Deck 3: Frequency Distributions
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/116
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 3: Frequency Distributions
1
A psychologist is interested in the social interactions of preschool children. She measures the number of verbal interactions that each child at a preschool engages in during a day. Here is the frequency distribution of the data. 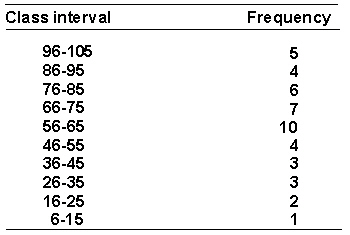 The 50th percentile point is _________.
The 50th percentile point is _________.
A) 65.50
B) 62.15
C) 65.00
D) 74.00
 The 50th percentile point is _________.
The 50th percentile point is _________.A) 65.50
B) 62.15
C) 65.00
D) 74.00
65.00
2
A researcher has collected some data on the amount of time in seconds (to the nearest 0.1 second) that it took trained rats to run through a maze. The data is shown below arranged in a frequency distribution of grouped scores. 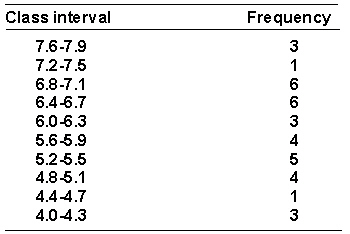 The cumulative percentage for the interval 5.2-5.5 is _________.
The cumulative percentage for the interval 5.2-5.5 is _________.
A) 13.89%
B) 47.22%
C) 22.22%
D) 36.11%
 The cumulative percentage for the interval 5.2-5.5 is _________.
The cumulative percentage for the interval 5.2-5.5 is _________.A) 13.89%
B) 47.22%
C) 22.22%
D) 36.11%
36.11%
3
A psychologist is interested in the social interactions of preschool children. She measures the number of verbal interactions that each child at a preschool engages in during a day. Here is the frequency distribution of the data. 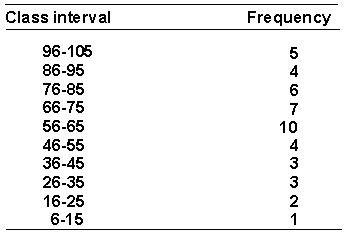 The cumulative frequency for the interval 46-55 is _________.
The cumulative frequency for the interval 46-55 is _________.
A) 4
B) 9
C) 0.29
D) 13
 The cumulative frequency for the interval 46-55 is _________.
The cumulative frequency for the interval 46-55 is _________.A) 4
B) 9
C) 0.29
D) 13
13
4
The distribution of scores of high school seniors on a sixth grade math test would probably be _________.
A) positively skewed
B) negatively skewed
C) normal
D) symmetrical but not normal
A) positively skewed
B) negatively skewed
C) normal
D) symmetrical but not normal

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
A psychologist is interested in the social interactions of preschool children. She measures the number of verbal interactions that each child at a preschool engages in during a day. Here is the frequency distribution of the data. 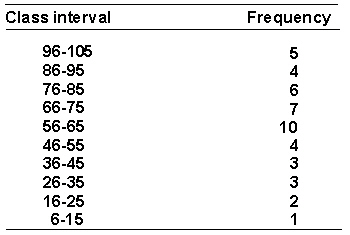 The real limits of the interval 56-65 are _________.
The real limits of the interval 56-65 are _________.
A) 56.5-65.5
B) 55.5-65.5
C) 55-67
D) 56-65
 The real limits of the interval 56-65 are _________.
The real limits of the interval 56-65 are _________.A) 56.5-65.5
B) 55.5-65.5
C) 55-67
D) 56-65

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
If a curve is symmetrical, _________.
A) most of the scores fall at the lower values of the X axis
B) most of the scores fall at the higher values of the X axis
C) if folded in half, the two sides of the curve coincide
D) most of the scores fall at the higher values of the Y axis
A) most of the scores fall at the lower values of the X axis
B) most of the scores fall at the higher values of the X axis
C) if folded in half, the two sides of the curve coincide
D) most of the scores fall at the higher values of the Y axis

