) 11
A) 22
B) 21
C) 20
D) 11

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 145 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
In employing a correlated groups design, one possible drawback is _________.
A) the increased number of statistical computations
B) random errors are likely to be greater
C) reduction in the degrees of freedom
D) none of these
A) the increased number of statistical computations
B) random errors are likely to be greater
C) reduction in the degrees of freedom
D) none of these

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 145 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
If the homogeneity of variance assumption is violated in an independent groups t test, this means _________.
A) the populations from which the samples were drawn have different standard deviations
B) you should use the sign test
C) the sample sizes should be equal and N greater than 30 to use the t test
D) the populations from which the samples were drawn have different standard deviations and the sample sizes should be equal and N greater than 30 to use the t test
E) all of these
A) the populations from which the samples were drawn have different standard deviations
B) you should use the sign test
C) the sample sizes should be equal and N greater than 30 to use the t test
D) the populations from which the samples were drawn have different standard deviations and the sample sizes should be equal and N greater than 30 to use the t test
E) all of these

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 145 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
Student's t test for correlated groups really reduces to _________.
A) the sign test
B) Student's t test for single samples using difference scores
C) Students t test for independent groups
D) none of these
A) the sign test
B) Student's t test for single samples using difference scores
C) Students t test for independent groups
D) none of these

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 145 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
In a t test for two independent samples, the unbiased estimate of the population variance is
A)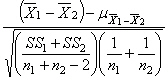
B)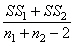
C)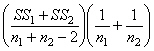
D)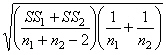
A)
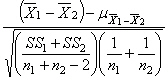
B)
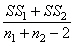
C)
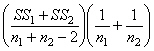
D)
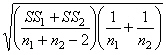

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 145 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
The power of the t test increases with _________.
A) increases in N
B) increases in the effect of the independent variable
C) decreases in the sample variance(s)
D) all of these
A) increases in N
B) increases in the effect of the independent variable
C) decreases in the sample variance(s)
D) all of these

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 145 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
The z test for independent groups is seldom used because _________.
A) it lacks sensitivity
B) it is too complicated
C) we seldom know the population variances
D) the sampling distribution of z under H 0 is unknown
A) it lacks sensitivity
B) it is too complicated
C) we seldom know the population variances
D) the sampling distribution of z under H 0 is unknown

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 145 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
A correlated groups design is more sensitive than an independent groups design if _________.
A) there are large inter-subject differences
B) there are small inter-subject differences
C) the experimental treatment effect is strong
D) there is a high correlation between paired scores
A) there are large inter-subject differences
B) there are small inter-subject differences
C) the experimental treatment effect is strong
D) there is a high correlation between paired scores

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 145 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
Having just made what you feel is to be a Type II error, using an independent groups design and a t test analysis, which of the following might you do in the next experiment to reduce the probability of a Type II error?
A) increase N
B) change to a correlated groups design
C) try to reduce the variance by better experimental control
D) all of these
A) increase N
B) change to a correlated groups design
C) try to reduce the variance by better experimental control
D) all of these

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 145 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
The null hypothesis for a nondirectional H 1 using the t test for correlated groups asserts that _________.
A) µ 1 - µ 2 = 0
B) µ D = 0
C)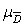 = 0
= 0
D) D -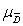 = 0
= 0
E) none of these
A) µ 1 - µ 2 = 0
B) µ D = 0
C)
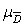 = 0
= 0D) D -
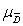 = 0
= 0E) none of these

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 145 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
For which of these tests do you need to know the sampling distribution of the relevant statistic in order to use the statistic for hypothesis testing?
A) z test
B) t test
C) sign test
D) all of these
A) z test
B) t test
C) sign test
D) all of these

