Deck 2: Basic Mathematical and Measurement Concepts
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/110
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 2: Basic Mathematical and Measurement Concepts
1
Reaction time in seconds is an example of a(n) _________ scale.
A) ratio
B) ordinal
C) interval
D) nominal
A) ratio
B) ordinal
C) interval
D) nominal
ratio
2
Consider the following points on a scale: 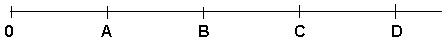 If the scale upon which A , B , C , and D are arranged is an interval scale, we can say _________.
If the scale upon which A , B , C , and D are arranged is an interval scale, we can say _________.
A) B = 2 A
B) B - A = D - C
C) B = 2 A and B - A = D - C
D) None of these choices is correct.
 If the scale upon which A , B , C , and D are arranged is an interval scale, we can say _________.
If the scale upon which A , B , C , and D are arranged is an interval scale, we can say _________.A) B = 2 A
B) B - A = D - C
C) B = 2 A and B - A = D - C
D) None of these choices is correct.
B - A = D - C
3
The number 83.476499 rounded to three decimal places is _________.
A) 83.477
B) 83.480
C) 83.476
D) 83.470
A) 83.477
B) 83.480
C) 83.476
D) 83.470
83.476
4
Given the data X 1 = 1, X 2 = 4, X 3 = 5, X 4 = 8, X 5 = 10, evaluate 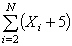 .
.
A) 47
B) 53
C) 48
D) 32
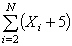 .
.A) 47
B) 53
C) 48
D) 32

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 110 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
We have collected the following data: X 1 = 6, X 2 = 2, X 3 = 4, X 4 = 1, X 5 = 3 For these data, 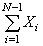 is equal to _________.
is equal to _________.
A) 16
B) 10
C) 7
D) 13
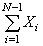 is equal to _________.
is equal to _________.A) 16
B) 10
C) 7
D) 13

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 110 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
Given the data X 1 = 1, X 2 = 4, X 3 = 5, X 4 = 8, X 5 = 10, evaluate 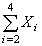 .
.
A) 17
B) 27
C) 28
D) 23
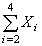 .
.A) 17
B) 27
C) 28
D) 23

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 110 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
When rounded to two decimal places, the number 3.175000 becomes _________.
A) 3.17
B) 3.20
C) 3.18
D) 3.10
A) 3.17
B) 3.20
C) 3.18
D) 3.10

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 110 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
Given the data X 1 = 1, X 2 = 4, X 3 = 5, X 4 = 8, X 5 = 10, evaluate 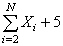 .
.
A) 53
B) 47
C) 48
D) 32
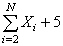 .
.A) 53
B) 47
C) 48
D) 32

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 110 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
Consider the following points on a scale:  If the scale upon which points A , B , C , and D are shown is an ordinal scale, we can meaningfully say _________.
If the scale upon which points A , B , C , and D are shown is an ordinal scale, we can meaningfully say _________.
A) B - A D - C
B) B C /2
C) B = 2 A
D) C>B
 If the scale upon which points A , B , C , and D are shown is an ordinal scale, we can meaningfully say _________.
If the scale upon which points A , B , C , and D are shown is an ordinal scale, we can meaningfully say _________.A) B - A D - C
B) B C /2
C) B = 2 A
D) C>B

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 110 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
Given the data X 1 = 1, X 2 = 4, X 3 = 5, X 4 = 8, X 5 = 10, evaluate ( ΣX) 2 .
A) 56
B) 784
C) 206
D) 28
A) 56
B) 784
C) 206
D) 28

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 110 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
A discrete scale of measurement _________.
A) is the same as a continuous scale
B) provides exact measurements
C) necessarily uses whole numbers
D) b and c
A) is the same as a continuous scale
B) provides exact measurements
C) necessarily uses whole numbers
D) b and c

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 110 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
At the annual sailing regatta, prizes are awarded for 1st, 2nd, 3rd, 4th, and 5th place. These "places" comprise a(n) _________.
A) nominal scale
B) ordinal scale
C) interval scale
D) ratio scale
A) nominal scale
B) ordinal scale
C) interval scale
D) ratio scale

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 110 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
Which of the following numbers is rounded incorrectly to two decimal places?
A) 10.47634 ≈ 10.48
B) 15.36485 ≈ 15.36
C) 21.47500 ≈ 21.47
D) 8.24501 ≈ 8.25
E) 6.66500 ≈ 6.66
A) 10.47634 ≈ 10.48
B) 15.36485 ≈ 15.36
C) 21.47500 ≈ 21.47
D) 8.24501 ≈ 8.25
E) 6.66500 ≈ 6.66