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
A researcher has collected some data on the amount of time in seconds (to the nearest 0.1 second) that it took trained rats to run through a maze. The data is shown in the frequency distribution of grouped scores that follows. 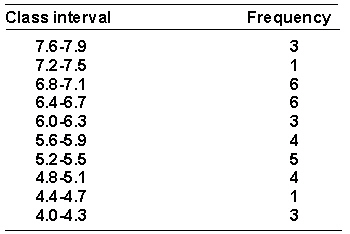 The percentile rank of a score of 6.5 is _________.
The percentile rank of a score of 6.5 is _________.
A) 61.81%
B) 59.72%
C) 9.37%
D) 9.03%
 The percentile rank of a score of 6.5 is _________.
The percentile rank of a score of 6.5 is _________.A) 61.81%
B) 59.72%
C) 9.37%
D) 9.03%

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
A psychologist is interested in the social interactions of preschool children. She measures the number of verbal interactions that each child at a preschool engages in during a day. The resulting data are shown in the following frequency distribution. 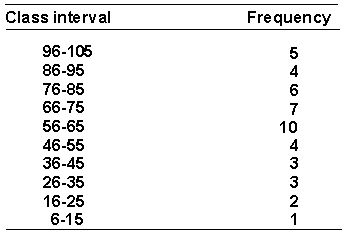 The relative frequency for the interval 76-85 is _________.
The relative frequency for the interval 76-85 is _________.
A) 0.13
B) 0.09
C) 0.16
D) 0.11
 The relative frequency for the interval 76-85 is _________.
The relative frequency for the interval 76-85 is _________.A) 0.13
B) 0.09
C) 0.16
D) 0.11

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
Assume your task is to group the raw scores given below into a frequency distribution of approximately 12 intervals of equal width. 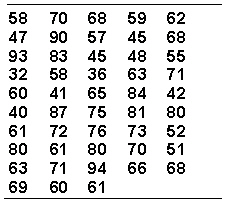 The interval containing the most scores is _________.
The interval containing the most scores is _________.
A) 60-64
B) 62-66
C) 62-67
D) 60-65
 The interval containing the most scores is _________.
The interval containing the most scores is _________.A) 60-64
B) 62-66
C) 62-67
D) 60-65

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
A researcher has collected some data on the amount of time in seconds (to the nearest 0.1 second) that it took trained rats to run through a maze. The data is shown below arranged in a frequency distribution of grouped scores. 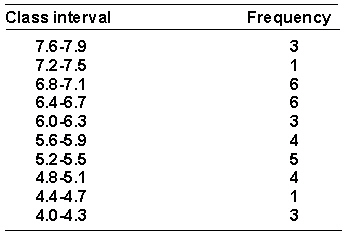 The 75th percentile point is _________.
The 75th percentile point is _________.
A) 6.42
B) 6.87
C) 6.82
D) 6.47
 The 75th percentile point is _________.
The 75th percentile point is _________.A) 6.42
B) 6.87
C) 6.82
D) 6.47

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
A researcher has collected some data on the amount of time in seconds (to the nearest 0.1 second) that it took trained rats to run through a maze. The data is shown below arranged in a frequency distribution of grouped scores. 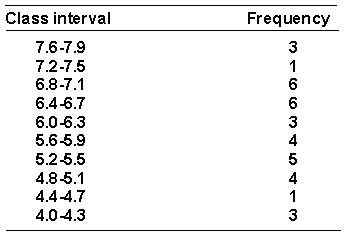 The real limits of the interval 6.4-6.7 are _________.
The real limits of the interval 6.4-6.7 are _________.
A) 6.3-6.8
B) 6.4-6.7
C) 6.35-6.75
D) 6.45-6.75
 The real limits of the interval 6.4-6.7 are _________.
The real limits of the interval 6.4-6.7 are _________.A) 6.3-6.8
B) 6.4-6.7
C) 6.35-6.75
D) 6.45-6.75

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
Assume your task is to group the raw scores given below into a frequency distribution of approximately 12 intervals of equal width. 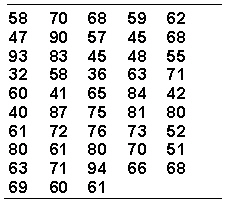 The value of i is _________.
The value of i is _________.
A) 5.5
B) 4
C) 6
D) 5
 The value of i is _________.
The value of i is _________.A) 5.5
B) 4
C) 6
D) 5