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 145 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
Which of the following are assumptions underlying the use of the t test for independent groups?
A) the variance of each population is known
B) the sampling distribution of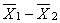 must be normal
must be normal
C) the samples are drawn from populations having equal variances
D) all of these
E) the sampling distribution of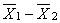 must be normal and the samples are drawn from populations having equal variances
must be normal and the samples are drawn from populations having equal variances
A) the variance of each population is known
B) the sampling distribution of
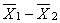 must be normal
must be normalC) the samples are drawn from populations having equal variances
D) all of these
E) the sampling distribution of
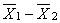 must be normal and the samples are drawn from populations having equal variances
must be normal and the samples are drawn from populations having equal variances
Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 145 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
The mean of the sampling distribution of 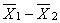 = _________.
= _________.
A) µ
B) 0
C) 1
D) µ 1 - µ 2
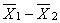 = _________.
= _________.A) µ
B) 0
C) 1
D) µ 1 - µ 2

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 145 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
A health educator wants to evaluate the effect of a dental film on the frequency with which children brush their teeth. A random selection of 8 children are used for the experiment. First, a baseline of the number of times the children brush their teeth over a month's period is established. Next, the children are shown the dental film and again the number of teeth brushings are recorded for a month. The following data are recorded.  Using a = 0.05 2 tail , what do you conclude?
Using a = 0.05 2 tail , what do you conclude?
A) retain H 0 ; the film has no effect on the frequency of tooth brushing
B) reject H 0 ; the film affects the frequency of tooth brushing
C) accept H 0 ; the film has no effect on the frequency of tooth brushing
D) reject H 0 ; chance alone is a reasonable explanation of the data
 Using a = 0.05 2 tail , what do you conclude?
Using a = 0.05 2 tail , what do you conclude?A) retain H 0 ; the film has no effect on the frequency of tooth brushing
B) reject H 0 ; the film affects the frequency of tooth brushing
C) accept H 0 ; the film has no effect on the frequency of tooth brushing
D) reject H 0 ; chance alone is a reasonable explanation of the data

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 145 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
In the t test for independent groups, _________.
A) we estimate µ 1 - µ 2
B) we estimate s 2
C) we estimate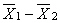
D) df = N - 1
A) we estimate µ 1 - µ 2
B) we estimate s 2
C) we estimate
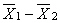
D) df = N - 1

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 145 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
A health educator wants to evaluate the effect of a dental film on the frequency with which children brush their teeth. A random selection of 8 children are used for the experiment. First, a baseline of the number of times the children brush their teeth over a month's period is established. Next, the children are shown the dental film and again the number of teeth brushings are recorded for a month. The following data are recorded.  The obtained value of the appropriate statistic is _________.
The obtained value of the appropriate statistic is _________.
A) 3.13
B) 3.14
C) 3.58
D) 3.57
 The obtained value of the appropriate statistic is _________.
The obtained value of the appropriate statistic is _________.A) 3.13
B) 3.14
C) 3.58
D) 3.57

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 145 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
A professor of women's studies is interested in determining if stress affects the menstrual cycle. Ten women are randomly sampled for an experiment and randomly divided into two groups. One of the groups is subjected to high stress for two months while the other lives in a relatively stress-free environment. The professor measures the menstrual cycle (in days) of each woman during the second month. The following data are obtained.  Assume you are evaluating H 0 using the t test. Using a = .05 2 tail , t crit = _________.
Assume you are evaluating H 0 using the t test. Using a = .05 2 tail , t crit = _________.
A) +2.262
B) +2.306
C) ±2.262
D) ±2.306
 Assume you are evaluating H 0 using the t test. Using a = .05 2 tail , t crit = _________.
Assume you are evaluating H 0 using the t test. Using a = .05 2 tail , t crit = _________.A) +2.262
B) +2.306
C) ±2.262
D) ±2.306

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 145 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
In a correlated t test, if the independent variable has no effect, the sample difference scores are a random sample from a population where the mean difference score ( µ D ) equals _________.
A) 0
B) 1
C) N
D) cannot be determined
A) 0
B) 1
C) N
D) cannot be determined

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 145 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
Based on your answer to problem 30, using a = .05 2 tail, what do you conclude about H 0?
A) accept H 0 ; stress does not affect the menstrual cycle
B) retain H 0 ; we cannot conclude that stress affects the menstrual cycle
C) retain H 0 ; stress affects the menstrual cycle
D) reject H 0 ; stress affects the menstrual cycle
A) accept H 0 ; stress does not affect the menstrual cycle
B) retain H 0 ; we cannot conclude that stress affects the menstrual cycle
C) retain H 0 ; stress affects the menstrual cycle
D) reject H 0 ; stress affects the menstrual cycle