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 110 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
"Brand of soft drink" is measured on a(n) _________.
A) nominal scale
B) ordinal scale
C) interval scale
D) ratio scale
A) nominal scale
B) ordinal scale
C) interval scale
D) ratio scale

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 110 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
After performing several clever calculations on your calculator, the display shows the answer 53.655001. What is the appropriate value rounded to two decimal places?
A) 53.65
B) 53.66
C) 53.64
D) 53.60
A) 53.65
B) 53.66
C) 53.64
D) 53.60

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 110 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
Given the data X1 = 1, X2 = 4, X3 = 5, X4 = 8, X5 = 10, evaluate ΣX 2 .
A) 56
B) 784
C) 206
D) 28
A) 56
B) 784
C) 206
D) 28

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 110 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
The number 9.44650 rounded to two decimal places is _________.
A) 99.45
B) 99.46
C) 99.44
D) 99.40
A) 99.45
B) 99.46
C) 99.44
D) 99.40

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 110 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
Given the following subjects and scores, which symbol would be used to represent the score of 3?

A) X 8
B) X 4
C) X 3
D) X 2

A) X 8
B) X 4
C) X 3
D) X 2

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 110 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
Given the data X 1 = 1, X 2 = 4, X 3 = 5, X 4 = 8, X 5 = 10, evaluate Σ X.
A) 1
B) 18
C) 27
D) 28
A) 1
B) 18
C) 27
D) 28

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 110 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
Consider the following points on a scale:  If the scale upon which A , B , C , and D are arranged is a nominal scale, we can say _________.
If the scale upon which A , B , C , and D are arranged is a nominal scale, we can say _________.
A) B = 2 A
B) B - A = D - C
C) both a and b
D) neither a nor b
 If the scale upon which A , B , C , and D are arranged is a nominal scale, we can say _________.
If the scale upon which A , B , C , and D are arranged is a nominal scale, we can say _________.A) B = 2 A
B) B - A = D - C
C) both a and b
D) neither a nor b

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 110 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
A continuous scale of measurement is different than a discrete scale in that a continuous scale _________.
A) is an interval scale, not a ratio scale
B) never provides exact measurements
C) can take an infinite number of intermediate possible values
D) never uses decimal numbers
E) never provides exact measurements and can take an infinite number of intermediate possible values
A) is an interval scale, not a ratio scale
B) never provides exact measurements
C) can take an infinite number of intermediate possible values
D) never uses decimal numbers
E) never provides exact measurements and can take an infinite number of intermediate possible values

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 110 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
Number of bar presses is an example of a(n) _______ variable.
A) discrete
B) continuous
C) nominal
D) ordinal
A) discrete
B) continuous
C) nominal
D) ordinal

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 110 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
Which of the following variables has been labeled with an incorrect measuring scale?
A) the number of students in a psychology class - ratio
B) ranking in a beauty contest - ordinal
C) finishing order in a poetry contest - ordinal
D) self-rating of anxiety level by students in a statistics class - ratio
A) the number of students in a psychology class - ratio
B) ranking in a beauty contest - ordinal
C) finishing order in a poetry contest - ordinal
D) self-rating of anxiety level by students in a statistics class - ratio

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 110 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
Given the following set of numbers, X 1 = 2, X 2 = 4, X 3 = 6, X 4 = 10 , what is the value of ( Σ X )/ N ?
A) 5
B) 4
C) 6
D) 5.5
A) 5
B) 4
C) 6
D) 5.5

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 110 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
Given the following set of numbers, X 1 = 2, X 2 = 4, X 3 = 6, X 4 = 10 , what is the value for ΣX ?
A) 12
B) 156
C) 480
D) 22
A) 12
B) 156
C) 480
D) 22

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 110 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
In a 10-mile cross-country race, all runners are randomly assigned an identification number. These numbers represent a(n) _________.
A) nominal scale
B) ratio scale
C) interval scale
D) ordinal scale
A) nominal scale
B) ratio scale
C) interval scale
D) ordinal scale

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 110 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
Using an ordinal scale to assess leadership, which of the following statements is appropriate?
A) A has twice as much leadership ability as B
B) X has no leadership ability
C) Y has the most leadership ability
D) all of these
A) A has twice as much leadership ability as B
B) X has no leadership ability
C) Y has the most leadership ability
D) all of these

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 110 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
In the race mentioned in question 26, a comparison of each runner's finishing time would represent a(n) _________.
A) nominal scale
B) ratio scale
C) interval scale
D) ordinal scale
A) nominal scale
B) ratio scale
C) interval scale
D) ordinal scale