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
A psychologist is interested in the social interactions of preschool children. She measures the number of verbal interactions that each child at a preschool engages in during a day. The resulting data are shown in the following frequency distribution. 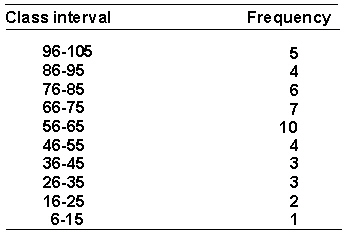 The percentile rank of a score of 40 is _________.
The percentile rank of a score of 40 is _________.
A) 16.33%
B) 16.00%
C) 9.67%
D) 16.67%
 The percentile rank of a score of 40 is _________.
The percentile rank of a score of 40 is _________.A) 16.33%
B) 16.00%
C) 9.67%
D) 16.67%

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
A researcher has collected some data on the amount of time in seconds (to the nearest 0.1 second) that it took trained rats to run through a maze. The data is shown in the frequency distribution of grouped scores that follows. 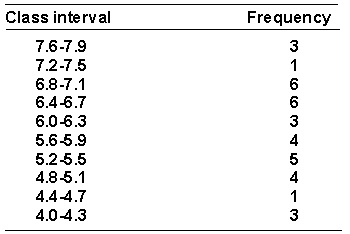 The relative frequency for the interval 5.2-6.6 is _________.
The relative frequency for the interval 5.2-6.6 is _________.
A) 0.03
B) 0.14
C) 0.11
D) 13
 The relative frequency for the interval 5.2-6.6 is _________.
The relative frequency for the interval 5.2-6.6 is _________.A) 0.03
B) 0.14
C) 0.11
D) 13

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
If a large psychology class took a test on theoretical biophysics, the distribution of scores would probably be _________.
A) positively skewed
B) symmetrical
C) negatively skewed
D) ogival
A) positively skewed
B) symmetrical
C) negatively skewed
D) ogival

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
Assume your task is to group the raw scores given below into a frequency distribution of approximately 12 intervals of equal width. 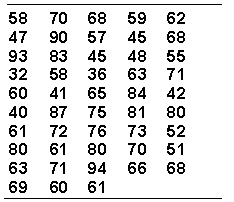 The lowest class interval is _________.
The lowest class interval is _________.
A) 30-35
B) 32-36
C) 32-37
D) 30-34
 The lowest class interval is _________.
The lowest class interval is _________.A) 30-35
B) 32-36
C) 32-37
D) 30-34

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
An accountant is preparing a graph showing the number of sports cars of various makers purchased this year. The number will be plotted on the ordinate and the various manufacturers on the abscissa. The proper type of graph for this data is a(n) _________.
A) frequency polygon
B) histogram
C) bar graph
D) ogive
A) frequency polygon
B) histogram
C) bar graph
D) ogive

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
Assume your task is to group the raw scores given below into a frequency distribution of approximately 12 intervals of equal width. 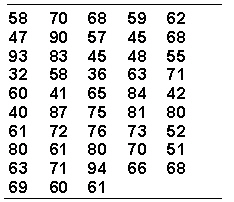 The highest frequency for any interval is _________.
The highest frequency for any interval is _________.
A) 6
B) 8
C) 10
D) 7
 The highest frequency for any interval is _________.
The highest frequency for any interval is _________.A) 6
B) 8
C) 10
D) 7

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
A psychologist is interested in the social interactions of preschool children. She measures the number of verbal interactions that each child at a preschool engages in during a day. Here is the frequency distribution of the data. 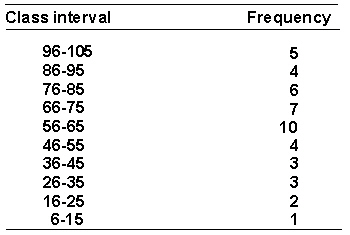 The cumulative % for the interval 46-55 is _________.
The cumulative % for the interval 46-55 is _________.
A) 8.89%
B) 20.00%
C) 0.64%
D) 28.89%
 The cumulative % for the interval 46-55 is _________.
The cumulative % for the interval 46-55 is _________.A) 8.89%
B) 20.00%
C) 0.64%
D) 28.89%