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 145 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
A health educator wants to evaluate the effect of a dental film on the frequency with which children brush their teeth. A random selection of 8 children are used for the experiment. First, a baseline of the number of times the children brush their teeth over a month's period is established. Next, the children are shown the dental film and again the number of teeth brushings are recorded for a month. The following data are recorded.  Assume you are evaluating H 0 with the t test. The df for determining t crit equal _________.
Assume you are evaluating H 0 with the t test. The df for determining t crit equal _________.
A) 8
B) 16
C) 7
D) 14
 Assume you are evaluating H 0 with the t test. The df for determining t crit equal _________.
Assume you are evaluating H 0 with the t test. The df for determining t crit equal _________.A) 8
B) 16
C) 7
D) 14

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 145 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
A professor of women's studies is interested in determining if stress affects the menstrual cycle. Ten women are randomly sampled for an experiment and randomly divided into two groups. One of the groups is subjected to high stress for two months while the other lives in a relatively stress-free environment. The professor measures the menstrual cycle (in days) of each woman during the second month. The following data are obtained.  The obtained value of the appropriate statistic for evaluating H 0 is _________.
The obtained value of the appropriate statistic for evaluating H 0 is _________.
A) t obt = - 4.73
B) t obt = - 4.71
C) t obt = - 3.05
D) t obt = - 0.47
 The obtained value of the appropriate statistic for evaluating H 0 is _________.
The obtained value of the appropriate statistic for evaluating H 0 is _________.A) t obt = - 4.73
B) t obt = - 4.71
C) t obt = - 3.05
D) t obt = - 0.47

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 145 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
A professor of women's studies is interested in determining if stress affects the menstrual cycle. Ten women are randomly sampled for an experiment and randomly divided into two groups. One of the groups is subjected to high stress for two months while the other lives in a relatively stress-free environment. The professor measures the menstrual cycle (in days) of each woman during the second month. The following data are obtained.  Assume you are evaluating H 0 using the t test with a = .05 2 tail . The correct conclusion is _________.
Assume you are evaluating H 0 using the t test with a = .05 2 tail . The correct conclusion is _________.
A) accept H 0; stress does not affect the menstrual cycle
B) retain H 0; we cannot conclude that stress affects the menstrual cycle
C) retain H 0; stress affects the menstrual cycle
D) reject H 0; stress affects the menstrual cycle
 Assume you are evaluating H 0 using the t test with a = .05 2 tail . The correct conclusion is _________.
Assume you are evaluating H 0 using the t test with a = .05 2 tail . The correct conclusion is _________.A) accept H 0; stress does not affect the menstrual cycle
B) retain H 0; we cannot conclude that stress affects the menstrual cycle
C) retain H 0; stress affects the menstrual cycle
D) reject H 0; stress affects the menstrual cycle

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 145 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
A professor of women's studies is interested in determining if stress affects the menstrual cycle. Ten women are randomly sampled for an experiment and randomly divided into two groups. One of the groups is subjected to high stress for two months while the other lives in a relatively stress-free environment. The professor measures the menstrual cycle (in days) of each woman during the second month. The following data are obtained.  Assume you are evaluating H 0 using the t test. The df for determining t crit are _________.
Assume you are evaluating H 0 using the t test. The df for determining t crit are _________.
A) 4
B) 9
C) 8
D) 3
 Assume you are evaluating H 0 using the t test. The df for determining t crit are _________.
Assume you are evaluating H 0 using the t test. The df for determining t crit are _________.A) 4
B) 9
C) 8
D) 3