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 110 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
A nutritionist uses a scale that measures weight to the nearest 0.01 grams. A slice of cheese weighs 0.35 grams on the scale. The variable being measured is a _________.
A) discrete variable
B) constant
C) continuous variable
D) random variable
A) discrete variable
B) constant
C) continuous variable
D) random variable

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 110 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
The number of legs on a centipede is an example of a(an) _______ scale.
A) nominal
B) ordinal
C) ratio
D) continuous
A) nominal
B) ordinal
C) ratio
D) continuous

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 110 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
What are the real limits of the observation of 6.1 seconds (measured to the nearest second)?
A) 6.05-6.15
B) 5.5-6.5
C) 6.0-6.2
D) 6.00-6.20
A) 6.05-6.15
B) 5.5-6.5
C) 6.0-6.2
D) 6.00-6.20

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 110 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
A nutritionist uses a scale that measures weight to the nearest 0.01 grams. A slice of cheese weighs 0.35 grams on the scale. The true weight of the cheese _________.
A) is 0.35 grams
B) may be anywhere in the range 0.345-0.355 grams
C) may be anywhere in the range 0.34-0.35 grams
D) may be anywhere in the range 0.34-0.36 grams
A) is 0.35 grams
B) may be anywhere in the range 0.345-0.355 grams
C) may be anywhere in the range 0.34-0.35 grams
D) may be anywhere in the range 0.34-0.36 grams

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 110 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
Given the following set of numbers, X 1 = 2, X 2 = 4, X 3 = 6, X 4 = 10 , what is the value of ( ΣX ) 2 ?
A) 480
B) 484
C) 156
D) 44
A) 480
B) 484
C) 156
D) 44

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 110 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
The sum of a distribution of 40 scores is 150. If we add a constant of 5 to each score, the resulting sum will be _________.
A) 158
B) 350
C) 150
D) 195
A) 158
B) 350
C) 150
D) 195

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 110 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
Given the following set of numbers, X 1 = 2, X 2 = 4, X 3 = 6, X 4 = 10 , what is the value of N ?
A) 2
B) 4
C) 6
D) 10
A) 2
B) 4
C) 6
D) 10

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 110 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
Classifying subjects on the basis of sex is an example of using what kind of scale?
A) nominal
B) ordinal
C) interval
D) ratio
E) bathroom
A) nominal
B) ordinal
C) interval
D) ratio
E) bathroom

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 110 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
Sex of children is an example of a(n) _________ scale.
A) ratio
B) nominal
C) ordinal
D) interval
A) ratio
B) nominal
C) ordinal
D) interval

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 110 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
Given the following set of numbers, X 1 = 2, X 2 = 4, X 3 = 6, X 4 = 10 , what is the value of X 42 ?
A) 4
B) 6
C) 100
D) 10
A) 4
B) 6
C) 100
D) 10

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 110 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
What is 17.295 rounded to one decimal place?
A) 17.1
B) 17.0
C) 17.2
D) 17.3
A) 17.1
B) 17.0
C) 17.2
D) 17.3

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 110 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
iven the following set of numbers, X 1 = 2, X 2 = 4, X 3 = 6, X 4 = 10 , what is the value of Σ X 2 ?
A) 156
B) 22
C) 480
D) 37
A) 156
B) 22
C) 480
D) 37

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 110 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
What is (4 - 2)(3 × 4)/(6/3)?
A) 24
B) 1.3
C) 12
D) 6
A) 24
B) 1.3
C) 12
D) 6

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 110 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
1/2 + 1/4 equals _______.
A) 1/6
B) 1/8
C) 2/8
D) 3/4
A) 1/6
B) 1/8
C) 2/8
D) 3/4

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 110 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
1/ X + 2/ X equals _______.
A) 2/ X
B) 3/2 X
C) 3/ X
D) 2/ X 2
A) 2/ X
B) 3/2 X
C) 3/ X
D) 2/ X 2

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 110 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
X = Y / Z can be expressed as _______.
A) Y = ( Z )( X )
B) X = Z / Y
C) Y = X / Z
D) Z = X + Y
A) Y = ( Z )( X )
B) X = Z / Y
C) Y = X / Z
D) Z = X + Y

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 110 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
An individual is measuring various objects. If the measurements made are to determine into which of six categories each object belongs, the measuring scale used must have been a(an)_______ scale.
A) nominal
B) ordinal
C) interval
D) ratio
A) nominal
B) ordinal
C) interval
D) ratio

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 110 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
Where 3 X = 9, what is the value of X ?
A) 3
B) 6
C) 9
D) 12
A) 3
B) 6
C) 9
D) 12