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
A researcher has collected some data on the amount of time in seconds (to the nearest 0.1 second) that it took trained rats to run through a maze. The data is shown below arranged in a frequency distribution of grouped scores. 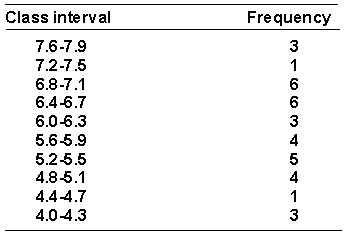 The cumulative frequency for the interval 6.0-6.3 is _________.
The cumulative frequency for the interval 6.0-6.3 is _________.
A) 20
B) 0.57
C) 17
D) 57
 The cumulative frequency for the interval 6.0-6.3 is _________.
The cumulative frequency for the interval 6.0-6.3 is _________.A) 20
B) 0.57
C) 17
D) 57

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
Given the distribution of grouped scores shown in the following table. 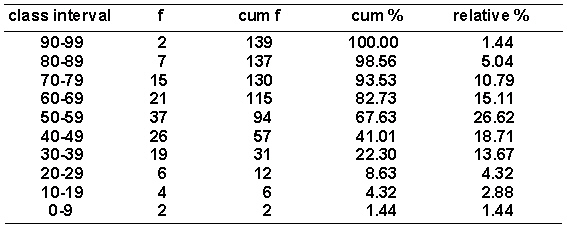 What percentage of cases fall within the class interval containing the most cases?
What percentage of cases fall within the class interval containing the most cases?
A) 18.71
B) 26.62
C) 67.63
D) 41.01
 What percentage of cases fall within the class interval containing the most cases?
What percentage of cases fall within the class interval containing the most cases?A) 18.71
B) 26.62
C) 67.63
D) 41.01

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
In graphing frequency distributions, _________ is usually plotted on the abscissa.
A) frequency
B) class width
C) the score value
D) interval width
A) frequency
B) class width
C) the score value
D) interval width

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
What indicates the proportion of the total number of scores that occurred in each interval?
A) relative frequency distribution
B) cumulative frequency distribution
C) cumulative percentage distribution
D) none of these
A) relative frequency distribution
B) cumulative frequency distribution
C) cumulative percentage distribution
D) none of these

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
What indicates the number of scores that fell below the upper real limit of each interval?
A) relative frequency distribution
B) cumulative frequency distribution
C) cumulative percentage distribution
D) none of these
A) relative frequency distribution
B) cumulative frequency distribution
C) cumulative percentage distribution
D) none of these

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
Given the distribution of grouped scores shown in the following table. 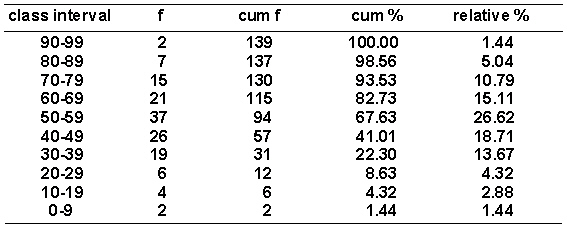 How many occurrences are there for the interval 60-69?
How many occurrences are there for the interval 60-69?
A) 115
B) 37
C) 15
D) 21
 How many occurrences are there for the interval 60-69?
How many occurrences are there for the interval 60-69?A) 115
B) 37
C) 15
D) 21

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
The purpose of a frequency distribution is to _________.
A) present scores and their frequency of occurrence
B) present data in a more meaningful way than just presenting the raw scores
C) provide more information than a graph
D) all of the above
E) a and b
A) present scores and their frequency of occurrence
B) present data in a more meaningful way than just presenting the raw scores
C) provide more information than a graph
D) all of the above
E) a and b

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
If i = 7, the scores are integer, and the minimum value of the distribution of scores is 8, what would the lowest class interval be?
A) 0-7
B) 7-14
C) 8-16
D) 8-15
E) 7-13
A) 0-7
B) 7-14
C) 8-16
D) 8-15
E) 7-13

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
The range of a set of scores with a maximum value of 92 and a minimum value of 26 is _________.
A) 65
B) 66
C) 67
D) 92
A) 65
B) 66
C) 67
D) 92