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 145 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
A health educator wants to evaluate the effect of a dental film on the frequency with which children brush their teeth. A random selection of 8 children are used for the experiment. First, a baseline of the number of times the children brush their teeth over a month's period is established. Next, the children are shown the dental film and again the number of teeth brushings are recorded for a month. The following data are recorded.  Assume you are evaluating H 0 with the t test.Using a = .05 2 tail , t crit = _________.
Assume you are evaluating H 0 with the t test.Using a = .05 2 tail , t crit = _________.
A) +2.365
B) ±2.365
C) ±2.145
D) +2.365.
 Assume you are evaluating H 0 with the t test.Using a = .05 2 tail , t crit = _________.
Assume you are evaluating H 0 with the t test.Using a = .05 2 tail , t crit = _________.A) +2.365
B) ±2.365
C) ±2.145
D) +2.365.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 145 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
In the t test for independent groups, the unbiased estimate of the population variance 2 is _________.
A) s 12 alone
B) s 22 alone
C) a weighted average of s 12 and s 22
D) ( ΣS 1 + ΣS 2)/( n 1 + n 2 - 2)
E) c and d
A) s 12 alone
B) s 22 alone
C) a weighted average of s 12 and s 22
D) ( ΣS 1 + ΣS 2)/( n 1 + n 2 - 2)
E) c and d

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 145 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
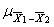 equals _________.
equals _________.A) µ 1 - µ 2
B) 0
C) 1
D) it depends on the sample

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 145 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
If a test is a robust test,
A) it is sensitive to its underlying mathematical assumptions
B) it doesn't estimate any population parameters
C) it is insensitive to its underlying mathematical assumptions
D) it often may be used despite violations of its underlying mathematical assumptions
E) it is insensitive to its underlying mathematical assumptions and it often may be used despite violations of its underlying mathematical assumptions
A) it is sensitive to its underlying mathematical assumptions
B) it doesn't estimate any population parameters
C) it is insensitive to its underlying mathematical assumptions
D) it often may be used despite violations of its underlying mathematical assumptions
E) it is insensitive to its underlying mathematical assumptions and it often may be used despite violations of its underlying mathematical assumptions

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 145 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
Using the t test for independent groups, a directional alternative hypothesis predicts _________.
A) µ 1 > µ 2
B) µ 1 = µ 2
C) µ 1 µ 2
D) µ 1 > µ 2 or µ 1 µ 2 , depending on the direction
A) µ 1 > µ 2
B) µ 1 = µ 2
C) µ 1 µ 2
D) µ 1 > µ 2 or µ 1 µ 2 , depending on the direction

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 145 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
A professor of women's studies is interested in determining if stress affects the menstrual cycle. Ten women are randomly sampled for an experiment and randomly divided into two groups. One of the groups is subjected to high stress for two months while the other lives in a relatively stress-free environment. The professor measures the menstrual cycle (in days) of each woman during the second month. The following data are obtained.  Construct the 95% confidence interval for ì 1 - ì 2. The 95 % confidence interval = _________.
Construct the 95% confidence interval for ì 1 - ì 2. The 95 % confidence interval = _________.
A) -10.712 - -3.688
B) -8.341 - 1.405
C) -9.264 - -2.627
D) -10.204 - -3.348
 Construct the 95% confidence interval for ì 1 - ì 2. The 95 % confidence interval = _________.
Construct the 95% confidence interval for ì 1 - ì 2. The 95 % confidence interval = _________.A) -10.712 - -3.688
B) -8.341 - 1.405
C) -9.264 - -2.627
D) -10.204 - -3.348

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 145 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
In testing the null hypothesis, the correlated t test allows one to utilize information on _________ in the test of significance.
A) magnitude and direction
B) magnitude only
C) direction only
D) separation between the groups
A) magnitude and direction
B) magnitude only
C) direction only
D) separation between the groups

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 145 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
A major advantage to using a two condition experiment (e.g. control and experimental groups) is _________.
A) the test has more power
B) the data are easier to analyze
C) the experiment does not need to know population parameters
D) none of these are correct
A) the test has more power
B) the data are easier to analyze
C) the experiment does not need to know population parameters
D) none of these are correct