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 110 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
What is the value of 0.05 rounded to one decimal place?
A) 0.0
B) 0.1
C) 0.2
D) 0.5
A) 0.0
B) 0.1
C) 0.2
D) 0.5

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 110 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
If an investigator determines that Carlo's score is five times as large as the score of Juan, the measuring scale used must have been a(an)_______ scale.
A) nominal
B) ordinal
C) interval
D) ratio
A) nominal
B) ordinal
C) interval
D) ratio

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 110 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
X 6 / X 2 equals _______.
A) X 8
B) X 4
C) X 2
D) X 3
A) X 8
B) X 4
C) X 2
D) X 3

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 110 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
If IQ was measured on a ratio scale, and John had an IQ of 40 and Fred an IQ of 80, it would be correct to say that Fred was twice as intelligent as John.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 110 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
When doing summation, the number above the summation sign indicates the term ending the summation and the number below indicates the beginning term.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 110 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
For X + Y = Z , X equals _______.
A) Y + Z
B) Z - Y
C) Z / Y
D) Y / Z
A) Y + Z
B) Z - Y
C) Z / Y
D) Y / Z

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 110 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
With nominal scales there is a numerical relationship between the units of the scale.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 110 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
A therapist measures the difference between two clients. If the therapist can say that Rebecca's score is higher than Sarah's, but can't specify how much higher, the measuring scale used must have been a(an)_______ scale.
A) nominal
B) ordinal
C) interval
D) ratio
A) nominal
B) ordinal
C) interval
D) ratio

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 110 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
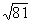 equals _______.
equals _______.A) ±3
B) ±81
C) ±9
D) ±27

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 110 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
6 + 4 * 3 - 1 simplified is _______.
A) 29
B) 48
C) 71
D) 17
A) 29
B) 48
C) 71
D) 17

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 110 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
2 4 equals _______.
A) 4
B) 32
C) 8
D) 16
A) 4
B) 32
C) 8
D) 16

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 110 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
X ( Z + Y ) equals _______.
A) XZ + Y
B) ZX + YX
C) ( X )( Y )( Z )
D) ( Z + Y )/ X
A) XZ + Y
B) ZX + YX
C) ( X )( Y )( Z )
D) ( Z + Y )/ X

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 110 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
S X 2 and ( S X) 2 generally yield the same answer.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 110 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
The symbol " S " means:
A) add the scores
B) summarize the data
C) square the value
D) multiply the scores
A) add the scores
B) summarize the data
C) square the value
D) multiply the scores

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 110 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
In a race, Sam came in first and Fred second. Determining the difference in time to complete the race between Sam and Fred involves an ordinal scale

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 110 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
Determining the number of students in each section of introductory psychology involves the use of a ratio scale.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 110 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
The number of students in a class is an example of a continuous variable.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 110 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
Measurement is always approximate with a continuous variable.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 110 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
In rounding, if the remainder beyond the last digit is greater than 1/2, add one to the last digit. If the remainder is less than 1/2, leave the last digit as it is.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 110 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
Nominal scales can be used either qualitatively or quantitatively.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 110 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
A discrete variable requires nominal or interval scaling.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 110 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
It is legitimate to do ratios with interval scaling.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 110 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
Classifying students into whether they are good, fair, or poor speakers is an example of ordinal scaling.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 110 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
When rounding, if the decimal remainder is equal to 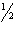 and the last digit of the answer is even, add 1 to the last digit of the answer.
and the last digit of the answer is even, add 1 to the last digit of the answer.
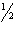 and the last digit of the answer is even, add 1 to the last digit of the answer.
and the last digit of the answer is even, add 1 to the last digit of the answer.
Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 110 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
It is standard practice to carry all intermediate calculations to four more decimal places than will be reported in the final answer.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 110 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72
An ordinal scale possesses the attributes of magnitude and equal interval.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 110 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73
With the exception of division, one can perform all mathematical operations on a ratio scale.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 110 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
74
The real limits of a discrete variable are those values that are above and below the recorded value by one half of the smallest measuring unit of the scale.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 110 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
75
A fundamental property of a nominal scale is equivalence.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 110 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
76
All scales possess magnitude, equal intervals between adjacent units, and an absolute zero point.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 110 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
77
An interval scale is like a ratio scale, except that the interval scale doesn't possess an absolute zero point.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 110 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
78
Most scales used for measuring psychological variables are either ratio or interval.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 110 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
79
If the remainder of a number = 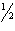 , we always round the last digit up.
, we always round the last digit up.
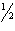 , we always round the last digit up.
, we always round the last digit up.
Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 110 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
80
With an ordinal scale one cannot be certain that the magnitude of the distance between any two adjacent points is the same.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 110 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