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
The true limits of 7.0 are _________.
A) 6.5-7.5
B) 6.0-8.0
C) 7.0-7.1
D) 6.95-7.05
A) 6.5-7.5
B) 6.0-8.0
C) 7.0-7.1
D) 6.95-7.05

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
Which of the following is (are) not a symmetrical distribution?
A) a bell-shaped curve
B) a J-shaped curve
C) a rectangular curve
D) an inverted U-shaped curve
E) a bell-shaped, J-shaped, and an inverted U-shaped curve
A) a bell-shaped curve
B) a J-shaped curve
C) a rectangular curve
D) an inverted U-shaped curve
E) a bell-shaped, J-shaped, and an inverted U-shaped curve

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
Interval or ratio data may be plotted as a _________.
A) bar graph
B) histogram
C) frequency polygon
D) b and c
A) bar graph
B) histogram
C) frequency polygon
D) b and c

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
Given the distribution of grouped scores shown in the following table. 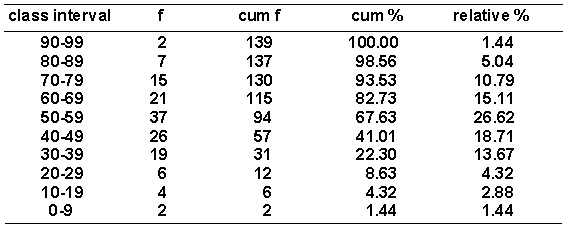 How many occurrences fall below the upper real limit of the interval 70-79?
How many occurrences fall below the upper real limit of the interval 70-79?
A) 115
B) 137
C) 130
D) 15
 How many occurrences fall below the upper real limit of the interval 70-79?
How many occurrences fall below the upper real limit of the interval 70-79?A) 115
B) 137
C) 130
D) 15

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
If the range of a distribution were 89 and the data were reported as whole numbers, what would the width of the class interval be if one chose to group the distribution into approximately 14 class intervals?
A) 14
B) 89
C) 5
D) 6
E) 7
A) 14
B) 89
C) 5
D) 6
E) 7

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
Given the distribution of grouped scores shown in the following table. 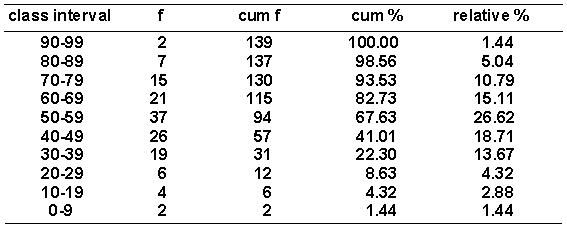 What is the cumulative percentage below the lower real limit of the interval 90-99?
What is the cumulative percentage below the lower real limit of the interval 90-99?
A) 137
B) 5.04
C) 100.00
D) 98.56
 What is the cumulative percentage below the lower real limit of the interval 90-99?
What is the cumulative percentage below the lower real limit of the interval 90-99?A) 137
B) 5.04
C) 100.00
D) 98.56

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
Given the distribution of grouped scores shown in the following table. 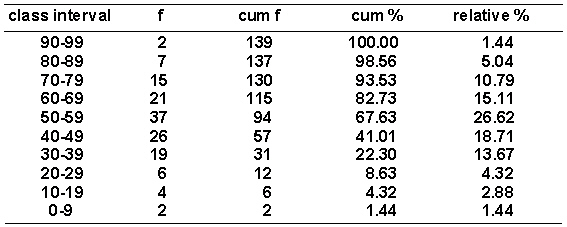 N equals _______.
N equals _______.
A) 139
B) 145
C) 137
D) 135
 N equals _______.
N equals _______.A) 139
B) 145
C) 137
D) 135

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
Your new Mercedes weighs 1850 kilograms when measured to the nearest kilogram. The real limits of its weight are _________.
A) 1800-1900
B) 1840-1860
C) 1849-1851
D) 1849.5-1850.5
A) 1800-1900
B) 1840-1860
C) 1849-1851
D) 1849.5-1850.5