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 145 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
A professor of women's studies is interested in determining if stress affects the menstrual cycle. Ten women are randomly sampled for an experiment and randomly divided into two groups. One of the groups is subjected to high stress for two months while the other lives in a relatively stress-free environment. The professor measures the menstrual cycle (in days) of each woman during the second month. The following data are obtained.  Assume there is a real effect and estimate the size of the effect. _________.
Assume there is a real effect and estimate the size of the effect. _________.
A) 0.8102
B) 0.6810
C) 0.4322
D) 0.5776
 Assume there is a real effect and estimate the size of the effect. _________.
Assume there is a real effect and estimate the size of the effect. _________.A) 0.8102
B) 0.6810
C) 0.4322
D) 0.5776

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 145 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
A health educator wants to evaluate the effect of a dental film on the frequency with which children brush their teeth. A random selection of 8 children are used for the experiment. First, a baseline of the number of times the children brush their teeth over a month's period is established. Next, the children are shown the dental film and again the number of teeth brushings are recorded for a month. The following data are recorded.  Assume there is a real effect and estimate the size of effect, using Cohens d. = _________.
Assume there is a real effect and estimate the size of effect, using Cohens d. = _________.
A) 1.10
B) 0.03
C) 1.11
D) 0.02
 Assume there is a real effect and estimate the size of effect, using Cohens d. = _________.
Assume there is a real effect and estimate the size of effect, using Cohens d. = _________.A) 1.10
B) 0.03
C) 1.11
D) 0.02

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 145 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
The t test is _________ likely to result in a Type II error than the sign test for a repeated measures design.
A) more
B) less
C) equally
D) probably
A) more
B) less
C) equally
D) probably

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 145 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
A school psychologist is interested in determining if children with attention deficit disorder (ADD) learn better if English literature is read to them rather than having them read the material themselves. A random sample of 10 sixth graders with ADD is selected and divided into two groups of 5 each. One of the groups has a story read to them (Listening Group) and the other reads the story themselves (Reading Group). A quiz on the story is given after each group has finished reading or hearing the story. The following scores were obtained with 20 being a perfect score.  Assume there is a real effect. The size of the effect, using equals _________.
Assume there is a real effect. The size of the effect, using equals _________.
A) 1.72
B) 0.58
C) 0.32
D) 1.65
 Assume there is a real effect. The size of the effect, using equals _________.
Assume there is a real effect. The size of the effect, using equals _________.A) 1.72
B) 0.58
C) 0.32
D) 1.65

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 145 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
Which of the following tests analyzes the difference between the means of two independent samples?
A) correlated t test
B) t test for independent groups
C) sign test
D) all of these
A) correlated t test
B) t test for independent groups
C) sign test
D) all of these

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 145 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
Using Cohen's criteria, the size of effect found in problem 59 is _________.
A) small
B) medium
C) large
D) Cohen's criteria doesn't apply
A) small
B) medium
C) large
D) Cohen's criteria doesn't apply

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 145 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
Five students were tested before and after taking a class to improve their study habits. They were given articles to read which contained a known number of facts in each story. After the story each student listed as many facts as he/she could recall. The following data was recorded. 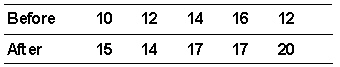 What do you conclude using a = 0.052 tail?
What do you conclude using a = 0.052 tail?
A) reject H0; the class appeared to improve study habits
B) retain H0; the class had no effect on study habits
C) retain H0; we cannot conclude that the class improved study habits
D) accept H0; the class appeared to improve study habits
 What do you conclude using a = 0.052 tail?
What do you conclude using a = 0.052 tail?A) reject H0; the class appeared to improve study habits
B) retain H0; the class had no effect on study habits
C) retain H0; we cannot conclude that the class improved study habits
D) accept H0; the class appeared to improve study habits

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 145 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
A school psychologist is interested in determining if children with attention deficit disorder (ADD) learn better if English literature is read to them rather than having them read the material themselves. A random sample of 10 sixth graders with ADD is selected and divided into two groups of 5 each. One of the groups has a story read to them (Listening Group) and the other reads the story themselves (Reading Group). A quiz on the story is given after each group has finished reading or hearing the story. The following scores were obtained with 20 being a perfect score.  What do you conclude, using a = 0.05 2 tail ?
What do you conclude, using a = 0.05 2 tail ?
A) Reject H 0
B) Retain H 0
 What do you conclude, using a = 0.05 2 tail ?
What do you conclude, using a = 0.05 2 tail ?A) Reject H 0
B) Retain H 0