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
When constructing bar graphs, the bars do not touch each other because _______.
A) it looks nicer
B) it emphasizes the lack of quantitative relationship between the categories
C) it is traditional
D) none of these
A) it looks nicer
B) it emphasizes the lack of quantitative relationship between the categories
C) it is traditional
D) none of these

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
A distribution which has a predominance of scores at the lower values of the distribution and which tails off at the higher end is _______.
A) positively skewed
B) negatively skewed
C) normally distributed
D) symmetrical
A) positively skewed
B) negatively skewed
C) normally distributed
D) symmetrical

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
In a frequency polygon the points are plotted over _______ at a height corresponding to the frequency of the interval.
A) the midpoint of each interval
B) the lower real limit
C) the upper real limit
D) none of these
A) the midpoint of each interval
B) the lower real limit
C) the upper real limit
D) none of these

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
When individual scores are combined into groups, _________.
A) information is lost
B) data is added
C) a meaningful visual display can result depending on the interval width
D) information is lost and data is added
A) information is lost
B) data is added
C) a meaningful visual display can result depending on the interval width
D) information is lost and data is added

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
All frequency distributions should be of grouped scores.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
In grouping scores, the wider the intervals, the more information that is lost.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
Consider the following score diagram.  This score diagram is called a _________.
This score diagram is called a _________.
A) histogram
B) frequency polygon
C) box plot
D) stem and leaf diagram
 This score diagram is called a _________.
This score diagram is called a _________.A) histogram
B) frequency polygon
C) box plot
D) stem and leaf diagram

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
In constructing a frequency distribution of grouped scores, i should be rounded to one more decimal place than in the raw scores.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
If a curve is negatively skewed, most of the scores occur at the higher values and the curve tails off toward the lower end of the horizontal axis.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
A bell shaped curve is an example of a skewed distribution.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
Consider the following stem-and-leaf diagram.  This score distribution is _______.
This score distribution is _______.
A) positively skewed
B) negatively skewed
C) symmetrical
D) neither skewed or symmetrical
 This score distribution is _______.
This score distribution is _______.A) positively skewed
B) negatively skewed
C) symmetrical
D) neither skewed or symmetrical

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
The percentile point for a distribution of scores must have a value equal to one of the scores.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
A percentile point is defined as _________.
A) the percentage of scores that fall below a specified scale value
B) the value on the measurement scale below which a specified percentage of the scores fall
C) P50
D) P20
A) the percentage of scores that fall below a specified scale value
B) the value on the measurement scale below which a specified percentage of the scores fall
C) P50
D) P20

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
In constructing a frequency distribution of grouped scores, the intervals must be continuous and mutually exclusive.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
If the frequency of any score is zero, it should not be listed in a frequency distribution.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
The percentile rank of a score is defined as _________.
A) the percentage of scores that fall below the score in question
B) the percentage of scores that fall below a specified scale value
C) the number of scores that fall below the score in question
D) a and b
A) the percentage of scores that fall below the score in question
B) the percentage of scores that fall below a specified scale value
C) the number of scores that fall below the score in question
D) a and b

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
Given the distribution of grouped scores shown in the following table. 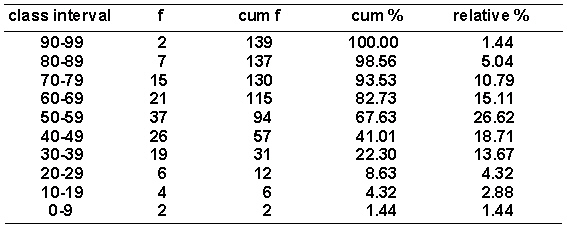 What is the value of i ?
What is the value of i ?
A) 10
B) 9
C) 9.5
D) 10.5
 What is the value of i ?
What is the value of i ?A) 10
B) 9
C) 9.5
D) 10.5

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
In a frequency distribution of grouped scores, all intervals should be of exactly the same width.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
A curve is negatively skewed when _________.
A) most of the scores occur at the lower end of the horizontal axis and the curve tails off toward the higher end
B) it is folded in half and the two sides do not coincide
C) most of the scores occur at the higher end of the horizontal axis and the curve tails off toward the lower end.
D) b and c
A) most of the scores occur at the lower end of the horizontal axis and the curve tails off toward the higher end
B) it is folded in half and the two sides do not coincide
C) most of the scores occur at the higher end of the horizontal axis and the curve tails off toward the lower end.
D) b and c