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 145 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
In an independent groups design the nondirectional alternative hypothesis states _________.
A) µ 1 > µ 2
B) µ 1< µ 2
C) µ 1 ≠ µ 2
D) µ 1 = µ 2
A) µ 1 > µ 2
B) µ 1< µ 2
C) µ 1 ≠ µ 2
D) µ 1 = µ 2

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 145 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
In analyzing the results of the correlated t test, the _________ scores are analyzed.
A) standardized
B) normalized
C) raw
D) difference
A) standardized
B) normalized
C) raw
D) difference

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 145 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
Using Cohen's criteria, the size of effect found in problem 54 is _________.
A) small
B) medium
C) large
D) Cohen's criteria doesn't apply
A) small
B) medium
C) large
D) Cohen's criteria doesn't apply

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 145 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
The z test for independent groups is almost never used because it requires that _________ be known.
A) µ 1
B)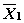
C) s 2
D) s 2.
A) µ 1
B)
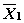
C) s 2
D) s 2.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 145 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
The t test assumes that the independent variable affects the _________ of the populations.
A) means
B) standard deviations
C) means and standard deviations
D) none of these
A) means
B) standard deviations
C) means and standard deviations
D) none of these

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 145 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
If n 1 = n 2 and n is relatively large, then the t test is relatively robust against _________.
A) violations of the assumptions of homogeneity of variance and normality
B) violations of random samples
C) traffic violations
D) violations by the forces of evil
A) violations of the assumptions of homogeneity of variance and normality
B) violations of random samples
C) traffic violations
D) violations by the forces of evil

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 145 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
The use of the t test for independent groups assumes _________.
A)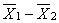 is normally distributed
is normally distributed
B) s 12 = s 22
C)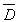 is normally distributed
is normally distributed
D) all of these
E) is normally distributed and s 12 = s 22
is normally distributed and s 12 = s 22
A)
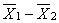 is normally distributed
is normally distributedB) s 12 = s 22
C)
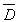 is normally distributed
is normally distributedD) all of these
E)
 is normally distributed and s 12 = s 22
is normally distributed and s 12 = s 22
Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 145 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
The sampling distribution of 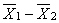 has a mean value equal to _________.
has a mean value equal to _________.
A) 0
B)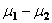
C) N
D)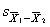
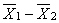 has a mean value equal to _________.
has a mean value equal to _________.A) 0
B)
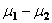
C) N
D)
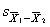

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 145 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
In the t test for independent samples, there are _________ degrees of freedom.
A) n 1 - 1
B) n 1 + n 2
C) n 1 - n 2 + 2
D) n 1 + n 2 - 2
A) n 1 - 1
B) n 1 + n 2
C) n 1 - n 2 + 2
D) n 1 + n 2 - 2

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 145 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
Five students were tested before and after taking a class to improve their study habits. They were given articles to read which contained a known number of facts in each story. After the story each student listed as many facts as he/she could recall. The following data was recorded. 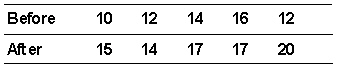 Assume there is a real effect. using
Assume there is a real effect. using 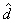 , the size of effect for the improvement, equals _________.
, the size of effect for the improvement, equals _________.
A) 0.56
B) 0.52
C) 1.42
D) 1.37
 Assume there is a real effect. using
Assume there is a real effect. using 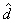 , the size of effect for the improvement, equals _________.
, the size of effect for the improvement, equals _________.A) 0.56
B) 0.52
C) 1.42
D) 1.37

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 145 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
Using the independent groups t test, the size of the effect of the independent variable can be estimated using _________.
A) t obt
B) r obt
C)
D) r 2
A) t obt
B) r obt
C)