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
A histogram is like a bar graph except with a histogram the bars don't touch each other.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
A frequency polygon results in a curve that looks as though the scores were continuously distributed.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
Given the distribution of grouped scores shown in the following table. 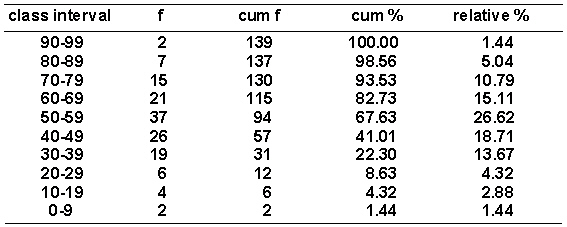 The 50th percentile point equals _________.
The 50th percentile point equals _________.
A) 53.38
B) 52.54
C) 52.88
D) 54.31
 The 50th percentile point equals _________.
The 50th percentile point equals _________.A) 53.38
B) 52.54
C) 52.88
D) 54.31

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
Consider the following stem-and-leaf diagram.  If the numbers in the left column are deciles, the median of the distribution falls in the range of _______.
If the numbers in the left column are deciles, the median of the distribution falls in the range of _______.
A) 80 - 90
B) 60 - 69
C) 70 - 79
D) can't answer; need more information
 If the numbers in the left column are deciles, the median of the distribution falls in the range of _______.
If the numbers in the left column are deciles, the median of the distribution falls in the range of _______.A) 80 - 90
B) 60 - 69
C) 70 - 79
D) can't answer; need more information

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
Given the distribution of grouped scores shown in the following table. 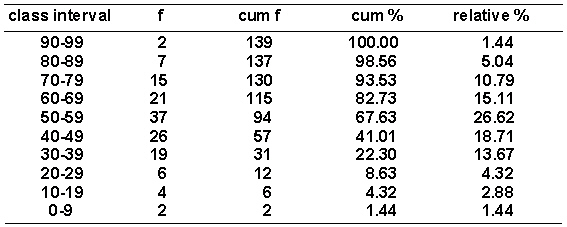 The percentile rank of a score of 41 equals _________.
The percentile rank of a score of 41 equals _________.
A) 25.42%
B) 25.11%
C) 16.47%
D) 29.42%
 The percentile rank of a score of 41 equals _________.
The percentile rank of a score of 41 equals _________.A) 25.42%
B) 25.11%
C) 16.47%
D) 29.42%

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
When constructing the frequency distribution it is customary to show the real limits of the class intervals in the table.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
A "U" shaped distribution is an example of a symmetrical distribution.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
A frequency distribution of grouped scores is used for distributions that have relatively few scores to stretch them out.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
A frequency distribution presents the score values and their frequency of occurrence.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
A relative frequency distribution indicates the number of scores that fall below the upper real limit of each interval.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
For the frequency distribution shown in the following table, N = 4. 


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
When constructing frequency distributions there must be 12 class intervals.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
One reason for constructing frequency distributions is to be able to visualize the shape of the distribution.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
In a cumulative percentage curve, percentage is shown on the abscissa.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
To determine the width of the class interval, i, divide the range by the number of class intervals.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
Bar graphs are generally used for nominal or ordinal data and histograms are generally used for interval or ratio data.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72
A stem and leaf diagram contains more information than a histogram.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73
When constructing a distribution of grouped scores, the only requirement regarding the lower limit of the lowest interval is that the interval includes the lowest score in the distribution.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
74
In a frequency distribution the more intervals the better, regardless of whether some intervals have zero frequency.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
75
A cumulative frequency distribution indicates the number of scores which fell below the upper real limit of each interval.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
76
A relative frequency distribution indicates the total number of scores which occurred in each interval.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
77
The vertical axis, i.e., the Y axis of a graph, is called the abscissa.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
78
For the frequency distribution shown in the following table, = 25. 


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
79
Given a distribution of grouped scores, if an interval is shown as 2-8, the interval is 6 units wide

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
80
The percentile rank of a score is equal to the percentage of scores in the distribution that fall below the score in question.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