D) r 2

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 145 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
A physical therapist wants to know if football players (guards in this experiment) recover full strength following injuries. A group of injury free guards were given a strength test as were a group of guards who had finished a rehabilitation program following an injury. The groups were matched in height and weight. The following strength ratings were recorded. 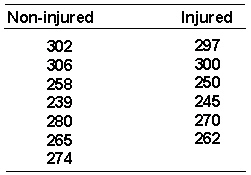 What do you conclude using a = 0.01 2 tail ?
What do you conclude using a = 0.01 2 tail ?
A) reject H0
B) retain H0
 What do you conclude using a = 0.01 2 tail ?
What do you conclude using a = 0.01 2 tail ?A) reject H0
B) retain H0

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 145 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
The power of a correlated t test increases if the correlation between the paired scores is _________.
A) 0
B) high
C) low
D) cannot be determined
A) 0
B) high
C) low
D) cannot be determined

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 145 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
Five students were tested before and after taking a class to improve their study habits. They were given articles to read which contained a known number of facts in each story. After the story each student listed as many facts as he/she could recall. The following data was recorded. 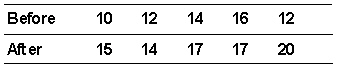 The obtained value of the appropriate statistic to evaluate H0 is _________.
The obtained value of the appropriate statistic to evaluate H0 is _________.
A) 3.92
B) 3.06
C) 4.12
D) 2.58
 The obtained value of the appropriate statistic to evaluate H0 is _________.
The obtained value of the appropriate statistic to evaluate H0 is _________.A) 3.92
B) 3.06
C) 4.12
D) 2.58

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 145 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
The sampling distribution of t is different for single samples than for correlated groups.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 145 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
The t test for independent groups is a robust test.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 145 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
The estimate of s 2 used in the t test for independent groups is an estimated based on the variances of both samples.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 145 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
In an independent groups design, if the independent variable has a real effect, µ 1 ≠µ 2 .

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 145 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
Ties are included in the analysis when using the t test for correlated groups.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 145 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
The z test for independent groups is seldom used because s 2 is unknown.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 145 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
If the correlation is zero between paired scores, the t test for correlated groups is more powerful than the t test for independent groups.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 145 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
A robust test is relatively insensitive to violations of its underlying mathematical assumptions.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 145 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
A school psychologist is interested in determining if children with attention deficit disorder (ADD) learn better if English literature is read to them rather than having them read the material themselves. A random sample of 10 sixth graders with ADD is selected and divided into two groups of 5 each. One of the groups has a story read to them (Listening Group) and the other reads the story themselves (Reading Group). A quiz on the story is given after each group has finished reading or hearing the story. The following scores were obtained with 20 being a perfect score.  The 95% confidence interval for equals _________.
The 95% confidence interval for equals _________.
A) 0.25 - 6.72
B) 0.31 - 4.47
C) 0.42 - 6.78
D) 0.47 - 5.64
 The 95% confidence interval for equals _________.
The 95% confidence interval for equals _________.A) 0.25 - 6.72
B) 0.31 - 4.47
C) 0.42 - 6.78
D) 0.47 - 5.64

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 145 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
In the t test for correlated groups, a directional H 1 may predict µ D > 0.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 145 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
In a correlated groups design, the reasonableness of the null hypothesis is usually tested by assuming the sample set of difference scores is a random sample from a population of difference scores with µ D = 0.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 145 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72
The power of the t test increases with increases in sample variability.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 145 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73
Homogeneity of variance means that µ 1 = µ 2 .

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 145 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
74
The t test for correlated groups is just like the t test for single samples except that it analyzes difference scores.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 145 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
75
The power of the t test increases with increases in the effect of the independent variable.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 145 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
76
In a correlated groups design with a directional H 1 , if H 0 is correct, the sample set of difference scores must be a random sample from a population of difference scores with µ D = 0.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 145 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
77
The t test for correlated groups uses both the magnitude and direction of the difference scores.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 145 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
78
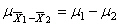

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 145 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
79
If the homogeneity of variance assumption is not met, it is invalid to use the t test for independent groups.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 145 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
80
In an independent groups experiment, if the independent variable has no effect, µ 1 ≠ µ 2 .

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 145 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



